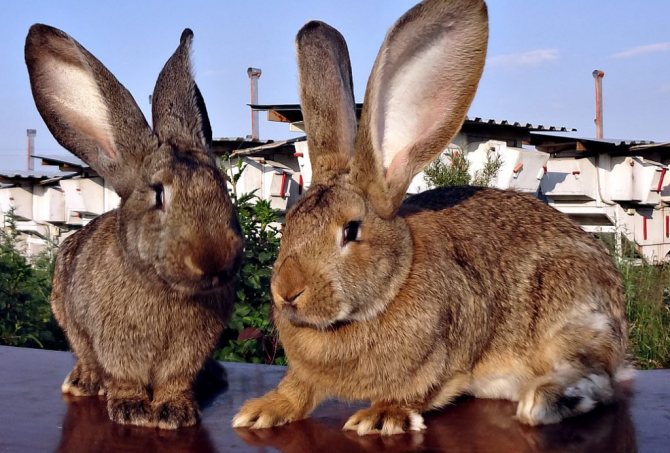
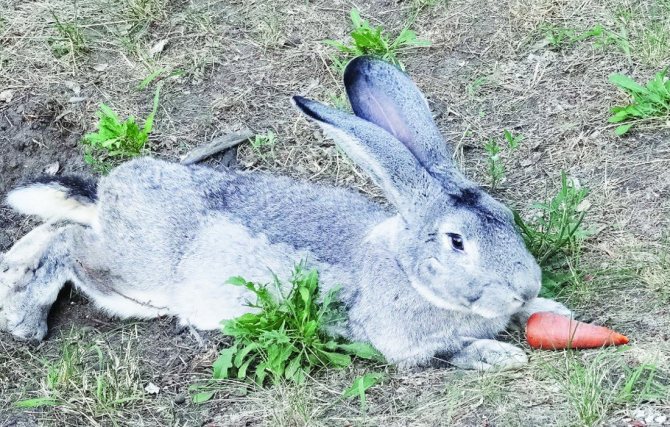
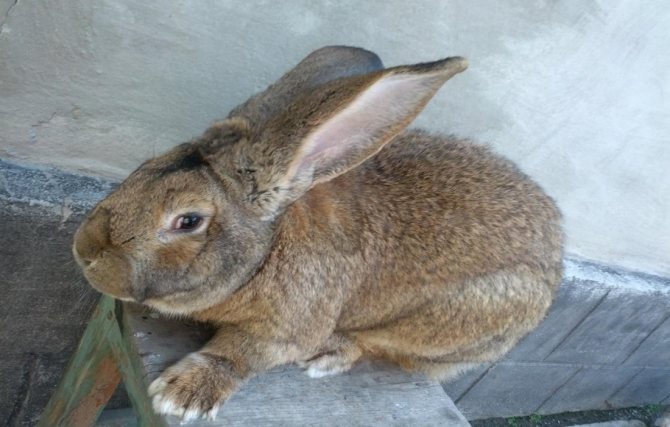
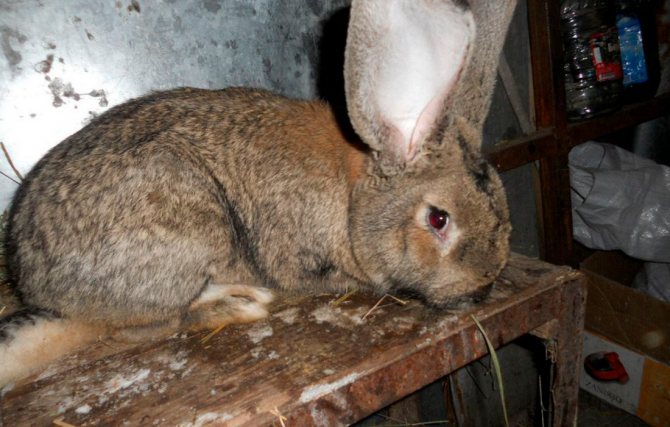
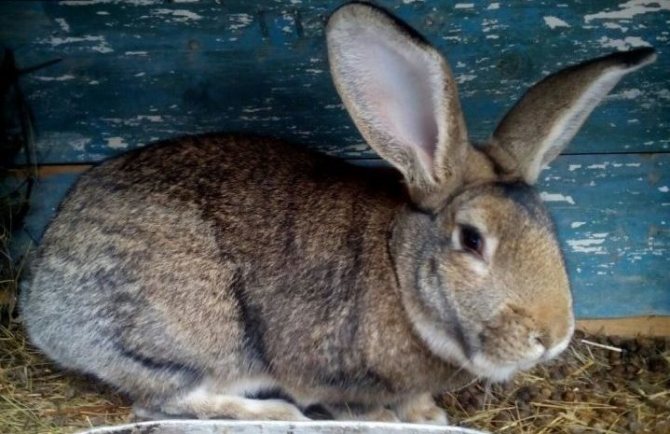
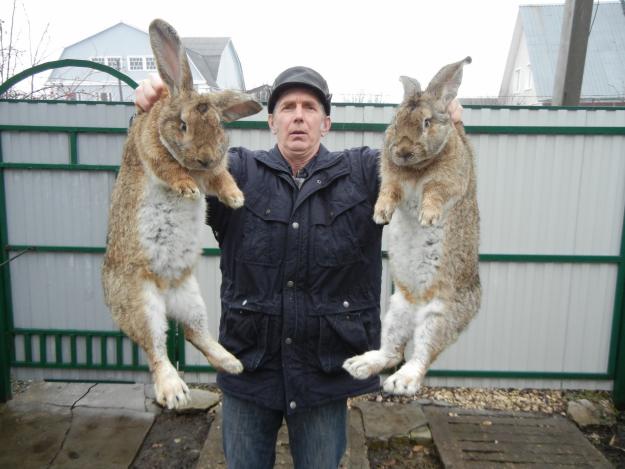
Representatives of the oldest breed of Flandre rabbits have a second name - the Belgian giant. A small animal cannot be called a giant. And, indeed, its dimensions are comparable to those of a medium-sized dog. Excellent physical performance attracts breeders when breeding them for meat and skins.
Rabbit Flandre has intelligence and quick wits. You can safely give him a nickname - he will respond to it. Playful, kind, harmless - animals of this breed are increasingly used as pets. They do not conflict with other animals, do not show aggression towards adults, and find contact with children of all ages.
History of origin
The first mentions of flanders date back to 1860, and world breed standards were officially introduced in 1893. The exact data on the time of creation of the breed has not been preserved: some believe that it has existed since the end of the 15th century, but most sources attribute its appearance to the 17-18th centuries. The place of origin - the historical province of Flanders, which previously belonged to Belgium - does not cause controversy, as it is reflected in the name. The widespread distribution of these fluffies in the 19th century was facilitated by the import of several individuals into the United States, where giants are still leading among farm rabbits.


The Flemish giant in size and body weight significantly exceeds its "congeners"
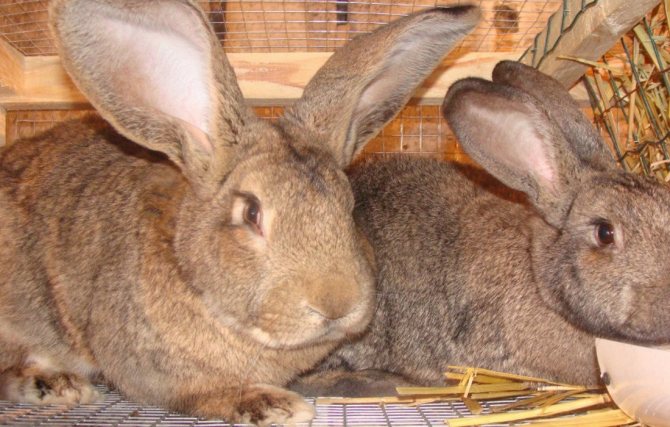
Over time, in many countries, other subspecies were bred by livestock breeders: German, Spanish, Belgian, English, as well as white and gray giants, included in the Russian State Register of Breeding Achievements in 1993 and allowed for breeding and cultivation on the territory of the Russian Federation. In terms of external characteristics, representatives of different subspecies have some differences from the "basic" type, however, they have enough in common.
Feeding features
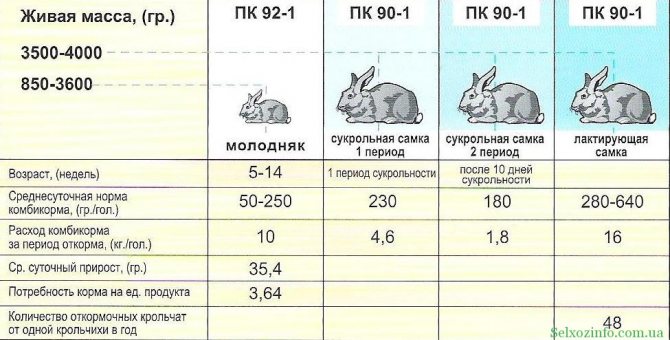
For large breeds of rabbits, feeding twice a day is recommended. It is best to give hay ad libitum so that the animal has access to it all the time. The ideal diet should include at least 40 grams of grain and a mash. She is an indispensable part of the Flanders' daily menu.


Necessary feeds included in the mash:
- raw pumpkin, thoroughly peeled from seeds;
- boiled potatoes;
- fodder beets;
- raw carrots;
- white cabbage or cauliflower.
Some breeders are wondering if rabbits can be given zucchini? Of course, it is possible, and even necessary, but it is better to clear them of seeds.
Vegetables prepared for feeding must be grated and mixed with compound feed. The purchase of compound feed is associated with large cash costs, which can be avoided by preparing this feed yourself. This requires the following ingredients:
- wheat or barley in the amount of 30 kilograms;
- corn - 15 kilograms;
- oats - 5 kilograms.
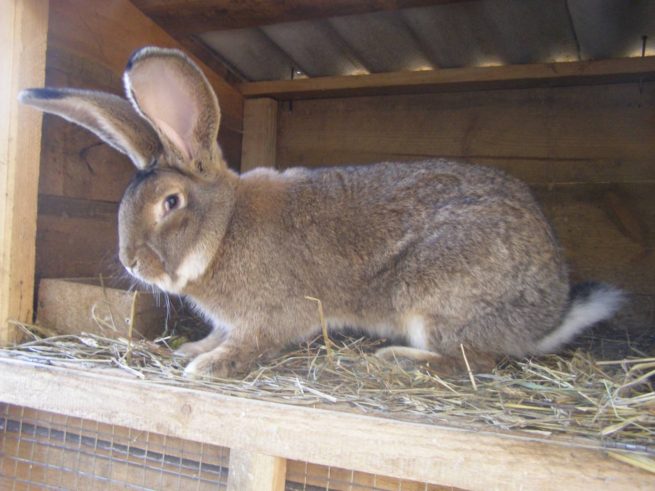
Description of Flandre rabbits
Flemish giants can hardly be called "cute", as they are very massive and awkward. Despite this, some animal lovers keep Flanders as pets. If we consider rabbits as a source of meat or skins (a in the direction of use, they are referred to as meat-skin), then the appearance does not matter at all.In this case, consumer qualities and quantitative indicators are considered important.
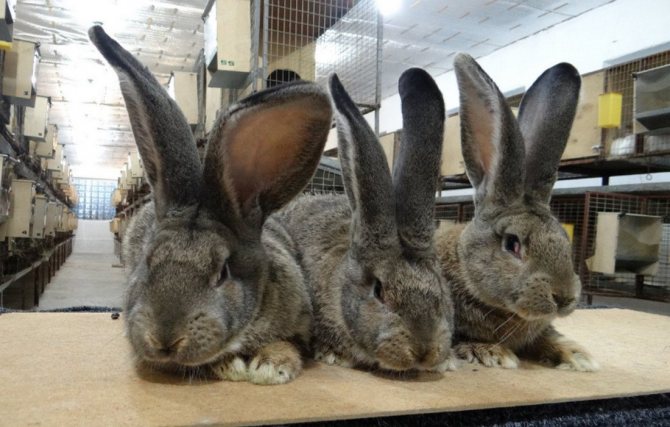
For the Belgian giants, a proportional physique is characteristic. The body is slightly elongated and curved, its length usually does not exceed 70 cm. The breed is distinguished by a large head, long (about 18 cm) and massive ears, swollen cheeks. The thickness of the coat is 3.5 cm. The weight of an adult animal is most often 7-8 kg, however, there are animals whose body weight is 10-12 kg.
According to the standards, the breed provides for various types of color, including suits ranging from black and opal to white and blue. From the following video, you can learn about the main differences between a white flanders and a white giant:
Another feature of these animals is character. They are not capricious, calm and balanced. Representatives of the Flemish giants rarely show aggression, thanks to which they get along well with people as pets.
Overview
Many photos indicate the advantage of the Flandre breed over other varieties of rabbits. It's all about reputation; over the years, the eared pet has received regalia and the status of one of the most recognized and widespread. The Belgian giant does not require special care, it is enough to monitor their health from time to time and keep the cage clean. Their females have good milk production and fertility, with not the highest nesting 5-7 times a year they can bring up to 12 babies.
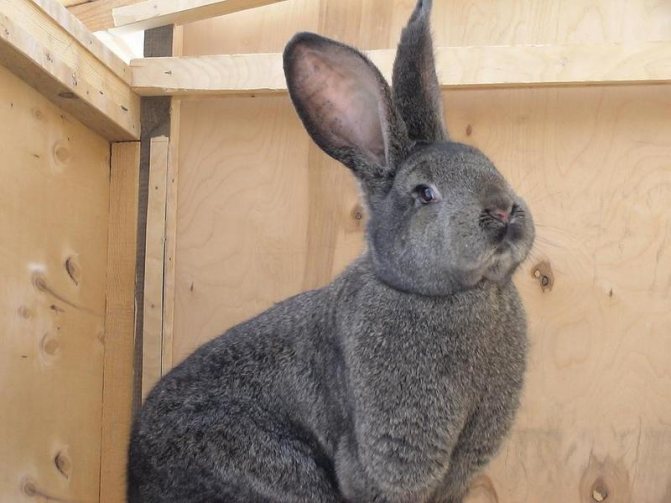


Origin
The Belgian eeyore is associated with a historical area in France called Flanders. However, it has no direct relation to this regional point. The origin of the species is attributed to Belgium, but its historical descendants, the Patagonian rabbits, came from Latin America. According to various sources, the first Flanders was brought to Europe more than three hundred or four hundred years ago.
Appearance
Photo and video descriptions of this historical breed testify to its large size. Large parameters are largely reflected in mobility - they have an elongated torso, large and long legs, as a result of which rabbits seem clumsy. The Belgian handsome man has a rather large head, as well as dense cheeks of a slightly puffy appearance. The average length is neither more nor less - 17-19 cm. The body is about 65-70 cm, the girth of the chest is 35-40 cm, and the weight is about 8-10 kg.


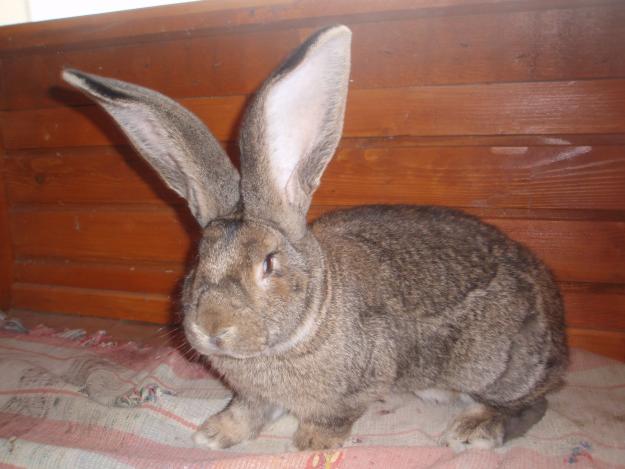
In addition, Flandres is known for its large and almost vertical ears. The photo gives a reason to distinguish the color of a giant in such standard shades: sand, silver, sand orange, gray-red, blue, white, dark gray and black. However, sometimes the color scheme deviates from the standard frames. It should be noted that quite often giant rabbits are used at home and are regarded as the first full-fledged decorative eared ones.
Productivity
For those who plan to start breeding Flandre rabbits, it is important to take into account that females reach sexual maturity only at the age of eight months, that is, almost twice as late as in other breeds. The average number of young rabbits in a litter is 6-8, sometimes it can reach 9-12 individuals. Females have high milk production, so a large number of young animals should not be considered a disadvantage.


A female can lead more than a dozen young rabbits in a litter
Rabbits grow rapidly and by the end of the second month of life they usually weigh about 1.6 kg, after the third month they recover by another kilogram. Six months after birth, the average weight of the rabbit is 5.5 kg, and by the beginning of the ninth, the mass of healthy individuals reaches 7 kg.
The average meat yield is 55%, which is much less compared to purely beef breeds. However, taking into account the large live weight, from an adult crawl weighing 6 kg, you can get 3.3 kg of meat, which is not so little.
In terms of the quality of skins, flanders are also inferior to specialized fur breeds. But due to the fact that raw materials of impressive size can be obtained from one individual, the skins of the Flemish giants are in constant demand.
Breed standard Belgian Giant.
And yet, I cannot just “bury” this wonderful breed in my mind, I insist on observing the breed standard for a true local Flanders, an indigenous Belgian or Flemish giant, which is registered in regional catalogs. Nobody has canceled them yet, and they exist in parallel with the European Union in a number of countries. As for the previously mentioned reference book by L. Utkin, it also says that the color of the agouti (gray-hare) is the property of wild rabbits, Gray Giants and Flanders. I'll use the Swiss catalog as an example. It was published after the first editions of European standards, is freely available and describes the rabbit breeds in great detail.
Common data.
The Belgian Giant (Flanders) belongs to large breeds. It is Flandre that appears in the standard, and not Flander, as it is sometimes called in local dialects. Although the essence does not change from this.
General form:
- Head: large, set close to the shoulders, rectangular, broad forehead, well developed muzzle.
- Ears: Strong, set upright, well covered, 18 to 19.5 cm long.
- Neck: not pronounced.
- Chest: Fully formed, broad.
- Shoulders: Muscular, closed.
- Forefeet: Medium length, straight, strong.
- Posture: medium height.
- Back: Long, broad, well formed.
- Pelvis: closed, well placed, rounded, of medium height.
- Hind feet: Strong and parallel.
- Belly line: high, well defined.
- Fur: dense, dense, coarse, with a large amount of undercoat, abundant cover and awn.
- Hair length: 33-37mm.
- Skin: soft, tight-fitting.
VERY CHARACTERISTIC a distinctive feature of the Flanders is the shape of their auricles. Besides the fact that they are very large, they also have an expansion in the middle part, which makes them look like a scoop of a spoon. This trait is not typical for other large rabbits.
Color and shine:
Distinguish between homozygous: gray and heterozygous - iron gray.
Why, you ask, why are two different coat colors allowed? After all, it has just been said that the breed must be monochromatic. We can only state that the allowed two-color is the result of a certain consensus of breeders of past centuries. It happened historically. At a certain stage, further work on weeding out the color of the "savages" was deemed inappropriate. Obviously, as it was not possible to achieve our plan. But the fact that agouti rabbits with a homozygous set of genes were not included in the standard already speaks volumes. It was they who could bring down all the work done, return all the livestock to the starting point.
Immediately, I note that although homozygous and heterozygous flanders are easy to distinguish, both of these colors are quite similar in perception and can change during life even in one rabbit. In addition, darkening or lightening is clearly visible on different parts of the body. If you look at the rabbit's hair under magnification, it does not look the same, the hair color is distributed in three annular zones with different shades and lightening. Each has its own pair of genes, plus a few others that distribute these zones along the width and thickness of the hair. This fact is taken into account in the standard, which allows certain liberties for color and sub-color. In general, the former have a predominantly gray bias, the latter towards agouti. Often the color of agouti is simply referred to as gray. But the authors of the catalog still, given some deviations in one direction or another, identified it as iron gray.In fact, the Flandre breed standard allows for significant deviations from gray or iron gray in certain areas of the body.
Gray cast iron (without agouti inclusions):
- The base color can change from above to a moderate blackish, subject to the presence of brown specks.
- The edges of the ears and the parietal region are black.
- The wedge on the forehead is small and has a rusty color. The belly and ponytail below are light.
- Inside, it changes slightly towards an increase in brownish spotting. The iris of the eyes is brown.
- Claws of dark colors of the horn.
- Subcolour: The undercolour is about two-thirds of a hair's length and is colored blue, after which the color starts black.
Iron gray (interspersed with agouti):
- The general color is brown, in the depth there are more or less black ends of the guard and coarse hairs. Thanks to this, the body casts a dark shade. Depending on the direction of stroking, it takes on a lighter or darker shade. It should be balanced and cast as much as possible on the stomach and on the inside of the limbs.
- The color of the chest and dewlap is slightly lighter than the color of the body. On the neck, a rusty brown wedge defines its appearance. The rim of the ears is blackish, like the withers above, but they are spotted.
- A sign of agouti is also a lightened area around the eyes, jaw, as well as its continuation. The color of the belly is white with a bluish tinge.
- The spots on the lower back are brown. Preference is considered when in front of the body, white is not visible.
- The iris of the eyes is brown.
- Nails of dark colors of the horn.
- Subcolour: at the base the color is light, then it becomes more and more blue, and finally turns into brown. This is followed by a pale black ring that becomes bright at the end of the hair.
Flandre at the exhibition. Expert assessment.
Rabbit weight:
The catalog does not show the dynamics of weight gain, but only the final figure for 8 months: 7.0 kg or more. She completely refutes the tales about the fact that the Flanders existed only in the old days, were kids and only the Germans "made" a giant out of them. We will use averaged data for different farms, given that they can differ significantly even within the same farm. For medium-sized rabbits, such as Californians, New Zealanders, the spread is not as large as it might be in this case. After all, some individuals easily overcome the 10-kilogram line.
Growth curve up to 8 months.
Rabbits grow especially quickly in the beginning. The first months are added by the kilogram. Then the pace slows down, and the amount of feed consumed, on the contrary, increases. Thus, the growth curve ends upward bending after 4 months, smoothly transitions to a horizontal straight line after 8-9 months.
Permissible deviations:
A slight deviation from the giant type. Weak ears (texture). Dull color, an admixture of individual white hairs with the hair of the main color, white blotches in the edge of the ears, colorless upper ends of the hair, areas with insufficient brightness of the coat. Deviation in sub-color.
Inadmissible deviations:
Complete deviation from the giant type. Massive scattered white hairs or white patches. Black head, brown intermediate color, whitish tummy or dewlap with a predominance of iron gray. Lack of reddish brown intermediate color in grays. Colorless claw.
Content recommendations
Experienced rabbit breeders note that it is quite difficult to care for animals of this breed, since they are demanding on the conditions of detention. Flemish giants are thermophilic animals, therefore in some countries, where the mark on the thermometer drops below -10 ℃ in winter, they are kept in warm rooms. If flanders are left outside or in an unheated barn in frosty weather, there is a high probability that they can catch a cold and even die.
Due to their large size, such rabbits need spacious cages.The optimal dimensions of a single dwelling are 110 × 70 × 50 cm, and for a rabbit with young animals - 170 × 110 × 50 cm.
In the following video, you can get some useful information about some of the feeding and care habits:
Representatives of the breed are distinguished by good resistance to various infectious diseases. However, this does not mean that animal cages can be harvested less frequently than usual. Flemish rabbits, no less than their other brethren, need to maintain cleanliness and order that meet standard sanitary requirements.
With regard to nutrition, here it is necessary to remember one very important point. It is advisable to add biomycin to the food for giants.... Otherwise, the owner risks losing his pets, as they quite often die from bloating.
The fluffy giants should be fed not only with dry grass (fresh hay must be poured into the cage every day), but also with grain and various “wet mixes”. They should include mixed fodder and various vegetables in crushed form: boiled potatoes, pumpkin, cabbage, carrots, fodder beets. Salt can be added to the mash, but in very moderation. Even in the diet of flanders, they sometimes include fortified meat and bone meal, and also introduce medications (if necessary). It is imperative that giants, like any other animal, must always have access to fresh drinking water.


The daily diet of rabbits should contain hay and fresh vegetables.
Care and maintenance
Successful breeding and keeping healthy offspring requires special attention for its habitat. Considering the size of the animal, a more spacious cage should be selected. In no case, the cage should not have a mesh bottom - this can damage the pet's paws. The location should be kept warm and dry and drafts should be avoided. You need to feed the animal at least twice a day.


A healthy and well-nourished pet should eat fresh and boiled vegetables, hay, green grass, seeds, and plenty of cereals. It is important to diversify food, since with a uniform and balanced diet, the rabbit receives the vitamins most important for the body. In addition, there should always be clean water in the cage for consumption. It needs to be changed at least once a day. High-quality nutrition and regular intake of water stimulates the production of mammary glands in females, and this further provides dynamically developing offspring.
How to choose a bunny
If you decide to purchase rabbits, then it is best to do this on a large farm where professionals are engaged in breeding of pedigree animals. Having decided on the appearance and color, it is necessary to take into account the following recommendations:
- choose rabbits born to a 2-3-year-old female and fed on breast milk for a long time;
- do not buy an animal that is less than 2 months old, otherwise you risk getting an insufficiently strong baby;
- pay attention to the build, bite, coat condition and overall activity of the bunny.


The safest way is to purchase rabbits in specialized nurseries from experienced breeders.
Tips for choosing a rabbit of this breed when buying
It is recommended to purchase rabbits of this breed on the farm or in the nursery. The breed can be distinguished by the shape of the head and ears. First of all, you should look at their parents. A female's first litter is rarely successful. But even older rabbits can no longer give high-quality offspring. The average age of the female is optimal - 2-3 years. When a giant is taken as a decorative one, it is better to choose it from a small offspring.
The best buying age is 3-4 months. It is necessary to pay attention to the appearance of the bunny. Eyes should be bright, nose and eyes clean.It will not be superfluous to stroke the baby and make sure that the coat is clean, without tangles and pleasant to the touch. Behavior should be active enough.
Advantages and disadvantages of the breed
Some rabbit breeders believe that purebred flanders are not suitable for breeding in Russia due to climatic conditions. Giants do not tolerate frost well. For this reason, the preferred option is called rabbits of local breeds, which were bred on the basis of the Flemings. To agree with the above point of view or not is everyone's business. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the most significant pros and cons of the breed in order to be able to form your own opinion:
| Benefits | disadvantages | ||
| 1 | Resistance to infectious diseases. Giants are less prone to rabbit diseases than their brethren | 1 | Colds. The breed was developed in a region with a mild climate and frost-free winters. Therefore, in our country, year-round keeping of Flandre rabbits in street cages is unacceptable. If the animal is not moved to a warm room, it will easily get sick and may die. |
| 2 | Friendly nature. They are very calm animals that do not show aggression. Representatives of the species get along well with each other and with humans. | 2 | Bloating, especially in young rabbits. As a preventive measure, the owners have to constantly introduce medicinal additives into the feed. |
| 3 | High fertility. Females hatch from 6 to 10 rabbits in one round and are able to feed them without any problems | 3 | A small slaughter yield of meat - in comparison with special breeds, 5-7% lower |
| 4 | Large slaughter weight and size of the skin | 4 | Insufficient quality of the skin. Despite the large size and wool, which is distinguished by its density, there is very little undercoat in it, which significantly reduces the value of the products obtained. |
| 5 | Long ripening. The optimal age for slaughter for giants is 6 months, which is approximately twice as long as compared to rabbits of specialized meat breeds. | ||


A small amount of undercoat does not protect flanders from frost, which makes them vulnerable to colds
What are the difficulties of content?
Check out these articles as well
- Duck Star 53
- Top dressing of cherries in spring
- Processing trees in spring
- When to plant zucchini for seedlings
The easiest way to keep the Flandre rabbit breed is in shelving cages. The method is very simple: the cells are arranged in a wall, standing on top of each other. Thanks to this, you can not only save space, but also separate different individuals from each other (young animals from mothers, females from males, and so on).
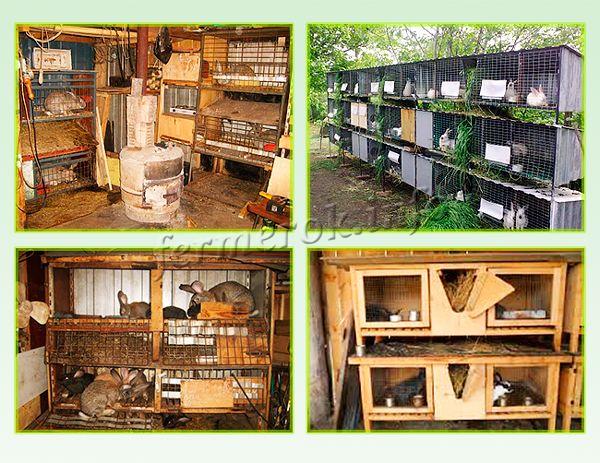


The easiest way to keep the Flandre rabbit breed is in shelving cages.
The size of each such "room" should correspond to the size of the animals living in them and their number. One adult needs a cage 110x70 cm and 50 cm in height. For a female with rabbits, you need twice as much space. The type of cages is selected on an individual basis - what the breeder can afford.
You can leave nothing on the floor when kept in cages, but only if the floor is wooden! When breeding animals in a rabbitry without cages, it is important to take care that there is no "secret passage" out of the room, otherwise the animals will quickly scatter. There should be only one exit (lockable) for walking. The floor is made of wood, concrete, a layer of straw is laid on it so that the animal is not cold.
No matter how the Flandre rabbits are kept, the room needs windows, an established ventilation system, and sometimes heating. Walking can and desirably be arranged - even in large cages and pens, individuals will be cramped. Fresh air and vitamin D are as necessary for them as for humans.
One of the major difficulties is the disease inherent in the species.
- Due to their heavy weight, Flandre rabbits may have corns on their paws (calluses or something like that). The problem is treated with a cream or ointment, which can be purchased at a veterinary store.
- Ear mite - is treated with a solution of sunflower, camphor oil mixed with tar. The resulting becoming mixes well and is buried in the sore ear. After 3 days, the disease disappears. However, if the tick has settled deep in the ear and managed to lay eggs, then after a while the procedure will have to be resumed, since the disease will return.
In order to avoid other, more serious problems, it is necessary to get the appropriate vaccinations for animals from an early age.
Also, the animal's fur coat can cause difficulties. In order for it to have a marketable appearance, you need to take care of it: clean it in time, make sure that the shine, color is not lost, does not fade, and so on. Sometimes the rabbit has to be bathed or brushed, but only in rare cases.
Reviews of rabbit breeders
Ekaterina, 45 years old, Ufa
Five years ago I decided to breed rabbits. My first purchases were animals of the Flandre breed. I have never regretted it. They turned out to be large and unpretentious. Minimum investment in time and money: vaccinations, adequate feeding and timely cleaning - that's all they need. Females are wonderful mothers. Now I breed other breeds, but I will never give up the Belgian giants.
Valery, 53 years old, Krasnoyarsk
I did not even suspect that this breed is so much better than its relatives. Flanders are distinguished not only by their impressive size and power, but also by their intelligence, obedient and quiet behavior, they allow themselves to be stroked and do not jump out of the cage. Not rabbits, but a dream. They live in my country house. Every day I feed them harvested hay, grass, young tree branches, barley, oats, grain feed for rabbits. I plan to introduce fruits and vegetables into my diet.
Konstantin, 38 years old, Lipetsk
I have been breeding rabbits for a long time, recently decided to try Flemish giants. It turned out that they are really large in size, while completely unpretentious, they eat everything you give. It turns out a decent yield of meat, there is no need to purchase it in the store. If you find where to donate the skins, you can also make a good profit. Therefore, I advise everyone who wants to have rabbits to take flanders without hesitation.
Mister Tail Explains: Breeding Prospects in Russia
Today, the breeding of this breed in our country is progressing at a good pace, due to its excellent fertility.
The female reaches puberty late - by eight months, but brings many rabbits.
For mating, the rabbit is placed next to the rabbit twice with a break of five days. The couple is left alone for a day and at this time all food is removed from the cage, leaving only water.
Before the birth, the pregnant rabbit is placed in a special cage with a queen cell - a nest for childbirth. The expectant mother is well fed and fed a lot. Pregnancy and childbirth are easy, without assistance. Often, flanders females give birth and 16 rabbits each, which weigh up to 100 g at birth.
In a month, babies reach 800 g, at two - 1.5 kg, at three - 2.5 kg, at four - 4.5 kg, by eight months they can weigh 7 kg. Adult rabbits - 10-15 kg, females - 8-10.
Disease resistance
The Belgian giants are not very healthy. They are characterized by:
- frostbite of the ears;
- joint diseases;
- thermal shock;
- skin problems (due to improperly selected flooring).
But rabbits carry infectious diseases much easier, the main thing is to vaccinate the animal on time.
Monthly rabbits are necessarily given injections for myxomatosis, pasteureliosis, viral hemorrhoids.
Then the animals are vaccinated every year (preferably in spring), with three different vaccines with an interval of 14 days.
Flandre breeding history (new facts)
It is known for certain that the Flanders breed (Belgian rabbit) was obtained in the 16th century in Flanders near the city of Ghent (Belgium). The first mention of the breed dates back to 1860. The breed has turned out as a result of experiments, naturalists.According to one version, mixing of blood was used to remove flandr:
- Old Belgian rabbits, (average weight 3.4 kg);
- European variant of the Patagonian rabbit (weight unknown);
- Patagonian mara (Dolichotis patagonum), the second name is the Patagonian hare (weight about 8.0 kg).
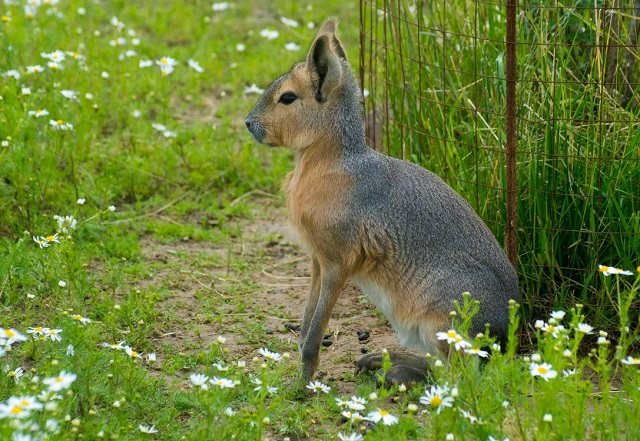


Photo. Patagonian mara. This animal may have participated in the emergence of the Flandre breed. However, the information is not reliable,
Patagonian mara is a rodent (pig) that looks like a rabbit. Crossbreeding of animals of different species capable of further reproduction is unlikely. Many people think that the mara bleeding is a hoax. Although hybrids of different species of animals (mule, hinny) are known, they are not capable of bearing offspring. Only after 1912 a separate detachment - lagomorphs - separated from the rodent detachment. Until that time, the rabbit and the maru were considered animals from the same order of animals.
The reasons for the multiple increase in the weight of Flandres, in comparison with the size of his parents, in a short period of time remain unknown. In the very first description of the breed standard from 1893, the weight is 6.4 kg. rabbit, and its progenitors at the same time weighed only 3.4 kg. It doesn't matter who you bred with, let it remain a mystery.
The main thing is that Flandre became the ancestor of almost all large rabbits in the world, and scientists were able to breed giants of the meat and meat-skin direction.
Flandre rabbit diet
- The main food for rabbits is crushed grain. Vitamins in feed. It is better to give not one type of grain, but grain mixtures. containing oats, barley, corn and others. A rabbit's stomach is not adapted to digest grass like a cow. Rabbits need grass as an auxiliary feed containing vitamins and in order for the stomach to work better. The main digestion of food in rabbits does not take place in the stomach, but in the cecum, it is huge in them.
- The rabbit should always have food in the feeder, rabbits, not an exception, Flandra constantly chew, this is their physiological feature
- In a rabbit, saliva is secreted constantly, and not periodically, as in other animals;
- The rabbit's teeth grow constantly; to grind the incisors, it is imperative to give roughage (branches, hay).