- 2 Briefly about the variety of these beauties
- 3 What should be the care?
- 4 How to distinguish fungal diseases?
- 5 Save a rose from powdery mildew
- 6 Viral diseases - a verdict for roses?
- 7 Spider mite and control measures
- 8 How to win the war against other pests?
- 9 Consequences of improper care
Protecting roses from disease
Roses not without reason, they are considered the queens of flowers. Accordingly, well-groomed ones are a decoration of any garden, regardless of the style of arrangement. Plants, however, need to provide good light and soil conditions and systematic maintenance. Protection procedures play a very important role - especially against fungal and physiological diseases. The main thing, if they appear, is prevention. What work to do to minimize the risk of disease?
- Cultivation of varieties resistant to this pathogen;
- Planting plants at a sufficient distance from each other (not densely);
- Avoid waterlogged or periodically flooded soils;
- Plant protection before the onset of winter (digging in and covering);
- Termination of fertilization at the end of summer (especially nitrogen);
- Limiting the moisture of the bushes during watering;
- The use of agents that increase the immunity of plants (eg Gamair, Trichodermin);
- Alternate use of fungicides (so that the pathogen does not adapt to the active substances).
Causes of rose diseases
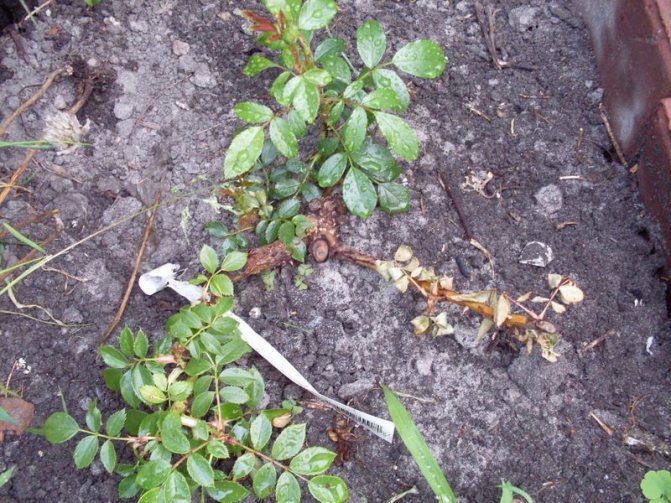
A plant can hurt if the gardener, due to inexperience, cuts the bush incorrectly and the damaged areas do not overgrow. You should not water the bushes in the evening. If the infected indoor flower is not removed from the windowsill in a timely manner, the disease will destroy the rest.
The fungus quickly infects roses that grow in a cool or, conversely, too warm room with high humidity. Watering should be done in a timely manner. If the grower overmoistens the soil or water the plant a little, then it weakens and quickly loses its immunity. It is important to fertilize the rose bush in a timely manner so that it has the strength to fight viruses and fungus.
Diseases of roses - symptoms and treatment
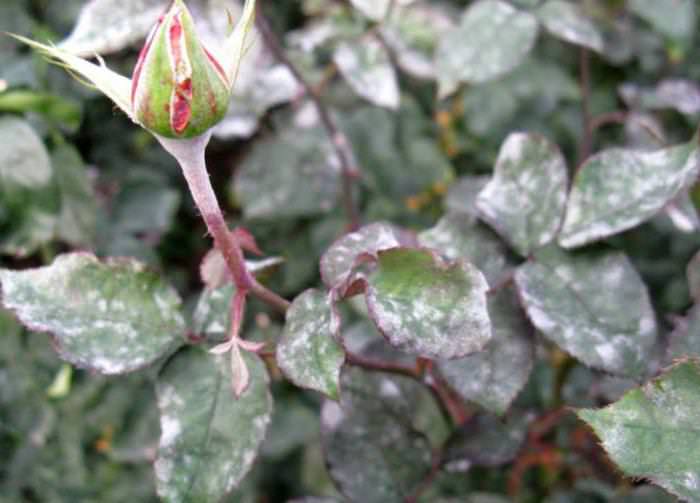
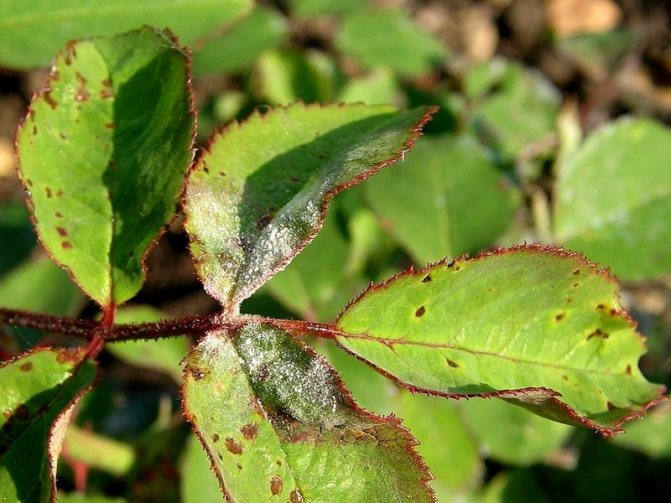
Powdery mildew
Symptoms: fungal disease, manifested by the appearance of a white bloom on the plant. Affects young developing leaves first. Later it is especially noticeable on old leaves and shoots. On the leaves, plaque appears on the upper side, and on the lower, there is no plaque. In addition, the top side of the leaf blade may turn red. No stains on the leaves. After a while, the affected leaves are deformed and fall off.

Defeat of shoots.
Scheme of treatments for roses from pests and diseases
The consequences of improper care
Pests and diseases can deprive you of a pet, but sometimes we ourselves can cause such a loss by making mistakes during care. For example, changing habitat conditions can lead to drying of the flower. In this case, the previous microclimate should be resumed and pruning should be carried out. And excessive moisture and excessive irrigation will lead to rotting. Reanimating such a plant is a rather difficult task. To do this, remove the rose from the pot and cut off the rotten roots. Next, we transplant the plant into new soil and prevent overflow. At the same time, complete drying out of the soil should be avoided.
But insufficient watering leads to drying out of the plant and without proper care the problem cannot be solved. All dead shoots should be removed, but only so that a few centimeters remain to the trunk. Then we water the inhabitant of the pot and place it under a plastic bag. In this way, the desired humidity can be ensured. As soon as young shoots appear, you need to start airing the "greenhouse" so that the plant gets used to dry air.
Protecting roses from disease
Roses not without reason, they are considered the queens of flowers. Accordingly, well-groomed ones are a decoration of any garden, regardless of the style of arrangement. Plants, however, need to provide good light and soil conditions and systematic maintenance. Protection procedures play a very important role - especially against fungal and physiological diseases. The main thing, if they appear, is prevention. What work to do to minimize the risk of disease?
- Cultivation of varieties resistant to this pathogen;
- Planting plants at a sufficient distance from each other (not densely);
- Avoid waterlogged or periodically flooded soils;
- Plant protection before the onset of winter (digging in and covering);
- Termination of fertilization at the end of summer (especially nitrogen);
- Limiting the moisture of the bushes during watering;
- The use of agents that increase the immunity of plants (eg Gamair, Trichodermin);
- Alternate use of fungicides (so that the pathogen does not adapt to the active substances).
The causes of powdery mildew
If the weather is sunny and warm outside, the flower is regularly watered, and the soil is cultivated, then the plant is unlikely to be susceptible to this fungus.
When can powdery mildew appear?
- If the weather is cold outside, high humidity, as well as in the season of heavy rains. The weather affects especially strongly when growing a plant in a garden or on a balcony. For a room rose, this is not too important;
- Excessive amount of nitrogen in the earth;
- Failure to comply with the watering regime of the flower.
Diseases of roses - symptoms and treatment
Powdery mildew
Symptoms: fungal disease, manifested by the appearance of a white bloom on the plant. Affects young developing leaves first. Later it is especially noticeable on old leaves and shoots. On the leaves, plaque appears on the upper side, and on the lower, there is no plaque. In addition, the top side of the leaf blade may turn red. No stains on the leaves. After a while, the affected leaves are deformed and fall off.
The reasons: Infection occurs during long, persistent warm but rainy weather. Improper care also contributes to its appearance - excessive watering, spraying the plant and too tight planting.
Prevention and treatment: it is better to spray the bushes for the sake of prevention in the pre-spring period - even before the leaves develop. Most often, a universal remedy (Miedzian 50 WP or Miedzian Extra 350 SC) is used - 2-3 times for 10 days. Alternatively, use natural remedies such as horsetail, nettle, and garlic. Old, fallen leaves should be collected with a rake and burned. After the onset of symptoms of diseases, the bushes must be sprayed several times, with an interval of several days, with drugs: Topsin-M, Alirin, Score, Gamair.
Downy mildew (Peronosporosis)
Symptoms: Initially, the disease is manifested by the appearance of light yellow, irregularly shaped spots on the leaves. Mostly affects the upper leaves. Over time, the spots can grow and turn red. On the underside of the leaf blade, a white, fluffy fungus forms, and on the upper side, there is no plaque. Infected leaves fall off. Peronosporosis can also affect shoots and flowers.


The reasons: Damp weather, poor air circulation and cultivation of varieties that are not sufficiently resistant to the fungus contribute to the disease. It is also often found on roses growing on heavy, non-penetrating soils.
Prevention and destruction: the fight against the disease looks the same as in the case of powdery mildew - in particular, it is recommended to use Miedzian during the leafless period. Cut and burn affected shoots. After the first symptoms appear, the plants are sprayed several times, for 7-10 days, with fungicides: for example, Score, Tiotar, Baymat.
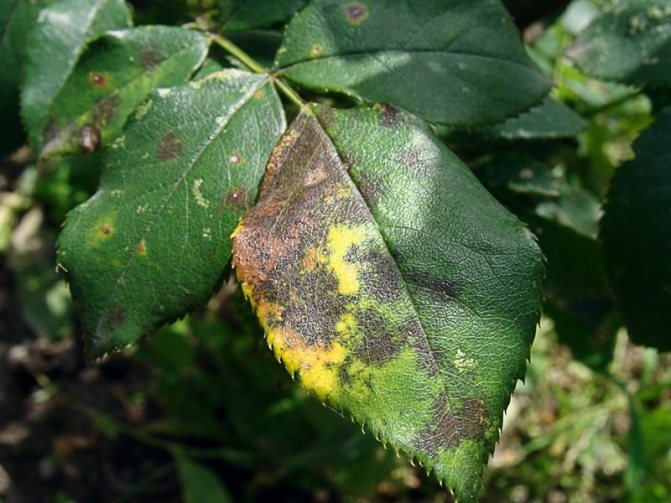
Black spot of rose leaves
Symptoms: considered the most dangerous disease in this group of plants. Initially manifested by the appearance of light brown spots. Later, the affected areas turn black, and their edges turn yellow. Leaves fall massively. In the autumn, the plant sometimes loses most of its leaves. Then it produces a large number of new, weak shoots that are not ready for the arrival of winter and freeze through. The pathogen hibernates in the left shoots and leaves.


The reasons: one of the reasons is moderate weather (15-27⁰С). The intense heat inhibits the development of the fungus. The appearance of spotting is also facilitated by soaking the plants and growing varieties that are not resistant to the fungus.
Prevention and treatment: affected leaves and shoots must be removed. In the period when there are still no leaves, it is recommended to spray roses, for preventive purposes, with a fungicide (Miedzian, Baymat). The procedure is performed 3-4 times for 10 days. In addition, during the entire growing season, it is worth spraying with natural preparations - from horsetail and nettle. Weeds must not be allowed to grow. Multi-component fertilizers should be used - preferably slow-acting. After the first symptoms appear, the bushes are sprayed several times, every 7-10 days with preparations: Score, Tiotar, Bravo.
Rose rust
Symptoms: Orange spots appear on the outside of the leaves. On the underside, dense clusters of spores form - rusty lumps. The disease affects most of the leaves, which are deformed, gradually dry up and fall off. Shoots are also affected. The appearance of rust increases in the spring - in April and May. The fungus hibernates on shoots and fallen leaves.


The reasons: Rust most often affects large specimens grown in heavy, swampy and poor soils.
Prevention and treatment: Avoid places with poor air circulation and planting in poor quality soil. The affected leaves must be removed and burned. Having noticed the first signs of the disease, the following drugs are used: Bravo, Score, Ditan Neotek 75. Spraying is repeated several times every 7-10 days. When spraying, pay special attention to the underside of the leaf blades.
Anthracnose
Symptoms: Initially manifested by the weakening of individual shoots. Elongated gray-brown spots appear on their surface. On the affected shoots, the leaves turn yellow and turn brown. Shoots in places of necrosis break easily.
The reasons: The development of the disease is facilitated by hot weather with high air humidity (favorable conditions for the development of anthracnose are air humidity of about 90% and a temperature of over 22 ° C). Often appears during vegetative propagation of roses - rooting of cuttings.
Prevention and treatment: Incinerate contaminated parts. If you notice the symptoms of the disease in time, the use of fungicides (Bravo, Topsin) can help.
Verticillosis
Symptoms: the disease leads to darkening of the shoots and fading, starting from the tops. Leaves wither and fall. The fungus infects the shoots from the base and causes vascular blockage. This can be seen on the cut of the shoot - woodiness is visible. As a result, a strongly weakened bush, after several seasons, dies.
The reasons: The fungus usually appears in the second half of summer, during wet weather or after improper care procedures.
Prevention and treatment: affected shoots and stems should be cut and burned (sometimes whole bushes). The cutting site must be lubricated with an antifungal agent (eg Funaben). Fallen leaves must be removed. For preventive purposes, plants can be added with diluted liquid manure with garlic.
Preventive measures
The rose is quite moody and requires attention to care. She is often sick and affected by harmful insects. It is difficult to treat the bush, so it is much easier to do timely prevention than to deal with the pathogen.
It is important to water it correctly, loosen the soil, weed the weeds and be sure to feed it. If all this is done, then the rose will have sufficient immunity so as not to contract diseases. To prevent insects from growing on the bushes, it is necessary to maintain an optimal moisture level and constantly spray the plant. So, you can save the bush from damage by many insects, for example, a spider mite.
But excess moisture has a detrimental effect on the flower and provokes the development of fungal infections. Therefore, the florist is advised to carefully monitor the illumination, correct watering and temperature in the apartment. At home, a houseplant is often affected by a spider mite. It is almost impossible to cure a bush from this pest. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended for prevention once every 30 days to treat the rose with special preparations against pests. On infected plants, this will reduce the number of mites that appear.
For the prevention of fungus and bacterial diseases, the flower is sprayed with fungicides. It can be Fitosporin, Sporobacterin. Usually, treatment once a month is enough to protect a delicate flower from diseases.
Now read:
- Variety of shapes and colors Calathea from the Marantov family
- How Chinese cabbage is grown outdoors
- Exquisite junkus (sitnik) spiral in the interior
- Taking care of evergreen succulent: wax ivy
About
Agronomist of the state agricultural enterprise "Garovskoye" of the Khabarovsk region of the Khabarovsk region.
Powdery mildew on roses - why is it dangerous
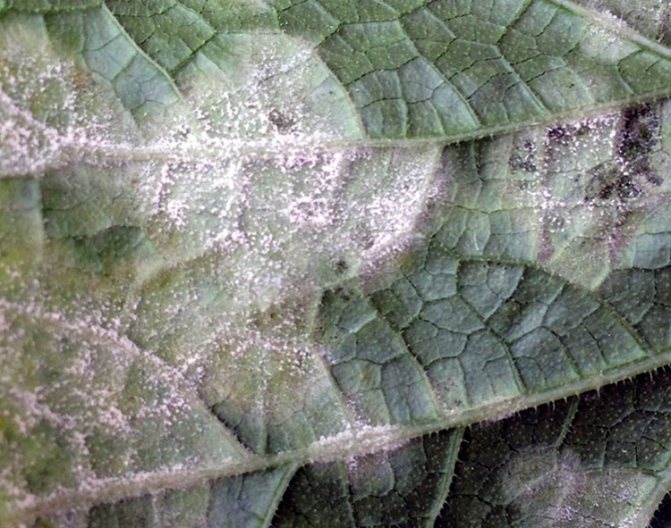
The disease is very aggressive, rapidly developing, covering the entire green surface of the plant. At first, the white spider webs of mushrooms, located in the form of separate spots, can be removed mechanically - they are simply erased with your fingers. But in subsequent stages, the spots merge, affecting an ever larger area, and penetrate into deeper layers. The plaque itself begins to darken and acquire a brown color. On its surface, you can see many black dots, which indicates the maturation of the mushroom body. Under the influence of this process, the leaves dry out, become brittle, curl and die off. Affected rosebuds either do not bloom, or bloom with sick and ugly flowers with an unpleasant odor.
Fight against downy mildew on shrubs
Downy mildew on grapes
Downy mildew on grapes is called mildew. This is the most dangerous disease of European crop varieties, brought to the south of France from North America in 1878. If left untreated, this disease can cause serious damage to the vineyard. Peronosporosis, or mildew, affects the leaves, tops of shoots, inflorescences, antennae, ridges and young grapes.


It is necessary to start processing grapes with mildew even before the first symptoms of the disease appear, that is, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of the plant with Acrobat TOP, Cabrio TOP, Delan and Poliram. Treatments are carried out before flowering, and then with abundant and frequent dew, rain and high humidity, once a week, and in dry weather, once every two to three weeks. During the season, two to eight sprays are carried out.
Growing grapes in the garden - planting and care
Preventive actions
Powdery mildew causes a lot of damage to garden roses, so prevention is an important aspect to avoid contamination at all. It is worth starting with choosing the right place: in shaded places, there are more chances for the development of flour. Dense plantings also impede good lighting, allowing spores to be transported more easily from plant to plant. Before planting a rose seedling, it is advisable to treat the soil with an antifungal solution.
The watering regime is very important: excess moisture will cause the activation of spores. To avoid waterlogging of the soil during the rainy period, roses must be planted in the soil with drainage.
Excess nitrogen is also a factor in the development of the disease, therefore, so that powdery mildew does not occur on roses, precautions when applying nitrogen-containing fertilizers and dressing are very important.
Regular weeding and preventive spraying with fungicides of roses will significantly reduce the likelihood of the occurrence and development of fungus. In the fall, all residues of vegetation on the site should be removed. If during the season it was necessary to fight the disease, then at the beginning of the next season it is necessary to repeat and thoroughly process the entire garden. Specimens that have died from the disease should be burned, and not thrown away as waste. The best prevention is the implementation of all points of agricultural technology required for a given crop.
Video "Fungal diseases of roses - powdery mildew"
What do you need to know before buying roses?
This truly royal flower easily wins hearts, and it is a shame when it dies as a result of improper care. In our article, we will consider not only the means of dealing with problems that have already arisen, such as pests, fungi and viruses, but also how to prevent them. To do this, you should learn a little more about the features of the plant.


Indoor rose
Rose is a collective name for various representatives of the Rosehip genus. At the same time, the main part of the varieties was obtained through breeding. Most of the species are thermophilic, but there are also some representatives that survive even in a rather harsh climate. Indoor plants are preferably placed on windows on the south side, as they love the sun. If you settle this representative of the flora in the shade, then it may not bloom at all.
Preference should be given to neutral soils. But if you want the flower to have a more pronounced color, then you need to plant it in soil with an alkaline reaction. It is very important that the land is well drained. In this case, you should not move the newly acquired resident to another pot. It is necessary to allow the plant to adapt to new conditions, and only then can a transplant be started.
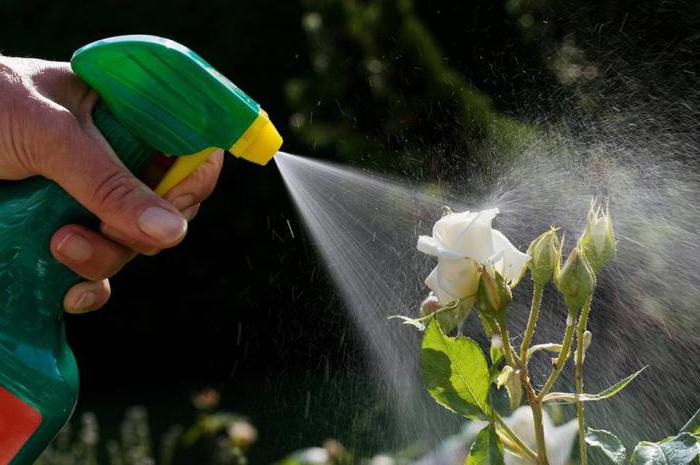
Controlling powdery mildew
If a rose bush is really affected by this type of fungus, then it is important to know how to get rid of powdery mildew without consequences and permanently. Three sprays are carried out during the growing season. Preparations must be specialized, or it can be fungicides that necessarily contain potassium bicarbonate.
Treatment is done with the following antifungal chemicals:
- Topaz100ES,
- Acrobat MC,
- Fundazol,
- Vitaros,
- Speed,
- Amistar Extra,
- Previkur.
- Fitosporin M
Useful properties of vermicompost
With the processes of detoxification at the level of biochemical reactions, in the case of feeding roses with biohumus, there is an enhanced development of the root system and, accordingly, its improved water supply. The drug is distinguished by the ability to accumulate in living cells surrounding the area of tissue affected by the parasite, low molecular weight antibiotic substances - phytoalexins, which damage the cells and membranes of fungi. Also, the beneficial effect is manifested in the activation of ion-exchange processes in the cells of the host plant and depolarization of the plasma membrane of the powdery mildew cell.


Measures to combat the use of folk methods
A good result of the treatment of powdery mildew on roses is given by folk remedies. Long-term experience in growing roses has led to the emergence of many recipes that are measures to combat the use of more familiar and environmentally friendly ingredients than agrochemicals.
Soda: 7 grams of fragrance-free liquid soap and 30 grams of soda ash is diluted in 5 liters of settled water at room temperature. Laundry soap can be used. Processing is carried out 2-3 times a week.
Copper sulfate: 7 grams of copper sulfate are diluted in 300 ml of hot water; in another container in 5 liters of water, stir until complete dissolution of 5 grams of laundry soap; then gradually pour a solution of copper sulfate into a soapy solution with constant stirring. They are processed 3 times a week.
Potassium permanganate: 2.5 grams per 10 liter bucket of water. Sprayed after five days.
Horsetail: 100 grams of green mass is brewed in a liter of boiling water. Insist for a day, then add another 6 liters of water and process every three days.
Ash: 1 kg of raw materials is diluted in 10 liters of settled water at room temperature. Withstand for a week, stirring 3-4 times per period. Processing is carried out every day. To increase the viscosity, you can add 5 grams of soap.
Mustard powder: 2 tablespoons of raw materials are diluted in 10 liters of heated water. The cooled mixture is sprayed with plants every day or every other day.
Garlic: The teeth of one middle head are ground into a gruel. Insist in 1 liter of water during the day.
Cow dung: the rotted mass is poured with water 1: 3 and kept for three days. After a while, water is added, doubling the volume and used to process leaves and shoots.
Whey: Prepare a mixture of the substance with water in a ratio of 1: 5 and process every 4 days.
Viral diseases - a verdict for roses?
In addition to fungal infections, there are also infectious diseases. One of the most terrible ailments of the rose can rightfully be called bacterial cancer. In this case, the stems and even the roots of the plant, depending on the type of disease, are covered with lumpy growths or rounded depressed spots. The affected areas gradually die off, but the bacteria continue to live in the soil for several more years.
To avoid mass infection, it is not enough just to remove the affected areas, they should be disinfected in a solution of copper sulfate for several minutes. In no case do not throw the soil in which the infected plant grew into the garden or vegetable garden, as you risk being left without a crop for several years.


Infectious burn on a rose
Rose jaundice is also dangerous. The causative agent of this infection is carried by pests such as leaf flies and leafhoppers. You can determine the disease by the yellowed veins of young leaves. In addition, over time, the leaves themselves begin to brighten and deform, if you do not take measures, then larger areas of yellow appear, and the plant weakens. The affected areas are cut and burned. And if the flower cannot be saved, then it should also be burned.
But these are not all diseases, it is worth paying attention to the rose wilting virus. In this case, the buds are not tied, the leaves become narrower and gradually dry out, and the young shoots do not grow. As a result, the bushes dry up completely. The same measures to combat the disease are applied as in the previous case.
There is also an infectious burn. Spots appear on the leaves with dry patches in the center. Their color can be either light brown or darker. Raspberry edging is characteristic. The affected areas rapidly increase in size with poor ventilation. After the spots ring the shoot, it dies off completely. It is best to cut off the infected shoots, but if the disease has not had time to develop, you can save the plant without such radical action.It is necessary to completely clean off the stain with a knife and cover the already healthy tissue with Ranet.
Regardless of the disease, the tools used for pruning must be disinfected. They are treated with either a solution of potassium permanganate or alcohol, otherwise there is a risk of transferring the infection to other plants and losing them. In addition, do not underestimate the danger that pests can pose, because they not only spoil the flora themselves, but also carry various viruses.
Basic rules for processing roses
How to fight and what remedy for powdery mildew to use on roses, each grower chooses for himself. But it is important to remember a few features that should be paid attention to:
- before processing, remove affected leaves, shoots and buds;
- after spraying, it is advisable to abundantly water the topsoil under the bush with the same product or replace it;
- processing must be carried out thoroughly, abundantly wetting the entire surface of the leaves, stems and other organs of the bush;
- the procedure should be performed in cloudy weather or at dusk, this will help prevent burns to the plant;
- when processing a diseased plant, it is advisable to process the entire site, garden, front garden;
- It is better to prevent powdery mildew on roses with folk remedies: they not only protect against infection, but also in case of illness will help to quickly defeat the disease, so in most cases the components are also fertilizing and means that increase the plant's immunity.
What should be the care?
Most varieties of indoor roses are susceptible to various diseases, and only with proper care of the inhabitants of the pot can a strong plant with good immunity be grown. It is imperative to maintain the required temperature regime. Despite the fact that the flower is thermophilic, during the dormant period from October to February, it is better to keep it in a cool room. Do not forget to regularly ventilate the room, even if it is frosty outside the window, and in the summer, move the inhabitant of the pot to the balcony or garden altogether.
The earth should not be allowed to dry out, since after this the plant does not recover well. Water the soil in time with warm water and fertilize. Top dressing is best done every two weeks. To maintain the desired moisture level, it is necessary not only to water the ground, but also to spray the leaves.
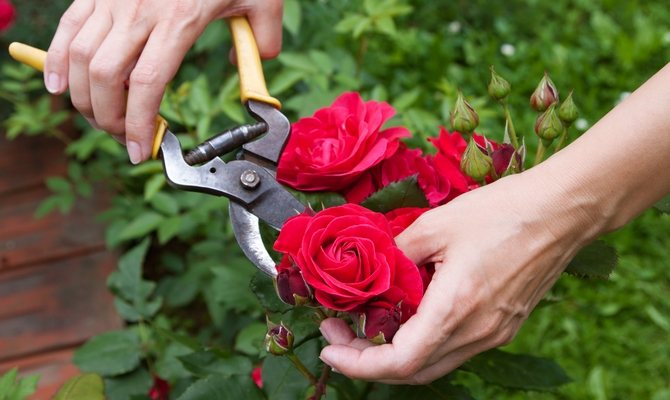


Pruning a rose
It is best to replant in spring and very carefully so as not to disturb the root system. Carefully remove the earthen lump with roots and place it in a new pot of slightly larger volume. In this case, the top layer of the earth should be removed, it has a characteristic white coating - protruding salt.
It is also important to carry out timely pruning. In the spring, all weak and small twigs are removed. It is enough to leave only 5 well-developed shoots. If their wood is sufficiently ripe, then these shoots are cut into 3–6 eyes, 4–5 can be left on the processes of moderate growth. But weak branches are shortened by only 3 eyes. Then the representative of the flora must be immediately taken out to a cool place, and as soon as the first green leaves appear, we place the flower on a well-lit window. It is worth noting that the cooler it is in the room, the longer the rest period will last.
Downy mildew on roses
Unlike powdery mildew, downy mildew can be caused by five different types of pseudo-fungi belonging to the Oomycete class. Another name is peronosporosis. With this disease, only young leaves and shoots are most often affected, and a mealy bloom appears on the lower surface of the leaf. A distinctive feature is the growth of shapeless spots on the upper side of the leaf, orange, purple, brown or brown. The leaves begin to corrugate. The green organs of the plant dry out and die off.
Less commonly, old leaves and buds are affected. There is a loss of color juiciness and brightness, wilting and drying.
The factors contributing to the onset of this disease are the same as those of powdery mildew. In most cases, peronosporosis appears due to the growth of a culture on acidic and heavy soils.
To protect roses from downy mildew, the same preventive measures are taken as for the aforementioned disease. However, such prevention will help to avoid ailments caused by other types of fungi. Folk remedies are also universal for both diseases.
Treatment is carried out by processing the plant and the soil under it. Sulfur is used, 70 grams of which is dissolved in a 10-liter bucket of settled water, and the following drugs: Glyokladin, Gamair, Fitosporin-M, Alirin-B, Planriz.
What to do as a preventive measure?
So that the powdery mildew fungus does not disturb the rose garden, they resort to preventive measures:
- Roses are planted in sunny and calm places.
- The soil for planting should be loose, nutritious, with neutral acidity.
- A sufficient interval is observed between the seedlings, the minimum distance is 25-50 cm. The planting of the bushes depends on the characteristics of the variety. Tall specimens are located farther than dwarf ones.
- The trunk circle must be dug up, all weeds and dry foliage must be removed.
- How to treat the bushes to prevent the development of powdery mildew? As a prophylaxis, pink bushes are treated with Bordeaux liquid in early spring before flowering and in late autumn after leaf fall. After the elimination of the disease, the treatment is fixed with additional treatment with a fungicide.
- Of the fertilizers, preference is given to organics and potassium-phosphorus complexes. Nitrogen-containing preparations are used until mid-July. Before flowering, superphosphate and potassium nitrate are added under the bush. These fertilizers increase the resistance of roses to fungus.


Treatment - When powdery mildew is found, the leaves are plucked from the bush. All leaves and shoots on which spores can overwinter must be removed.
- The bushes should be watered at the root, with warm water, preferably rainwater. Enough 1-2 waterings per week in the summer.
- In one place for 2 years in a row, it is better not to plant crops susceptible to disease.
- Choose varieties of roses that are resistant to fungus.
More often than others, a powdery mildew fungus affects remontant varieties and hybrid tea roses. These types should be given special attention.
The fight against powdery mildew on garden roses will end in success only with an integrated approach. The gardener, who took care of the health of the flower garden at the planting stage, the bushes are less susceptible to fungal and other diseases. Preventive measures reduce the likelihood of harmful effects to a minimum.
Choosing varieties of roses resistant to powdery mildew
If there is no possibility or desire to carry out thorough care, adherence to agricultural technology and treatment, or the conditions do not allow, then thanks to the selection, varieties of roses were bred that can withstand powdery mildew and peronospora. Disease resistance does not mean that the varieties are represented by a meager assortment, or the roses themselves will not be so beautiful. All groups of roses have such representatives.
- Cadillac. A miniature bush with red double flowers with an orange tint. The re-flowering shrub will be able to survive in shade and rainy weather.
- Westminster. Hybrid tea rose with varieties with different shades. Large double flowers have a delicate aroma. It is a hardy specimen.
- Crocus Rose. Sprawling bush with drooping shoots. It blooms with many rosettes. Also has several varieties. The bush can reach 120 centimeters even in the shade. Disease resistant.
- Rosaman Jeanon. Dense double flowers with delicate flowers of pale pink at the edges and cream on the inside. Delivers a delicate apricot aroma. Since it is resistant to diseases, it will get along well in group plantings.
- Gloria Day. Hybrid tea rose with large velvety orange flowers. It emits an intense aroma.Has varieties with other shades. The bush reaches 120 cm. It is an unpretentious representative, does not require special care. Suitable for growing by beginner growers.
- Halle. Tea-hybrid representative. Flowers look very impressive due to the rich orange color. Will grow in environments where there is a risk of powdery mildew disease.
- Hot chocolate. Very resistant to powdery mildew and downy mildew. The flowers are double, rich red-brown color. Has a scent.
- Aphrodite ChG. Hybrid tea rose with unpretentious character. Has a spicy scent and lush and double pale pink flowers
All of the above representatives tolerate acclimatization well in areas with high humidity. They can be grown in a greenhouse method, as they resist fungal diseases.
In the photo, the varieties of roses are the most resistant to powdery mildew.
Powdery mildew, downy mildew and similar diseases can cause serious damage to individual plants and the entire garden. Prevention and proper treatment will help avoid serious losses. Some varieties are less susceptible to infection, but you should not think that they do not require care and prevention, or cannot get sick at all. But often it is enough to comply with all the rules of agricultural technology to prevent diseases.
Briefly about the variety of these beauties
Now about the most common types of indoor roses. The most popular species are polyanthus and miniature plants. The first were bred by crossing climbing and tea varieties. Such representatives of the flora bloom all year round, while their small double flowers are odorless. But some miniature specimens can fill a room with an amazing aroma. They got their name because of their small size. But despite such compactness, the bushes are covered with dense foliage, and the terry inflorescences are distinguished by an elegant shape. The homeland of such roses is China.
More rare representatives can be called hybrid tea varieties, which were bred by crossing remontant and tea roses. The main difference between this type is a delicate refined aroma and rather large flowers.
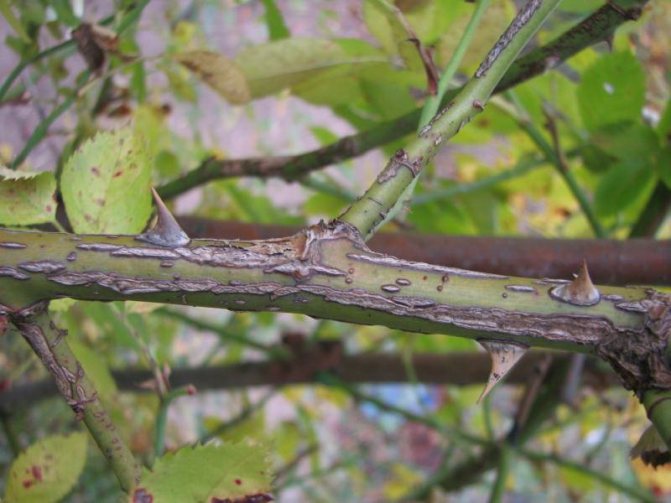
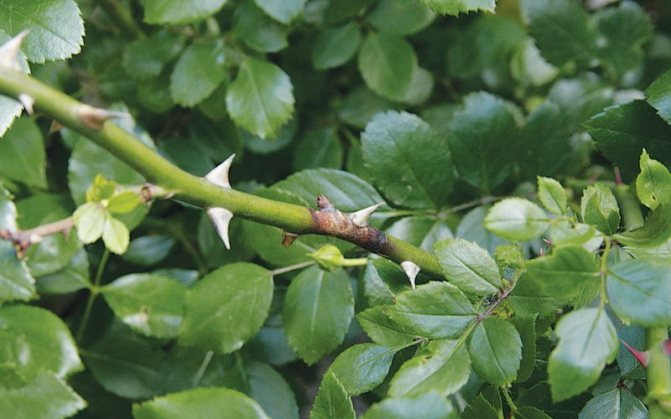
Infectious burn or stem cancer (Latin Coniothyrium wernsdorffiae)
It is provoked by the fungus Coniothyrium wernsdorffiae. The plant becomes infected in the autumn-spring dormant period. Spores penetrate through cracks in the stem of a rose formed from frost, or wounds left after improper pruning, or without treatment with garden var.
The disease affects all types of roses and can spread to blackberries and raspberries through poorly disinfected instruments. Spores of stem cancer are carried by water, humid calm weather and late, after July 20, fertilizing with nitrogenous fertilizers contribute to reproduction.
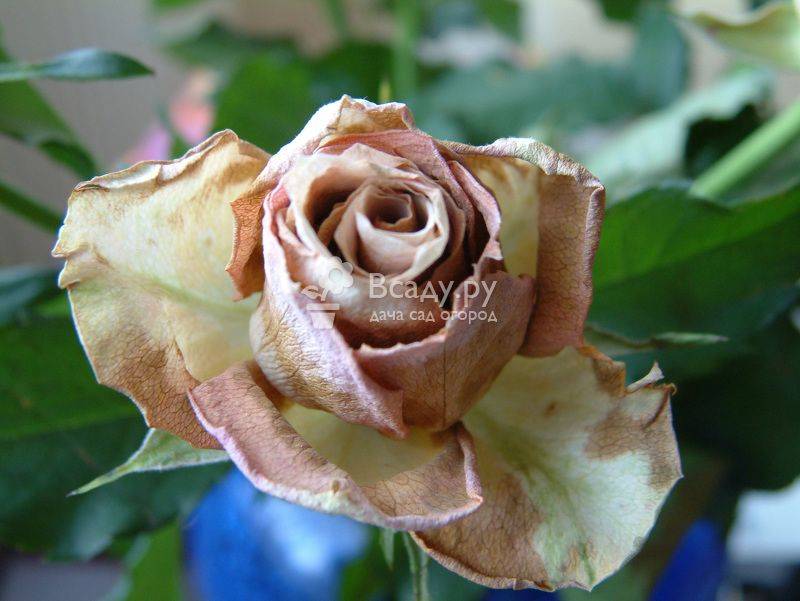


The consequences of an infectious burn on a rosebud
Diseases of roses and their treatment require a lot of time and attention. It is necessary to constantly monitor the behavior of the infection, and if it continues to develop, it is better to remove the bush completely, and if neighboring plants are infected, destroy the entire rose garden so that fruit and vegetable crops do not get sick.
Signs of an infectious burn
- Disease of the garden rose manifests itself on the stem, dark brown ulcers appear, which, when girdled along the entire diameter, lead to the death of the shoot. Black dots (pycnidia) begin to grow on the ulcers, which serve as a source of further infection.
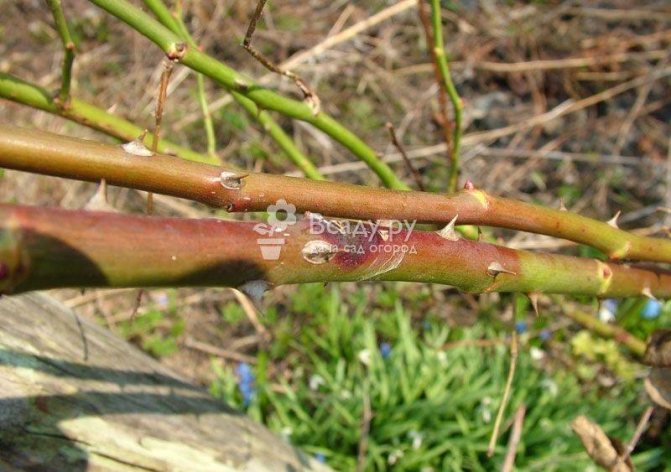


Signs of stem cancer on a rose
Infection burn treatment
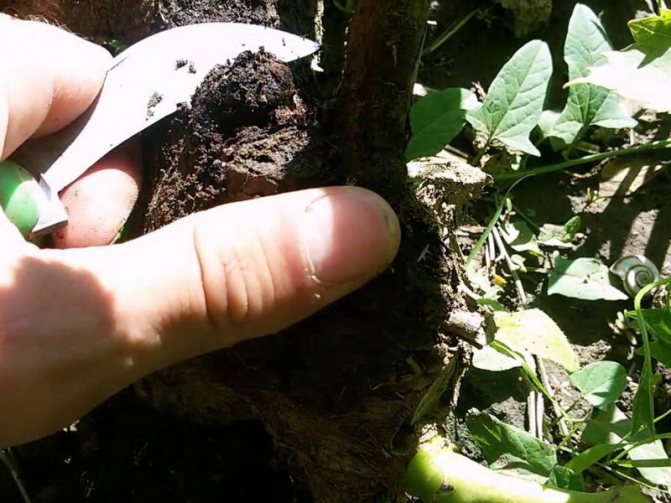
- Remove diseased shoots without damaging the ulcers on the stem;
- Clean small wounds to a healthy base, using a paper knife is most convenient. Cover with garden pitch;
- Before budding, it is important to prevent rose disease, treat the affected bush with 3% Bordeaux liquid, this will destroy the spores so that the pests of roses do not spread them;
- Spray the infected shoots every week with the HOM fungicide until they are cured.
How to prevent an infectious burn
- Prevent freezing of the plant, which leads to cracks in the stem;
- Protect roses from frost at moderate humidity and a temperature of no more than 10 degrees Celsius;
- Before sheltering, treat the soil with 3% copper sulfate or 1% Bordeaux liquid;
- Disinfect the tool before cutting;
- In the second half of July, spray with potash fertilizers.
Diseases of the room rose flower
Often the plant begins to shed its leaves after a couple of days and quickly dies. The florist reflects on the wrong care of the rose and tries to find his mistakes in care. It happens that the reason is not in the improper maintenance of the plant, but in the defeat of insects, viruses or fungi.
In addition to insects visible on the surface and soil, it can be sick with a fungal infection. The flower grower must become familiar with plant diseases in order to recognize the disease in the early stages. Many pathogens are stored for a long time in the remains of a dead bush. Therefore, all fallen leaves, branches, flowers and weeds pulled from the flower pot are destroyed.
If the leaves in the pot are not removed in winter, the eggs, larvae and spores persist and the plant becomes infected with them again. For prevention, the soil is treated with a solution of copper sulfate or oxychloride. Before pruning a houseplant, the entire tool is disinfected. Places where branches are cut must be treated with pitch.
Purchased plants often die not from the indoor climate, but because of the abundance of fertilizers. The rose is prepared for sale and stuffed with chemical additives. These substances stimulate the plant to bloom and look spectacular.
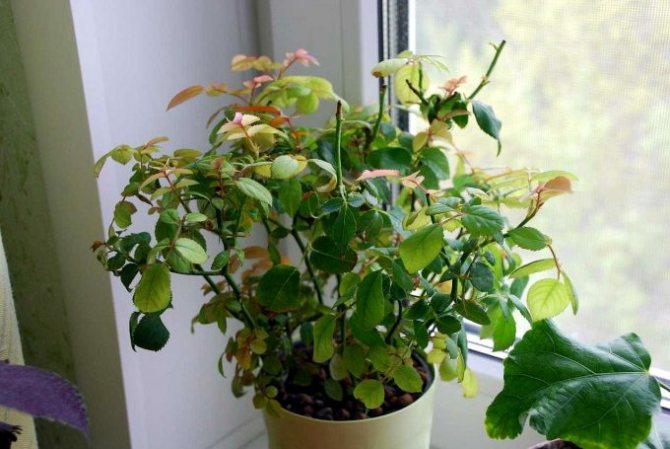


The importance of proper care
During adaptation, a purchased houseplant may feel bad. He just needs to get used to new conditions, lighting, temperature, microclimate. If the bush turns yellow, then some of the buds are cut off from it so that it does not waste energy. Delicate rose does not tolerate heat in the room. It is better to move it to a cool room with good lighting. It is sprayed daily. The soil must not be dry. If the bush continues to wither, then most likely the reason is its defeat by a virus or pests.
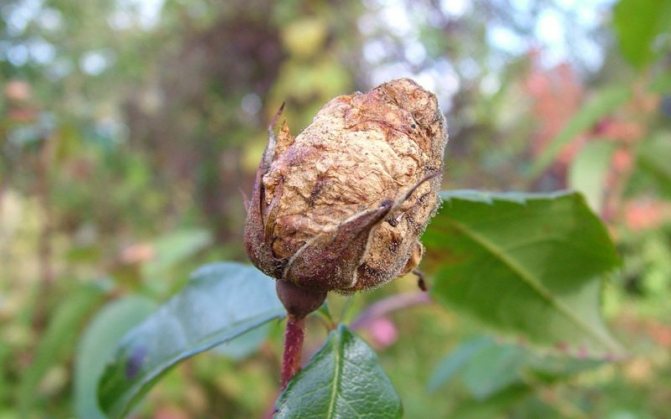
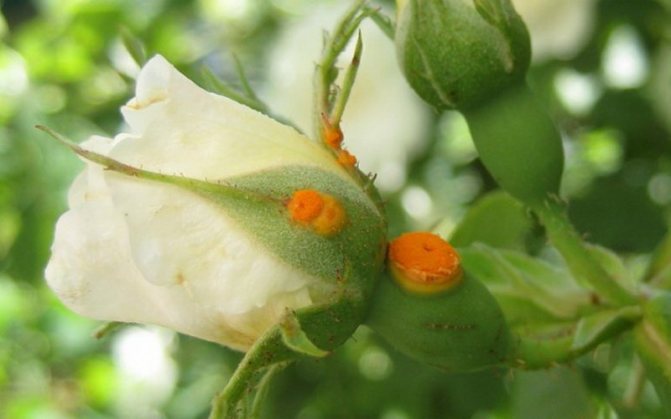
Rust of roses (Latin Phragmidium disciflorum)
It occurs in the spring due to infection with the Phragmidium fungus. It affects the entire ground part of the plant in late April - early May, spores are transferred by water. Above on the leaves and shoots, growths (spermogonia) of yellow color appear, by autumn they turn black. Pustules appear on the lower part of the leaf plate, which are dusty with spores and infect neighboring plants. Rust affects berry bushes, ornamental and conifers.
Signs of rose disease: photo, description
- The foliage is covered with red and brown spots. After a while, the leaf plate dries up and falls off;
- Shoots change shape and twist, begin to crack and spray spores.
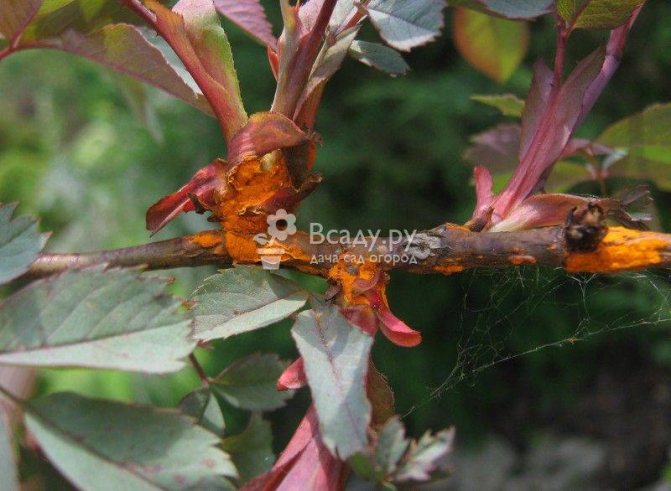


Rose rust is one of the most dangerous fungal diseases
Rust on roses, treatment
- Treatment with preparations containing zinc and copper (fungicides "Abiga-Peak", "Topaz", "Bayleton", copper sulfate);
- Spraying with 1% Bordeaux liquid.
Rust prevention
- At the end of summer, it is necessary to thin out roses from dry leaves and branches;
- At the beginning of autumn, treat with 3% copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid;
- Spray with chemical immunomodulators ("Elina - extra", "Zircon", "Immunocytofit").
Choosing a treatment method
The correct method of treatment depends on the nature of the pathogen. The spread of the fungus can be easily prevented by trimming the leaves and affected areas. Mold is treated with sulfur, and in case of bacterial diseases, the grower will have to excise the stem along with the resulting ulcer. With rot, all affected parts (branches, buds) are removed from the bush.
After winter, the bush becomes vulnerable and weak, therefore, during this period, you should look after its health more carefully. He can get bacterial cancer, rot, or get an infectious stem burn.
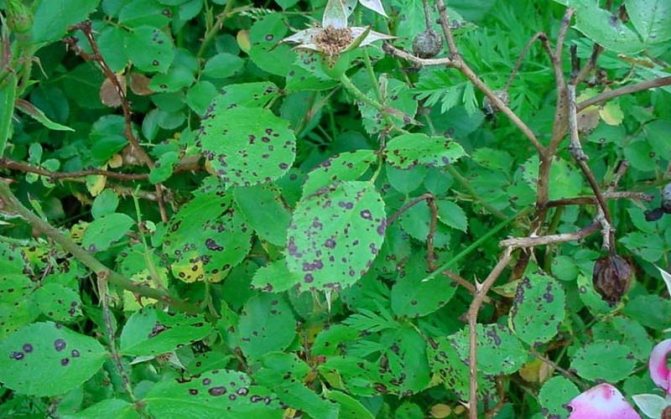
Black spot (lat.Marssonina)
It is caused by the fungus Marssonina rosae, falling on the plant and affects the leaf plate, flower petals and sepals. Spores are carried by water droplets, and black spot develops in July and August.
How to recognize a disease
On diseased plants, small dark spots appear, which quickly increase in diameter up to 15 mm. Conidia with fungal spores form on them. Leaves fall in sequence from top to bottom. The rose weakens and gradually dies.
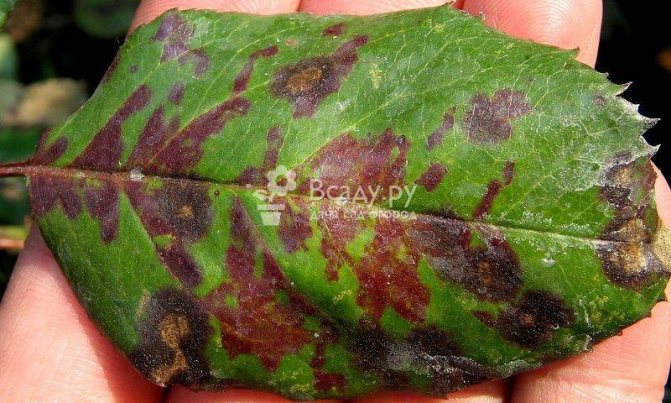


Black spot almost completely destroys leaves
Black spot on roses treatment and prevention measures
- Leaves and shoots affected by black spot are cut off, they cannot be sent to compost, therefore they are burned;
- Sick roses are treated with fungicides containing copper and zinc (Fundazol, Kaptan);
- In the fall, before covering the plants for the winter, they are sprayed with 3% copper or iron sulfate.
Signs of defeat
The symptoms of powdery mildew are quite characteristic: they do not allow this disease to be confused with any other. When damaged, plant organs are covered with a powdery cobweb grayish-white thick bloom - mycelium. It looks like flour has been sprinkled on the leaves. After the spores mature, drops of liquid can be observed on the plaque - this is where the name of the disease comes from. Later, at the end of summer, the bloom becomes brown, and small dark brown balls appear on the surface of the leaves and stems - spores.
Usually, infection occurs in the first month of summer - it is at this time that the spores of the fungus are released, which previously hibernated in the fruit body on plant debris. It starts from the lower leaves, gradually capturing the entire flower.
Favorable factors for the spread of the disease are heat, high air humidity, sharp temperature changes during the day and night. Usually, a temperature of 22 ° C and above and an air humidity of 60-90% are sufficient.


There are several reasons for the spread of the disease on roses:
- planting infected seedlings;
- improper agricultural technology;
- thickened plantings;
- excess nitrogen fertilizers;
- deficiency of nutrients, in particular phosphorus and potassium;
- lack of preventive measures;
- the presence of weeds in the rosearium;
- poor air permeability of the soil.
Fungal spores are carried from plant to plant with the help of wind and water, as well as by contact with a diseased plant. In winter, the mushroom goes to weeds, and in spring it returns to roses.
Mineral fertilizers, despite their ease of use, are not very desirable in many farms, so people are often interested in how to fertilize plants with home-made compost, sheep, pork, cow, horse, rabbit manure, chicken droppings, charcoal, nettle, yeast.
Powdery mildew or rose conidiosis (Latin Sphaerotheca pannosa)
It is caused by a fungus that infects leaves and shoots, less often flowers and buds. For the development of spores (conidia), warm weather (from 20 degrees Celsius) and a high level of air humidity in summer are favorable. The fungus is transferred through the air, water during watering and rain, insects. Powdery mildew affects almost all ornamental plants, fruit and vegetable crops, so it is important to start fighting the disease in time.
Signs of rose infestation, disease and treatment
- The leaves of roses are covered with dark red spots, in the future the leaf plate is deformed, dries and disappears;
- The shoot is covered with loose pustules that look like pads. Fungal spores mature in them.
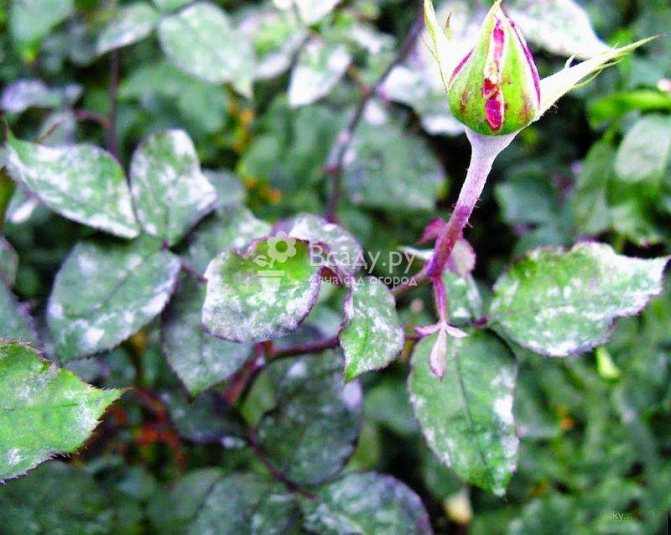


Signs of rose disease - powdery mildew on the shoot and leaves
How to avoid powdery mildew infections
- Thin bushes and prevent planting from thickening;
- Do not overfeed with nitrogenous fertilizers, observe the timing of their introduction (until mid-summer);
- During the formation of buds, treat with fungicides ("Topsin-M", "Bayleton", "Fundazol");
- Every 2 weeks spray the rose bushes with a 10-day infusion of mullein;
- From mid-July, top dressing with potassium sulfate.
How to win the war against other pests?
Of course, rose diseases cause huge damage to indoor flowers, but insects should not be underestimated either. For example, small beetles settle inside a flower and gnaw its leaves. But caterpillars can not only make small holes in the green parts of the plant, but also gnaw them completely. You can get rid of such unwanted guests with the help of preparations containing karbofos.
If the leaves of a flower are deformed, and the plant itself is lagging behind in development, then, most likely, it was struck by a rosy sawfly. The females of this insect lay eggs under the bark of a representative of the flora world. But this is not the worst thing, such a pest feeds on young buds and shoots of roses, which causes incredible damage. To destroy the sawfly, the plant should be treated with special carbophos-containing preparations or fufanon. But insecticidal agents are indispensable if the rose is hit by a scabbard. It can be recognized by brown plaques that will cover the foliage and stem. In addition, the plant lags behind in development, sheds leaves, and if you ignore the symptoms and do not provide timely assistance, it will die altogether.
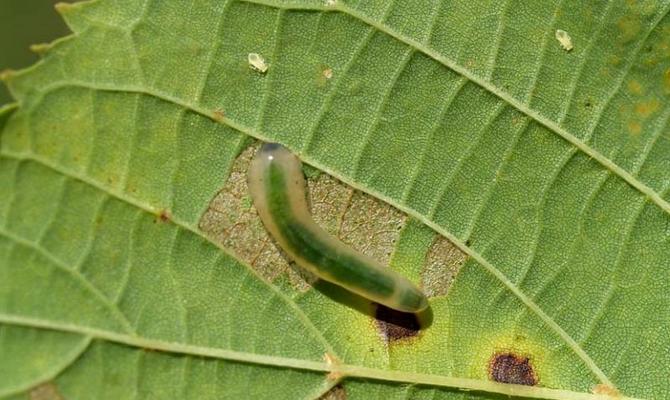


Rosaceous sawfly
You can find out that the plant was affected by the cut aphid by the following symptoms. First, young shoots and buds will swarm with colonies of small pests. Secondly, the foliage of the flower will take on an unnatural look, begin to curl, deform, and finally dry out altogether. Timely treatment with tobacco infusion or soapy water will help to overcome the problem. Moreover, if you decide to give preference to the second tool, you should use an insecticidal soap.
The infusion of yarrow has also proven itself well. To prepare it, fill half a liter jar with dried grass and fill it with water. The remedy is infused for 3-4 days. To enhance the effect, you can add a small bar of soap. There are also chemicals that can help fight this insect. These include feverfew, actellic and other drugs based on karbofos. If the colonies are insignificant, then they can be dealt with using the biological method by placing several ladybirds on the plant.
Downy mildew or rose peronosporosis (lat.Pseudoperonospora)
It occurs due to infection with a fungus and infects plants in early summer. Spores are spread by rain and wind. The development is favored by a sharp drop in temperature, swampy soil, high humidity, as well as a shaded area with poor air ventilation. The disease affects many ornamental plants, vegetables and berries.
Signs of rose disease, and their treatment with a photo
- Formless spots of dark red or purple color appear on the leaf plate; over time, the foliage begins to lose its shape, curls and falls off;
- Cracks appear on the stems of roses, the leaves of the buds darken and die off;
- With the help of a magnifying glass, you can see the spider webs on the back of the sheet.
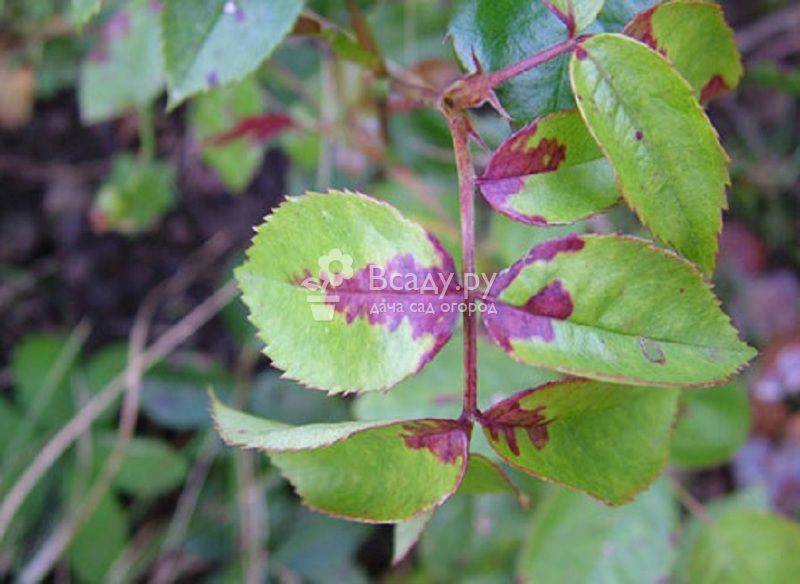


Signs of downy mildew on rose leaves
Treatment and protection measures against peronosporosis
- Plants diseased with downy mildew should be completely uprooted, burned away from healthy ones;
- For small lesions, treat roses with fungicides ("Strobi" or "Ridomil Gold");
- During the formation of buds, spray with agents that include copper and zinc (Bordeaux liquid, "Kuprozan", "Ditanom-M45";
- Treat in a timely manner with dressings containing potassium and phosphorus.
Spider mite and control measures
Let's start about the most dangerous pest, which is practically impossible to avoid. The main reason for its appearance can be called insufficient humidity in the room. Therefore, for prevention, the plant should be regularly sprayed and even bathed in the shower. Basically, a tick appears in late autumn and winter, because during this period many owners of indoor roses do not pay enough attention to the prevailing microclimate and allow the soil to dry out.
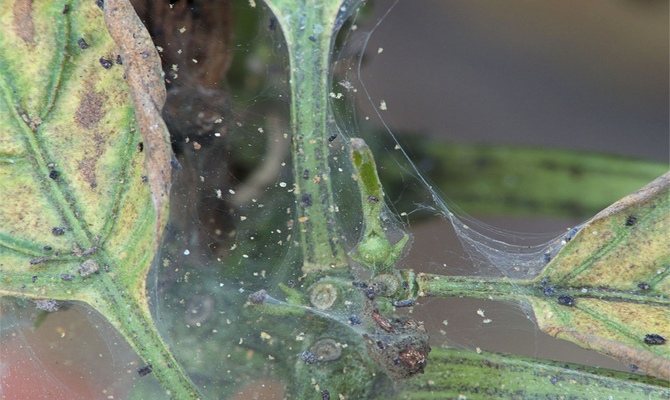


Signs of a spider mite
To minimize the likelihood of damage, even only purchased plants should be treated with special non-toxic preparations. Garlic infusion will do an excellent job. To prepare it, you will need a liter of water and 170 g of vegetable. The remedy is infused for 5 days. You can also use tobacco infusion, while a small layer of mustard powder or wood ash is poured onto the ground. The prophylaxis is repeated several times a year. Some of the most effective and non-toxic chemicals are Strela, Aktellik, Neoron. Also, Akarin and Vertimek have shown themselves to be good. The flower is completely sprayed with a solution, and for the best effect it is recommended to process an earthen lump. The procedure is repeated 3 times with an interval of 7 days.
Small pests are usually located on the underside of leaves and look like small red, red or dark brown dots. By slightly wetting the flower, you can see how the tick begins to move. The larvae of this insect are light-colored and are also found on the green part of the plant. Over time, the foliage turns brown and falls off.
Gray rot of roses (lat.Botrytis cinerea)
It occurs due to infection with the fungus Botrytis cinerea and moves along the plant from top to bottom.
Signs of infection
Dark spots appear on the affected areas, if they encircle the sprout, then it dies. Yellowish spots appear on the leaves and petals. Over time, a gray fluffy mycelium begins to appear on them. The development of a gray rot fungus is facilitated by prolonged rains and an increase in air humidity, poor ventilation when grown in greenhouse conditions.
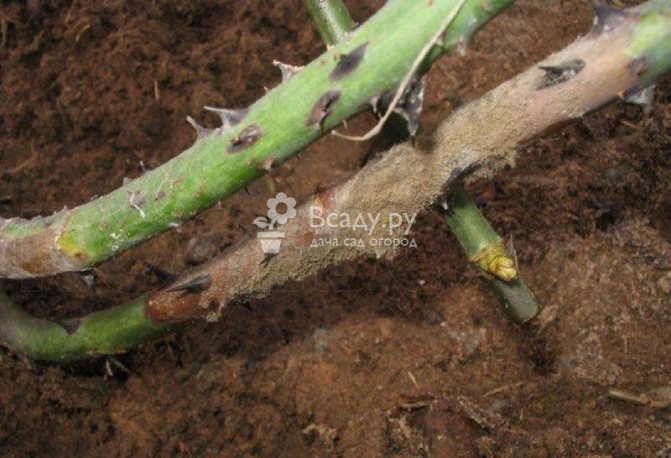


Gray rot on the stem of a rose in disrepair
How to cure and prevent rose disease
- Treat diseased plants every 2 weeks with fungicides (Euparen, Fundazol);
- Periodically water the ground with garden prophylactic drugs or growth stimulants, which include potassium permanganate;
- Cut and burn diseased plant parts. Avoid the accumulation of fallen dry leaves and branches.
How to distinguish fungal diseases?
Now we will talk about fungal diseases that most often affect indoor rose varieties. They are quite difficult to diagnose, contagious and can only be treated with certain drugs. Most often, the fungus infects the weakest representatives of the flora. High humidity combined with high temperature are optimal conditions for its development. Quite often, such diseases are brought in with the ground, dust, or newly acquired green inhabitants.
If spots are found on the surface of the leaves, then most likely we are talking about such a disease as spotting. Ignoring the danger, you risk saying goodbye to the flower, as the spots will increase in size over time, and as a result, the green foliage will simply dry out and fall off. Most often, yellow roses are susceptible to this disease. Most of the symptoms appear in the second half of the growing season.
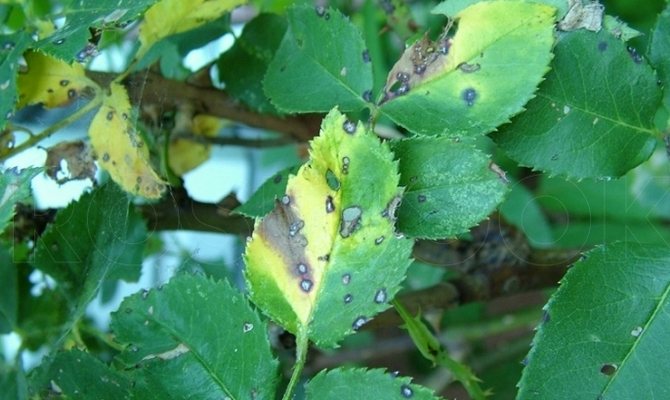


Rose spot
Promotes the spread of the fungus: thickening of the crown, excessive moisture and poor ventilation, too dense soil in the pot. If you notice the affected areas, immediately remove them and treat the plant with copper or sulfur preparations. Also, until complete recovery, avoid spraying with plain water and pay special attention to watering. The treatment of roses with a special antifungal soap has also proven itself quite well.
Viral mosaic - disease of roses and their treatment (lat.Rose mosaic virus)
It occurs due to infection by a virus and is transmitted through infected tools during pruning and grafting. Infection begins from the lower leaves: they become covered with light small spots and fall off.
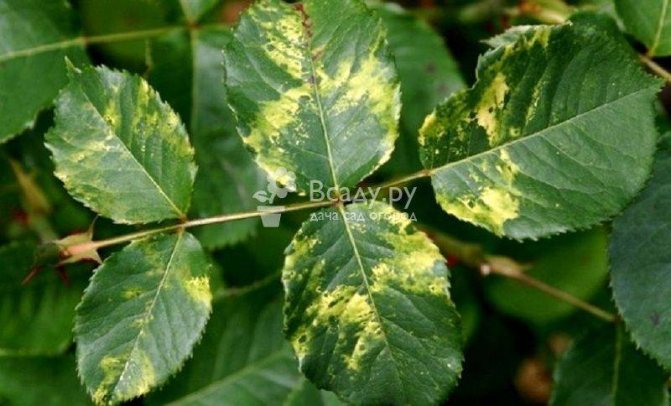


Viral mosaic on rose leaves
For the entire garden, the development of rose disease can be dangerous and the fight against them should begin immediately. A viral mosaic can spread to bushes of lilacs, currants, gooseberries, and less often raspberries.
Prevention measures against mosaic - a dangerous disease of the garden rose
- When planting, visually check the plants for diseases;
- Mandatory disinfection of the cutting tool in 1% iodine solution.
How to protect roses from diseases
- It is necessary to plant rose seedlings only in places with constant sunlight and good ventilation, on fertile soil with an acidity (pH) level of at least 6.5-7.6.
- With the arrival of March, before the buds bloom, you need to feed. The first is with urea or manure infusion (in a ratio of 1:20 with water). The second top dressing two weeks later - with potassium nitrate for better flowering and juicy color.
- Top dressing during flowering is not needed.
- After cutting the roses, they feed it with manure infusion, loosen and mulch the soil.
You will probably be interested in one of the following topics:
Viral infections
Mosaic
The disease affects the chloroplasts of the rose bush, the color of the leaves and stems changes. Brown, green, yellow spots appear in these areas. Outwardly, they look like a bright mosaic. In addition to the spots, the plant stops developing, the leaves change shape. Flowers and buds are getting smaller. Infection with a viral infection occurs by processing with an instrument. Optimal environment for mosaics: indoor temperature from 20 to 25 degrees with high humidity.
As a preventive measure, disinfection of all equipment used for processing with iodine solution is done. In addition, the soil in the flower pot is loosened, weeding is done in a timely manner and the infected flowers are removed from the windowsill.
For treatment, a florist will need karbofos. The mosaic quickly affects all the bushes, so you need to process and treat the flower immediately.
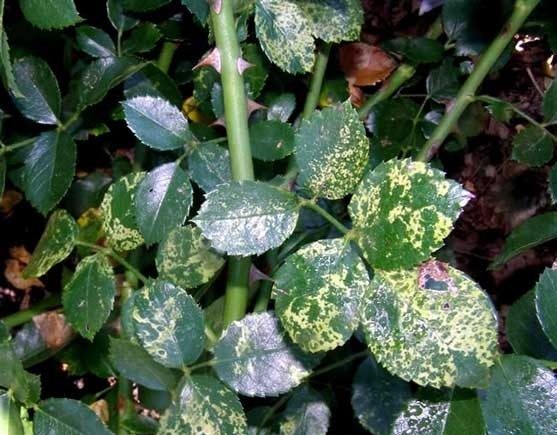


A viral disease affects the leaves of the rose. They become covered with brown, purple spots, which later turn gray. The leaf plate begins to dry, then holes appear in it. Rose leaves quickly begin to turn yellow and crumble. In this case, the pathogen can easily overwinter in fallen leaves. It should be removed, it is best to burn it so as not to accidentally infect all the plants in the house. All inventory must be processed.
Popular: Methods to protect and rid seedlings from a black leg
And also infection can occur during watering or when fertilizing a bush. The disease often develops at a high indoor temperature. When infected, all affected areas are cut off. These areas are covered with crushed activated carbon. The entire tool should be treated with alcohol solutions.
For the treatment of brown spot use drugs "Strobi", "Skor", "Topaz", "Profit". Processing is carried out three times with an interval of ten days. A solution with soap and copper sulfate helps to fight spotting. For its preparation, 30 grams of vitriol and 200 g of soap are used. Enrich the product with five grams of baking soda.


Florist reviews
elena11
“Control measures: Avoid excess nitrogenous fertilizers in the soil, especially for flowering plants. It is necessary to avoid crowding of plants, stagnant humid air. At the initial stage, when single spots appear, cut off the affected leaves and shoots. Treat the plant with a solution of soda ash (50 g of soda, 40 g of laundry soap per 10 liters of water). In case of severe damage, spraying with 0.5% copper oxychloride, 1% colloidal sulfur, topaz, thiovite, and a mixture of antibiotics (100 IU / ml terramycin, 100 IU / ml penicillin, 250 IU / ml streptomycin, in a ratio of 1: 1: 1) is used.You can use drugs such as "Topaz", "Vectra", "Skor", "Bayleton", etc. "
Source forum.
Lenusya
“Regular penicillin helped my rose, diluted 1 bottle for 0.5 liters of water and sprinkled and poured abundantly. Oddly enough, it helped. "
Source forum.
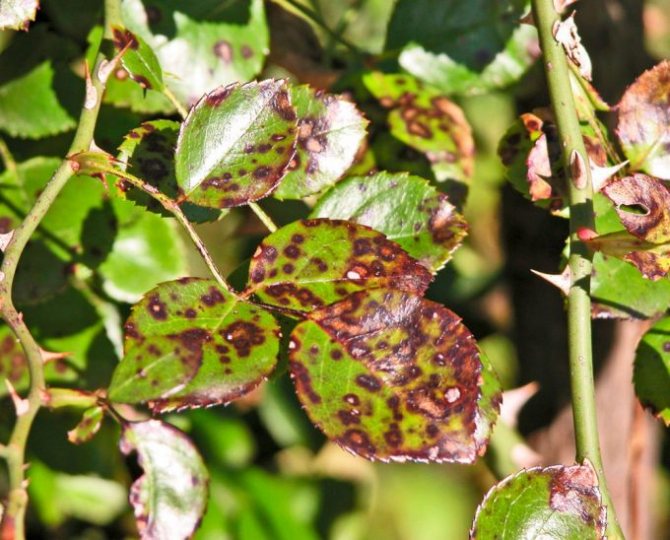
Rose leaf disease black spot: photo and how to treat


Rose leaf disease black spot in the photo
Disease of roses black spot is also called marsonina after the name of the fungus - the causative agent of the disease. In the second half of summer, dark brown, almost black, spots of various sizes are formed on the leaves. Leaves turn brown and often fall off prematurely. Spots can also appear on the green bark of annual shoots.
Plants with prematurely fallen leaves sometimes start to grow again, as a result of which they greatly weaken and bloom poorly the next year.
Under the skin of the leaves, the mycelium of the fungus, the causative agent of the disease of roses, develops spotting, forming radiantly growing strands.
As you can see in the photo, with this disease of roses, the radiance is clearly visible at the edge of the spots:


With this disease of roses, the radiance is clearly visible at the edge of the spots.


The mycelium of the fungus, the causative agent of rose disease, develops under the skin of the leaves.
This disease of rose leaves is more pronounced with a thickened planting, in shaded places, with poor airflow of the site.
Measures to combat this disease include:
- correct agricultural practices that increase the resistance of plants;
- careful collection and in the fall of affected leaves and burning them;
- spraying plants during the growing season with preparations containing copper, which are used to combat rust.
- for the treatment of this disease of roses, it is recommended to use a special preparation (Skor to protect roses) for spraying, which is a systemic fungicide of preventive and curative action.
Treatments must be started when the first signs of the disease appear and repeated after each rain or abundant growth.
These photos show how to treat black spot rose disease:


What else is good to know
In addition to powdery mildew, the rose can be susceptible to other diseases. The most common:
All the rest can be found in the reference book on diseases - there are quite a few of them. Also read the article on fungicides to know how to treat it all.


When beautiful flowers bloom in the garden, you must admit that it is pleasant, but if something happens to the flowers, the mood spoils. Often a white bloom appears on the leaves of a rose or buds and you don't always understand what to do, how to treat, how to treat it. And in this article I will try to answer in as much detail as possible all the exciting questions about this unpleasant matter.
Fungal disease burn of rose branches: photos and control measures


Fungal disease burn of the branches of roses in the photo
Branch burn is a fungal disease in which, on the branches, first reddish spots appear, later darkening in the middle; the reddish-brown edging persists for quite a long time. Growing up, the spots ring the branches. Above the affected area, tissue build-up may form. Diseased branches usually dry out at the end of summer.
Excess moisture under the winter shelter contributes to the development of the "burn".
To avoid severe damage to roses, you should remove the shelter earlier in the spring. Sick and frozen branches must be cut and burned in a timely manner.
As shown in the photo, when treating this disease of roses, plants need to be sprayed with preparations containing copper, as in the fight against rust:


Correct agricultural technology (timely fertilization, loosening and watering) helps to reduce the harmfulness of the disease. It is necessary to achieve good maturation of wood until the end of the growing season of plants.
For the winter, plants with already fallen leaves should be covered, if possible, in dry weather, so that high humidity is not created under the shelter.Before the shelter, unripe shoots with green leaves are removed, and the plants are sprayed with a 3% Bordeaux mixture or 1.5% ferrous sulfate solution.
Fungicide treatment
If you are late with treatment, then folk remedies will no longer help. It is necessary to move on to fungicides - specially developed preparations for combating fungal diseases.
They are of two types:
Chemicals are more dangerous for you and the environment. But on the other hand, they are effective, especially systemic fungicides. They penetrate the tissues of the plant and kill the pathogen there.
Biofungicides are not harmful to nature. On the contrary, there are those that improve soil fertility. But their effectiveness in the fight against diseases is low. They are good for preventive purposes, to strengthen the plant. They are sometimes used as growth stimulants.
Fitosporin-M
The active substance of this drug is soil bacteria, which are in a dormant state. Before using it, they must be activated, otherwise the drug will be useless.
Fitosporin is produced in the form of:
The preparation in vials is usually used for indoor plants. But the powder and paste must be prepared for use.
You cannot take water to dissolve powder or paste just from the tap. It may contain chlorine. It kills bacteria. Therefore, the water must be defended. Or take rain, well, boiled, thawed.
When the powder is diluted with water, the resulting mixture should settle for three hours. During this time, the bacteria will wake up and start working.
Dilute the paste in advance a few days before spraying.
For better adhesion of the solution, add one teaspoon of liquid soap to a ten-liter bucket of water.
A working solution from a powder is prepared in a ratio of 1 part of phytosporin + 2 parts of water. Therefore, it ends quickly, and every time you need to direct a new one.
It is more economical and convenient to use the paste. It is dissolved in water in the same ratio, but it is a concentrate. It can be stored throughout the season and diluted with water before use, and can also be added to other spray solutions.
Features of the disease


In plants affected by downy mildew, oily, round or angular specks of greenish-yellow color are formed on the front surface of the leaf plates, which are limited by veins. Later, on the seamy surface of the foliage, a barely discernible bloom of a violet-gray hue appears. Over time, the spots get larger and connect with each other. As a result, the affected foliage becomes wrinkled, droops and dries up, after which it crumbles into fragments that can transfer pathogens to nearby plants. Due to the fact that in a sick bush, the foliage begins to actively die off, the fruits set and develop more slowly than usual, while they become faded and lose their taste.
If a plant is strongly affected by peronosporosis, then because of this it can die very quickly. All cultivated plants are affected by this disease: both vegetables, fruit shrubs and trees, and indoor, as well as garden flowers. During one growing season, the disease can form up to 20 generations and spray more than one million zoospores. Various pests, for example: aphids, whiteflies, etc., "help" the peronospora to spread.
Disease development
Powdery mildew pathogens are excellently viable: they survive without any problems on plant remains even in the most severe winters, and they can wait for a suitable host for 5-6 years. Spores are spread in a variety of ways: with the help of insects such as aphids and whiteflies, and with the wind, and with drops of rain or irrigation water.
With the onset of humid and warm (from + 11 ° C) days, spores begin to actively develop on the plants that have become their "home", leading to extensive infections within a few days.Changing the weather to a drier and hotter one stops the destructive activity of the fungus, but the pathogen itself still retains the ability to grow and develop.
Related article: Cercosporosis of plants, how to treat
Its development occurs according to the following scenario: under favorable conditions, mycelium begins to sprout from the spores that have settled on the surface of the sheets, very quickly penetrating the thickness of the green leaf and suppressing the natural processes taking place in it. After 2-3 days, the mycelium fibers break through in the form of that very whitish plaque, which becomes an obvious sign of the inevitable death of the culture and, at the same time, a source of infection for still healthy specimens.
Signs and dangers of powdery mildew
In late spring, summer and even autumn, on previously healthy rose plants (both outdoor and indoor), a white powdery bloom may seem to appear from nowhere. All ground parts of the plant are covered with it - leaves and shoots (primarily young), buds and even thorns.
This "powder" is easily erased even with a finger, so that inexperienced growers may not attach importance to an incomprehensible phenomenon. And in vain - after a few days, the plaque will appear in the same place again, and it will greatly increase in size and capture all new areas, because this is a sign of damage by powdery mildew, which can quickly destroy both the infected plant itself and neighboring crops.
It is not only roses that suffer from this disease. The fungus also actively affects many other garden and garden plants - pear and apple, zucchini and beets, currants and gooseberries, grapes and strawberries, cabbage and cucumbers.
The culprits of this disease are microscopic powdery mildew parasitic fungi, whose spores are easily carried by wind, precipitation, and even transmitted from plant to plant through clothing and poorly disinfected garden tools. The pathogen hibernates in cracks in the bark, in leaf litter and even under the scales of dormant buds, and in the spring it begins to grow and multiply. The leaves and buds of the affected bushes wither, turn yellow and fall off - a white bloom (mycelium) greatly impedes photosynthesis. New leaves sometimes appear in their place, but most often they will be shriveled and underdeveloped. The plant itself is greatly weakened. If you do not take measures to cure powdery mildew, the rose will die.
The most vulnerable to the fungus that causes powdery mildew are hybrid tea and remontant roses.
Fungal white bloom on roses most often develops in conditions of poor lighting and thickening of rose bushes, poor soil aeration, sharp fluctuations in temperature and humidity of air and soil, excess nitrogen fertilizers and a lack of calcium in the substrate. All this leads to impaired immunity, weakening of plants and, as a result, to the appearance of powdery mildew.
How to identify powdery mildew and why it is dangerous
First of all, the stalks, petioles and young shoots that are below the rest are infected. A white bloom forms on them, in which mycelium can be recognized. After the spores mature, water drops appear on it. In the absence of timely treatment, ulcers spread to the entire plant.
As a result, its appearance becomes unattractive, and the aroma emanating from roses changes for the worse. This can be attributed to a lack of nutrients.
Leaves captured by powdery mildew suffer from necrosis, turn yellow due to lack of photosynthesis. Flowers stop blooming, buds become much smaller.
The plant at the last stage of this disease is a bare stem, on the surface of which you can see only a felt bloom. Due to its structure and characteristics of the latter, the rose does not develop. The resulting cracks become a haven for rot pathogens. Such a bush is unlikely to be able to winter.
The disease has several names. In addition to the generally accepted, there are such folk designations as "linen", "ash" and "torment".Obvious symptoms make the diagnosis much easier.
Pathogens can be transferred from a diseased plant to a healthy one with the help of insects, wind or pests.
The peak of fungal activity begins in June.
Why does white bloom appear on the leaves and buds of roses
There may be several reasons for the appearance of white bloom on roses:
- Powdery mildew (downy mildew);
- Gray rot;
- Pests (spider mites, rosaceous scale insects, rosé leafhoppers, etc.)
Most often, roses are affected by powdery mildew. Powdery mildew can be real and false. Next, we will talk about how they differ, and what symptoms they have.
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew loves to settle on young shoots, leaves and buds. Favorable time for her is late summer and early spring. The causative agent is parasitic fungi. The disease spreads very quickly, as doctors say, by airborne droplets. The disease can be brought into the garden with a diseased cuttings.
The reasons for the appearance of powdery mildew:
- Excess nitrogen fertilizers;
- High humidity;
- Dry soil around the roots;
- Dense planting of rose seedlings;
- High air temperature.
Powdery Mildew Symptoms
At the initial stage, a grayish (closer to white) bloom appears on the leaves in the form of spots on both sides of the leaf (below and above). Gradually, the leaves curl, dry up and fall off. Shoots take on a curved shape, flowering stops, the plant begins to lag behind in growth. As a result, the rose loses its attractive appearance.
Unfortunately, powdery mildew is quite difficult to treat, therefore, it is better to carry out prevention and choose resistant varieties. Resistant varieties include roses with hard, shiny foliage, but roses with soft, matte leaves are more susceptible to this disease.
How to treat roses for powdery mildew
If a white bloom on the leaves of roses appeared due to this disease, then the sooner you start fighting, the more chances you have to save the plant. In the initial stages, you need to remove all diseased leaves, shoots, or buds and burn them.
Next, spray the plant with horsetail infusion: pour 1 kg. fresh herbs or 150 grams of dry bucket of water and let it brew for a day. After a day, the infusion must be boiled for 30 minutes, allowed to cool and strain. Store the prepared solution in a plastic container. Before use, it is diluted with water 1: 5.
You can treat a diseased plant with nettle infusion. The infusion is prepared from 1 kg. fresh nettles (or 200 grams of dried) and 5 liters of water. Leave to infuse for 2 weeks, stirring the solution daily. When fermentation begins, some drill meal is added to the solution (to reduce odor). The finished infusion is filtered and diluted in water 1:10.
You can also prepare a solution of 2 parts of ground sulfur and 1 part of lime. Pollinate roses with this solution in warm, dry weather. Before processing, the rose is sprayed with warm, clean water.
Helps to cope with powdery mildew copper - soap solution, which is prepared from 300 grams of laundry soap (grate) and 9 liters of hot water. Dissolve the soap in water. Copper sulfate is diluted with water in a separate bowl (30 g of copper sulfate are taken for 9 liters of soap solution). When copper sulfate is diluted in a small amount of water, it is poured into a soapy solution in a thin stream, stirring constantly.
The prepared solution is allowed to cool and the roses are sprayed.
You can also treat the rose with colloidal sulfur (dilute 100 grams of sulfur in 10 liters of water).
Downy mildew
This disease is caused by parasitic fungi that appear in the winter on the remnants of rose leaves. Damp and hot weather or excessive watering contributes to the manifestation of this disease.
Downy mildew symptoms
Unlike powdery mildew, with this disease, a white bloom appears on the leaves of the rose from the lower part of the leaf. This plaque is more like mold.Over time, the white bloom changes color to brown, or red, the leaves are deformed.
What to do
It is important to see the disease at the initial stage, since at the beginning of the disease, the plant can still be saved by removing the affected parts of the plant and burning them.
Prophylaxis
- Select planting material. Selection of resistant varieties for planting. Thorough examination of seedlings for the presence of disease. Planting disease-resistant rose varieties.
- Plant correctly. Plant in a sunny area in well-drained soil. Observe the distance when landing.
- Observe correct farming practices. Moderate watering with warm water. Apply fertilizers according to the recommended rates.
- Loosen the soil. Timely loosen the soil, remove weeds. Destroy plant debris.
- Carry out preventive treatment. Dust with wood ash at least 3 times per season. Spray with Fitosporin.
Powdery mildew treatment with fungicides
If traditional methods did not give the desired result, and the condition of the rosary is constantly deteriorating, you will have to use special preparations. Their functions are to stop negative processes and completely eliminate the pathogen. Additional bonuses include a restorative effect.
Fungicides can be biological or chemical.
The former are considered safer. Many people use them as growth stimulants. Unfortunately, they do not differ in high efficiency in relation to a severely neglected ailment. Funds from this category are most often used for prevention.


Fungicides of chemical origin can harm both humans and the environment. They should not be overused. The advantages of these drugs include a quick and powerful therapeutic effect.
| Means, cost | Preparation | Application |
| Fitosporin-M
RUB 60 for 200 g. | Powder: take 1 part of the preparation for 2 parts of the settled water. The resulting mixture is left alone for 3 hours. Paste: the composition is made from it in advance. The proportions are the same, the shelf life is much longer. To ensure fixation, liquid soap (1 tsp) must be added to the solution. | Used for treatment and prevention. The frequency of processing depends on the weather. If the summer is rainy, it should be done once a week. |
| Alirin B RUB 80 for 20 tab. | You will need 1 ml of liquid soap, 2 fungicide tablets, 10 liters of liquid soap. The first ingredient is poured as desired. To accelerate development, the composition can be supplemented with a growth stimulant (Zircon, Epin). If the solution is going to be used for prophylaxis, the indicated dosages are halved. | With the help of the drug, the disease is prevented and treated. |
| Fundazol
RUB 40 for 10 g. | The systemic fungicide can be purchased in powder form. For 10 liters of water, there are 10 g of the drug. | Spray three times. |
| Tilt KE RUB 300 for 100 ml. | For 1 liter of liquid, take 0.4 ml of a concentrated emulsion. | The healing effect lasts for 2 weeks. The treatment is carried out if the air temperature is below +30 ° C. |
With prolonged use of the same drug, pathogenic microorganisms develop addiction.
General description and photo
The cause of the defeat in downy mildew and powdery mildew are varieties of fungi of the same family. But only in a characteristic symptom they manifest themselves in different ways: if the "correct" powdery mildew forms on the outside of the leaves, then in the case of its no less insidious brother, the disease manifests itself on the reverse side.


However, of course, neither dew nor flour can appear on the leaves - the whole point is in the overgrown reproductive organs of the insidious fungus, which look like a whitish bloom, sometimes acquiring a purple hue. On the opposite side of the leaf, infection appears as brownish or pale green spots. The plant itself begins to wither, its development is suspended.Over time, the affected leaves dry out and crumble into pieces, and the spores that have ripened on their surface become a source of further infection.
Rose bacterial cancer disease: photo and treatment of flowers
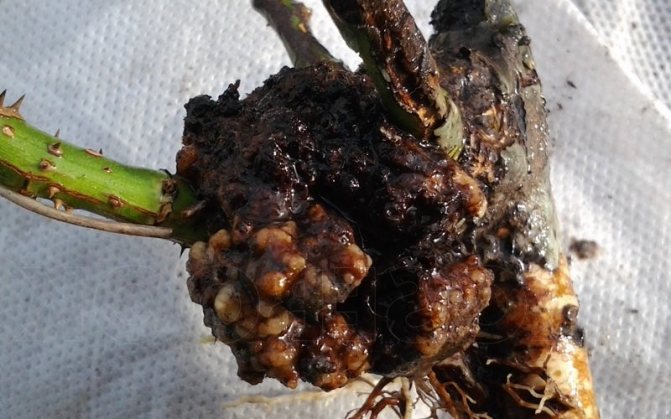


Disease bacterial cancer roses in the photo
With bacterial cancer of roses, growths of various sizes are formed on the root collar and roots of plants. Sometimes they are barely noticeable, but often reach several centimeters in diameter. The growths have an uneven tuberous surface. They consist of soft tissue, at first white, then brown, and in the soil are decomposed by bacteria.
There are also hard lignified growths that grow every year. Less often, the aboveground part is affected - trunks and branches, mainly in climbing and standard remontant roses. Here, lumpy nodules and tumors of various sizes are formed.
The cancer-causing bacteria infect many plants belonging to different families. Infection occurs through wounds on the roots of plants, from the soil, where bacteria can persist for a very long time.
The development of the disease is facilitated by high soil moisture, abundant manure fertilization, root damage, and an alkaline reaction of the soil.
When transplanting a plant with an affected root collar, it is necessary to destroy, and cut off the growths on the lateral roots. For the treatment of this disease of roses, after pruning, the roots are immersed for 5 minutes in a 1% solution of copper sulfate, and then washed in water and dipped in a liquid mixture of clay and sand. Avoid excessive manure fertilization, destroy insects that damage the roots, do not dig up the soil near the bushes.
Look at the photo of rose cancer treatment:


Gray rot on roses: how to deal with the disease


Gray rot on roses
Mainly buds with pedicels, tops of young stems and leaves suffer from gray rot of roses (botrytis) - in damp weather they are covered with a gray fluffy bloom.
First of all, this disease of garden roses attacks weakened plants, and most often - with white and light pink flowers. The buds on roses affected by Botrytis do not open, they rot and fall off. Small brown spots appear on the petals, the leaves turn yellow and also fall off.
The foci of infection remain in plant debris in the form of mycelium, which forms spores in spring. Then the spores of the fungi are carried by insects and the wind. Therefore, an undesirable "neighbor" for roses is, for example, garden strawberries, which are very susceptible to Botrytis.
Gray rot appears on roses with thickened plantings, or if the rose garden is irrigated late in the evening, when the leaves of the roses do not have time to dry before nightfall.
How to deal with gray mold of roses on a personal plot? Measures for the control and prevention of this disease of roses are the same as against other fungal diseases.
What does a powdery mildew affected rose look like?
The florist is unlikely to confuse this disease of roses with another pathology. Outwardly, the bush looks as if it was sprinkled with something white or milk was spilled on it. This is the powdery mildew mycelium. As the spores mature, the plant becomes covered with dew-like droplets of liquid. In common people, powdery mildew is also called linen or flour. Its causative agent: the fungus Sphaerotheca pannosa. Bushes are most often affected by it in the first half of summer.
The spores of the pathogen are found in plant debris and immediately after winter they begin to be released, affecting healthy specimens. The lower leaves are affected first, then the fungus moves to the upper parts of the plant. The optimal environment for the development of the pathogen is considered to be warm, humid weather with a sharp drop in temperature. It usually happens in June. The fungus spreads quickly in rose bushes and is additionally carried by insects and wind.
Rust of roses: photo and treatment in the fight against the disease


Rust of roses in the photo
With this disease of roses in flowers, the affected parts of the shoots are bent and thickened. In the spring, orange dust appears on the stems at the opening buds and at the root collar. These are spring sporulation of the fungus - the causative agent of the stem form of rust. The fungus overwinters in plant tissues infected in previous years. The disease develops more intensely in years with warm and humid springs.
Rust fungi not only take away nutrients from the plant, but also strongly disrupt its physiological functions: they increase transpiration, reduce photosynthesis, make breathing difficult and impair metabolism.
In case of rose disease, rust on the leaves on the underside in summer forms small, red-yellow pads of summer spores, which can give several generations and infect new plants.
In the second half of summer, winter sporulation begins to appear on the underside of the leaves in the form of small rounded black pads.
Look at the photo - if this rose disease strongly affected the plant, the leaves turn yellow and fall prematurely:
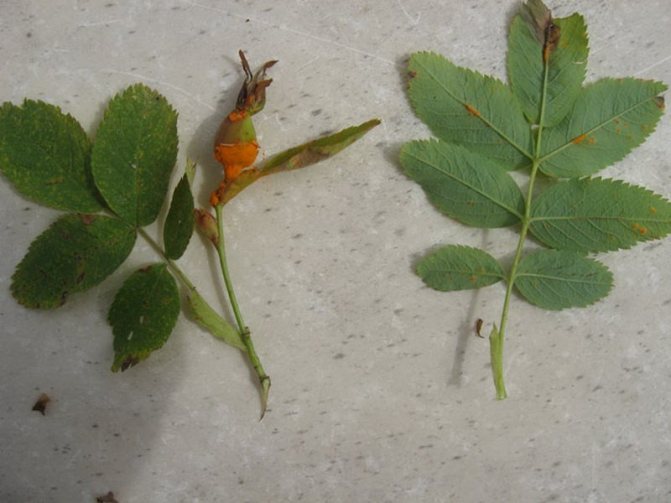


Affected parts of rose shoots
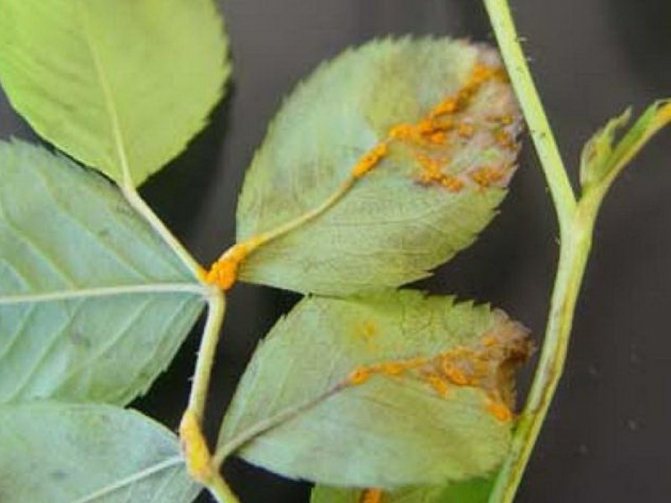


In case of rose disease, rust on the leaves on the underside in summer forms small, red-yellow pads of summer spores
The spread of spores of a rust fungus occurs with the flow of air, water, and planting material.
To protect roses from this disease, unilateral nitrogen fertilization should be avoided. In autumn, it is necessary to remove and burn the affected foliage, and in early spring (before bud break), spray the plants and the soil around them with iron vitriol (1-1.5%). The soil under the bushes should be loosened and mulched to reduce infection.
For the treatment of rose rust, it is necessary to carefully and timely cut off the shoots affected by the stem form of rust, from the moment the buds bloom, re-spray the plants with Bordeaux mixture (1%) or its substitutes ("Oxyhom", "Abiga-Peak", "Hom", " Copper oxychloride "," Ordan ").
Next, you can familiarize yourself with a photo and description of such rose diseases as black spot, bacterial cancer, gray rot, branch burn and cytosporosis.
How to prevent
If all agrotechnical measures are carried out correctly and on time, it is possible to prevent the appearance of powdery mildew on roses.
Provide the right conditions for boarding
Buy rose seedlings only from specialized stores or nurseries. Don't trust the market so you don't get disappointed later.
The purchased seedling must be healthy, well developed, and have at least three shoots.
Ask his age, which group he belongs to, vaccinated or self-rooted.
In spring, roses can be planted until the end of May. In autumn, the deadline is October 20. And sometimes even earlier, it all depends on the weather.
If you cannot plant a seedling right away, then to preserve it, wrap the roots with a damp cloth, and the whole bush with a damp newspaper, put it in a plastic bag and tie it. Now, in a cool place, it can be stored for up to ten days.
Dig a hole for planting a seedling in accordance with the size of the roots. It should not be deep and very wide. Dig it so that you can spread the roots well in it.
Pour compost mixed with soil at the bottom of the hole. Place a seedling in it. Spread out the roots. Cover with earth so that the grafting site is 3-5 cm deep. If it is deeper, the grafting site falls into the cold soil layers. From this, the rose grows poorly. If it is planted higher, then wild animals will actively begin to grow. It will be difficult to get rid of them later.
Then the rose must be watered abundantly. After that, spud 15 cm. When the buds start to grow, uncook. If the rose was planted in the fall, then you do not need to bother.
Try to plant roses in a place with good sun light. But not on the south side. There pests will attack her. Climbing roses should be planted in a well-ventilated area. Ideally planted on the east or west side of the house.
Inspect roses regularly
So that the rose does not hurt, it must be examined regularly. So you can see the first signs of powdery mildew.Look carefully at the stems, leaves on both sides, buds, flower petals. If you notice diseased plant parts, remove them immediately. And then spray the plant itself with the fungicide.
Remove weeds and fallen leaves
The soil around the rose bushes should always be free of weeds and fallen leaves. If they are not removed in time, they will become a source of rose diseases. In the fallen leaves, causative agents of fungal diseases winter, in particular powdery mildew. Remove cut, diseased leaves immediately. This will prevent further spread of the infection.
Disinfect the instrument
During trimming, it is imperative to decontaminate the tool. Otherwise, you yourself will transfer the disease from a diseased plant to a healthy one. For disinfection, you can use any alcohol-based or chlorine-based product available to you. Just do not heat the instrument. From this, its cutting part deteriorates, the quality of the metal changes.
Don't overdo it with nitrogen fertilizers
The fact that you have gone too far with nitrogen, you can easily understand by the abundance of powerful rose stems and dark green leaves, a small number of buds, late flowering. Such a plant becomes a delicacy for aphids. She colonizes him. All this taken together is a direct path to the occurrence of fungal diseases, including powdery mildew.
Provide adequate amounts of potassium and phosphorus
The provoking factor for the appearance of powdery mildew on roses can be a deficiency of nutrients. In particular, potassium and phosphorus. It is these macroelements that are responsible for strengthening the plant's immunity, its immunity to fungal diseases, the development of the root system, and resistance to low temperatures. Therefore, you must strictly follow the feeding schedule.
During the season, you need to carry out three mandatory feeding:
The first is in April, when the plant wakes up after winter. During this period, the rose needs more nitrogen, and phosphorus and potassium in the same proportion. For feeding, you can use any complex mineral fertilizer. Pay attention only to the proportional ratio of the components. A few days after mineral feeding, apply organic fertilizer (mullein infusion). This will improve the structure of the soil.
The second is when tying buds. The share of nitrogen fertilizers is decreasing, while that of potash and phosphorus fertilizers is greatly increasing. The principle of deposit is the same as in the first case.
The third - after the first flowering. They refuse nitrogen fertilizers, feed them only with phosphorus and potassium fertilizers.
Spray roses with protective products
To prevent the appearance of powdery mildew on roses, carry out preventive treatment of the bushes with fungicidal solutions. For prevention, you can use biofungicides, such as phytosporin. Be sure to process it in early spring, before the buds start to move, and also before hiding for the winter. During the growing season, you can use folk remedies, spraying roses every two weeks with soap and soda solution or milk serum.
In the fall, harvest dry foliage and dig up the soil
If you do not remove dry foliage under the rose bushes and dig up the soil under them, then the spores of pathogens of fungal diseases will safely survive the winter. You will cover the roses, the leaves will begin to rot, the parasitic fungi are good and comfortable there. Why, because of your laziness, ruin roses? When harvesting leaves, do not compost them. They can infect him. Better burn the leaves.
Choose varieties that are resistant to powdery mildew initially
When choosing a rose for planting in your rose garden, pay attention to its resistance to powdery mildew. Don't blindly trust the seller. Take a look at the reference book, chat on the forums. Only after that, decide to buy a new resident.
Experienced growers advise the following varieties:
- Purple tige
- Sommersonne;
- Cadillac;
- Hot chocolate;
- Aphrodite.