Lovers of decorative species should also be aware of the presence of potential diseases that require treatment.
Such types of Milkweed as Multiflorous, Bordered, Cypress, Tirucalli, Ribbed, Pallasa, Belozhilkovy, Mila, Triangular are very popular in home cultivation.
Euphorbia: leaves turn yellow and fall, what should I do?
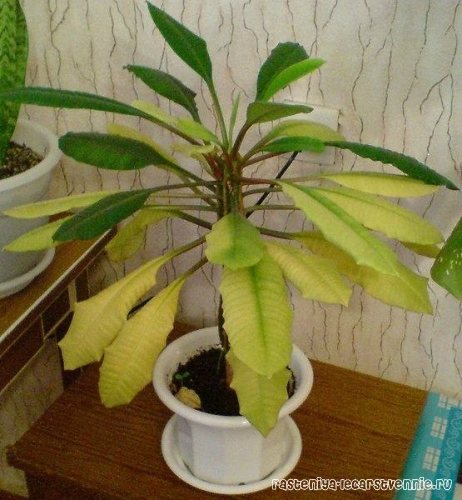

There is a great variety of indoor plants - more capricious and less unpretentious, luxurious, flowering and decorative deciduous. All of them need the organization of certain care, and in the absence of it or with the addition of various diseases in indoor crops, well-being and, accordingly, appearance can be greatly impaired. Therefore, it is very important to determine the cause of such changes in time and correct it. And the topic of our conversation today will be the euphorbia flower. Why does milkweed sometimes have problems, leaves turn yellow and fall, and what should the mistress of the flower do in such a situation? Let's talk about this.
Euphorbia is a very common culture that also bears the name euphorbia. Despite all its unpretentiousness, such a plant can sometimes hurt. Its leaves can turn yellow and fall off, which significantly affects the decorativeness of such a culture.
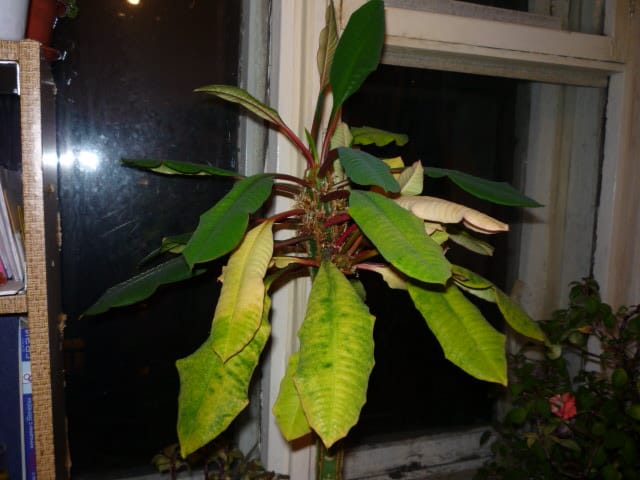
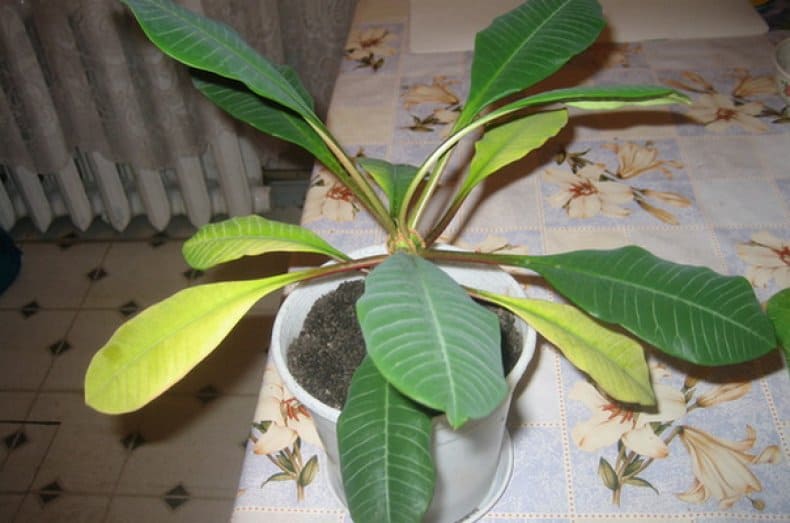
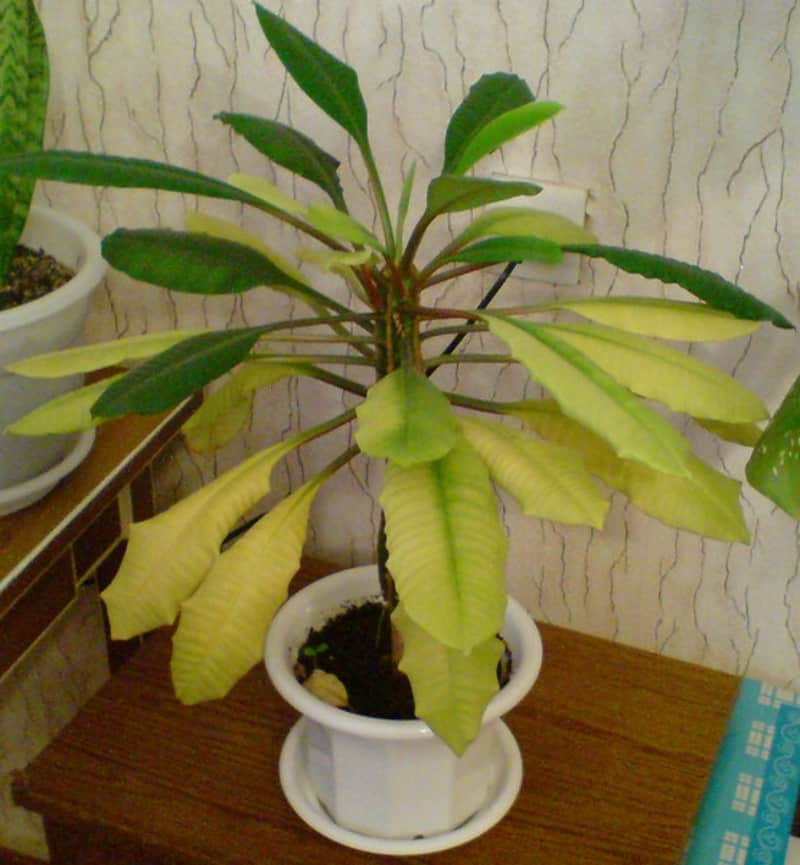
So, if the foliage turns yellow partially, in spots, it may well be that direct sunlight falls on it. It may well leave real burns on the flower. Over time, the injured leaf will completely turn yellow and fall off. To prevent such a problem, it is advisable to place the euphorbia pot not in the sun, but in partial shade, but in a well-lit place.
As autumn approaches, almost all indoor plants slow down their growth rates, preparing for wintering. Euphorbia does the same. Approximately in the first or second month of autumn, the milkweed falls off its foliage, having previously turned yellow a little.
It is believed that such a phenomenon is completely normal, does not require any correction and all kinds of interventions. After the spurge has rest, it will again delight the eye with bright green leaves in the spring.
In addition, readers of Popular About Health need to remember about the structural features of indoor milkweed - its cap of leaves is formed on the upper part of the trunk, and the lower leaves gradually turn yellow and fall off by themselves. This is also a natural occurrence and should not cause panic. In order for the plant to remain evenly leafy and look attractive, it is worth turning it from time to time with different sides to the sunlight so that the illumination is uniform.
Sometimes euphorbia loses leaves due to the influence of some more serious factors - pests or ailments. So, if the foliage shrinks, turns yellow and falls off - what to do with milkweed at the same time? It is worth carefully examining your pet and, if necessary, use a magnifying glass. A similar problem can be caused by an attack by a mealybug or spider mite and other parasites that can suck juices from foliage.Suspecting the presence of pests, it is imperative to isolate the plant and carry out its treatment with the help of special preparations - insecticides.
Yellow spots on milkweed leaves can be attributed to a viral infection - tobacco mosaic. True, they are often complemented by spots of a different color. The leaves themselves are deformed. Often such a virus is carried by all kinds of insects, for example, the whitefly. To date, there are no methods of treating tobacco mosaic; to prevent it, indoor plants are treated with insecticidal preparations.
Quite often, yellowing and untimely dropping of milkweed leaves is the result of inadequate care for euphorbia. So, this culture can behave in a similar way in excessive humidity. Decay of the root system is fraught with crown falling and flower death. If you realize that the plant is suffering from excess moisture, remove it from the old soil and pot, carefully examine the roots and remove those that look rotten. Sections can be treated with activated carbon powder. Then place the plant in a new soil mixture and a new pot and do not forget to arrange for it a sufficient drainage layer of rubble, expanded clay or perlite. Also, in the future, be sure to control the degree of moistening of the milkweed.
It is worth remembering that euphorbia needs a systematic supply of nutrients. This culture is capable of drawing out everything useful from the soil in a fairly short time, and the deficiency of the elements it needs can become the reason why the leaves turn yellow. To prevent such a problem, it is necessary to systematically apply fertilizers to the soil. It is advisable to carry out such manipulations every two weeks, starting in May and ending in September. Of the fertilizers, it is best to use complex mineral compositions.
In some cases, a sharp and incomprehensible yellowing (and then falling off) of the leaves is a consequence of sudden changes in temperature. Therefore, when ventilating the room during the cold season, it is imperative to protect euphorbia from drafts.
Performing any manipulations with milkweed, you must remember about the toxicity of its milky juice. Such a substance can provoke rather strong irritations on the skin or mucous membranes, and its accidental ingestion is fraught with the occurrence of poisoning. Therefore, any work with euphorbia requires caution, in addition, you need to remember the safety of children and pets.
In fact, indoor spurge is a completely unpretentious plant that can be easily grown on your windowsill. You just need to organize proper care for him and promptly eliminate all kinds of problems.
Causes of yellowing of leaves
But sometimes milkweed leaves begin to turn yellow and fall off. This can happen for natural reasons.
The leaves of the plant may turn yellow due to disease.
When autumn comes, the plants slow down and prepare for wintering. Euphorbia is no exception. In September-October, the flower begins to actively turn yellow and leaves fall off. This natural process does not require intervention, and it should not be frightening any more. Having somewhat lost its decorative effect, the spurge will rest, and in the spring it will delight you with new young leaves.
The peculiarity of this plant is that the cap of the leaves is formed on the upper parts of the trunk, therefore, the lower old leaves periodically fall off. This shouldn't bother you either.
But Euphorbia can lose foliage when sick. If milkweed leaves turn yellow, you should definitely examine it for the presence of pests. Mealybugs, spider mites, and other parasites suck the juice out of the leaves. As a result, the leaves fall off and the plant dies. If such a problem is found, isolate the flower from other plants and treat it with special preparations.
The yellowing of the crown can begin due to problems with the root system. Examine the spurge, maybe there is simply not enough space for it. In this case, transplant the overgrown flower into a larger pot.
Once every 2 weeks from spring to autumn, you need to feed the plant with fertilizers.
Yellow spots on the leaves can appear due to tobacco mosaic, from which the plant must also be urgently treated.
Milkweed leaves turn yellow when excessive moisture is present. A decaying root system causes the crown to fall off, and the flower may die. In this case, you need to transplant it into a new pot with fresh soil and good drainage.
Euphorbia depletes the soil very quickly, and lack of nutrients can cause yellowing of the leaves. To prevent this problem, once every 2 weeks from spring to autumn, you need to feed the plant with fertilizers.
Yellowing and falling leaves can cause sudden changes in temperature. If you ventilate the room in winter, then the pot with the plant must be protected from a draft.
It is important to know that milkweed juice is poisonous and can irritate the skin. Therefore, handling a flower requires special care, and it is better to protect children from contact with it.
Euphorbia reacts very painfully to any change in conditions of detention and perceives it as stress. Typically, the reaction to this is loss of foliage. Be careful when growing this plant, and it will delight you with its exotic look without causing much trouble.
Euphorbia (as the decorative flower is scientifically called) is a modest, unassuming plant. But some growers, especially beginners, do not take into account the individual nuances of growing and care, and then they wonder why the milkweed's leaves suddenly turn yellow and fall off.
Why do the lower leaves turn yellow and fall off in milkweed? Euphorbia: leaves turn yellow and fall off
Why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall?
In autumn, for milkweed, the process of yellowing and leaf fall is natural. But if this happens in the summer, there may be problems with watering. Either the plant does not have enough moisture, or, conversely, it is being poured over. Also, the ambient temperature may be too low. It is possible that the pot is in a cold draft. It is necessary to attach the plant to a place more comfortable for it.
Favorable conditions of detention
- Watering milkweed. The most important point of well-being. Since this representative of the flora belongs to succulents, he does not like moisture too much. Moreover, overflow is destructive for him, and often the plant cannot be saved. For everything to be safe, watering should be moderate. This means: in the summer, water once a week, in the spring and autumn - once every two weeks, and in the winter, once a month is enough. Before watering, check the earthen ball - it should have time to dry out between waterings! But drying out of the soil should not be allowed. Use soft water at room temperature for watering.
- It is preferable to transplant the plant into a shallow pot. In a large flowerpot, it is difficult to maintain a favorable watering regime.
- The best place for milkweed. The plant loves sunlight, but direct rays are destructive for it. It feels good on a south or southeast window. The optimum temperature during the growth period is 22 - 25 degrees.
- Top dressing for green and strong leaves. From spring to autumn, it is recommended to feed your pet every 2 weeks with special fertilizers intended for cacti. Lack of nutrients negatively affects the plant: milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off.
- In winter, the plant should have a dormant period. For this, it is desirable for him that the ambient temperature is not higher than 15 degrees. Watering is moderate. If the temperature is higher in winter, additional lighting should be provided, otherwise the stem will bend. A fluorescent or LED lamp will do.
Milkweed secret
In addition to creating a favorable environment for your pet, you can further support it.To do this, use epin, a drug that allows you to adapt to stressful situations. It also promotes plant growth and stimulates the immune system. It will be useful in the following cases:
- The plant has survived drought or waterlogging;
- Not enough light and heat;
- The soil is depleted;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Attacks by viruses, fungi or insects.
How to help milkweed with epin:
- To support the vitality of milkweed and awaken its dormant immunity, prepare a solution. It is convenient to do this in the following way. Pull the entire contents of the ampoule into a syringe. It will turn out to be 1 ml. To process the plant, a lot of solution is not needed. Enough 0.1 ml per half liter. Water must be taken settled or filtered, you can also boiled. Its temperature should be slightly warm.
- If your plant is dusty, you need to clean it before spraying. You can use a brush to remove dust.
- It is advisable to carry out the processing procedure in the bathroom with the curtains drawn (the solution is still poisonous).
- It is necessary to spray until the green mass is completely wetted.
- Pour out the rest of the solution.
- After the plant is dry, the curtains can be pulled back.
- Processing of milkweed, which is in an unfavorable environment, must be carried out every 10 days.
- The remaining epin can be stored in a syringe wrapped in a napkin on the refrigerator door.
What diseases and pests adversely affect the condition of the leaves
If all the conditions for keeping milkweed, caring for it are met, and the flower still withers, withers, turns yellow, falls off, it means that it is sick. Fungal and viral diseases can cause this condition.
Root and stem rot
The disease is noticeable by black dents on the stem. They appear slightly above ground level, grow, spread along the stem. Later they get inside and destroy plant tissues. The stem breaks, the flower dies.
The following circumstances could lead to decay:
- overfeeding with nitrogen;
- frequent watering;
- high air temperature;
- lack of light;
Systemic fungicides (Ridomil, Previkur) are used to treat euphorbia in the early stages of the disease. They stop watering the flower, change the nutrient medium.
Gray rot
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus. Brown spots form on the leaves of the plant, as if rotten. The spots grow, cover the entire leaf. The increased humidity of the air accelerates the development of the fungus, which is why the pathogen does not leave a healthy spot on the leaves, they turn gray.
The plant becomes infected through soil, water. The fungus lives in this environment for a long time. Circumstances complementing the threat of the disease:
- oversaturated air;
- insufficient ventilation of the room;
- excess nitrogen in the earth.
Fungal disease is treated with systemic fungicides (Bona Forte, Bravo and others). As a preventive measure, in order to avoid illness, it is necessary to monitor the humidity of the air, plant the plant in disinfected soft soil.
Rust
The surface of the leaves is covered with brown, as if rusty, oval-shaped layers. Then they join and form rusty ribbons. Usually mushrooms appear on the inside of the leaves, may be on petioles. Occasionally, red ribbons appear on the stalk of the milkweed.
If the flower is not treated, it will die. Fungicides will help save spurge. Proper watering and spraying will prevent the appearance of rust.
Alternaria
Fungal disease is manifested by the appearance of large dark spots on the foliage of the euphorbia. More often they infect emaciated aged leaves. Excessive humidity, too warm air intensify the development of a fungal infection. The source of the disease may be soil in which live pathogens have been preserved.
"Skor", "Ridomil Gold" are systemic fungicides that will cure the fungus if it has managed to hit the flower.Biological fungicides (Fitosporin, Baktofit and others) are used as preventive measures.
Bacteriosis
With this disease, spurge grows poorly, develops, does not bloom. The foliage and the stem are covered with brown, rusty spots. Strange discharge with an unpleasant odor follows from the stains. Excess moisture, nitrogen in the soil contributes to the early development of the disease.
Milkweed is handled with care, because it is through mechanical damage that the infection enters the plant.
Powdery mildew
Fungal disease. Leaves appear on the leaves with a fluffy dark gray bloom. Before this, the foliage dries up. The disease is contagious, the infection is carried by the wind. Too hot weather, dryness, lack of moisture in the soil aggravate the situation. Proper care of milkweed will help prevent disease. If the flower is sick, they are treated with antifungal drugs (Topaz, Fundazol).
Tobacco mosaic
The causative agent of the disease is a virus. The infection is most commonly carried by whiteflies. Sick leaves are deformed. Spots appear on the leaf plate: white, yellow and even reddish. As a preventive measure, they are treated with insecticides. Infected cuttings can be the source of the disease. Planting healthy cuttings will eliminate the tobacco mosaic.
Red spider mite
A half-millimeter spider mite eats up the young leaves of the milkweed. It is small enough to see a harmful insect with the naked eye. The appearance of white, yellow spots on the leaves of the plant indicates the presence of a tick. Infected seedlings are separated from healthy ones, poured over them with a solution of laundry soap, which is rubbed on a fine grater.
From the tick, the plant is treated with acaricides, for example, "Aktara". At the first sign of a tick, urgent action is taken as insects spread quickly.
Symptoms of the disease are manifested in a change in the shape of milkweed leaves, they curl, look underdeveloped, ugly. Then they begin to turn yellow and fall off. In some areas, the color disappears. The plant stops growing and developing.
Sometimes yellow and light green insects are collected by hand, they can be seen with the naked eye. Branches with large lesions are removed. The flower is treated with Fitoverm, Aktellik, Decis.
Root mealybug
The parasites infect the milkweed root system. They gather on the roots of the plant in colonies in the form of scattered flour. With severe infestation, pests are visible.
The plant stops growing and developing. Milkweed leaves turn yellow, dry out, and fall off.
At the first signs of the appearance of insects, in order to save the euphorbia, it is dug up by the root, freed clean from the soil, and treated with insecticides. The dish from under the flower is disinfected, fresh earth is poured. Before planting, the roots are carefully examined for any parasites.
Whitefly
Accumulations of insect larvae can be observed from the inner underside of the milkweed leaves. They live by feeding on the sap of plant cells. They appear as yellow and white markings. The leaves of the plant curl up, change the green color to yellow, die off.
Whitefly offspring are greenish, and the adult parasite is white. The midge is easy to see. Heavily infected areas are removed, and the spurge is treated with insecticides at least once every three days.
Mosquitoes on milkweed
The mosquitoes themselves are not dangerous to the flower. But they leave their larvae on the plant, which will feed on milkweed. The offspring of mosquitoes, although small (larvae 0.5 cm), pose a serious threat to young seedlings. Sick seedlings are separated from healthy ones. As a preventive measure, the soil is treated with insecticides. To get rid of mosquitoes, sticky tapes are hung.
The causes of yellowing, leaf death lie in improper care.Subject to all the recommendations of florists, the threat of infection is minimal. In order for the euphorbia to be healthy, to please with flowering, it is necessary to regularly inspect the plant and take measures in time.
Why Milkweed Milk turns yellow and leaves fall. Why do milkweed leaves sometimes turn yellow?
Many owners complain that milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off. This beautiful ornamental plant has a scientific name - Euphorbia. It is quite unpretentious, but there are features in care that a florist needs to know, especially a beginner.
The scientific name for milkweed is euphorbia.
Features of plant care
Euphorbia will take it easy if it grows in the sun, but it is imperative to avoid sunburn on the leaves. It is better to provide the plant with light partial shade.
The flower loves warmth, so even in winter it needs a comfortable temperature.
The flower loves warmth, so even in winter it needs a comfortable temperature, around 18 ° C. It perfectly tolerates dry air of heated rooms and does not need to be sprayed. Euphorbia should not be placed in drafts.
Watering your plant should be taken very seriously. Euphorbia does not tolerate too much drying out of the soil, and high humidity can cause rotting of the roots. It is necessary to water with settled water at room temperature. Before the procedure, it is better to check the condition of the ground with your finger. If it is dry 1-2 cm deep, then the plant can be watered. In summer, spurge requires more moisture, in winter - less.
In order for Euphorbia to grow healthy and beautiful, it should be fertilized regularly during the period of active growth.
Causes of yellowing of leaves
But sometimes milkweed leaves begin to turn yellow and fall off. This can happen for natural reasons.
The leaves of the plant may turn yellow due to disease.
When autumn comes, the plants slow down and prepare for wintering. Euphorbia is no exception. In September-October, the flower begins to actively turn yellow and leaves fall off. This natural process does not require intervention, and it should not be frightening any more. Having somewhat lost its decorative effect, the spurge will rest, and in the spring it will delight you with new young leaves.
The peculiarity of this plant is that the cap of the leaves is formed on the upper parts of the trunk, therefore, the lower old leaves periodically fall off. This shouldn't bother you either.
But Euphorbia can lose foliage when sick. If milkweed leaves turn yellow, you should definitely inspect it for the presence of pests. Mealybugs, spider mites, and other parasites suck the juice out of the leaves. As a result, the leaves fall off and the plant dies. If such a problem is found, isolate the flower from other plants and treat it with special preparations.
The yellowing of the crown can begin due to problems with the root system. Examine the spurge, maybe there is simply not enough space for it. In this case, transplant the overgrown flower into a larger pot.
Once every 2 weeks from spring to autumn, you need to feed the plant with fertilizers.
Yellow spots on the leaves can appear due to tobacco mosaic, from which the plant must also be urgently treated.
Milkweed leaves turn yellow when excessive moisture is present. A decaying root system causes the crown to fall off, and the flower may die. In this case, you need to transplant it into a new pot with fresh soil and good drainage.
Euphorbia depletes the soil very quickly, and lack of nutrients can cause yellowing of the leaves. To prevent this problem, once every 2 weeks from spring to autumn, you need to feed the plant with fertilizers.
Yellowing and falling leaves can cause sudden changes in temperature. If you ventilate the room in winter, then the pot with the plant must be protected from a draft.
It is important to know that milkweed juice is poisonous and can irritate the skin. Therefore, handling a flower requires special care, and it is better to protect children from contact with it.
Euphorbia reacts very painfully to any change in conditions of detention and perceives it as stress. Typically, the reaction to this is loss of foliage. Be careful when growing this plant, and it will delight you with its exotic look without causing much trouble.
Features of plant care
Euphorbia will take it easy if it grows in the sun, but it is imperative to avoid sunburn on the leaves. It is better to provide the plant with light partial shade.
The flower loves warmth, so even in winter it needs a comfortable temperature.
The flower loves warmth, so even in winter it needs a comfortable temperature, around 18 ° C. It perfectly tolerates dry air of heated rooms and does not need to be sprayed. Euphorbia should not be placed in drafts.
Watering your plant should be taken very seriously. Euphorbia does not tolerate too much drying out of the soil, and high humidity can cause rotting of the roots. It is necessary to water with settled water at room temperature. Before the procedure, it is better to check the condition of the ground with your finger. If it is dry 1-2 cm deep, then the plant can be watered. In summer, spurge requires more moisture, in winter - less.
In order for Euphorbia to grow healthy and beautiful, it should be fertilized regularly during the period of active growth.
Why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall. Turns yellow and falls
Why does the plant shed its leaves and what to do with it? This is due to:
- Burns - the plant gets them due to direct sunlight. To solve this problem, you need to put the flower in partial shade.
- Natural reasons - with the onset of autumn, euphorbia prepares for winter and its leaves can turn yellow and fall off. This is a completely natural phenomenon, which should not be feared and should not interfere with this process. He will rest and green leaves will appear again in the spring.
- Diseases or pests - you should carefully examine the plant and identify the cause, whether it is sick or infected with a pest. It is necessary to save the plant understanding what exactly caused the yellowing and falling of the leaves.
- Improper care - due to improper watering or maintenance, the leaves can also turn yellow and fall off. Care should be reviewed and errors corrected.
Watering should be moderate because, due to abundant watering, the roots begin to rot and the leaves and the entire flower suffer from this. Lack of nutrients can also be the reason - additional feeding is necessary. The temperature of the content and the lighting are also important.
Ways to fight
What to do if the spurge turns yellow and sheds its leaves? The characteristics of the diseases show that almost all of them occur with inadequate care of green pets.
Violation of agricultural technologies leads to certain deviations in development. Infectious diseases primarily affect weakened plants... Compliance with all the rules practically eliminates the risk of infection. However, it does happen sometimes.
The gardener's task is recognize the threat in time... It is necessary to conduct regular examination of green pets, and if a disease is detected, take action.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
Why Milkweed Leaves Turn Yellow. Diseases
If you have a question: "Why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off and what to do about it?" - most likely it's all about improper care. Insufficient lighting leads to pallor of leaves and dropping. Rapid temperature changes lead to wilting or loss of leaves.
Why does the spurge dry (turn yellow) and shed its leaves?
"Autumn syndrome", when the leaves of the room milkweed turn yellow and dry, and subsequently fall off, signals insufficient watering or excessively dry air.
Why did the euphorbia drop its leaves?
This is due to excessive watering. It will also affect the color: the leaves will be unevenly colored.
The most common infectious diseases include fungal and viral diseases:
- alternaria;
- root and stem rot;
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- bacteriosis;
- mosaic
Gray rot
A fungal disease characterized by the appearance of brown rotten spots on the leaves. Gradually increasing, the spots cover the entire leaf.
High humidity of the air leads to the fastest development of the fungus, as a result, the leaves become gray.
Infection is possible through air, water and soil, in which the fungus persists for a long time. Factors that increase the risk of infection:
- too humid air;
- lack of ventilation;
- oversaturation of the soil with nitrogen.
To combat the fungus, systemic fungicides (antifungal substances) are used. Prevention - avoid waterlogging and use rather loose substrates for planting.
Alternaria
The appearance of the fungus is indicated by large spots on the leaves, often dark.
Older or weakened leaves are at greater risk.
Waterlogging and hot air accelerate the development of the fungus.
The pathogen can be found in the soil and in the remains of diseased plants.
For treatment, systemic fungicides are used (Ridomil Gold, Skorr). If the air humidity is high enough, biological fungicides should be used for prophylaxis.
Root and stem rot
It is characterized by the appearance on the stem, just above the soil surface, of dark depressed spots. Gradually, the infected area grows, penetrates deeply and affects the internal tissues. The stem breaks and dies. The causative agent (pathogen) remains in the soil for a long time.
This situation is most often caused by excessive nitrogen application and too abundant watering, a hot climate and a lack of lighting, as well as an increased density of substrates.
When the first signs of infection appear, treatment with systemic fungicides is carried out, watering is stopped, and the substrate is replaced with a drier one.
Powdery mildew
The causative agent is also a fungus and manifests itself in the appearance of a fluffy plaque (powdery mildew).
Leaf tissues dry out under bloom.
If left untreated, infection can lead to the death of the succulent.
The fungus is transmitted from a diseased plant through the wind. The situation is aggravated by a dry and hot climate, overdried substrate.
The fungus is not capable of harming a healthy green body, so proper care is the best prevention. If the infection nevertheless progresses, antifungal agents are used.
Bacteriosis
Bacteriosis is accompanied by poor growth and cessation of flowering. Stems and leaves infect rotten spots, from which a cloudy liquid with a pungent odor is released. The pathogen can be in the remains of diseased plants for a long time.
The likelihood of infection increases with high humidity, abundant watering and high nitrogen content.
The possibility of mechanical damage should be excluded, since it is through them that the pathogen penetrates.
Tobacco mosaic
A viral infection in which the leaf is deformed, and signs of chlorosis are noticeable on the veins.
The main signs are the appearance on the leaf blade of a pattern consisting of the smallest multi-colored spots, colors from white to yellow and red.
Insects, especially the whitefly, are the most common carriers of the virus.
It is better not to use infected cuttings. For prevention, it is necessary to carry out insecticidal treatment.
Rough growths on milkweed
Such a deviation in development cannot be called a disease, it is just a defensive reaction to open sunlight.
Coarse brown thickening is detrimental to appearance, but is by no means dangerous.
It is impossible to treat this and it is not necessary, and if this type is undesirable, then you need to protect it from the scorching sun.
Diseases
If you have a question: "Why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off and what to do about it?" - most likely it's all about improper care. Insufficient lighting leads to pallor of leaves and dropping. Rapid temperature changes lead to wilting or loss of leaves.
Why does the spurge dry (turn yellow) and shed its leaves?
"Autumn Syndrome"when the leaves of room milkweed turn yellow and dry, and subsequently fall off, it signals insufficient watering or excessively dry air.
Why did the euphorbia drop its leaves?
it associated with excessive watering... It will also affect the color: the leaves will be unevenly colored.

The most common infectious diseases include fungal and viral diseases:
- alternaria;
- root and stem rot;
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- bacteriosis;
- mosaic
Gray rot
A fungal disease characterized by the appearance of brown rotten spots on the leaves. Gradually increasing, the spots cover the entire leaf.
High humidity of the air leads to the fastest development of the fungus, as a result, the leaves become gray.
Infection is possible through air, water and soil, in which the fungus persists for a long time. Factors that increase the risk of infection:
- too humid air;
- lack of ventilation;
- oversaturation of the soil with nitrogen.
To combat the fungus are used systemic fungicides (antifungal agents). Prevention - avoid waterlogging and use rather loose substrates for planting.
Alternaria


The appearance of a fungus is indicated large spots on leaves, often dark.
Older or weakened leaves are at greater risk.
Waterlogging and hot air accelerate the development of the fungus.
The pathogen can be found in the soil and in the remains of diseased plants.
For treatment, systemic fungicides are used (Ridomil Gold, Skorr). If the air humidity is high enough, biological fungicides must be used. for prevention.
Root and stem rot
It is characterized by the appearance on the stem, just above the soil surface, of dark depressed spots. Gradually, the infected area grows, penetrates deeply and affects the internal tissues. The stem breaks and dies. The causative agent (pathogen) remains in the soil for a long time.
This situation most often leads excessive nitrogen application and too abundant watering, hot climate and lack of lighting, as well as increased substrate density.
When the first signs of infection appear, treatment with systemic fungicides is carried out, watering is stopped, and the substrate is replaced with a drier one.
Powdery mildew


The causative agent is also a fungus and manifests itself in the appearance of a fluffy plaque (powdery mildew).
Leaf tissues dry out under bloom.
If a take no action, infection can lead to death succulent.
The fungus is transmitted from a diseased plant through the wind... The dry and hot climate aggravates the situation, overdried substrate.
The fungus is not able to harm a healthy green body, so the best prevention is proper care... If the infection nevertheless progresses, antifungal agents are used.
Bacteriosis
Bacteriosis is accompanied by poor growth and cessation of flowering... The stems and leaves are striking rotten spots, from which a cloudy liquid with a pungent odor is released. The pathogen can be in the remains of diseased plants for a long time.
The likelihood of infection increases at high humidity, abundant watering and increased nitrogen content. Should to exclude the possibility of mechanical damage, since it is through them that the pathogen penetrates.
Tobacco mosaic
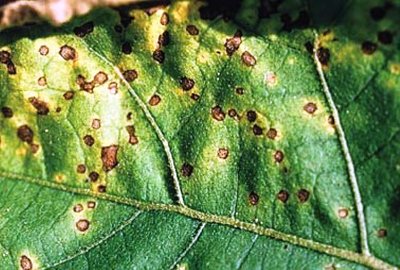

A viral infection in which the leaf is deformed, and signs of chlorosis are noticeable on the veins.
The main signs are the appearance on the leaf blade of a pattern consisting of the smallest multi-colored spots, colors from white to yellow and red.
Most often, insects become carriers of the virus, especially - whitefly.
Infected cuttings are better do not use... For prevention, it is necessary to carry out insecticidal treatment.
Rough growths on milkweed
Such a developmental deviation cannot be called a disease, this is just a defensive reaction to open sunlight.
Coarse brown thickening is detrimental to appearance, but is by no means dangerous.
It is impossible to treat it and not necessary, and if this view is undesirable, then you need to protect it from the scorching sun.
White-veined spurge withers. Requirements for location in the house
The plant requires certain conditions for keeping in the room, related to the temperature regime and the need for light.
Lighting
Euphorbia white-streaked is a light-loving plant that requires bright sunlight, except perhaps only the scorching rays that cause burns on the leaf blades.
In the shade, the succulent will wither, stop growing and simply stop growing green mass, and if it forms a young leaf, it will turn out to be weak, pale and several times smaller than ordinary foliage that develops under normal conditions.
The plant will be able to grow in partial shade, albeit not as actively as in good lighting. In such a situation, growers are advised to rotate the spurge around the axis of the flower container.
In summer, the flower is taken out into the garden and placed under the scattered crown of trees, and in winter, additional illumination with a fluorescent lamp will be useful.
Temperature
White-veined spurge needs constant access to heat. The favorable temperature for him is from 20 to 23 degrees Celsius. The critical maximum is 25 degrees; at higher thermometer readings, the leaves turn yellow and dry, and the achenes stop developing.
During wintering, the plant also needs sufficient warmth and prefers, even at rest, to be at a minimum temperature of 15 degrees above zero, optimally - 18 degrees. When kept colder, the plant dies.
Air humidity
The succulent has no requirements for high environmental humidity; the usual room microclimate is quite suitable for it. It is not harmed by the proximity to the heating system battery if there is a short distance to the device. Still, it is impossible to put a flower too close.
The plant is especially sensitive to the presence of fresh air: after airing, it visibly revives. However, it does not tolerate drafts.
a source
Favorable conditions of detention
- Watering milkweed. The most important point of well-being. Since this representative of the flora belongs to succulents, he does not like moisture too much. Moreover, overflow is destructive for him, and often the plant cannot be saved. For everything to be safe, watering should be moderate. This means: in the summer, water once a week, in the spring and autumn - once every two weeks, and in the winter, once a month is enough. Before watering, check the earthen ball - it should have time to dry out between waterings! But drying out of the soil should not be allowed. Use soft water at room temperature for watering.
- It is preferable to transplant the plant into a shallow pot. It is difficult to maintain a favorable watering regime in a large flowerpot.
- The best place for milkweed. The plant loves sunlight, but direct rays are destructive for it. It feels good on a south or southeast window. The optimum temperature during the growth period is 22 - 25 degrees.
- Top dressing for green and strong leaves. From spring to autumn, it is recommended to feed your pet every 2 weeks with special fertilizers intended for cacti. Lack of nutrients negatively affects the plant: milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off.
- In winter, the plant should have a dormant period. For this, it is desirable for him that the ambient temperature is not higher than 15 degrees. Watering is moderate.If the temperature is higher in winter, additional lighting should be provided, otherwise the stem will bend. A fluorescent or LED lamp will do.
Why does indoor milkweed turn yellow and fall off the leaves: how to save it
During the next watering of indoor plants, I noticed that the tips of the leaves of the milkweed turned yellow. I shared this problem with my mother, she said that the flower lacks calcium. After feeding with calcium, the plant slowly recovered and new leaves grew on it. In this article I will tell you why the leaves of milkweed can turn yellow and how to save it.


Video: Why does the fat woman fall off the leaves. Money tree problems and solutions
Other affected areas are discolored.
The plant looks depressed normal growth and development stops.
To fight insects, you need, first of all, collect them by hand
.
It is not difficult to notice them, they are yellow or light green. Severely affected shoots will have to be removed.
For further processing, drugs are used:
Whitefly larvae greenish color
, and the adult is a white midge, the presence of which can be easily noticed.
When larvae appear, the affected areas should be cut off, and healthy parts should be sprayed with insecticides. Once every 3 days
.
If infestation progresses, insects become visible on the root collar.
As the roots are damaged, the plant grows larger slows down growth.
The leaves first turn yellow, then dry and die off.
If insects are found, you should carefully dig the euphorbia from the ground, remove the remains of soil from the roots and treat with an insecticide solution.
Pot you need disinfect and fill with fresh earth
... At each transfer, it is necessary
examine the roots carefully
for the detection of this disease.
Spider mite small enough
, only half a millimeter, light brown or red. It feeds on young leaves. If white or yellow spots appear on them, this could be a sign of the presence of a tick.
To isolate infected seedlings, sprinkle with warm soapy water. To kill ticks, use acaricides
.
It must be remembered that this insect reproduces very fast
, and measures to combat it must be taken
immediately
.
The size of the larvae is about half a centimeter, and they are especially dangerous for seedlings.
If larvae are found, the best option would be transplant immediately
healthy seedlings, isolating them from the infected.
For prevention, you can treat the soil with an insecticide
... Dry sand sprinkled with a thin layer on top is also not attractive to mosquitoes. Adults arriving can also be fought in the traditional way -
Insect-proof Velcro
.
What to do if the spurge turns yellow and sheds its leaves? The characteristics of the diseases show that almost all of them occur with inadequate care of green pets.
The reasons
Euphorbia belongs to unpretentious plants, but with improper care, its leaves can turn yellow and fall off. He loves warmth and hardly tolerates drafts, for the same reason it is undesirable to water him with cold water. Although it is a tropical plant, it is better not to put it in direct sunlight, as its leaf blades can get burned. Therefore, diffused light is most suitable for him.
Since autumn, its growth slows down significantly, as it begins to prepare for winter, slowly shedding its lower leaves. Therefore, do not be intimidated, but simply reduce the frequency of watering. After hibernation, new leaves begin to grow on it, from this moment the frequency of watering is increased.
If his leaves began to turn yellow in spring or summer, then the reason for this phenomenon is most often:
- Lack or excess of nutrients.
- Improper lighting.
- Drafts.
- Improper watering.
- Diseases or insect pests.
- Unsuitable pot.
If its leaves turn yellow after transplanting into a plastic pot, then try replanting it into a ceramic pot, as the roots can "breathe" in it. During this procedure, be sure to add organic fertilizers to the soil. Then the flower will slowly recover.
By the appearance of milkweed, you can understand what kind of minerals it lacks:
- Magnesium - Spots appear between the veins on the leaves.
- Copper - Greens become lethargic and light spots appear on them.
- Manganese - The color of indoor greens turns yellow-gray.
- Molybdenum - The leaf blades curl up with yellow spots appearing between the veins.
- Nitrogen - Leaves become dull.
- Calcium - The tips of the leaf plates turn yellow and crumble.
Causes of foliage problems and what to do about it
Although the flower is not too capricious, this does not mean that there is no need to care for it. The main condition for growing indoor milkweed is location. From direct sunlight, the leaves of euphorbia can get burned, which means that the shadow side is more suitable. Draft is just as dangerous as cold temperatures. Euphorbia is a heat-loving flower.
If the leaves turn yellow and fall off
It happens that the leaves of the plant turn yellow and fall off. Illness can cause yellowing.
By autumn, the spurge grows more slowly, and begins to prepare for winter. During this period, the leaves turn yellow. Do not be afraid, since this is a normal natural phenomenon. The flower will relax, calm down, and by spring the young foliage will become even more magnificent. For euphorbia, the fall of the lower old leaves is characteristic, and the new ones grow higher. But this is also not a cause for concern.
Drops the leaves
It happens that a flower sheds its foliage long before preparing for winter. This is a distress signal.
Sometimes a stressful condition can cause yellowing and falling leaves:
- lack of fertilizers;
- lack of light;
- the presence of drafts, cold snap;
- improper watering.
If these factors are excluded, nevertheless, sometimes this happens: the leaves wither, fall, obviously, the problem is serious.
The stem and leaves wither
Euphorbia for a short time consumes a lot of useful raw materials from the ground, and then lacks nutrients, which can cause the stem to wilt, yellow leaves.
The flower needs constant nutrition. It needs to be fed more often, at least twice a month, especially in winter.
The angle of inclination of the leaves has changed
If you take care of the milkweed incorrectly, its leaves will droop, the leaves will bend. This means that the problem lies in the roots of the plant, they have rotted from excess moisture. To preserve euphorbia, it is transplanted:
- They carefully take it out of the pot, examine it, cut off the decayed roots with a knife.
- The cut sites are powdered with activated carbon.
- At the same time, one should not forget about the drainage from expanded clay or crushed stone.
- They plant euphorbia in a new pot with a different soil.
When working with a plant, you must be careful, remember that the milk of the flower is poisonous. In contact with the skin, it can cause severe burns, irritation, an allergic reaction.
In winter, euphorbia is not watered as often as in summer. After winter, the plant needs more moisture, increased watering is resumed.
Dry air
With the onset of the heating season, the indoor air becomes dry. Many flower growers often place indoor plants on windowsills, next to heating radiators. It is not surprising why these flowers then begin to wither.
To avoid this, they must be rearranged away from the heating devices. If this is not possible, place an automatic humidifier or a container filled with water near the plants. Euphorbia does not need spraying, but once a month it must be wiped with a damp sponge to remove accumulated dust.
Milkweed secret
In addition to creating a favorable environment for your pet, you can further support it.To do this, use epin, a drug that allows you to adapt to stressful situations. It also promotes plant growth and stimulates the immune system. It will be useful in the following cases:
- The plant has survived drought or waterlogging;
- Not enough light and heat;
- The soil is depleted;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Attacks by viruses, fungi or insects.
How to help milkweed with epin:
- To support the vitality of milkweed and awaken its dormant immunity, prepare a solution. It is convenient to do this in the following way. Pull the entire contents of the ampoule into a syringe. It will turn out to be 1 ml. To process the plant, a lot of solution is not needed. Enough 0.1 ml per half liter. Water must be taken settled or filtered, you can also boiled. Its temperature should be slightly warm.
- If your plant is dusty, you need to clean it before spraying. You can use a brush to remove dust.
- It is advisable to carry out the processing procedure in the bathroom with the curtains drawn (the solution is still poisonous).
- It is necessary to spray until the green mass is completely wetted.
- Pour out the rest of the solution.
- After the plant is dry, the curtains can be pulled back.
- Processing of milkweed, which is in an unfavorable environment, must be carried out every 10 days.
- The remaining epin can be stored in a syringe wrapped in a napkin on the refrigerator door.


Best regards, Galina.
Euphorbia (euphorbia) is widespread practically all over the planet
, some of its species are found only on the African continent.
The euphorbia family belongs to succulents, that is, they retain moisture inside themselves for a long time.
Despite the fact that milkweed juice contains toxic substances
, for many pests this is not a hindrance. Table of contents:
- Diseases
- Pests
- Ways to fight
Lovers of decorative species should also be aware of the presence of potential diseases that require treatment.
If you have a question: why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off and what to do about it? - most likely it's all about improper care. Insufficient lighting leads to pallor of leaves and dropping. Rapid temperature changes lead to wilting or loss of leaves.
Why does the spurge dry (turn yellow) and shed its leaves?
"Autumn Syndrome"
when the leaves of the room milkweed turn yellow and dry, and subsequently fall off, it signals insufficient watering or
excessively dry air.
Why did the euphorbia drop its leaves?
it associated with excessive watering
... It will also affect the color: the leaves will be unevenly colored.
The most common infectious diseases include fungal and viral diseases:
- alternaria;
- root and stem rot;
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- bacteriosis;
- mosaic
Fungal disease, characterized by the appearance of brown rotten spots on the leaves. Gradually increasing, the spots cover the entire leaf.
High humidity of the air leads to the fastest development of the fungus, as a result, the leaves become gray.
Infection is possible through air, water and soil, in which the fungus persists for a long time. Factors that increase the risk of infection
:
- too humid air;
- lack of ventilation;
- oversaturation of the soil with nitrogen.
To combat the fungus are used systemic fungicides
(antifungal agents). Prevention - avoid waterlogging and use rather loose substrates for planting.
The appearance of the fungus is indicated large spots
on leaves, often dark.
Older or weakened leaves are at greater risk.
Waterlogging and hot air
accelerate the development of the fungus.
The pathogen can be found in the soil and in the remains of diseased plants.
For treatment, systemic fungicides are used (Ridomil Gold, Skorr). If the air humidity is high enough, biological fungicides should be used. for prevention
.
It is characterized by the appearance on the stem, just above the soil surface, of dark depressed spots.Gradually, the infected area grows, penetrates deeply and affects the internal tissues. The stem breaks and dies. The causative agent (pathogen) remains in the soil for a long time.
This situation most often leads excessive nitrogen application
and too
abundant watering
, hot climate and lack of lighting, as well as increased substrate density.
When the first signs of infection appear, treatment with systemic fungicides is carried out, watering is stopped, and the substrate is replaced with a drier one.
The causative agent is also a fungus and manifests itself in the appearance of a fluffy plaque (powdery mildew).
Leaf tissues dry out under bloom.
If a take no action
, infection
can lead to death
succulent.
The fungus is transmitted from a diseased plant through the wind
... The dry and hot climate aggravates the situation,
overdried substrate
.
The fungus is not able to harm a healthy green body, so the best prevention is proper care
... If the infection nevertheless progresses, antifungal agents are used.
Bacteriosis is accompanied by poor growth and cessation of flowering
... The stems and leaves are striking
rotten spots
, from which a cloudy liquid with a pungent odor is released. The pathogen can be in the remains of diseased plants for a long time.
The likelihood of infection increases at high humidity
, abundant watering and increased nitrogen content.
Should to exclude
the possibility of mechanical damage, since it is through them that the pathogen penetrates.
A viral infection in which the leaf is deformed, and signs of chlorosis are noticeable on the veins.
The main signs are the appearance on the leaf blade of a pattern consisting of the smallest multi-colored spots, colors from white to yellow and red.
Most often, insects become carriers of the virus, especially - whitefly
.
Infected cuttings are better do not use
... For prevention, it is necessary to carry out insecticidal treatment.
Such a developmental deviation cannot be called a disease
, this is just a defensive reaction to open sunlight.
Coarse brown thickening is detrimental to appearance, but is by no means dangerous.
It is impossible to treat it and not necessary
, and if this view is undesirable, then you need to protect it from the scorching sun.
When aphids appear, the milkweed foliage is deformed, then turns yellow and falls off.
Watering
He loves timely watering, if you overdo it with this procedure, then his roots can rot, and the top will turn yellow and crumble. Another reason for leaf fall is insufficient moisture supply. With rare watering, the soil dries up for a long time. Therefore, it is necessary to water only when the topsoil dries out no deeper than 1 centimeter. And the water for irrigation must necessarily be at room temperature and separated, otherwise the plant can lose foliage from cold water or get sick.


Video: The simplest method of treating lemon scabbard. Diaspididae treatment
Violation of agricultural technologies leads to certain deviations in development. Infectious diseases primarily affect weakened plants
... Compliance with all the rules practically eliminates the risk of infection. However, it does happen sometimes.
The gardener's task is recognize the threat in time
... It is necessary to conduct regular examination of green pets, and if a disease is detected, take action.
Euphorbia white-veined plant is unpretentious, but there are several subtleties of care, the knowledge of which helps to grow luxurious specimens.
Diseases and pests
If he is properly looked after, and the indoor flower still withers, turns yellow, withers, then he got sick or picked up pests. With timely treatment, there is a chance to save the spurge from complete death. Unfortunately, there are those diseases for which there is no cure, in this case only timely prevention will help.
Alternaria
Large dark brown spots appear on the leaf plates, after which they turn yellow and fall off. The lower leaves are most often affected. This fungal infection occurs in too humid and hot environments, or when transplanted into contaminated soil. First, the infected leaves are cut off, then the entire top is treated with the Skor fungicide. To protect an indoor flower from this fungus, it is treated for prophylactic purposes with any biological fungicides, for example, "Fitosporin".
Bacteriosis
The plant infected with bacteriosis grows sluggishly, cannot boast of a lush top, and spots of weeping rot with an unpleasant odor appear on the leaf spots. Unfortunately, euphorbia cannot be saved from this disease. Therefore, it is important to observe proper care for it, not to overdo it with nitrogen and make sure that there is no mechanical damage, since the fungus gets inside through the wounds.


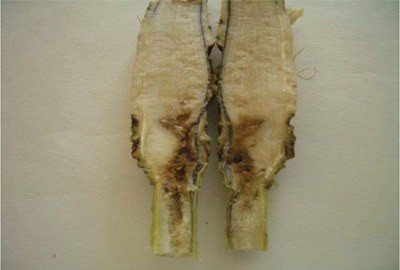
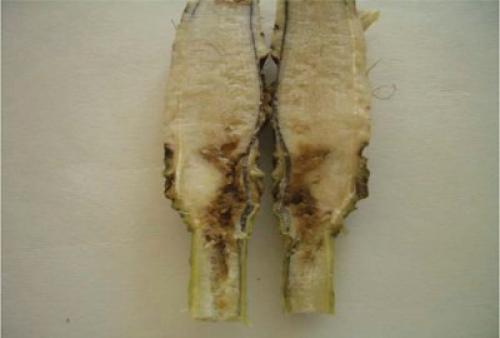
Root and stem rot
The fact that he got sick with root rot can be understood by the black spots on the stem, which are becoming more and more every day. If they do not catch themselves in time, they will penetrate inside the stem and begin to bring the flower to complete death.
The reason for the appearance of rot is most often an excess of nitrogen in the soil, frequent watering and a lack of lighting. When the first signs of infection are detected, they regulate the care of it, limit watering. Then it is thoroughly treated with the fungicide "Ridomil" or "Previkur".
Powdery mildew
This is a very common fungal disease and manifests itself as a dark gray, fluffy coating on the leaves or stem. Leaves affected by powdery mildew turn yellow and dry out. The infection is airborne in hot weather.
If the flower is rarely watered, then it becomes very susceptible to this disease. You can get rid of powdery mildew with any antifungal drugs, the most effective of which is Topaz.
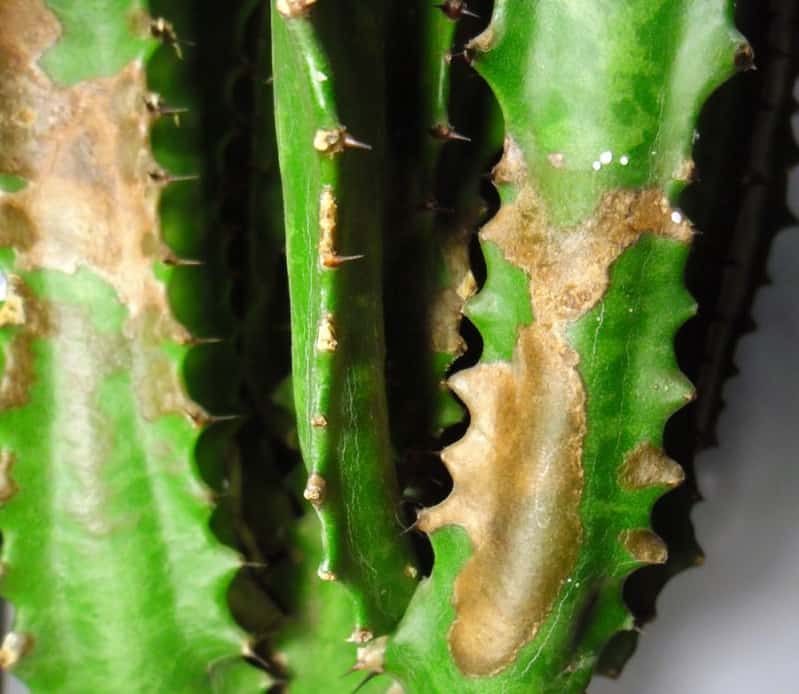
Rust
This disease can be easily identified by red raised spots on the underside of the leaves, which gradually grow and cover the entire area. If treatment is not started on time, the fungus penetrates into the milkweed stalk, which then breaks down. In this case, the flower can no longer be saved, therefore it is very important to detect this disease at an early stage.
The infected plant must be taken to another room where there are no indoor flowers. After that, all the affected parts of the apex are cut off from the infected milkweed, then it is treated once a week with a synthetic fungicide, for example, 1% Bordeaux liquid.


Gray rot
This disease manifests itself as brown rotten spots on the leaves. They spread very quickly, especially in a humid environment. This fungus is activated in conditions of high humidity, an excess of nitrogen in the ground, and insufficient ventilation of the room. Therefore, when this disease is detected, watering is temporarily suspended, the room is thoroughly ventilated and the air humidity is reduced. And the flower is transplanted into new soil and treated with any systemic fungicides.
Tobacco mosaic
This virus is carried by insects. After infection, yellow or white spots appear on the leaf blade, which can sometimes be red, and the green itself is deformed. If the disease is at an initial stage, then the flower is treated with insecticides, and a very neglected one cannot be saved. To prevent the greens from picking up the tobacco mosaic, it must be treated with any insecticides for preventive purposes.
Spider mite
It is quite difficult to see it with the naked eye. Most often, the presence of cobwebs on the greenery testifies to the infection of milkweed with this pest. The tick from the underside of the leaves sucks out all the nutritious juices, after which the greens wither and fall off.
If you look at this leaf in the light, you can see many holes.To get rid of the tick, each part of the flower is carefully wiped with a sponge dipped in soapy water. Laundry soap is more suitable for this. This solution can be replaced with Aktara. It should be remembered that the tick spreads very quickly.
It can be seen with the naked eye, it multiplies very quickly, so the procedure for getting rid of it should be started immediately. The leaves, attacked by this pest, curl, deform, after which they turn yellow and fall off, and the plant itself stops developing. This is due to the fact that aphids suck out all the nutritious juices from the room greens.
After removing the deformed parts, all greens are treated with Aktellik or each part of the top is wiped with a sponge dipped in soapy water. Before this, the soil is covered with plastic wrap so that the solution does not drain to the roots. The procedure is repeated every week until the aphids disappear completely.


Pests
The danger can come from various insects that parasitize the plant and harm it.
Aphid


When aphids appear, the milkweed foliage is deformed, then turns yellow and falls off.
Other affected areas are discolored.
The plant looks depressed normal growth and development stops.
To fight insects, you need, first of all, collect them by hand.
It is not difficult to notice them, they are yellow or light green in color. Severely affected shoots will have to be removed.
For further processing, drugs are used:
- fitoverm;
- derris;
- actellik;
- decis.
Whitefly
Whitefly larvae parasitize on the lower part of the leaves, where feed on cell sap... The first sign of their appearance is yellow or white spots on the leaf blade. Further, the milkweed foliage curls, turns yellow and, finally, falls off.
Whitefly larvae greenish color, and the adult is a white midge, the presence of which can be easily noticed.
When larvae appear, the affected areas should be cut off, and healthy parts should be sprayed with insecticides. Once every 3 days.
Root mealybug


The roots are infected, where parasites accumulate in the form of mealy clusters.
If infestation progresses, insects become visible on the root collar.
As the roots are damaged, the plant grows larger slows down growth.
The leaves first turn yellow, then dry and die off.
If insects are found, you should carefully dig up the spurge from the ground, remove the remains of soil from the roots and treat with an insecticide solution.
Pot you need disinfect and fill with fresh earth... With each transfer, you must examine the roots carefully for the detection of this disease.
Red spider mite
Spider mite small enough, only half a millimeter, light brown or red. It feeds on young leaves. If white or yellow spots appear on them, this could be a sign of the presence of a tick.
To isolate infected seedlings, sprinkle with warm soapy water. To destroy the tick, they are used acaricides.
It must be remembered that this insect reproduces very fast, and measures to combat it must be taken immediately.
Mosquitoes on milkweed


Adult mosquitoes of the Sciara family do no harm, however, they lay larvae that will parasitize the plant.
The size of the larvae is about half a centimeter, and they are especially dangerous for seedlings.
If larvae are found, the best option would be transplant immediately healthy seedlings, isolating them from the infected.
For prevention, you can treat the soil with an insecticide... Dry sand sprinkled with a thin layer on top is also not attractive to mosquitoes. Adults arriving can also be fought in the traditional way - Insect-proof Velcro.
Why does the white-veined spurge shed its leaves? Diseases
If you have a question: "Why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off and what to do about it?" - most likely it's all about improper care. Insufficient lighting leads to pallor of leaves and dropping. Rapid temperature changes lead to wilting or loss of leaves.
Why does the spurge dry (turn yellow) and shed its leaves?
"Autumn syndrome", when the leaves of the room milkweed turn yellow and dry, and subsequently fall off, signals insufficient watering or excessively dry air.
Why did the euphorbia drop its leaves?
This is due to excessive watering. It will also affect the color: the leaves will be unevenly colored.

The most common infectious diseases include fungal and viral diseases:
- alternaria;
- root and stem rot;
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- bacteriosis;
- mosaic
Gray rot
Fungal disease, characterized by the appearance of brown rotten spots on the leaves. Gradually increasing, the spots cover the entire leaf.
High humidity of the air leads to the fastest development of the fungus, as a result, the leaves become gray.
Infection is possible through air, water and soil, in which the fungus persists for a long time. Factors that increase the risk of infection:
- too humid air;
- lack of ventilation;
- oversaturation of the soil with nitrogen.
To combat the fungus, systemic fungicides (antifungal substances) are used. Prevention - avoid waterlogging and use rather loose substrates for planting.
Alternaria


The appearance of the fungus is indicated by large spots on the leaves, often dark.
Older or weakened leaves are at greater risk.
Waterlogging and hot air accelerate the development of the fungus.
The pathogen can be found in the soil and in the remains of diseased plants.
For treatment, systemic fungicides are used (Ridomil Gold, Skorr). If the air humidity is high enough, biological fungicides should be used for prophylaxis.
Root and stem rot
It is characterized by the appearance on the stem, just above the soil surface, of dark depressed spots. Gradually, the infected area grows, penetrates deeply and affects the internal tissues. The stem breaks and dies. The causative agent (pathogen) remains in the soil for a long time.
This situation is most often caused by excessive nitrogen application and too abundant watering, a hot climate and a lack of lighting, as well as an increased density of substrates.
When the first signs of infection appear, treatment with systemic fungicides is carried out, watering is stopped, and the substrate is replaced with a drier one.
Powdery mildew


The causative agent is also a fungus and manifests itself in the appearance of a fluffy plaque (powdery mildew).
Leaf tissues dry out under bloom.
If left untreated, infection can lead to the death of the succulent.
The fungus is transmitted from a diseased plant through the wind. The situation is aggravated by a dry and hot climate, overdried substrate.
The fungus cannot harm a healthy green body, so proper care is the best prevention. If the infection nevertheless progresses, antifungal agents are used.
Bacteriosis
Bacteriosis is accompanied by poor growth and cessation of flowering. Stems and leaves infect rotten spots, from which a cloudy liquid with a pungent odor is released. The pathogen can be in the remains of diseased plants for a long time.
The likelihood of infection increases with high humidity, abundant watering and high nitrogen content.
The possibility of mechanical damage should be excluded, since it is through them that the pathogen penetrates.
Tobacco mosaic
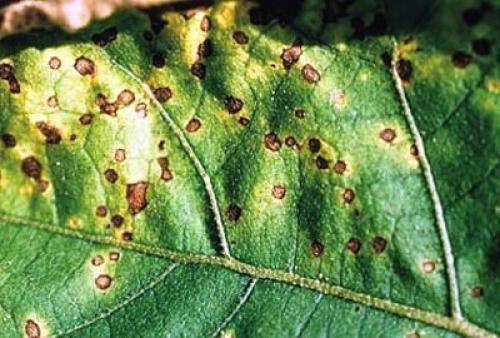

A viral infection in which the leaf is deformed, and signs of chlorosis are noticeable on the veins.
The main signs are the appearance on the leaf blade of a pattern consisting of the smallest multi-colored spots, colors from white to yellow and red.
Insects, especially the whitefly, are the most common carriers of the virus.
It is better not to use infected cuttings. For prevention, it is necessary to carry out insecticidal treatment.
Rough growths on milkweed
Such a deviation in development cannot be called a disease, it is just a defensive reaction to open sunlight.
Coarse brown thickening is detrimental to appearance, but is by no means dangerous.
It is impossible to treat this and it is not necessary, and if this type is undesirable, then you need to protect it from the scorching sun.
Why euphorbia turns yellow and sheds leaves. Turns yellow and falls
Why does the plant shed its leaves and what to do with it? This is due to:
- Burns - the plant gets them due to direct sunlight. To solve this problem, you need to put the flower in partial shade.
- Natural reasons - with the onset of autumn, euphorbia prepares for winter and its leaves can turn yellow and fall off. This is a completely natural phenomenon, which should not be feared and should not interfere with this process. He will rest and green leaves will appear again in the spring.
- Diseases or pests - you should carefully examine the plant and identify the cause, whether it is sick or infected with a pest. It is necessary to save the plant understanding what exactly caused the yellowing and falling of the leaves.
- Improper care - due to improper watering or maintenance, the leaves can also turn yellow and fall off. Care should be reviewed and errors corrected.
Watering should be moderate because, due to abundant watering, the roots begin to rot and the leaves and the entire flower suffer from this. Lack of nutrients can also be the reason - additional feeding is necessary. The temperature of the content and the lighting are also important.
How to transplant euphorbia. Description of white-lobed milkweed
Euphorbia white-veined (white-veined) is native to the island of Madagascar. There, the plant covers vast spaces with a continuous carpet, forming almost impenetrable thickets. At the beginning of the last century, it appeared in botanical gardens, greenhouses, and then in residential buildings.
Plant origin and habitat
This plant is also called euphorbia, it is from the Euphorbia family. The genus is very numerous, in nature there are about two thousand species. Among them there are grasses, shrubs and even trees.
The familiar plant came to Russia from Africa, but in our country, quite a lot of its "close relatives" grow on the fields and roadsides.
Photo gallery: wild spurge in Russia


Fischer's spurge is popularly known as the "root man"


Fire spurge (decorative) is often used in landscape design


Poisonous steppe spurge in Russia is widespread
What does the plant look like?
Whoever has seen the spurge up close at least once understands why it bears the name white-veined: the whole point is that whitish veins are clearly visible on its leaves. The appearance of the plant is unusual, flower growers refer it to cacti and palms at the same time. This is because the plant throws out a rosette of leaves from the end of a long and thorny stem.
Euphorbia belongs to stem succulents, its trunk is rounded, as the plant matures, it gradually lignifies from below. In adult specimens, lateral shoots extend from the main stem. At home, it reaches a height of 1.5–2 m. The leaves are obovate, narrowed at the base.
Why Mille's spurge sheds leaves. Description Milkweed Mil
Euphorbia Mila, or Euphorbia beautiful, or Euphorbia Mila - this perennial shrub reaching in its homeland (up to two meters high), succulent prefers even conditions and not very cool content in winter. Endemic to Madagascar.
The bush is profusely branched. The stem is grayish, slightly ribbed.At the tops of the shoots, elliptical pale green leaves are born, 3.5 cm long and 1.5 cm wide, each of them is equipped with two stipules, transformed into sharp thorns. The leaf blades of Milkweed Mille fall off with age, but strong thorns remain forever, so only the tops of the stems are covered with leaves.
The bracts of Mil's milkweed have the brightest color of all milkweed (scarlet, orange or yellow), they are round, up to 12 mm wide. Inflorescences consist of 2-4 groups of flowers, each of which is surrounded by bracts. The inflorescences are carried out from a bizarre tangle of thorns on long green legs.
In the post-Soviet space, Mil's spurge is not cultivated in open ground, most often the plant is grown at home, in winter gardens or greenhouses. Euphorbia Mila is a small shrub with thorns, densely covered with small flowers. In the photo you can see large-flowered varieties bred by breeders. Milkweed's stalks are powerful, fleshy, covered with decorative leaves of a pale green color.
The crown of thorns blooms usually in spring and pleases with its bright flowering until the end of autumn. The flowers themselves do not have much decorative value, but the bright bracts are a true decoration of the milkweed. They can be bright pink, snow-white or scarlet, and their size usually depends on the conditions of detention.
At home, the plant is unpretentious in care. Euphorbia Mila grows rather slowly, increasing in height by only a few centimeters per year. If you believe in acceptance, then Milkweed Mil is simply necessary for people suffering from any chronic ailments. The energy of the flower helps to increase the body's defenses and improve the mood of the residents. It is not recommended to place the pot with the plant in the children's room, as the bright leaves of Milkweed contain poisonous milky juice and tend to cause allergic reactions. It is necessary to take care of the plant with care; it is recommended to use rubber gloves when transplanting and pruning.


Features of the
Most often, spurge can be found on the windowsills of apartments, houses or official institutions. The plant feels good both in a lighted room and in an area of average light intensity. It is generally accepted that this plant is one of the first in the world by its genus, since it has up to 2 thousand species. It can grow in the form of a grass or shrub, as well as in the form of a small tree. A few hundred years ago, the sap of the plant was used in many fields of medicine. They could be healed and harmed at the same time. The patient received severe poisoning at the slightest mistake of the aesculapius.
Lovers of indoor plants are advised to grow euphorbia, provided that there are no preschool and primary school children in the house. If you have pets, then the flower should grow in a room where access to pets is closed. In its leaves, the culture has resin, rubber. There is also milky juice in them.


The beneficial properties of a flower are expressed in its ability to have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect on the human body. The plant is a urine and diaphoretic. Milkweed juice actively fights leukemia, therefore the roots of the plant, its leaves and juice from them are used as raw materials for pharmaceutical tinctures. They, in turn, treat stomach ailments as well as skin ailments.
It is surprising that, having poisonous elements in the juice, the plant is still susceptible to diseases and pest attacks.


Care for milkweed belozhilkov
Euphorbia can grow indoors with any orientation to light. Just do not put it in direct sunlight - the leaves can get burned, and in general the plant begins to wither ... It is very thermophilic, therefore, in winter, temperatures of at least 16-18 degrees are desirable. Euphorbia does not like drafts either.But dry air in winter tolerates well and does not need spraying.
You need to be careful with watering: water only with settled water at room temperature, abundantly in summer (but only after the top layer of the earthen coma has dried!), In winter - moderately. Both overdrying and overflowing immediately affect the appearance of the milkweed - the leaves wither, wither. Overfilling is even more dangerous. If, after drying, drooping leaves briskly rise again and the decorativeness of milkweed is restored, then overflow (especially in combination with low temperatures that cause hypothermia of the earthy coma) can cause root rot and lead to the death of your green pet.
Why are there problems with foliage and what to do about it?
Turns yellow and falls
Why does the plant shed its leaves and what to do with it? This is due to:
- Burns - the plant receives them due to direct sunlight hitting it. To solve this problem, you need to put the flower in partial shade.
- Natural causes - with the onset of autumn, the spurge prepares for winter and its leaves can turn yellow and fall off. This is a completely natural phenomenon, which should not be feared and should not interfere with this process. He will rest and green leaves will appear again in the spring.
- Diseases or pests - you should carefully examine the plant and identify the cause, whether it is sick, or infected with a pest. It is necessary to save the plant understanding what exactly caused the yellowing and falling of the leaves.
- Improper care - due to improper watering or maintenance, the leaves can also turn yellow and fall off. Care should be reviewed and errors corrected.
Read also Crusher for shredding branches price kharkiv
Opal foliage
Most often this happens for natural reasons. For example, with the onset of autumn, when the plant prepares for winter. In this case, no treatment is required. With the arrival of spring, the leaves will reappear on the flower... Also, the shower may fall off due to improper care. To solve this problem, it is necessary to correct mistakes in the care and maintenance of the plant.
Withers


lack or excess of water - it is necessary to strictly control watering;- lack of lighting - the plant should be in a well-lit place, but not in direct sunlight, to avoid burns;
- low or high temperature - it is necessary to keep the flower at a certain temperature in winter + 10 ... + 15, in summer + 20 ... + 25;
- lack of nutrients - to feed.
Went down
Why did the spurge leave the leaves? The main reason why the spurge has dropped its leaves is the improper care of the plant. Leaves sag in case of root problemthat begin to rot due to excess moisture. In order to save the plant, you need to transplant it. Remove the decayed parts of the roots before transplanting.
Why does the euphorbia flower shed its leaves? Euphorbia: leaves turn yellow and fall off
Why do milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off?
Olesya
Hello Olesya!
In autumn, for milkweed, the process of yellowing and leaf fall is natural. But if this happens in the summer, there may be problems with watering. Either the plant does not have enough moisture, or, conversely, it is being poured over. Also, the ambient temperature may be too low. It is possible that the pot is in a cold draft. It is necessary to attach the plant to a place more comfortable for it.
Favorable conditions of detention
- Watering milkweed. The most important point of well-being. Since this representative of the flora belongs to succulents, he does not like moisture too much. Moreover, overflow is destructive for him, and often the plant cannot be saved. For everything to be safe, watering should be moderate. This means: in the summer, water once a week, in the spring and autumn - once every two weeks, and in the winter, once a month is enough. Before watering, check the earthen ball - it should have time to dry out between waterings! But drying out of the soil should not be allowed.Use soft water at room temperature for watering.
- It is preferable to transplant the plant into a shallow pot. In a large flowerpot, it is difficult to maintain a favorable watering regime.
- The best place for milkweed. The plant loves sunlight, but direct rays are destructive for it. It feels good on a south or southeast window. The optimum temperature during the growth period is 22 - 25 degrees.
- Top dressing for green and strong leaves. From spring to autumn, it is recommended to feed your pet every 2 weeks with special fertilizers intended for cacti. Lack of nutrients negatively affects the plant: milkweed leaves turn yellow and fall off.
- In winter, the plant should have a dormant period. For this, it is desirable for him that the ambient temperature is not higher than 15 degrees. Watering is moderate. If the temperature is higher in winter, additional lighting should be provided, otherwise the stem will bend. A fluorescent or LED lamp will do.
Milkweed secret


In addition to creating a favorable environment for your pet, you can further support it. To do this, use epin, a drug that allows you to adapt to stressful situations. It also promotes plant growth and stimulates the immune system. It will be useful in the following cases:
- The plant has survived drought or waterlogging;
- Not enough light and heat;
- The soil is depleted;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Attacks by viruses, fungi or insects.
How to help milkweed with epin:
- To support the vitality of milkweed and awaken its dormant immunity, prepare a solution. It is convenient to do this in the following way. Pull the entire contents of the ampoule into a syringe. It will turn out to be 1 ml. To process the plant, a lot of solution is not needed. Enough 0.1 ml per half liter. Water must be taken settled or filtered, you can also boiled. Its temperature should be slightly warm.
- If your plant is dusty, you need to clean it before spraying. You can use a brush to remove dust.
- It is advisable to carry out the processing procedure in the bathroom with the curtains drawn (the solution is still poisonous).
- It is necessary to spray until the green mass is completely wetted.
- Pour out the rest of the solution.
- After the plant is dry, the curtains can be pulled back.
- Processing of milkweed, which is in an unfavorable environment, must be carried out every 10 days.
- The remaining epin can be stored in a syringe wrapped in a napkin on the refrigerator door.


Best regards, Galina.
Euphorbia white-veined. Common problems
| Leaves fall | Two reasons are considered - lack of moisture or phosphorus in the soil. | The watering regime is normalized. If there is no moisture deficit, an extraordinary fertilizing with fertilizer with a high phosphorus content is carried out. |
| Darkening of leaves | Insufficient, poor lighting. | Rearranged to a lighter place, if necessary, artificially illuminated. |
| Stem decay | A combination of low temperatures with high soil moisture. | The damaged area is cut out, if possible, treated with a fungicide. Watering is temporarily stopped until the soil is completely dry. Watering is resumed gradually. |
| Lethargy leaves, stem shrinkage | Lack of moisture. | Watering is carried out as the soil surface dries up. |
| The appearance of white bloom on the leaves | Mealybug lesion. | The leaves are wiped with alcohol, washed with soapy water. Depending on the degree of damage, it recommends 1-3 times treatment with insecticides. |
| The appearance of silvery or yellow spots on the underside of the leaf | Possibly thrips damage. Examine the plant carefully. | If a pest is found, treat the flower with insecticides three times at weekly intervals. |
Why euphorbia sheds leaves
All these factors are stress for the plant, and to any stress, even the most insignificant, the white-veined euphorbia reacts by rapidly shedding its leaves. [K]
Mass fall of the leaves of white-veined milkweed is also observed in autumn, when the light becomes less. Depending on the degree of lighting and the correctness of watering, the plant can shed either part of the leaves, or go for the winter without any hair at all. But in the spring, leaves will certainly appear on it. Some growers, in order to activate the process of the appearance of leaves, arrange a hot shower for milkweed in the spring (two to three times). But we did not use this technique.
If in white-veined milkweed only the lower leaves turn yellow and fall off, this is a natural process, it is typical for it to have leaves only in the upper part of the trunk. And so that it grows evenly leafy on all sides and has a beautiful appearance, from time to time turn it in different directions towards the light. And from spring to autumn, feed your green friend with flower fertilizers at least once every two months (it is better to take those intended for cacti).
The flowers of the white-veined milkweed are small, not of interest. If you do not need seeds, remove them by blotting the milky juice with a tissue. The peculiarity of this milkweed is that when the seeds ripen, it shoots them wherever it hits, and numerous seedlings quickly germinate in other pots. Then you get tired of pulling them out.
Euphorbia is a poisonous plant?
Just remember that milkweed milk juice is poisonous, so be careful when caring for this plant.
Any loose soil with the addition of sand is suitable for it. Drainage is required. It is better to take a pot wide (but corresponding to the size of the plant) and shallow, since the white-veined milkweed has a superficial root system. Transplant it as it grows. For a large plant, the container is taken heavier so that it does not tip over. Or stabilize the pot by placing more stones on the bottom.
They write that white-veined euphorbia is damaged by aphids, scale insects, spider mites ... Pests were not noticed on our milkweed.












