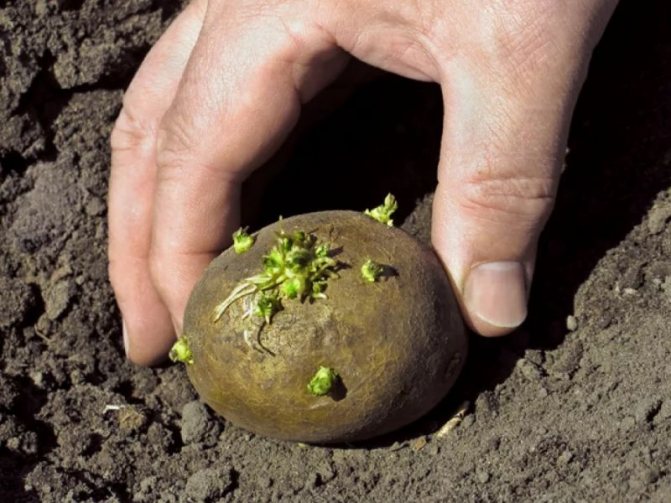
It's time to plant potatoes just around the corner. In order for the harvest to be really rich and fertile, you need to prepare for planting now. In Russia, potatoes are the second product on the table after bread.
That is why everyone who has a dacha or a house in the village strives to grow this vegetable on their own. When planting, fertilizers are of great importance.
With their help, you can achieve a good harvest, so you should not neglect the choice of high-quality fertilizer.
In the spring we have a lot of work, we plant cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, eggplants on seedlings. It is important to know all the intricacies of growing and fertilizing the soil. It is also important to know how and when to plant tomatoes according to the lunar calendar in 2020. But in this article, we will talk in detail about potatoes.
The importance of fertilizing potatoes when planting in a hole
For normal development, potatoes need a complex of nutrients: nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, copper, manganese. During growth, the culture from the soil absorbs many elements.

Thanks to feeding:
- yield increases;
- the quality and taste of tubers improves;
- the required amount of nutrients is stored in the ground;
- the immunity of plants to diseases increases.
Important! For the full development of potatoes, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are required. Nitrogen helps to build green mass, phosphorus and potassium contribute to the formation of quality tubers.
Potatoes need:
- at the beginning of the season - nitrogen;
- during flowering - magnesium, potassium and phosphorus.
During growth and development, potatoes consume a large amount of nutrients from the soil. After each harvest, the soil becomes less nutritious, depleting more and more every year. Therefore, the land must be fertilized so that it always remains fertile, otherwise next year it will be possible to harvest a weak potato crop.


Interesting! According to the calculations of agronomists, 1 kg of potatoes draws out from the soil: 5 g of nitrogen; 10 g of potassium; 2 g phosphorus; as well as zinc, copper, manganese, boron and other trace elements.
In order to get a rich harvest of potatoes every year, it is necessary to regularly restore the fertility of the soil by introducing fertilizers into it.
Potatoes absorb nutrients from the soil throughout the growing season, especially during bud formation and flowering. Therefore, it is very important to fertilize root crops when planting them in the ground.
Hilling potatoes: why and why you need it
Hilling potato furrows with a hoe is another important process for the full development of the plant. This procedure must be carried out at least twice during the period of potato growth.
The procedure, of course, takes a lot of time and effort, but it helps to form a good root system and avoid the disappearance of nutrients from the soil.
It is this vegetable that must be periodically hilled so that the harvest is fertile.


It is especially important to carry out this procedure if the soil consists of clay. Hilling is useless for sand.
As the main tool, a hoe can be used (but this is no longer so relevant), a walk-behind tractor (the technique is not cheap, but it greatly simplifies work in the garden), a disc hiller (manual device) or a cultivator.


Hilling should not be done when the plant has already begun to bloom. It is necessary to carry out the procedure up to this point.
So, heavy soil in any case needs periodic hilling. Only loose soil can improve the quality of the crop by a few percent.But it is highly undesirable to do this if the soil is dry. It is worth waiting for the rain or watering the beds yourself.


Organic fertilizers
Almost all organic matter is a waste product of plants, animals and bacteria. Therefore, they are classified as biological fertilizers. Organics feeds the vegetable crop with the necessary nutrients, and also improves the structure of the soil.
Each type of biofertilizer has its own application characteristics.
Manure
Manure contains many micro and macro elements. Thanks to the use of manure, the soil becomes looser, more fertile, which increases productivity.
Advice! For potatoes, it is best to use mullein or horse dung.
Such an organic fertilizer is applied at the rate of 400 kg per hundred square meters during the autumn or winter digging of the soil, deepening it by 40 cm.This procedure must be carried out especially in the northern regions of the country, since in the process of decomposition, manure releases heat, which heats the planted tubers in spring.


Additionally, at the same time, it is also recommended to fertilize the soil with potassium sulfate and superphosphate at the rate of 2 tbsp. spoons for 1 mv. m.
Interesting! Instead of applying manure in the fall, you can sow green manure.
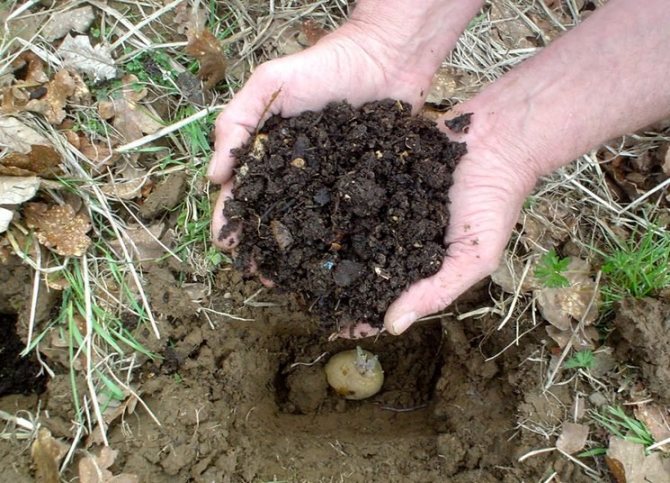
Also rotted manure is introduced during potato planting.
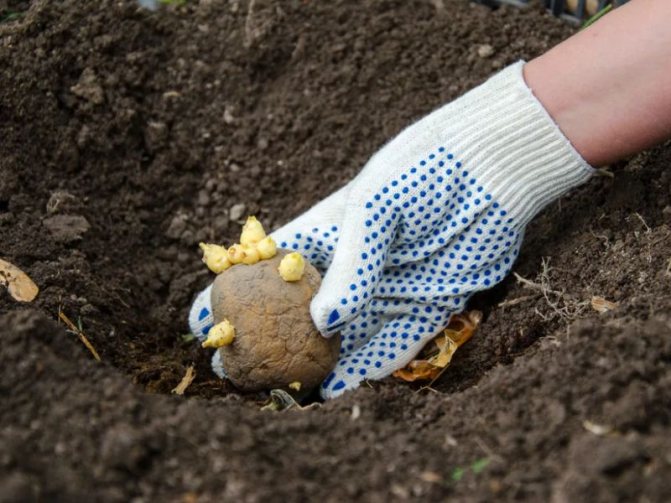
Add 150 g of organic matter to each well.
Important! Cannot be used for fertilization fresh manure, as it may contain parasites and pathogens. In addition, ammonia compounds will evaporate from it, which kill beneficial bacteria in the soil.
Manure is introduced into the soil not every year, but once every 3-5 years.
Chicken droppings
This biofertilizer contains many useful substances and quickly dissolves in the soil. Thanks to these characteristics, this organic is considered one of the most popular.
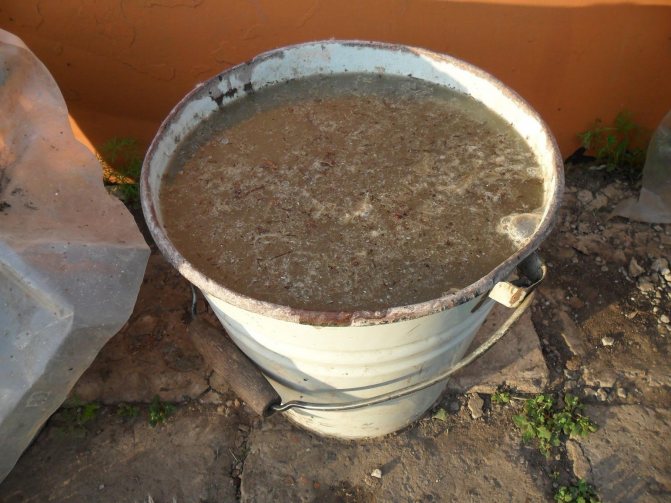
Chicken manure is used exclusively in diluted form:
1 part of the fertilizer is diluted 20 times with water.
You can make the solution even weaker so as not to burn the plant roots during feeding.
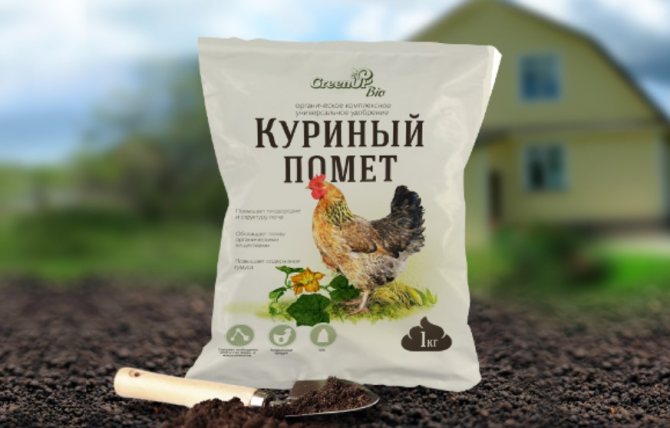


1 liter of chicken manure solution is poured under one potato bush.
Ash
Wood ash is no less popular, which contains a large amount of phosphorus, potassium, calcium and other trace elements that contribute to the development of root crops. Ash improves the quality of the soil. It is brought in dry or diluted. You can apply both a separate fertilizer and together with other top dressing.


Approximately a fist of ash is poured into each hole at a consumption rate of 10-15 kg of dry matter per 1 hundred square meters.
Additionally, you can add potassium chloride and ammophoska in a few peas.
Compost
The cheapest type of organic fertilizer. For the preparation of compost, a special place is taken, where foliage, the remains of plants, vegetables and fruits are piled up for a certain period. Over time, all this overlaps and forms a nutrient mixture.
Approximately a fist of compost is added to each planting hole along with 1 tbsp. spoon of ash.


Green manure
Instead of manure, you can use rotted and fermented green mass. You can use any available greens to prepare the green fertilizer.
Preparation:
- The whole green mass with soil residues is loaded into the barrel (you can add a couple of handfuls of urea).
- Next, warm water is poured to the brim.
- The barrel is covered with foil.
- The mass is infused for 15 days.


Green fertilizer is applied to the holes during potato planting - 1 liter of the product per 1 hole.
Signs of nutritional deficiency
A plant that systematically does not receive one or another element necessary for development changes its appearance. By observing the growing potatoes, you can find out which element is missing.
- Nitrogen. Lack of it affects the growth of potatoes. Stems and leaves grow poorly, instead of a rich green color, they become pale.
Tubers on such bushes are tied, but remain small.Reduced starchiness.
- Potassium. The deformation of the sheet plate occurs - it wrinkles, the size of the sheet is small. In the second half of the growing season, the top of the bush begins to turn yellow, then darken.
Root crops obtained from such plants are poorly stored.
- Phosphorus. Lacking phosphorus, the potato bush produces few stems. Flowering occurs later than usual. The foliage curls (the edges curl upward), takes on a reddish or eggplant hue.


Black spots may appear inside the tubers during storage. The taste of such potatoes deteriorates markedly.
- Magnesium. Foliage, starting from the lower plates, is discolored. The veins on the leaf plate retain their color. Gradually discolored areas of the tops dry out.
- Calcium. Young leaves at the tops of the bushes become striped. The clarified areas on the leaves soon die off, the top of the bush is deformed.
- Bor. The top of the bush turns yellow, bends and dies off. The trunk of the bush thickens unnaturally. Tubers are formed small, with black inside.
- Iron. On the leaf plate, the areas between the veins brighten (whiten), which retain their shade.
- Copper. Curliness of leaves is observed, plant wilting. At the same time, there is no lightening of the foliage.
- Manganese. The leaves turn yellow between the veins, and red-brown spots appear on them. Signs of starvation are expressed only at the top of the bush.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
To determine with high accuracy the lack of one or another element, you can donate the soil from the garden for analysis to the laboratory.
Mineral fertilizers
Using mineral fertilizers for feeding potatoes in compliance with all norms and recommendations, you can grow healthy potatoes.
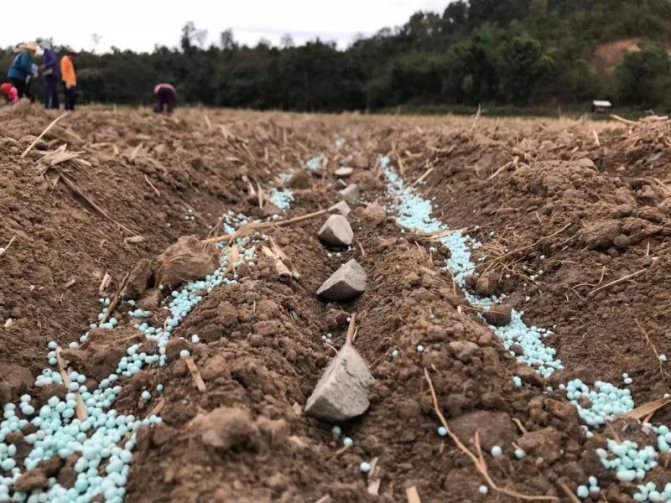
When adding agrochemistry to increase the yield make in each well 0.5 tsp of nitrophoska and 10 g of bone meal.
Urea
This is the most common mineral fertilizer for potatoes. Urea is most effective on alkaline soils.
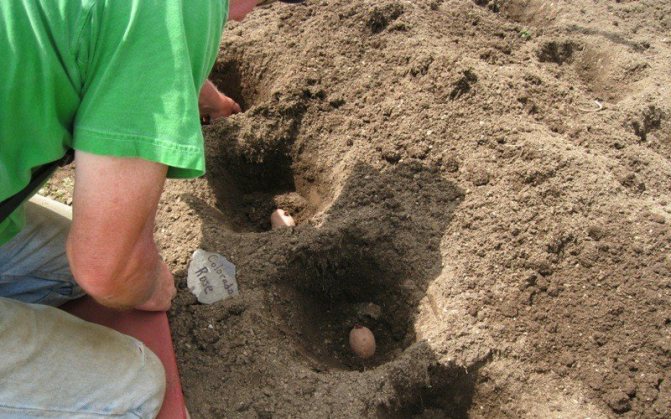
When added during planting, 1 teaspoon of the product is added to each well.


Advice! First, the fertilizer is lightly sprinkled with soil, and then the tubers are laid out.
We use 1.5-2 kg of fertilizer per one hundred square meters.
Watch the video! Fertilizer for potatoes when planting in a hole
Ammonium nitrate
The cheapest mineral fertilizer that can be used annually. Ammonium nitrate Sold in granules, from which a solution is then made or mixed with fungicides to soak the seed.


Application rates:
- 10 g of granules in 1 well with depleted soil.
- 5 g in 1 well with normal soil.
Watch the video! Top dressing of potatoes with ammonium nitrate
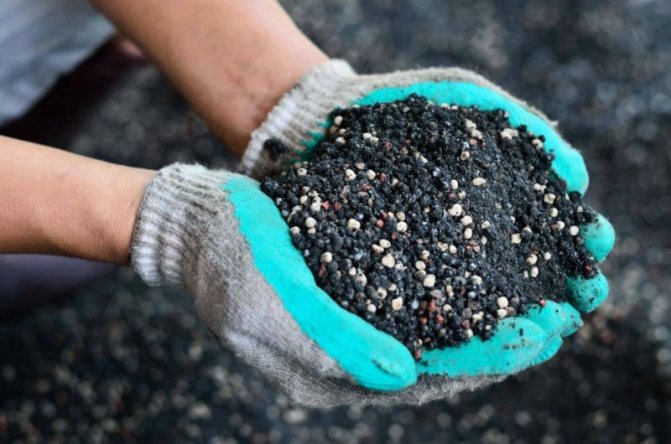
Complex fertilizers
Enrich the soil with all the necessary nutrients for potatoes.
Complex fertilization allows:
- to strengthen the root system of the culture;
- accelerate the formation and maturation of tubers;
- increase immunity to fungal diseases.
The most effective for this culture are:
Ammofoska
Contains phosphorus, nitrogen and potassium. Promotes an increase in yield and prolongs the storage life of tubers after harvest.


Nitrophoska and nitroammofoska
Contain ammonium and potassium nitrate, calcium chloride, superphosphate and other fertilizers. Possesses fungicidal and nutritional properties.
In each well add 0.5 teaspoon of nitrophoska and 10 g of bone meal.


Azofoska
Nitrogen fertilizer that can be used to feed potatoes. Azofoska contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and sulfur in a form available to plants.
Azofoska is used as an independent top dressing or in combination with mineral fertilizers.
Add 3 g of funds to one hole during planting.


Superphosphate
This agent is the best among the phosphorus-containing fertilizers.Superphosphate contains an optimal amount of sulfur, calcium, phosphorus and other elements that a plant needs to build up green mass and accumulate nutrients in root crops.
Fertilizer is applied at a rate of 2 kg per 1 hundred square meters of soil for developed gardens and fields.


Advice! Superphosphate acts more effectively as a self-fertilizing, so it should not be carried along with other fertilizers.
To increase the starch content in potatoes, soil the bushes with magnesium sulfate. For foliar feeding, dilute 15 g of the product in 10 liters of water. Spraying is carried out.
Giant
Fast dissolving granules, which include macro and microelements, organic substances, humic compounds.
When planting potatoes, add 1 teaspoon of the product to each hole.
You can also dilute 50 g of the drug in 10 liters of water and water the planted tubers.


Fertika
Crystalline instant powder that contains 20% phosphorus.
The drug is introduced into each well during the spring planting of potatoes, 1 tbsp. spoon.


Fasco
Complex mineral fertilizer containing organic and mineral substances. Increases productivity by 2 times and shortens the ripening time of tubers.
Funds are paid during the digging of the site at the rate of 60 - 150 g per 1 sq. M.


How to calculate the right amount of top dressing?
The chemical composition of the soil affects the required amount of fertilizing for tuber crops. Potatoes love slightly acidic soils. Ideal for her - from 5.5 to 6.5 pH. For each personal plot, it is necessary to individually calculate the rate.


Knowing the level of soil fertility, it is advisable to use such fertilization options based on for 1 are:
Find out also
What to do if potatoes have large tops
for fertile soil, the following ingredients should be taken and mixed in the indicated dosages:
- humus - 2 kg;
- superphosphate - 2-2.5 kg;
- potash top dressing - 1-1.5 kg;
for medium-fertile soil, it is necessary to use the following fillers:
- humus or compost - 2.5-3 kg;
- nitrogen fertilizing - 3 kg;
- phosphate fertilizers - 3 kg;
- potash top dressing - 2.5 kg.
Depleted soil needs 1 kg of ammonium nitrate, 3 kg of superphosphate and 100 kg of humus.
The best formulations of organic and mineral fertilizers per hole
For potatoes, it is best to apply a fertilizer mixture at the time of planting in the hole. Thus, the culture will receive the maximum amount of nutrients.
Popular formulations to add to wells.
Recipe 1:
- 1 bucket of humus;
- 1 glass of ash;
- 3 tbsp. spoons of nitrophosphate;
- all mix and put a handful in each hole.
Recipe 2:
- 1 bucket of humus;
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of ammonium nitrate;
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of potassium sulfate;
- 2 tbsp. spoons of superphosphate;
- 1.5 cups dolomite flour to reduce the acidity of the soil.
- a handful of the mixture is added to the hole.
Also, you can put just 1 tbsp in the holes. tablespoons of nitroammophoska, while organic matter is not needed.
From organic matter, it is better to use a mixture of 0.7 kg of dry humus and 6 tbsp. spoons of wood ash. Add a handful of the mixture.
Terms of introduction
You cannot add all the necessary nutrients at one time. This will not give the expected result.
Fall
The first soil fertilization is carried out in the fall during the digging of the site. Organic matter (manure, compost) and mineral fertilizers (potassium chloride) are introduced. During the winter, they will moult with the remains of plants, increasing the fertility of the soil.
Potato organic matter is introduced in the fall. Manure is scattered over the site at 5-10 kg per 1 square meter and everything is dug deeply.
In the fall, they also apply per 1 sq. M:
- double superphosphate - 40-70 g;
- potassium sulfate - 25-30 g.
Spring
In the spring, the soil is fertilized with nitrogen agents that contribute to the proper vegetation of potatoes. Mineral-organic mixtures are often used.
Digging for 1 sq.m:
- Potassium sulfate - 25-30 g.
- Nitroammofosk - 20-30 g.
- Ammonium nitrate - 20-50 g.


When landing in a hole:
- Nitroammofosk - 4-5 g.
- Ash is a handful.
When the aboveground part grows to 12 cm in height, the potatoes are additionally fed with calcium nitrate.
Fertilizing after planting
Also, potatoes need to be fed after planting. Fertilizer should be applied as deeply as possible. If the nutrients are close to the surface, the roots of the crop will not be able to absorb them.
A wooden stake is driven in between 3 potato bushes, which is pulled out during feeding. Liquid fertilizers are poured into the hole, and everything is covered with soil.
The first
For the first time after planting, potatoes are fertilized after 10-15 days.
If the plants develop slowly, nitrogen is added:
- in 10 liters of water;
- bred 0.5 kg of mullein;
- pour 0.5 liters under 1 plant.
The second
The second time the potatoes are fertilized during the formation of the tubers. Potassium-phosphorus fertilizers are applied.
- 15 g superphosphate;
- 15 g of potassium sulfate;
- 1 bucket of water
- pour 0.5 liters under each bush plant.
Watch the video! Fertilizer for potatoes
Third
The last time fertilization is applied 20 days before harvest. The fertilizer will help nourish the tubers with vitamins and nutrients, thereby increasing their shelf life.
- 0.25 l of manure;
- 25 g superphosphate;
- 1 bucket of water
- pour 0.5 liters under 1 plant.
Watch the video! Super fertilizer for potatoes
Growth stimulants
Mineral fertilizers contribute to the nutrition of potatoes - their compositions include elements that act as building materials for the future harvest. There are also growth stimulants that increase resistance to diseases and adverse conditions that accelerate metabolic processes. They work on potatoes in the same way vitamins do on humans. When treated with growth stimulants, the yield increases by 10-30%. There are some of the best potato stimulants out there.
Epin
It has a pronounced anti-stress effect - it helps potatoes to endure sudden temperature changes, drought, prolonged cloudy weather; increases resistance to disease. Higher yields result in tubers growing faster. Increases productivity by 15-30%.
Epin is intended for processing seed tubers a few hours before planting. For 1 glass of water, 1 ml of the stimulant is consumed - this is enough to process 50 kg of potatoes. Also, the procedure is carried out at the beginning of flowering - 1 ml of Epin leaves for 5 liters of water. If the plants are suffering from frost, drought or lack of sunlight, they are sprayed every 7-10 days until the weather or plant condition improves.


Gibbersib
The drug helps to increase the resistance of the culture to pathogenic microorganisms - bacteria, fungi, viruses. This is an excellent prevention of common scab, late blight, leaf spot and other potato diseases. It guarantees an increase in yield by 15-30%.
The manufacturer recommends spraying the plants during the budding period, flowering and after it. The disadvantage of the drug is that it quickly decomposes in the sun, potatoes should be processed in the evening. 0.1 g is consumed per 2 liters of water.


Silk
It is the best natural stimulant with a pleasant pine scent. Increases productivity by 25-30%. It contains needles, which are the main active ingredient.
Fir extract has a beneficial effect on potatoes:
- helps to survive in extreme situations;
- stimulates plant growth;
- increases resistance to disease.
Also in the composition there are dietary supplements and natural triterpenic acids. Because of this, Silk must be handled very carefully so as not to accidentally burn the skin. The drug is produced in sachets, with a volume of 1.5 ml - it is dissolved in 200 ml of hot water (about 60 degrees), then the seed tubers are moistened with the solution.
In the summer, spraying is carried out with a solution prepared somewhat differently - a package of the drug is dissolved in 1.5 liters of water.Spraying is carried out twice: during budding and during flowering.


Poteytin
If tubers are treated with Poteytin, seedlings appear 7 days earlier than those that are not processed. The stems grow powerful, the potato can more easily tolerate the attack of pests and the development of various diseases. Increases productivity by 16-24%.
It is advisable to spray the tubers three times: before germination, planting and storage. For 750 ml of water, 1 ml of the stimulant is consumed. During the budding period, the same solution is prepared, but in different quantities - 1 ml of Poteitin per 10 liters of water.


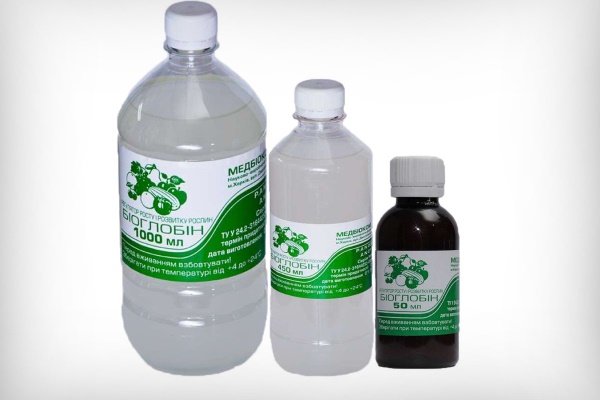
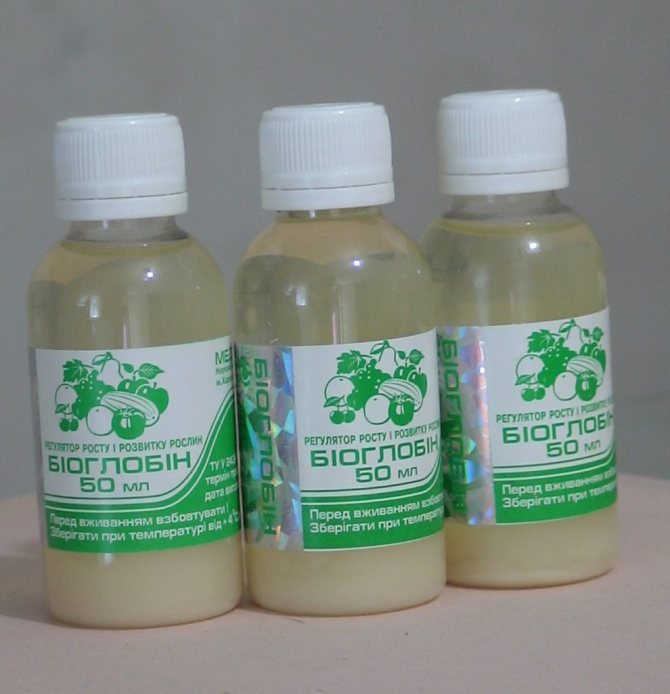
Bioglobin
An effective Ukrainian drug, rich in proteins that stimulate cell division. The additive works within 24 hours, but during this period the potato cells divide twice. The root system grows 4 times, and the yield - 2 times. At the beginning of vernalization, a month before planting, the tubers must be soaked in the solution for half an hour - 2.5 g of Bioglobin are consumed per 10 liters of water. This leads to an increase in eyes, rapid emergence of potatoes.
Then the emerging seedlings are sprayed with the same solution, after a day they are covered with earth. Two more treatments will help to consolidate the result: 21 days after the emergence of repeated shoots, at the end of flowering. Bioglobin can be combined with fungicides, potassium permanganate, foliar dressing.