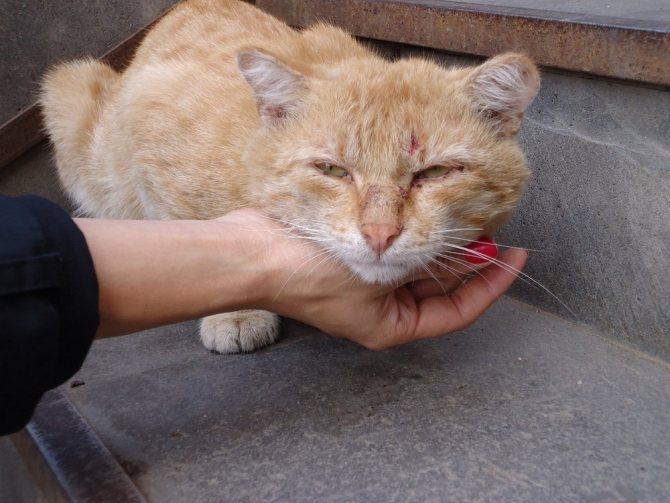
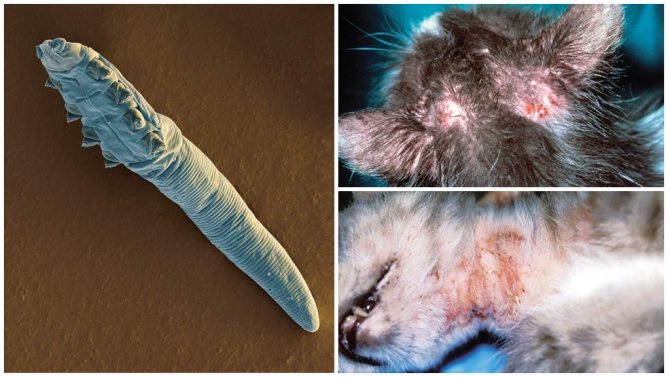
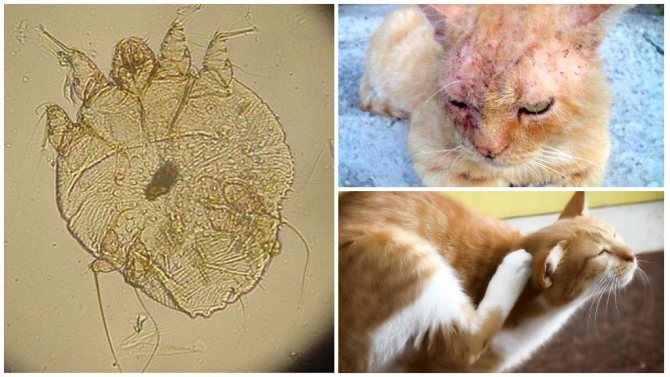
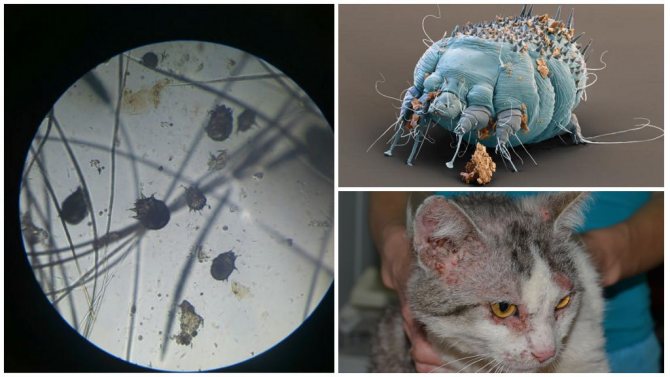
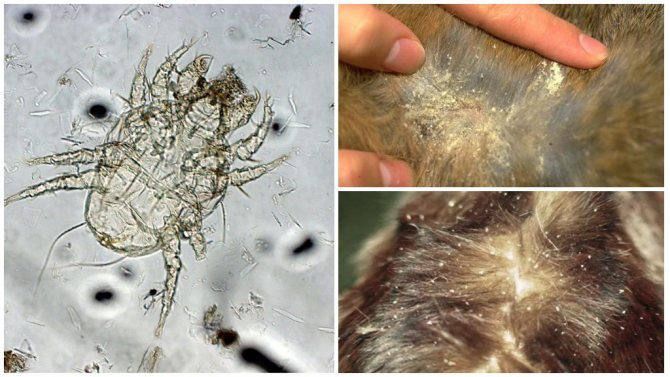
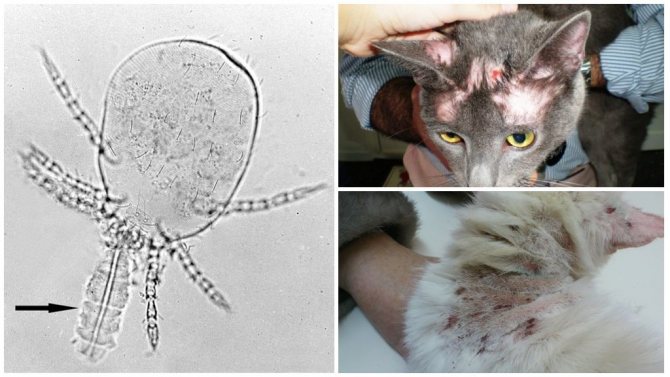
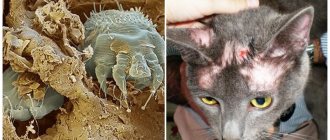
One of the most common parasitic diseases in cats is the subcutaneous tick. Today, all breeders are well aware of the symptoms and treatments for this disease. And those who first encountered constant itching in an animal, excessive hair loss, excessive anxiety and other not very pleasant phenomena should not panic, but try to start treating the pet as soon as possible and rid it of parasitic ticks.

Types of diseases caused by subcutaneous mites
The activity of subcutaneous ticks can cause a number of infectious diseases in pets, most often they are:
- Demodectic mange is the main disease of the parasitic type that occurs due to inflammatory processes caused by the waste products of ticks. It is expressed in external lesions of the skin and coat.
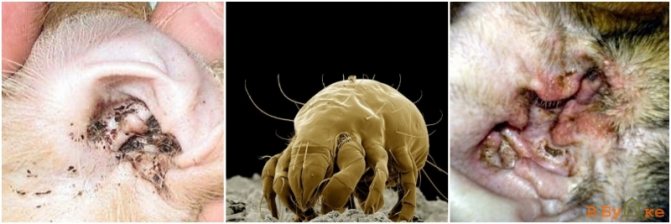
- Ear scabies, which is inherently one of the most common types of demodectic mange. It occurs when ticks enter the cat's ear or touch the lymph nodes associated with this part of the body. Parasites have a certain interest in cat ears, since they are a rich source of food, because in addition to skin cells, they contain earwax, dandruff and other formations. When affected by such scabies, you can notice black dirt in the ears of the pet, which is actually the waste products of parasites that have settled there and frozen blood residues. The accumulation of such dirt causes a specific unpleasant odor, reminiscent of decay.
- Hemobartonellosis usually occurs due to the bites of ixodid ticks, but in some cases this disease can be caused by suppuration and an allergic reaction arising from the activity of subcutaneous parasites. The main symptom is emerging anemia, the disease is highly contagious.
Signs and symptoms of a subcutaneous tick
As already mentioned, these parasites can be in the upper layers of the cat's skin for a long time and remain unnoticed.
However, if the rapid multiplication of subcutaneous mites begins, then a number of characteristic symptoms appear, by which it is possible to establish the fact of their presence.
The main features include:
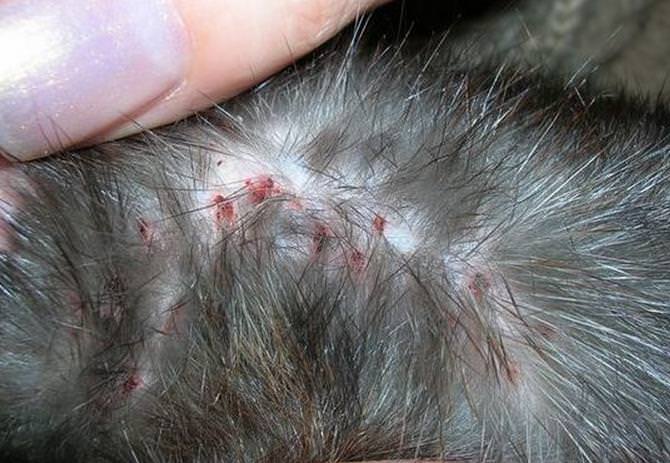

- Skin irritation, which is expressed by reddening of individual areas.
- The appearance of a nodular rash or the formation of abscesses.
- Visual deterioration animal fur.
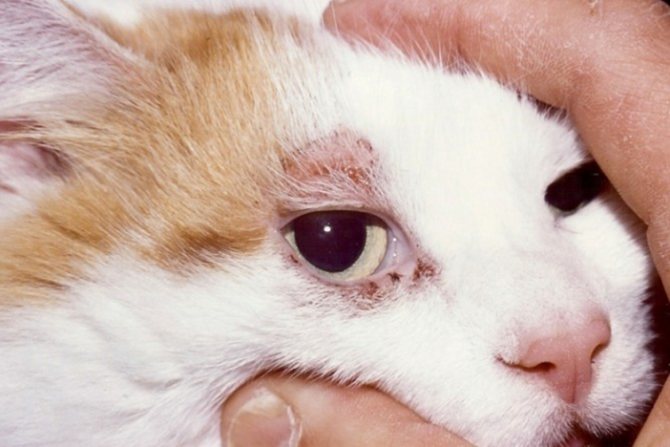
- Loss of hair growing around the eyes, and severe dryness and flaking of the skin in the same areas. This symptom is very common when affected by subcutaneous ticks and is called demodectic glasses.
- Change in skin pigmentation.
- The appearance of acne.
- Severe itching, due to which the cat scratches certain parts of the body.
- The appearance of small bleeding wounds.
- Decreased appetite, apathy and general weakness of the animal usually manifest in the most severe forms of damage and are the result of a violation of the functioning of internal organs.
- Dandruff
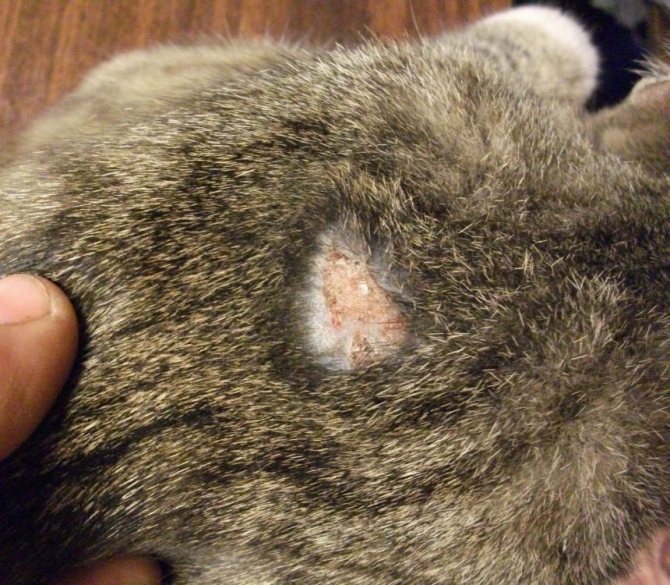
- The formation of specific growths with a hardened structure can reach from 0.2 to 1.2 cm in length. The growths can be moist due to the constant secretion of the ichor.
Forms of the disease
There are 2 forms of subcutaneous tick lesions:
- Localized... This is the initial stage of the disease in which minor symptoms occur. Usually, a cat does not notice damage to the skin and coat.
- Generalized... The disease is in an advanced stage, which occurs several weeks after the penetration of the parasite into the skin. On the limbs of the pet, you can see clear signs of the presence of a tick. If a disease is detected at this stage, completely cured cats are sterilized, withdrawn from breeding. This has an understandable reason - the tendency to demodectic mange can be inherited.


Causes and ways of infection
Demodectic mange is an infectious disease that can spread very quickly, the main ways of charging are:
- Contact of an infected animal with a healthy cat.
- Transmission of the disease from cats to kittens.
- Transmission of parasites from person to animal.
- Intrauterine infection.
- Keeping a cat in violation of sanitary standards.
- Poor nutrition, which causes the cat to not get the required amount of vitamins and minerals, which leads to a weakened immune system and susceptibility to disease.
- Bad heredity, which occurs if one of the cat's parents has suffered a severe form of demodicosis.
Any animals can become infected with subcutaneous ticks, but there is also a risk group, representatives of which are more susceptible to this disease:
- Older cats.
- Cats that have recently suffered from other types of parasitic or dermatological diseases, especially if they have not been completely cured.
- Cats with weakened immune systems.
Complications
Without a timely response and comprehensive treatment, animals affected by a subcutaneous tick may experience serious complications, which are as follows:
- The ingestion of unwanted microflora into the body, including various types of fungi, which can provoke the parallel development of other diseases.
- The emergence of abscesses of the hair follicles.
- Violation of the process of the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
- Necrosis of skin tissues and subsequent decay, as well as the decay of products of the inflammatory process.
- Intoxication of the animal's body as a whole.
Useful Tips
- Never wash your cat with an antiparasitic drug intended for dogs! These products have a completely different composition and are more toxic. Ingredients that are not harmful to dogs are very dangerous to cats, even fatal.
- If you have to deal with a Demodectic animal, remember to wear a cape and gloves. No, Demodexes are harmless to humans, but you can accidentally bring the parasite into your apartment, thereby infecting your pet.
- If the pet has already been affected by a subcutaneous tick and has been safely cured, preventive measures should still be taken. Moreover, after an illness, the cat will feel unwell for some time. This is due to the fact that the drugs used to treat the skin are absorbed into the bloodstream and are not excreted for three months.
- With the veterinarian's permission, periodically take preventive measures with an antihistamine that will prevent infection, eliminate possible itching, relieve discomfort and reduce allergic reactions. The drug will be prescribed by a specialist.
- Remember that in a dry environment, parasites, including demodexes, do not survive. And if you find an ulcer on the cat's skin, it should be dried immediately (for example, hydrogen peroxide, it is safe for animals), and then immediately show the pet to the veterinarian.
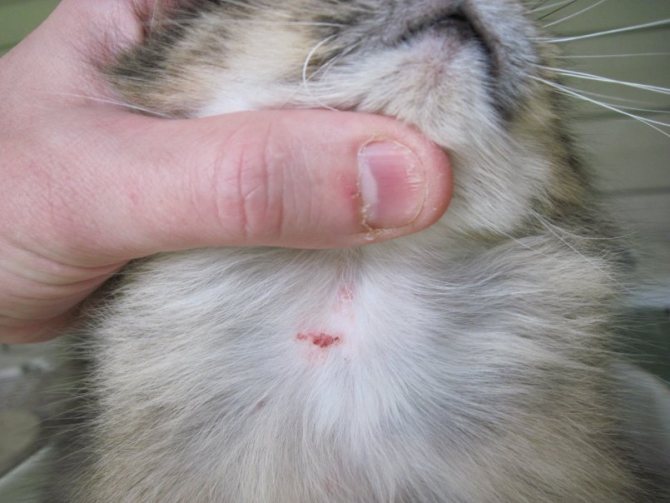
- Try to regularly examine your pet for affected areas, especially if the cat has begun to itch frequently.Carefully use a magnifying glass to look for even the slightest signs of a subcutaneous tick: bulging bumps, bald patches, pustules, redness, dandruff, discharge of ichor from wounds, sores and bald patches.
- At the slightest suspicious signs in the form of lethargy, temperature, refusal of water and food, aggression, changes in mucous membranes, etc. take your pet to a doctor immediately. It is possible that the animal became a victim of a subcutaneous tick.
- Whatever drugs you use, for prevention or treatment, always read the instructions carefully so as not to inadvertently harm your pet. Study the composition, indications, application, purpose, dosage, contraindications and shelf life.
Diagnostics
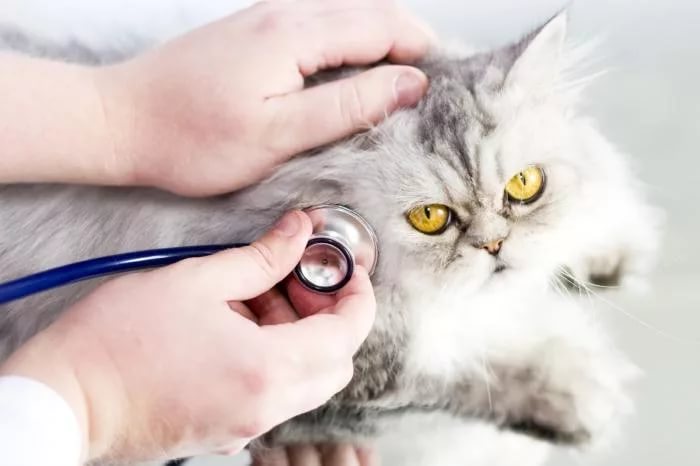
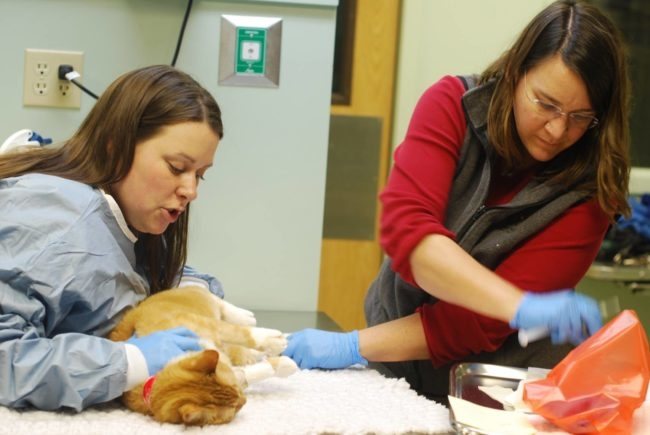
The process of diagnosing subcutaneous ticks in cats is rather complicated, it can only be carried out by specialists in laboratory conditions.
Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out as follows:
- In the presence of appropriate symptoms, a laboratory analysis of skin particles is performed to make a diagnosis. and the contents of the formed tubercles.
- Particles of the skin for analysis are taken by squeezing it from both sides so that the parasites can be squeezed out. Often, several subcutaneous mites can also be found in completely healthy pets. However, if such an amount was recorded in the presence of concomitant symptoms, then a second test will be required. The identified parasites are often placed in an artificially created habitat for them in order to be able to observe the process of their reproduction and the development of the created colony.
- An analysis of the pet's waste products, blood is carried out, as well as a study of its condition using ultrasonic methods. Such a diagnosis is necessary to detect possible complications that may be caused by the activity of subcutaneous mites or accidental ingestion of secondary microflora into the pet's body.
Establishing a diagnosis
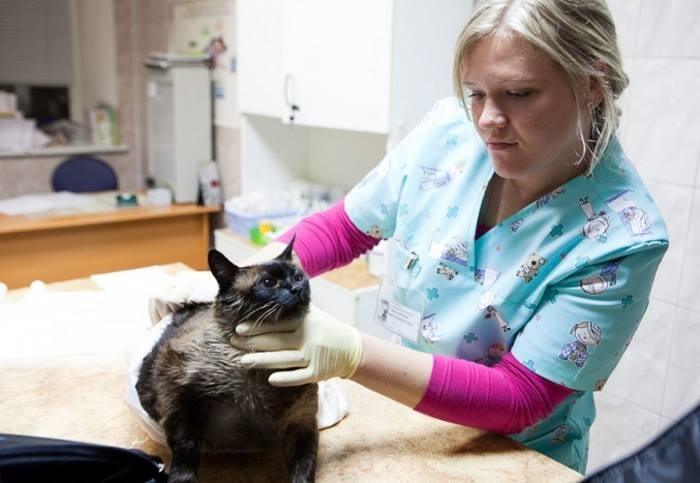
Getting an accurate diagnosis is important because some of the symptoms are similar to ringworm or other dermatitis. The veterinarian relies not only on external examination, but also conducts a number of examinations. The complete picture is given by scraping from the affected areas. In this case, it is possible to identify the presence of parasites and determine the stage of their development.
It is worth considering that if the analysis showed the presence of only adults in the skin, then the cat is not a carrier of the disease and is not dangerous to other animals. A swab taken from the ear is also informative.
If a tick is not found in the scraping, then an analysis from another site will be required. Stool analysis is often done because the animals lick themselves thoroughly. Thus, the parasite enters the body. Tests also help to establish a diagnosis in the absence of obvious external symptoms.
The disease is diagnosed without fail in the laboratory of the nearest veterinary clinic. A scraping is taken from the skin of an animal, examined to exclude such pathologies: various dermatitis, eczema.


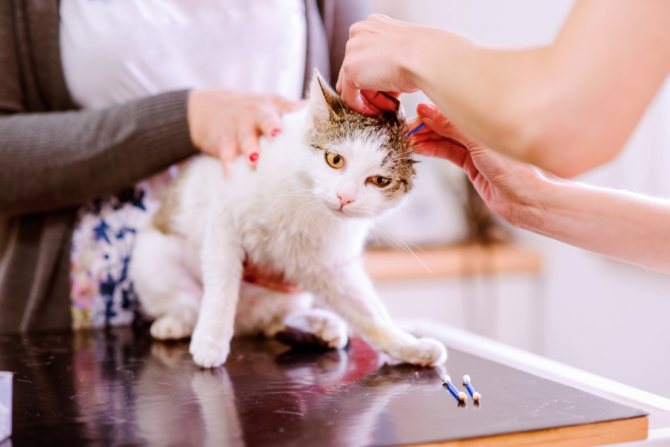
To diagnose the disease, a scraping is taken from the skin of the animal.
- At the same time, the lymph nodes located near the affected area become inflamed and enlarged.
- Bald patches on the face become visible.
- Gradually, the lesions grow, merging into an ugly mask on the facial area.
- Small seals appear, filled with a viscous white exudate containing insect larvae and decay products of their vital activity.
- Further, the deterioration of the skin occurs.
- Skin hyperemia, coarsening are manifested, scales subsequently appear.
- The infected areas are painful. The animal suffers from constant itching, continuously combing the infected area. Wounds can bleed and fester, and the skin becomes covered with age spots.
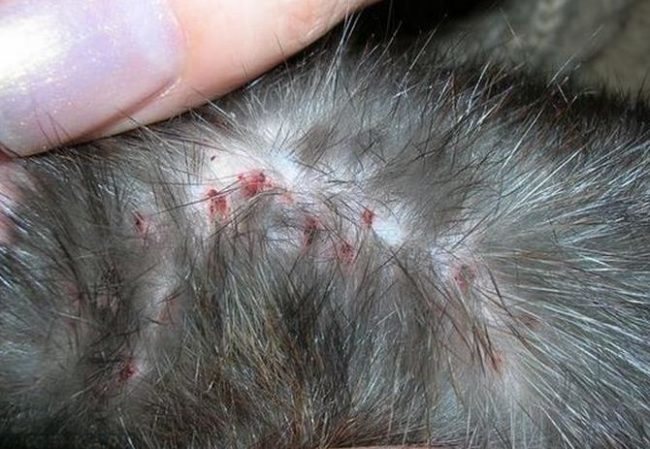

At the places where the tick penetrates under the skin, spots appear and itchy skin begins.
It is believed that this type of parasite is harmless to humans. When insects get on human skin, they die, but in some cases, if a person has chronic or inflammatory processes in the body, this can be dangerous.
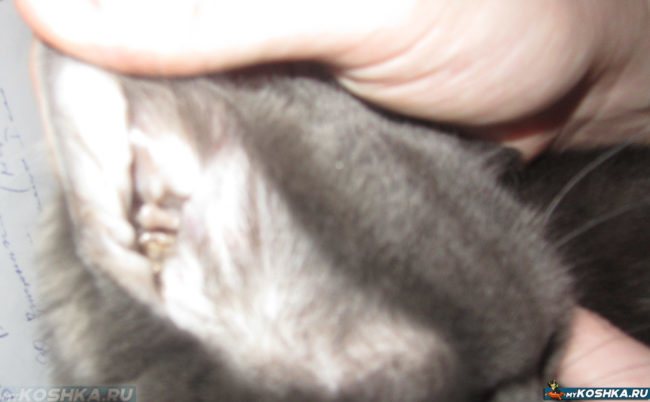

Preventive examination of the cat's ears.
With a localized form, only one or several areas of the skin are affected, does not fall on the rest of the cat's body, and is not visible on the paws.
The generalized degree of infection with demodicosis is characterized by the presence of foci throughout the body, affecting the paws of the pet. Often, internal organs become infected, which is manifested by the pet's lack of appetite, lethargy, and apathy. This form is very difficult, and it costs the owner a lot of work and patience to cure it. After this form of pathology has been transferred, sterilization of the animal is recommended in order to avoid heredity.
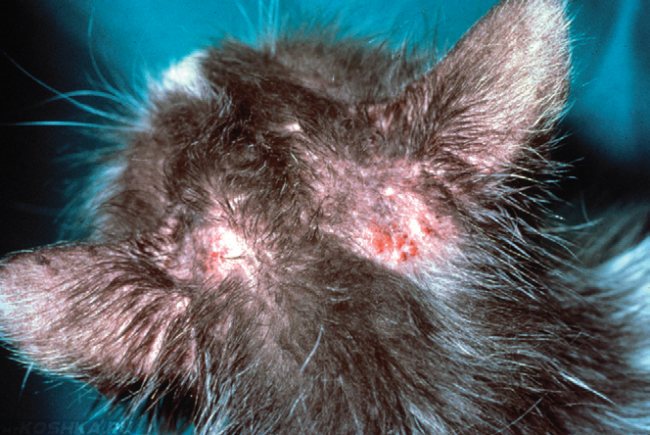

With a generalized degree of infection with demodicosis, foci of the disease spread throughout the cat's body.
Treatment in cats
Treatment is usually complex, since skin and hair lesions are only an external manifestation of the disease, and the parasites themselves negatively affect the entire body as a whole.
An appropriate course can be prescribed only by a specialist, depending on the stage of the disease, the severity of the lesion, the complications that have arisen and the individual characteristics of the situation.
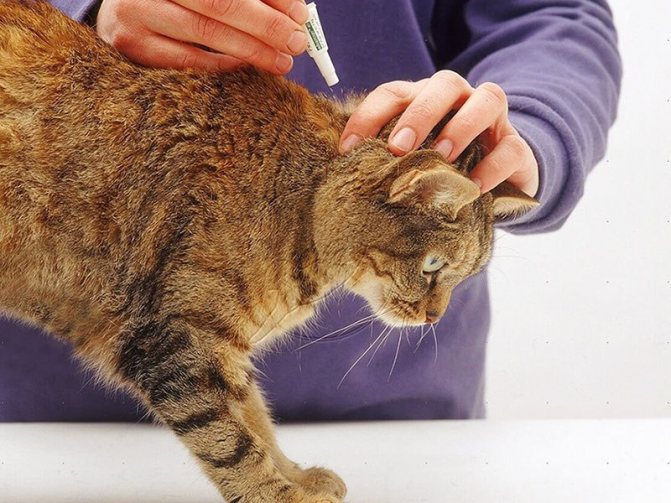
- Initially, it is necessary to destroy the parasites on the surface and in the upper layers of the skin. To do this, use soapy water or 1% water-based chlorophos solution.
- Simultaneously with the treatment of the animal, the entire room is disinfected and pet care products.
- If the lesion has not yet had time to take a serious form and there are only a few foci, then the wool in these places should be clipped and shaved. These areas are additionally treated with Vishnevsky ointment or special lotions for cats.
- When treating the most severe forms of the disease, systematic treatment of the pet is necessary, which is carried out every five days with a solution of chlorophos 2%.
- The most positive result is achieved with subcutaneous administration of drugs that are prescribed by a veterinarian. Ivermectin is most often used, the frequency of its use and dosage are also determined by a specialist depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease and its severity, but at the same time do not exceed the norms specified in the instructions for the drug.
- Some animals have an individual intolerance to ivermectin or other prescribed drugs, as well as individual components that make up their composition. In order to avoid negative consequences, the first subcutaneous injection of the agent should be of a trial nature. To do this, first, the animal is given an anti-allergenic drug, and then the minimum dose of the prescribed drug. If there are no allergic reactions or other side effects, then further use of the product must be carried out in accordance with the recommendations given by the veterinarian. From such treatment, weakness or uncontrolled increased salivation may occur, these symptoms go away on their own after a few days, but if this does not happen, then taking the drugs should be stopped and seek new advice from a specialist.
- Particular attention must be paid to the treatment of kittens, since they still have rather weak immunity. All procedures are carried out in accordance with the instructions of the veterinarian, it is not allowed to change the regime or the specifics of treatment. This will help prevent the formation of new lesions.
- The entire course of treatment should be accompanied by a correct and balanced diet. The food given to the cat must contain a large amount of different groups of vitamins, minerals and essential elements and compounds. Most likely, you will additionally need to take a vitamin course.
Since subcutaneous mites often cause a complication in the form of ear scabies, an additional set of measures will need to be taken to treat this disease:
- Clean the cat's ears from the dirt accumulated in them with a clean cotton swab, which must first be moistened with camphor alcohol.
- Instill no more than three drops of Octovedin, Demos or another agent prescribed by a specialist.
- Treat the skin around the ears with a special healing ointment, for example, Wilkinson's ointment.
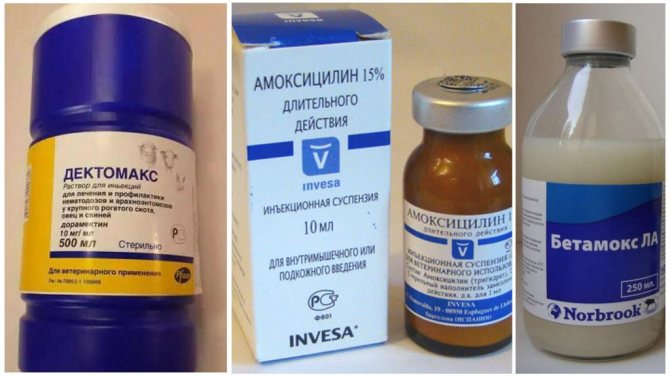
All drugs used during treatment are prescribed by a specialist, but the following types are most often used:
- Ivermectin in tablet form is a versatile drug with an antiparasitic effect, widely used in veterinary medicine and has a high degree of effectiveness. It causes paralysis and the subsequent death of ticks, it is forbidden to use it in conjunction with other drugs of a similar nature. The price for a pack of domestically produced tablets is about 60 rubles.
- Ivermec in liquid form is an analogue of ivermectin, which is intended for subcutaneous injection. It is more effective, since the active ingredients quickly enter the bloodstream. The cost is about 45 rubles for a bottle of 1% solution with a volume of 1 ml.
- Safroderm ointment is intended for external treatment of the affected areas of the animal's body. The agent is an antiseptic, additionally allows to speed up the process of wound healing and relieve local inflammation. The approximate cost is 80 rubles for a 25 ml bottle.
- Mikodemocid is a solution, the main active ingredient of which is 0.7% chlorophos. The drug disrupts the processes responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses in the body of the tick, which leads to subsequent paralysis and death of the parasite. The cost is about 200 rubles for a 100 ml bottle.
- Immunoparasitan is not an independent drug for the destruction of subcutaneous ticks or the treatment of diseases caused by them. It is used as an additional agent, which is taken in combination with drugs prescribed by a veterinarian. The main purpose of using Immunoparasitan is to increase the immune responses and resistance of the cat's body to the existing parasites. Containers with a volume of 8 ml can be purchased at veterinary pharmacies, the cost is 180-200 rubles.
There are also a large number of folk remedies for removing parasites of this type, but it must be remembered that they cannot replace the main course of treatment and a visit to the veterinarian, they are recommended only as additional and auxiliary measures.
The most common ways to deal with ticks are:
- Use a decoction of chamomile, which can be used to wipe the affected areas on the animal's body or bathe it every 2-3 days.
- Using calendula tincture to treat affected areas.
- Increasing the dryness of the skin by any available means, which will create unfavorable conditions for the existence of parasites.
- Washing a cat using a gel or soap, one of the components of which is birch tar.
- Treatment of places where hair loss was noticed with kerosene. After a few days, the treated areas will need to be additionally rinsed with water.
All such folk methods of treating a pet are recommended to be applied in practice, only after consulting a veterinarian about this.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures that prevent the development of demodicosis are reduced to strengthening the cat's immunity. This requires:
- provide your pet with a balanced and nutritious diet;
- regularly give the animal vitamin and mineral complexes;
- do all the vaccinations provided on the schedule;
- carry out deworming;
- regularly handle and disinfect the bedding of the animal, its bowl and toys;
- provide complete care;
- in case of any doubts about the state of health, it is better to show the cat to the veterinarian in order to clarify the diagnosis and receive recommendations for treatment.


It is important that with demodicosis, the tick from cats is not transmitted to humans. Therefore, you can carry out full-fledged care without using special protective equipment. However, it is recommended to follow the rules of personal hygiene and constantly wash your hands after treating the skin of the animal.
Prevention of infection
Due to the fact that there are no vaccinations that could protect the cat from these parasites, it is important to follow some preventive measures to minimize the likelihood of such ticks activating and the occurrence of serious diseases.
The complex of such measures includes:
- Preventing contact of your pet with other animals, if their state of health is capable of causing even the slightest fear and suspicion.
- Periodic visual inspection of your pet. At the slightest signs of damage, urgently contact a veterinarian, since it is much easier to get rid of the disease in the early stages.
- During potentially dangerous periods, use a variety of preventive wool treatments or antiparasitic collars for cats.
- Monitor the conditions of keeping the pet, compliance with sanitary standards, as well as the quality and balance of nutrition.
- After treating a cat for demodicosis or other similar diseases, it is necessary to disinfect the premises, and disposal or careful handling of care items or objects with which the infected pet has had contact with special products.
How is demodicosis diagnosed?
This diagnosis can only be made by a veterinarian if you yourself do not have a similar education. The fact is that there are a huge number of diseases that are similar to each other, so your cat may have an ailment that is not of interest to us at all, but any other one, treating which, like demodicosis, means ruining your pet's health.

Only a veterinarian can make a correct diagnosis.
Your task as the owner is to notice the dangerous manifestations of the disease in time, grab your ward in an armful and go to an appointment at the veterinary clinic. There, the veterinarian will conduct one of the studies for you to identify demadecosis (trichogram, biopsy, or immediately prescribe drugs to treat the disease, provided that he has no doubts about the diagnosis.