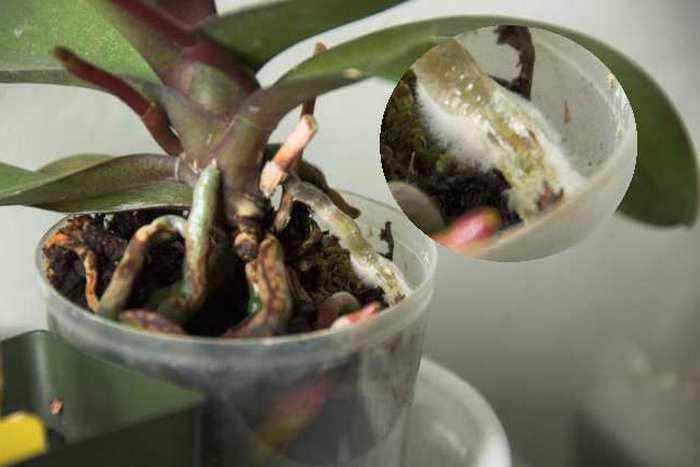
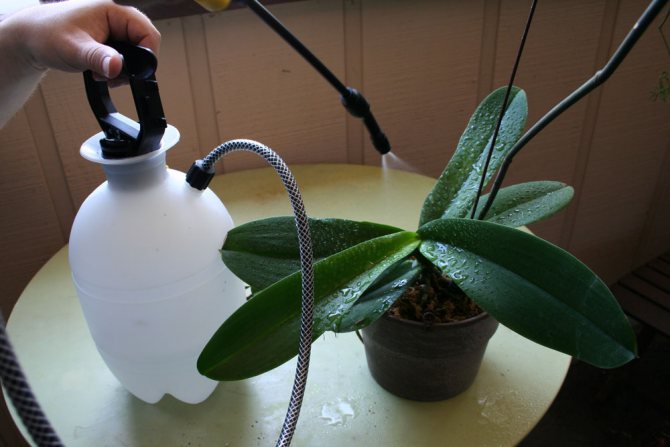
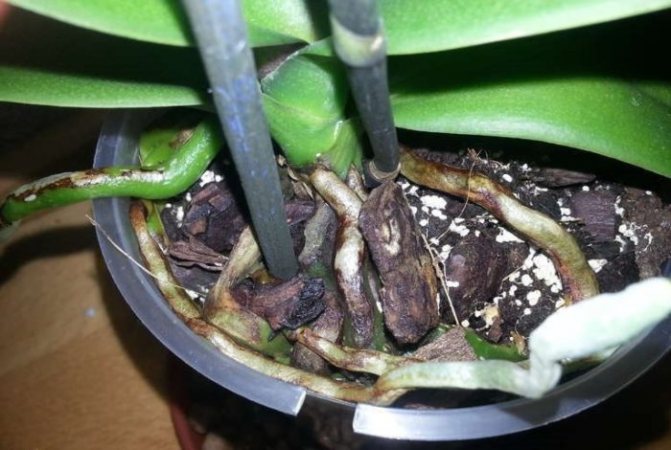
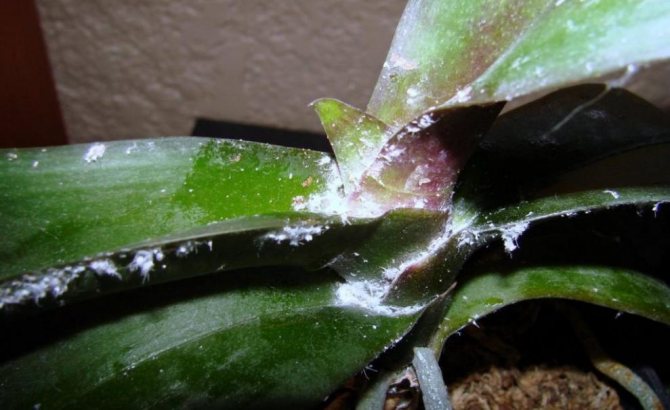
In this life not only people and animals are sick, but also plants... Orchids are no exception. Tropical beauties, falling into unfamiliar conditions for them, become weakened, any infection begins to cling to them or the one that sat in them earlier is activated.
So that the plant does not die, the exact cause of orchid disease must be identified... When it is installed, then you can apply the necessary set of measures for the treatment of the orchid.
Important! Before treating the plant, determine the exact cause of the disease.
Description
If a decision is made to purchase a tropical beauty for home cultivation, then the Phalaenopsis orchid will be the best.
Even a novice florist can handle this plant. This exotic flower is represented by a huge number of varieties. They are distinguished by their relative unpretentiousness. The flower petals of the Phalaenopsis orchid are similar to the wings of tropical butterflies. They are different in shape and color. They appear on the plant several times a year. The flowering period can last from two to three months. This does not require additional lighting and humidification. The smooth, leathery leaves are green in various shades. There are certain growing rules under which plants will develop and bloom normally. Phalaenopsis orchid diseases occur when the temperature regime is not observed, waterlogging and lack of ventilation. Caring for an exotic plant is not difficult. However, it differs from the activities that are performed when growing other indoor plants.
Urgent resuscitation at home
What it is?
Urgent resuscitation is a treatment that allows you to save plants in a short time and prevent orchids.
When is it required?
On a note. The main sign by which one can understand that the flower will soon die is the presence of dry and sluggish leaves, a dried peduncle.
If 1-2 leaves are withered below, then this is normal. But with the extension of this process to the entire sheet plate, urgent action must be taken. Help your orchid if it gets sick and save it from death.
How to save?
Here is a detailed plan for how to reanimate an orchid yourself:
- Rinse the roots, remove the affected ones.
- Prepare a container, pour expanded clay on the bottom, and carefully steamed and cleaned sphagnum on top.
- Moisten the mixture well.
- Lay a leaf rosette and until the plant has roots with a length of 3-5 cm, keep it under cover.
- To resuscitate an orchid, the following conditions must be observed: temperature 22-28 degrees, humidity - 70-100%. Lighting should be 12-14 hours a day.
Phalaenopsis orchid: diseases, care
Hybrids of the tropical beauty are specially bred for indoor cultivation. It will be necessary to observe the daytime temperature in the range from 20 to 24 degrees Celsius, at night - from 15 to 18 degrees Celsius. Often the conditions of the room do not allow observing this parameter exactly. In this case, it is necessary to achieve a difference between day and night temperatures, which should be at least two or three degrees. Sufficient air humidity is 50 - 70%.Plants are placed on windowsills of any light, protected from drafts and cold air.

Particular attention is paid to the soil. Choosing it incorrectly can lead to orchid disease. A special composition is used as a soil:
- bark substrate - 3 parts;
- sphagnum - 2 parts;
- charcoal - one piece.
An orchid planter should provide good aeration of the soil. It is better to use special transparent plastic pots designed for growing these plants. Watering properly will help prevent disease in your home orchid.
Special attention is paid to plant nutrition. Over-fertilization can lead to orchid disease. At home, after purchasing a plant, minimal feeding is required. An oversupply of fertilizer can result in the plant not blooming and the leaves can become tarnished and broken.
How is the disease treated?
If you notice signs of infection in an orchid, disinfect the plant immediately:
- Remove all peduncles (regardless of whether there are lesions on them or not).
- Dissolve 15 ml of liquid soap in a liter of clean water, mix well.
- Using a cotton swab, wipe the plant with a soapy compound, carefully removing all insects visible on the leaves and stems.
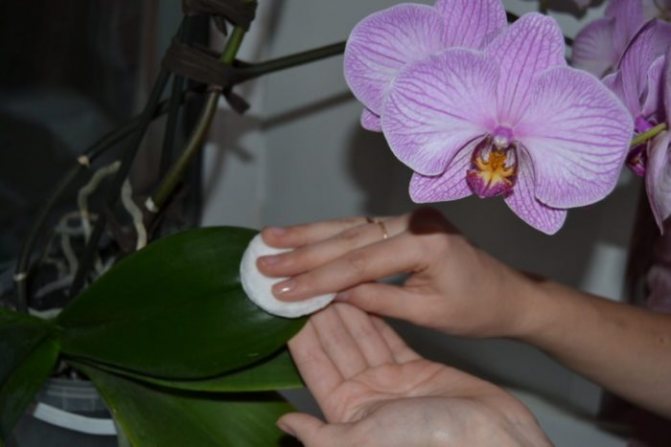


After this procedure, quarantine the plant for a few days. Watch him. If its condition has not worsened, return the orchid to its original place and pay more attention to caring for it.
Important! With a fungal infection, you need to transplant the orchid into a clean substrate and a new pot. After removing the plant from the old container, rinse all roots with warm water (+35 degrees), remove diseased parts. In case of an infectious lesion, the root system should be soaked in a fungicidal solution for 15 minutes.
Chemical and biological agents
Pest control is in many cases more difficult than fungus control. The mealybug clings to its territory and will not leave it so easily.
The most effective drugs that can kill the parasite are:
- Fitoverm;
- Bankcol;
- Mospilan;
- Aktara.
All of the above insecticides fight both adults and larvae. After treating the plant with the drug, close it with a plastic bag and leave it for 25–35 minutes. This will help enhance the effect of the remedy. Do not carry out treatment in a room in which someone lives: take diseased plants out into the street or at least on a non-residential balcony.
Observe precautions when working with chemicals: protect all exposed areas of the body, face, eyes from accidental ingestion of the composition, do not drink, smoke or eat while processing plants.


Treatment with folk methods
Folk recipes will help to cope with pests only at the initial stages of the development of the disease. Do not expect magical results from them if the parasite has already captured more than 50% of the flower.
The most effective remedies:
- Garlic infusion. Take 5 garlic cloves, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave for a day. Strain the finished mixture and treat the affected areas of the flower with it.
- Infusion of onions. Peel and chop one medium-sized onion. Pour the raw material with warm purified water, leave the mixture to infuse for 2-3 hours. Strain the broth and sprinkle it on the orchid.
- Pepper infusion. Take 50 g of hot pepper, pour 500 ml of boiling water over it, then put it on the stove and boil for 5 minutes. Cool the finished mixture, strain. Treat the diseased plant with a decoction.


What to do with white dots?
The only possible method for getting rid of white indented spots or white dots on an orchid is through careful grooming:
- normal watering regime;
- timely treatment of pathologies.
If you monitor the condition of your orchid, then the consequences of the illness will soon disappear.
Fungal ailments
Orchid diseases can be provoked by severe waterlogging, violation of temperature and ventilation conditions. In this case, favorable conditions are created for the intensive development of fungi. They are the source of disease. Fungal diseases cause root rot.
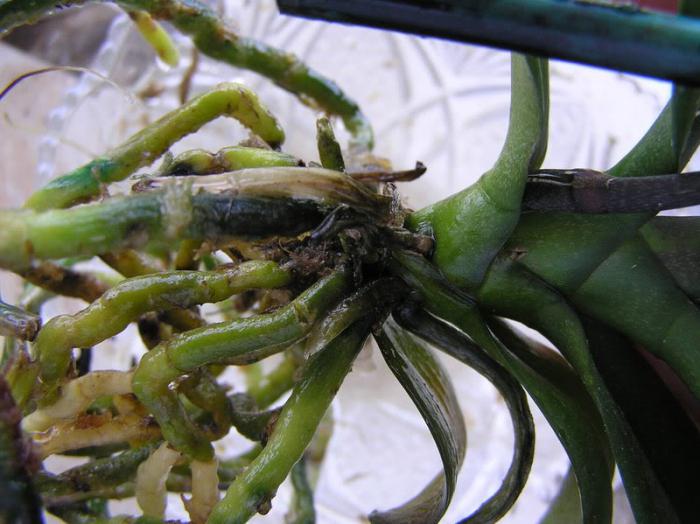


This ailment can lead to the death of the orchid. The root system, affected by rot, decomposes, and the leaves and stem of the plant dry out completely.
Fungal tracheomycosis is no less dangerous. Orchid diseases caused by this pathogen affect the vascular system of the plant. At the same time, the lower leaves of the orchid gradually turn yellow and the lower parts of the stem, neck and roots rot. Growth stops as a whole. The disease is practically incurable and leads to the death of the plant. All kinds of blotches cause diseases of orchid leaves. These include: powdery mildew, rust, anthracnose, septoria, stangosporosis, phyllostictosis, cercosporosis. Also, these ailments affect flowers.
Fungicides are used to treat fungal diseases. It is advisable to use biological products that are less toxic than chemical products.
How are diseases different from pests?
Reference. Phalaenopsis disease is a common occurrence, the main cause of which is improper care. Diseases can be fungal, viral, and rot is also common.
Each of them has its own symptoms that make it possible to distinguish them from pests. Most often, when a flower is affected by a disease, the leaves almost instantly darken, dry up and fall off (more about leaf diseases can be found here). And when insects visited the plant, the whole process takes place gradually: the leaves become covered with spots, slowly fade and only then fall off. This allows the grower to react in time and save the flower.
Diseases of bacterial origin
Weakened injured plants are susceptible. Orchid diseases are caused by bacteria that invade the tissues. At the same time, root rot quickly affects the entire plant. The plant dies within a week. Bacterial spots infect the leaves of the plant.
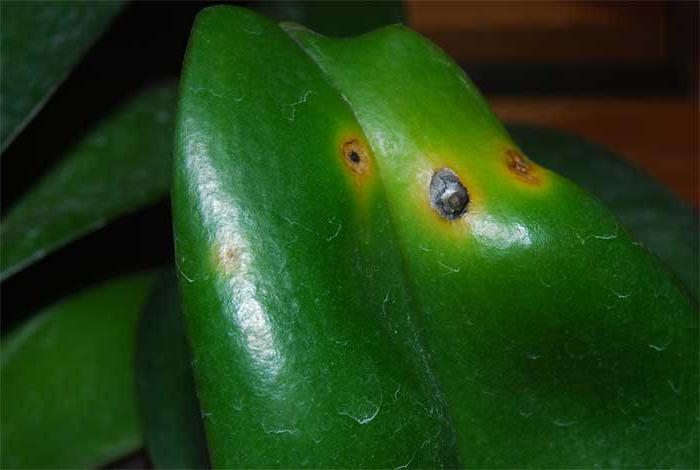


After the entry of pathogenic bacteria, the disease develops rapidly. Oily spots appear, the diameter of which reaches two centimeters. Bacterial diseases of orchids are fatal, and their treatment does not provide for special drugs that can prevent them. The use of synthetic antibiotics is proposed. The symptoms of bacterial and fungal diseases are similar. And if it is difficult to accurately determine the nature of the damage to the plant, it is advisable to use fungicides and antibiotics together.
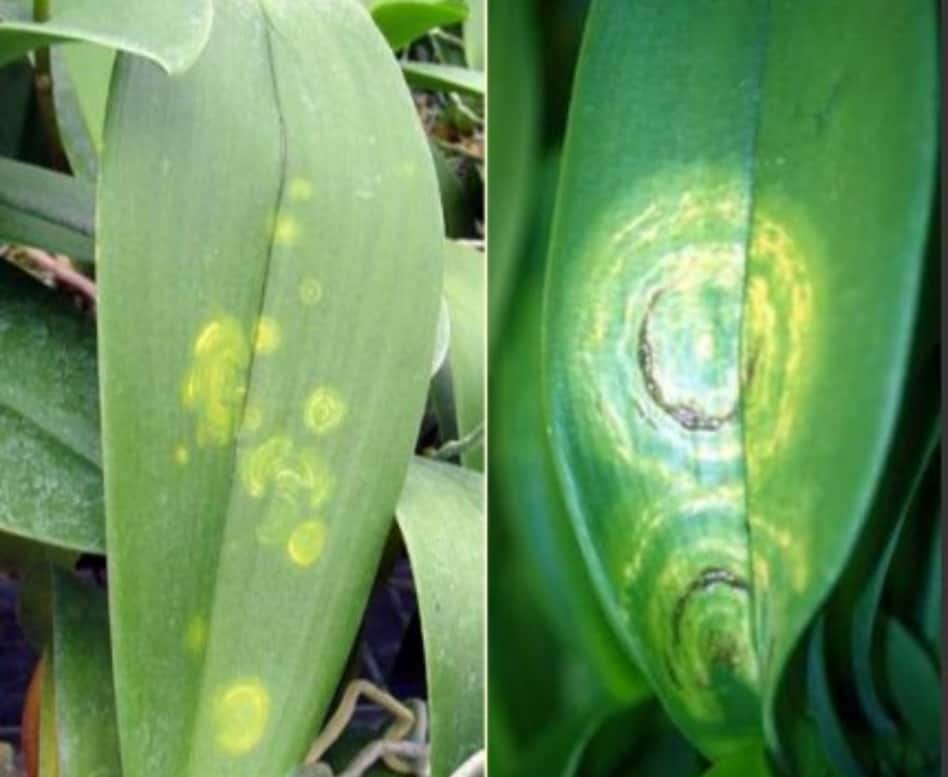
Certain signs of viral infection of orchids
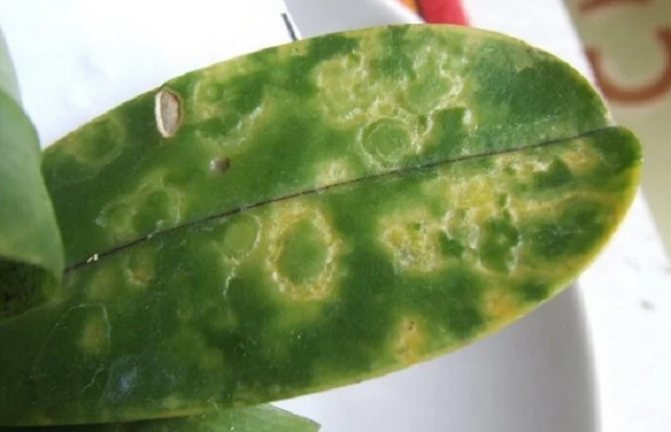
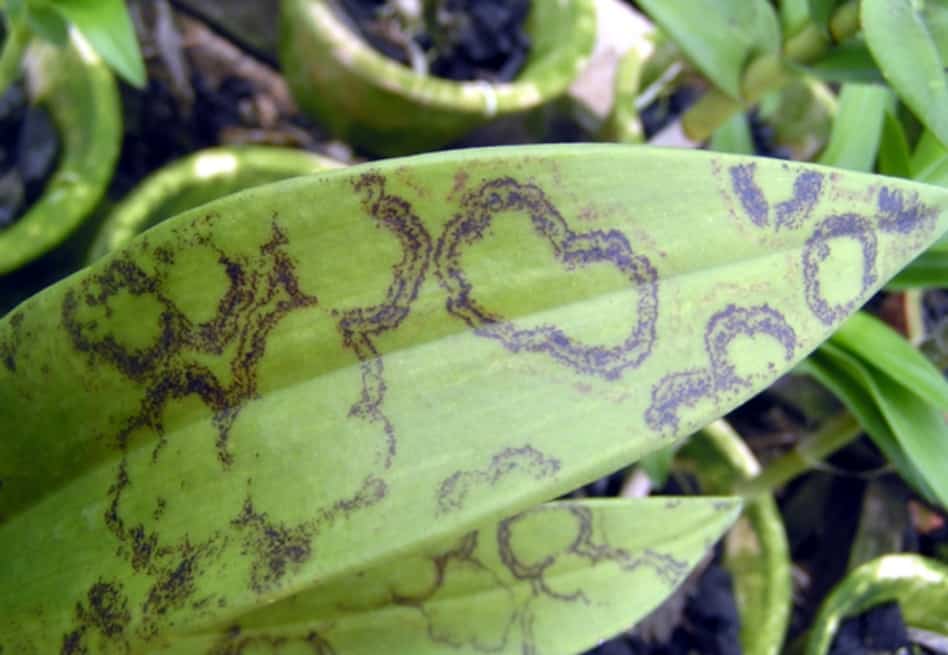
There are general symptoms that leave no doubt that the orchid is infected with a viral disease. First of all, this is the striped color of the petals - white, pinkish or dark strokes, or the presence of teeth or cuts on them against the background of weak growth and depressed state of the plant.
If young leaves appear with visible yellowish patterns: spots, strokes, various geometric shapes - rings, ovals, rhombuses, there is also every reason to assume that the orchid is infected with some kind of virus. Upon further observation, the pattern changes color - it turns black or becomes reddish-brown, and then dark brown and depressed.
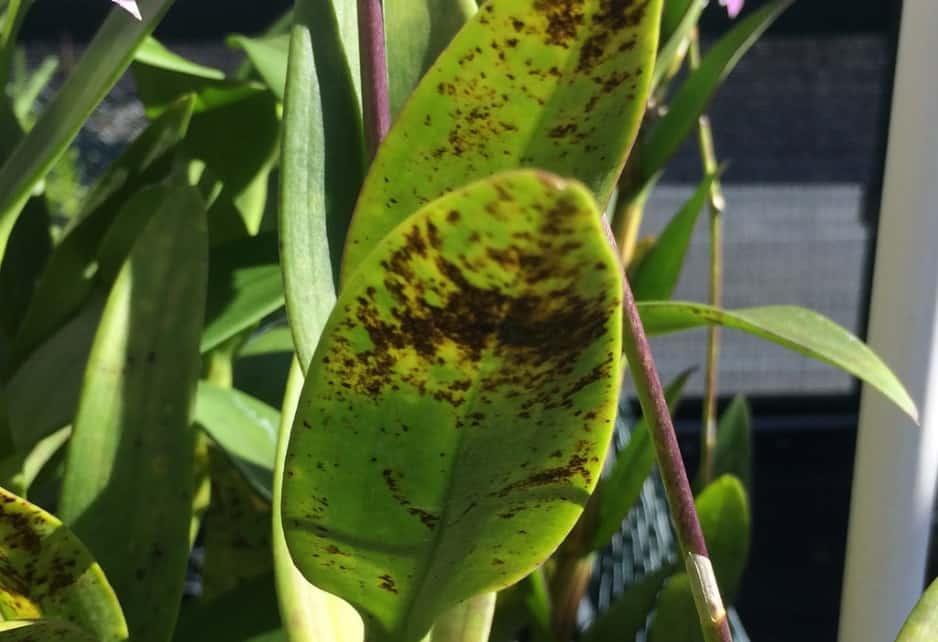


Viral diseases
At home, these ailments cannot be determined. This requires laboratory research. Orchid diseases appear in the form of all kinds of spots of various configurations. There are viral infections that can cause a plant to suffer for several years. Others cause the rapid development of the disease. These infections are practically not cured. Weakened orchids are primarily infected."Care - diseases" - this connection is directly related to the state of the plant. In case of a viral infection, it can be saved from death by changing the conditions of detention. Very often, it is the external conditions, and not the condition of the plant itself, that are the cause leading to the onset of orchid disease, and their treatment must begin, first of all, with the elimination of unfavorable conditions of detention.
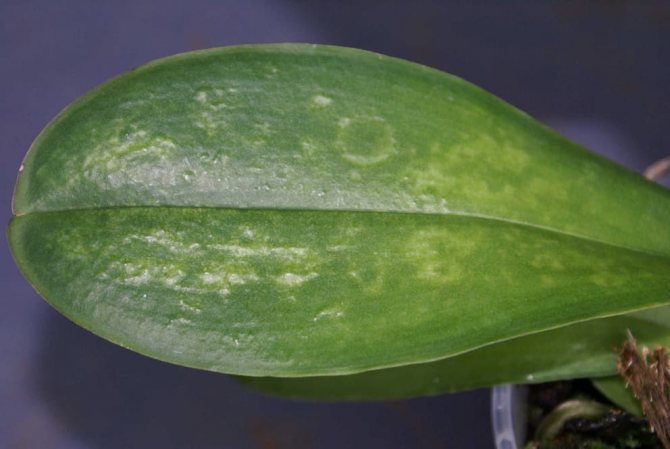
Plaque causes
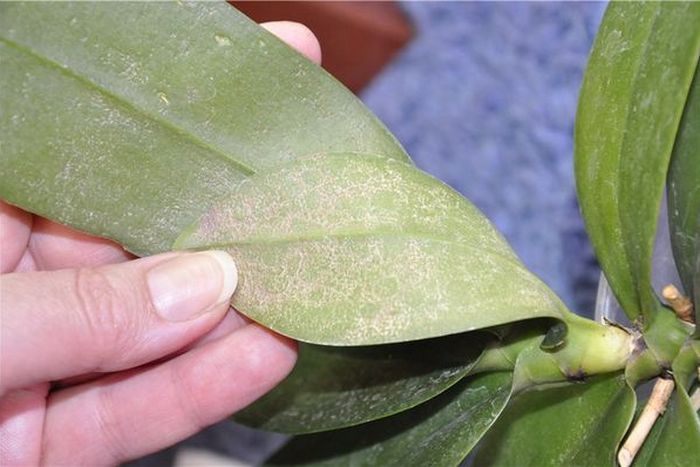
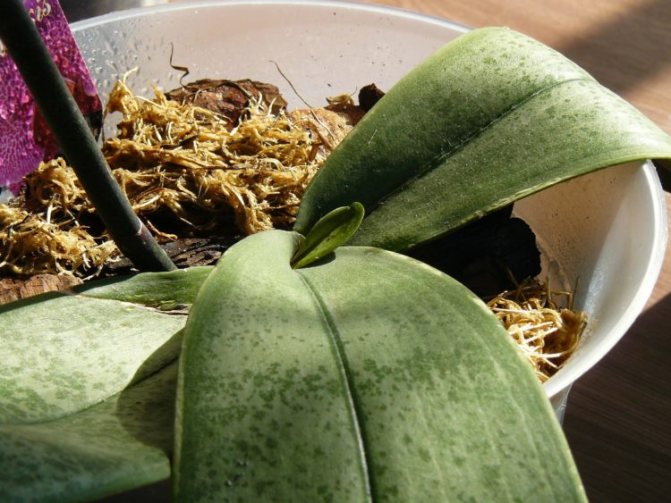
White bloom on orchids is a phenomenon, the main cause of which is powdery mildew.
Outwardly, the problem manifests itself as follows: first the leaves from the back are covered with an opaque film, then the mold affects the roots. Over time, the substrate and the walls of the pot are covered with a white and indelible bloom.
This phenomenon is caused by the following pests:
- mealybug;
- aphid;
- spider mite.
The cause of the disease can be the wrong conditions of the plant, as well as the varietal predisposition of the flower to the disease.


Powdery mildew causes white bloom
The most common mistakes made by florists, as a result of which white spots appear on the phalaenopsis:
- too low humidity and air temperature in the room;
- stagnant water in a pot;
- frostbite of the leaves, caused by a draft;
- coldness coming from glass in autumn and winter.
Pests
Phalaenopsis orchid is fabulously beautiful. Diseases and pests cloud the cultivation of this plant. Unfortunately, there are a lot of both. They affect, first of all, weakened plants. But it often happens that even with good care, pests will appear on the tropical beauties surrounded by attention and care. At the same time, the affected orchids are isolated. Diseases and pests can spread to other, uninfected plants. The quarantine will last until complete recovery. When dealing with pests, it is necessary to be able to identify them and have information on the fight against them.
Preventive measures so that the flower does not become covered with white fluff
In order to avoid such problems with the orchid, some preventive measures should be followed:
- Water the orchid only when the soil is completely dry.
- Periodically arrange a warm shower for flowers to remove excess moisture from the sheet plates.
- When the temperature drops, reduce the number of waterings.
- When shortening daylight hours, use phytolamps.
- Observe the temperature regime.
- Perform a preventive treatment every three months.
- Transplant orchids only into proven soil.


Scabbard (Coccidae) and false scabbard
Indoor plants are damaged by various pests. Moreover, many of them are equally dangerous for different flower cultures. Most often, orchids suffer from scale insects and false scales. These pests have the same external data. Orchids are most commonly affected by the Scabbard Palm.
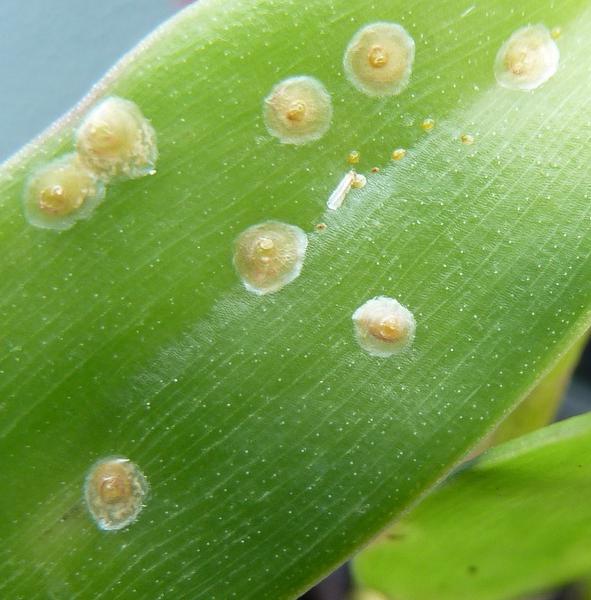


Oval-shaped pests reach a diameter of one or two millimeters. Scutellum covered with white waxy hairs. They multiply intensively and completely cover the plant. Scabbards are sucking insects that feed on plant sap. With a massive resettlement, they are able to destroy the orchid.
What provokes an infection of orchids
A fluffy, harmful bug can very rarely appear on flowers that are properly looked after. A healthy plant diligently produces special substances that repel insects.
Favorable conditions for the appearance of parasites are sometimes created by the growers themselves. The most common ones are:
- Lack of hygiene. Phalaenopsis need to regularly carry out moisturizing spraying, wiping the leaves and showers. Without these procedures, the flower withers and weakens.
- Contaminated soil. Poor quality substrate can be infested with larvae.
- Violation of the humidity regime. Overdrying, like waterlogging, negatively affects the condition of orchids and reduces their immunity.
- Failure to comply with the quarantine of new flowers. All purchased plants must be kept separate from the rest for at least a month.
- Low lighting. Lack of light is favorable for the development of insects.
The worm is brought into the room by people, animals and even ants. This is why keeping the plant clean and maintaining the care and hygiene of the plant is a top priority.
Pest control
To destroy the scabbard, special preparations are used. Before using it, you must thoroughly clean the entire plant from the pest. Carry out wet processing. After that, the substrate and orchids are sprayed with special preparations. When fighting the scabbard, the use of "Fitoverin", "Aktelik" or "Aktara" is recommended. Processing is carried out strictly according to the instructions attached to the preparations. Re-treatment will be necessary, which is performed after a week or ten days. The treated plant is transplanted into a new planter filled with fresh substrate. As a preventive measure, wipe the leaves with an interval of five days.
Puffs
Puffs are a real nightmare for any grower, since this pest multiplies very quickly, is able to move quickly and jump over. However, experienced orchid owners assure that in most cases the podura feed on the microflora that has formed inside the pot, and not on the plant tissues themselves. Therefore, for phalaenopsis, they do not pose a great danger.
Nevertheless, this phenomenon should not be ignored, since the appearance of sublevels (or, as they are also called, springtails) is associated with improper care, namely, excessive watering. By diagnosing your plants for parasites with the help of an apple, you can find a small number of them even with healthy plants. But when the moisture content of the substrate is constantly high, podura begin to multiply very quickly and "eat up" the decaying parts of the orchid.
Treatment
You can get rid of these harmless parasites with the help of folk remedies. An infusion of garlic or onion will help, you can also spread potato cubes on the ground, which will attract suckers - and after a couple of days, remove the cubes along with the pests.


The most effective method for a large population of sublev is to reduce watering by 2 times. That is, if you water phalaenopsis once every 7 days, you should start watering it once every 14 days. This method is usually very effective. When the roots decay, the orchid should be transplanted, the diseased roots should be removed and the plant should be treated with Phytosporin for prophylaxis. This will also help get rid of uninvited guests.
More serious drugs for treating plants from suns are insecticides:
- Initiative.
- Bazudin.
- Mospilan.
- Aktara.
The solution should be prepared strictly according to the instructions, applying all safety measures for working with drugs.
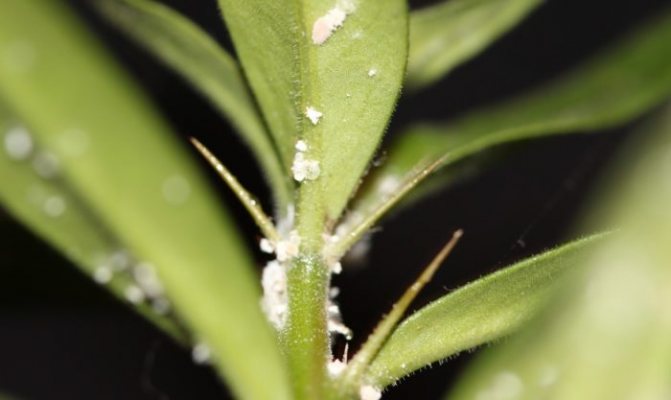
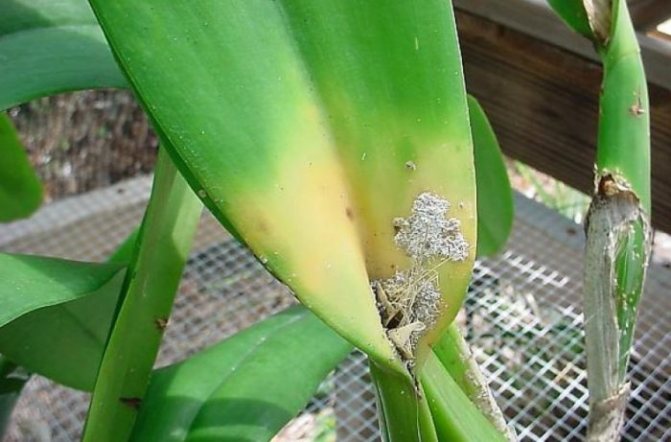
Mealybug
One of the types of quite dangerous pests that affects orchids. Diseases and pests require timely treatment. The mealybug looks like a small fluffy oblong lump. The white-bodied insect has long antennae. Its location is difficult to determine. The usual habitat is the leaf axils in the root zone of the orchid.
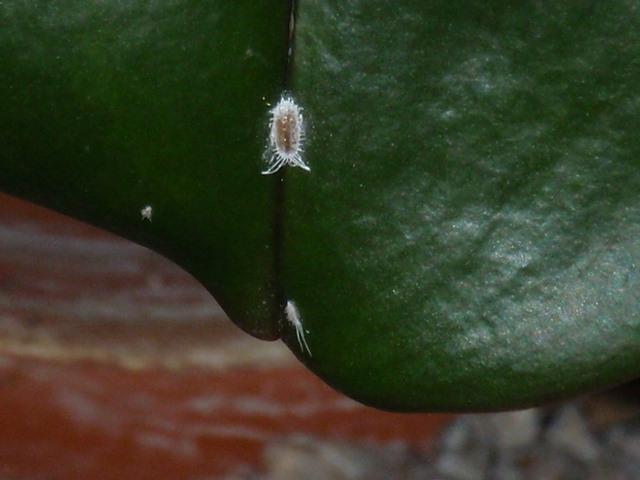


They feed on the sap of the plant. The defeat is noticed when the plant begins to wither. At the same time, the leaves turn yellow and wither.
What is the danger of white bloom on an orchid?
The worm feeds on the cell sap of the plant, and is also able to inject a special food enzyme into the bite of the leaves, which leads to a decrease in the vitality of the plant. In addition, the sticky plaque secreted by the pest leads to the development of a sooty fungus, which interferes with the full respiration of the leaves and the process of photosynthesis. Against this background, the plant becomes pale and loses the elasticity of the leaves. If left untreated, the orchid may die.
In the case of the development of powdery mildew, the plant begins to slow down in growth, and flowering may be poor or completely absent. As the fungal mycelium spreads further, the leaves become lethargic, turn yellow, and subsequently fall off. In the absence of adequate treatment measures, the flower dies over time.
Pest control methods
If an insect infestation was missed, and its presence was noticed after an orchid disease, a thorough examination of the affected plant parts is carried out. Dried leaves and roots are removed. The affected areas are treated with water with the addition of laundry soap. Insects are removed with pointed sticks. The substrate is treated with a special preparation Fitoverm. It is used in accordance with the instructions. Three times processing is carried out with a weekly interval. The plant must be quarantined for a month. During this period of time, the orchid is carefully examined.
How to determine what happened?
The difficulty in making a correct diagnosis is that some of the external signs are similar to those of pests. So that to make a final diagnosis, you have to carefully examine the flower.
If not only symptoms of damage were found on it, but also insects, then most likely they are the cause of the problem. In addition, you need to know the main symptoms of common orchid diseases. Then it will be possible to understand for sure whether it is a pest or a disease.
What parts of the plant are damaged?
Most often, the defeat is inflicted on the leaves, roots and stem of the plant. The leaf plate begins to turn yellow, wither and dry out. The stem darkens and decays. The root system is most often affected by rot, as a result of which its roots rot and die off (read how to care for orchid roots here).
Spider mites
Among the pests of orchids, ticks are considered the most dangerous. They are quite small. They can be identified visually by the external signs of plant damage. This is the appearance of a silvery coating.
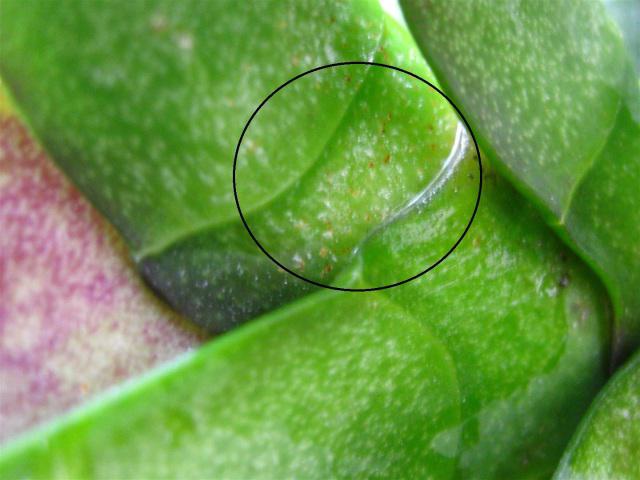


The mites feed on the cell sap of the orchid. Intensive reproduction of these pests can lead to significant damage to the plant.
Step by step instructions on how to deal with home remedies and chemicals


Let's figure out how to get rid of the white bloom that affects the plant on home orchids. Flower treatment depends on the exact cause of the plaque on the leaves or other parts of the plant. When infected with powdery mildew or mealybug, various therapeutic measures are required.
But mandatory general actions:
- isolating the infected orchid from other plants;
- removal of all damaged parts (leaves, buds), cover the cuts with crushed activated carbon;
- only after the removal of the infected leaves can the treatment begin.
How to treat powdery mildew infection?
It is necessary to remove the top soil layer and pour new soil into the pot. It is advisable to take a special soil substrate, and not ordinary land from the garden. Sprinkle the new soil from above with ash (thickness up to 2 cm). What are the next steps to take?
- For mild damage, safe homemade decoctions can be prepared. You can take horsetail herb (100 g per 1 liter of water), garlic (50 g of chopped slices per 2 liters of water), onion husks (200 g per 10 liters of water). Be sure to boil and insist. Dilute with water before processing. Spray through a spray bottle.
- In case of mass destruction, chemical treatment is indicated. These are copper-containing fungicides or antifungal agents. Colloidal sulfur or Fitosporin is suitable. Look for the dosage on the package.
- Disinfection of the place where the pot stood with an antiseptic. The goal is to kill the remaining spores.
What to do if a mealybug appears?
Collect all insects from the plant by hand, wipe the leaves with diluted alcohol or soapy water (water and laundry or tar soap).
If you see that there are too many insects, the help of chemicals is required.
- We need to take insecticides. These are Aktara, Aktellik, Mospilan, Fitoverm. Observe the dosage for home flowers. Treat with protective gloves.
- Next, place the orchid in a bag, spray the plant and tie the bag for 2-2.5 hours.


After the expiration date, remove the orchid and wash with soapy water.- Repeat the treatment 3-4 times, the time interval between procedures is 10-14 days.
Mandatory additional actions are disinfection with an antiseptic of the soil in the pot and the place where the pot stood. Also you need to carefully examine the neighbors of the infected orchid, or better, send all neighboring flowers to quarantine for 14 days.
From the video you will learn how to treat an orchid for a mealybug:
Also, sometimes orchids turn yellow, turn black, their roots change color, leaves crack. You can read about these problems on our website.
Nematodes: description, methods of control
Roundworms - nematodes are among the numerous pests of orchids. Small worms penetrate the stem and roots. They feed on the sap and nutrients of the orchid. Diseases and pests are interrelated. As a result of the vital activity of nematodes, the plant weakens and is exposed to various diseases. The combined effect of diseases and pests leads to the death of the plant. To eliminate the pest, the substrate is treated. Prepare a solution of drugs "Dekaris" or "Levimizil" at the rate of 1 tablet per liter of water. They spill the substrate. Soaking the whole plant, which is previously removed from the flowerpot, in the prepared solution has a more effective effect.
Outcome
Summing up, it should be noted that most of the problems of our indoor pets arise as a result of improper care. That is why tireless control over the condition of orchids is considered the best prevention:
- Observe the correct ratio of temperature, humidity and lighting.
- Transplant freshly purchased plants in a timely manner.
- Always keep new orchids in quarantine conditions, no matter how reliable the supplier is.
Thanks to careful maintenance, your plants will always be healthy and will delight you with lush and sometimes aromatic blooms.
Have you encountered orchid pests? How did you fight? Share useful information in the comments.
Thrips: detection, remedies
Quite often, pests can be found in acquired plants. The first step after the purchase is to discover unwanted surprises that may be hidden in the substrate. Identifying insects is easy. It is necessary to prepare a small container of water for bathing the pots with the plant. Insects trapped in the substrate will leave within ten minutes.
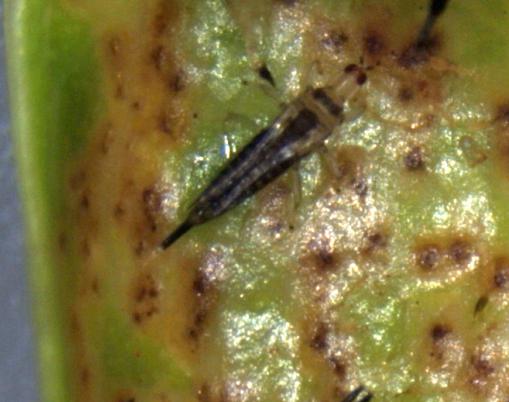


Thrips are tiny black bugs that move quickly. They live in the substrate of orchids. Tiny insects infect almost the entire plant. They feed on its juice, as well as young roots and leaves. The timely detection of insects can save the flower. The affected orchid is isolated from other indoor flowers. It is washed thoroughly with warm water. The damaged areas are removed, leaving only healthy tissue.
Whitefly
Whitefly is a pest that attacks not only indoor flowers, but also garden plants. Many farmers are faced with the activity of this pest and note that the plants very quickly become weakened and dry out.
The butterfly is microscopic in size, and, as the name of the pest suggests, is white. One of the most characteristic signs of a whitefly attack on orchids is yellowing and drying of the leaves. Flying from plant to plant, the parasite lays its larvae in the root system, on the back of the leaves, and in more advanced cases, they can be seen at the top.


However, phalaenopsis whitefly affects quite rarely, since it prefers thin-leaved plants. Infection can occur from another species of orchid, such as dendrobium or oncidium. Nevertheless, the fight should be aimed at destroying the entire population: both adults and larvae.
Treatment
It is important to carry out treatment in a comprehensive manner, using several methods at once. It is recommended to use the treatment of the plant with household chemicals, as well as preparations:
- The orchid should be washed with a solution of laundry soap using a soft rag or cotton swabs.
- After the destruction of the bulk of insects, the leaf part and the substrate are treated with a solution of preparations of your choice: Fitoverm, Aktara, Vermitic.
Since the most optimal environment for a whitefly is high humidity and extremely high temperatures, the best prevention will be to optimize the conditions for keeping the orchid.
Aphids: places of damage, methods of control
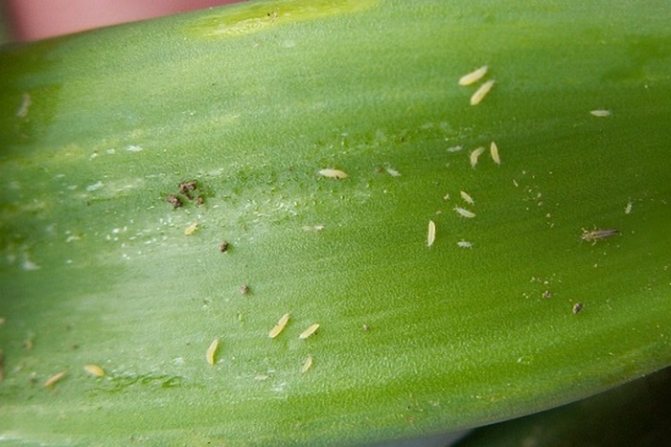
This dangerous pest can be detected with the naked eye. Entire colonies of pests affect almost all parts of the plant. The underside of leaves, buds and flowers, shoots, if damaged, discolor. The plant weakens greatly, stops developing normally. This leads to orchid disease. The whole plant is covered with sticky insect secretions.
If a pest is found, they are mechanically removed. Severely affected areas of the orchid are removed. After that, a double spraying with a weekly interval with special preparations is carried out. For the destruction of aphids, the use of drugs is recommended: "Decis", "Aktelik", "Fitoverm".
Aphid
Aphids are a very common insect. Aphids can appear on orchids in the same way as on any other flowers. It multiplies very quickly, so if you do not identify it immediately, it will settle throughout the flower. The first symptom may be white bloom - if you see it on the stem and leaves - sound the alarm. This plaque is the scales that are shed by growing individuals during the adolescence period. Start looking at the underside of the leaves - this is where aphids usually live. Be sure to check all the nooks and crannies - buds, leaf axils, new sprouts. If it is not immediately possible to find a lodged aphid on an orchid, after a short time the entire plant from stem to flowers will be affected by this parasite.


Aphids are one of the most dangerous pests of orchids. It feeds on juices, which it sucks out of the epidermis, simultaneously injecting harmful substances that kill the flower. In addition, waste products remain on the surfaces of the plant - a sticky sweet liquid in the form of dew, which is very attractive to ants. As a result, the leaves curl and deform, the stem becomes covered with black mold due to the developing fungus.
Getting rid of aphids on orchids is not easy, but it can be done. This will help both improvised means and industrial preparations. What is the best way to treat an orchid from aphids?
Treatment
- Be sure to isolate the infested orchid. Be sure to check the rest of the plants carefully.
- Remove all damaged leaves, flowers and buds.
- Wash the entire plant thoroughly with soapy water. You can use laundry soap or any other soap - both solid and liquid.
- You can make a decoction of citrus peels - pour boiling water and leave for about three days. With this infusion, you can spray the plant with an interval of 4-5 hours.
- In the most severe cases, chemical insecticides can be used. Such drugs as Neoron, Permethrin, Actellik, Arrivo, Aktara, Inta-Vir and Fitoverm help well to fight aphids on orchids. Do not forget to carefully read the instructions and observe safety precautions - after all, many drugs are toxic to people and pets.
Preventive measures
The most common way a pest appears on indoor plants is by purchasing an infested orchid. Before purchasing a flower, it is necessary to carefully examine, if there are doubts about its health, it is better to refuse this instance.
To prevent the emergence of pests, the recommended conditions for keeping house flowers should be observed. Orchids need sufficient lighting, if there is little natural light, you can install a special lamp. It is important to remove dry leaves in time, in which parasites like to hide. Worms do not like humid air, create high humidity around orchids. Wipe the leaves of the plant more often. It is recommended to arrange a warm shower for the plants once a month. This procedure will wash away pests accidentally carried by the wind. The flower is removed from the pot, the roots, stem, leaves, peduncles are washed. After the shower, excess moisture is soaked with a napkin. Stagnant water causes rot.
What is dangerous


The appearance of white bloom can be caused by two reasons, each of which poses a mortal danger to the plant:
- The plant can become infected with powdery mildew. In this case, a coating, similar to a thin layer of flour, initially appears on the underside of the leaves. As the mycelium ages, the plaque takes on a dirty gray color and the stain becomes damp. If you do not take action, gradually the fungus also spreads to the upper part of the leaves, buds, inflorescences and roots. The affected areas are deformed and after a while begin to rot. Plants may die without treatment.
- The mealybug can attack the orchid. This insect is covered with protective white hairs, and the plaque on the leaves affected by it looks like tiny cotton wool flakes. The pest drinks the juice of the orchid, injecting poisonous substances back, which makes the plant weaker, slows down development and becomes more vulnerable to infections. In addition, a sooty fungus, which is also dangerous, likes to settle on the sticky secretions of the worm. If you do not take action, the leaves are deformed, marbled red and yellow streaks appear on them. Photosynthesis is disrupted, the plant weakens more and more and eventually dies.
Root diseases and flowering problems
Diseases of the roots cause problems with flowering, but we will talk about diseases of the root system later, but weak flowering is a problem that often occurs. The main reasons for the lack of buds are as follows:
- improper watering;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- violation of the rest regime;
- insufficient lighting.
Another problem is that buyers forget to check with the seller what kind of plant they purchased and how exactly it blooms, as well as generally find out the description of the plant. It is important to understand that different types of orchids produce buds and bloom at different times of the year. It often happens that the owner is looking forward to the first flowers, but only the green mass is growing.
Note! Lack of light is the most common cause of plant wilting. Most varieties of orchids do not tolerate even partial shade well. They need good lighting, so the plant should be placed on the windowsills, and not in the corner of the room. The exceptions are varieties such as Phalaenopsis and Pafiopedilum, which can bloom in partial shade.
How to understand that an orchid lacks light? It's not hard. Pay attention to the color of the leaves. The natural shade is soft green, light and even slightly muted. Bright green tones are a sign of a lack of lighting. If the leaves turn yellow, then this is a signal that an excessive amount of ultraviolet radiation is getting on the plant.
What to do in a similar situation? Place the plant either in a more illuminated place (in the case of bright green leaves - a vivid example in the photo), or in partial shade (if you notice yellowness).
An equally common reason for the lack of peduncles in orchids is root diseases. It is very difficult to identify this problem, especially if the plant is already in bloom. The latter can be observed even in the case of root rot. But if the plant does not please with either flowering or buds for a long time, it's time to check the root system. Rot (most common) is caused by over-watering. Remember to bathe the plant in a bowl of water for 20-40 minutes once a week. This flower is enough. But you do not need to fill it with water so that it stands in the pot.
What to do in a similar situation? The best solution is to transplant the flower into a new pot and remove the damaged areas of the roots. In principle, transplanting is useful as a periodic occurrence in plant care.
Why are leaflets so important?
Phalaenopsis orchid leaves play an important role in its life.... Together with the roots, they participate in photosynthesis by absorbing light. The flower also breathes through them - at the bottom of each leaf there are microscopic pores that absorb oxygen and moisture.
Along with all their functions, in most cases they are also a kind of alarm that notifies that the orchid is sick. You should listen to such signals, because diseased leaves cannot fully provide the plant with all the necessary substances, the whole flower suffers from this.
How to repair a damaged orchid
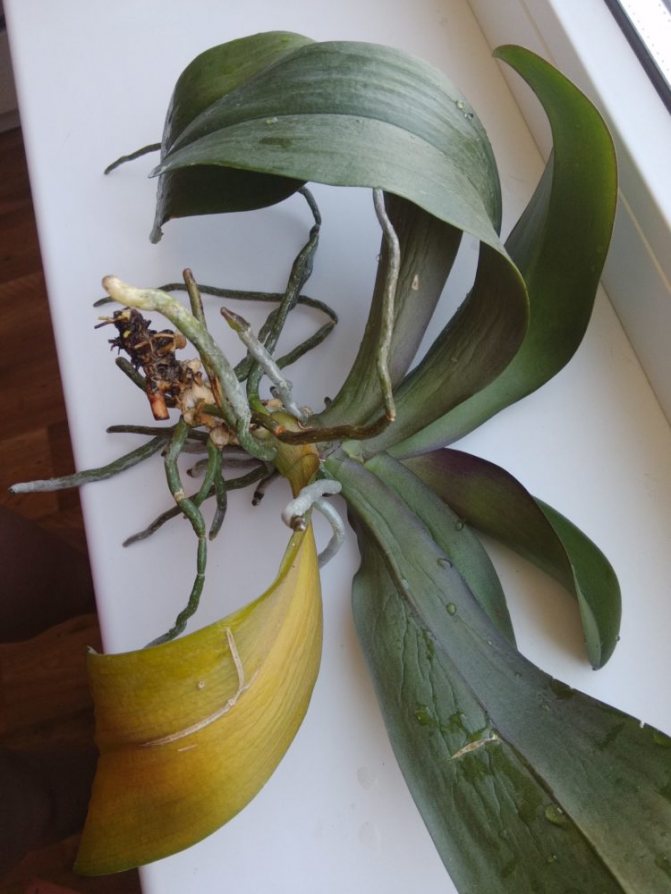
In most cases, a damaged orchid can be revitalized by stimulating the growth of new roots or leaves. Phalaenopsis orchid has amazing recovery properties with the right approach and following the recommendations. If the orchid has not died, but only leaves remain of it, even in this case, a new healthy and strong plant can be grown.
How to revive phalaenopsis without roots
From the neck of a healthy leaf, you can grow roots and get a new healthy plant. To do this, you should prepare a special nutrient solution, taking boiled cooled water, add 1 - 2 tablets of activated carbon to it.
You will also need a drug to stimulate root formation, for example, Kornevin or Epin.
For the formation of roots, you can use the upper living part of the plant, which has a growth point or a healthy leaf. After cutting the cutting or leaf, it must be placed in a dry, warm and shaded place for about 2 hours so that the cutting site has time to tighten.
After that, the prepared planting material must be placed in a solution of a root formation stimulator for 20 minutes. Next, you need to put an activated carbon tablet into the water, using a small container, and place the prepared cuttings.
For germination, the containers should be placed in a warm place (temperature within 25 ° C), and provide them with sufficient lighting (diffuse). The room where the cuttings are located must be regularly ventilated.
The leaves of the plant should be wiped daily with sweet water, diluting 3 teaspoons of sugar in a liter of boiled water.
About once a week, plants need to be sprayed with a special leaf feed. Water should be added if necessary, since the cuttings should be immersed in water by 1 cm. When the length of young roots reaches 5 - 7 cm, young plants can be transplanted into pots. This happens after about 2 months.
How to save a plant after insufficient or over-watering
If the plant does not receive a sufficient volume of water, its roots begin to dry out, and the leaves gradually wither, while bringing watering back to normal does not always help. To remedy the situation, you must:
- Dilute 1 ml of vitamin B in 1 liter of water and immerse the plant in this solution for about half an hour;
- After that, the plant should be removed, and sphagnum moss should be placed in the remaining solution for about 2 minutes;
- After the time has elapsed, the moss must be removed, the excess water must be allowed to drain so that the moss remains moist and put on the bottom of a plastic bag, preferably with a lock, and a sick orchid must be placed on top of the moss.
- The bag must be tightly closed and left in a shaded place, keeping the temperature around 25 ° C.
It is necessary to ventilate such a greenhouse several times a day for about 30 minutes., taking care not to evaporate condensate. It usually takes at least a month to recuperate.
Sunburn
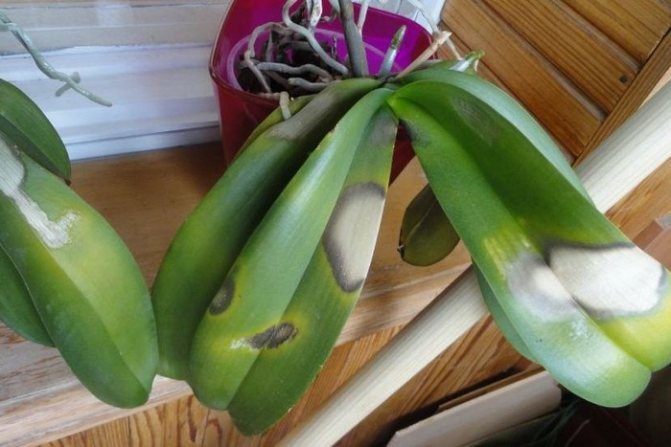


Due to its characteristics, the relatively harmless disease is confused with serious fungal or bacterial diseases. If the orchid looks like it came back from the beach, with big brown spots, white in the middle, it has suffered from sunburn. Consequences of intense exposure to sunlight. The problem arises in the spring, the plant is exposed on the balcony. For treatment:
- Move the plant to a slightly shaded area.
- Provide protection from the midday sun for plants standing on the windowsill.
- Cut off the affected leaves when they completely wither.
You can avoid leaf burns by gradually accustoming the orchid to sunny conditions in the spring. Applies to plants displayed on balconies and terraces.
Falling flowers
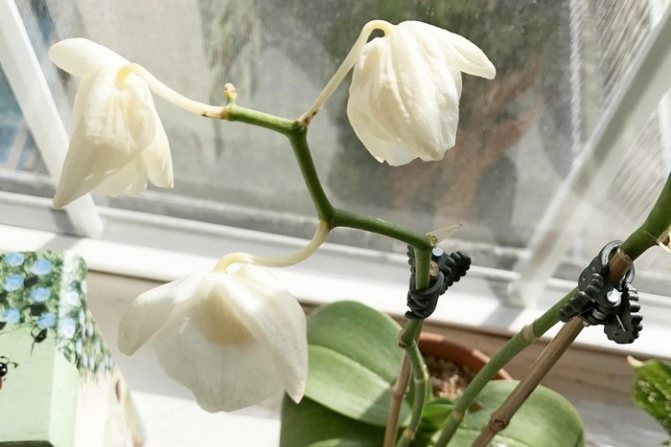


When leaves fall ill, flowers should be expected to wither and fall. If the flowers fall off despite the healthy appearance, the problem may be with care. You need to check the conditions:
- Cold drafts for a long time.
- Direct contact with a stream of warm air.
- Lack of light, especially in winter.
A sudden change of place from the windowsill to the lighted balcony leads to the fall of flowers. Orchids need to be taught gradually to different lighting conditions and temperatures.
Prophylaxis
General "rules of prevention are well known, but not all growers adhere to them. Remember that the health of a home orchid depends on the quality of compliance with preventive measures.
- Adequate lighting. Phytolamps can be used as an additional light source.
- Purity... Remove fallen and dried leaves from the soil in time.
- Optimum humidity. It should not be too high, but it should not be dry in the room either.
- Watering. You do not need to water and spray the plant abundantly. It is better to blot the drops remaining on the green parts with a napkin.
- Leaves care. Once every 3-4 weeks, wipe the orchid leaves with soapy water or take a warm shower.
- Top dressing. Do not use nitrogen fertilizers too often and abundantly. Better to replace them with fluoride and potassium.
Flowering period
Features of the
Orchids can bloom in any season. It depends on their condition and conditions of detention.
Flowering is always pleasing and possible at any time.
The flowering period can range from one and a half to six months. As a rule, flowering occurs twice a year, although there are cases of triple flowering. The sizes of flowers vary from 2 to 15 cm. On one peduncle, their number can reach up to 40 pieces. It depends on the degree of branching of the peduncle and the level of comfort of the conditions of detention. There are peduncles up to 1m long with hundreds of large petals. In the attached photos you can see all the variety of colors - solid white, purple, purple, pink, yellow, red, with various combinations of specks, specks and veins.
If the plant does not bloom
Usually, three months after the last flowering, phalaenopsis bloom again. If this does not happen, then it may be necessary to eliminate one of the probable reasons:
- low lighting (after installing additional lighting, expect flowering);
- overfeeding with nitrogen-containing fertilizers (you need to wait until all the nitrogen is processed by the plant, and during this time feed only using phosphorus);
- the plant is tired and needs a longer time to restore the lost strength (you need to wait a little, and then stimulate it).
Stimulation consists in insufficient watering and the use of drugs "Ovary" or "Bud". It also does not hurt to lower the night temperature so that its difference from the daytime is 6 ... 8 degrees.
Post-flowering period
Most often, after the last petal has fallen off, the faded arrow dries up and must be cut off. But sometimes it stays green. In such a situation, you can:
- do not touch her at all;
- cut to the height of the bifurcation;
- cut it off completely.
After cutting, the green stem can be placed in a container of water. It is very likely that the baby will tie on it. On an uncircumcised arrow, lateral branches may grow over time. Over time, they can bloom with white flowers, though not so abundantly.
Photo
Photos of external signs of the disease:
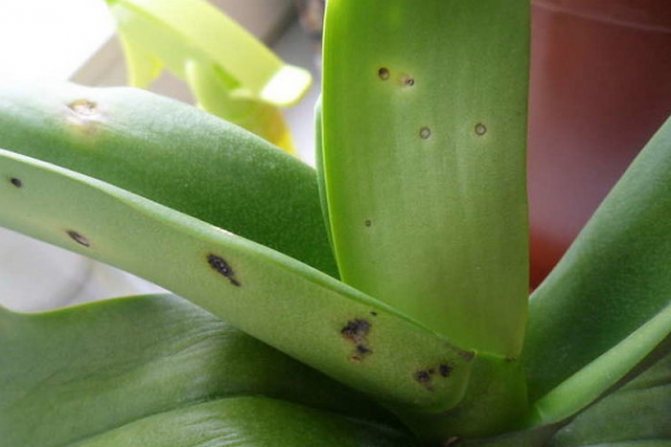
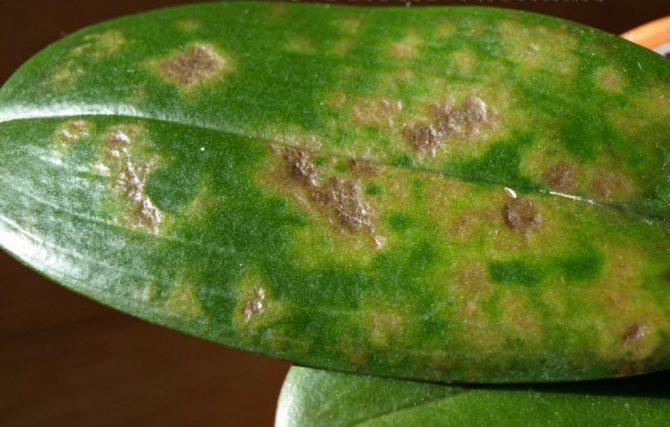
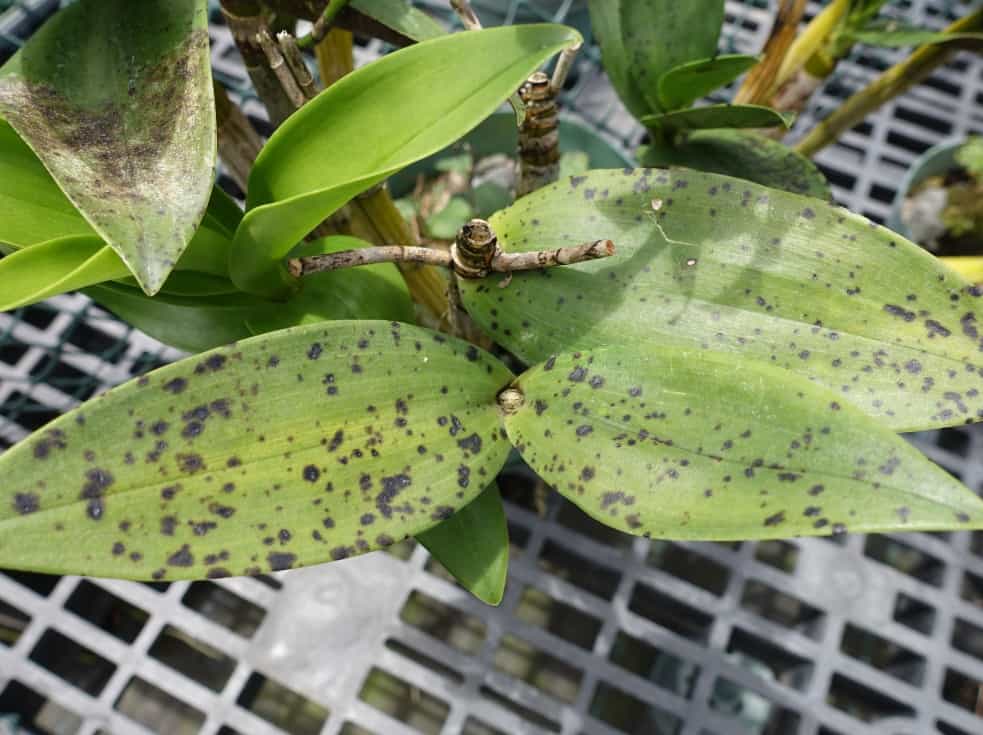
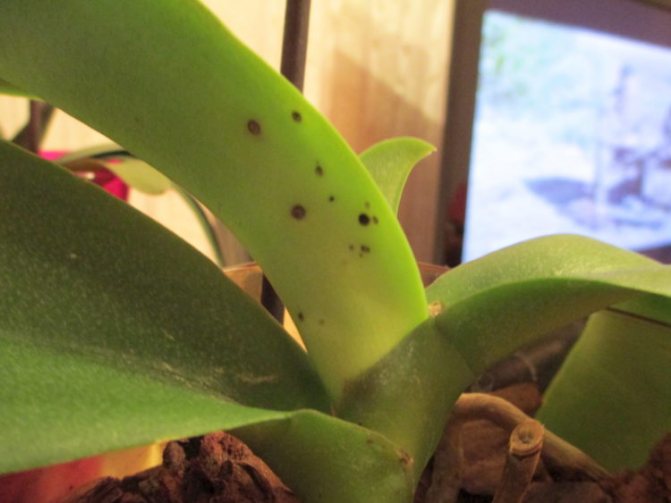
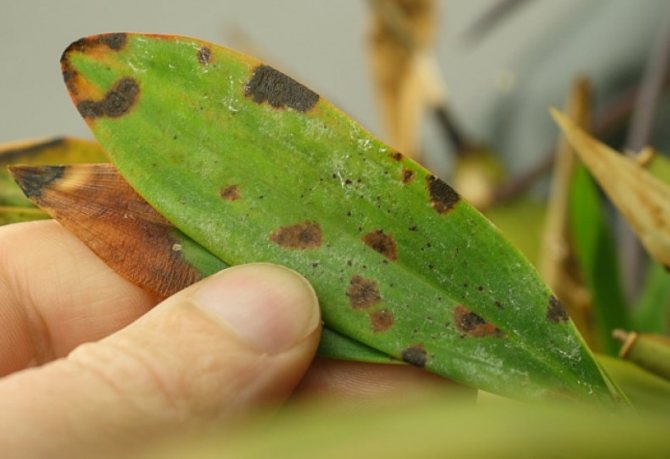
Anthracnose
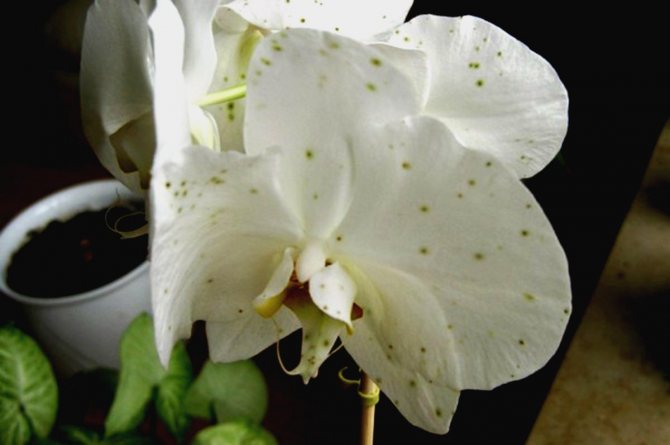
Problems with orchid leaves also occur with anthracnose. Its characteristic feature is small dots on the leaves, which later increase in size, turning into specks, and then merge. The places of such mergers become black and become, as it were, depressed. At the last stage of the development of the disease, yellow spots appear.
Causes of occurrence:
- High air humidity
- Stagnant water in the leaf axils
- Poorly ventilated area
Prevention and treatment
To prevent the development of anthracnose, the plant should be kept at a humidity level of somewhere around 50-60%. In this case, the room should be periodically ventilated. And also when watering, you need to ensure that irrigation water does not accumulate in the leaf sinuses and cores of the pseudobulbs. At the first suspicion of anthracnose, the plant must be isolated from the rest so that the infection does not develop further.
To rid the orchid of anthracnose, you need to cleanse all affected areas of dead tissue, and treat the cut sites with charcoal or cinnamon powder. Additionally, the plant is washed with a solution of copper-containing fungicides at intervals. Any type of orchid is susceptible to anthracnose, but most often lycast, miltonia, phalaenopsis, oncidium and papiopedilium are affected.


Anthracnose on orchid leaves
Violations of care and conditions of detention
In addition to infectious diseases, when growing orchids, there are violations that have arisen exclusively against the background of improper care and maintenance conditions. They are easier to treat and usually do not require the use of chemicals.
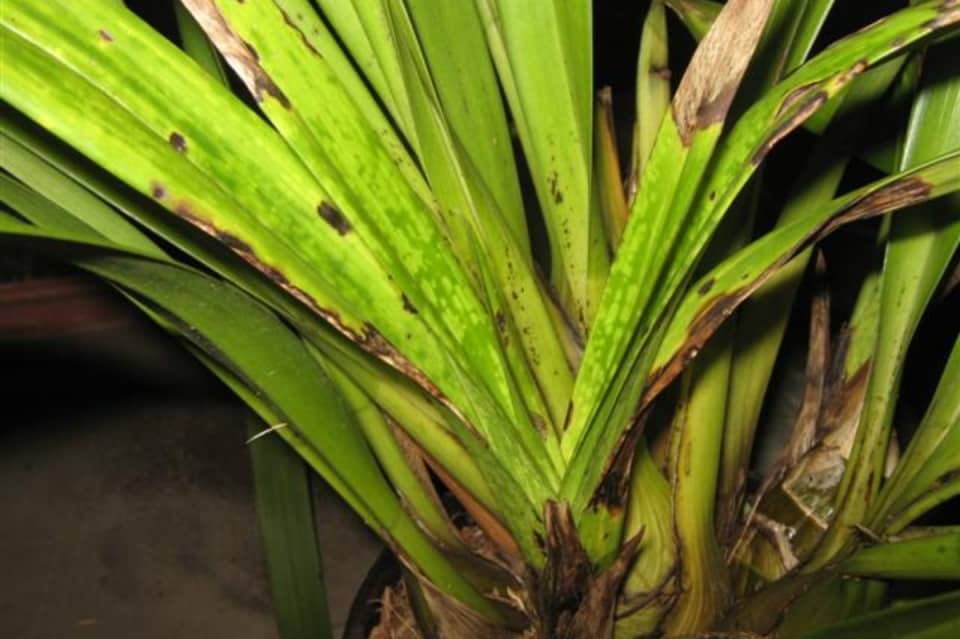
Leaf burns
A common leaf disease among orchids that occurs when the sun is active from the second half of spring to the end of summer. The appearance of burns on the leaf blades is associated with direct sunlight. In this case, light areas with a pronounced brown edge are formed. If measures are not taken in time, this leads to drying out of the vegetative parts, the appearance of through holes (see photo).
If you find burns on the leaves, you urgently need to shade the plant, reduce the amount of watering to a minimum. If there are severely affected areas, then they need to be cut off, the edges should be treated with wood ash. During the entire recovery period of the orchid, feeding must be completely excluded.
Waterlogging
Watering regime is an important part of orchid care. Due to an excess or lack of moisture in the soil, metabolic processes are disturbed, in particular, photosynthesis. This leads to lethargy or swelling of the leaf plates, and the risk of rot development increases.
As a preventive measure, the plant should be properly watered, and after abundant watering, it is imperative to dry the sticky spots on the leaves, for example, with a napkin or filter paper. If swelling is found, watering should be reduced and scheduled spraying should be limited.
Leaf deformation
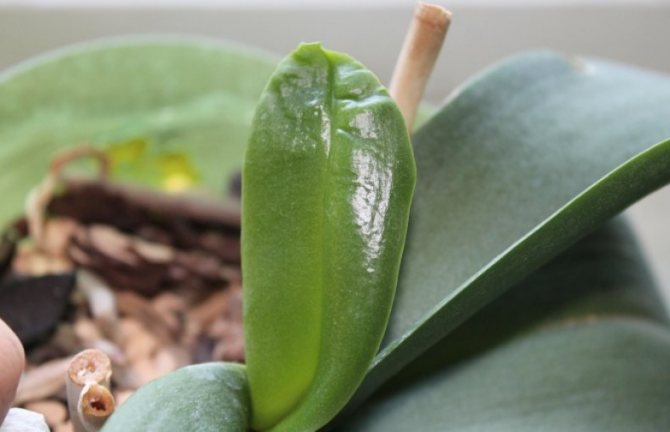


Changes in the structure of the leaf blade of an orchid can be associated with many reasons. Such a problem arises against the background of infection with diseases and pests, prolonged exposure of the flower to the sun or with a lack of water. Leaf deformation can also be associated with a deficiency of potassium and phosphorus in the soil, especially during the period of budding and flowering.
Withering buds
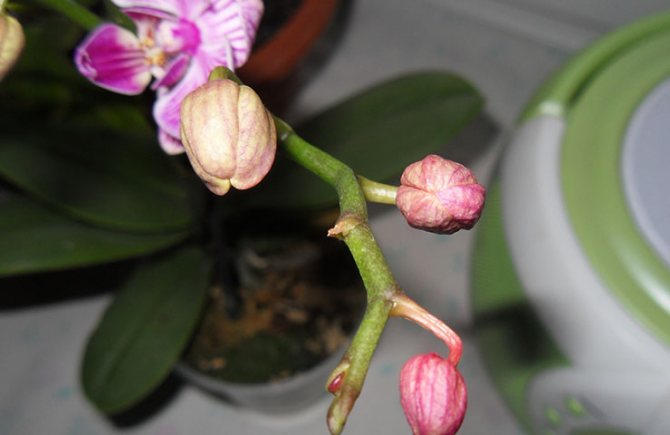


There can be several reasons for this problem. Often, wilting of the formed buds is observed due to improper watering, but it can also be the cause of a bacterial or fungal infection.
Most often wilting is observed when the plant is kept in a room with insufficient lighting, in order to avoid this, you need to plan the location of the pot and use fluorescent lamps when there is a lack of light. In addition, the wilting of buds can occur against the background of hypothermia of the plant, especially at a late beginning of flowering. In this case, it is necessary to correct the temperature regime, not to allow the temperature to drop below 22 ° C, and the humidity below 65%.
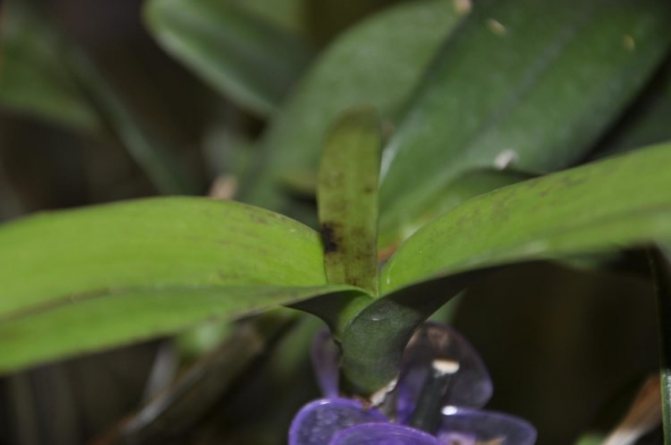
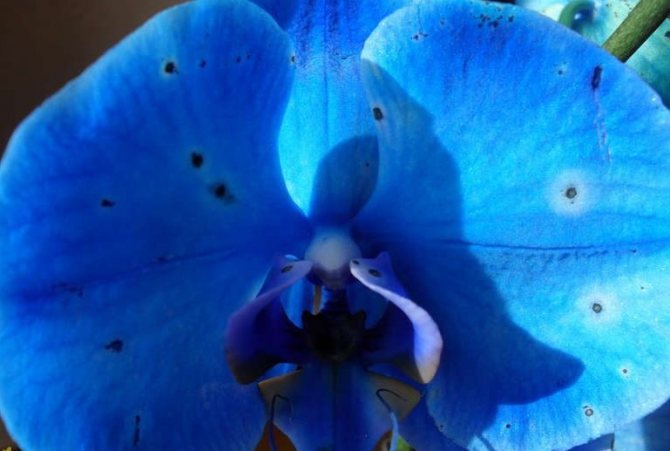
Darkening of flowers
Small dark spots on flowers are a common problem in all orchid species. It can occur as a result of even minor mechanical damage, for example, when transporting a plant. In addition, the spotting of the petals appears after moisture gets on them during watering, the formation of condensation. Less often, spots are formed when the plant is kept under constant exposure to direct sunlight.
What to do with lethargy?


Leaf lethargy is most likely due to insufficient watering.... It is necessary to restore the regime, you can also soak the roots in a 0.1% solution of succinic acid (40 min-1 hour).
If watering is excessive, remove the plant from the pot and dry the roots. Then plant in looser soil. If overheated, transfer to a cool place. If lethargy occurs from root disease, then rotten and dried out areas must be removed.
You will learn about what to do if the flowers of an orchid wither from our article.
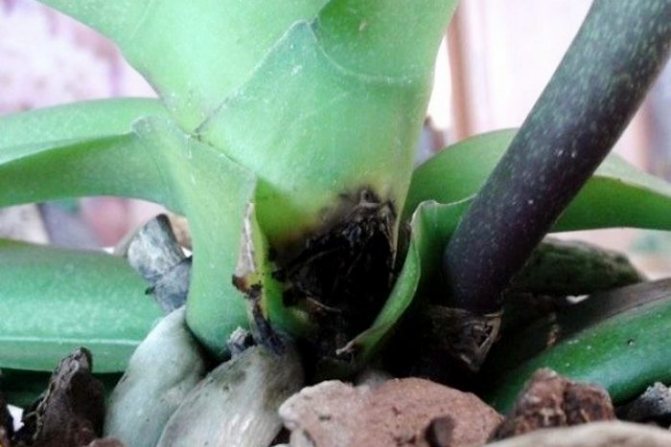
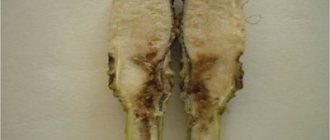
Root rot
Keep in mind that the roots can be affected by both rot and fungus. Often they are affected by such types of rot as:
- Gray. It affects both roots and leaves. You can determine the presence of a problem by the dark areas with a bloom of gray in different places of the plant. Often the problem is with the leaves. After them, the soil, the roots, and the flowers suffer. The cause of rot is high humidity and low room temperature. Excessive use of fertilizers with an increased concentration of nitrogen can also affect the appearance of gray rot. Keep in mind that gray mold is a fungus. If spots are found, remove by cutting out all affected areas, and spray healthy areas with fungicides. When reappearing, you cannot use the same drug, you need to select another one. The appearance of gray rot is typical for cattleya, phalaenopsis, cymbidium and other varieties of orchids with white flowers. For prevention, when watering, you need to use drugs to increase the resistance of orchids to diseases, in addition, do not put the orchids close to each other.
- Root. It appears on the roots of the plant. They become soft and die off over time. Brown leaves are another indication of the presence of the disease. Root rot is caused by high temperature and humidity in the room. If you have already seen the problem, spray the roots with a solution of foundationol (0.2%) or topsin (0.2%). Repeat the procedure three times every 20 days. The disease often involves cymbidium, miltonia, and pafiopedilum. Prevention can be the use of a quality substrate.
All of these orchid root system problems are considered the most common. Moreover, in most cases it is possible to cope with them. The main thing is to notice the problem in time and quickly start treatment.