Other eye problems
How to cure eye diseases in a rabbit at home? To prevent ophthalmological problems in animals, it is recommended to approach the issues of keeping rabbits responsibly. A number of basic rules that must be followed by the breeder of these cute and affectionate animals:
- Placing a cage with eared tetrapods in a draft-free area.
- A good diet rich in vitamins and minerals, in particular food fortified with vitamin A.
- Timely vaccination.
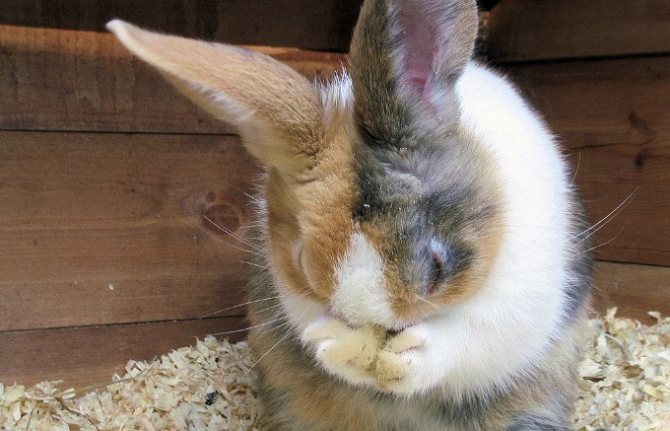
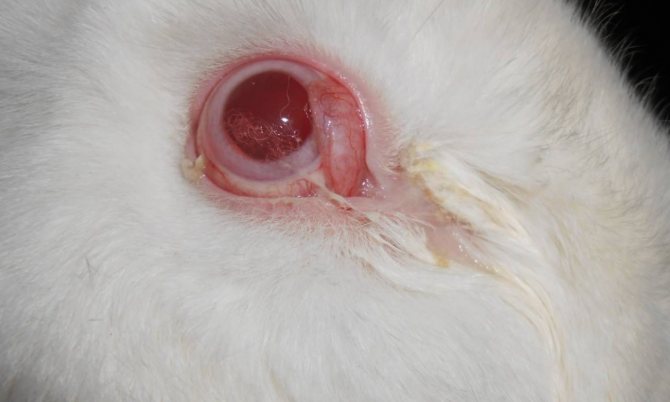
Almost all eye diseases sooner or later lead to pore eyes, and often owners notice the problem only after finding rabbit eyes stuck together from pus.
Eyes can fester as a result of infectious diseases or mechanical damage. In the second case, it is possible for a secondary infection to enter the damaged eye, which will require treatment with antibiotics.
Eye conditions can relate to:
- centuries;
- the cornea;
- sclera of the eye;
- eyeball;
- conjunctiva:
- lacrimal ducts.

Mistake # 1. Blowing powdered sugar into the eye.
The "folk" remedy is supposedly an absorbable thorn. In fact, powdered sugar is highly hygroscopic and can reduce swelling of the mucous membranes. But she does not cure a thorn. Moreover, trying to treat uveitis with a powder on your own, you will get a blind animal.
Mistake # 2. Treatment of dacryocystitis with ointments. Since dacryocystitis occurs with pasteurellosis, owners may think that an antibiotic ointment will help with pore eyes. In fact, the ointment can clog an already inflamed nasolacrimal canal, making the situation worse.
Mistake number 3. Hope that hereditary volvulus of the eyelids will go away on its own with age instead of going to a veterinarian for surgery. Ends with perforation of the cornea and complete blindness of the animal, as usually the volvulus is present in both eyes.
Often the cause of eye diseases in a rabbit is problems in the nasolacrimal canal.
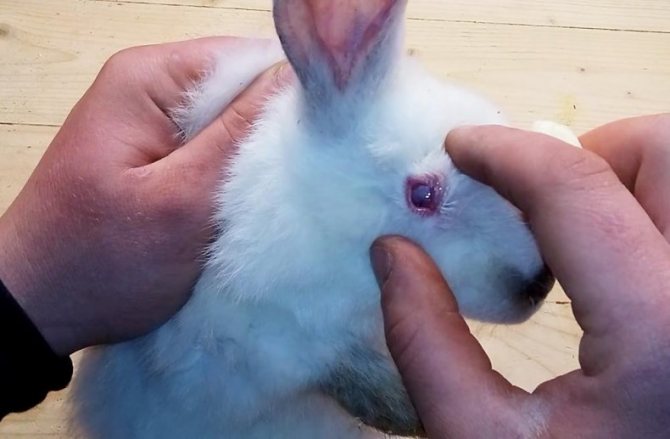
Dacryocystitis
The disease is secondary, its development in lagomorphs is due to the anatomical proximity of the lacrimal canal from the nasal passages and roots of the teeth. Therefore, the causes of the disease:
- inflammation of the teeth or obstruction of the canal by overgrown roots of premolars and incisors;
- the appearance of dacryocystitis indicates pastorella. In the case of primary bacterial invasion, the causative agent is the bacterium Pasteurella multocida, which lives on the nasal mucosa. Animals can get sick when there are unsanitary conditions in the cage, poor ventilation and a strong smell of ammonia.
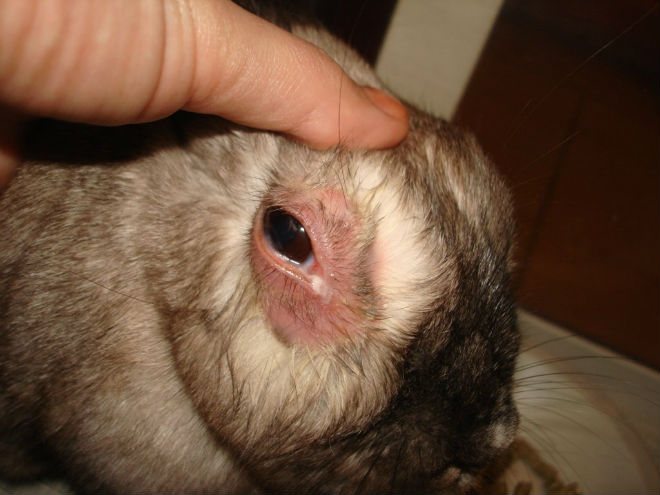

The appearance of dacryocystitis is associated with diseases of the nasal passages or teeth.
Signs of dacryocystitis:
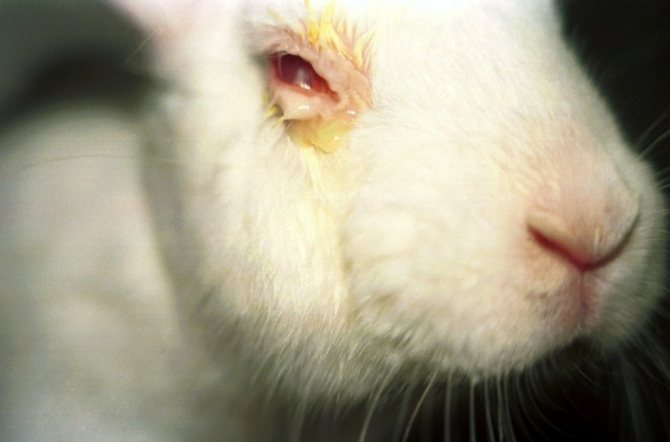
- the appearance of white pasty pus;
- tearing.
What to do in this situation: ointments are not used for treatment, since their dense structure leads to blockage of the channels. The measures involve flushing the ducts with saline with an antibiotic, the use of anti-inflammatory eye drops. Antibacterial drugs are instilled into the nasal ducts, when teeth become the cause of inflammation, they are removed.
Epiphora
This is the name of increased tearing of the eyes.As a rule, this is not a separate disease, but a symptom of mucosal irritation. In what cases does the epiphora appear:
- inflammation in the lacrimal sac;
- obstruction of the lacrimal canal;
- curled eyelashes or eversion of the eyelids;
- overgrown roots of the teeth, squeezing the ducts;
- traumatic eye injury or infection.
Rinsing will help reduce tearing, this will reduce congestion and irritation. For treatment, it will be necessary to eliminate the cause of the condition, after the extraction of the teeth, antibiotics will be prescribed.
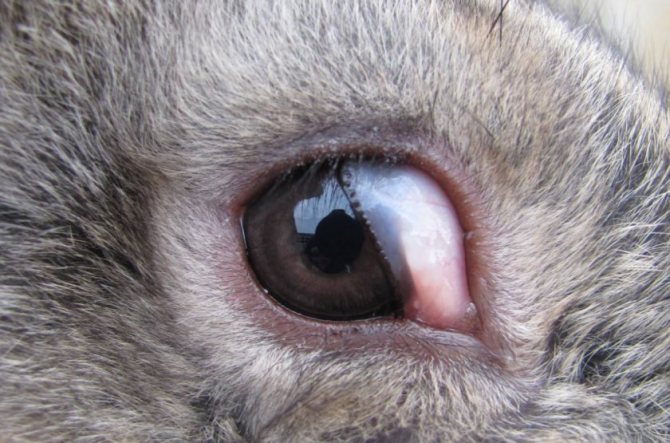
Exophthalmos
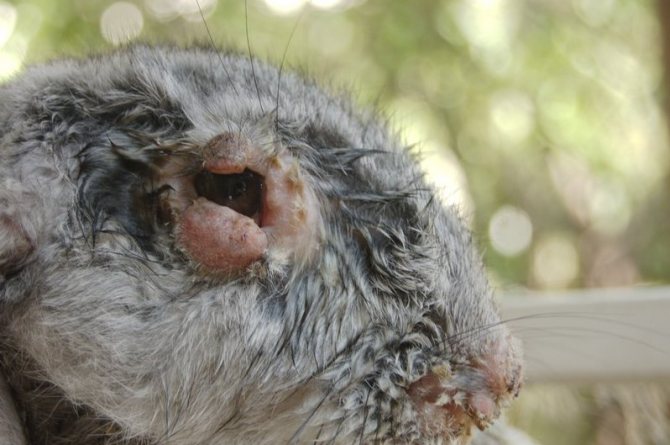
The cause of exophthalmos is an abscess that has formed behind the eyeball. Dental problems provoke its occurrence: improper growth or grinding of teeth, caries. Under pressure, the orbit leaves the orbit, protrudes outward, the pupil loses its mobility. As a result, the animal cannot close the eyelids, the corneal mucosa dries up, becomes cloudy, eroded areas form on it, and they gradually transform into ulcers. The disease cannot be cured, so the eyeball is removed.
Description of the breed
White giants are impressive in appearance. They inherited their large dimensions from Flanders, which is considered the world record holder in terms of weight.
White giants are impressive in appearance
The average weight of albinos is 3.5 to 6 kg. The large weight complements the body length, which often reaches 60 cm. The main features of the breed's constitution include:
- elongated dense body;
- wide chest, reaching 40 cm or more in girth behind the shoulder blades;
- elongated, large head;
- rounded, straight ears, the length of which is 15 cm;
- tucked up strong paws, which are set quite wide relative to the body, and therefore the animals are better controlled with a large body.
As for the color, for all, without exception, purebred offspring, the fur assumes a perfectly white suit. Certain blotches, a yellowish or grayish shade of fluff can be traced only in those individuals who were born in the process of crossing with other varieties of rabbits.
The completely red eyes of the animal are also a characteristic feature of the violation of melanin synthesis. Due to the absence of such pigment, the iris becomes completely colorless. Therefore, the blood vessels underneath are easily visible from the outside. It is they who provide the red color to the eyeball.
In addition to the obvious signs of the exterior of the breed line, there are two more features that deserve attention:
- Poorly developed fur on the limbs. Such a characteristic, in combination with a large body weight, suggests certain inconveniences in keeping livestock. If the rabbit is kept in open-air cages with a slatted floor, he quickly develops corns, which are quite difficult to get rid of on his own. Therefore, it is better to make the flooring in the cage from solid materials.
- Chest in females. This element of appearance is not manifested in all animals. That is why, after comparison, many breeders confuse it with a double chin. Perceiving this as a consequence of overfeeding, they begin to sharply reduce the calorie content of the diet. In fact, such education has nothing to do with obesity and, on the contrary, is a sure sign of the rabbit's excellent health.
Classification
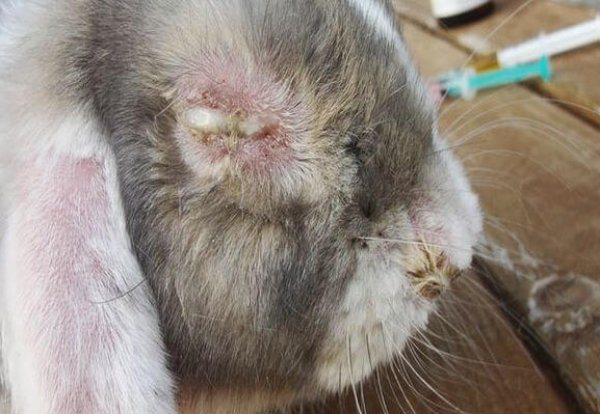

Ophthalmic diseases in rabbits are conditionally differentiated into types:
- inflammatory processes;
- congenital pathologies;
- infectious invasion.
Although the classification is rather arbitrary, treatment measures will depend on the cause of the problem. In some cases, the disease is easily treatable, sometimes it is necessary to completely remove the visual organ.
In terms of frequency of occurrence, infectious infection is in the first place, when pathogenic microflora penetrates directly into the eye.Sometimes the process goes to the organ due to inflammation of the teeth or mucous membranes in the sinuses.
An attentive owner will immediately see that the pet has eye problems:
- the rabbit squints its sore eye;
- scratches it;
- tearing and suppuration appear;
- eyes turn sour and stick together.
The formation of tumors of various etiologies is also found in rabbits. When they form in the eye area, they become an ophthalmic problem. Elements are small and large, formed in a single copy, sometimes they are multiple formations. For diagnosis, tissue scraping is taken for histological examination, and treatment is carried out based on the result. As a rule, the rabbit's eye is removed.
Although the classification is rather arbitrary, treatment measures will depend on the causes of the problem. In some cases, the disease is easily treatable, sometimes it is necessary to completely remove the visual organ.


In terms of frequency of occurrence, infectious infection is in the first place, when pathogenic microflora penetrates directly into the eye. Sometimes the process goes to the organ due to inflammation of the teeth or mucous membranes in the sinuses.
An attentive owner will immediately see that the pet has eye problems:
- the rabbit squints its sore eye;
- scratches it;
- tearing and suppuration appear;
- eyes turn sour and stick together.
The formation of tumors of various etiologies is also found in rabbits. When they form in the eye area, they become an ophthalmic problem. Elements are small and large, formed in a single copy, sometimes they are multiple formations. For diagnosis, tissue scraping is taken for histological examination, and treatment is carried out based on the result. As a rule, the rabbit's eye is removed.
Ophthalmic diseases can be divided into three types: inflammatory processes, infection, and congenital. Unfortunately, many ailments end with surgery followed by removal of the optic organ.
The most common diseases among the diseases are infectious abscesses that arise due to the ingestion of infectious agents behind the organ of vision. The first sign is the discharge of pus from the eyes. A rabbit can become infected if an infection enters the bloodstream or a disease of the molars. There are no other ways of treatment other than surgery followed by removal of the eye. After the operation, the animal is prescribed a course of antibiotics.
The appearance of neoplasms is a condition far from new to rabbits. Until now, the reasons for their appearance have not been fully clarified. Neoplasms have a different appearance and can appear in a single or multiple form, have very large sizes. So, they can appear in the amount of several pieces on one of the visual organs.
Read more: Why does the bark burst on a cherry how to treat
Productivity
The large weight of white giants is the main reason that such animals are bred to obtain valuable dietary meat. The yield of rabbit meat from one head, 65 days old, is 47%. If correct feeding is observed, this indicator increases to 59-60% by the 275th day of the animal's life. At the same time, livestock meat products are in high demand due to their delicate texture and excellent taste.
There is a high demand for skins of this breed of rabbits.
But of course, these rabbits are raised not only for meat productivity. There is a high demand for skins of this breed of rabbits. They are distinguished by high density, silkiness and softness of the pile. A wide range of different garments and accessories are made from such raw materials.
Reference. According to the results of the research, it was revealed that on an area of 100 sq. mm of rabbit skin grows on average 18-22 thousand hairs.At the same time, there are about 20-23 downy hairs for each core villus.
Especially spacious cages are used for breeding such rabbits. They should have a simple design that will make daily cleaning as easy as possible. The floor of such a cage must be made of solid material. Also, you should immediately install a large drinking bowl and a feeder inside.
The aviary must be divided into two halves. The first is open. The animals will walk in it during the day. The second half is a shelter closed on all sides for females and young animals.
Both young and adult livestock are recommended to be kept exclusively on the street. Summer heat and mild winter frosts allow you to quickly harden the body of living creatures, which significantly reduces the likelihood of disease. Animals should only be moved into the premises if the temperature drops below -20 degrees. Such air cooling is fraught with frostbite.
As for the content of the breed's rabbits, they should be handled with extreme caution during inspection and transportation. Their bones and spine are fragile and easily damaged. In addition, babies gain weight much faster than their bone tissue has time to strengthen. Therefore, if the bunny is scared, he, having made an inaccurate sharp movement, can break the paw himself.
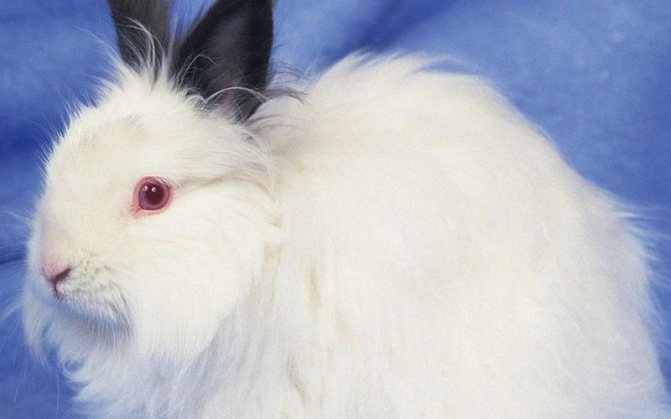
Albino bunny
Also, it is worth noting that young animals should be seated in separate cells already at the age of 2-3 months. In rabbits, rapid puberty is traced and, if they are not planted in a timely manner, they begin to indiscriminately mate. And at such a young age, it leads to a slowdown in growth, and also implies a high probability of the development of pathologies in the offspring.
Types of eye diseases, their localization
Exophthalmos
| Disease | Causes of occurrence | Symptoms | |
| Entropium, in common parlance "twist of the eyelids" | As a complication after keratitis; prolonged conjunctivitis; convulsive contraction of the circular muscle of the eyelids; cartilage deformation; hereditary predisposition * | The edge of the eyelid, together with the eyelashes, is wrapped inward towards the eyeball; due to friction of the eyelashes against the cornea, secondary keratitis (inflammation of the cornea) or corneal perforation occurs; dead cells are rejected, forming purulent outflows from the eye | |
| Ectropium (drooping eyelids) | Heredity; complication after keratitis; conjunctivitis; paralysis of the facial nerve. | The edges of the eyelids hang outward; the bare conjunctiva becomes inflamed due to mechanical stress or infection; transparent tear streaks initially appear; in advanced cases, decay begins | |
| Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids) | surface | Mechanical damage: bruises, wounds, burns; irritation of the eyelids as a result of mechanical, chemical or thermal exposure | When superficial, there are three stages: 1. itching, redness of the eyelids; 2.thickening of the edges of the eyelids, the appearance of scales, narrowing of the palpebral fissure, loss of eyelashes, redness of the conjunctiva; 3.the formation of pustules around the eyelashes and ulcers after opening the pustules |
| deep | Swollen and sore eyelids; purulent discharge from the inner corner of the eye; the eye is closed; the conjunctiva is edematous, protruding to the palpebral fissure | ||
* In Rex rabbits, due to a mutation of the gene responsible for the development of hair, the eyelashes on the eyelids often bend inward and rub against the cornea, causing secondary keratitis up to the perforation of the cornea. White New Zealand rabbits are prone to turning the eyelids.
Curled eyelashes, irritating the cornea, at best lead to an eyesore.
Hereditary ectropium is not very common in rabbits, but it can result from damage to the eyelid in a fight or due to illness.
Allergy
Rabbits have watery eyes with acute individual intolerance to any components. Other symptoms:
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- itching;
- rash;
- sneezing, runny nose;
- swelling of the eyelids.
Allergies occur to food, dust, cosmetics, fabrics, etc. It is important to find out the cause and isolate the rabbit from the allergen. You cannot get rid of it, but you can alleviate the course of an allergic reaction. Antihistamines, eye drops will help.


Sometimes tearing is accompanied by a runny nose, the animal rubs its eyes and nose. Then you need to take samples in the laboratory to identify allergies.
Other eye problems
Exophthalmos
The eyes of pets are often watery and sour due to debris from hay, grass, dust. Such problems can arise from a containment breach. In particular, the cage should not stand in a draft. It is necessary to clean the tray 2 r. per day. Do not spray perfume or household chemicals near rabbits. Watery eyes should be washed with an infusion of chamomile, strong tea. Such procedures will be useful for prevention purposes.
Discharge may appear due to blockage of the nasolacrimal canal. If this happens, you need to show the rabbit to the veterinarian. You should also identify the annoying factor. This is usually unsuitable bedding (straw or sawdust) and needs to be replaced.
Diseases of the organs of vision in rabbits can develop due to poor grinding of teeth or violations of their development. The animal grows so-called hooks that touch the nasolacrimal canal and cause lacrimation. It is imperative to contact a veterinarian, as the rabbit will not be able to grind them off on its own. To prevent the hooks from appearing, the animals need to be given wood rods.
Other diseases of the organs of vision include:
- occlusion (obstruction) of the cornea;
- cataract of the eye;
- volvulus of the eyelids;
- uveitis of the eye;
- abscess;
- neoplasms.
Occlusion or obstruction is characterized by the growth of connective tissue on the cornea. Treatment: surgery, then antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, "Prednisolone") are prescribed. If the case is advanced, the diseased eye is removed.
The main symptom of cataracts is lens opacity. As a result, visual function is impaired. As drug therapy, drops "Quinax", "Albendazole", "Fenbendazole" are used.
Uveitis is manifested by inflammatory processes in the vascular membranes of the eyes. Symptoms include redness, watery eyes, photophobia, and visual impairment or loss. For uveitis, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and vasodilators are used.
In rabbits, folds of the skin of the eyelids (called volvulus) may not develop properly. In this case, eyelashes grow towards the mucous membrane of the eye and injure it. Pathology is treated surgically: the animal is subjected to plastic surgery of the eyelids.
An abscess may develop as a result of an infection, and the space behind the eyeball fills with pus. The diseased eye is removed, then antibiotics are applied.
Eye neoplasms are treated mainly with a surgical method, chemotherapy and radiation are also carried out.
Injury
In hay or straw there are particles of objects dangerous for the cornea. The pet is also capable of damaging the shell with the sharp part of the food. At the same time, the rabbit's eyes are watery, he is worried, he tries to scratch them with his paws. Because of this, they become inflamed, redden, and swollen.
If trauma is the cause of tearing, the following actions are required:
- Put on a special protective collar on the rabbit to prevent self-injury of the animal with its paws when combing.
- Drip the medicine prescribed by your doctor several times a day.
- Carefully handle the hay to avoid re-injury.
Diseases of the conjunctiva, types of conjunctivitis
With entropium and ectropium, which are not hereditary, it is not the eyelids that are treated, but the diseases that precede these problems.In advanced cases, when volvulus / inversion has already formed, surgery is indicated. The eyelids are closed.
Superficial blepharitis treatment:
- lotions 1% baking soda solution;
- treatment of the edges of the eyelids with disinfecting ointments: - furacilin; - sodium sulfacyl; - mercury oxides;
- cauterization of ulcers: - iodine solution; - brilliant green; - percentage solution of nitric acid silver;
- antibiotics, novocaine therapy, sulfa drugs are used;
Treatment of gross blepharitis: the main emphasis on antibiotics, since the process is within the eyelid, symptomatic treatment is the same as for superficial. For any diseases of the eyelids, it is impossible to do without the help of a veterinarian.


The causes of diseases, united under the general name "conjunctivitis", can be different:
- mechanical damage: foreign body getting into the eye;
- chemical action: - acid; - alkali; - lime dust; - cauterizing agent; - ammonia in uncleaned cells;
- low or high temperature;
- pathogenic microflora.
In rabbits, in addition to pasteurella, chlamydia, staphylococcus and treponema, conjunctivitis can be caused by the myxomatosis virus. In the latter case, the animal is slaughtered.
The symptoms of conjunctivitis are common:
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- photophobia;
- blepharospasm (the eye closes by itself);
- itching (the animal scratches the eye);
- clear or purulent discharge from the eye;
- soreness of the eyelids.
Conjunctivitis is of several types:
- follicular;
- fibrinous;
- purulent;
- acute catarrhal;
- chronic catarrhal.
When treating any of them, the first step is to find and eliminate the cause.
| Conjunctivitis | Treatment | |
| Catarrhal | acute | Eye washing with astringent solutions: - resorcinol - 0.5%; - alum - 0.5%; - zinc sulfate - 0.25%; - boric acid - 3% |
| chronic | ||
| Purulent | Antibiotics in / m; silver nitrate 1%; tetracycline eye ointment; emulsion of levomiticin; sodium sulfacil ointment | |
| Fibrinous | Anesthesia; rinsing the eye with a solution of boric acid 2%; antibiotic ointment in the eye; the animal is kept warm | |
| Follicular | Cauterization of the follicles of the third eyelid with silver nitrate with further rinsing of the eye with saline; use tetracycline or any antiseptic eye ointment between moxibustion | |
Conjunctivitis with a mechanical cause is more treatable than any other form, especially if left untreated.
Feeding
The diet of rabbits can and should be varied. Only in this case it will be possible to provide the animal's body with all the nutrients and vitamins necessary for normal life.
Throughout the year, high-quality hay should be the main component of the white giants' menu. Such food normalizes the digestive tract of animals, promotes the growth of muscle mass due to the content of a large amount of protein and vitamins. But when feeding rabbits with such food, a number of points must be observed:
- feed the pets exclusively fresh hay;
- periodically, stocks should be checked for the presence of mold and signs of decay, and if they are found, such food should be excluded from the diet of rabbits;
- harvesting must be carried out on lawns and clearings as far as possible from the roadway and industrial enterprises.
In the spring-summer period, rabbits must be fed fresh vegetation. Meadow clover, dandelion leaves and stems, burdock, sow thistle are beneficial for their body. You can also harvest young nettles. But collecting herbs from the meadow is allowed only if the owner of the living creatures knows exactly what each specific species looks like. Otherwise, you can mistakenly prepare poisonous greens, which can lead to a number of intestinal diseases.
To avoid this risk, use fresh green food from plants growing in the garden.Rabbits and adults are happy to eat sunflower leaves, tomatoes, melons (melon, watermelon, zucchini), pepper.
From vegetables and fruits, it is advisable to include the following in the diet:
- carrot;
- zucchini;
- cucumbers;
- apples;
- pears.
You can also feed banana flesh and skins to animals. But their consumption must be limited, as in large quantities they cause stomach upset.
Many livestock owners use foliage and branches of various trees for feeding. But the choice of such food should be approached responsibly. Leaves and shoots of apple, pear, acacia have a good effect on the digestion and health of rabbits. But do not feed the animals with oak greens. She is able to cause diarrhea in them.
Rabbit vinaigrette
Another useful component of feeding white giants is the so-called vinaigrette. This mixture is prepared as follows:
- Fresh grass and tree foliage are cut (not very finely) into enameled dishes.
- Cutted waste from vegetables and fruits is also added there.
- All this is thoroughly mixed and poured with boiling water.
- The entire contents of the container are boiled for two hours, filtered and allowed to cool down.
\
Rabbits eat such food with pleasure. It is rich in nutrients, vitamins and greatly enhances furry growth.
Inflammatory and infectious diseases
Conjunctivitis
The cause of conjunctivitis can be infectious diseases, an allergic reaction, or sawdust or hay in the eyes, a cell that has not been removed in time, or a lack of vitamins.
The symptoms of conjunctivitis are:
- rabbits with red eyes;
- lacrimation;
- discharge of pus and, as a result, sticky eyelids.
Conjunctivitis can also be present in young rabbits. Infectious conjunctivitis in rabbits can be brought in by a female rabbit. Usually, the eyes of rabbits open on the 10-12th day of birth. If the eyes of the rabbits are stuck together, they must be washed with a shaker several times. The open eye of the rabbit should be clean and mobile, the mucous membrane is transparent, it should not fester, there should be no redness around the eye. If one of the listed characteristics is in doubt, or if the baby's eyes are constantly wet, then it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist.
Keratitis
This is an inflammation of the cornea. In such cases, the veterinarian prescribes anti-inflammatory ointments or drops, rinsing the eyes. In some cases, drugs are also prescribed to regenerate the cornea. Antibiotics are sometimes prescribed. The cause of keratitis can be exogenous factors, that is, those factors that affect the very cornea of the eye. Also, the reasons can be endogenous factors that penetrate through the circulatory system.
A rabbit has keratitis if:
- clouding of the mucous membrane;
- violation of the specularity of the shell;
- purulent discharge;
- narrowed eyes.
Read next: How long do decorative rabbits live at home?
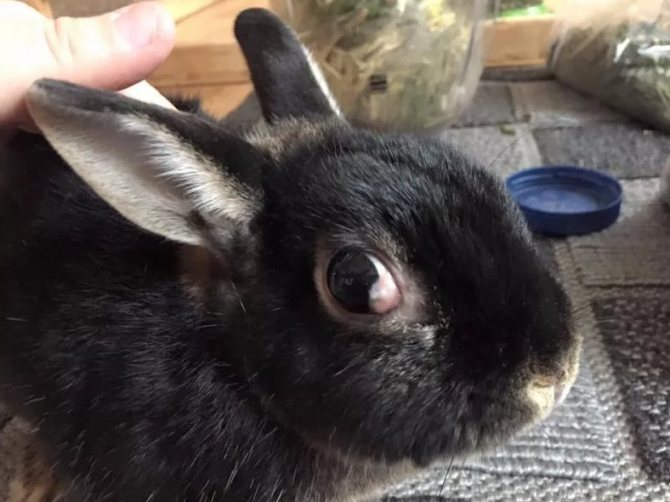
From the Greek language "ueva" is translated as "grape". In appearance, the choroid resembles a bunch of grapes. Uveitis is an inflammation of the choroid of the eyeball.
The causes can be infections of a viral or bacterial etiology, helminthiasis, eye or head trauma.
Symptoms:
- Increased pupil size
- Lachrymation;
- Adhesions in the lens and iris;
- Changing the shape of the lens.
To prevent the formation of adhesions, eye drops, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
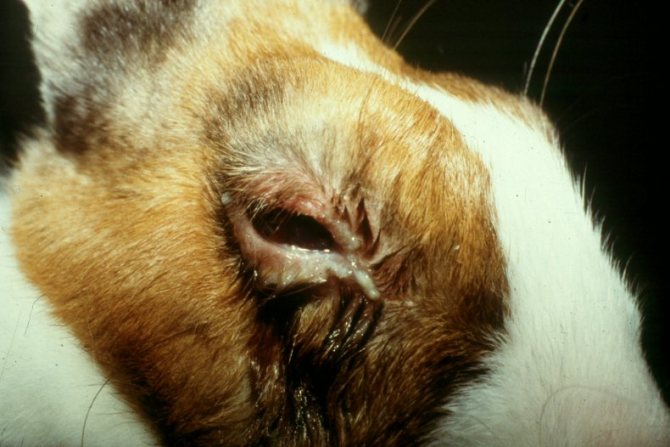
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is a disease that is a consequence of another ailment. The main symptom is that the rabbit's eyes fester. In some cases, infected gums and teeth may be the cause. Dacryocystitis is often a consequence of rhinitis or conjunctivitis. If your rabbit's eyes are stuck together, rinse them out.When the eye opens, you need to contact your veterinarian for advice.
After determining the cause of the disease, treatment is carried out with a number of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Myxomatosis
The cause is infection with the myxoma virus, which is carried by blood-sucking or rodents. This is one of the most dangerous diseases. In most cases, the animal cannot be cured; it must be slaughtered.
The rabbit's eyes are sticky, swollen, the eyelids swell and fall. Local nodular formations appear on the body. When myxomatosis is affected, the nodular lump can be observed near the rabbit's anus. The incubation period of myxomatosis is from 2 to 20 days.
In cases of revealing a dangerous ailment, it is necessary to notify the veterinary sanitary service. A veterinary service specialist selects material from the affected area of a sick rabbit and sends it for examination. When the diagnosis is confirmed, quarantine will be established for a period of 2 weeks, if there are no recurrent diseases.
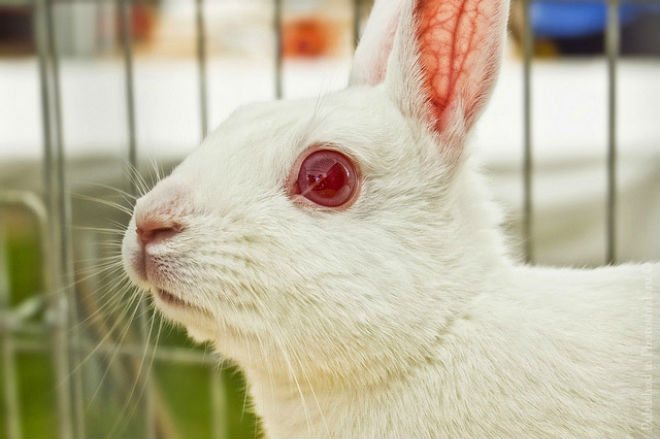
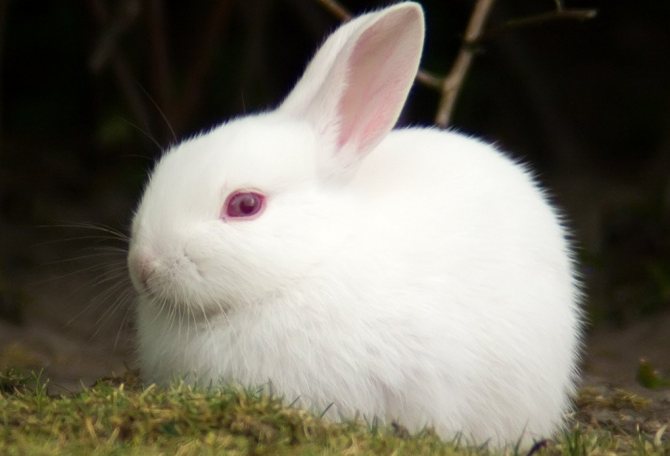
When red eyes are normal in rabbits
The owners of red eyes from birth can be white rabbits, or albinos. Albinism is not a disease. Albinos are found among all representatives of the animal world, most often in mammals. And although people like white animals, this is unnatural for them.
Learn more about white rabbits.
White is actually the absence of natural pigment. A certain gene is responsible for the production of pigment, which for some reason does not cope with its duties. For the same reason, albinos lack the color of the eyes inherent in their species.
The iris of the eyes of these animals is colorless, almost transparent. Blood vessels are visible through it. This is why white rabbits and other albinos have red or pink eyes.


Congenital
Congenital diseases include those that arise as a result of a deviation during fetal development or are hereditary.
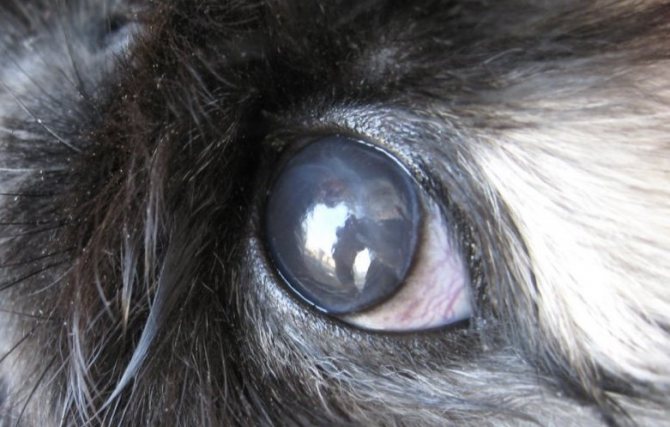
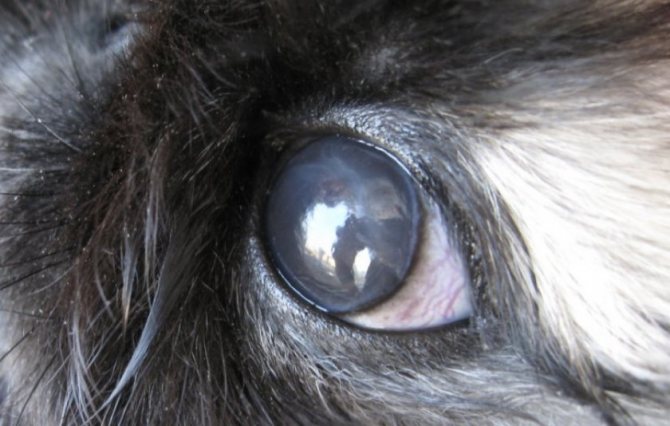
Cataract
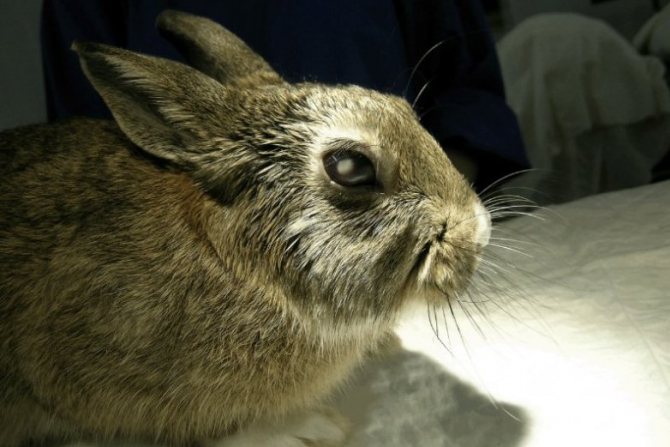
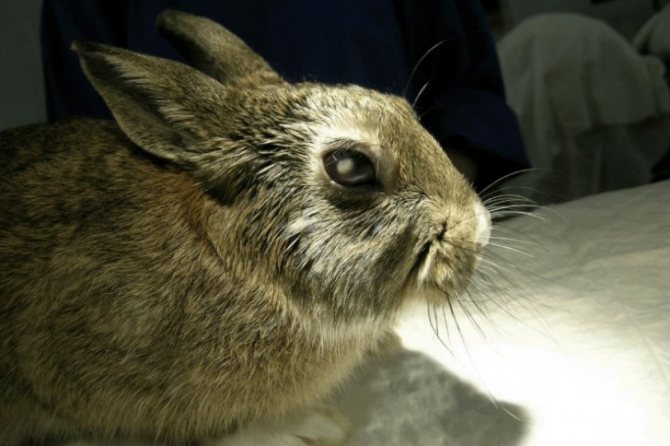
This is a disease that causes darkening of the lens of the eyeball, as a result of which its capacity is significantly reduced. Since the lens acts as a conductor that transmits light, clouding affects visual acuity. In the case of severe cloudiness, the eyes completely lose the ability to transmit visual information.
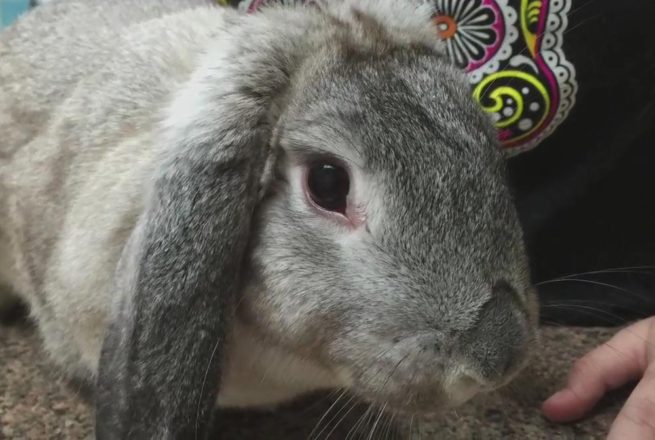


The main reason, according to doctors, is the mother's poor diet or the presence of infectious or parasitic diseases during gestation. Congenital cataract occurs in the fetus even at the stage of formation, so it is problematic to identify a specific cause.
Symptoms:
- clouding of the lens, which looks like a whitish spot overlapping the pupil;
- white or translucent discharge from the eyes;
- puffiness of the eyes;
- disorientation in space;
- the formation of a white angle on the iris of the eye.
Diagnosis: The diagnosis is made by a veterinarian based on an external examination and additional research. It is necessary not only to make sure that it is a cataract, and not a similar infectious or parasitic disease, but also to identify the cause. The disease is not always congenital, therefore, an infection of the visual organs can be the cause.
Sowing is carried out, as well as taking urine and blood tests to identify the presence of the pathogen. If none are found, the cataract is considered congenital.
Treatment: Since cataract is a denaturation of a protein that is part of the lens, treatment consists of removing the damaged area. The denatured protein cannot be returned to its original state, just as it is impossible to make the egg white after frying again liquid and translucent.
However, treatment is not limited to removal. If the cause is the activity of pathogenic organisms, then drug therapy is carried out so that a relapse does not occur.
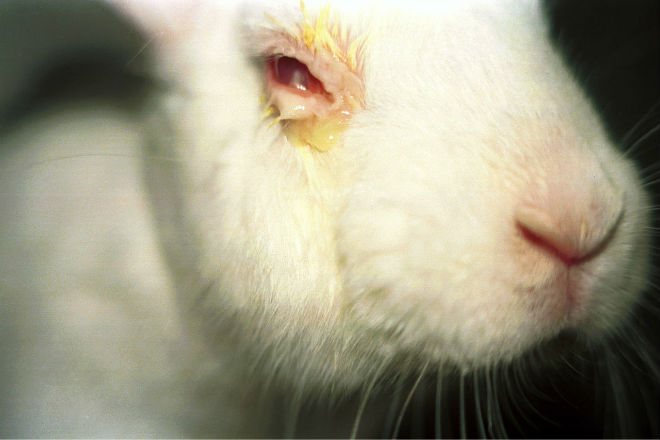


Much depends on the stage at which the treatment is carried out, therefore it is extremely important to consult a specialist immediately after the onset of characteristic symptoms.
Important! In the case of an operation at the last stage, there is a high chance of developing glaucoma.
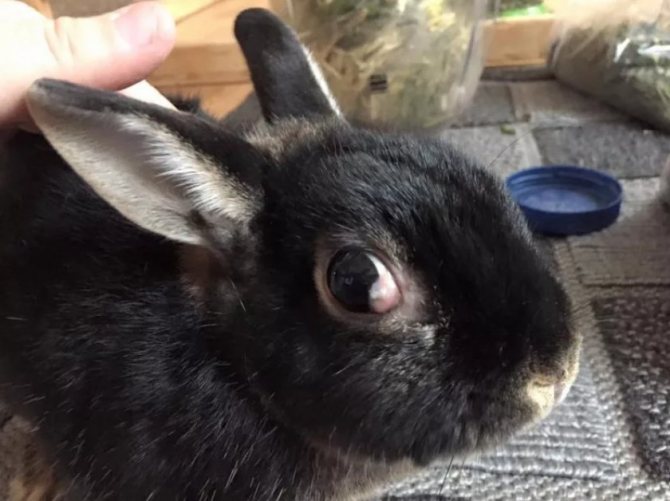
Glaucoma
It occurs due to an increase in pressure inside the eyeball. As a result, there is a gradual decrease in visual acuity, which ultimately ends in blindness. With a constant increased pressure of the fluid inside the eye, the cells of the retina, which are responsible for the transmission of visual information, die off.
Congenital glaucoma is caused by poor genetics. If the father or mother was diagnosed with glaucoma, then the chance of giving birth to young animals with such ailment increases several times. An alternative reason is poor nutrition or the presence of any infectious diseases in the rabbit during gestation, which was reflected in the form of a malformation.
Rabbit Glaucoma Symptoms:
- bulge of the eye;
- decreased vision, which leads to partial disorientation;
- redness of the white of the eye.
Diagnosis: the diagnosis is made by a veterinarian after an external examination and measurement of intraocular pressure. After that, the specialist determines the degree of neglect and decides how to treat the animal and whether it makes sense.
It should be understood that treating an old rabbit with several years of life left is quite dangerous, so you should not blame the doctor for inaction.
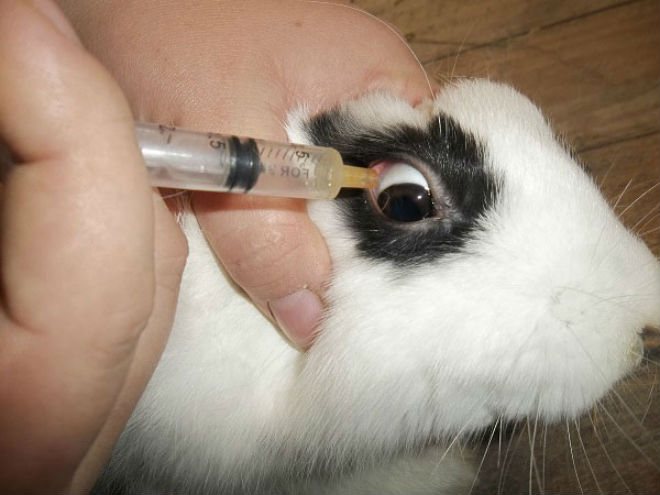

Treatment: it is not easy to identify this ailment even in humans, let alone animals that cannot tell about the problem. As a result, this leads to the fact that the rabbit gets to the veterinarian at the last or penultimate stage, when it is already useless to treat the organ. In most cases, the eye is removed, after which symptomatic therapy is prescribed.
Did you know? Rabbits can only distinguish between blue and green, as well as their shades. Their organs of vision do not see the red color.
In rare cases, drugs are prescribed to help lower intraocular pressure. However, this is only supportive treatment and does not correct the problem. The animal still gradually loses its sight, however, this affects its vital activity to a lesser extent.
Congenital eye diseases are called rabbits with which animals are born.
Cataract


Congenital diseases include cataracts - clouding of the lens of the eye.
The disease is characterized by clouding of the lens of the eye, refers to congenital ailments. Pathology occurs in newborn rabbits, the reasons for the development have not been precisely established. It is believed that intrauterine trauma leads to violations. The lesion looks like a small light speck on the eye, sometimes it covers the entire pupil.
Cataracts develop in older animals, sometimes parasites or diabetes cause the defect. At first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, a signal of its development is the appearance of a white spot in the eye, casting blue.
The disease cannot be completely cured, eventually leading to blindness, but supportive therapy helps to slow down the process. For senile manifestations, drops "Quinax" are recommended, which activate metabolism in the organ. For young rabbits, surgery is performed using the phacoemulsification method. In case of parasitic infections, anthelmintics are prescribed inside: "Albendazole" or "Fenbendazole".
Glaucoma
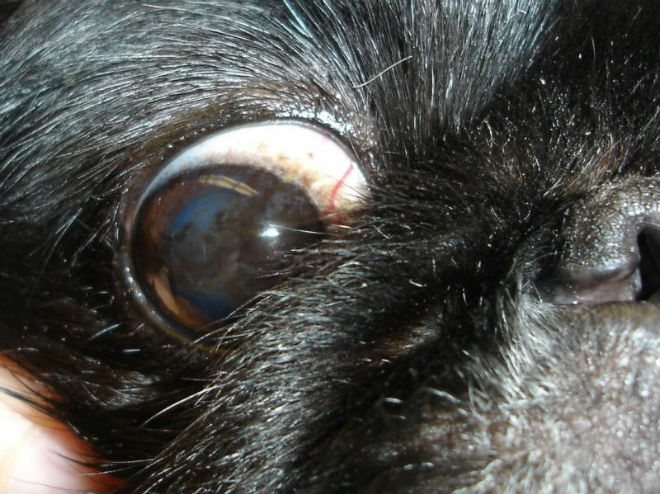

The pathology of the organ is characterized by increased intraocular pressure, over time the condition leads to loss of vision. It has been proven that the disease is inherited in white New Zealand rabbits. The disease is determined in the third month of the rabbit's life, sometimes it develops with age. At first, the disease manifests itself in a paroxysmal manner:
- the animal is worried about pain;
- the eye bulges out.
In advanced cases, changes in the eye lead to inflammation and loss of vision.The diagnosis can only be made by a veterinarian during an ophthalmological examination, but treatment with vasodilators does not work, therefore, removal of the organ is preferable.
Corneal occlusion
In occlusive processes, the cornea is overgrown with connective tissue. The factors causing the pathology have not yet been clarified. The problem is thought to be caused by decreased innervation in the borderline region between the cornea and conjunctiva. It is more common in young males from 5 months. The overgrown conjunctiva is removed by surgical methods. In difficult cases, the entire organ is subject to removal. Subsequently, the rabbit is given antibiotics and corticosteroids ("Prednisolone").
Blurred eyes. In most cases, opacity of the optic organ is congenital. Such a phenomenon is often found in young rabbits that have recently been born. The defect looks like a light-colored spot (partial clouding) or the entire eye is clouded. There are no cures. Blocking the lacrimal canals - this disease should not be attributed solely to genetic ones.
It can occur due to improper tooth growth. Researchers say that some breeds of rabbits have a predisposition to this disease. During the disease, the lacrimal canal is blocked, which goes from the ear through the nasal cavity. As a treatment, it is supposed to rinse the eye, remove excess fluid from the canal.
Read more: Keela cabbage: control measures, how to get rid of the disease, video and photos. What you need to know about the keel of cabbage How to help cabbage if it has overcome the keel
Myxomatosis is another common acquired eye disease in rabbits. It is accompanied by purulent inflammatory processes, conjunctivitis. The disease is characterized by the formation of purulent tumors in the eyes. This problem most often appears in rabbits with a non-standard eyelid structure. At the moment, there are only assumptions why there are changes in the anatomical structure of the eyelid.
This can be either a genetic feature or a disease caused by a bacterium unknown to science. The part of the upper eyelid where the eyelashes are located does not have an even surface, but has slight roughness. Symptoms: corneal ulcer and conjunctivitis. Irritation of the visual apparatus appears, due to the fact that eyelashes grow incorrectly. Symptoms of the disease can be observed in young rabbits up to the second week after birth. As a treatment, surgical eye plastic is used.
Origin story
Rabbits of pure white color are quite rare in various breed lines. It is extremely difficult to get one in the selection process. Breeding a breed for which albinism is a characteristic feature is even more difficult. But, it was this goal that the breeders of one of the German institutes set themselves. This direction of work was dictated by the requests of the fur industry, in which white fur was especially highly valued.
For a certain period of time, albino rabbits of the Flandre breed (Belgian giant) were selected as the basis for the breed line. In these animals, the color is predominantly gray, but in some individuals, due to the peculiarities of genetics, the synthesis of melanin, which is responsible for this color, is disrupted. As a result, a snow-white rabbit with red eyes is born. It was these animals that were purposefully selected by German breeders for the founding of a new breed. Over time, the characteristic was firmly entrenched in animals and began to be passed on to subsequent generations. But with the development of the new breed, a number of negative aspects appeared, including:
- weak immunity;
- extremely low fertility;
- inability to cope with harsh climatic conditions;
- weak endurance.
Breeders from Belgium managed to partially solve such problems, to which almost all livestock were transported in 1928.But the breeders from the USSR finally corrected all the negative aspects in the breed line. To enhance the fertility of animals, the rate of their development and resistance to the local harsh climatic conditions, they were crossed with representatives of the gray giant and chinchilla breeds.
As a result, crossing other albinos with a rabbit of Belgian origin yielded results, and the white giant was firmly entrenched in the territory of the Soviet Union. But, at the same time, the size and mass of living creatures, which she inherited from the flanders, suffered to a certain extent.
Mechanical and chemical damage to the eyes of rabbits and their treatment
Mechanical damage to the eyes of rabbits occurs as a result of fights between animals, prickling of the eyes with seninki during feeding, bruises, if, when frightened, the rabbit stumbles upon the corner of the feeder or other object.
Such damage usually goes away on its own, although the eye can look creepy. Often in this case, there is profuse lacrimation from the eye. The eye is closed. There may be swelling of the eyelids.
To prevent secondary infection, in this case, you can drip the rabbit into the eyes with a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Chemical irritation of the eyes in a rabbit can only be caused by ammonia fumes from decaying urine in an uncleaned cage. In this case, not medical, but sanitary measures are needed.
If the eyes are clogged with earth or lime from the walls, the eyes of the rabbit are washed with saline. If the rabbit's eyes were rinsed almost immediately after clogging, then no further action is required. Otherwise, drops with an antibiotic are instilled.
A rabbit's eyes may begin to watery due to an allergic reaction. In this case, no eye treatment will help until the allergen is identified and eliminated.
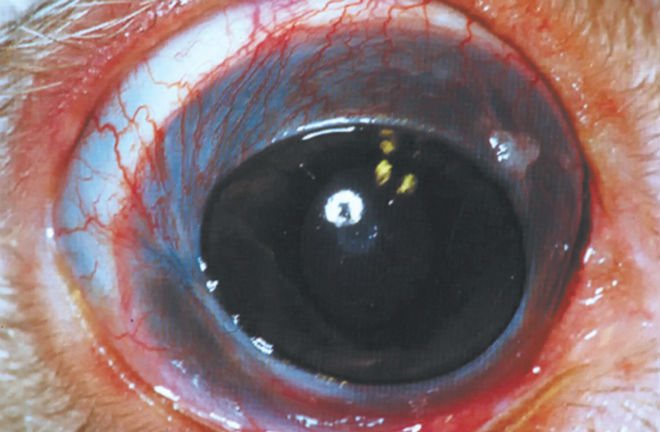

Important! An allergic reaction often occurs if the hay is contaminated with mold.
This hay is often called dusty due to the fact that when shaken into the air, a lot of dust rises, which is actually mold spores. These same spores often cause respiratory tract damage in rabbits.
To eliminate the problem and prevent an allergic reaction in a rabbit, such hay will have to be shed for at least 10 minutes.
Dust and small debris that enter the rabbits' organ of vision (usually hay particles) can all lead to minor eye injuries, which subsequently develop into serious diseases if nothing is done. Hence the mucous discharge and pus. You can cure rabbits from such diseases with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Corneal ulcer
As a rule, such an ailment is formed due to the development of glaucoma. However, sometimes domestic rabbits simply suffer from a lack of tear fluid. That is, the shell of the eyeball is not moisturized, hence the appearance of a corneal ulcer. In most cases, you will be able to save the animal if you decide on a surgical intervention.
Prevention measures
Timely preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of lacrimation in rabbits. The following preventive measures are recommended:
- regular cleaning of the rabbit cage (preferably twice a day), cleaning the room with the rabbits there, observing the rules of hygiene;
- elimination of sources of strong odors;
- avoiding drafts in a room with rabbits;
- treatment with water or steam of hay affected by mold;
- the correct diet of the animal with the obligatory inclusion of hay and hard vegetables or fruits;
- periodic examination of the animal with the aim of early detection of symptoms;
- preventive vaccination.
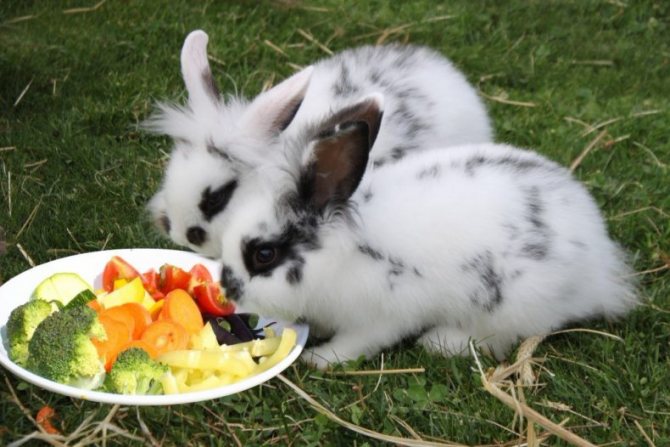


Hard vegetables in rabbits' diets reduce the risk of watery eyes
As you can see, there are many factors that cause watery eyes in rabbits. This can be caused by the conditions of their detention, various diseases or congenital pathologies.In almost all cases, the situation can be corrected, the main thing is to detect the problem in time and not delay taking measures to eliminate negative factors.
Eye diseases associated with pasteurellosis
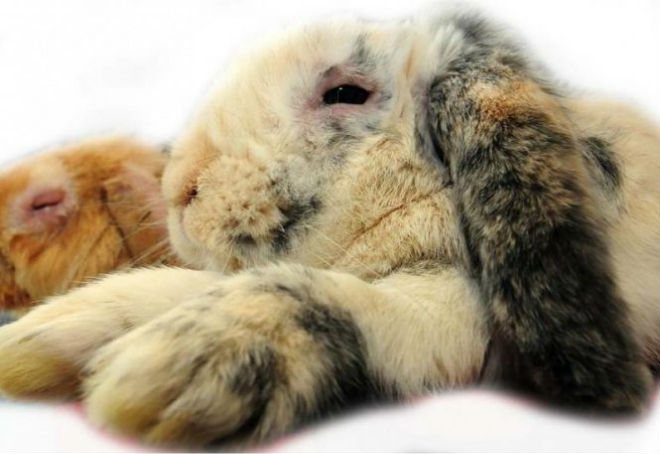


Initially, the rabbit is brought to the veterinary hospital with conjunctivitis, festering eyes, lacrimation, blockage of the nasolacrimal canal, inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis). When diagnosed, it turns out that these are symptoms of pasteurellosis. Along with the treatment of pasteurellosis, it is necessary to treat eye diseases. This is especially true for dacryocystitis and obstruction of the lacrimal canal.
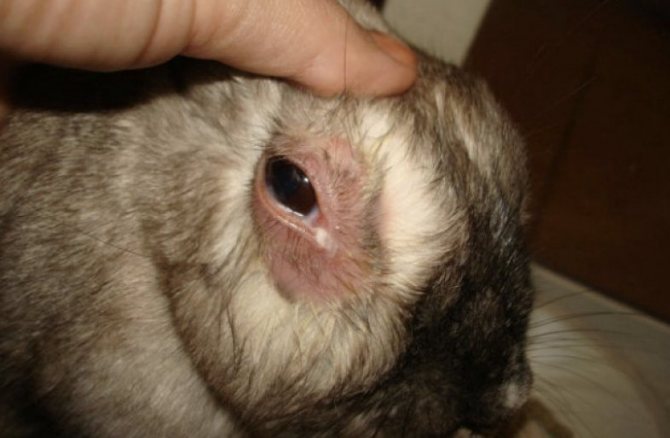
Inflammation of the lacrimal sac is externally expressed in redness and baldness of the nearby skin, as well as the release of pus in advanced cases.
Any local methods of treating eyes with pasteurellosis without affecting the underlying disease will not give a result, but will transfer the course of eye diseases into a chronic form. Therefore, the therapy of pasteurellosis and eye diseases is carried out simultaneously. Dacryocystitis and canal blockage are often interrelated and are treated in parallel.
Dacryocystitis
An eye disease that is congenital in nature, as it occurs with abnormal growth of molars, which change the shape of the nasolacrimal canal. As a result, at first, the eye begins to water, since the discharge of the lacrimal gland does not have the opportunity to get through the nasolacrimal canal into the nose. The blocked channel becomes inflamed. Later, when a secondary infection sits on the inflamed surface, the outflows become purulent.
Treatment is possible only by surgery, as it is necessary to remove improperly growing teeth. The operation is performed in a veterinary clinic. Accordingly, the treatment of dacryocystitis is possible only for decorative rabbits. It is easier for a farmer to kill such a rabbit.
After removing the incorrectly growing tooth, the nasolacrimal canal is cleaned. In advanced cases, drainage is required. Since advanced cases automatically imply suppuration and infection of the canal, antibiotic eye drops are used to eliminate the secondary infection.
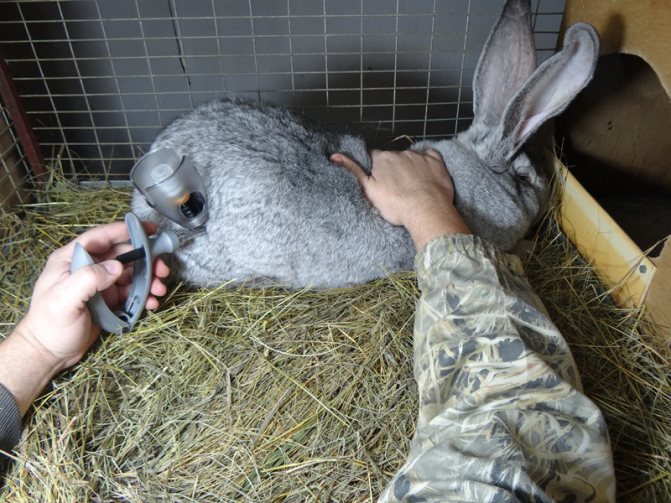
In the photo, the drainage of the nasolacrimal canal, popularly called the "obstruction".
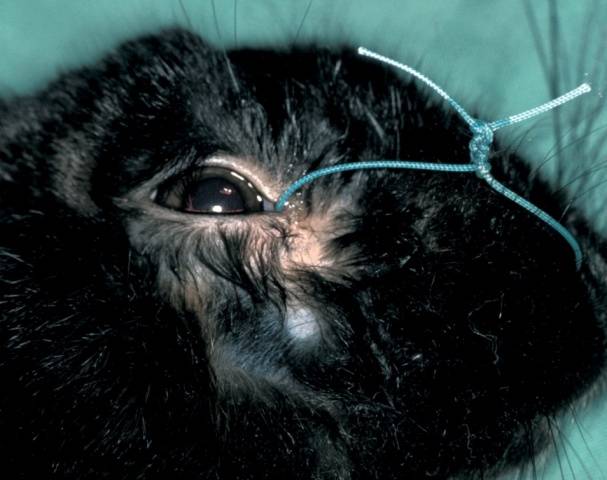

The principle of operation is simple: periodically it is necessary to pull the cord back and forth to clear the channel and get rid of dried mucus.
Breeding
Puberty in females and males of albinos occurs 4 months after birth. But, most breeders agree that they should be allowed to mate no earlier than the 6th month. Sexual hunting occurs regularly in rabbits.
Rabbits bring up to 10 cubs in one litter. For a year, one female has about 6 rounds. Moreover, she is ready for re-mating within 2 days after the birth of offspring. Rabbits are distinguished by a developed maternal instinct. They constantly warm young animals, they do not have the habit of eating newborn rabbits. In addition, 240-250 g of milk is formed in the mammary gland of a rabbit per day, which is quite enough for feeding the offspring. But, such a volume of colostrum is formed only under the condition of a properly selected diet.
Rabbits with their mother are left up to 2 months of age. After that, the babies are weaned.
A large number of domestic specialized enterprises are engaged in breeding albino rabbits. Such pets are not uncommon in small subsidiary farms. The reason for this is the snow-white skins of animals, which are highly valued by fur factories, as well as dietary meat with high taste. But when breeding white giants, nevertheless, you should first familiarize yourself with the peculiarities of their maintenance and feeding.
Rabbit breeding has become very popular lately. As a popular joke goes, "rabbits are not only valuable fur, but also 3-4 kilograms of dietary, easily digestible meat."
Well, on top of that, there are also lovers of decorative rabbits, for whom these cute animals become real friends. Like any living creature, these pussies can get sick from time to time. The article will focus on possible eye diseases in rabbits, how to prevent, recognize in time and how to treat.