One of the main problems that summer residents who grow grapes face almost every year is powdery mildew or powdery mildew. This harmful disease of grapes is widespread in all countries with developed viticulture, usually in areas with dry and hot summers. However, grapes can be saved. You will learn how to completely suppress powdery mildew in early spring so that in the fall the annual vine is free of infection even in the most susceptible grape varieties, you will learn from our article.
Description of the disease
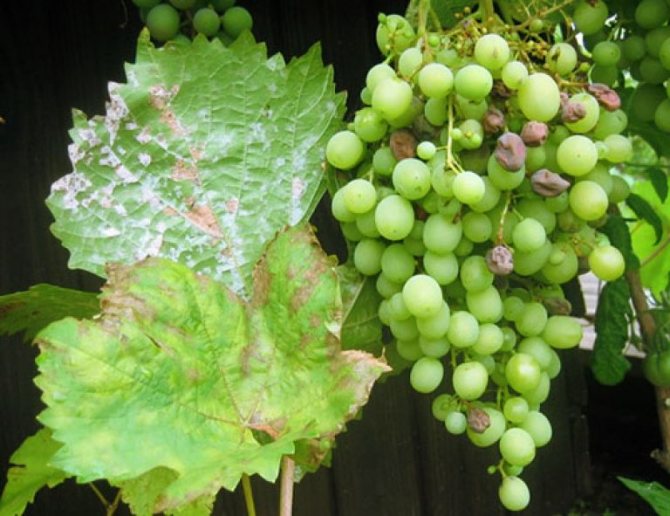
Oidium is a fungal disease that affects the entire grape bush. Let's give a brief description of the disease with photos:
- the plant is covered with a grayish-white bloom;
- first, the fungus infects shoots and leaves;
- if the plant is not treated in time, then the inflorescences will also become infected;
- the disease develops rapidly and infects nearby vines. So the whole harvest and grape bushes can perish;
- incubation period - only 1-2 weeks;
- the pathogen develops only on living parts of plants.

Advantages and disadvantages of folk remedies
Benefits:
- Do not harm the environment, animals, humans, fish and birds;
- As a rule, the ingredients for making folk remedies are very cheap, if not even free;
- When processing plants, there is no need to use personal protective equipment;
- You can carry out multiple processing of plants.
Disadvantages:
- They are not always effective in the fight against the causative agent of the disease, they are more suitable for the preventive treatment of the vine.
Reasons for the appearance
The disease occurs as a result of infection with fungal spores, which are carried by the wind. Once on the bush, they begin to develop intensively and penetrate into living cells.
But the favorable factors for the onset of the disease also include:
- warm (+ 25 ... + 30 ° С) and humid weather, but the presence of moisture is not a prerequisite, the determining factor is high temperature (up to + 30 ° С). With prolonged dry and hot weather, rains can even stop the progression of the disease;
- winters with temperatures above -30 ° C (in colder weather, spores may die);
- high density of branches and leaves (with poor pruning), as well as densely planted seedlings.
Did you know? It is believed that grapes are found only in countries with warm climates, but they are successfully grown in Sweden, Scotland and Norway.
What is oidium and when does the disease progress?
Farmers know this disease as powdery mildew. This is the most common grape disease of all. The cause of infection is a fungal formation that affects everything green that is on the vine and settles on the berries. After such an infection, the grapes are unsuitable for making wine or brandy. Eating is acceptable, but the bitter taste will not allow the grapes to be put up for sale.
A few decades ago, when grapes were just beginning to be grown in the middle lane, no one knew about oidium, the vineyards grew successfully and bore fruit richly. Recently, the situation has changed, the fungus has even reached the northern corners.
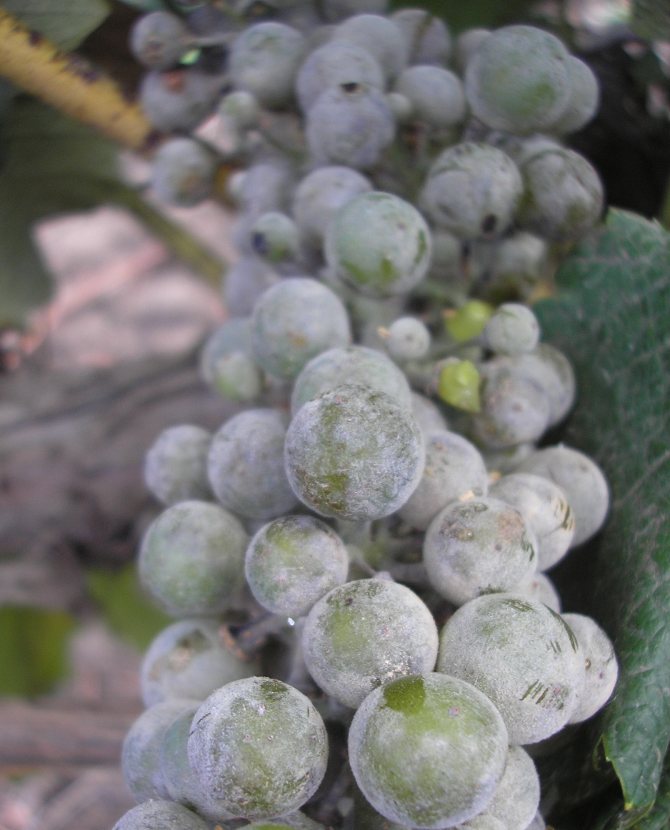


At temperatures above +18 ° C, the fungus germinates
The most dangerous set of circumstances for the vine is cold winters and sultry summers.Fungal spores live under the scales of the eyes throughout the winter, infect shoots and do not make themselves felt until the onset of heat.
At temperatures above +18 ° C, the fungus germinates and begins to destroy leaves at a high speed. High humidity speeds up the infection process even more, but not dripping moisture. Rain and watering the leaves wash away the spores and inhibit their development. True, watering also harms the grape leaf itself, so farmers water the grapes only at the root.
Tip: before planting, decide on the grape variety, choose strong and disease-resistant. Eliminate unnecessary shoots. Choose fertilizers that do not contain excess nitrogen.
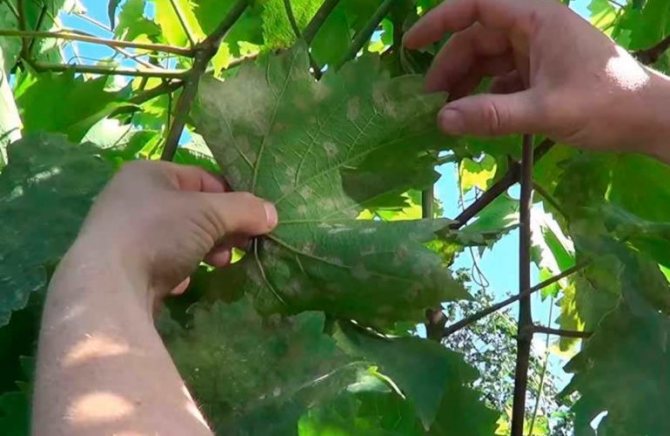
Signs of oidium on grapes
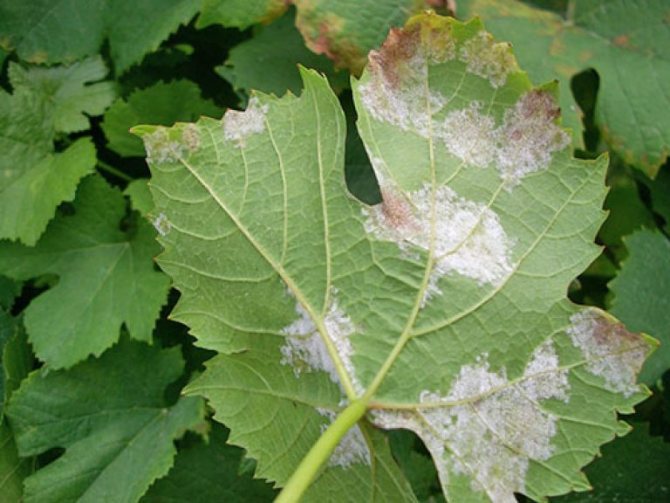
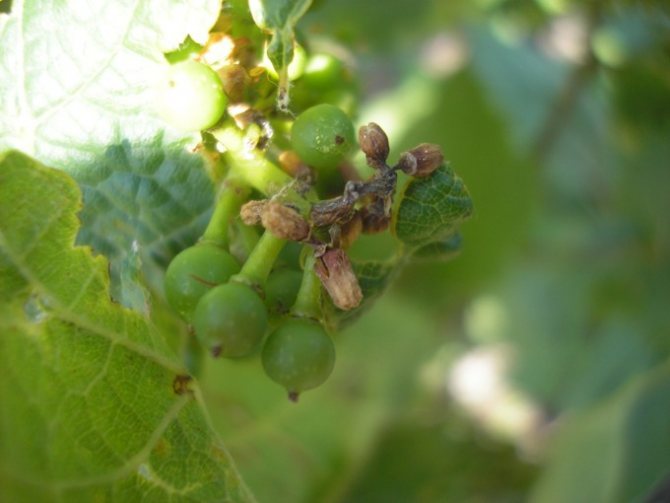
The disease almost does not affect strong and well-developed plants; weaker or younger specimens are affected.
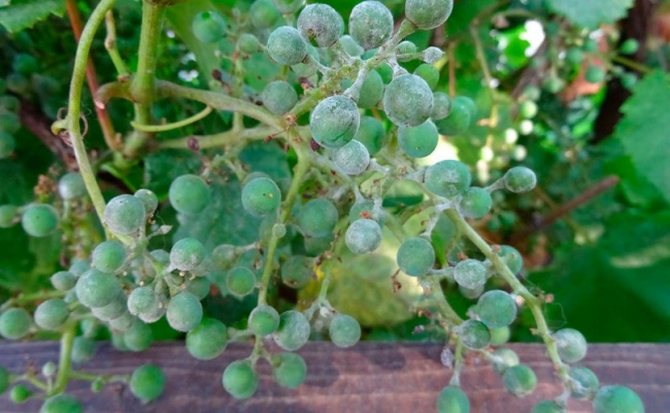


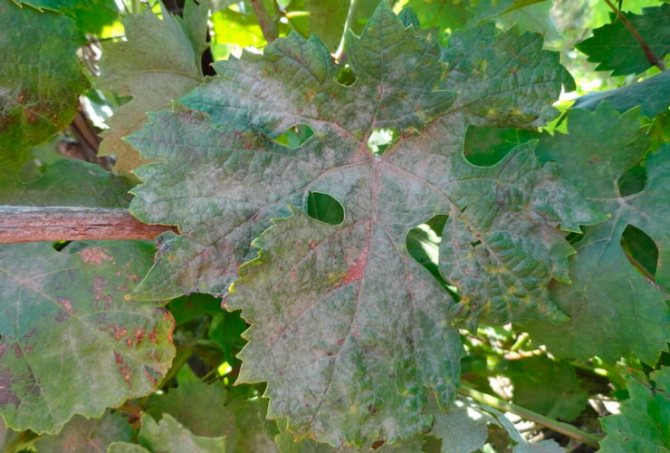
The disease is evidenced by the following signs that appeared on the vine:
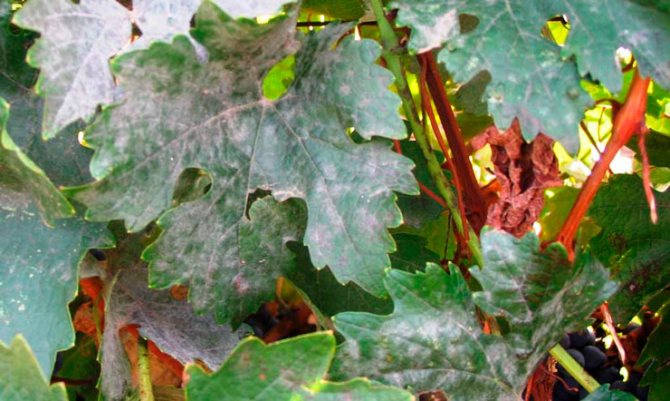
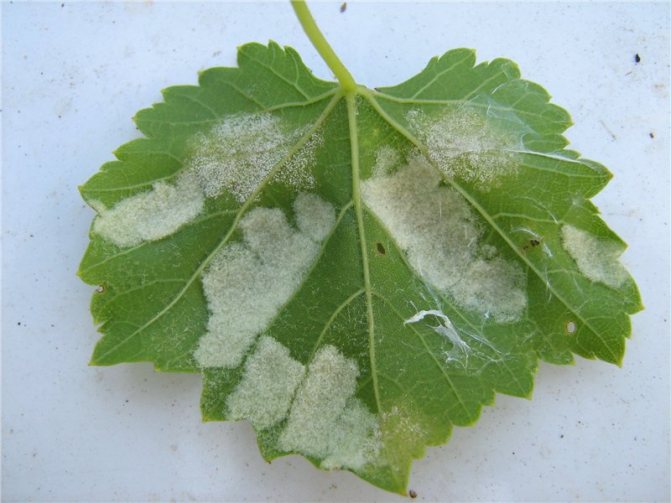
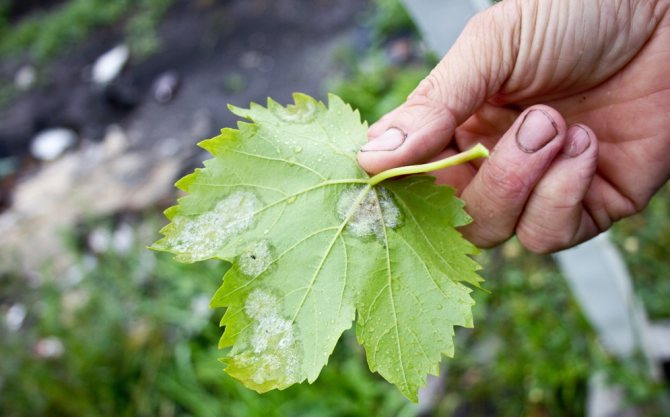
- the leaf blade, and later the stems, are covered with a white coating, very similar to flour;
- when the spores mature, the color of the plaque changes to grayish;
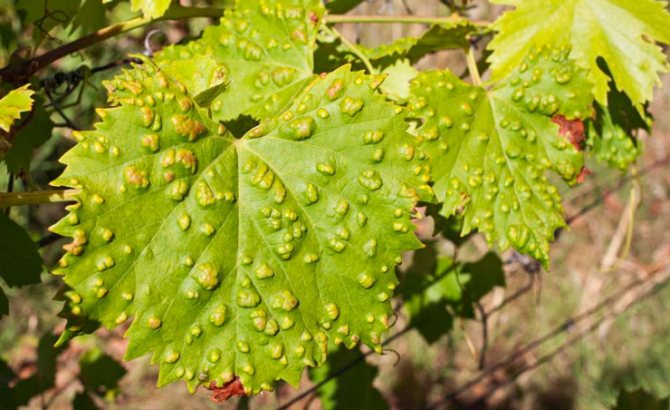
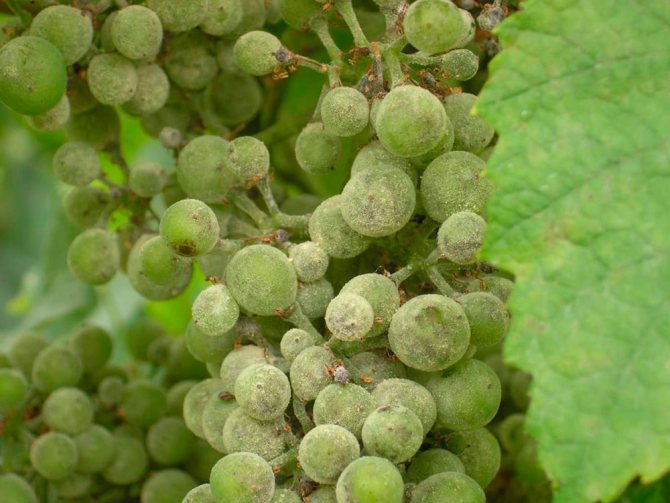
- green shoots are covered with brown spots, which do not disappear even after lignification. These shoots are not suitable for harvesting cuttings;
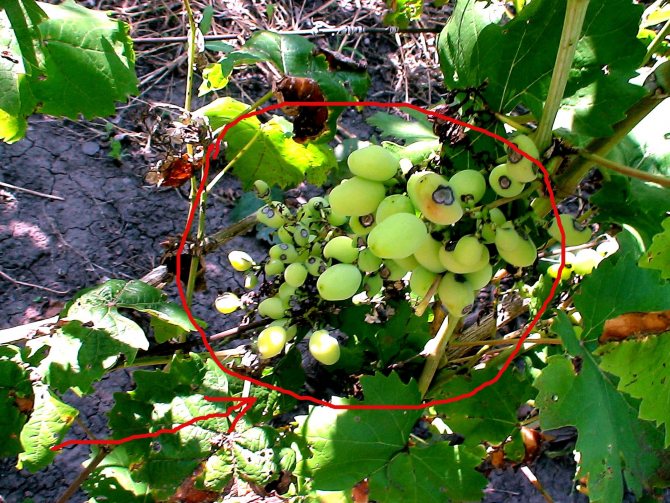
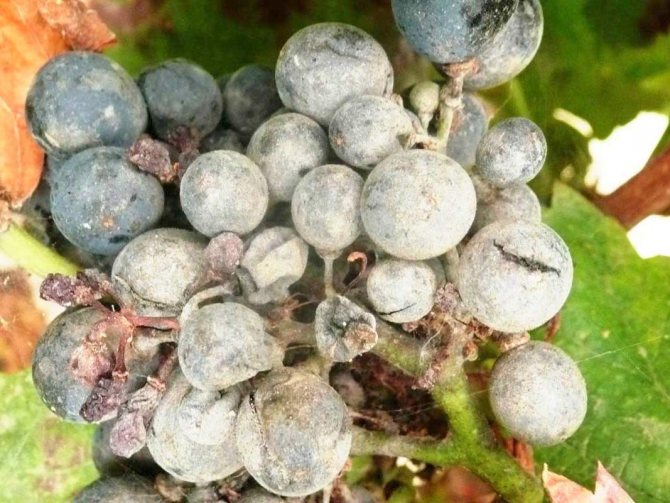
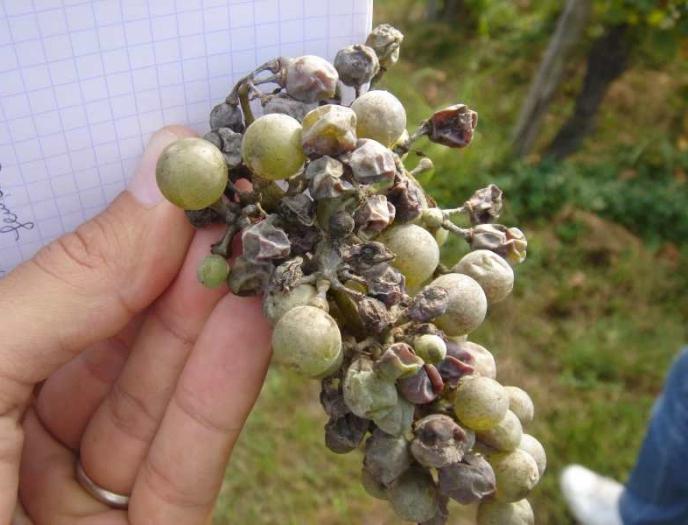
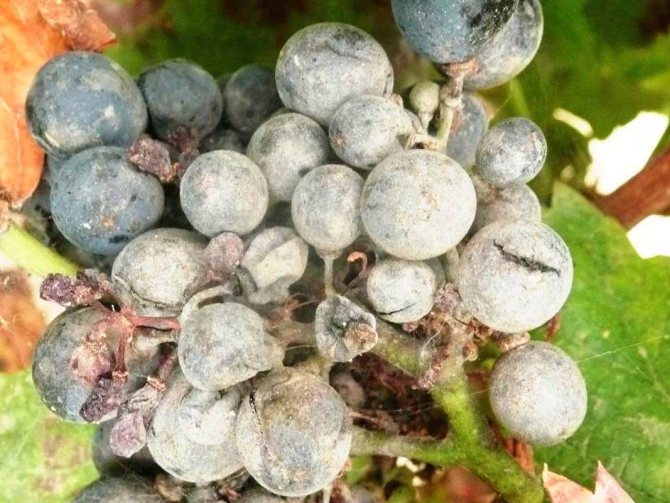
- the berries are also covered with a bloom, begin to stagnate and may crack. The most vulnerable are young fruits with sugar content below 8%;
- at the stage of coloring the berries, a reticular pattern appears on the skin, and it becomes tough;
- if the fruits are infected at a late stage of ripening, then they can grow further, but acquire a sour taste;
- at a later stage, the leaves curl, and the berries dry out;
- rubbing the plaque with your fingers creates an unpleasant smell of stale fish.
Did you know? Planting parsley under a grape bush can prevent many grape diseases.
Powdery resistant varieties
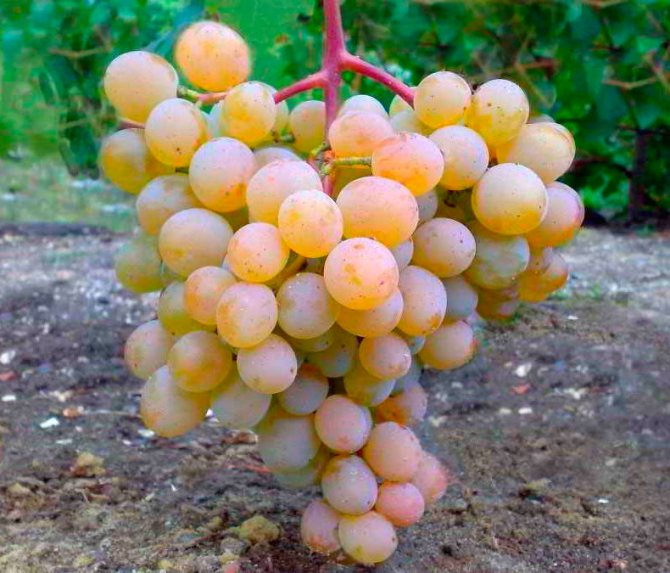


To date, there has not yet been created such a grape variety that would not be amazed by powdery mildew. However, there are varieties that are very resistant to both powdery mildew and other diseases caused by various pathogenic fungi.
It has already been mentioned above that all European grape varieties are the least resistant to powdery mildew. The most resistant to powdery mildew was recognized as such a variety as Vostorog, as well as hybrids created on its basis: Talisman, Delight oval (Baklanovsky), Delight ideal, Gift to Zaporozhye, Timur, etc. Also, they are highly resistant to all fungal diseases, including powdery mildew. such grape varieties as: Victoria, Kishmish Zaporozhye, Galbena-no, Aleksa, White Miracle, Velvet Muscat, Platov's Jubilee, Gift to Ukraine, Pink Timur, Matryoshka, Denal, Golden Don, Lark, Caucasus and Sasha. And also rarely affected by oidium varieties created on the basis of the species - Vitis Labrusca, for example: Alden, Alwood, Fredonia, Isabella large-fruited, New York Muscat, Pocklington, Supaga, Juodupe, Mars, Venus and Ainset Sidlis. There are also varieties that are resistant to a whole range of diseases, including fungal diseases. These varieties include: Marinovsky, Platovsky, Crystal, Harmony, Millennium, Amethyst of Novocherkassk, Lancelot, Beautiful Flora, Kishmish Klyuchikova, Pleven, Eurostandard, Bogotyanovsky, Archny, Anthony the Great and Nadezhda AZOS.
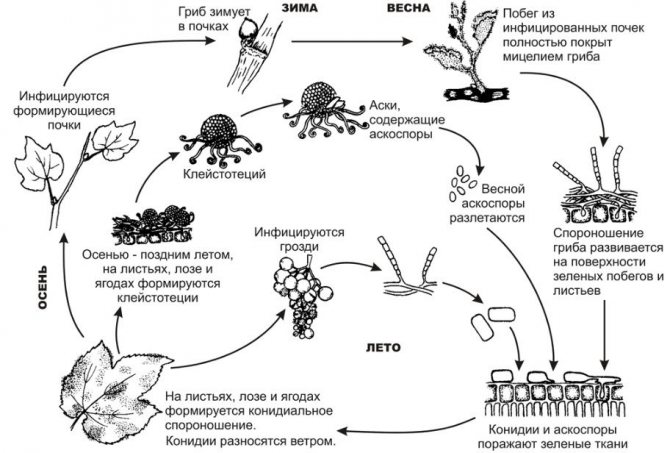
Pathogens and stages of development
The fungus develops in the conidial and marsupial stages. Its life cycle consists of the following stages:
- Hibernates in buds in the form of mycelium.
- In spring, hyphae begin to grow: shoots and young foliage (the upper part of the leaf plate) are covered with mycelium spots.
- Conidia are formed on the mycelium.
- Conidia crumble and are carried by the wind to new plants.
- Germinating, conidia form hyphae, which attach to the plant with appressoria, and penetrate inside with haustoria. The optimum humidity for germination is 70–95%, and the temperature is + 16… + 25 ° C.
- New conidia are formed 5–12 days after infection. At temperatures above + 30 ° C and humidity below 35–40%, conidiophores die.
- In autumn, fruiting bodies with asci (bags) grow on the affected tissues, inside of which spores form. Fruit bodies are weakly retained by appendages and are easily washed off by rains. Once in the ground, they die.

Powdery mildew: false or real


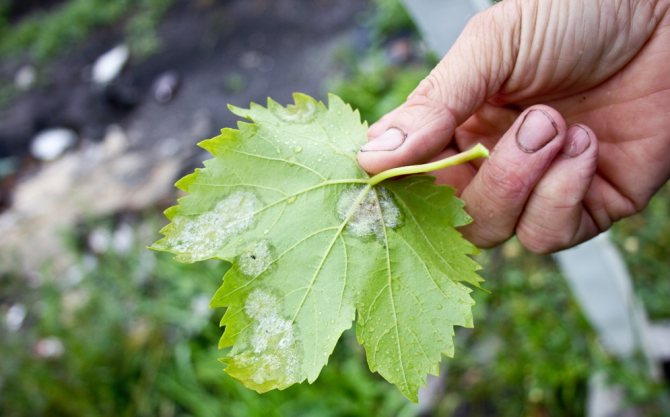
Powdery mildew on a bunch of grapes
Fungal infections are increasingly attacking berries in the garden, making the fruit unusable and unfit for further processing. Powdery mildew on grapes is the most common disease known to every gardener. Its second name is oidium. The "troublemaker" - the causative agent of the disease - lives only in living culture. The spores of the fungus overwinter in the scaly structure of the vine. At an external temperature of 18-25 ° C, the heat begins to actively germinate. The higher the humidity, the more actively the mycelium grows. Symptoms of grape disease vary at different times of the year. But the end is one - the plant loses flowers, fruits, leaves. Cracked, rotting berries are not suitable for further use.
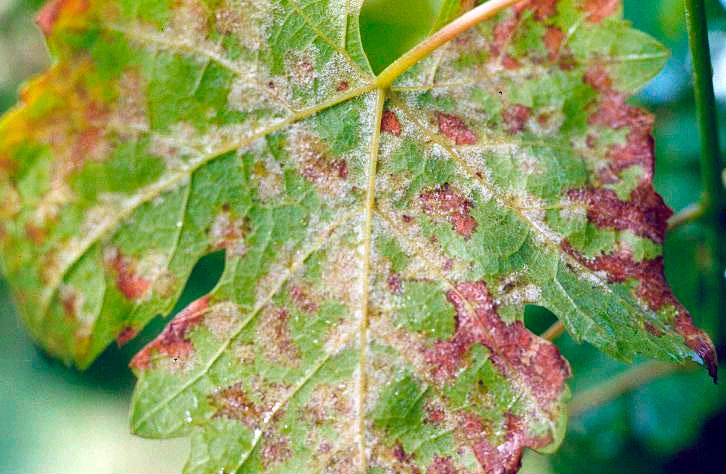
American fungus - downy mildew of grapes (mildew) - multiplies and develops in all terrestrial areas of the vine. It is expressed on foliage by orange, yellow light brown spots with an oily tint. Well-distinguishable circles of different sizes on a young leaf blade and irregular angular shapes elongated along the veins on old leaves. On the back of the leaf, at the site of the formation of spots, mycelium appears after a while. Affected clusters turn yellow. The brush is deformed and takes on a brown tint. Spores tolerate frost in the ground and fallen leaves. If you do not take measures, in such conditions they will remain active for about 5 years.


Mildew
Methods for treating the disease
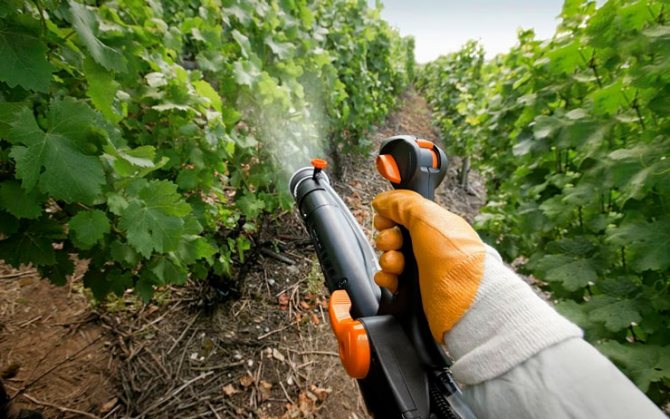
Like any disease, powdery mildew is easier to prevent than to cure. But if time is lost, it is important to know how to process the plants. You can use both chemical agents and folk methods.
Find out how to process and how to deal with mildew on grapes.
Preparations and effective remedies
When the first signs of oidium are found, it will help get rid of it:
- spraying with 2% lime-sulfur solution;
- use drugs "Topaz", "Fundazol" or "Aktara" (according to the instructions);
- treat the bushes with 1% colloidal sulfur. If the temperature is above + 20 ° C, then pollination with sulfur (fine grinding) can be carried out, at a lower temperature it is ineffective;
- if the infection was observed in previous years, then you can use the drug "Horus". Spraying is desirable for young greenery. This chemical is effective in cool weather;
- if "Horus" did not help, then "Strobi" should be used (used no more than 3 times per season);
- the complex preparation "Kabriotop" is used not only to combat powdery mildew, but also to combat anthracnose and mildew;
- Oxyhom treatment consists of 4 treatments. The first - 10-14 days before flowering, the second - after flowering, the third - during the formation of fruits, and the last - at the stage of technical maturity;
- during the ripening period of berries it is not advisable to use "chemistry", potassium permanganate (5 g per 10 l) will suspend the disease for a while.


Important! Sulfur-containing preparations are effective for about 10 days, therefore, if the lesion is severe, the treatment is repeated after 2 weeks. If the rain washes away the chemicals, the spraying is repeated.
Folk remedies
The fight against the disease is possible using folk remedies. Popular measures include:
- baking soda). Dissolve 3 tbsp in 3 liters of water. l. soda and 1 tbsp. l. soap. Spraying is carried out immediately;
- copper sulfate is used before bud germination. 10 g of vitriol is used for 10 liters of water;
- for the ash solution, 1–1.5 kg of ash and 10 liters of water are taken. The product can be infused for 4–5 days or boiled for 20 minutes.Before processing add 20-30 g of soap;
- colloidal sulfur + Bordeaux mixture (1: 1) Is also a fairly effective method.
Read more about why grapes rot and how to save a plant.
Agrotechnical measures in the fight against powdery mildew
Treatment of grapes from powdery mildew will be successful with an integrated approach to the problem. In the list of agrotechnical measures, it is worth mentioning:
- Planting healthy, fungal-resistant varieties: Rkatsiteli, Aligote, Sauvignon, etc.
- Thinning of plantings of grapes. Breakage of old and affected leaves (especially those touching the ground), peduncles.
- Destruction of overwintered spores. Spraying grapes and root circles with Nitrafen (3%) or DNOC (1%) is carried out in early spring, immediately after the opening of the vine.
- Pruning dead wood, stepchildren. Bushes should be well ventilated and sunlit.
- During the period of growth of the lesion, no fertilizing of the bushes is carried out at all. In other cases, preference is given to phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and less to nitrogen fertilizers.
- For prophylaxis 6-7 times a season, a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%) is used. Processing begins immediately after exposing the bushes in the spring. But no earlier than three weeks before eating the berries, the processing should be stopped.
Prevention measures
The likelihood of infection with powdery mildew is reduced if:
- remove excess shoots. In early May, excess buds are removed. With the growth of shoots from 10 cm to 40 cm, 2 more pruning is carried out, contributing to thinning and good ventilation of the bush;
- fertilize plants, for example, ash (300 g for each bush) or Fertika fertilizer before flowering;
- burn the leaves and the cut vine.
Tank mixtures are considered effective methods of prevention, this is when not one, but several drugs are used at once. This eliminates the addiction effect of the fungus to a particular fungicide.


Several treatments are carried out:
- before flowering, the bushes are sprayed with the following composition: "Ecosil" (40 drops), "Ridomil" (20 g) and "Topaz" (2 ml). Preparations are diluted in a bucket of water;
- after flowering, you can apply "Kataran";
- when pouring the fruits, the previous mixture is used, but "Ridomil" is replaced by "Ordan" (25 g).
For prevention, you can use "Oxyhom" (2 times). The first spraying is carried out when the shoots reach a length of 20-30 cm, the second - after 2 weeks.
There are some more unusual methods of protection against powdery mildew. An interesting technique was proposed by the Latvian professor Gunvaldis Vesmins, which consists in the use of saprophyte microorganisms:
- In the spring, fill the 1/3 liter barrel with humus and fill it with water (+ 20 ... + 25 ° С). Cover with burlap and leave warm for about a week, stirring occasionally.
- Re-processing is carried out after 7 days.
- Before flowering - one more treatment.
Important! With any method of prevention, it is important that the pathogen does not appear from the outside, therefore, the beginning of treatments should be checked against the beginning of the development of the disease last year and the fight should be started in advance.
The essence of the method lies in the fact that the mycelium of the parasite is a nutrient substrate for the saprophytic microflora, which eats the pest. Treatments should be carried out in the evening or in cloudy weather.
Video: Methods of dealing with powdery mildew on grapes
Scientist Peter Crisp has established that milk fat is a breeding ground for microorganisms that compete with oidium pathogens. Treatment with 10% milk solution every 7 days prevents the development of the disease.
How to fight and how to treat for treatment?
Elimination involves a complex effect on the fungus: special chemicals and folk remedies are suitable, and the "emergency" method, which can be used immediately upon detection of the parasite, is sulfur treatment. But it is better to use such a substance at an air temperature of +20 degrees and above.In this case, the tissues of the fungus will react better with sulfur and absorb it.
Processing is carried out taking into account the following features:
- It is necessary to dissolve 100 grams of sulfur in ten liters of water.
- All plants are sprayed with the resulting composition in the morning or evening.
- The procedure is carried out daily for one and a half to two weeks, depending on the degree of damage and the effectiveness of the method.
If the concentration is reduced by half, the composition can be used as early as spring as a prophylactic agent. If sulfur does not help, it is necessary to use stronger biological agents or ready-made preparations.
Biological preparations
One such remedy is humus. It is poured into a one-liter barrel in an amount that will take up a third of it. The rest of the barrel is filled with warm water, then the container must be covered with a dense cloth that allows air to pass through for one week.
After this time, the liquid from the barrel is filtered to remove humus and used to spray on the grapes. Just two sprays per season are enough with an interval of 7 days. Additionally, the procedure can be carried out after the beginning of flowering, if signs of oidium began to appear on the inflorescences.
An alternative remedy is the drug phytosporin, which has the following advantages:
- the product is safe for people and animals;
- due to its broad spectrum of action, phytosporin fights simultaneously against fungi, bacteria and harmful insects;
- additionally has a protective effect, creating a protective layer on the treated surfaces that prevents the development of diseases.
Fitosporin is sold in gardening stores as a white powder or dark paste. Before use, it must be dissolved in water in accordance with the instructions in the instructions.
Chemicals
The most effective are concentrated chemical agents of broad action.
These include:
- Aktara;
- Acrobat;
- Rubigan;
- Speed;
- Bayleton;
- Vitaros;
- CM;
- Topaz.
Usually, to completely eliminate oidium spores, it is enough to process the grapes every one and a half weeks (a total of four treatments are required), but if you notice the disease in time and the parasite has just begun to spread, two treatments may be enough.
Such substances are very effective, they can harm the plant if the correct dosage is not observed when preparing a solution from a concentrate. They can also leave chemical burns on the hands, therefore, when preparing the solution and spraying, it is recommended to use protective gloves and long-sleeved clothing.
Folk remedies
When preparing them, it is also necessary to observe the proportions of the components used so as not to damage the plant and at the same time achieve the desired effect.
The most effective are the following formulations:
- One part of the mullein is filled with three parts of water and settled for three days. The finished composition should be diluted again with water in a ratio of 1 to 3.
- Add a tablespoon of liquid soap and three tablespoons of baking soda to 4 liters of water. The composition can be used immediately.
- For ten liters of boiling water, add two tablespoons of mustard powder and mix thoroughly. You can spray the grapes only after the mixture has completely cooled.
- Sifted ash in the amount of one kilogram is diluted in 10 liters of warm water and infused for five days. Once a day, the composition must be stirred so that the ash does not settle in lumps and dissolve. Before using - add a tablespoon of grated laundry soap.
Each of these products can be applied once every few days for a long period, since these formulations are not harmful to the plant. But if no effect is observed after two weeks, it is better to use store-bought chemicals that will cope with the fungus at any stage of its development.
Grape processing in autumn
Autumn is the main time for harvesting grapes. How to treat the bushes from powdery mildew at this time, if chemical preparations are already prohibited from using? If in the autumn period the signs of the disease, as in the photo, are not revealed, then the processing should be postponed to a later time.


It is best to carry out the procedure after harvest. If the disease has made itself felt, then chemicals can be used as needed.
Note!
Covering grape varieties must be processed after sap flow.









































