Radish pests and control
Radish is considered a fairly pest-resistant vegetable crop. But some insects pose a danger to him, mainly cruciferous pests, which also infect cabbage, turnips and radishes.
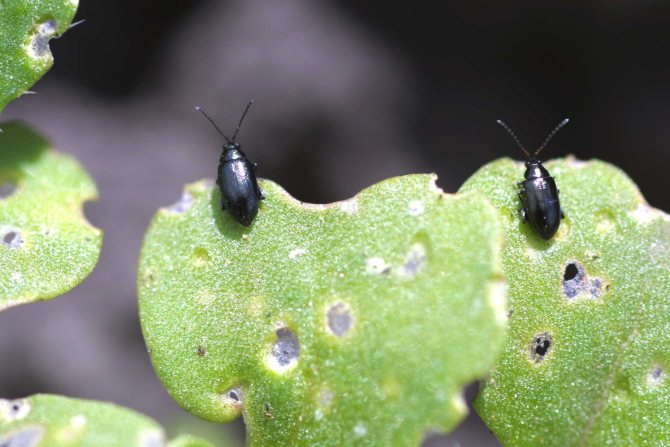
Cruciferous flea
The pest looks like a small black bug up to 3 mm in length. The cruciferous flea feeds on radish leaves, and the pest larvae eat the roots. The insect hibernates in the upper layers of the soil.

The cruciferous flea does not like the heat, so it is most active in spring.
Dusting the plantings with wood ash, tobacco or mustard helps best from the cruciferous flea; it is recommended to spray the powders over the beds immediately after germination. Chemicals Aktara, Decis and others also help to cope with the flea.
White butterfly
The danger for radishes is not adult butterflies, but their caterpillars. The first time they appear at the end of June, and the second - in September. You can recognize them by their yellowish-green color with a black pattern. The harm lies in the fact that the caterpillars of the white hare feed on the tops and can completely eat the radishes in a few days.
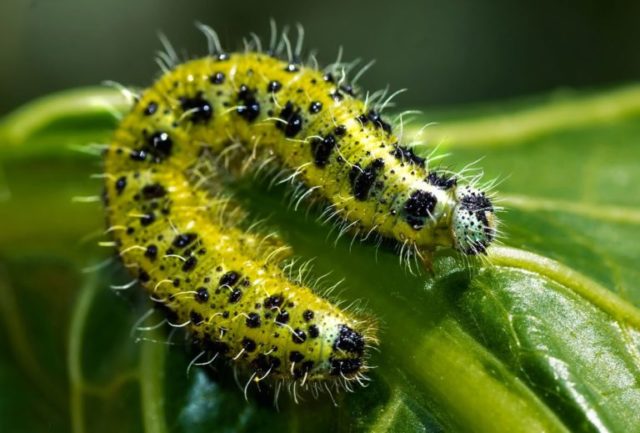


Whitefish caterpillars can destroy radish tops
To protect against planting butterflies, it is recommended to spray with herbal infusions of tomato tops, sage, wormwood - harsh aromas scare off the whites. If caterpillars have already appeared on the leaves, then you can get rid of them with the help of Actellik or Kinmix.
Advice! If there are quite a few hawk caterpillars on the tops, you can collect them manually, and then take preventive measures to scare away the butterfly.
Spring cabbage fly
In late spring, the cabbage fly poses a threat to radish - it is most active from mid-May to early June. The female flies lay eggs in the soil in the beds, and the hatched larvae begin to feed on the roots of the radish and often eat them from the inside. The tops acquire a characteristic bluish tint and wither.
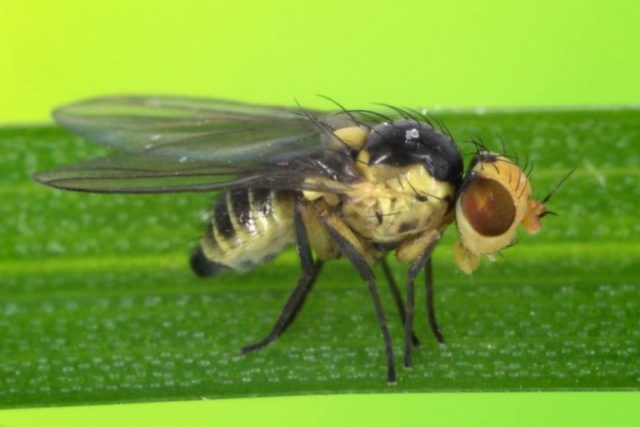


The cabbage fly lays eggs in the radish beds, and the larvae begin to eat the roots
To scare away insects, the beds are recommended to be pollinated with tobacco dust and crushed bay leaves. This should be done 5 days after germination. Actellic and other insecticides can be used for symptoms of severe infestation.
Cruciferous bug
The insect is a spotted red-black beetle. The female bug lays its eggs on the leaves, and the hatched pests hibernate in plant debris in the beds. In mid-spring, they wake up and begin to eat the tops; activity continues until August.
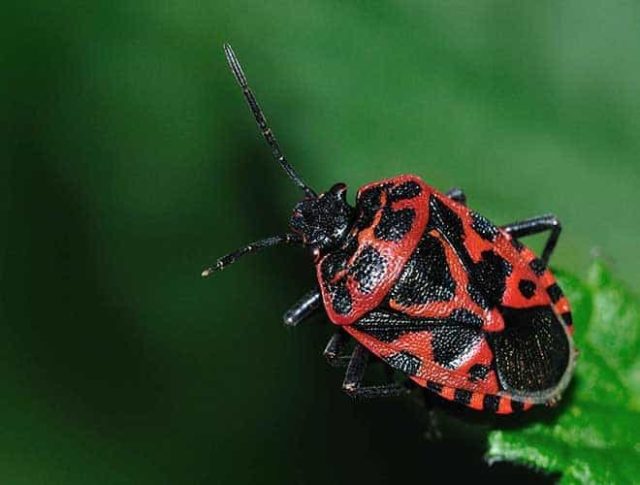


The cruciferous bug is very visible on green leaves.
To prevent the spread of the pest, it is recommended to spray radish with infusion of tansy in spring. Adults can be collected by hand or sprayed with Aktara and Belofos several times.
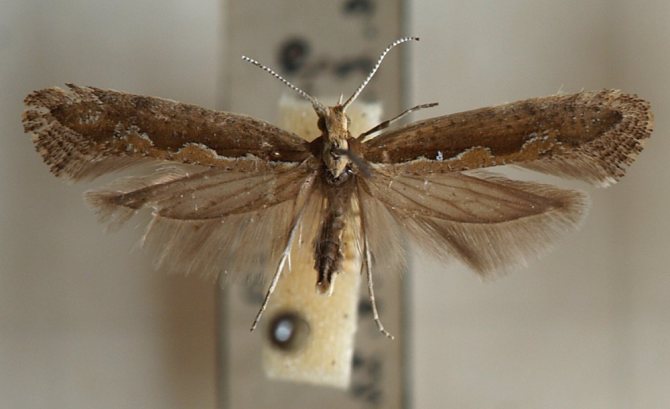
Cabbage moth
A yellow butterfly with brown spots on its wings lays eggs in the tops. The emerging caterpillars feed on the tissues of the leaves, leaving recognizable "grooves" in them, which lead to wilting and rotting of the radish.
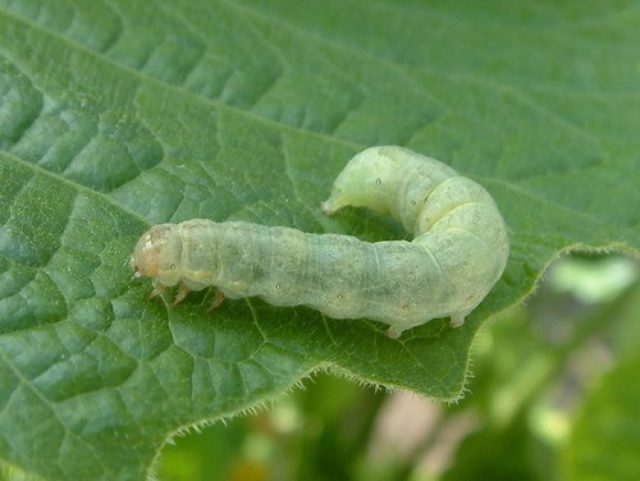


The moth caterpillars merge in color with the leaves, and it can be difficult to notice them.
You can treat radishes from pests with the help of Ripcord and Anometrin preparations.For the prevention of beds, it is recommended to spray with infusion of tomato tops or ash.
Rapeseed sawfly
The adult pest looks like a small brown insect with a black head, and the sawfly caterpillars are olive or greenish-gray, with dark longitudinal stripes on the sides. The sawfly feeds on the leaves of vegetable crops and can eat them up to the stalks, which will lead to the death of the radish.


If you do not fight the rape sawfly, you can lose up to 90% of the crop
To get rid of the pest, plantings need to be sprayed with Bitoxibacillin or folk remedies - infusions of chamomile and tansy. Kinmix and Fury, as well as a solution of mustard powder, help well with caterpillars.
Advice! To prevent sawfly infection, radish seeds can be soaked in Actellik's solution for 15 minutes before planting.
Aphid
Greenish-yellow, brown or dark gray insects form whole colonies on the tops of a vegetable crop and densely stick around the leaves from the inside out. The tops gradually discolor, lose juices and dry out.


Aphids are very small in size, but appear on radishes in huge quantities
With a massive invasion of aphids, insecticides Inta-Vir, Admiral and Iskra-Bio have a good effect. If there are still few pests on the leaves, you can limit yourself to folk remedies - soapy water or infusions of lavender, onions and calendula.
Gardeners reviews
And bath
“Radish, like any early ripening crop, is very picky about soil fertility and responsive to fertilizers. To protect seedlings from cruciferous fleas, they are dusted with tobacco dust mixed with lime or ash (1: 1). To some extent, sprinkling of seedlings with road dust scares off the flea ”.
Apple
“It is better to prevent the emergence of a pest than to deal with it later. The radish needs to be watered daily, then the flea will not appear. "
Elain
“Cruciferous flea. If the plants are already strong, then they will survive, and if only "two leaves" - they will ruin the infection. My radishes are safe if the lettuce grows nearby. It has been tested for two years. "
Radish diseases and their treatment
Radish can suffer not only from pests, but also from ailments. Most often, diseases develop due to improper care, against the background of waterlogging of the beds or with scarcity of soil.
White rust
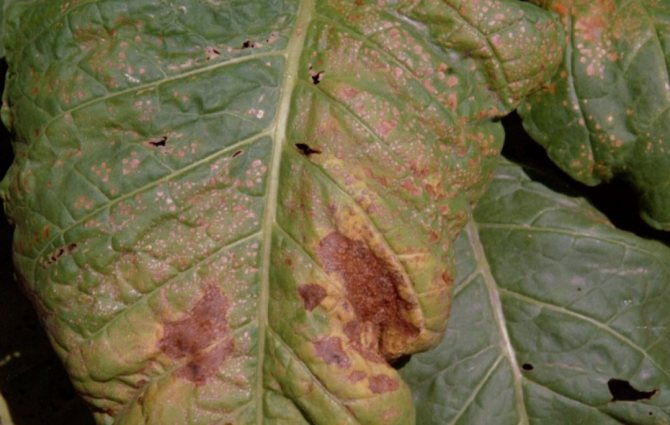
White rust disease affects many cabbage crops. You can find out about the presence of an ailment by white and yellowish oily spots on the leaves. A whitish coating appears on the underside of the leaf. With severe damage, the leaves dry out and fall off, and the petioles bend and stop growing.
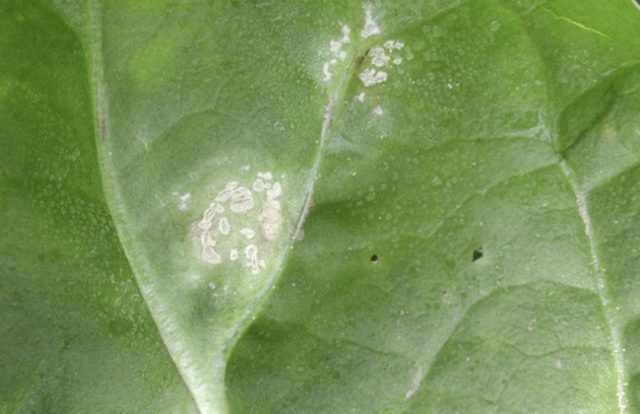


If the radish is badly damaged by white rust, it is better to destroy it and take care of healthy plantings.
Treatment of white rust is carried out by spraying with copper sulfate. In this case, all affected leaves must be removed and burned so that the fungus does not spread through the garden.
Keela
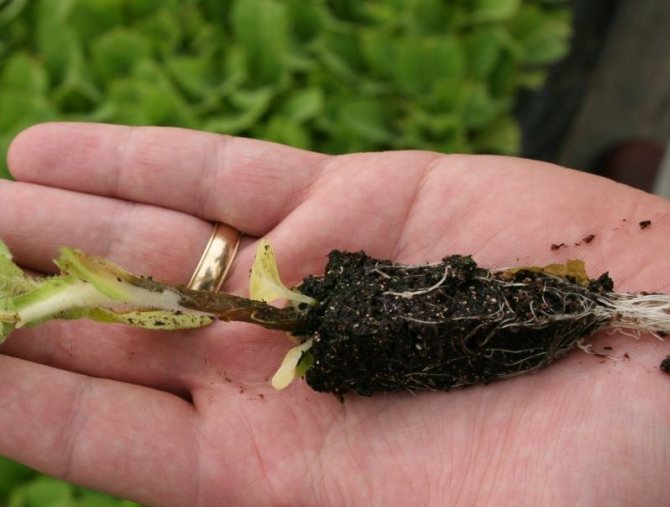
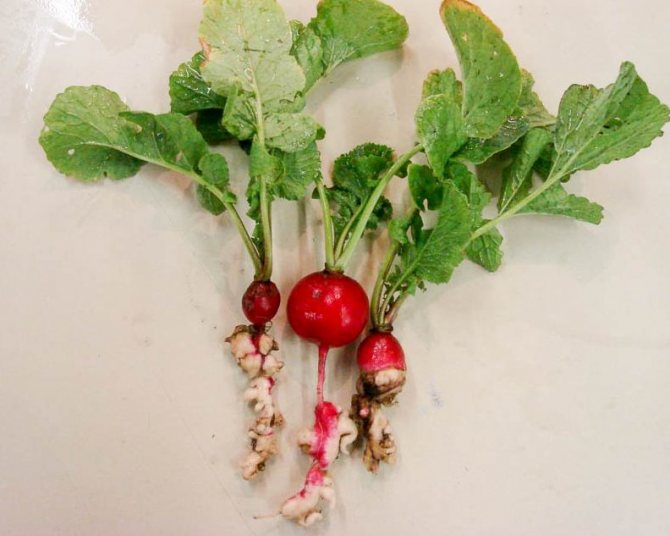
Keel's disease is a dangerous virus that appears most often on waterlogged, heavy soils. The disease affects root crops, they become covered with dark growths and begin to rot.
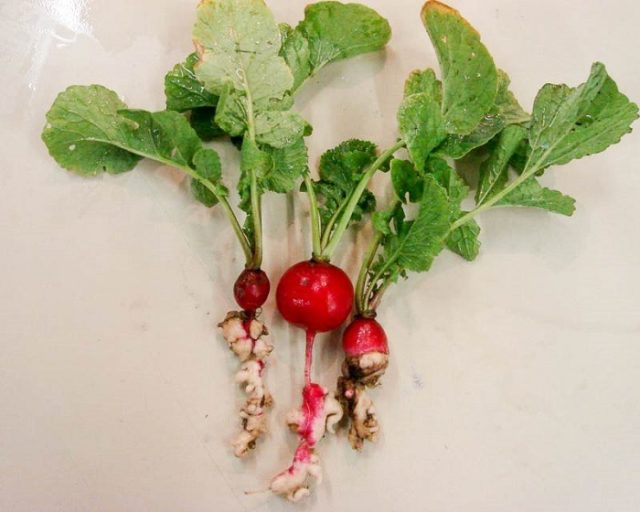


You can recognize Keela by the large swellings on the roots and tubers of the radish
If the radish is already infected with Keela, then it only remains to destroy it. After that, the soil must be disinfected with bleach, since the virus can remain in the ground for up to 5 years and pass on to other plants.
Radish Mosaic
The incurable diseases include the CaMV viral mosaic. You can recognize it by discoloration of veins on the leaves, twisting of the edges of leaf plates, the appearance of mosaic spots. A radish infected with a disease does not always die, but it stops growing and does not bear large fruits.


Mosaic-affected radishes are not suitable for seed propagation, the virus remains in the seed
It is impossible to cure the mosaic, so diseased plants simply destroy and disinfect the soil.
Blackleg
A dangerous disease of radish often affects young seedlings - with a black leg, the root collar darkens and dries up. Sometimes the disease develops in mature plants and affects the ripening root crop. At the same time, the tubers darken and soften, begin to rot and become covered with a whitish bloom.
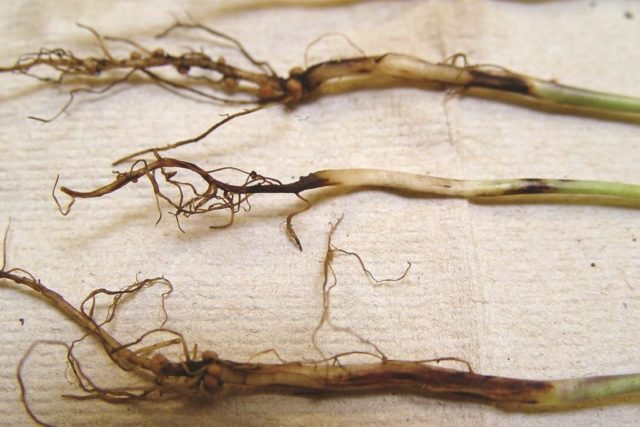


Black leg develops in radish in conditions of waterlogging
For the prevention of blackleg, the soil in the beds should be periodically limed with slaked lime. If the vegetable crop is already sick, it cannot be saved, the affected plants are simply destroyed.
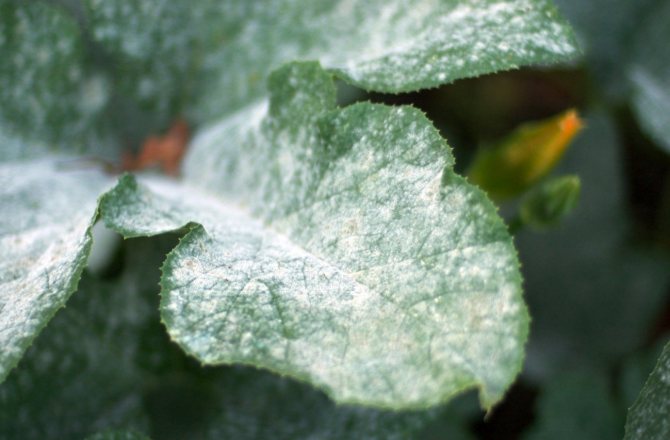
Peronosporosis
Peronosporosis disease is characterized by yellow spots and a light bloom on the tops. The fungus begins to develop on the underside of the leaf plates, after a while small yellow spots appear on the upper side of the leaves. Over time, the tops of the radish dries up and falls off.
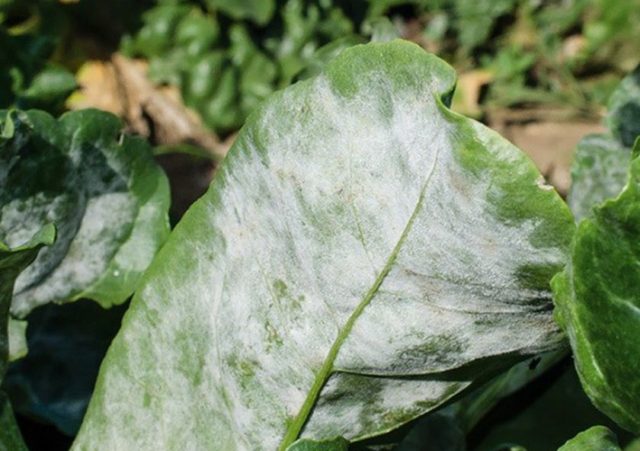


Peronosporosis leaves a white coating on the lower part of the leaf plate
In the early stages, the disease can be cured with Fitosporin or other fungicidal preparations. In case of serious infestation, it is better to destroy the radish.
Attention! A good prevention of peronosporosis is soaking the seeds in a weak solution of potassium permanganate before planting in the ground.
Gray rot
The first symptoms of the disease are grayish or brown spots on the leaves. When the fungus spreads, radish tubers suffer, they become covered with a fluffy gray-gray bloom, soften and begin to rot.
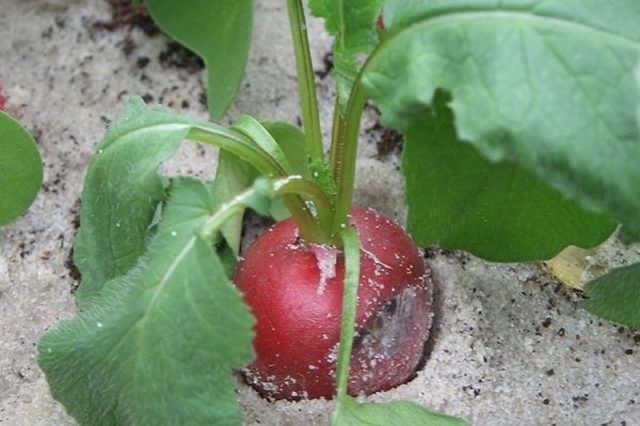


Gray rot most often develops when the soil is boggy and in cool weather
Radish treatment is carried out with Bordeaux liquid, and seriously damaged tubers are destroyed. For prophylaxis, the seeds are treated with preparations containing sulfur before sowing, and the beds with growing radishes are fertilized with potash dressings.
Composition and calorie content per 100 grams
The beneficial properties of radishes are due to the chemical composition of the root crop. Knowing how much kcal per 100 grams of product, as well as what minerals and vitamins are contained in radishes, you can understand how useful this vegetable is.
| Content | Nutrient | Quantity in mg | Percentage of the norm per day |
| Vitamins | Thiamine | 0,01 | 0,7 |
| Riboflavin | 0,04 | 2,2 | |
| Pantothenic acid | 0,18 | 3,6 | |
| Pyridoxine | 0,1 | 5 | |
| Folates | 6 μg | 1,5 | |
| Ascorbic acid | 25 | 27,8-29,0 | |
| Macronutrients | Potassium | 225 | 10,2 |
| Calcium | 39 | 3,9 | |
| Magnesium | 13 | 3,3 | |
| Sodium | 10 | 0,8 | |
| Phosphorus | 44 | 5,5 | |
| Chlorine | 44 | 1,9 | |
| Trace elements | Boron | 100 mcg | — |
| Vanadium | 185 mcg | — | |
| Iron | 1 | 5,6 | |
| Iodine | 8 mcg | 5,3 | |
| Cobalt | 3 μg | 30 | |
| Lithium | 23 μg | — | |
| Manganese | 0,15 | 7,5 | |
| Copper | 150 mcg | 15 | |
| Nickel | 14 mcg | — | |
| Fluorine | 30 mcg | 0,8 | |
| Chromium | 11 mcg | 22 | |
| Zinc | 0,2 | 1,7 |
The chemical composition of radish is also rich in starch and dextrins, mono- and disaccharides, as well as essential and nonessential amino acids. The calorie content of radish is only 20 kcal, and the formula for the share of BZHU is 1: 0.1: 2.8. Low in calories and low in protein, the vegetable is considered very beneficial in a weight loss diet.
Signs of diseases and pests of radish
The damage of radish by fungi and pests is evidenced by noticeable symptoms on the leaves. If warning signs appear, you need to carefully study the vegetable plantings and carry out urgent processing.
What to do if radish leaves are in a hole
Holes in the tops appear when the plantings are affected by insects. In particular, leaves can gnaw through:
- cruciferous flea or bug;
- rape sawfly or butterfly caterpillars;
- slugs, they leave not only holes on the leaves, but also a characteristic sticky trail of silvery color.
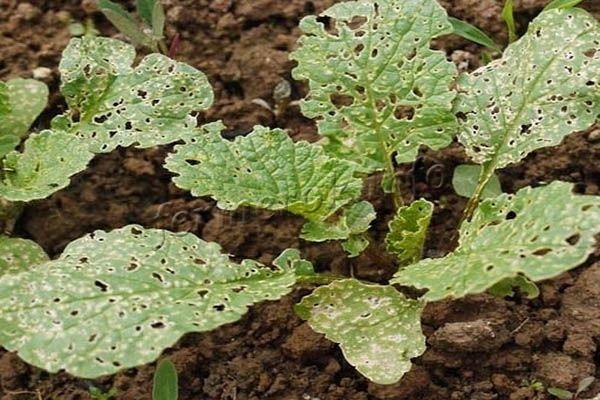


If the tops of the radish are covered with holes, we are clearly talking about the presence of pests.
Pests from the leaves of the crop can be collected by hand or washed off with water with low pressure. To prevent insects from returning to the beds again, vegetables need to be sprayed with Aktellik and Karbofos, or radishes should be treated from pests with folk remedies - infusions of tansy, tobacco, wormwood.
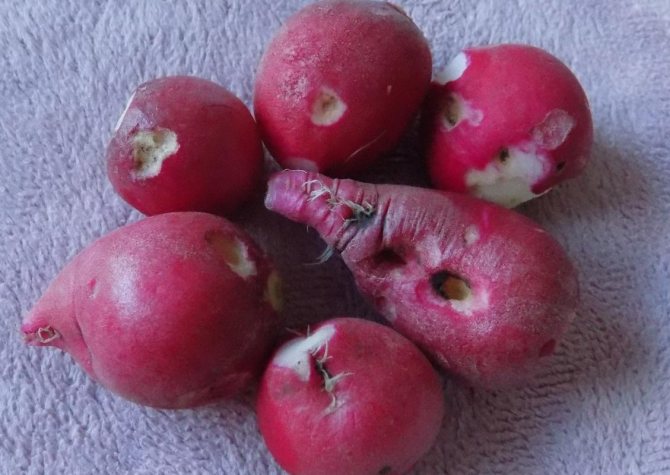
Dark spots on radishes
Black-brown spots on roots, which can turn into depressions, are most often indicative of peronosporosis or gray rot. Treatment does not always give a result, if the fungus has infected not only the leaves, but also the underground tubers, then most likely it will not be possible to save the vegetables.
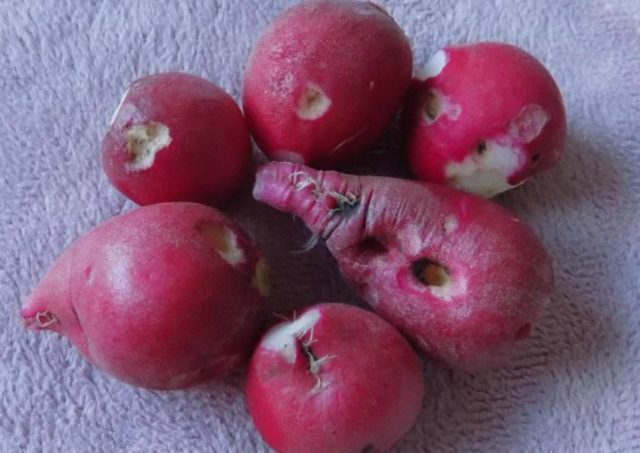


The spots on the root vegetables of the radish are usually rotted places due to the fungus.
Nevertheless, the beds can be treated with Bordeaux 1% liquid or Ridomil Gold, with a weak lesion, the drugs will be useful.
Why does the radish turn black inside
A ripe vegetable may turn out to be black on the inside, usually this indicates an advanced peronosporosis or black leg. Also, blackening can be caused not by fungal diseases, but by simple decay of vegetables from waterlogging or acidification of the soil.
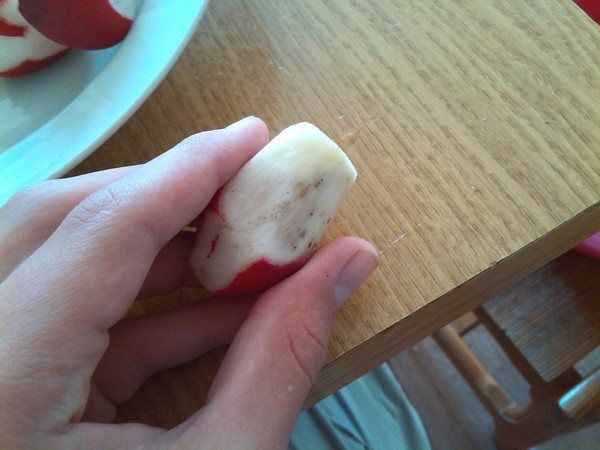


If a ripe radish turns black from the inside, then the crop may be infected with peronosporosis or black leg.
The affected radish must be eliminated, and the soil must be disinfected. This will eliminate possible pathogens and protect the next crop.
What to do if the leaves dry
Radish leaves can dry out for a variety of reasons - under the influence of powdery mildew or other fungi, or when damaged by pests. You need to carefully examine the tops and see if there are holes, dark spots and other signs of insects or ailments on it. If the plant has not yet had time to completely dry, then it can be saved with the help of Bordeaux liquid or insecticidal preparations.


Drying of the tops is a symptom of most fungal diseases.
Important! Sometimes the yellowing of the leaves can be due to a simple lack of moisture. Radish loves water, therefore, when growing a crop, the soil should not be allowed to dry out.
Why radish leaves turn yellow
Vegetable leaves can acquire a yellow tint for many reasons. For example, yellowing of the tops is caused by:
- lack of nitrogen in the soil;
- viral mosaic;
- most fungal ailments;
- lack of sunlight or moisture.
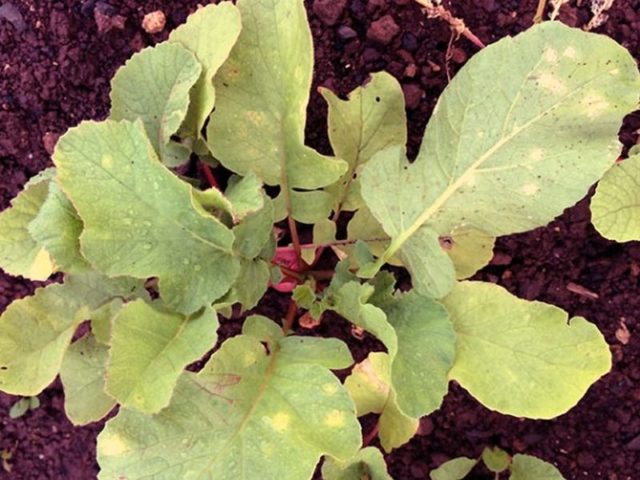


Radish leaves can turn yellow due to diseases and improper care.
If the radish began to turn yellow immediately after germination, then the reason may lie in the black leg - a dangerous incurable disease. One of the root crops must be removed from the soil and examined. If the suspicions are confirmed, then all the affected plants will have to be destroyed and the soil disinfected.
Preventive methods for protecting cruciferous plants
In order for the radish to grow and bear fruit well, the pests, the control measures for which we have considered in the material, should not multiply and feel comfortable on your site. This requires:
- ensure cleanliness in the aisles, remove leaves and grass;
- carry out preventive treatments of plants;
- remove infected plants on the site, the putrid smell attracts pests;
- do not store sheaves of straw, dung heaps, overheating leaves;
- observe the norms of irrigation and fertilization, control the acidity of the soil;
- regularly use ashes and ashes as a top dressing for radishes.
It is important to take into account that radishes, cabbage, turnips are affected by the same insects as radish pests, and the fight against them on all cruciferous crops is carried out in a complex manner.
Prevention measures
Dealing with pests and fungi can be difficult. But simple preventive measures can prevent damage to radishes:
- For planting in the garden, you need to choose varieties resistant to ailments and purchase seeds from trusted producers.
- Crop rotation prophylactically protects from fungi and viruses, or annual change of the location of the beds. It is not recommended to sow radishes in the same area 2 times in a row.
- Before planting, the seeds should be treated with biostimulants, they strengthen the culture's immunity.
- To repel pests, it is useful to plant aromatic cilantro, thyme, basil and other herbs next to radishes.


In the fall, the beds dig up and remove all plant debris in which pests and fungal spores winter
During the warm season, the beds need to be inspected every week, this will allow you to notice the alarming symptoms in time.
What to remember
- Plant nearby pest repellent plants. Fragrant plants help scare off many pests: wormwood, cilantro, basil, thyme, etc.
- When fighting diseases apply folk remedies... If they did not help or the situation is already running, use purchased drugs.
- Observe the rules of crop rotation. Plant a different type of plant in your garden every year. And for the prevention of pests, properly prepare the seeds for planting and regularly inspect the beds.
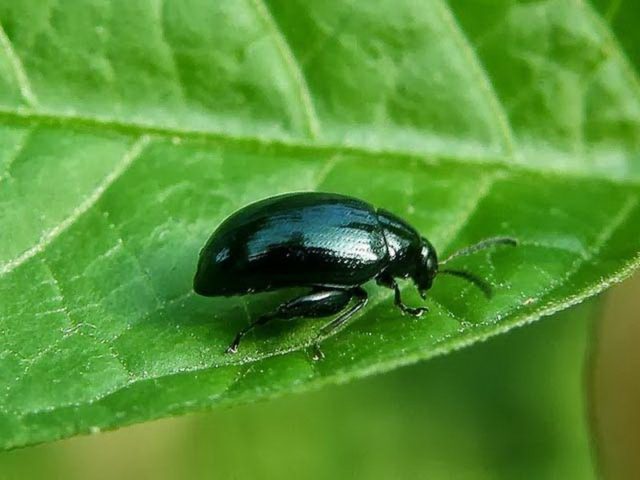
Babanukha


Babanukha, or cabbage (horseradish) leaf beetle, can be recognized by a small body (3-4 mm) of black, dark blue color with a green tint.
Their larvae are dirty yellow, 5 mm long. This pest attacks all cabbage plants. Hibernates under post-harvest residues, in soil and manure. It leaves wintering in spring. First it feeds on weeds, and then migrates to cultivated cabbage crops. From this period, females begin to gnaw through holes in the leaf plates and lay eggs there. Several generations of beetles are hatched during the season.
Control measures.
To prevent the invasion of this parasite, it is necessary first of all to fight the weeds in order to deprive them of their original source of nutrition. In order to prevent the overwintering of the larvae, the post-harvest remains are removed and destroyed. The earth is well dug up so that the beetles die of the cold.
With the mass distribution of babanukha, insecticides that are allowed for the treatment of radish are used - "Aktellik" and others.
Cabbage moth
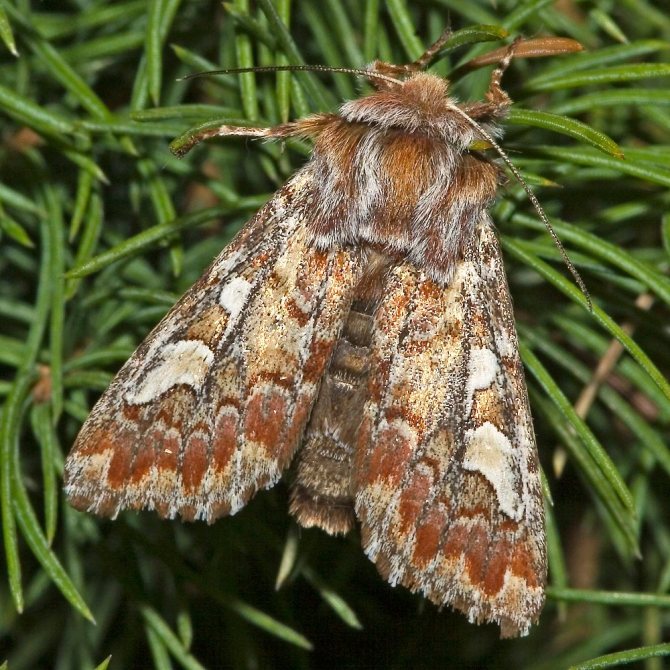


The moth caterpillars of the cabbage moth feed on the leaves of radishes and other cruciferous plants.
They carry out their harmful activities throughout the month. They overwinter in the soil. It is easy to recognize the moth - it is dark yellow in color with dark spots on the front wings. With a wingspan, it reaches a size of 2.5 cm. Eggs are laid on the underside of the leaves. Its caterpillars are yellow with light stripes on the sides.
Control measures.
You can fight a fire rat by attracting it with a bright light, and then catching it. Weeds must be destroyed. Digging the ground in autumn. It is better to sow radishes before the butterfly leaves.
In case of minor damage, eggs and caterpillars must be destroyed mechanically. You can apply foliar and root dressing with potassium and phosphorus. When overcoming the threshold of harmfulness of 10%, it is recommended to use insecticides ("Lepidocid", "Bicol", "Fitoverm", "Agravertin", etc.).
Vascular bacteriosis
Vascular bacteriosis affects adult plants, much less often seedlings. A characteristic symptom of this bacterial disease is blackening of the veins (vessels) on the leaves. The leaves begin to turn yellow, crumble and fall off.
The development of vascular bacteriosis is facilitated by frequent rains and damage to crops by pests. The infection lives in seeds, mother liquors and plant debris.
Control measures. To prevent contamination of radishes with this disease, special attention should be paid to the selection of seeds. Before sowing, they must be kept in hot water (+50 ° C) for 20 minutes. Then they should be dried. It is necessary to select seeds only from healthy plants, disinfect before planting.
It is also necessary to carry out the autumn cleaning of post-harvest residues. Do not neglect the rules of crop rotation. Pest control is an important part of prevention.
Rapeseed sawfly
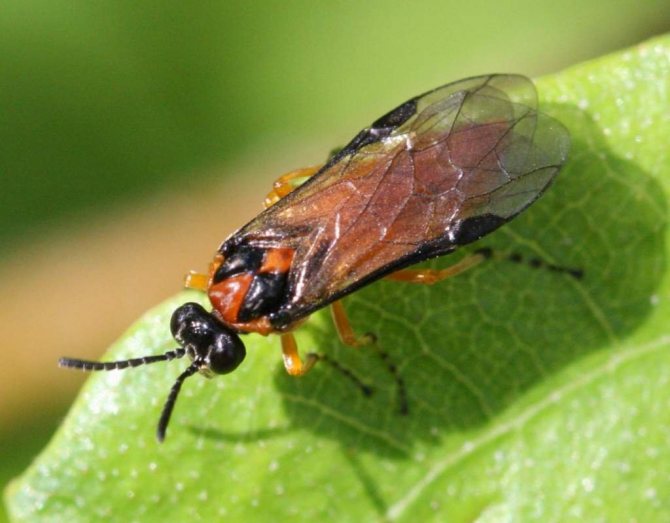


The rape sawfly is able to completely gnaw the leaves of the radish, leaving only veins.
Also damages buds and young shoots. Thus, it prevents the fruit from setting and provokes the death of the crop.
Control measures... It is necessary to follow the agrotechnical rules for caring for vegetables: loosening the soil, eliminating weeds, observing crop rotation, getting rid of plant residues.
From folk remedies for combating rape sawfly, black henbane tincture is used: a pound of dried leaves is infused in a small amount of water. After 12 hours, the infusion is filtered and brought to a volume of 10 liters. Before use, stir in 30-40 g of soap.
You can also try processing with a decoction of tomatoes. When observing 3-5 individuals of rape sawfly on one plant, it is necessary to resort to spraying with insecticides. It is better to do this with biological preparations such as "Lepidocide", "Entobacterin", etc.
White rust
It appears as a result of the development of the fungus Albugo Candida. Parts of the plant affected by this disease become hypertrophied and chlorotic. White spores or pads appear, flowers are deformed. Organic spots can be observed on the tops of the leaves, and concentric pads on the underside. Over time, diseased tissues are affected by necrosis. Prolonged cold and high humidity are considered favorable for the disease.
Fight white rust with the following measures:
- Get rid of infected plants.
- Treat with fungicides.
So, let's summarize. In order for the radish to grow without diseases, it needs to create favorable conditions. For planting, it is recommended to choose only resistant varieties that are not afraid of diseases. It is best to take preventive measures to prevent disease, and then the radishes will grow healthy, large and tasty.