Livestock »Horses
0
1337
Article rating
If you decide to become the proud owner of a horse, then you should figure out how to keep the animal healthy. In this article, we will analyze in more detail the topic "Diseases of horses". It is important to recognize the symptoms of the disease in time, as well as choose the correct treatment tactics. The article just gives an answer to the question of what horses are sick with.
Horse diseases
Symptoms of horse diseases
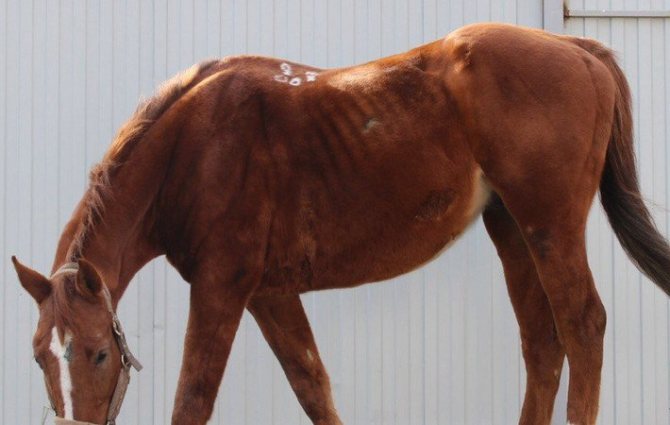
A sick horse will let you know about his illness by noticeable signs, they can be detected with the naked eye. The following symptoms indicate a horse's illness:
- The coat loses its shine, becomes dull and untidy.
- The horse stops eating.
- The eyes of the individual become sick, the characteristic shine disappears.
- The character of the horse changes, the animal may become more restless or, conversely, fall into an apathetic state.
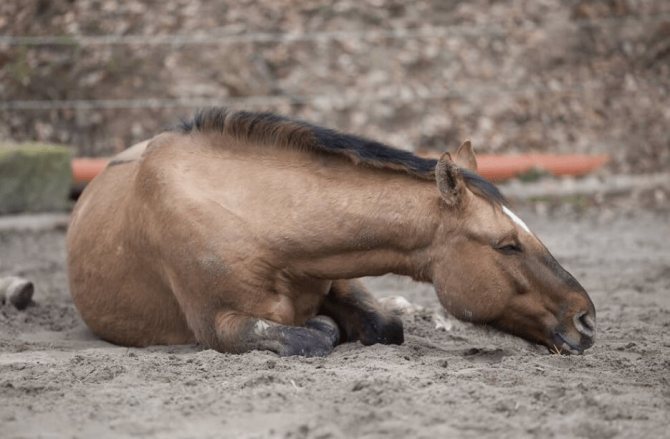
- Walking becomes wobbly and unstable, the animal can roll over on its side and fall.
- The nature of the excrement often changes.
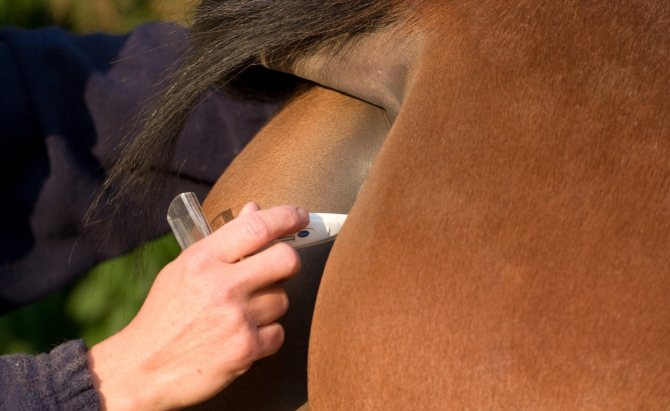
If you yourself noticed this or that symptom, then this indicates that the horse is sick and needs help. Livestock breeders do not recommend self-medication: a really correct diagnosis can only be made by a doctor, that is, a veterinarian, after which an effective treatment will be chosen. Only a specialist will be able to carry out a complete diagnosis, which will include laboratory tests and physiological measurements: pulse, respiratory rate, heart rate and temperature.
Despite the fact that almost the whole picture will open before the veterinarian, the doctor will still ask the owner how the horse's behavior has changed, what symptoms were noticed at home. For example, you can talk about a recent onset of diarrhea or cough, and so on.
Speaking about horse diseases, it is customary to distinguish two main groups of ailments, which are most often diagnosed in artiodactyls:
- Horse diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ailments of horses that relate to the work of the musculoskeletal system.
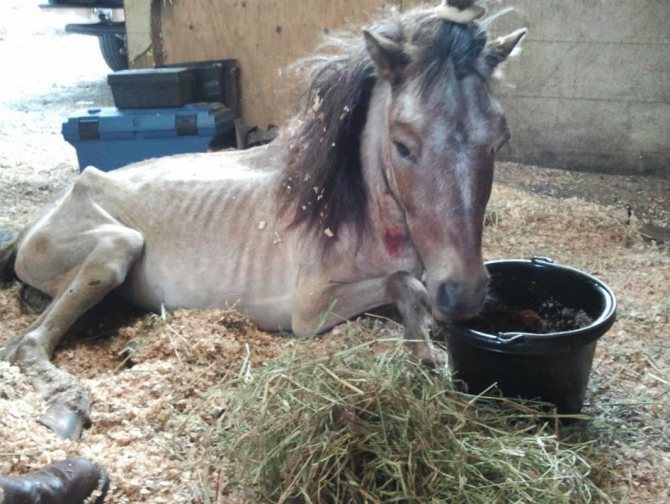
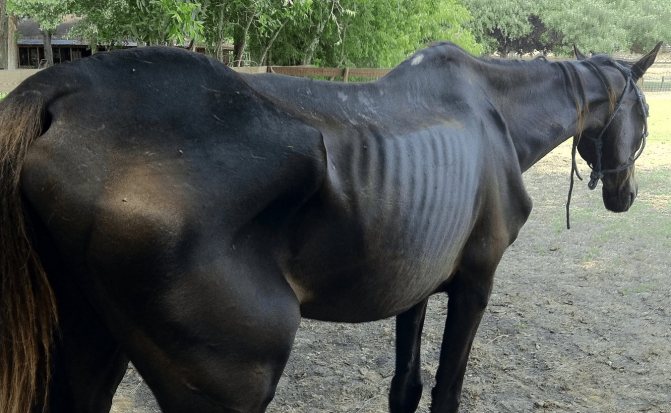
It is worth saying that in his life a horse cannot avoid at least one case of the disease, even despite proper care and balanced nutrition.
Hoof care - cleaning and trimming
Constant care of the horse's hooves allows you to maintain their health and prevent developing pathologies in time. Basic maintenance procedures include proper cleaning and pruning. They are carried out every 1-2 months.
Trimming is carried out very carefully so as not to damage the limb. Moreover, in the process, the following instructions are followed:
- The hoof is pre-soaked in water for 2-3 minutes. Then the animal is fixed with belts in the machine.
- With a special brush and hook, they clean off the adhering dirt and debris, first from the horny wall, and then from the side of the sole.
- Special attention is paid to the indentations and the arrow area. The dirt is cleaned from the heel area towards the toe.
- The performer tightly clamps the horse's leg between his legs. Further, the overgrown sections of the horny wall are evenly cut off with forceps.
- With the help of a rasp, grind off all burrs and irregularities. After that, the sole is smoothly leveled and the hoof is polished. Do this from the heel to the toe.
It is worth noting that although the procedure is simple, if possible it is better to entrust it to an experienced specialist.
Horse health indicators
To understand that not everything is in order with the horse, it is worth figuring out which horse's indicators are considered normal. For acquaintance, we give a table in which the indicators of normal vital activity will be indicated.
| Criterion | Normal readings |
| Temperature indicator | from 37.7 to 38.5 ° C |
| Respiration rate per minute | 9-16 breaths at rest |
| Heart rate per minute | 25 to 48 beats in one minute at rest |
| The appearance of the mucous membranes | Normal color is pink, the surface is moist |
| The presence of discharge | A healthy horse should not have discharge in principle. |
Now it's time to figure out in more detail what ailments an artiodactyl can suffer from. For convenience and easy perception, it is necessary to divide the diseases into several groups. Let's start with a description of skin diseases in horses.
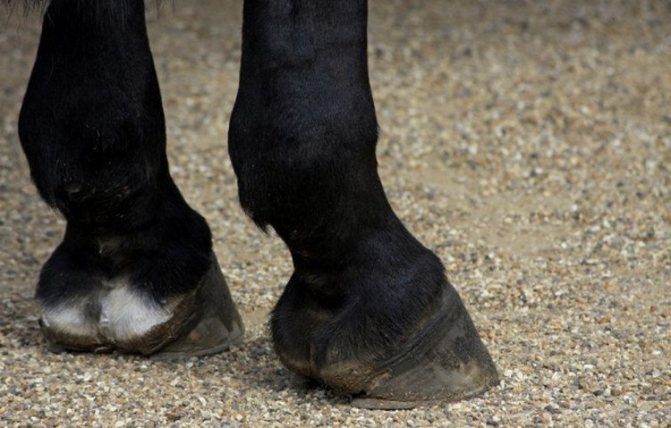
Signs of a healthy hoof
Every experienced horse owner knows that any damage to the hoof can lead to serious complications for the animal. Therefore, regular inspection of the hoof horn should be carried out. And in order to timely identify the incipient pathology, it is necessary to clearly know what a healthy hoof looks like.
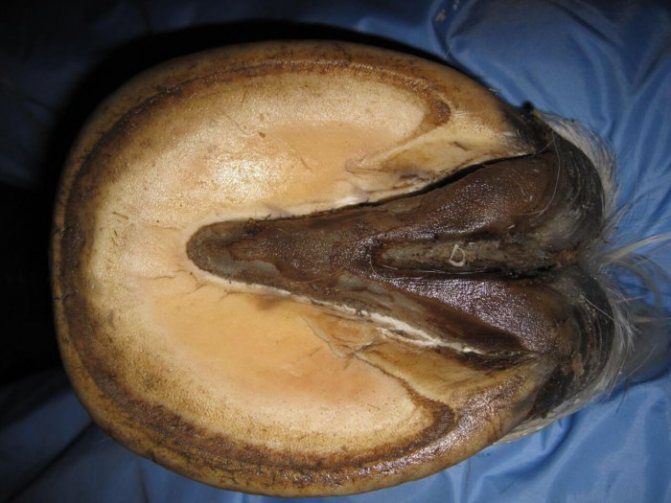
Healthy hoof
Signs of the health of the horny capsule are the following:
- the wall of the shoe is covered with an intact thin layer of stronger horny tissue, on which there are no cracks or dents;
- the sole of the hoof is slightly bent inward and has a uniform color over the entire surface without red and yellowish spots (hints);
- horn arrow assumes the original shape with sharp edges and the absence of cracks;
- the corolla in the lower part is rounded and smoothly connects with the crumb;
- there are no cracks or signs of damage on the crumb;
- there is no pronounced separation between the sole and the edges of the wall.
During the stroke, the foot touches the ground surface throughout its entire area. If there is a small gap in the heel, the foot is most likely deformed and needs correction.
Equine skin diseases
Skin problems occur in every second horse, they cause a lot of trouble and discomfort to the animal, but, fortunately, most often they are not contagious. In order to help the little animal, you will have to spend a lot of time and effort, not to mention material costs. In addition, it must be taken into account that during the period of treatment it is worth relieving the horse from physical exertion and training, since movement and friction against the saddle or girth can bring pain.
As for the frequency and frequency of the appearance of skin diseases, it is noted that they most often manifest themselves in the summer, when the horse sweats more, is exposed to the bites of gadflies and other insects. In winter, skin diseases also occur, but lice, mites and other skin parasites are already the cause. Let's find out which diseases belong to this group.
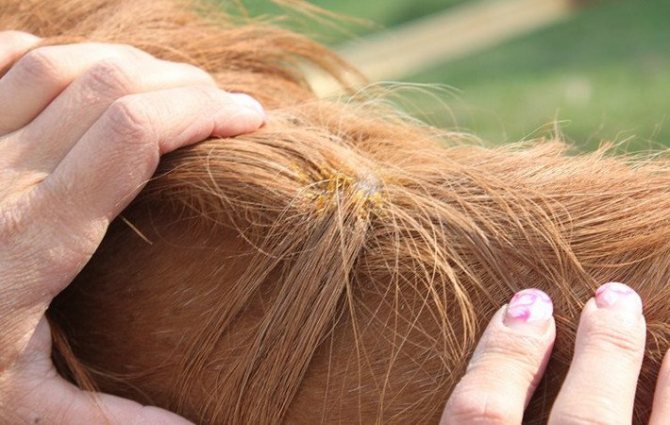
Horse scabies, or dermatosis
The causative agent of scabies is the scabies mite, which actively reproduces under the skin after infection. It is noted that the hooves of the animal are most often affected. It is dangerous that the owner is unlikely to be able to immediately detect the tick itself and understand what is wrong with the horse. Such carelessness threatens that an infectious disease will soon cover the whole stall, infecting the rest of the horses.
The symptomatology of the disease is as follows:
- It is possible to suspect the development of scabies if the horse is constantly scratching against nearby objects, thus satisfying the need for combing.
- On the areas affected by scabies, alopecia develops: hair falls out, you can also notice the presence of scabs.
- The animal becomes restless and nervous, ceases to obey.
- A general deterioration in the condition of the skin can be noted, it becomes dry and rough.
As for treatment, first of all, the horse must be isolated to prevent further spread of the sore. Local treatment with ointments and solutions should be carried out only after consultation with a veterinarian and only with those modern drugs and methods that will be prescribed.
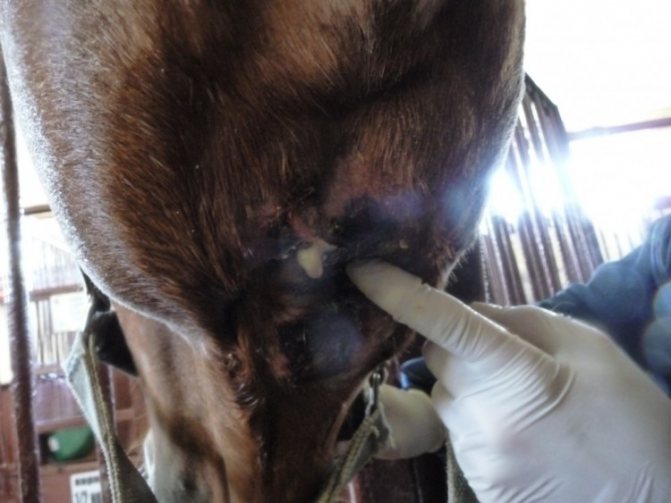
Bump in horses
Mokrets, or prickly heat, most often develops due to the fact that the conditions of keeping horses do not correspond to the norm. For example, litter does not change on time. Outwardly, the disease manifests itself in the form of cracked skin and wounds, which can later turn into ulcers. Most often, biting midge develops on the legs, like scabies. If you do not start treatment on time, there is a high probability that an infection will get into the wound and inflammation will begin. In this case, the treatment will be not only local, but also complex, since antibiotics will be required.
How to recognize a biting midsection at the very beginning?
- The horse alternately raises the hooves, and tries to keep the leg bent for as long as possible.
- Outwardly, you can observe the modified skin, wounds appear that can bleed and fester
Eczema in horses
Another common equine skin disease in veterinary medicine is eczema. She appears due to the fact that the horses are kept in unsanitary conditions. The fact is that the raw skin of horses is more prone to irritation, which later develops into a chronic inflammation called eczema. The first thing to do is to move the animal to a separate stall. This should be done not because the horse is contagious, but because health problems often change the character of the horse, making him restless and even aggressive.
Signs of Equine Eczema:
- The horse twitches, is nervous, as it is in pain and cannot scratch the wounds.
- Horse skin becomes dry, wrinkled, crusting and even a rash can be seen.
- Appetite may deteriorate, the horse loses weight.
Heat (shortness of breath)
This condition is usually diagnosed already at the stage when it develops into a category of chronic diseases. It develops due to the fact that some alveoli in the lungs stop working, as they become overgrown with connective tissue. Often the fuse occurs against the background of untreated bronchitis or any other disease associated with damage to the respiratory system, most often the lungs. The development of the fuse will be accompanied by the lack of ventilation in the stalls.
- unproductive dry cough;
- heavy shallow breathing.
Read also: Buck horse suit
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system of horses
Horses are animals with a well-developed muscular system, but, despite this, they suffer from ailments associated with limited mobility, especially hoof diseases in horses are diagnosed. As soon as the slightest signs of ailments of the musculoskeletal system become noticeable, it is important to seek medical help without delay, otherwise the horse may lose the ability to walk. Let's figure out which diseases are most common in this group.
Joint rheumatism
Joint inflammation, or rheumatism, is common in horses. Usually the hooves are affected, since they have a huge load. Rheumatism can affect one leg or all at once. The reasons can be varied, ranging from malnutrition and leg injuries, to the fact that the horse has a tendency to rheumatism at the gene level, that is, the horse may have a hereditary predisposition.
Alarming symptoms:
- Increase in temperature indicators.
- The gait changes, the horse prefers to sit or lie down, as it hurts to stand on his feet.
- On close examination, you can see inflamed enlarged joints that cause pain to the animal.
Limb nips or pricks
Horses walk and move a lot, especially if the owner changes pastures from time to time. It is quite natural that on the way the horse may step on a sharp object, which will lead to the development of inflammation. Most often, unsound horses suffer: their hooves are not protected. It is dangerous that a foreign object in the sole that is not noticed in time can lead to the development of inflammation and even gangrene. It is extremely important to remove the splinter in time and not to heal the horse. In addition to a splinter, a big problem is the situation when the horse stretches its legs, this also negatively affects the gait and the ability to walk in general. You can suspect heat or namin on the following grounds:
- The horse refuses to walk long distances.
- The gait changes.
- The joints are strained and inflamed.
Tendon injury
Stretching the tendon appears if the animal has worked and worked hard, for example, it can be a long walk or excessively long sports. Usually, the injury occurs on the metatarsal bone, this place is the most vulnerable in the bone apparatus.
Stretching symptoms:
- The affected area of the limb swells and causes pain on palpation.
- The horse may limp on a sore leg.
Home treatment involves completely immobilizing the limb, for this it is fixed with elastic bandages, cloth and splints, if required. During the treatment, the horse is on vacation, that is, it is strictly forbidden to involve it in work or training.
Hoof decay
This is a dangerous condition in which the hoof acquires the characteristic black color of decay, while pus with a sharply repulsive odor is released from the sole. The cause of this lesion is an infection, which usually gets inside through trauma. However, there are other causes of hoof decay, such as dirty stalls, improperly sized horseshoe, improperly trimmed hoof, inexperienced shoeing, and so on.
Signs of suppuration of the hoof:
- Blackening of the limb.
- The hoof becomes softer to the touch.
- The horse categorically refuses to step on sore limbs.
- The presence of an extraneous putrid odor from the wound is noted.
In case of delay in treatment, the horse runs the risk of losing a leg by surgery or even dying from blood poisoning.
Typical injuries
Due to the peculiarities of the use of horses and the structure of their bodies, these animals occasionally suffer injuries. For example, a fall causes bone and muscle injuries to the back. Rest with massage and the issuance of anti-inflammatory drugs helps to cure them. Laser therapy is also helpful for this type of injury.
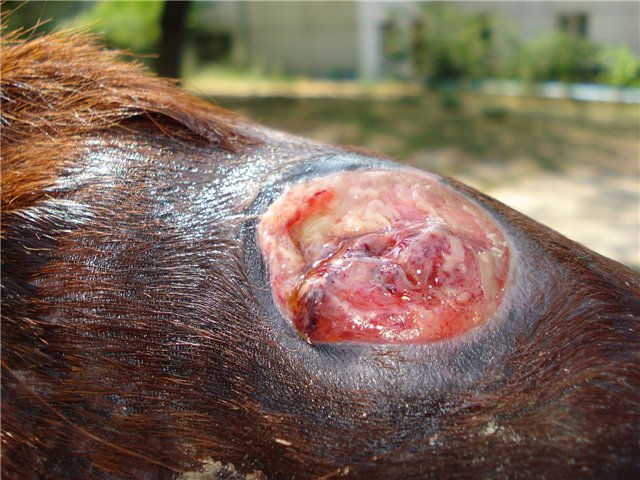

A similar injury is caused by the impact of the hock on a hard surface. To prevent it from happening, you need to put on boots, especially when the pet does not tolerate moving well. Treatment is only needed in cases of lameness or infection. A safety ring is put on the elbow so that it heals faster.
A notch is an injury to the front leg when a tendon or heel is damaged. Appears due to a blow with a hind hoof. First, the serifs are cleaned and then an antiseptic bandage is put on. If the serif is serious, it can take a long time to recover.
A splint or bone occurs between the wrist and the metacarpus, on either side of the leg, and even on the hind limbs. They are found during the period when young animals are taught to work. The limbs are poorly balanced, so horses need orthopedic horseshoes. Lameness can occur with injury, but pain often goes away quickly. If the limp persists, an X-ray of the limb should be done to make sure there is no fracture.
Jumping and galloping too much can injure horses' tendons. More often the problem occurs with the front legs. The fibers of the tissue break, causing pain. Then the sore spot swells and heats up. It is important to make compresses on time with ice packs and change often.A supporting bandage is applied to the limbs. Laser therapy shrinks swelling. The sick animal is prescribed rest. If the tendon is severely damaged, it may take a year of rest to recover.

From the bite and blows of relatives, due to falls and accidents, horses receive various wounds. If the pet is kept clean and dry, some wounds heal quickly. Stabs are the most dangerous, due to the penetration of infections. Such must be restored from the outside and from the inside. For this, poultices, rinsing with cold water and stopping bleeding are used. Large wounds will have to be sutured. It is advisable to give them an injection against tetanus.
To avoid unpleasant consequences from injuries, each horse breeder must have a first-aid kit on duty. It should include: disinfectant and tampons, medicinal ointment, bandages, dressings, adhesive plasters, cotton cloth, cold compresses and poultices, insect repellent, thermometer and rounded scissors.
Video "Rearfoot frog rot"
Diseases associated with digestion
This group includes all ailments that affect the process of absorption of food, its digestion, and then excretion. It should be said that, in general, the causes of problems in the work of the digestive tract are improper nutrition, feed of inadequate quality, as well as deviation from the feeding schedule.
Cramping or colic
Colic or cramping is not uncommon in horses and is most often caused by poor nutrition or nutritional imbalances. If you do not provide assistance in time, then in the worst case, the horse can die due to a physical rupture of the stomach. What causes spasms? This condition can develop due to the fact that food in the stomach increases in size and presses on the walls of the stomach and intestines, even excessive consumption of too cold water can provoke such symptoms. Excessive gas formation also contributes to this. It is worth saying that colic causes truly hellish pain, so the condition of the horse can be critical.
How colic manifests itself externally:
- The horse is nervous, worried for no apparent reason.
- During an attack, the head turns towards the lower abdomen, and the back tries to bend.
- Also, when colic occurs, excessive sweating in the horse, the development of shortness of breath, can be noted.
Helminthic invasions
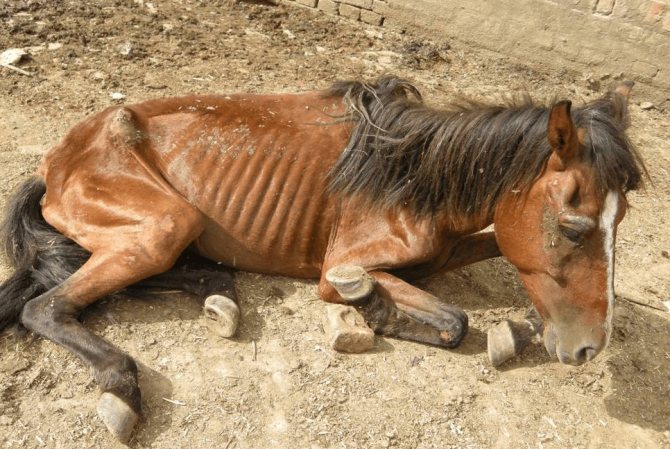
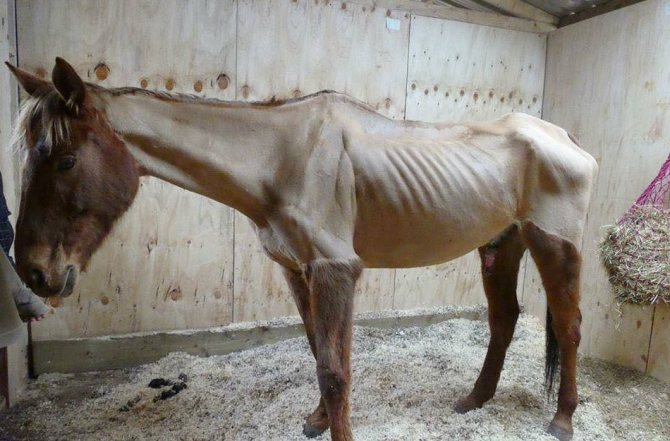
Worm infestations in horses are diagnosed quite often, these can be ordinary roundworms, filamentous worms, and so on. All these protozoan parasites enter the gastrointestinal tract of an animal through food, and, depending on the subspecies, can migrate to other internal organs, for example, to the heart or liver.
Symptoms of an invasive parasitic disease:
- The horse is losing weight dramatically.
- The nature and appearance of the hairline changes.
- Appetite changes in waves, sometimes it grows, then it disappears altogether.
- Diarrhea may develop.
- Together with traditional excrement, an admixture of mucus appears in the stool, sometimes you can see the worms themselves in the feces.
Laminitis
Laminitis in horses can be traumatic or metabolic.
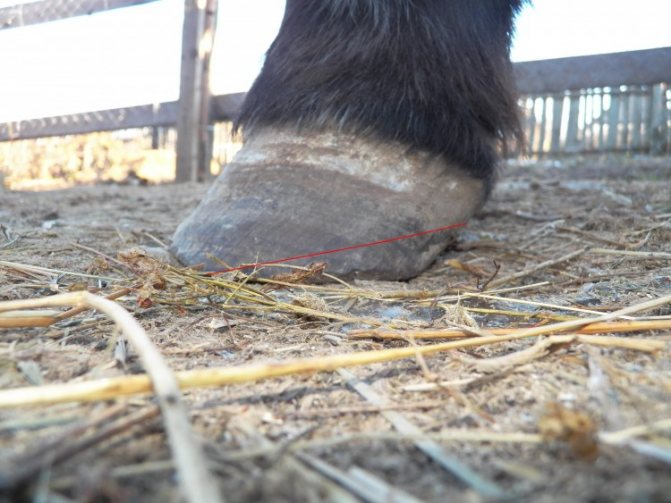


Reasons for trauma to the hoof tissue:


How to ride a horse: tips and step-by-step instructions, technical features and taming a horse (video + photo)
- Excess weight
- Maceration - the separation of cells in tissues
- Too hard ground
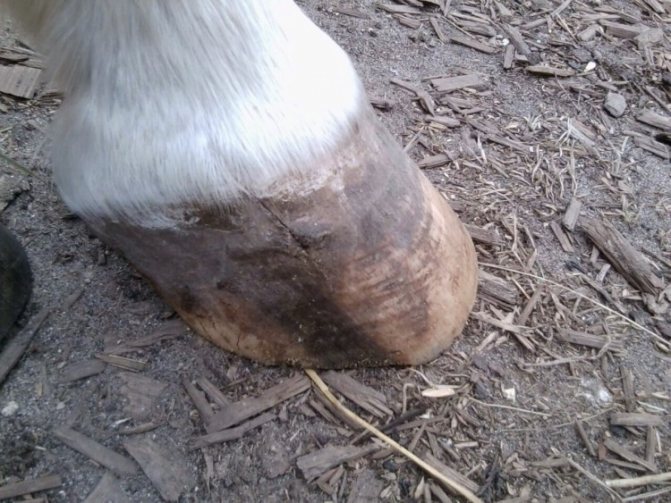

Metabolic causes (the formation of toxic substances that irritate the hoof tissue):
- Overfeeding wet grass
- Excessive consumption of concentrated feed
- Delayed afterbirth
- Colic
- Food or medication poisoning
- The death of a large number of worms during deworming
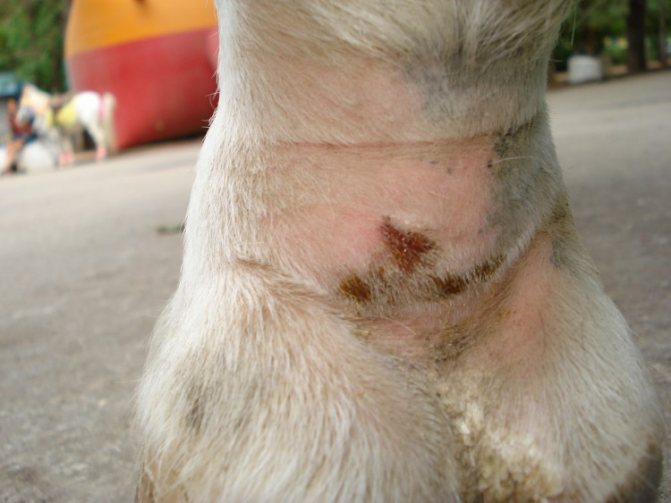

With laminitis, the horse limps and begins to adopt various postures to relieve pain. The animal refuses to eat, its pulse increases.
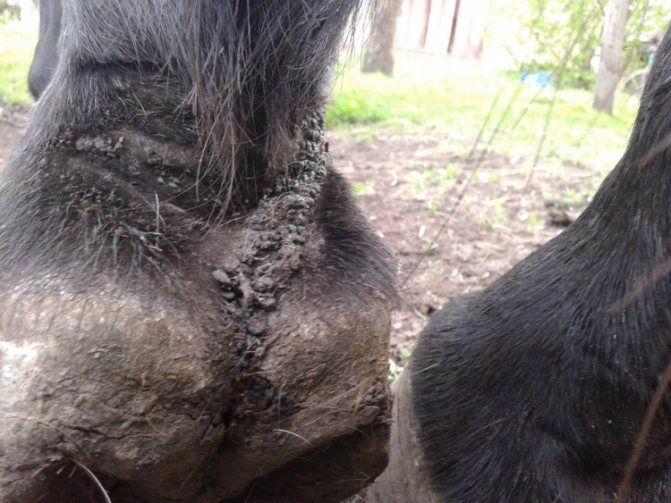

In order to cure a sick horse, you need to get rid of the causes that caused it: lay a dry bedding, feed the horse with hay before feeding, etc.


Treatment for laminitis is quite lengthy. Anti-inflammatory ointments, liniments, powders, ice baths will help alleviate the suffering of a horse. In some cases, the intervention of a surgeon is necessary.
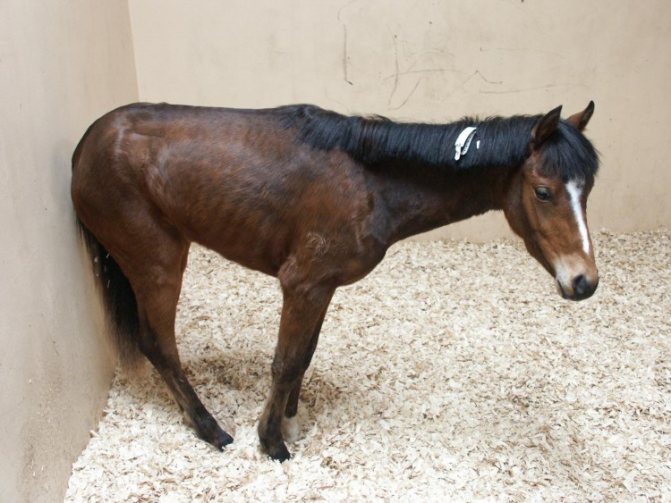

The photo shows a horse with laminitis. There is a strange brown bump on her hooves, a sign of illness.
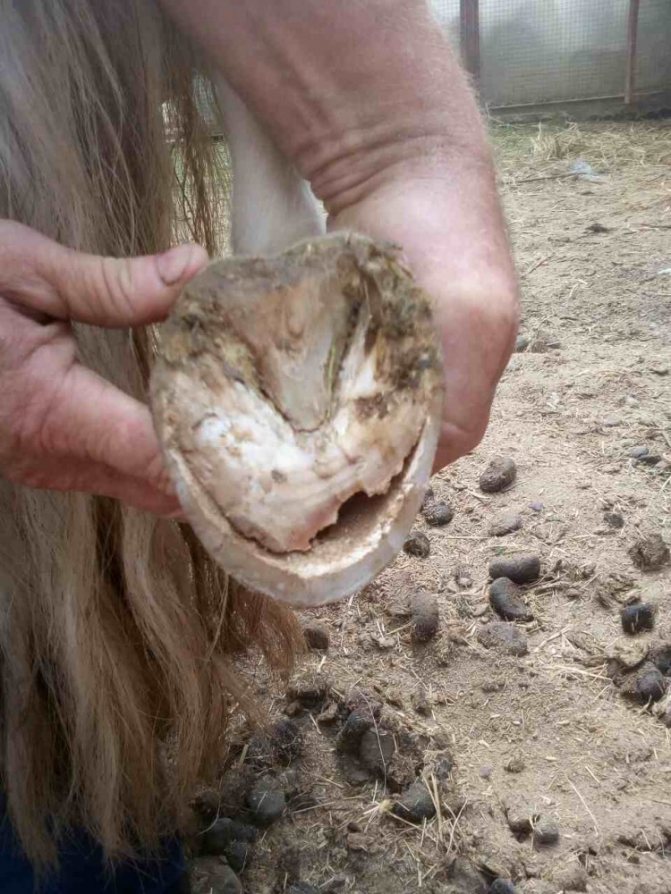

Respiratory diseases
The final group of diseases is respiratory diseases, which are caused by infections or viruses. Horses have a well-developed respiratory system, however, like all living organisms, they can become infected by traditional contact. Often horse breeders do not pay enough attention to the usual coughing or occasional shortness of breath in an animal, and in vain, because this may be the first alarm bell that a horse is getting sick. Below we will try to talk about infectious or viral respiratory ailments in more detail, describing those that are most common.
Horse flu, or influenza
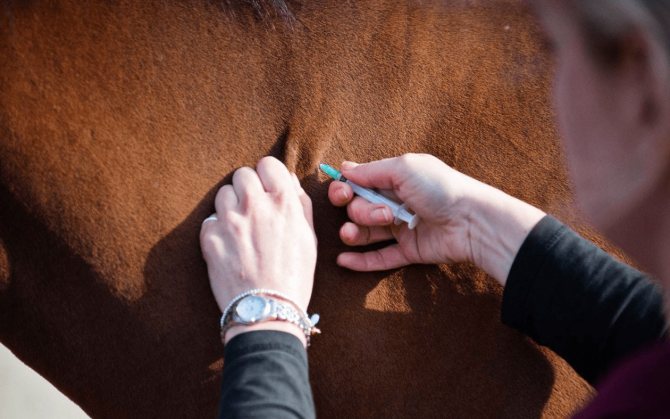
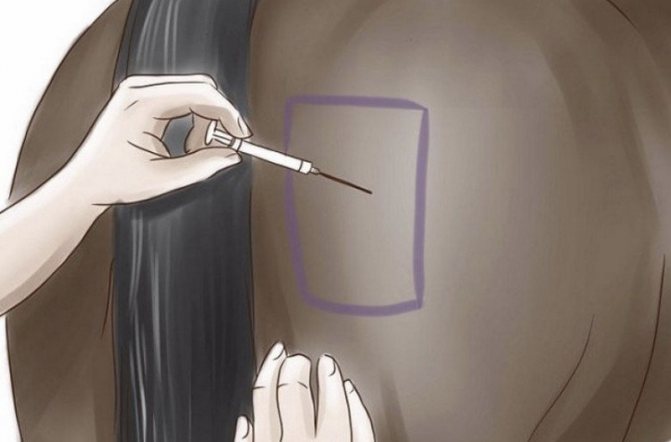
Equine influenza is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases that develop in the upper respiratory tract up to the larynx. If you notice alarming symptoms in your pet, you should not self-medicate, you will need a thorough examination by a veterinarian and subsequent professional treatment according to his instructions. Such caution is necessary, because the flu is dangerous in its consequences, especially if it is not treated. However, it is worth mentioning that the farmer can protect the horse from this disease by vaccination, which has recently become more and more popular.
Flu symptoms:
- Dry type cough develops.
- Mucous discharge from the nostrils, mouth and sometimes eyes is observed.
- The temperature rises sharply to a critical level.
- The general condition of the horse is unsatisfactory, it does not eat or drink, does not want to get up.
- The color of the mucous membranes is pale, almost white, while gum inflammation is often observed.
Siberian leprosy
Another dangerous horse disease that needs to be mentioned is anthrax, leprosy, or rabies. Nowadays, this highly contagious disease of horses is not as common as it used to be, and this cannot but rejoice the breeders. It should be said that about 75% of cases of all infections with Siberian leprosy end in the death of the animal, it is not possible to save the horse. This is due to the fact that the disease acts aggressively, the symptoms appear suddenly and progress rapidly: it can take only one day from the manifestation of the first sign to death.
The fungus causes rabies in horses, which is dangerous not only for cattle and animals, but also for humans. That is why you need to take precautions and monitor compliance with sanitary standards when keeping pets.
Anthrax symptoms:
- The pulse quickens, in one minute the heart makes more than 115 beats - this is a symptom of the acute stage.
- Chills characteristic of high temperature appear.
- The mucous membrane is dry, inflamed.
- Respiration is frequent, shallow.
- A white coating forms on the upper side of the tongue, which once again confirms the fact of infection with a fungus, and multiple tumors appear on the body.
- The animal looks bad, lies, showing no interest in anything.
- A complete lack of appetite is characteristic.
- In the terminal stage, the pulse slows down, convulsions appear, the horse dies.
Unfortunately, it is not possible to help the horse, the miracle of cure happens only in one case out of a hundred, when they turned to the veterinarian for help on time. In the event of the death of a horse, it is imperative to inform the relevant veterinary services. This is to prevent the spread of the disease to other farms.The corpse of the horse is disposed of by a special veterinary service, which also performs complete disinfection of the stall and yard.
Sap and wash at horses
Glanders belongs to the group of infectious diseases of horses, sometimes in a chronic form. During infection with glanders, the lower parts of the respiratory system are affected, that is, in fact, it is a lung disease. In addition, the development of characteristic nodes on the body is noted, which eventually grow together and degenerate into ulcers. People can also become infected with glanders, so you need to take the necessary precautions when treating glanders in an animal. The horses themselves become infected with glanders upon contact with a sick animal, having contact with a biological fluid: saliva, blood or sperm. Sap has a popular name: equine breeding disease. Despite the frightening symptoms, glanders can be successfully treated, but it is important to start it on time.
Myt also affects the respiratory system, but the upper section is already affected, in contrast to glanders. Myt is most often diagnosed in foals, because their immunity is not yet strong enough, for this reason, myt is in the first place in diagnosis among all diseases of foals, including newborns. What is the reason for washing in young animals?
- Power supply errors.
- Poor ventilation in rooms with horses.
- Insufficient outdoor grazing.
- Poor immunity.
- Ignoring the survey before the breeding period.
Myt is treatable, but you need to be prepared for the fact that it will take a long time in order to eliminate washes completely. As for the symptoms, the following can indicate the presence of washing in a horse:
- Decreased appetite.
- Increased body temperature.
- The development of ulcers in the mouth.
- Increased lymph nodes.
- Dry cough.
- Pain on neighing and swallowing.
Now you know what horses are sick with, and you can understand that the animal is not healthy. The owner's task is to make sure that the horses remain healthy and not sick.
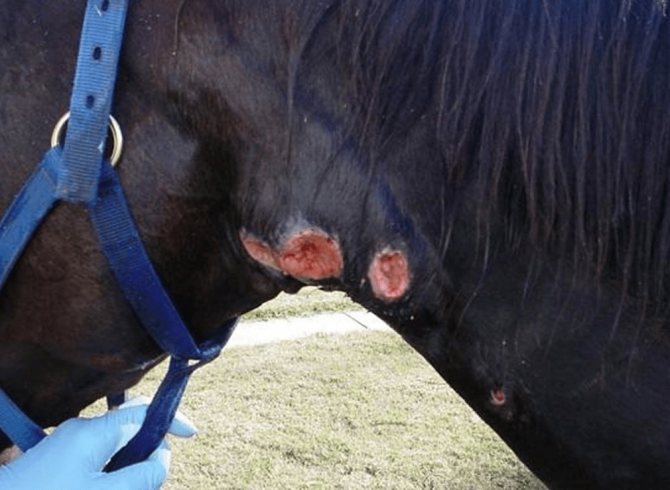
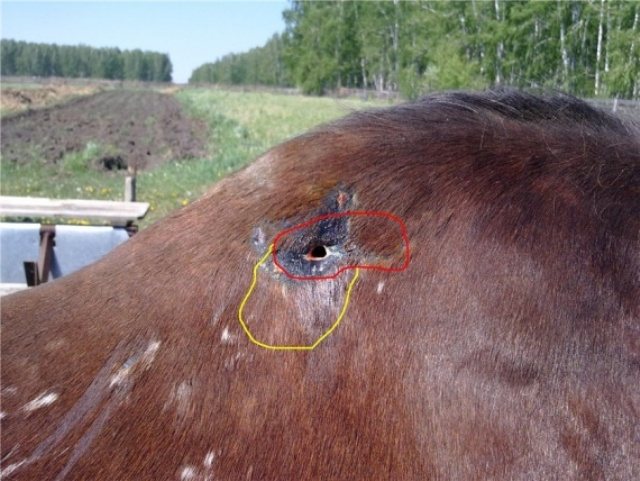
Glanders
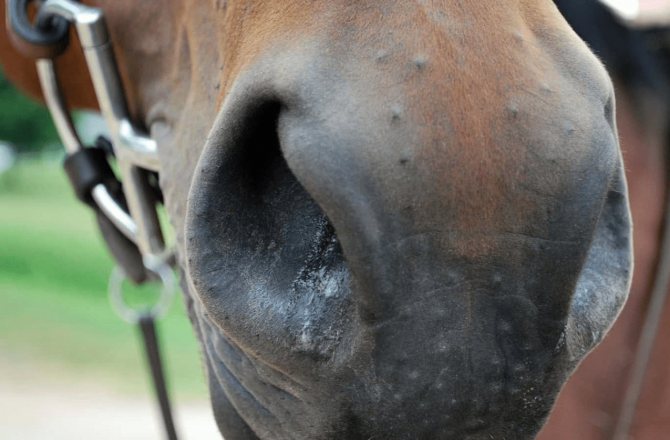
The source of the disease is the bacterium pseudomanada. Horses are infected by contact. Disease symptoms:
- Cough
- Nasal discharge
- Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph node tissue) with ulceration (often occurs in the nose)
- Swelling of the legs


The disease can occur in an acute form or without symptoms. Treating a disease is a rather dangerous business, so sick horses are destroyed, and quarantine is imposed on the farm.


The photographs of the infected animals show that horrible ulceration is developing on the horses, a characteristic feature of glanders. If you notice something like this on your horse's body, it's time to sound the alarm.