Gooseberry care: tips and tricks
Gooseberry is a berry of the Currant genus, of the Gooseberry family. Homeland - the African continent, it grows in America, Asia, Southern Europe, the Caucasus. Gooseberries were discovered in the 16th century; by the 18th century, breeders had bred about a hundred varieties. The bushes reach a height of 1.2 m, some varieties yield up to 25 kg per bush.
The bark is brown, peeling, on the shoots thorns in the form of thin thorns. Leaves are oval, rounded, with denticles, bright green. The plant is frost-resistant, withstands low temperatures down to -30 ° C. Berries - green, red, there are varieties with black fruits, purple.

Currant goldfish


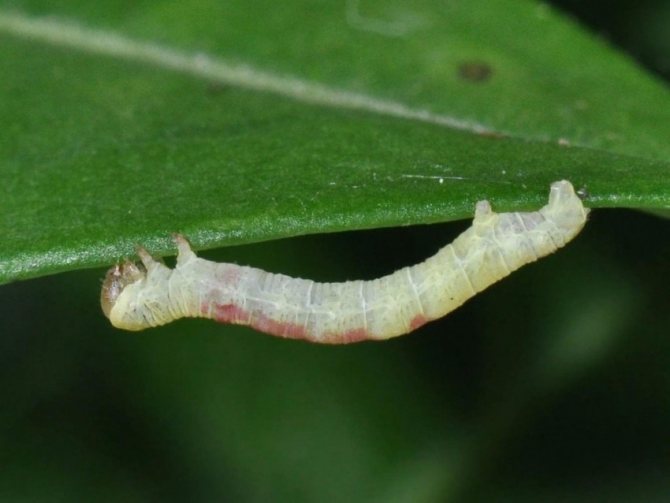
Gold currant damages primarily gooseberry branches. The larvae of this beetle eat away the core of the shoots of the plant, starting from the top and descending lower and lower.
The yield of the bush drops sharply, and the berries remain small. In winter, the larvae of the goldfish are inside the shoots, pupate in the same place.
Young beetles begin their emergence from shoots in late spring (May) - early summer (June). Approximately 8-10 days after this release, female beetles begin to lay eggs on the bark of the shoots, as well as on the leaf stalks.
They cover the eggs with their secretions, which freeze on the bark, forming a hard oval shield. Then, after 12-16 days, the larvae crawl out from under the shield and begin their dirty work.
Control measures - This is the cutting and burning of affected branches; correct and timely pruning of the bush; planting healthy seedlings.
Gooseberry Care Tips
For gooseberries, as well as for currants, timely care in the open field is necessary. It is planted more often in the fall, but it is also possible in the spring.
He prefers:
- Sunny places, hills, where there are no north and east winds.
- Neutral or low acid soil.
- The distance between the bushes is at least one meter, in rows - up to three meters.
In order to avoid fungal diseases, it is not recommended to place gooseberry bushes in the lowlands. For planting, take annual or biennial seedlings with roots up to 30 cm. Soak them in a growth stimulator. In the fall, they are planted a month or one and a half before the first frost appears. Thus, the plant will take root and young roots are formed.
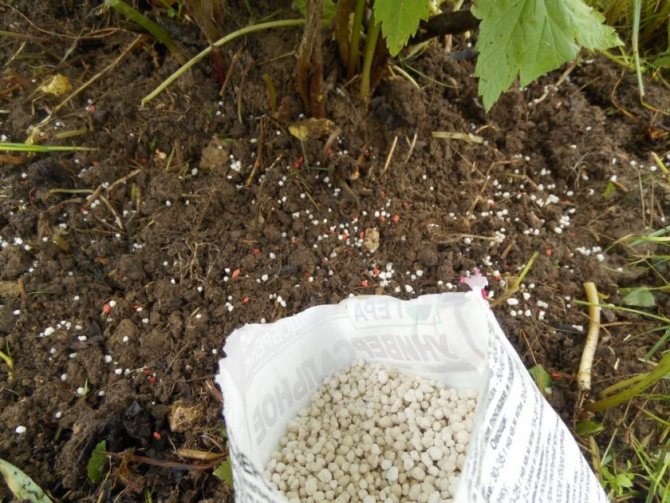
Humus 10 kg, superphosphate 150 g, potassium salt 60 g are poured into the landing hole. The seedling is deepened by 6 cm, the aerial part is preliminarily cut, leaving 3-4 buds.
The plant propagates by layering, cuttings, dividing the bush. The gooseberry growing season begins in early spring. It blooms in May, the berries appear depending on the growing strip, in July-August.


Recommendations for spring work:
- Pruning is carried out every year to obtain a bountiful harvest and prevent thickening of the bush. Cardinal pruning is not done in a single dose, so as not to destroy the bush. Pruned in spring and autumn, if young leaves have already appeared, you need to postpone until autumn.
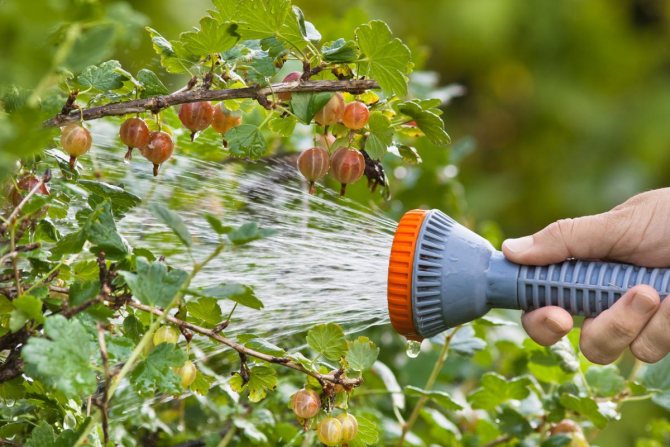
- From above, the bushes are not watered, they provide drip (this is necessary to avoid rot) or watered in grooves, grooves up to 15 cm deep.
- They loosen the earth with a hoe, a rake.
- In the early years, feeding is not applied if the bushes are sufficiently fertilized during planting.Then, once every three years, they must feed the plant without mixing organic and inorganic fertilizers. For depleted soil, nitrogenous fertilizers are needed every year, fertile every two or three years.
- The shelter is removed on time, otherwise the bushes will rot due to overheating.
When grown correctly, the plant bears fruit for about 20 years.
The consequences of the appearance
The main goal of the reproduction of insect pests on the surface of the bush is to provide themselves and their offspring with the necessary food base for growth and development, therefore, often with mass development, they lead to the complete or partial destruction of the green mass of plants.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself
Everything about gooseberries: description, properties, cultivation features, wild species It is the center of the photosynthetic apparatus, since the leaves contain specific cells that convert solar energy into chemical energy.
As a result, the plant is unable to fully maintain vital activity and metabolism.
In addition, the foliage creates a special microclimate for the shoots, protecting them from intense sunlight.
In case of complete loss of leaves, this can lead to the death of a valuable fruit crop from lack of nutrition or drying out of the shoots.
If the parasite failed to completely destroy the leaves, such a plant will remain viable, but its yield and development activity will be inhibited. In addition, immunity will also be suppressed by the gooseberry, and this in some cases, in addition to parasitic invasion, can cause an infectious disease caused by all kinds of viruses, bacteria or fungi.


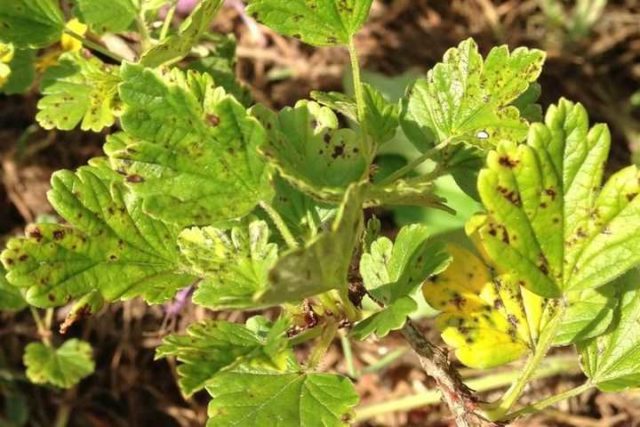
What caterpillars eat gooseberry leaves
The following insects are considered to be the most dangerous for the gooseberry leaf and other fruit shrubs:
- Aphid - as the insect develops, it feeds on the sap of the leaves, which gradually causes them to curl. This leads to the formation of lumps of green plant mass, in which aphids multiply en masse. In case of untimely elimination of the pest, the insect leads to a slow withering of the bush.
- Yellow sawfly - after hatching, the parasites intensively feed on the green mass of the gooseberry, in just a couple of days this leads to the complete disappearance of the leaf on the bush.
- Moth - caterpillars parasitize twice a season: the first time they are able to completely eat up the entire green mass of plants in early spring, and then in August. Thus, the bushes can grow with leaf pathologies throughout the growing season.
- Leaf roll - This parasite feeds on sap and green mass of bushes, braiding them with cobweb bloom. Such a lesion is observed twice a season: in spring and during the ripening period of berries. This causes not only oppression of the gooseberry and twisting of the green mass, but also a deterioration in the quality of its fruits.
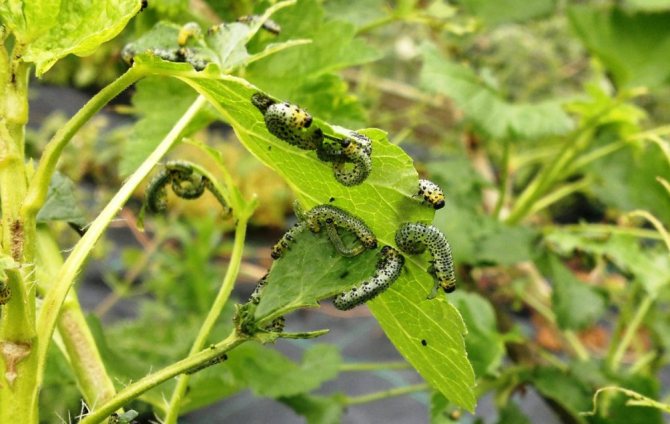


In addition, the bushes can be affected by less dangerous pests that are not capable of causing massive death of leaves, but negatively affect the fruiting and development of gooseberries. These include the spider mite, gall midge, leaf gnaw, glass and goldfish.
Gooseberry care in spring
Timely spring activities for the care of fruit and berries in the future will lead to a large harvest. Experienced gardeners recommend doing them before the formation of the first buds. For this:
- They remove the winter shelter - the timing depends on the region, in the central and southern regions in early March, in the northern ones later. Then they rake out the mulch, the remains of last year's vegetation, branches. After that, all the garbage is burned, since fungal spores and insect larvae hibernate in it. If the bushes are not covered, but simply bent to the ground, they need to be raised.
- When the snow melts, cover the ground with dense material for several weeks so that the pests do not lay offspring.
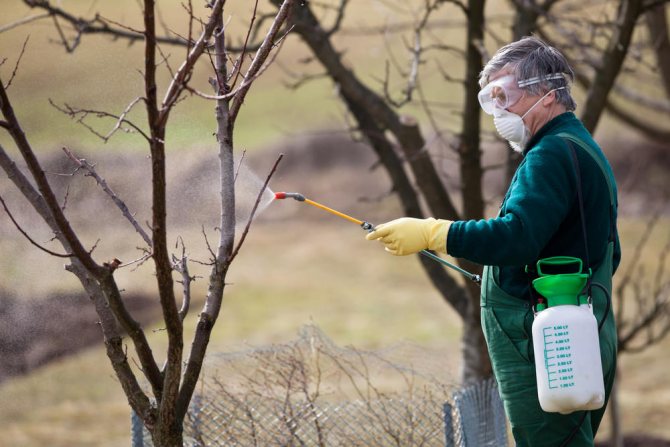
- They are treated for pests and diseases - water the plant and the soil around with boiling water, but only until the buds appear. To do this, use a metal watering can. They are also sprayed with copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid, fungicides: Fitosporin, Aktofit. In this case, the processing is carried out at an air temperature not lower than +14 ° C.
- Watered at the root or using a drip system during flowering. The top layer of soil is moistened by 30-40 cm, but not with cold water. Because of this, immunity decreases, there is a risk of being affected by fungal diseases.
- Do sanitary pruning at the beginning of March - remove dried, frozen, damaged, diseased, weak, twisted branches, criss-crossing shoots that are too close to the ground. The cut is made above the kidney, 6 mm away from the eye, at a slope of 50 °.
- In early May, the ground around the bush is loosened to a depth of 8 cm. Then it is mulched with straw, hay, peat, sawdust. This will reduce evaporation and prevent weeds. Dig up 10-15 cm between the rows.
- Feeding is done from the second year of planting. At the beginning of the growing season, add urea or ammonium nitrate. Scattered under the bushes, embedded in the soil by 5 cm, watered. For adult bushes - 40-60 gr, young - 30-40 gr. Potato peelings are also used - one kilogram per 10 liters of boiling water. After cooling, add 200 g of wood ash or bird droppings 1:20. Pour a bucket under each bush. Manure and humus. Before flowering, potassium sulfate is introduced - 40-50 grams under the bush. This is provided that the plants were not fertilized in the fall.
Varieties of pests
A lot of insects can develop on the gooseberry, its branched stems become the best habitat and production of offspring of many species. However, such a neighborhood should not always cause alarm, since often the shrub becomes an object of protection for small creatures. That is why, below, we consider species that are extremely dangerous for culture, capable of instantly eating up foliage and affecting its shoots.
Did you know? The gooseberry is considered a traditional type of vegetation in Europe and Africa, but its first description was given only in 1536 by the French scientist and physician Jean Ruel.
Gooseberry fire
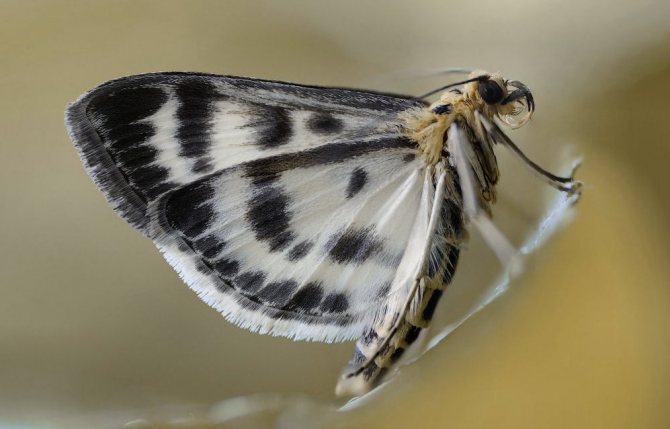
An adult of this pest is a small grayish-white butterfly with a wingspan of up to 3 mm. The wings are often covered with brown stripes and scales, which is their characteristic feature.
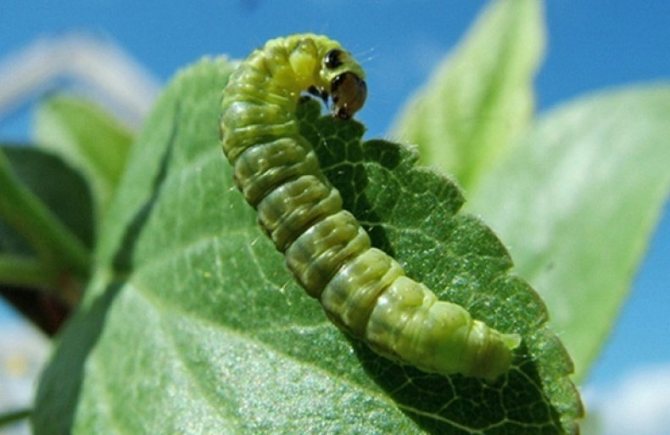
In the spring, this pest lays eggs inside the flowers, due to which the young larva almost completely eats away the berries from the inside. As it develops, the small larva grows into a green caterpillar with a black head.
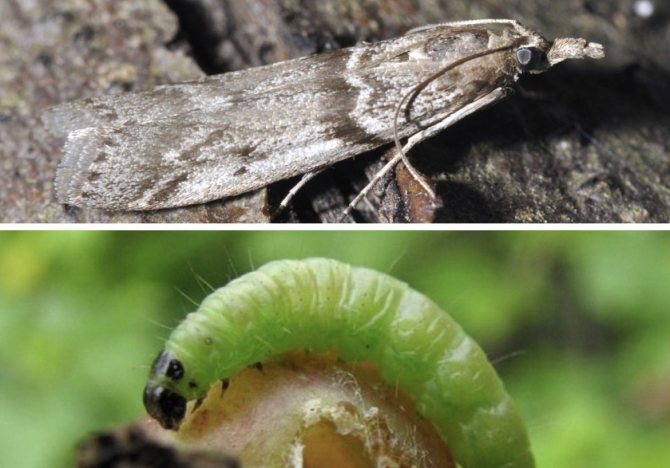


In the course of life, it affects the pulp of the berries, which then turn red and rot prematurely. In this case, the fruits are covered with a characteristic spider web, thanks to which the appearance of the pest can be best recognized.
About a month after birth, the caterpillars of the firefly go down to the root layer of the soil, take the form of a pupa and hibernate in the upper layers of the soil. This insect is typical for many fruit crops, characterized by juicy berries, including currants.
Video: Protecting gooseberries from gooseberry moth caterpillars
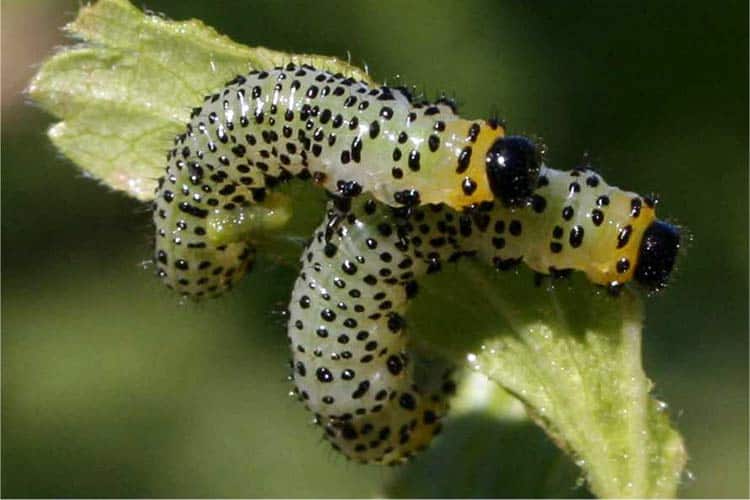
Yellow sawfly
A typical sawfly is a red-black or yellow-black insect up to 7 mm long. This creature appears en masse around the second half of May, after young foliage appears on gooseberries and other fruit shrubs. At this time, there is a massive reproduction of the sawfly, after which the insect lays eggs along the leaf veins.
A few weeks after laying, small bluish-green caterpillars with a dark head emerge from the eggs. Over the main color of insects, black dots are visible, located over the entire surface of the body.
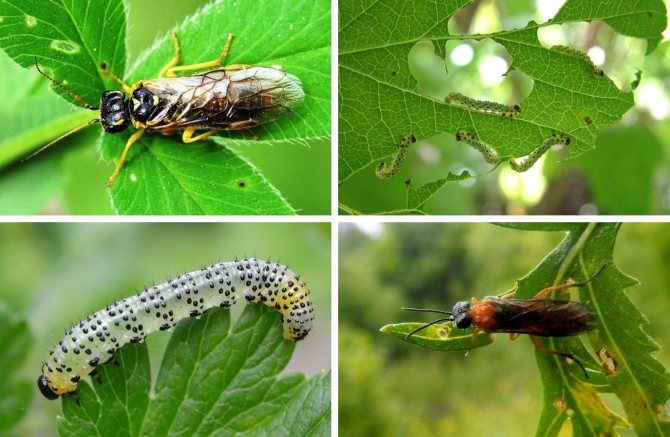


The life span of caterpillars is about a month, after which they burrow into the root layer of the soil. At a depth of 5–7 cm, insects form pupae, after which their development continues in the next season.
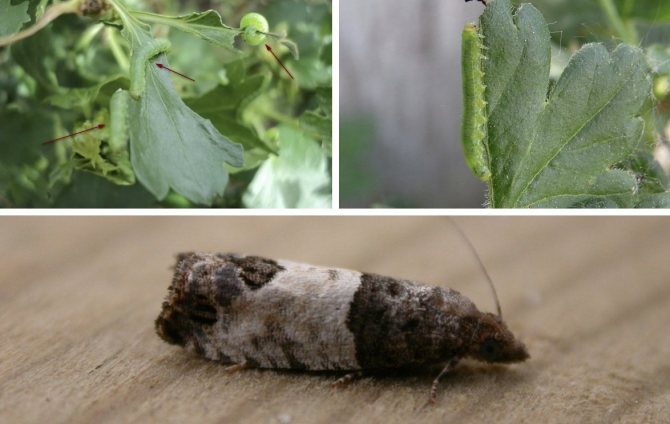
Moth
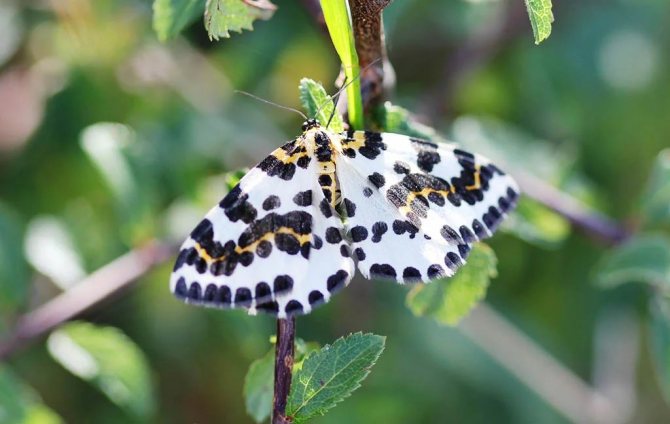
The most common pest of the gooseberry bush and currant is the moth. It is a rather large butterfly with a wingspan of 40-50 mm. The insect's wings are covered with a bright ornament of various black dots, as well as yellow and brown stripes. At the same time, the head of the butterfly has a dark shade, and the abdomen is distinguished by an ornament of yellow-black spots.
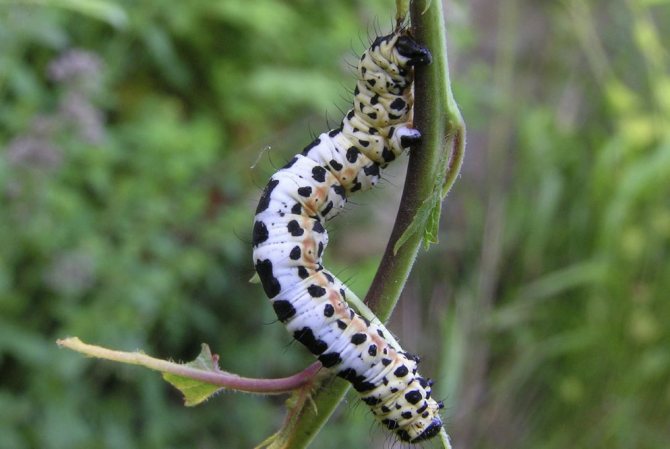
For the first time, plant breeders meet with moths in early spring. The larvae of the pest emerge from the root layer of the soil and massively populate the surface of the gooseberry. These are large tracks up to 40 mm long. Their back has a gray-white tint, and the abdomen is yellow, with all kinds of black transverse stripes. At the onset of a favorable period, the larvae pupate on the green mass or shoots, after which butterflies appear after about a month.
Around the end of July, butterflies visit the gooseberry again and lay eggs on the back surface of the leaves, from which the larvae reappear. They hibernate in pupae, in the root layer of the soil of the bush, while after hatching, at least 1 month passes before the first pupation. Due to this development cycle, the bushes are affected by the pest at the beginning and end of the growing season, which almost always provokes severe consequences for the culture.
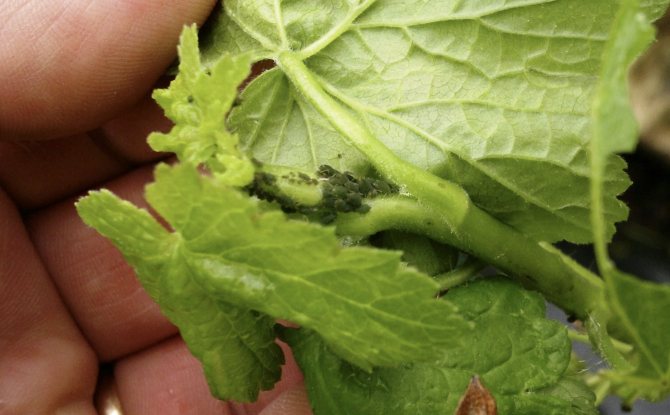
Aphid
Almost every gardener met with aphids, this pest is common in the temperate climatic zone and is the main parasite of most fruit crops. The average individual is a small insect about 2 mm long. It has an ellipsoidal, soft body, green or light green in color.
Important! Aphids are prone to instant reproduction, one female per season is able to give several generations of offspring at once. That is why the fight against the pest should be started immediately.
As the aphid multiplies, it forms eggs; before hibernation, they are small dense formations of black color. Pests lay their pests in the zone of young buds. In the spring, young individuals appear from the eggs, which feed on the juice of the kidneys. This often leads to the death of plants at the beginning of the growing season, especially if the plant has low immunity.


Kidney leaflet
The leafworm belongs to a small group of butterflies from the order Lepidoptera... These creatures are of medium size, with an average wingspan of 20-30 mm. The main color of an adult insect is of all kinds of gray shades, on top of which an ornament of alternating spots and stripes of various shapes and sizes appears.
The life cycle of the pest begins with a small pale green caterpillar. Insects appear on the bush in early spring, after the onset of the average daily air temperature of about + 10 ° С. The parasitic pest forms a pupa from which a butterfly grows.
For 2 months, she lays eggs on the back of the leaf, which makes it possible to form up to 2 generations of young individuals. After the onset of cold weather, the caterpillars concentrate near the buds and form a cocoon, in which they hibernate until the next year.


Summer gooseberry care
In the summer, they continue to work in the garden:
- Regularly loosen the top layer of soil no more than 6 cm, remove weeds. In hot and dry summers, the soil is mulched to retain moisture longer.
- Watered with warm water after sunset.
- If the bush is tall, it is tied to a support so that the branches do not break from the weight of the berries.
- Fertilize with organic substances during fruiting (in equal amounts compost and peat, manure with soil, chicken droppings with water 1:15), mineral fertilizers after harvest, in August with potassium and phosphorus (25 grams per bush).


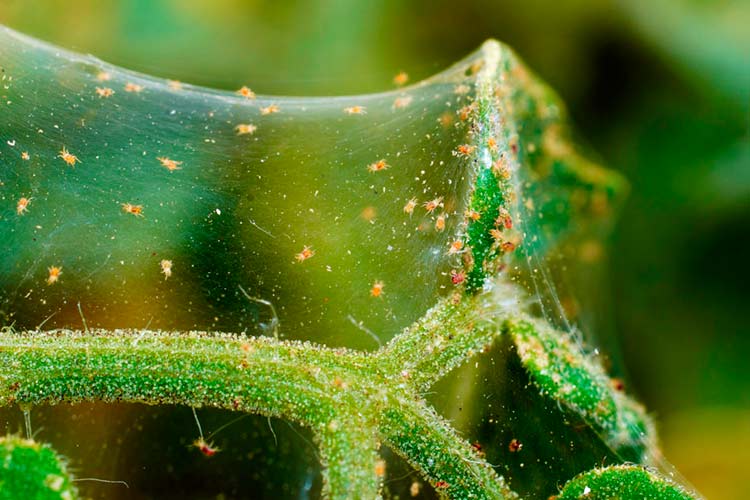
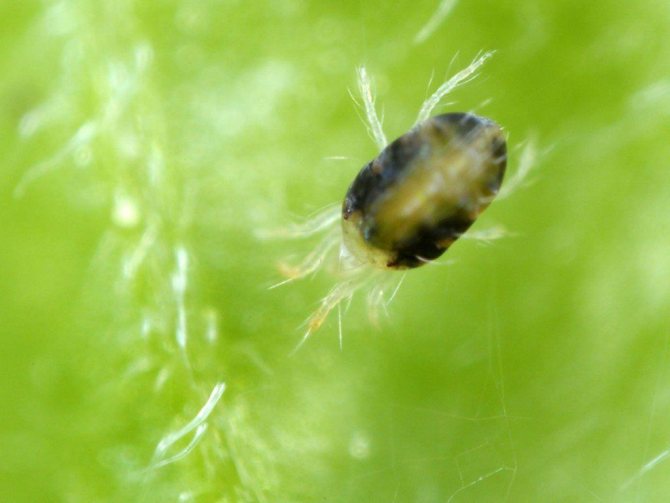
Spider mite


It appears in early spring on the underside of the leaves, then entangles them with cobwebs.
It feeds on the sap of the leaves, sucking it out. The leaves begin to turn yellow and gradually die off.
Reproduction of spider mites is just rapid, especially in hot weather. They can give from 5 to 8 generations during the summer.
The ticks themselves, as well as their larvae and eggs, are so small that it is almost impossible to see without a magnifying glass. The spider mite hibernates in the axils of fallen leaves, under lumps of soil.
Control measures... We spray the bushes with an infusion of wormwood, which we do as follows: we take half a bucket of chopped flowering wormwood and fill it with water (10 l), let it brew for one day, then boil for 30 minutes, cool, filter, dilute with water 1: 1 and, for better adhesion, add soap, about 40 g.
And it is also good to process gooseberries with tobacco infusion - stir 400 g of tobacco in 10 liters of hot water and leave to infuse for two days, then add 40 g of soap.
With great success, you can use infusions or decoctions of garlic, potato tops, onion husks, burdock leaves, celandine, tansy.
If the gooseberry bushes are severely affected and folk remedies no longer help, then you should seek help from chemicals that are best used either before flowering, or immediately after harvest.
Gooseberry care in the fall
In order for the plant to overwinter normally, it is necessary to care for the bushes in the fall. Several events are held.
- The root zone is processed - they are cleaned of foliage, debris, rotten, crushed berries. Weeds and wheatgrass are removed. Then they are burned.
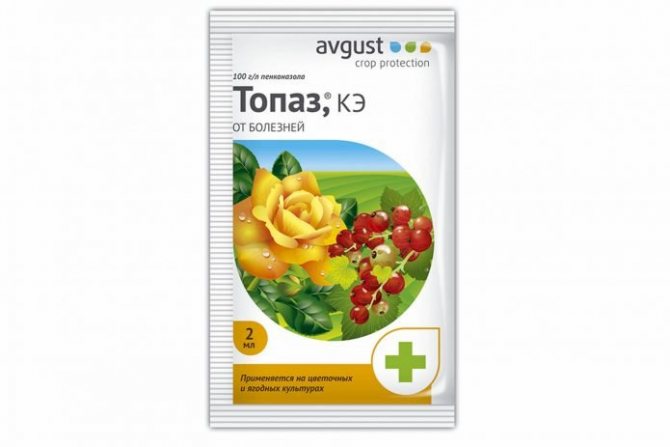
- Prevention of diseases and pests is carried out - after harvesting, plants, soil are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate. They also use Topaz, Fundazol. If the plant is affected by a disease, it is destroyed or all damaged parts are removed.
- Pruning is done from mid-October until frost. Sharp disinfected secateurs. They cut out underdeveloped, broken, non-bearing branches located too close to the ground. Long ones are shortened by 1/3. Then the bushes are thinned out and the places of the cuts are sealed with garden pitch. If the bush is mature, more than five years old, the old stems are cut. Leave strong shoots, up to 6 pieces, evenly spaced throughout the crown.
- They feed - for autumn feeding you need: phosphate, potash fertilizers.
- Watering - in dry and warm weather from late September to mid-October. A groove dug around is filled with water. After being absorbed, it is covered with earth.
Methods of struggle, rules of application
After the first signs of the appearance of a pest on the site, an effective fight against parasitic insects should be immediately deployed. For this, there are a lot of all kinds of tools, as well as techniques that are not inferior in efficiency to one another. Moreover, it is customary to divide them into traditional (based on chemical solutions) and folk (prepared from improvised means).
Chemicals
Chemical means of protection have been actively used in agronomy for many years. They give instant results and are capable of destroying parasites even in the event of mass development. However, only a certain group of substances can be called safe for the crop, as well as the environment.
We advise you to pay attention to the principle of using Topaz fungicide for gooseberries.
"Inta-Vir"
This agent belongs to contact chemicals that affect the intestinal and nervous systems of insects. Due to this, within a few hours after application, the caterpillars lose their ability to eat food and die a day after treatment.
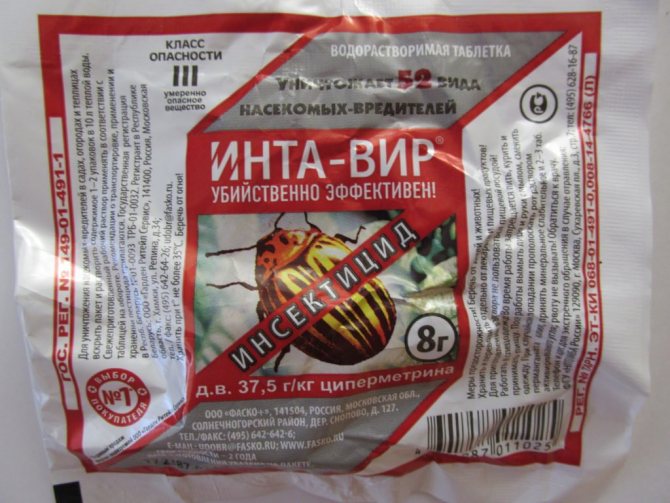


"Inta-Vir" is widely used for all kinds of gooseberry pests and has a lethal effect on 52 species of parasites, but the best remedy helps to cope with aphids and glassworms.
The working solution is prepared from 1 tablet of the product and 10 liters of water. The shoots and leaves of the bush are treated with the resulting liquid at the rate of 2 l / bush. You need to spray the plants twice. The first time this is done before flowering, the second treatment is performed within a week after harvest.
"Decis"
The drug "Decis" enters the body of pests by the intestinal route. A few hours after the defeat, it provokes a blockade of the nervous system, which leads to disruption of the activity of the whole organism as a whole. The end result is the gradual death of the insects.
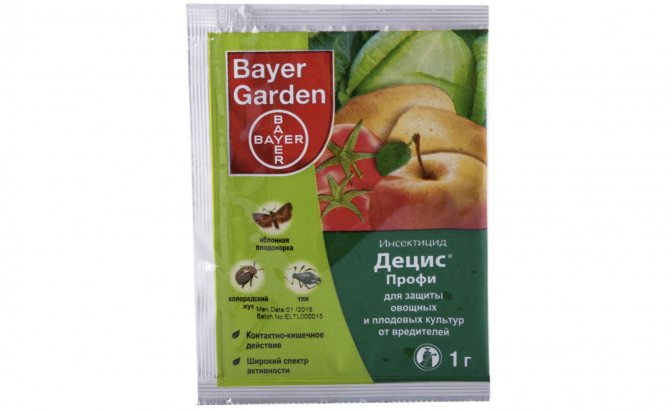


The effectiveness of the drug against all kinds of pests is extremely high and is approximately 8 points out of 10 possible. Prepare a spray solution from 1 g of concentrate and 10 l of water. Depending on the size of the bush, the flow rate of the working fluid is 10 l / 2-5 plants. The plantings should be processed twice, with an interval of 14–20 days, but no later than 30 days before picking the berries.
Important! In some cases, "Decis" can cause burns on young shoots, so they are sprayed with 1
–
2 year old seedlings with extreme care.
"Kinmix"
The main purpose of using "Kinmix" is to combat the development of small sucking parasites on fruit and ornamental crops in the area. The agent acts on insects in an enteric way, causing paralysis of the nervous system in them with subsequent death. The agent is used for a wide range of parasites, but it protects best against aphids and sawflies.
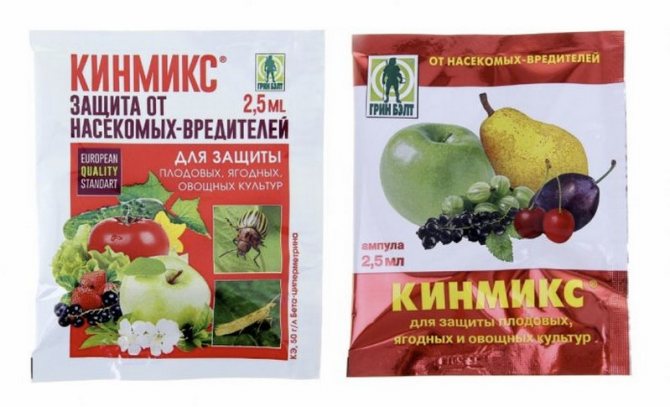


To prepare a mixture for spraying, dissolve one ampoule of concentrate in a liter of water. The resulting liquid must be brought to 10 liters, and then used for processing leaves and shoots with a flow rate of 1–1.5 l / bush. Plants can be processed throughout the growing season, but no more than 2 times, with an interval of 14 days. At the same time, at least 3 weeks should pass from the last spraying to picking berries.
Iskra-M
Iskra-M is used for a wide range of sucking and gnawing parasites of fruit and ornamental crops. The powerful contact effect of the drug for a long time helps to destroy most of the existing gooseberry pests, which will provide the plantings with excellent immunity for the entire season.
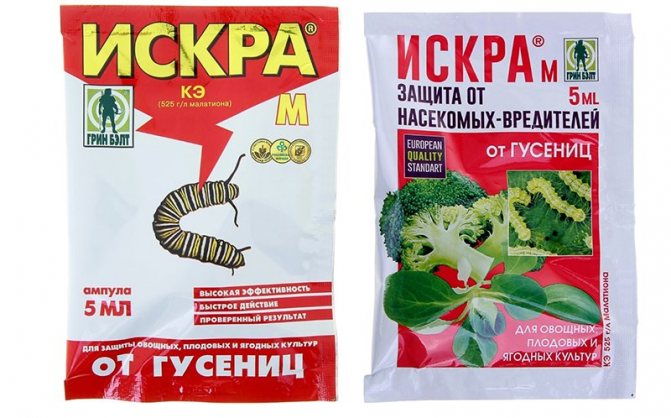


Prepare a treatment agent at the rate of 1 ml of concentrate / 1 liter of water. The resulting mixture is carefully sprayed over the entire surface of the bush at a rate of 1–1.5 l / bush. Such treatments are carried out throughout the growing season, twice, with an interval of 20 days, but not less than 20-30 days before picking berries.
Fitoverm
This insecticide is designed to combat any pests of fruit and ornamental plants, including indoor species. Is the drug derived from the waste products of the genus Streptomyces
and acts on parasitic species in an enteric manner, causing nerve-paralytic effects.
Prepare a product at the rate of 1 ml / 1 l of water, the resulting liquid is sprayed with bushes at a rate of 100 ml / 1 m² of plantings. Do such procedures at least 2 times, until the complete destruction of insects and their larvae, with a break of 14-20 days.


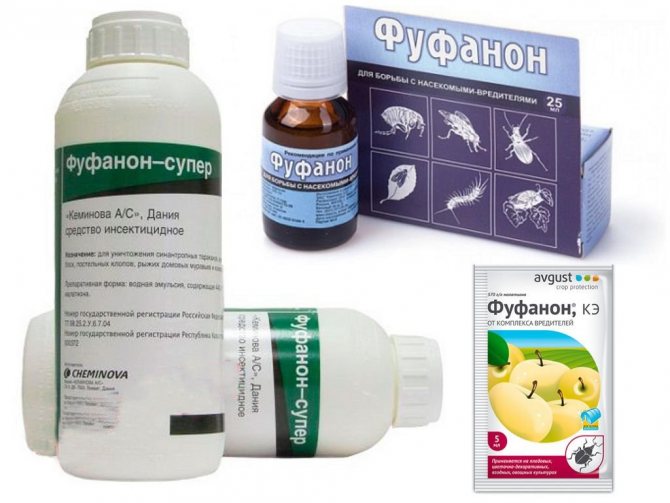
"Fufanon"
"Fufanon" is a complex insecticide that has a damaging effect on most types of gnawing and sucking parasites of fruit and ornamental crops. The drug enters the body by contact, causing all kinds of nerve damage to the body and the death of parasites.
To prepare a mixture for spraying plants, you need to dissolve 10 ml of the concentrate in 500 ml of water, and then bring the resulting liquid to 10 liters. The working solution is used at the rate of 1–1.5 l / bush, the frequency of treatments should be no more than 2 procedures.The last of them is carried out no later than 20-30 days before picking berries.

Folk remedies
In addition to highly active chemicals, it is possible to fight pests with the help of folk remedies. They are less dangerous for plants and future crops, and they are also not able to accumulate in berries. In addition, their use contributes to the transformation of simple truck farming into organic farming.
Did you know? Humanity has been using insecticides for many centuries. Even in Ancient Greece, sulfur fumigation was used as the best panacea not only for pests, but also for all kinds of infections of fruit species.
Ash
Such a product is prepared from 10 liters of pure water and 300 g of sifted wood ash. The mixture needs to be insisted for about 2 days, then strain thoroughly. Before use, add 40-50 g of liquid soap to the liquid and shake everything well.


This infusion is used for spraying bushes throughout the growing season, with an interval of 7-14 days. In this case, the processing must be carried out at least 2-3 times, no later than 2 weeks before harvesting the fruits.
Tobacco dust
This tool is prepared on the basis of half a glass of tobacco dust, grated laundry soap and 3 liters of water. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed and infused for about 3 days. The resulting liquid must be filtered, and then twice, with a break of 14 days, spray the plantings. Such procedures are carried out throughout the growing season.
Also read how to deal with lichen and moss on gooseberry bushes.
Vinegar
Plain table vinegar is considered the most affordable gooseberry pest control. To prepare it, it is enough to dissolve 3 tbsp in 10 liters of water. l. 9% vinegar. The tool is abundantly sprayed on the bushes at least 2-3 times, with an interval of 7-14 days. Such procedures are done throughout the growing season, but no later than 10–20 days before picking berries.


Mustard
The pungent smell and pungent properties of mustard are not tolerated by many insects, including gooseberry pests. To prepare such a tool is quite simple: you need to dissolve 100 g of powder in 10 liters of water. The mixture is infused for about a day, after which, before use, 40 g of grated laundry soap is added to it. The resulting liquid is generously sprayed on the bushes in several passes, with an interval of 7-14 days. If the gooseberry has undergone a massive defeat, the concentration of the substance is increased to 200 g / 10 l of water.
Ammonia
Liquid ammonia also has excellent insecticidal properties. To prepare a solution, 50 ml of liquid must be dissolved in 10 liters of water, and then add about 50 g of grated laundry soap to the mixture.
The tool is abundantly sprayed on the bushes throughout the season, such procedures are done in complexes, 2 visits each, with an interval between each of at least 14 days. In this case, the last procedure should be carried out no later than 20 days before harvesting.


After treatment with all kinds of plant protection products, it is not recommended to water for 2 - 3 days, otherwise the procedure will not give the necessary results.
Pest control of gooseberries
To prevent diseases and pests from infecting the gooseberry bushes, in the spring they do prevention according to all the rules. Appears when you ignore precautionary actions:
- Currant mite - the kidneys do not open, they die. Sprayed with infusion of garlic during the flowering period, after ten days. Take 50-100 grams per bucket of water.
- Spider mite. The leaves turn yellow, die off. Spray with onion peel, infusion of tobacco, wormwood, garlic, Metaphos.
- Blackcurrant aphid - there are red thickenings on the plant, the shoots are deformed. Before the appearance of the kidneys, spray with a 3% nitrophene solution. They are treated with an infusion of garlic during the budding period and then after 10 days. Or they use Vofatox, Metaphos.
- The glass-maker - she cuts into the shoots, makes moves there. The damaged branches are removed. Sprayed with 10% karbofos.
- Gooseberry sawfly - eats leaves to the veins. During bud break, after flowering they are sprayed with Karbofos, Aktellik.
- Moth is a butterfly. The berries turn yellow, rot, crumble. Destroy the affected parts, dig up the soil, spray with mustard infusion, Etaphos.
- Powdery mildew - white bloom on shoots, berries, leaves. Use drugs Hom, Topaz.
- Verticillous wilting - foliage turns pale, withers. Spray and pour a 2% solution of Fundazole under the root.
- Butterfly - moth - leaves curl, fall off. Actellik, Fufanol are used.
- Anthractosis, spotting, rust - fungal diseases of the gooseberry. Sprayed with copper sulfate, Kuprozan, Phthalon, Nitrofen.
- The mosaic cannot be treated. Bushes are destroyed.
Gooseberry moth


a - damaged shoot, b - butterfly
The gooseberry moth affects both the gooseberry and the currant, its caterpillars completely consume the entire leaf, leaving only the petioles.
Caterpillars hibernate under fallen leaves, and in April emerge from their cocoons and feed on buds and young leaves.
By the end of the gooseberry flowering, they finish their development and pupate (in June) on the leaves, attaching to them with cobwebs.
Then, after 3-4 weeks, butterflies fly out of these pupae and begin to lay eggs on the underside of the leaves, from which new caterpillars soon appear. And the gooseberry leaves are in danger again.
After the next devouring of the leaves, the caterpillars leave for the winter.
Control measures with gooseberry moth: thorough cleaning of fallen leaves (if any) in autumn and early spring; burning them to destroy caterpillars; digging up the soil; processing gooseberries with chamomile infusion or decoctions of tobacco, makhorka; if there is a lot of pest, then it is worth spraying with a solution of karbofos a couple of times (the first - in early spring, when caterpillars appear after wintering, the second - in summer, when they reappear, but no later than 20-30 days before harvesting).
What is the processing of gooseberries in the fall?
To ensure the best conditions, it is necessary to perform a number of measures for the processing of gooseberries:
- collect and burn old leaves and weeds;
- cut off old, diseased and broken branches;
- if necessary, water the plantings;
- process and dig up the soil around the bush;
- feed with mineral and organic fertilizers;
- process gooseberries from diseases and pests;
- mulch the soil under the bush.
All of the above measures for processing gooseberries after harvest, it is better not to postpone until later. Let's take a closer look at the agricultural technology for processing gooseberries.
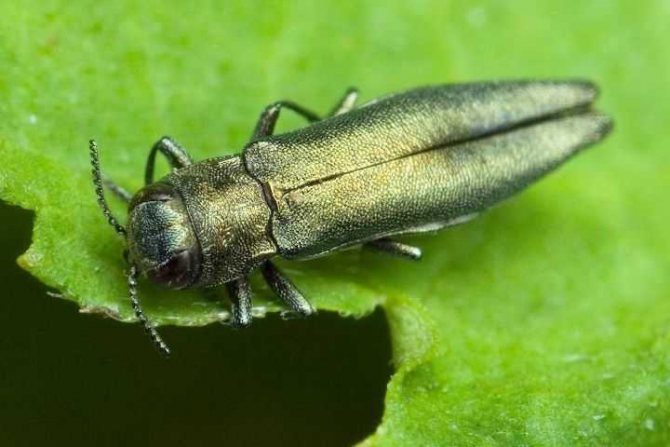
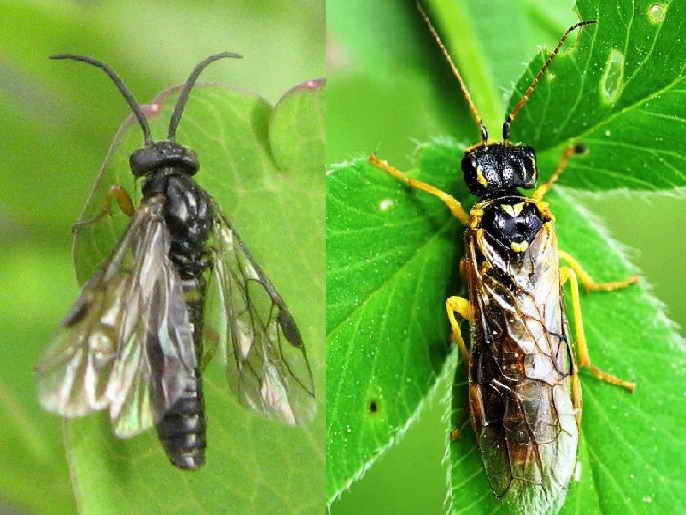
Currant glass


This is also a very dangerous pest of gooseberries and currants, its caterpillars make moves in the very core of the branches, moving from top to bottom.
The glass can easily be found along these paths, doing the spring pruning of gooseberries.
Caterpillars hibernate inside damaged branches. In the spring, they pupate there, and already at the beginning of June, butterflies, very similar to wasps, fly out of the formed pupae.
Their flight lasts up to 1.5 months. Butterflies lay eggs near the buds, as well as in cracks in the bark and in places of various injuries.
Appearing after a certain time (about 10-15 days), young caterpillars with renewed vigor, gnawing through the bark, penetrate into the shoot.
There they can live up to two years, feeding on the core. Gooseberry branches affected by currant glass first wither, then dry up and break.
Glass caterpillars can damage up to 50% of the branches if you do not take timely measures to destroy them.
Control measures - in autumn and spring, mandatory sanitary pruning, and without leaving hemp, followed by burning the cut branches; loosening the soil under the bushes (May-June) and processing it with a mixture of the following ingredients: tobacco, wood ash, mustard and ground pepper (300 g of ash, 1 tablespoon of mustard and pepper, 200 g of tobacco dust).
Sprinkle 3-4 tablespoons under each bush. And during the flight of butterflies, it is good to spray the bushes with infusions of dry mustard or celandine, a decoction of tansy, and only after harvesting can the bushes be treated with any chemical preparation.
This is the final article in a series of articles about our northern grape - gooseberry, about its useful properties, about the variety of varieties of this wonderful berry, about growing and caring for it, about how gooseberries reproduce, about its diseases. I would like to hope that these articles will help you, dear summer residents, to successfully grow gooseberries on your plots.


See you soon, dear readers and rich harvests!
How to handle gooseberries after harvest?
Gooseberry cultivation begins with weeding around the bush. If weeding was not carried out throughout the summer, then many small and large weeds grew under the bushes. They should not be pulled out, as the roots may remain in the soil, but carefully dig up with a shovel so as not to damage the gooseberry. It is also necessary to use a rake to collect the accumulated debris and fallen leaves, since many pests and pathogens of various diseases remain under it to winter.
Gooseberry pruning should be started at the age of 6. Basal weak shoots must be cut out the next year after planting the shrub, choosing 3 - 4 strong shoots. First of all, cut out broken branches damaged by diseases and pests, old and infertile. A well-formed bush should have up to 18 branches of various ages, sparse enough to allow light and air to enter the interior of the bush and facilitate subsequent harvests.
How to properly trim gooseberries - video:
After the foliage has fallen off during a dry autumn and a large harvest, it is necessary to water the gooseberries. Such watering on light and sandy loam soils is very important. This increases the growth of roots, and the bush is better prepared for frost.
For good development of the bush and regular fruiting, it is necessary to dig up and loosen the soil. Unlike spring digging, during autumn the soil is not broken, but turned over with a pitchfork, since large lumps retain moisture in the soil in autumn and spring. The roots of the gooseberry are located close to the soil surface, therefore, under the crown of the bush, processing should be done very carefully, to a depth of no more than 7 cm.
In connection with the abundant fruiting, gooseberries need enhanced feeding.
During digging, the following fertilizers are applied to the soil under one bush:
- up to 10 kg of compost or rotted manure;
- 20 gr. potash fertilizers (potassium sulfate);
- 30 gr. phosphate fertilizers (double superphosphate);
- 300 gr. furnace ash.
The best result will be given by liquid organic fertilizer in the form of a diluted infusion of mullein or bird droppings.
The task of these dressings is to prepare the shrub for the laying of flower buds next year.
It is advisable to sprinkle humus or peat mixed with ash on top of the soil dug under the bush to a thickness of no more than 10 cm.This layer covers both the inner zone of the bush and the bite strip. Due to mulching, the water-air, temperature and nutritional regime of the upper soil layer improves, the roots are protected from freezing, and the growth of weeds is reduced. It is advisable to mulch the soil before the onset of frost.
Hello dear readers!


The bright spring sun, warm wind and rains quickly remove snow from our summer cottages. And earlier than other plants in the garden, the snow disappears and the earth warms up on the trunk circles gooseberry and currants.
Plants begin to wake up, but along with them their enemies wake up: various pests, some of them wait out the winter under fallen leaves, others in the soil under these bushes.
The causative agents of various gooseberry diseases are also beginning to become active, you can read about them here.
Therefore, in order for the gooseberry to grow healthy and enjoy an excellent harvest, we need to take care of this from early spring. With what gooseberry pests can we encounter while growing it?
There are a lot of them, these are spider mites, gooseberry sawflies, gooseberry moth, gooseberry shoot aphid, gooseberry moth, currant gall midge, currant goldfish, currant glass.
Let's take a look at each of gooseberry pests in more detail.
Treatment of gooseberries from diseases and pests
In autumn, it is necessary to treat gooseberries from diseases and pests.
Iron vitriol is an effective means of combating fungal diseases; bushes are treated with a 3% solution after leaves fall. A 1-3% solution of Bordeaux liquid is also used.
To combat powdery mildew, a 5% baking soda solution is used. To protect against septoria, anthracnose or goblet rust, gooseberries and the soil under them should be treated with oxychloride (40 grams per 10 liters of water), soap-copper emulsion or ash infusion. All fallen leaves should be burned.
To protect against aphids, moths or sawflies, gooseberries should be treated in the fall with a solution of karbofos (20 grams per 10 liters of water), an infusion of ash (1 kg per 10 liters of water) or infusions of onion peels, chopped garlic or potato tops.
All the measures taken for the processing of gooseberries will have a beneficial effect on growth and yield.
How to grow healthy gooseberries - video
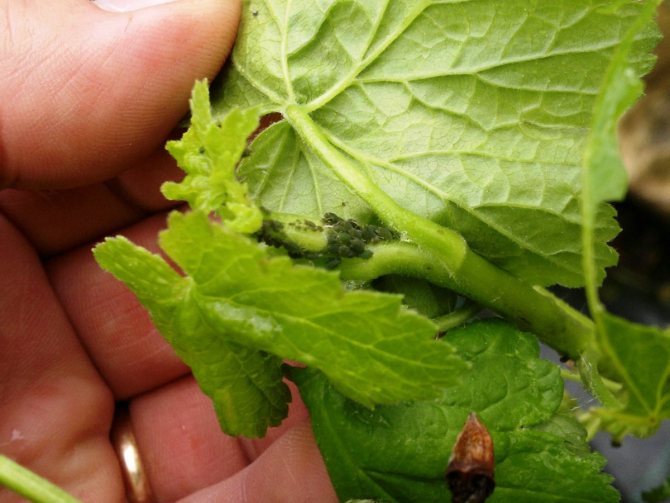
Gooseberry shoot aphid


The gooseberry shoot aphid is also a common pest, the eggs of which remain to winter on the shoots.
In the spring, larvae emerge from these eggs. They settle on the stalks of young leaves and consume their juice.
Then, some of them, in disguise, turn into winged female settlers and occupy all the new tops of young shoots.
Shoot growth slows down, leaves begin to deform and a dense clump of leaves forms at the top of the shoot. Inside this lump, large numbers of aphids live, feed.
The next year, the plants affected by the gooseberry shoot aphid develop very slowly, bud opening also occurs later.
Control measures with aphids the following: firstly, I recommend pouring hot water on the bushes (in early spring); secondly, during the period when the larvae begin to appear, spray the plant with fufanon, Iskra or another drug.
After that, spraying the gooseberry bushes is carried out only with folk remedies, the same as in the fight against spider mites. For example:
- in 10 liters of water, stir well 200-300 g of chopped garlic, then filter the resulting solution and process the plant;
- we insist in 10 liters of water 150-200 g of onion husks, after 4-5 days we filter the infusion and start spraying;
- pour 1.2 kg of green potato tops with ten liters of water, leave for 3-4 hours, filter and spray. If we have dry tops, then we take 600-800 g.
- we insist in 10 liters of water 4 kg of crushed burdock leaves for 2-3 days, then we filter the infusion and process the plant.
Features of autumn gooseberry care, including processing, feeding and pruning


Do you want to collect fifteen kilograms of delicious large berries from the gooseberries growing in your garden? Then you need to try to provide the shrub with the best conditions for growth and fruiting. Although some gardeners manage to get a good harvest without much effort, planting and caring for a plant like gooseberry is still of great importance.
The main mistakes in the fight against gooseberry diseases
Experts identify several typical mistakes that inexperienced gardeners make when fighting plant diseases:
- spraying without removing the affected parts of the plant beforehand;
- using the same chemical
- carrying out abundant and frequent watering of the bush;
- leaving the cut off affected parts of the gooseberry on the site.
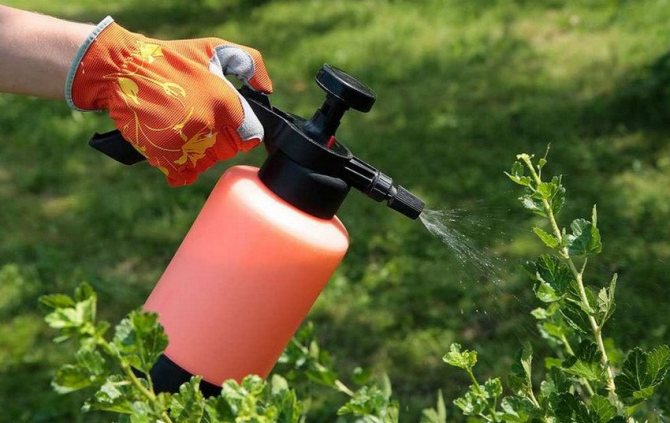


The type of instrument does not affect the effectiveness of the treatment.The main thing is to carefully process all the leaves and branches of the plant.
How to care for gooseberries from early spring to early fall
Plant young bushes in a sun-lit area, regularly prune old branches, water gooseberries, feed, loosen the soil, remove weeds, and do not forget about autumn gooseberry care. Thanks to these simple rules, you will be able to achieve excellent results - every year the bushes will be strewn with selected fruits, and common gooseberry diseases will bypass your garden.


Plant young shrubs in a sunny spot
Throughout the season, the care of gooseberry bushes does not stop. In the spring, remove all frozen and damaged branches, loosen the ground under the bush and add the first top dressing to it in the form of an aqueous solution of nitrophoska with urea. Before flowering, wood ash is poured around the gooseberry and the roots are fed with potassium sulfate and organic fertilizer "Berry" or "Breadwinner".
During the summer, weeds are weeded and loosened up the ground by ten centimeters and watered after each loosening. During a drought, it is also necessary to water the gooseberries - the care is that the plant does not have to spend energy to survive in adverse conditions. Only water at the root, otherwise there is a high probability of damage to the bushes with powdery mildew. When the first fruits begin to set, you need to feed the gooseberries for the third time, top dressing consists of nitrophoska and liquid fertilizer "Ideal".
Autumn processing of gooseberries is of particular importance, because you need to prepare the bushes in such a way that they will endure the winter well and give a good harvest next season. Let us dwell in more detail on the procedures that you will need to carry out in the autumn months.


Autumn processing of gooseberries is of particular importance, because you need to prepare the bushes in such a way that they will well endure the winter.
Gooseberry moth


1- butterfly, 2- caterpillar, 3- pupa, 4 and 5 - berries damaged by caterpillars, 6 - pupa in a cocoon in the soil
This is one of the most insidious and common pests of not only gooseberries, but also currants.
In the spring, when the leaves begin to bloom, butterflies fly out of the moth pupae wintering in the ground under the bush and lay their eggs inside the blossoming flowers.
In about 1-1.5 weeks, caterpillars appear from the eggs, which can eat out the contents of the ovaries within one month.
Affected berries begin to blush long before ripening, then rot and crumble. Or they continue to hang on the branches, entangled in cobwebs.
Control measures with a moth are the same as with a sawdust: we collect and destroy berries with caterpillars, dig up the soil and spray the gooseberry bushes with the same solutions.
We make an infusion of wood ash like this: we take one third of a bucket of ash, dissolve it in 10 liters of water, let it brew for two days, filter it and the solution is ready for processing the plant.
Infusion of dry mustard - infuse 100 g of mustard in 10 liters of boiling water for two days, then dilute the infusion with cold water in a ratio of 1: 1. This solution is best used at dusk or cloudy weather.
I want to tell you about another very effective way to combat fire flames. From autumn, although it is possible in spring, as soon as the snow melts, we completely cover the trunk circles of gooseberry bushes with pieces of roofing material or other similar material.
Thus, we will not let the moth butterflies fly out of the soil and they will die. It is advisable to repeat this technique the next year.
Preparing gooseberries for autumn processing
You can't just take and spray gooseberries in the fall. It is worth carefully preparing for processing:
- Examine the plants, determine with what or with whom to fight.
- If there are shoots damaged by powdery mildew, scab or septoria, it is better to cut them out immediately, without waiting for the autumn pruning.
- Remove the berries and leaves on the tops of the shoots remaining on the gooseberry bushes. It is the latter that are often chosen as a habitat by pests, especially aphids. The sawfly does not disdain them either.
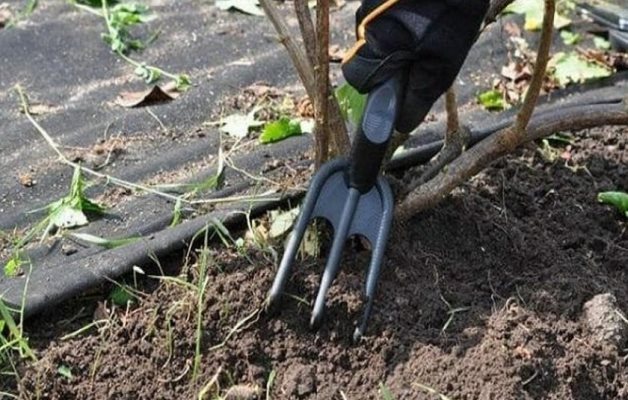


- Weed out the weeds in the root circle. Large ones with a long root system, such as dandelion, burdock, horsetail or bindweed, are best carefully dug out with a shovel or pitchfork.
- Remove dead leaves and old mulch from under the bushes.
- Loosen the soil in the root circle to a depth of 15-20 cm, destroying the larvae if possible.
Do not store leaves, mulch, dried branches on the site or lay them in compost heaps. The optimal solution, take it outside and burn it Especially if pests or signs of fungal diseases were noticed during the growing season.
.
Other problems and the fight against them + photo
In addition to the ailments and pests listed above, there are two more misfortunes that need to be discussed in order to get a complete picture of all possible problems. It will be about a mosaic of gooseberries and currant goldsmiths.
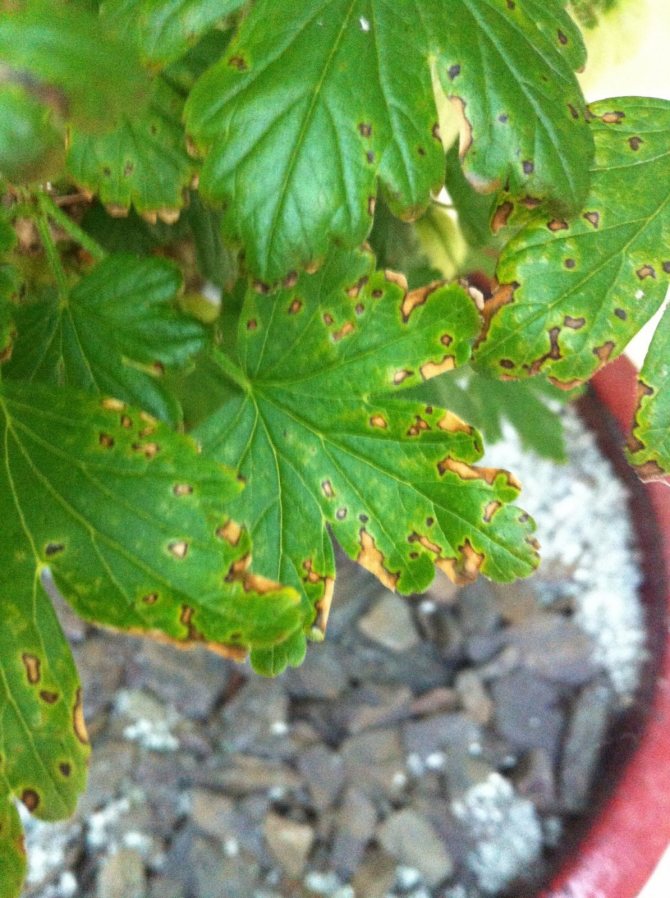
Gooseberry mosaic can be spread by insect pests such as aphids and herbivorous mites, as well as by using non-disinfected tools to trim infected bushes. The main distinguishing feature of the mosaic is a bright yellow pattern on the leaves along the main veins. The diseased bush ceases to grow, the yield decreases sharply, and the leaves grow small and wrinkled.
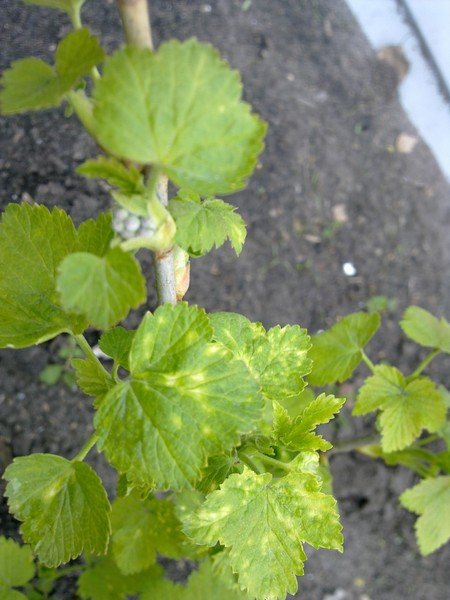


Mosaic is a viral disease and cannot be treated
Solution: it is impossible to cure a bush affected by the mosaic; all that remains is to get rid of it (dig it up and burn it). It remains to apply only preventive measures - to acquire healthy seedlings and use the above means to protect against sucking insects.
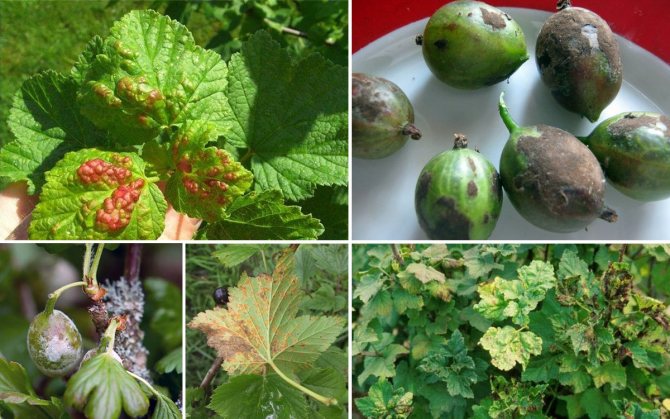
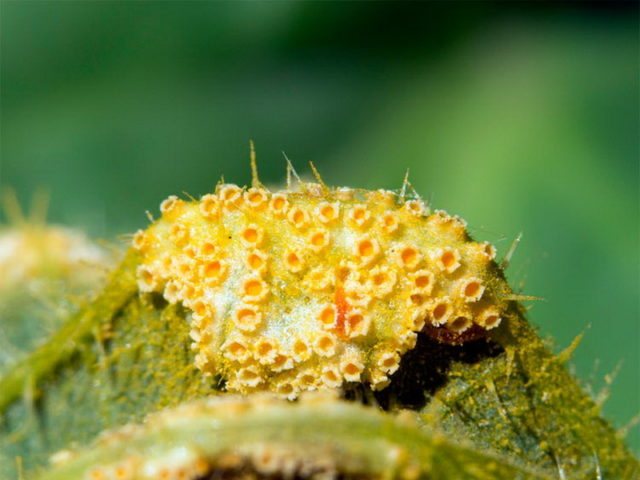
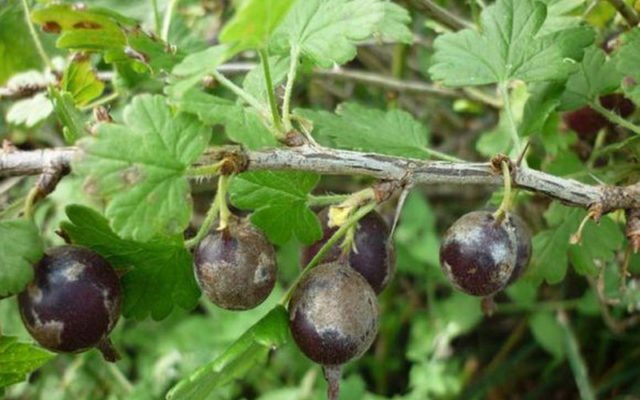
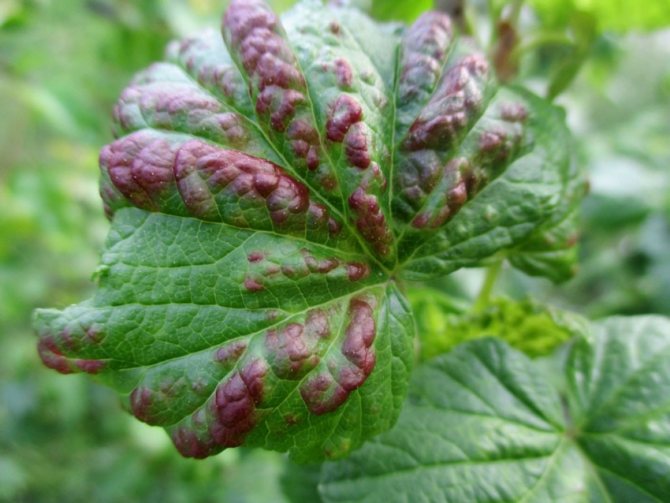
Currant goldfish affects gooseberry shoots - it makes passages in them, and hibernates there. In mid-June, the larvae that emerged from the clutches begin to eat the branches, which is why the gooseberry bush begins to hurt, the yield drops, and the berries become small.
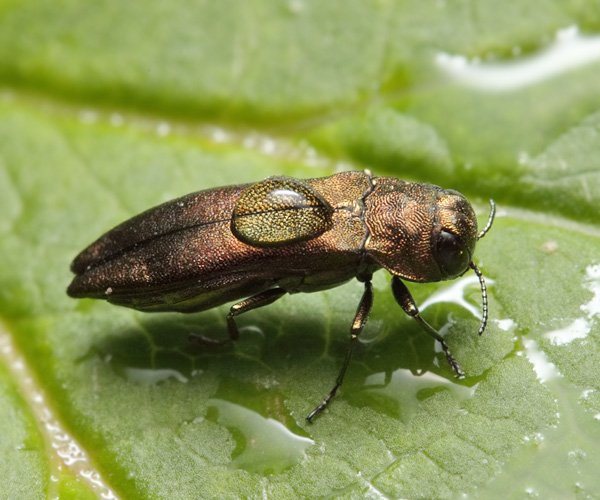


Currant goldfish mainly affects shoots - in them it also makes moves
Solution: branches affected by the pest are cut out and burned, and the bush itself must be periodically pruned (remove damaged, diseased, as well as weak shoots). Also, carefully monitor the quality of the purchased seedlings.
Fire
One of the most common gooseberry pests is the moth. Its activity begins with the arrival of spring. When the ground has warmed up well and greenery begins to appear on the shoots, butterflies begin to fly out of the pupae in the ground.
At the time of gooseberry flowering, their egg-laying period falls. They do this directly in blooming flowers. And after a week and a half, caterpillars that feed on ovaries hatch from the eggs.
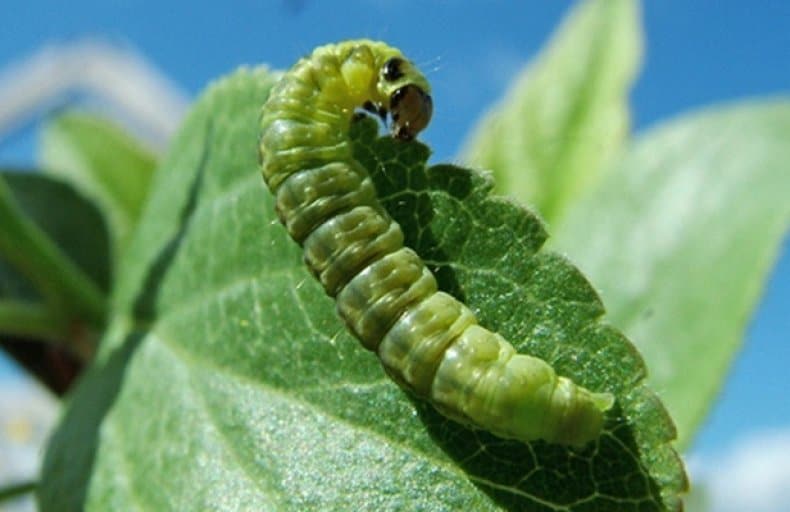


Berries that have been affected stop growing and begin to blush prematurely. Further, they decay and fall off. The fight against this pest consists in removing damaged fruits and spraying the affected bushes with a solution based on wood ash.
As a preventive measure, you can cover the area near the bush with roofing material or other sheet material in late autumn or early spring.
Glass-maker
Glassy can harm not only currants, but also gooseberries. If shoots have begun to fade on the bush and when they are cut there is a black spot in the center, this indicates the presence of a caterpillar. The glassy butterfly lays eggs in shoots that are cracked or damaged. Young caterpillars feed on the core of these shoots, moving further over time.
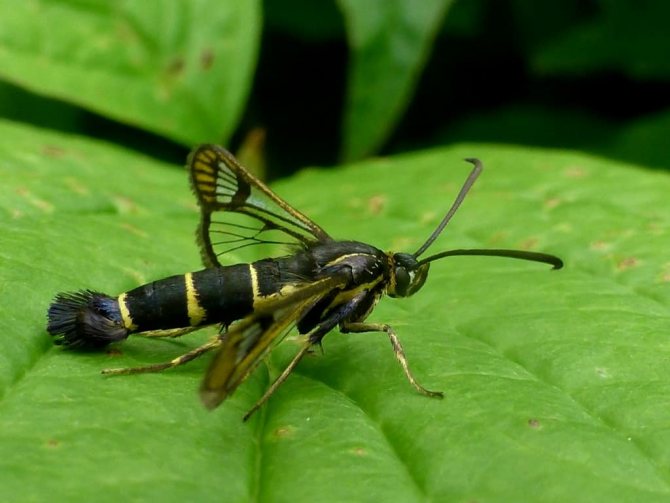


You need to fight with adults by treating shrubs with Fitoverm, Lepidocide and others. This procedure is recommended in late spring and early summer.
Gooseberry septoria
The disease caused by the fungus affects the leaves and berries.Brown spots with a white, transparent core and a dark border are formed on the plates. The peak of the development of the disease occurs at the beginning of June. These spots are the sphere of development of fungal spores.
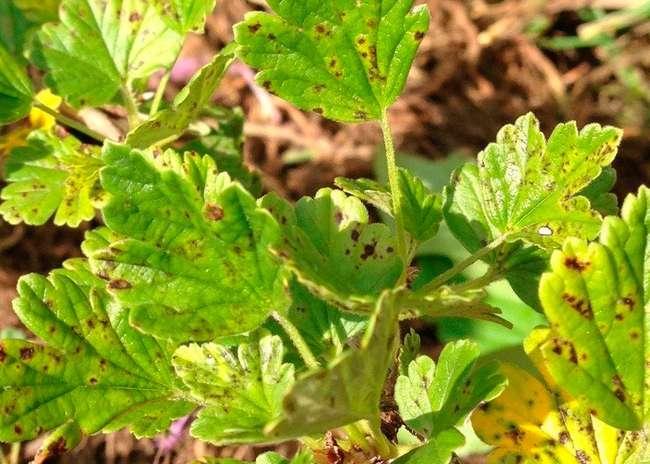


Favorable conditions: humid, hot weather and heavily thickened branches. Due to septoria, leaves fall, and the next year you can lose your crop.
You will have to fight septoria as follows:
- Dig up the ground around the bushes;
- Collect fallen leaves and berries in the spring and fall;
- Thin branches so that there is no thickening inside the bush;
- Apply potassium-phosphorus fertilizers;
- Spray with Fundazol, Fitosporin, Ordan, Abika-peak, Profit Gold.
How to treat gooseberry disease
Any disease of the gooseberry must be treated urgently to prevent the death of the plant. Typically, processing is carried out by the following means:
- copper sulfate and garden var;
- Bordeaux liquid and Fundazole;
- manganese sulfate;
- iron and copper chloroxide;
- zinc and boric solutions.
Home remedies are also popular, such as tar soap, soda ash, lye, and ash, to remove a variety of fungi.
Treatment of plants from fungus can be carried out throughout the warm season - from spring to autumn. Particular attention should be paid to prevention and treatment during bud setting and flowering. But during fruiting, gooseberries should not be sprayed - chemical and toxic substances can make the fruits of the shrub unsuitable for eating.
It is customary to carry out the processing on cloudy days so that the medicinal solutions from the leaves and shoots do not wash off the rain and do not dry out the sun. It is necessary not only to spray the leaves and shoots of the gooseberry, but also to spill the soil around it with medicinal solutions in order to protect the roots from diseases.
Important! It is necessary to process gooseberries from fungus in protective equipment, since some substances can be harmful to human health. It is imperative to wear gloves, a thick work raincoat or raincoat, and cover your face with a respirator or a thick bandage.
Diseases of the gooseberry bush, leaves and berries with a photo and description
Not only pests, but also ailments - fungi and viruses can negatively affect the health of the gooseberry. In order to cure the shrub in time, you also need to know gooseberry diseases and their treatment, ways of spreading and symptoms.
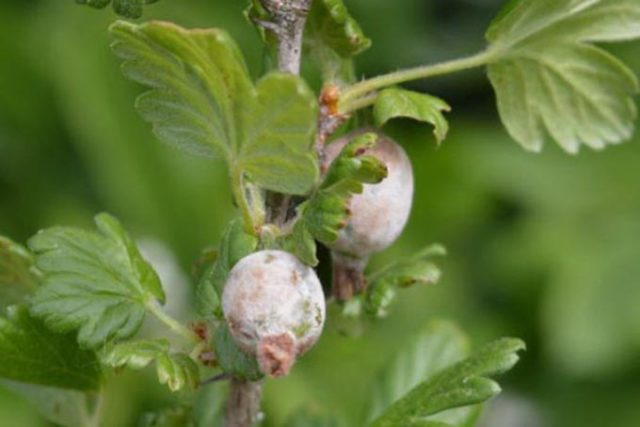
Spheroteka
Disease of gooseberries with white bloom on berries - spheroteka, or powdery mildew, it affects the shrub most often. The disease is caused by the fungus Sphaerotheca, which develops especially actively in warm and humid conditions. The main symptoms of the disease are a whitish bloom on the leaves, which becomes denser over time, affects the ovaries and fruits, and leads to premature shedding of fruits.
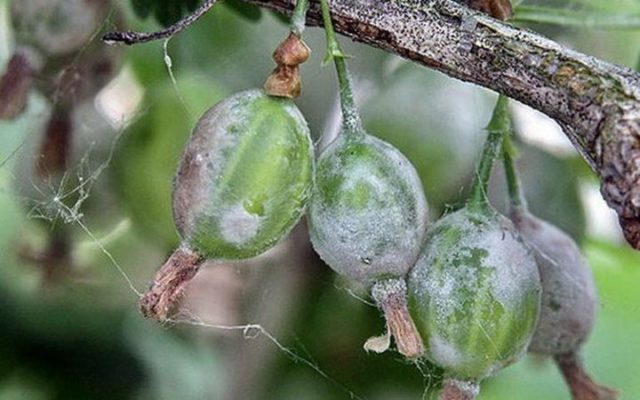


The fight against the disease is carried out with the help of Bordeaux liquid and copper sulfate, you can also use a solution based on tar soap.
Anthracnose
Another disease that leads to the appearance of mold on gooseberry berries and to leaf deformation is anthracnose. The disease is caused by a fungus of the genus Colletotrichum, which spreads to the plant from the soil. At first, small brown specks on the leaves become the symptoms of the disease. Subsequently, anthracnose leads to the fact that the leaves of the gooseberry completely turn brown, and the fruits are covered with dark mold.
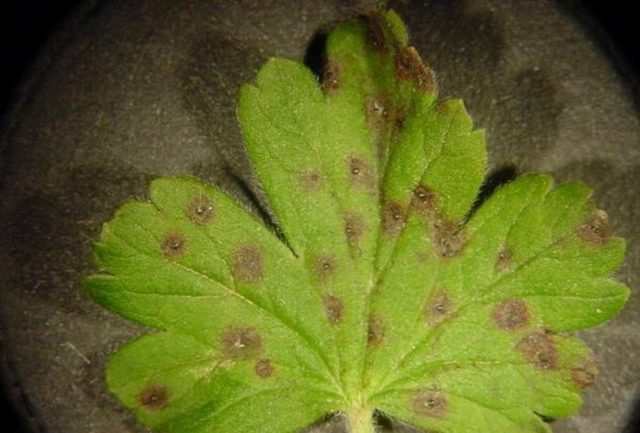


The fungus reproduces mainly in the rainy, warm months. To combat it, you need to remove all affected parts from the gooseberry and treat the bush with Bordeaux liquid, Kuprozan, colloidal sulfur and other fungicidal substances, and the disease is treated in early spring.
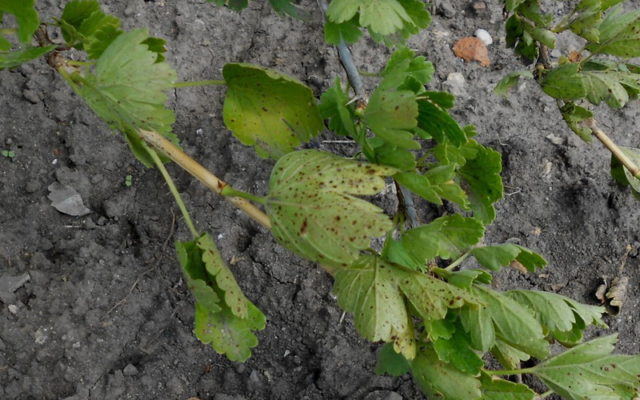
Septoria
Septoria disease is caused by the fungus Septoriaribis Desm and manifests itself primarily as gray spots with a dark border on gooseberry leaves. Then microscopic fruiting bodies of the fungus appear on the spots, which look like dark dots.Gooseberry leaves begin to dry, deform and fall off, and in one summer the shrub can completely lose its crown. The fungus spreads from the spores that have appeared in the ground at the roots of the gooseberry and, if untreated, can destroy the plant.


The fight against the disease is carried out with the help of fungicides - Bordeaux liquid and copper sulfate. It is also necessary to remove all affected parts of the shrub and clear the ground at its roots.
Advice! For the prevention and treatment of the disease, it is useful to feed gooseberries with complex mineral fertilizers - manganese, zinc, boron and copper.
Rust
Fungal disease rust appears on gooseberries most often when the shrub is close to cedar or sedge. The disease is manifested by the appearance of yellowish pads on the underside of the leaves, on flowers and fruit ovaries, and a fungus forms in these pads. Over time, rust forms a dense dark coating on the leaves and fruits, as a result of which the gooseberries begin to fall off and bear fruit worse.


To combat the disease, spraying with Bordeaux liquid and other fungicides is used. In this case, the treatment must be carried out three times - after the appearance of the leaves, during the budding period and immediately after flowering.
Gray rot
Disease gray rot, or scab, appears due to the fungus Botrytiscinerea and affects the lower shoots and roots of the gooseberry. The berries of the bush are first covered with a gray bloom, and then they begin to rot and crumble, the health of the plant is greatly deteriorating.


Gray rot occurs most often in conditions of neglect of the gooseberry and poor ventilation of its shoots. The disease can manifest itself at any time during the spring and summer. The disease lends itself well to treatment, but to heal the shrub, you will have to cut off all the diseased parts, and pour charcoal under the roots.
Ascochitosis
The ascochitis disease is provoked by the fungus Ascochytaribesia Sacc, which multiplies in plant debris under the roots of the gooseberry. The ailment is mainly affected by the leaves of the plant - in the spring, whitish or light brown spots with a dark border appear on them, and by the fall dark growths are formed - fruit bodies in which the fungus hibernates. Gooseberries, affected by ascochitis, begin to dry out and fall off, and their frost resistance and yield decrease.


To combat ascochitis, you need to cut off all parts of the shrub that have already been affected by the disease. Healthy leaves and shoots are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid and other fungicides.
Verticillary wilting
Verticillium disease is caused by spores of a fungus from the genus Verticillium, and the symptoms of the disease are manifested in the defeat of the gooseberry roots. Against this background, the leaves of the plant turn yellow and wither, but do not fall off, but remain on the bush. Verticillosis in the initial stages proceeds almost imperceptibly, and then develops very quickly. If you do not carry out emergency treatment, the shrub will die completely, the fungus will gradually rise along its shoots, clogging the vascular system, and will not allow the plant to receive nutrients.


The treatment of shrubs from verticillosis is that the plant is sprayed with Fundazol or Topaz formulations. It is important to observe prevention - regularly trim and fertilize the shrub, monitor the cleanliness of the soil around it.
Mosaic
Mosaic refers to viral diseases of the gooseberry - it can spread to the plant from other fruit bushes, and aphids often become the cause of mosaic infection. In the photo of the treatment of gooseberry diseases, you can see the symptoms - bright pale yellow patterns appear on the leaves of the bush, which run along the main veins. If the mosaic is not treated, then over time, the leaves begin to dry and become covered with wrinkles, the gooseberry will cease to bear fruit and will stop developing.
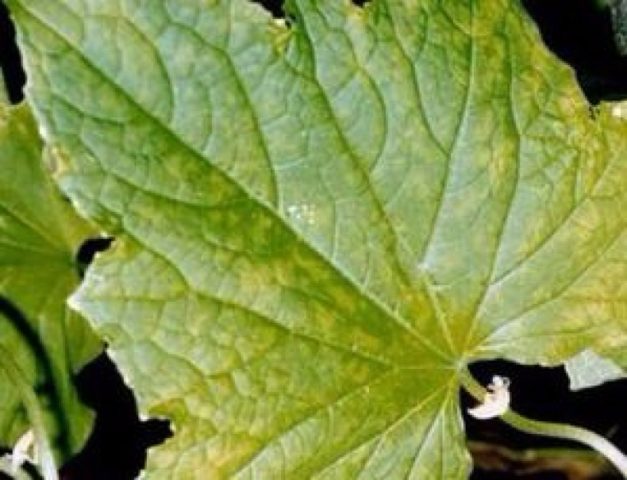


It is very difficult to cure the mosaic - chemical and home remedies hardly help against the disease.The only treatment option is to remove all affected parts of the shrub and then carry out regular treatment from pests that can carry the disease.
Alternaria
The disease is caused by the fungus Alternaria grossularia Jacz and affects not only leaves, but also shoots and gooseberry fruits. The first symptoms of Alternaria are gray-black spots that appear in the spring at the edges of the leaf plates, and by autumn a black-green velvety bloom appears on the leaves and shoots. The gooseberry leaves begin to dry out and fall off, the shrub weakens and becomes less resistant to cold. Alternaria most often gets on a plant from plant residues on the surface of the soil, in which spores of the fungus develop.
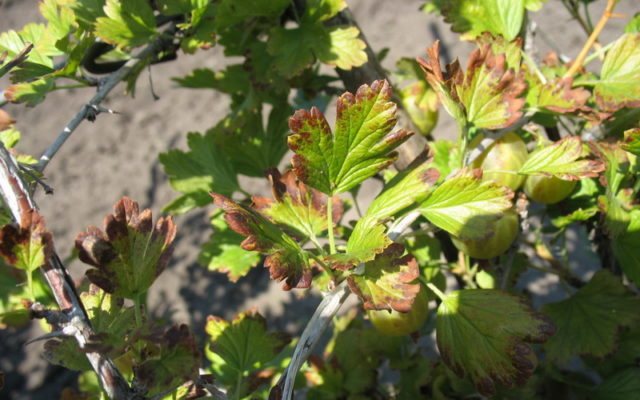


Alternaria is treated with Bordeaux mixture before flowering and after fruiting. It is also important to remove fallen leaves and other plant debris in time from the area where the gooseberry grows.
Drying of shoots
The disease is of fungal origin, and the spores of the fungus usually get on the gooseberry from the uncleared ground, on which the remains of foliage and small twigs lie. The disease affects the bark of the plant, it becomes less elastic and becomes covered with cracks, in which, over time, small rounded growths of black color appear, representing the actual body of the fungus.
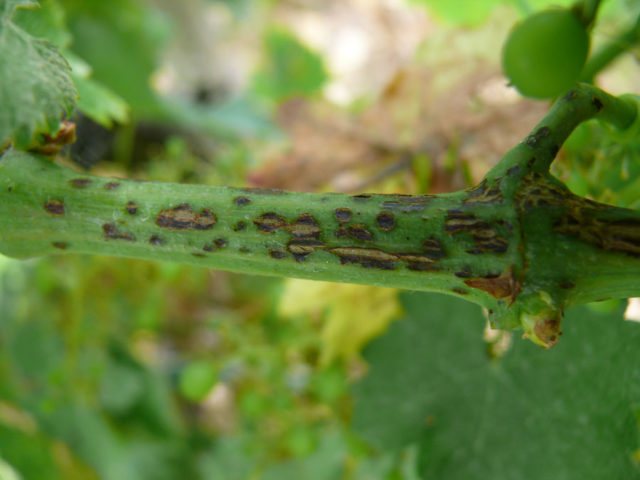


Treatment of the disease is carried out by radical pruning of all diseased parts, and gooseberries must be treated with copper sulfate and Bordeaux liquid.
Requirements for methods of elimination of pests
The methods used should not:
- make the rest of the garden vegetation suffer;
- affect birds and beneficial pollinating insects;
- adversely affect human health.


Otherwise, the fight against harmful insects can lead your garden to a lifeless state.


Weed control in the gooseberry bite zone in autumn
After the gooseberry bite zone was clean of fallen leaves, branches and other debris, only weeds crushed by a rake remained on it. Quite often, wheatgrass predominates among gooseberry weeds. Be aware that it strongly oppresses this culture, so it is strictly necessary to fight wheatgrass.
Of course, contact action herbicides can be used, that is, which act only when the poison comes into direct contact with the plant. Such herbicides should not be discounted, they are often used even in areas where medicinal plants grow. In our case, if there are few gooseberry bushes on your site, then after rain or abundant watering, armed with a small scoop, you can try to pick out the unfortunate wheatgrass with the maximum amount of its root system from the soil, because even if one centimeter of it remains in the soil, the wheatgrass will revive again ...
Moth
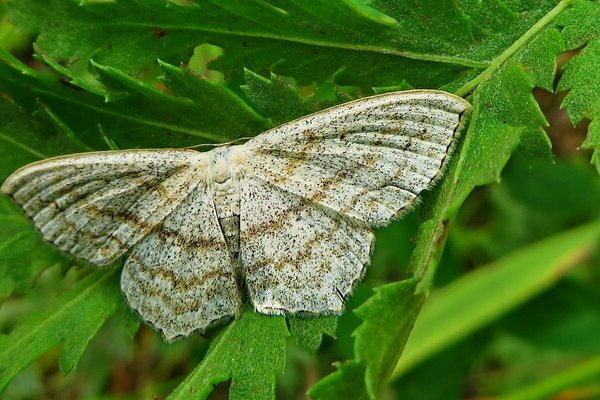


The caterpillars of this pest eat up the leaf so that only veins remain of it. But even in them, they can make holes. The wingspan of such a butterfly is up to fifty millimeters. Eggs are laid on the lower part of the leaf plate, in the first or second month of the summer period.
To destroy this pest, you can use the same drugs that are destroyed: 1) aphids;
2) gall midge;
3) fire.
To destroy the first generation of the pest, you need to spray before the buds and inflorescences begin to bloom.
To destroy the second generation of the pest, you need to spray when the plant has already faded.
If, after you have harvested, you find more larvae, then you need to carry out another spraying procedure.
You can collect the larvae of the pest by hand.
Prevention, seasonal features
As practice shows, timely prevention is always the best measure for pest control on the site. It allows you to avoid massive infections, as well as prevent a decrease in the yield of fruit species.
- To do this, you need to adhere to just a few simple rules:
- it is imperative to carry out preventive spraying of the bushes in early spring, before flowering and in late autumn;
- at the beginning of the growing season, pour boiling water over the gooseberry near-stem circle (avoiding contact with the plant itself);
- periodically weed the trunk circle;
- provide the bushes with the necessary microclimate and an intensive feeding system;
- at the end of the season, remove foliage and burn off all plant residues.
Digging the soil in the gooseberry bite zone in autumn
There are two ways - to dig or not to dig. Look, if you are a resident of the center of Russia, where freezing of the gooseberry root system is a rarity and additional mulching (in this case, only covering the roots with mulch) is not required for this culture, then it is quite possible to dig up the bite zone by placing a shovel along the growth of the roots and without deepening it is more than 5-6 cm.When digging the gooseberry bite zone in autumn, it is important that the lumps of earth are turned over, but not crushed, but it is also important not to allow the gooseberry root system to be exposed, otherwise the roots may suffer even in your zone. Digging will allow the hibernating stages of pests and diseases to be turned to the surface, and they will die, elementary freezing in the winter period. In addition, digging will enhance air and water exchanges and allow excess moisture to evaporate on warm and hot autumn days, and allow the roots to breathe and grow normally: after all, even during leaf fall, small absorbent roots continue to develop.
Pruning
Gooseberries are fast-growing crops prone to thickening, so they need annual sanitary and formative pruning, as well as anti-aging for plants over 7 years old.
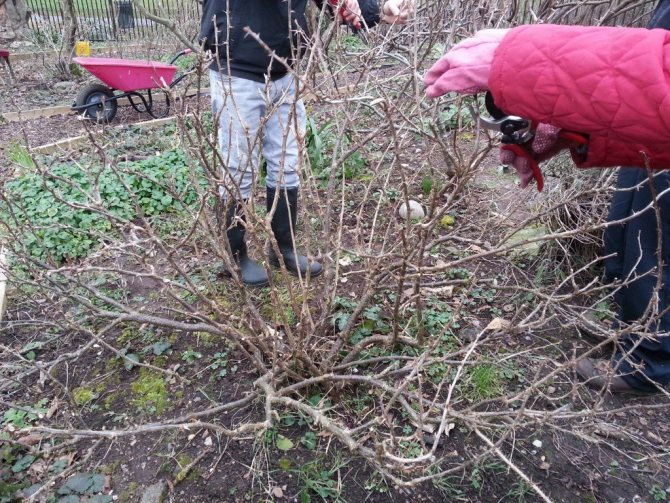


Gooseberries should be pruned every year
Late in autumn, after leaf fall, branches are cut out from the bushes:
- dried out, broken and damaged by diseases or pests;
- thickening crown, growing in the center of the bush and sloping too low to the ground or lying on it;
- crooked and thin immature;
- old shoots with almost black, dark brown bark (while leaving an equal number of replacing young shoots).
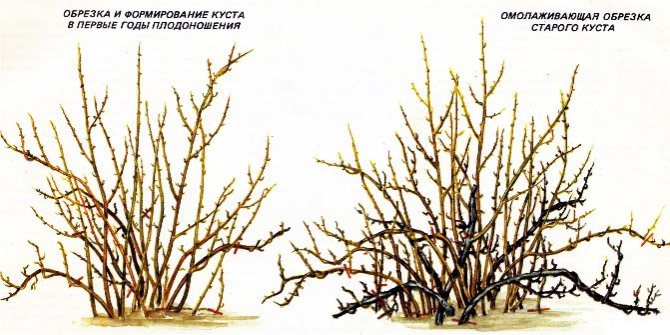

Rejuvenating pruning begins from the seventh year of the plant's life.
The very long shoots of this year are shortened by a quarter or a third of their length to stimulate lateral branching.
Video: pruning gooseberry bushes
Gooseberry bush - description
Gooseberry is a low shrub - up to one hundred and twenty centimeters in height, with peeling brown or gray bark. Thin needle-like thorns are located on cylindrical shoots. The leaves of the gooseberry are petiolate, cordate-ovate or round, three to five-lobed, dull, pubescent with short villi, the edges of the leaf plate are obtuse. Greenish or reddish flowers, single or several, grow from the axils of the leaves.
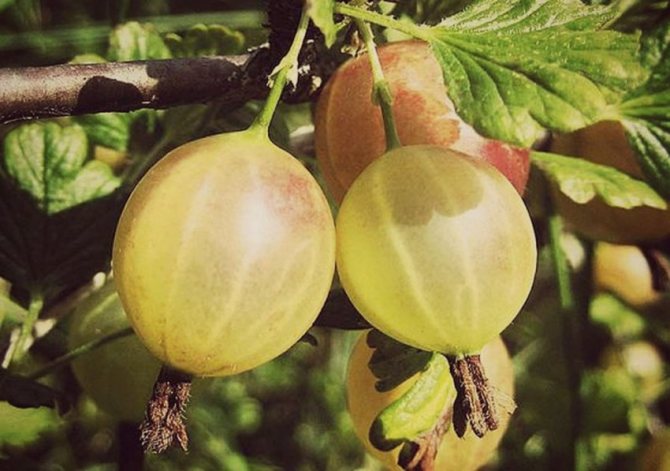
Gooseberry is the earliest of the berry bushes of honey plant. Gooseberries, oval or spherical, with distinct venation, 10 to 40 mm long, glabrous or covered with coarse bristles, ripen from June to August. If the original species has green fruits, then thanks to the labor of breeders today in gardening, red gooseberries (varieties Krasnoslavyansky, Ravolt), yellow gooseberries (varieties Yellow Russian, Rodnik), white gooseberries (varieties Triumph, Belarusian Sugar) and even black gooseberries (varieties Negus, Protector). Although the varieties of the usual color for this berry are still in demand - the green gooseberry varieties Malachite, Yubileiny, Uralsky Izumrud and many others.
This article is devoted to pests and diseases of gooseberries and the fight against them, but if you follow the rules for planting and caring for gooseberries, then all these troubles can be avoided.
- Pruning strawberries after harvest


Disease Resistant Gooseberry Varieties
To avoid problems with gooseberry diseases, choose varieties that are resistant to them:
- Neslukhovsky, Rodnik, Houghton, Malachite, Chernysh - resistant to powdery mildew;
- African and Negus are black gooseberry varieties that are resistant to most diseases;
- Isabella resembles grapes in taste and appearance, is practically not affected by fungal diseases;
- Russian red and yellow varieties are immune to powdery mildew and frost;
- Commander and Consul (with black berries) are resistant to powdery mildew, give a rich harvest;
- Salute is a very resistant variety with burgundy red berries;
- Cossack - resistant to many fungal diseases of the gooseberry.
Gooseberry fire caterpillars
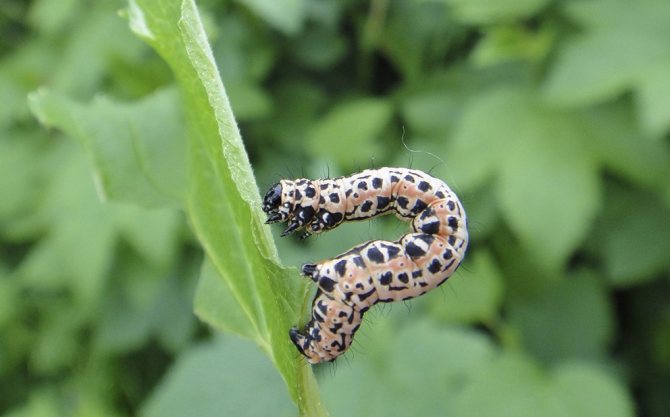
This harmful insect is 1.5 cm long and gray-green in color with round black dots. The head is also designed in black. The larvae of the firefly do not harm the leaves, but the ovaries. It is believed that one caterpillar eats up to 6 future berries a day.


How to spray gooseberries from the caterpillars of the fire? First of all, you need to select the appropriate insecticide. Gardeners also claim that mint planted near the bushes scares off adult insects. If you have one shrub on the site, then the larvae can be collected by hand and destroyed without using special chemicals.


How to deal with lichens on gooseberries
Sometimes gooseberry shoots are covered with a gray, greenish or rusty bloom. These are lichens. They appear in thickened gardens with poor ventilation, in lowlands, and also in the case of a close occurrence of groundwater. Lichens clog the holes in the bark and make breathing difficult. Pests hide in them for wintering. The bush can be easily rid of such a nuisance; you do not need to uproot it.
- Remove plaque with a coarse cloth.
- Disinfect the freed shoots with a 1% solution of copper sulfate (100 g per 10 l).
- Spray with a 3% solution of ferrous sulfate (300 g per 10 liters of water).
Processing should be done in early spring or late autumn, when there are no leaves on the gooseberry.
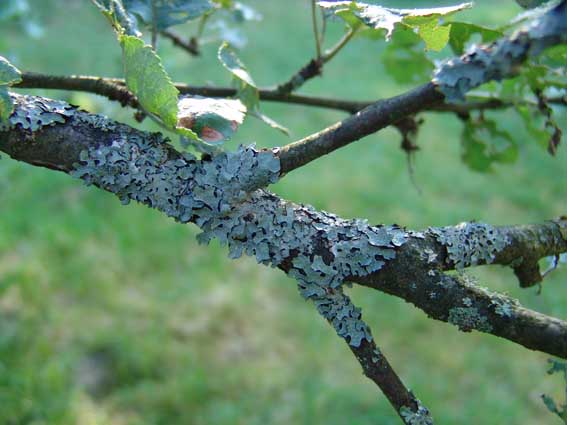


Spores of fungi and larvae of pests are often hidden under the scales of lichens.
How is gooseberry shelter carried out?


At low temperatures in the middle zone, it is enough to sprinkle bark on the mulch and cover it well with snow.
Preparation for winter should begin after late autumn watering and all measures for the prevention and treatment of the berry.
In the spring, the shelter is removed from the bush, and the plant independently takes its original position for several days. It is important to remove the covering material as quickly as possible, since in the event of a delay, the pagons can begin to take root.
Moth: fighting green gooseberry pest caterpillars in spring
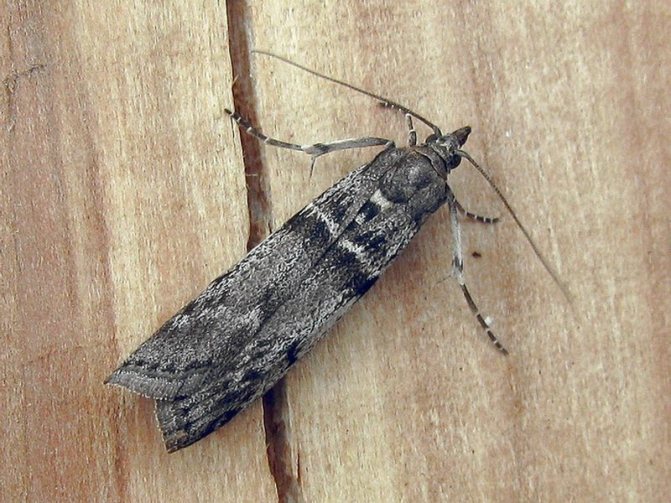


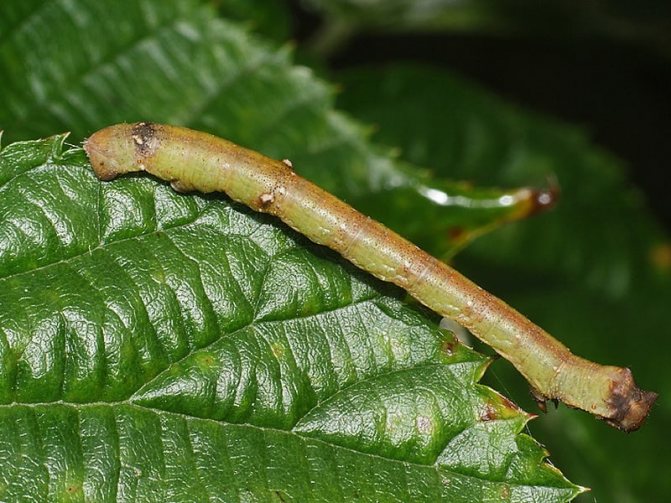
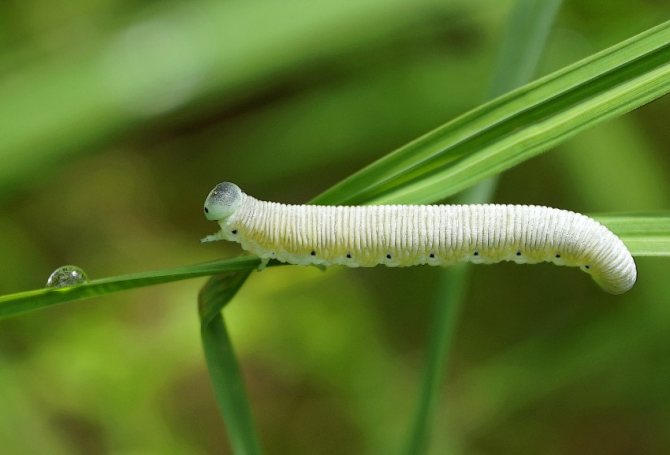
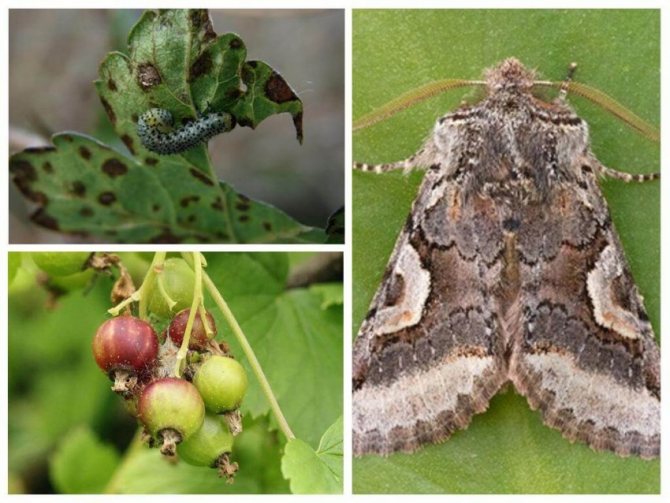
Gooseberry moth Zophodia convolutella Zell... - a moth with a wingspan of 26-32 mm, flies at dusk and at night, hides in the shade of bushes during the day. The front wings are gray with dark brown stripes, the hind wings are light brown, one-color with a silvery-white fringe, the wing pattern is variable. Caterpillars on gooseberries are 10-11 mm long, yellow-white with a black head at younger age, green at older age.
Gooseberry pest control begins in spring, because pupae overwinter in the soil under bushes at a depth of 1-3 cm. In spring, before the gooseberry bloom, butterflies emerge, feeding on nectar, the flight lasts 30-40 days. After fertilization, females lay eggs inside currant and gooseberry inflorescences, as well as on ovaries and leaves. Green caterpillars on gooseberries damage the berries by eating away the flesh and seeds. During mass reproduction, caterpillars entangle the fruits with cobwebs, holding them together in large lumps. Damaged berries rot and dry out, so the moth is often also called the gooseberry moth. Older caterpillars go under the bushes into the soil, weave cocoons and pupate, turning into brown pupae.
Control measures with caterpillars on gooseberries consist in spraying the bushes before flowering and immediately after it with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, actellik, kinmix, spark, Inta-Vir. Collection and destruction of damaged berries, autumn digging of soil under the bushes.
How to prepare gooseberries for winter
In the southern region, gooseberries do not require additional shelter. It is enough to mulch and cover with snow. And in the north, the berry grower needs help. At temperatures below 40 degrees, gooseberry shoots will die. How to get sheltered?
- It is necessary to first pour the earth into the root circle, and then mulch with any of the above materials. The layer should be about ten centimeters.
- The shoots must be tied with twine, and then the bush must be pressed to the ground. From above, the gooseberries are covered with burlap, and sprinkled with earth. An additional cover can be a wooden shield, which is covered with snow.
All these activities are carried out only after all autumn work on processing, pruning and watering plants has been completed.
In spring, it is enough to remove the shelter from the bush, and the shoots will straighten themselves within a few days.
Symptoms indicating that the plant has been attacked by pests
The symptoms of gooseberry disease will depend on which pest attacked the leaves of the berry bushes. Appearance is the main indicator of plant disease. Are the leaves starting to curl up? The shoot aphid may be the reason, it sucks the juice from the young leaves. A sign of the appearance of a pest will also be the formation of cobwebs and yellowing of the leaves, characteristic of spider mites. This very small insect is difficult to spot, but despite its size, it does colossal damage. You may not even pay attention to how the plant begins to die rapidly.


Gooseberry
Important! Many insects can only attack gooseberries. They will not touch other bushes, such as vines or tree leaves.
Aphid
Aphids are small insects that feed on plant sap. Usually she lives in small or large colonies, can pass to other plants by ants. The harm is caused not only by its suction of juice, but by possible transmitted diseases.
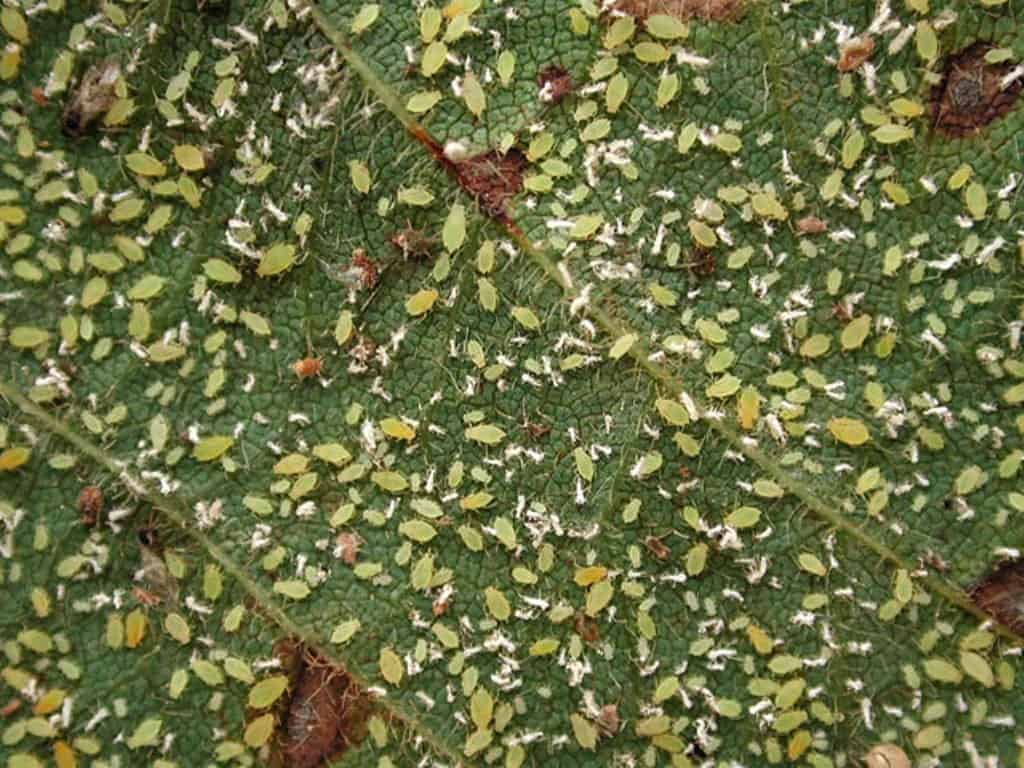


It is quite easy to notice this pest on a gooseberry bush by visual inspection of the plant, as well as by curling leaves and young shoots. If there is an anthill or a large accumulation of garden ants on the site, then in order to completely get rid of aphids, it is necessary to eliminate these insects as well.
In addition to purchased products against these pests, you can successfully use a soap solution prepared from 300 g of soap and 20 liters of water.
Gardeners reviews
Rita
Last summer I had a story with bulging burgundy bumps on the leaves - this is aphid. May 1 sprayed "Fitoverm", on May 12 there were clean leaves and blooming with might and main.
Nevada
To protect young plants from glass, sow coriander around them - the smell will discourage pests from appetite.
Pesticide Handling Rules
To ensure your own health, the safety of loved ones and the effectiveness of the measures taken, it is worth remembering nine rules that are followed when working with pesticides:
- Observe the terms and frequency of processing.
- Do not exceed dosage.
- Mix drugs correctly when working with combined products.
- Choose the right time: early in the morning or in the evening, after sunset, in calm weather, in the absence of rain.
- Use protective equipment.
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Dispose of drug residues correctly.
- To withstand waiting times - from the last processing to harvesting, it should take 20-30 days.
- Do not buy drugs by hand, as storage conditions may be violated, and do not stock up on pesticides for future use.
When purchasing a plot and planning the planting of gooseberries, it is rare for a summer resident to really represent the entire amount of work to be done in the future.And how many diseases and pests lie in wait on each bush! I am glad that there are even more protective measures and means of struggle, and the number of connoisseurs of fresh berries is not decreasing.
Gallica
Three types of gall midges can harm the gooseberry at once:
- Escaping;
- Leafy;
- Floral.
They affect the corresponding parts of the bush. Their greatest distribution falls on thickened plants. The appearance can be suspected by the vital activity of caterpillars, which will begin to destroy the plant.
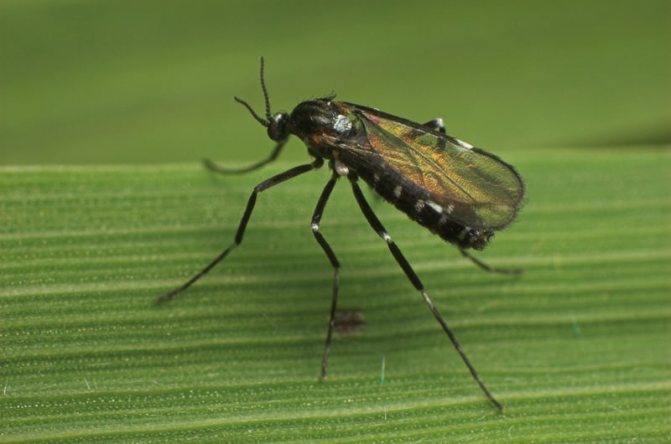


Advice! As a prevention of the appearance of these pests, mint can be planted near the gooseberry.
To control these pests, gardeners usually use insecticides or pheromone traps. From folk remedies, an infusion based on tomato tops is suitable. To prepare it, you need to cut off about 5 kg of green tops, pour 20 liters of water over it and let it stand for a day. At the end of this time, the solution is subject to filtering and the addition of 50-60 g of liquid soap. Spraying is carried out 2-3 times every 3 days.
Video about a simple way to shelter shrubs in winter
Do you know that quite recently, a hundred years ago, gooseberries were much more popular than currants? And spheroteka knocked him out of the distance, which is often called powdery mildew. In those years, the spheroteka, having appeared after the Colorado potato beetle (it is considered to be from the American continent), began to exterminate gooseberries in hectares, affecting everything: shoots, leaves, fruits, tender growths. The bush simply rotted in front of the owner, and the latter could not do anything about it.
Fortunately, thanks to the hard work of breeders, sphero-resistant varieties have appeared and those that, although they are sick with powdery mildew, are not so significantly. Yes, and no one canceled the treatment with fungicides, so gooseberries are gradually reviving. And in order to help the gooseberry catch at least currants across the squares, it is necessary to properly care for it. And not only in spring and summer, but also in the dank and rainy autumn period.
Few people know, but gooseberries are literally eternal and very productive, so the Malachite bush can exist productively for at least a decade and a half, annually increasing a kilogram of berry products. Thus, from a well-developed gooseberry bush, which you looked after properly, you can collect up to fifteen kilograms of both tasty and large berries at the same time, which can be stored for a long period, transported far, and consumed both fresh and recycled. Do not forget that gooseberry “royal jam” is still in vogue.
So, let's first briefly just list the main activities that we need to carry out during the autumn period with gooseberry bushes, and then we will describe each of them in more detail so that you have an idea of what and how to do, and at the same time you have a minimum of questions.
The first step is to pay attention to the gooseberry bite zone, clearing it of foliage and branches. Then you should weed out all the weeds, then dig up the bust zone, then carry out water-charging irrigation, then carry out autumn dressing, trimming closer to the middle of autumn, then pay attention to the row spacing, properly loosening or even digging them up and, finally, carrying out preventive processing, mulch the surface of the gooseberry bite zone.






























































