Currant anthracnose
Anthracnose appears on vegetable, fruit and ornamental crops most often in the second half of summer. At the germination and seedling stage, plants are also vulnerable to infection.
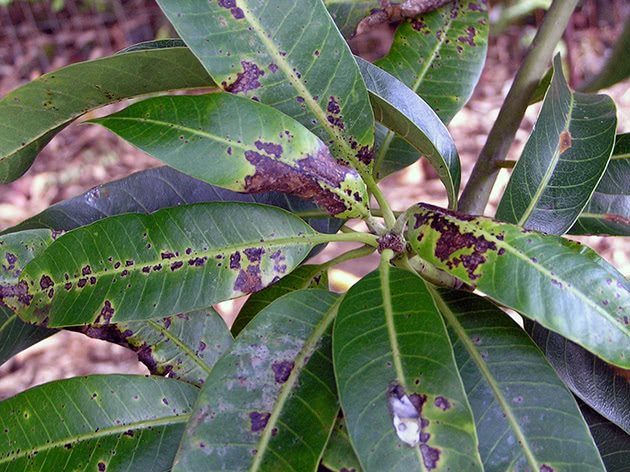
The disease affects the entire aerial part, most of all leaves and shoots. The characteristic signs of this fungal infection are the appearance of brown, dark brown spots and ulcers.
On the leaves, they have a round or oval shape up to 12 mm in diameter and a purple, pink or yellow border around the edges; on the shoots, the affected areas are elongated and depressed. On top of the spots, pads with fungal spores form.
With the development of the disease, the spots spread to healthy tissues, forming large necrotic areas. They coarse and crack in dry weather, causing the leaves to fall off and the shoots to break. Sick fruits are deformed and rotted.
Content
- Description
- Anthracnose treatment Anthracnose control measures
- Prophylaxis
- Ogurtsov
- Currant
- Anthurium
Why is the disease dangerous?
Anthracnose is quite dangerous for the health of all varieties of currants. The fungus can overwinter on the affected areas of the bush, and in the spring it provokes the formation of ascospores, which cause primary infection. Affected foliage gradually falls off, leaving only an insignificant part of greenery at the tips of the shoots. The disease actively spreads through plants in warm rainy weather.
The fungus destroys the petioles of the foliage in a short period of time and reaches the stalk. On young shoots, brown ulcers begin to form. Subsequently, conidiospores appear on the plants, which accumulate on the affected areas.
Anthracnose disease - description
Most often, anthracnose affects plants that are weakened or have mechanical damage. The disease is transmitted through contaminated seeds and plant debris. Spores can be spread by wind, insects, or raindrops. The disease progresses with high humidity.
How does the disease manifest itself? Anthracnose begins with the defeat of the leaves: spots of a reddish-brown color with a darker or yellowish border are formed on them. The spots grow, merge with each other. Depressions appear on the stems and branches of plants, which impede the movement of nutrients. These light brown oblong spots gradually increase, deepen, darken, a brown or dark purple rim is formed around them.
In dry weather, the affected areas become covered with cracks, and during the period of high humidity, the stems and shoots in the affected areas begin to rot and break. In advanced cases, the leaves turn brown, dry out, the entire surface of the plant dies. Increased humidity contributes to the development of anthracnose - for example, when at an air temperature of 22 ºC its humidity reaches 90%, as well as a lack of potassium and phosphorus in the soil and high acidity of the soil.
- Flower Jaundice / Leptomotropus
Top dressing
Plants with developed immunity are easier to treat.Currants are supported by complex feeds.
- For a 10-liter bucket of water, take 1 tbsp. spoon of potassium sulfate and ammonium nitrate, half a teaspoon of boric acid and 3 g of ferrous sulfate. Top dressing restores a depleted currant bush, helps to grow greenery and prevents leaf chlorosis;
- In the phase of ovary formation, top dressing is prepared with wood ash to improve the quality of the crop and increase the endurance of the currant. In a bucket of water, dissolve 200 g of ash, 1 bag of sodium humate, 2 tbsp. tablespoons of potassium sulfate and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of superphosphate;
- The use of "Immunocytofit" has a good effect: dilute 1 tablet of the drug in a bucket of water, add a solution of 1 tbsp. tablespoons of superphosphate and 2 tbsp. tablespoons of potassium sulfate.

When buying currants, you can choose varieties with high resistance to anthracnose:
- Black currant: Stakhanovka, Katun, Altai, Exhibition, Siberian daughter, Zoya, Belarusian sweet, Dove, Smart;
- Red currant: Faya fertile, Pervenets, Victoria, Chulkovskaya, Krasnaya Golanskaya, London Market.
Disease caused by fungi can be defeated. Increased attention to the garden will bring a quality harvest.
Anthracnose - treatment
Anthracnose control measures
Since the infection is fungal in nature, the fight against anthracnose is carried out with the help of fungicidal preparations. How to treat anthracnose when the signs of the disease leave no doubt? The most effective against anthracnose are drugs such as Cuproxat, Oxyhom, Acrobat MC and copper oxychloride, Ridomil Gold, Previkur, Skor or Fundazol, and the treatment of plants will have to be carried out two or three times with an interval of 10-20 days.
Microbiological preparations Gamair and Fitosporin-M are also used to curb the development of the disease. However, it is easier to prevent the development of the disease than to fight it for a long time and exhaustingly, and in order for your plants not to suffer from anthracnose, you need to take preventive measures to protect them.

Anthracnose disease - prevention
The causative agents of the disease can be on the seed, garden tools, in the water for irrigation, they can be carried by insects. During a period of high humidity, harmful microorganisms become active, and the disease progresses. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to observe crop rotation, carry out pre-sowing disinfection of seeds, remove plant residues from the garden and vegetable garden in the fall and dig up the soil.
Keep your garden tools clean and use sterile tools to trim, graft, and divide your plants. In addition, in early spring, before the start of sap flow, and in the fall, after leaf fall, treat the plants with Topsin-M solution, adding a growth stimulator Zircon, Epin or Immunocytophyte to it.
Preventive measures in the fight against anthractosis
The disease is easier to prevent than to cure. Prevention should be started at the preparatory stage. Anthracnose pathogens can be found on garden tools and seeds. To reduce the likelihood of infection, it is necessary to disinfect.
When favorable conditions arise, fungi are quickly activated. Weakened plants are the first to fall ill. Therefore, the purpose of preventive measures is to protect them. In order for all the plants to be strong, it is necessary to observe the crop rotation, to clean the backyard area in a timely manner.
Another important point is the treatment of crops with special preparations. Before planting, the seed must be soaked in compounds that accelerate growth. Their list includes Immunocytophyte, Zircon and Epin.
After the season is over, gardening tools should be well washed and dried. Store inventory in a clean and dry place, previously wrapped in oiled paper.Alcohol should be used during processing. Thus, the spread of the fungus is prevented.
Planted plants can weaken due to:
- excessive watering;
- transplants;
- mechanical damage;
- genetic predisposition;
- infertile substrate.
Therefore, in order to minimize the risk, it is necessary to follow the plan of agronomic measures. It is strictly forbidden to wipe the leaves with abrasive materials. This can cause scratches and cracks. Damage to the protective layer is a factor that can provoke infection.
When buying seed, you should choose varieties that are resistant to fungal disease.
The soil must be disinfected without fail, since the infection can enter the greenhouse from the outside. Fungus may be present in the soil that has not been treated. It remains viable for 5 years.
Plant anthracnose (vegetable)
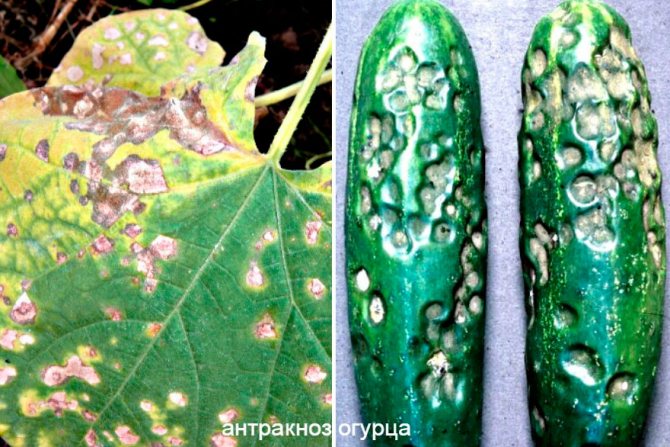
Cucumber anthracnose
Anthracnose affects both the leaves and stems and the fruits of cucumbers, and the disease can manifest itself even in the seedling period: on the seedlings in the area of the root collar, depressed brown spots form, turning into ulcers, from which the seedlings lie down. On adult plants, leaves are primarily affected - brown or yellowish spots ranging from 3 mm to 3 cm are formed along their edges.
In a greenhouse, sheet tissue falls out from the middle of the spots, leaving rounded holes; in open ground, such spots have a slit-like shape. Having struck the leaves and stems, the fungus passes to the fruit, forming light brown or pinkish depressed areas of an oblong shape, extending to a depth of 3-4 mm.
Diseases of cucumbers and their treatment
Plants affected by anthracnose in the root area are treated by adding a one percent solution of Bordeaux liquid or a half percent solution of Abiga-Peak under the root, having previously well saturated the soil with water. If necessary, such treatment is carried out 2-3 times a week, but protect cucumber leaves from these preparations - the affected leaves are treated with copper oxychloride or Polyram in accordance with the instructions. To combat anthracnose, drugs such as colloidal sulfur, Tiovit Jet and Cumulus can also be used. A good result was shown by spraying cucumbers with Quadris and Strobi solutions.
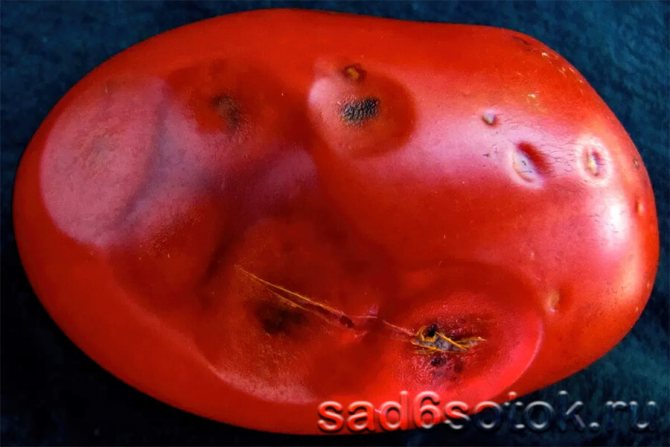
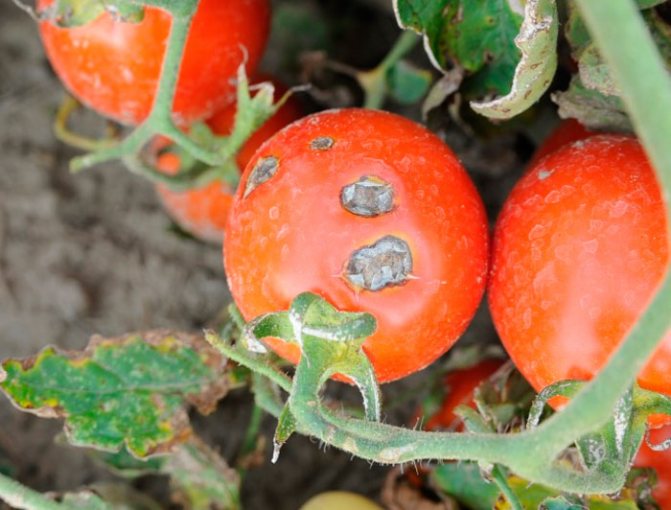
Tomato anthracnose
Most often, tomato anthracnose affects adult plants: first, the upper leaves wither - spots form on them, on which small black sclerotia appear. On unripe fruits, dark depressed areas with a diameter of up to 1 cm appear, which soften and turn black with the development of the disease. As a result, the fruits are mummified, and due to the maceration of the roots, the plant is easily pulled out of the ground. The disease usually manifests itself in late summer or early autumn. In case of mass infestation, large crop losses are possible.
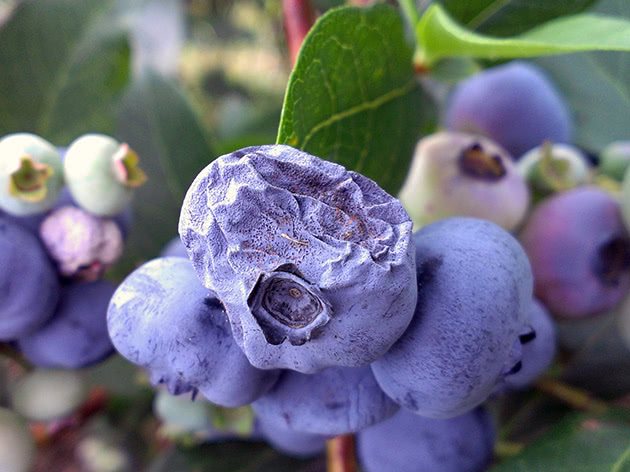


Among tomato varieties, there are hybrids that are more resistant to anthracnose, for example, Shelf, Longf and Life, but even if you grow varieties that are easily affected by this disease, taking preventive measures in time will help you significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease. The complex of such measures includes observance of crop rotation, pre-sowing seed treatment - dressing in a solution of Agata-25 or Immunocytophyte, compliance with agrotechnical conditions for growing crops and preventive treatment of bushes with a solution of Strobi or Quadris preparations.
Growing tomatoes in the open field - planting and care
If prevention did not help and the disease nevertheless manifested itself, professionals advise to treat anthracnose with Poliram, Tiovit Jet, Cumulus-DF, as well as colloidal sulfur, Bordeaux liquid or copper oxychloride in accordance with the instructions.
Potato anthracnose
Anthracnose also affects potato tubers and stems.Light brown spots appear on the stems, over time the stems become angular and shortened. Chlorosis develops on the lower leaves. In dry weather, the affected plants dry out, and in damp stalks they crumble, become slimy and rot. Vague dark brown spots appear on the tubers, in which wet rot develops during storage.
Growing potatoes - planting and care
To avoid contamination of potatoes with anthracnose, crop rotation should be observed: in the same place, potatoes are grown with an interval of 3-4 years. Only healthy tubers, treated with the Maxim fungicide, should be planted. Throughout the season, it is necessary to control weeds, especially those that belong to the nightshade. After harvesting, it is imperative to remove all plant residues from the site and plow or dig deep into the ground. Stored tubers should be kept at 1-3 ºC to contain the disease.
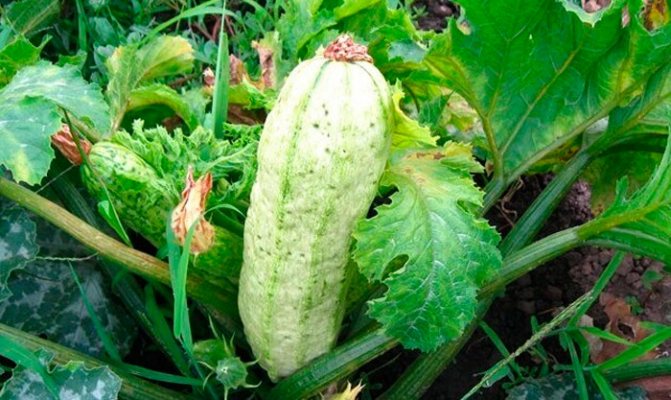
Zucchini anthracnose
In zucchini, anthracnose affects all terrestrial organs: yellow-brown spots form on the leaves, depressed areas covered with a pink bloom appear on the stems and fruits, and the root part of the plant affected by the disease most often dies. As usual, high humidity of the soil and air, as well as watering in the heat, promotes the development of anthracnose. If signs of disease appear, treat the plants with a solution of colloidal sulfur (50-60 g per 10 liters of water) or one percent Bordeaux liquid.
- Flower Jaundice / Leptomotropus


As a preventive measure, we recommend observing crop rotation, treating the seeds before sowing, carefully inspecting the seedlings before planting on the garden bed, removing weeds from the site in a timely manner, removing plant residues after harvesting, digging deeply into the ground in autumn and regularly disinfecting greenhouses.
Prophylaxis
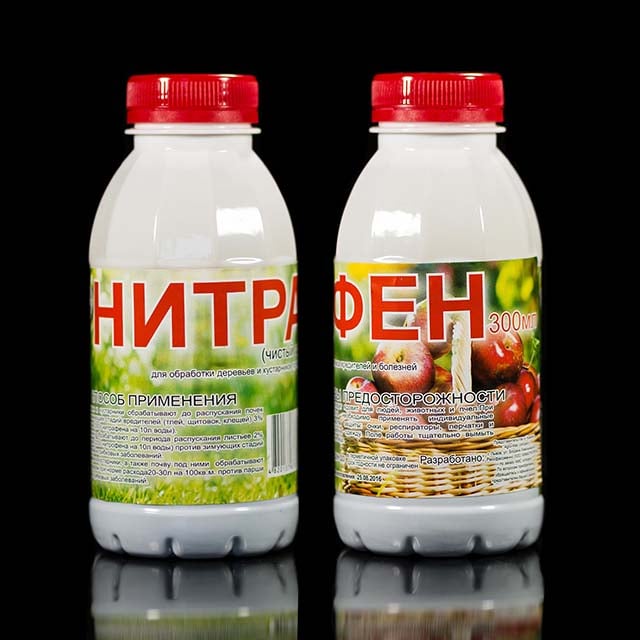
Fallen foliage is one of the main foci for the spread of infection, so it should be carefully collected and must be burned without leaving it on the site. Sanitary digging of the soil should be carried out twice a season - in early spring and autumn, when preparing fruit bushes for winter. The soil around the bushes should be treated with Nitrofen or DNOC. Preventive measures include the fight against harmful insects that can serve as distributors of fungal diseases. This article will tell you about growing and caring for Suvorov onions.
Regular inspection of the bushes and their pruning allows you to detect signs of the disease at an early stage, remove affected branches and take measures against further spread of the disease.
Anthracnose treatment on shrubs and trees
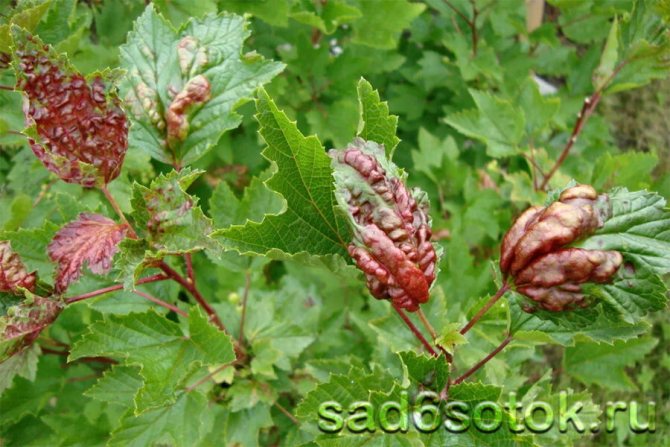
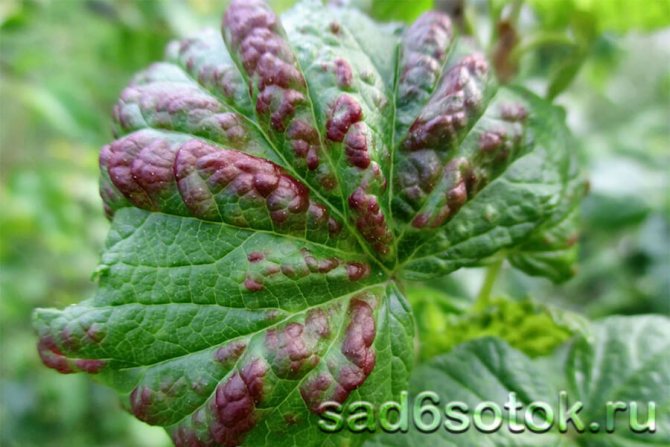
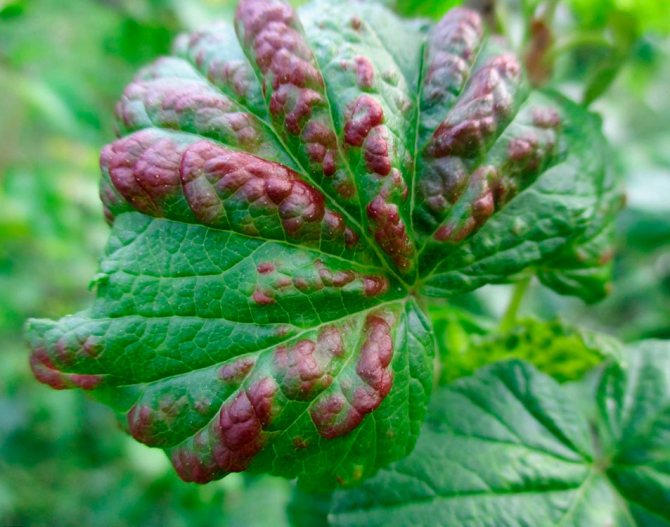
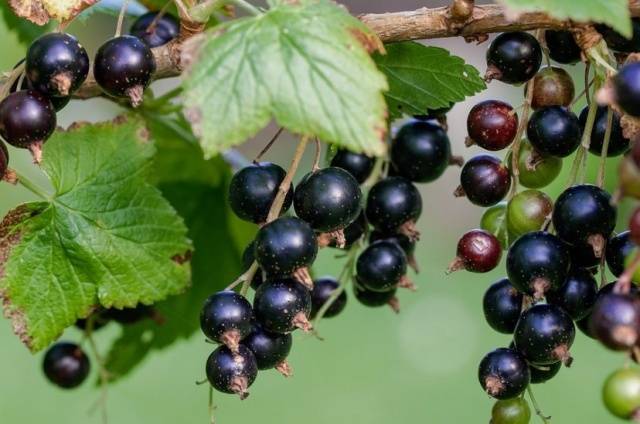
Currant anthracnose
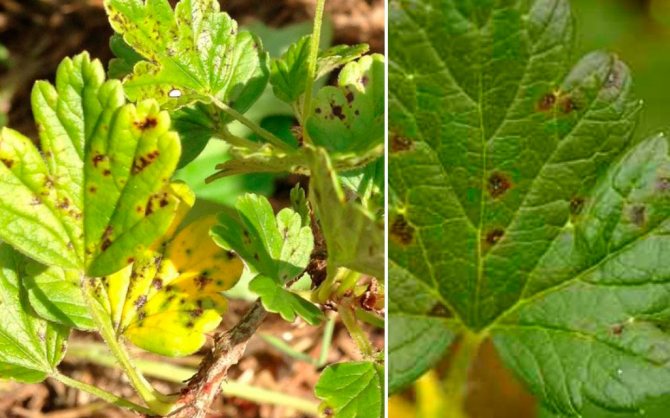
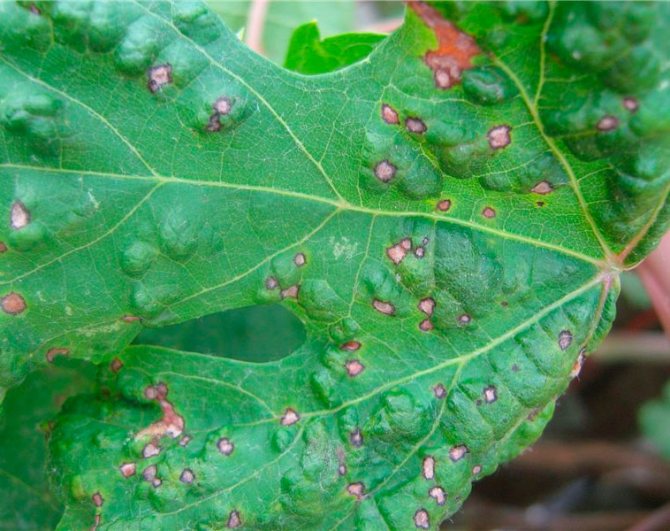
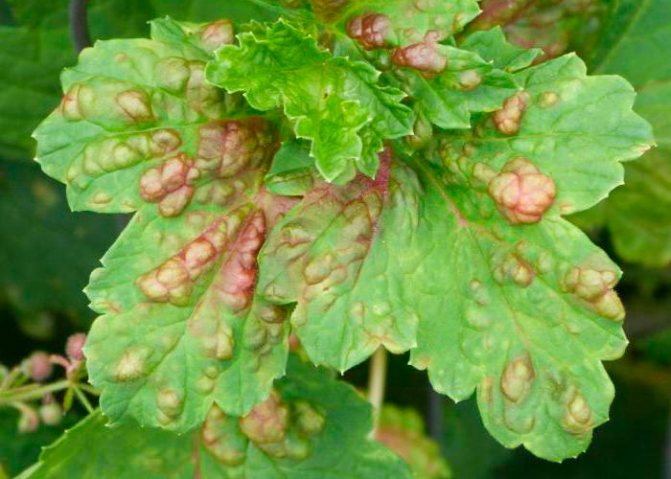
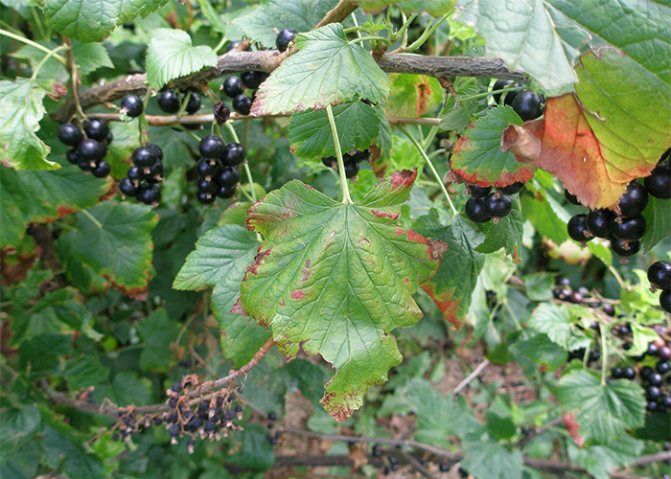
Anthracnose on currants is quite common. First, small brown spots with a diameter of about a millimeter appear on the lower leaves, which gradually grow and merge. With the development of the disease, the leaves dry and fall off. On the petioles and green shoots, depressed spots form, turning into wounds. Single whitish ulcers also appear on the berries. As a result, in the second half of summer, only small numbers of young leaves remain on the bushes. An interesting fact is that black currant anthracnose is less common than red anthracnose. The likelihood of developing the disease is greater during the rainy season.
Diseases and pests of currants - how to deal
The fight against anthracnose on currants is carried out in the same ways as on other crops:
- in autumn, fallen leaves and plant residues after pruning are collected and burned, since they are the main source of infection, and the bushes and the soil around them are treated with a 3% solution of Nitrafen or a 1% solution of DNOC and dug up. In early spring, before the buds swell, the treatment is repeated;
- immediately after the flowering of currants and two weeks after the first harvest of berries, preventive treatment of the bushes with one percent Bordeaux liquid or suspensions of Kaptan, Tsineb, copper oxychloride prepared in accordance with the instructions is carried out. Treatment of currant anthracnose is carried out by the already mentioned fungicides - Tiovit Jet, Cumulus-DF, colloidal sulfur;
- it is advisable to gradually replace the currants growing in the garden with anthracnose-resistant varieties: red currants - Bessemyanka, London Market, Chulkovskaya, Holland red; black currant - Dove, Velvet, Kryzhovichnaya, Stakhanovka, Altai, Katun.
Gooseberry anthracnose
Since gooseberries and currants are close relatives, anthracnose manifests itself on gooseberries in the same way as on currants, respectively, and the measures to combat the disease are the same.
How to deal with gooseberry pests and diseases
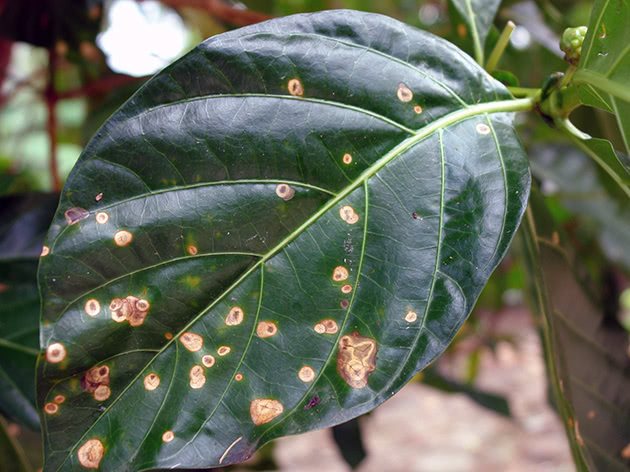
Raspberry anthracnose
Anthracnose on raspberries can be diagnosed by small rounded specks of gray-brown hue with a dark red rim, which appear on the leaves and, gradually growing, merge with each other. Small but deep ulcers can be seen on the shoots. Affected flowers, flower shoots and stem tops dry up, and the fruits are mummified.


It is necessary to think about protecting the raspberry from anthracnose already at the stage of buying seedlings, choosing varieties resistant to disease. When landing, try to maintain the distance provided by the scheme developed by specialists. Do not place the raspberry plant in low-lying areas and observe the watering regime.
Treatment of raspberry anthracnose is carried out in this way: the affected branches should be removed as soon as possible, and the bushes should be sprayed with a fungicide solution at the first signs of anthracnose. But it is better to treat raspberries from anthracnose preventively: for the first time, it is advisable to spray raspberry bushes in early spring, before the buds open, the second time - 10 days after the first treatment, the third - after the first harvest, and the last - in the fall, after leaf fall. As a fungicide, you can use one percent Bordeaux liquid or a solution of 50 g of copper oxychloride in 10 liters of water.
Pests and diseases of raspberries - how to treat
Grape anthracnose
Anthracnose does not affect grapes as often as other crops, but it can be very harmful. Those varieties that are not affected by powdery mildew and mildew are less resistant to the disease, since they are not treated with fungicides. The most resistant to anthracnose are Sauvignon, Rkatsiteli, Traminer and Riesling.
Anthracnose develops on all green organs of grapes, affecting only young tissues: the leaves are susceptible to infection at the age of up to 25 days, the shoots - only until they become lignified, and the berries before ripening. First, grayish spots with a dark or reddish border appear on the leaves of grapes, which gradually increase, and then the tissue inside the rim falls out. Brown spots are formed on the shoots, turning into deep coffee-colored ulcers with a dark purple border.
With a strong defeat, the shoots turn black, like charred, and break easily. The leaves grow on them small and chlorotic. Inflorescences are also covered with ulcers, after which they dry up and die off completely or partially.
Growing grapes - planting and caring for the garden
Treatment of grape anthracnose is carried out with one percent Bordeaux liquid. The first spraying with a fungicide should be done in the spring, as soon as new shoots grow up to 10 cm.A good result in the fight against the disease was also shown by the following preparations:
- Abiga Peak,
- Previkur,
- Fundazol,
- Ordan,
- Speed,
- Acrobat MC.
And also copper sulfate. Grape treatments are carried out regularly at intervals of two weeks. If it rains after spraying, the treatment should be repeated.Try to alternate drugs so that resistance does not arise - addiction to the drug. Be sure to trim and burn the anthracnose-affected areas before processing.
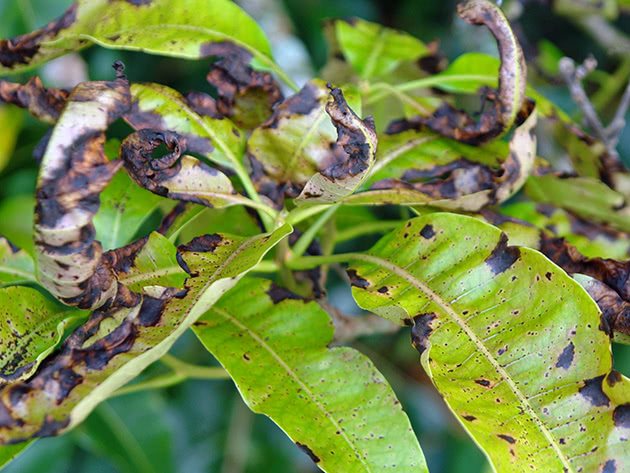


Strawberry anthracnose (wild strawberry)
Strawberry anthracnose can destroy up to 80% of the berry harvest. The danger of the disease is that, destroying the plant, it may not show signs of infection for a long time. Anthracnose affects all ground organs of garden strawberry, or strawberry, as this culture is usually called.
On the whiskers and the upper part of the leaves, small depressed spots of a red-brown hue appear, gradually transforming into ulcers. They merge, covering a large area, causing the leaves to die. From the leaves and whiskers, the disease passes to flowers and berries: the flowers look burnt and die off, and the infection penetrates the ovary through the stamens, as a result of which dark depressed spots with a diameter of 1.5 to 3 cm are formed on the fruits, which, when dry, become brown-brown ...
- Flower Jaundice / Leptomotropus
In a period of high humidity, the affected areas of the fruits are covered with a mucous crust of yellow or pinkish color, and in dry weather, diseased fruits are mummified.
Pests and diseases of strawberries - methods of struggle
You can avoid contamination of strawberries with anthracnose by using only healthy seedlings by immersing them in a fungicide solution for 30 minutes before planting. In the future, strawberries 3-4 times during the flowering period and the beginning of the formation of ovaries are sprayed with a fungicide solution. An excellent result in the fight against the disease was shown by the Italian drug Signum. And, of course, try to grow anthracnose-resistant strawberries - Daver, Light Charlie, Pelican, Pegan or Idea.
Cherry anthracnose
It affects anthracnose and stone fruit trees, such as cherries. By the middle of summer, dry, hard spots appear on the berries of a diseased tree, which grow and cover the entire fruit. Crop losses as a result of the development of anthracnose can be 50%, therefore, the fight against the disease must be started before its first signs appear.
In early spring, carry out a sanitary pruning of trees - the thinned crown airs faster and dries out after the rain, and fungal spores die under the sun's rays. After pruning, treat the tree with a 1% Bordeaux liquid on the still dormant buds, and after a week - with milk of lime (2 kg of lime per 10 liters of water). Add wood ash to the cherry tree trunk, and after a while, mulch it with manure.
Be sure to spend at least three additional fertilizing during the growing season: in early spring - with nitrogen fertilizer to stimulate shoot growth, and after flowering, in late summer or early autumn - with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. After harvesting, spray the tree with a solution of 100 g of copper sulfate in 10 liters of water, after the fall of leaves, collect the fallen leaves and process the cherries and the trunk circle with a solution of 500 g of urea in 10 liters of water.
Cherry diseases and their treatment
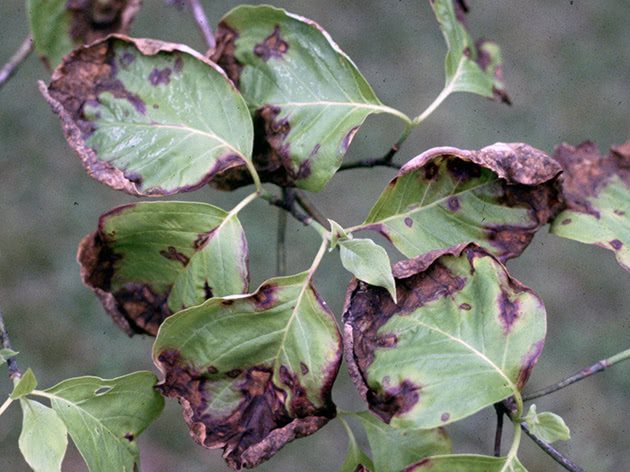


Watermelon and melon anthracnose
Since anthracnose is distributed everywhere, where high humidity occurs, it is also dangerous for pumpkin crops, for example, melons and watermelons. As in the case with other plants, anthracnose affects all ground organs of pumpkin, but the most dangerous disease is for the stems, which become brittle.
Diseased fruits stop developing, deform and lose their taste, since the sugar content in them decreases. Fruits develop rotting depressed spots covered with pinkish spore pads. The pads, merging, cover the fruits with a solid copper bloom, because of which anthracnose is called copperhead.
Growing melons outdoors - planting and care
As a preventive measure, after harvesting, it is necessary to collect and burn the tops, on which pathogens may remain, after which it is advisable to deep plow the area.Observe the crop rotation - plant pumpkin crops after pumpkin crops no earlier than 5-7 years later. The best predecessor for melons and gourds is alfalfa.
How to grow watermelons outdoors
Disinfection of seeds before sowing reduces the risk of anthracnose damage to a minimum, but if the disease does appear on the melon, treat the plants with Kuproksat solution three times: the first time during the formation of lashes, the second - during the formation of ovaries, the third - 2 weeks after the second. Note, however, that the final treatment must be done no later than three weeks before harvest.
From the experience of summer residents
Not all gardeners like to use chemicals, but they treat currant anthracnose with folk remedies on a weekly basis.


- In March or February, depending on the region, the dormant buds are scalded with hot water, the temperature of which is not higher than 70 0C;
- Spraying the bushes with a solution of laundry soap is used for the treatment of currant anthracnose. Half of the bar is grated and diluted in a bucket of water, at a temperature not lower than 22 0C;
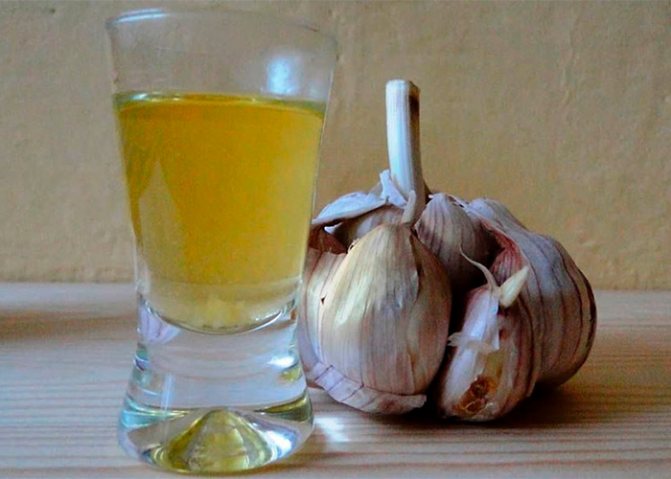
- The currant bushes are treated with an infusion of 150 g of chopped garlic and 10 liters of warm water: the pungent smell scares away pests, and one of the ways of spreading currant anthracnose is interrupted;
- Iodine solution is used in the treatment of currant bushes. Its antiseptic property is equivalent to that of a fungicide. Iodine destroys microorganisms and provides preventive support to plants. For a working solution, 10 drops of iodine are diluted in 10 liters of water.
Advice! If the currant was laid in the lowlands, drainage is arranged so that the moisture does not stagnate for a long time.


Anthracnose on flowers
Anthracnose anthurium
Even indoor plants are affected by the disease. Anthurium anthracnose occurs in conditions of high air temperature (above 20 ºC) against a background of high humidity. Small brown spots appear on the edges of the leaves, gradually growing and merging with each other, until the necrosis of the leaf tissue reaches the central vein, and the tissues covered by the fungus fall off.
You need to react immediately: isolate the anthurium from other plants, reduce its watering to a minimum, remove external signs of disease from the leaves, change the soil in the pot to a sterile substrate and do not forget to disinfect the pot itself. Before planting, hold the roots of anthurium for 10 minutes in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. After transplanting, treat the plant with one of the fungicides - Abiga-Pik, Previkur or Acrobat MC, and in case of a serious injury, it is better to resort to Skor, Fundazol, Ridomil Gold MC or other drugs of a similar effect.
Anthracnose on an orchid
The leaves of an orchid infected with anthracnose look as if hot coins have been pressed into them - the spots have very clear edges. On the leaves of phalaenopsis, the spots are black; on other types of orchids, they can be of any color, up to white. Loose formations appear at the base of the leaves of diseased orchids.


If it is possible to save at least part of the affected leaf, try to do it, and treat the cuts with crushed coal, brilliant green or cinnamon powder. It is, of course, desirable to replace the substrate, and treat the pot with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. Of the fungicides, orchids are suitable for preparations of the latest generation - Fitosporin-M. Trichodermin or Bactofit. You can also treat a diseased plant with organic preparations Mankozeb, Maneb or their analogues.
Anthracnose on cacti
Cacti can get sick with anthracnose only in case of a flagrant violation of the conditions of detention - high humidity, which succulents do not need at all. Depressions appear on cacti, which are sometimes surrounded by a bright border. The pulp of the cactus becomes an easy prey for the fungus, so you can't hesitate: cut out the affected areas with a sterile tool, grabbing healthy tissue, and then treat the wounds with crushed coal.
It is impossible to treat cacti with fungicides - these preparations are toxic for them. You just need to reduce the humidity as much as possible so that the fungus stops its activity. And don't worry, your cactus won't be affected by the drought.
The reasons for the development of the disease
The disease is caused by a fungus. The reasons for the infection of the plantings, the development of infection on the leaves, petioles and ripe berries are excessive moisture, the transfer of infection from diseased plants.
Remember: currant varieties that are not susceptible to anthracnose have not been bred, but proper care prevents the development of the disease.
It is necessary to fight the disease when the first signs of infection are detected. Since the spread of the fungus in the garden is rapid, it is necessary to process not only currant bushes, but also garden tools (secateurs, hoes), which are used for garden work.
Anthracnose preparations
Fungicidal preparations are used to treat plants from fungal diseases, so we offer you a description of those that are most often used. So, anthracnose fungicides:
- Abiga Peak - contact copper-containing fungicide of a wide spectrum of action. Moderately hazardous substance. With strict adherence to the instructions, it is not phytotoxic;
- Acrobat MC - a drug of systemic-local action, used to treat many fungal diseases. Toxic;
- Bordeaux liquid (mix) - a broad-spectrum contact fungicide designed to protect berry, melon, flower, vegetable and fruit crops from a whole range of diseases;
- Previkur - a systemic drug with protective and growth-stimulating properties. It is used against many diseases. Moderately hazardous substance with a mild irritant effect on the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes;
- Ridomil gold - systemic contact drug for combating a whole range of diseases;
- Speed - a systemic fungicide of preventive and therapeutic action against many diseases - scab, powdery mildew, late blight, leaf curl, Alternaria and other fungal diseases. Moderately dangerous;
- Tiovit Jet - contact fungicide and at the same time acaricide. It is used as a protective agent for fruit, vegetable, flower crops and grapes against fungal diseases. Moderately hazardous substance;
- Topsin-M - systemic fungicide of therapeutic and prophylactic action, effective in soil cultivation. Does not irritate mucous membranes and skin;
- Trichodermin - biological fungicide of therapeutic and prophylactic action, soil revitalizer. Safe for humans, bees, fish and birds. Not phytotoxic. Does not accumulate in plants and soil;
- Fitosporin-M - biological fungicide of contact action, microbiological preparation for the protection of garden, vegetable garden, greenhouse and indoor plants from fungal and bacterial infections. Low toxicity to humans, but dangerous to plants and bees;
- Fundazol - a drug of a wide spectrum of systemic action, a seed dressing agent. It has medicinal and protective properties, but after 2-3 treatments, the pathogens develop resistance .;
- Strobe - a local systemic fungicide of a wide spectrum of action, used to combat fungal diseases. Resistant to atmospheric precipitation;
- Quadris - a broad-spectrum fungicide with a prophylactic, curative and eradication effect and used to combat fungal diseases;
- Cuproxat - contact fungicide, preventive herbicide for plant protection against fungal diseases. The best preparation from copper-containing;
- Oxyhom - a systemic contact drug of a wide spectrum of action, used to combat fungal diseases. Hazardous substance;
- Ordan - contact-systemic fungicide used to combat Alternaria, late blight, anthracnose and other fungal diseases. Moderately hazardous substance.
The causative agent and its life cycle
Anthracnose is caused by the marsupial mushrooms Pseudopeziza ribis Kleb. Due to pathogens, the leaves begin to fall off prematurely, as a result of which the concentration of useful compounds, micro- and macroelements in the shrub sharply decreases. In areas where a moderately humid climate prevails, 70-75% of the crop may die afterwards.
The developmental cycle of anthracnose consists of two phases:
- Summer conidial - differs in the formation of a bed with a large number of conidia. They are passed on for generations and are capable of re-infecting currants and soil. The spread of fungi occurs during the growing season. Microspores are formed in the sheet in the form of a hole, spread over the surrounding tissues. The shape of the conidia is sickle-curved; they are located in the middle of the leaf. White glossy pads on leaves and diseased shoots are a sign of conidial sporulation.
- Hibernating marsupial - characterized by the autumn-winter formation of microspores in infected leaves. By the spring, infected fruiting bodies develop, the maturation of apothecia, bursae, and ascospores occurs. Fruit bodies are similar to narrow saucer bodies with short stalks. They are especially noticeable in fog, in dry weather they look like black lumps.
With the primary infection of the bushes in the spring, the source of the spread of infection is ripe ascospores, conidia remaining in last year's fallen leaves. With a massive defeat of currants during its active growth and development, pathology occurs due to conidia.
Reasons for the defeat of garden currants with anthracnose, symptoms indicating the appearance of fungus on garden plantings of currants, methods of treatment and prevention of the appearance of fungus on currant bushes. The use of all known methods will preserve the planting and yield of currants.
The causative agent of anthracnose is a fungus, which spores penetrate into the main organs of the plant, develops and thereby infecting the currants. First, the lower leaves are affected, then the disease passes to medium-aged leaves, in especially acute cases the stalks and berries are affected. At the same time, favorable conditions are created during wet weather, in principle, as for all fungal diseases of this kind.
Signs of bush damage
Tomato anthracnose
Control measures
Cucumber anthracnose


Control measures
Anthracnose symptoms can be noticed during the growing season. First, the lower leaves located at the base of the bush are affected, since they are closer to the wintering site of the fungus. Due to secondary infections, conidia accelerate the spread of the disease.
With a strong parasitic attack, 70% of the foliage falls in mid-July. The plant becomes completely infected - the aboveground parts (shoots, petioles, ovaries, peduncles) are infected.
The disease can be recognized using the following symptoms:
- numerous microscopic brown spots appear on the leaves. At first, their size is 1 mm, then they expand to 2-2.5 mm;
- the upper part of the leaf is covered with sporulation in the form of shiny black mounds;
- the space between the infected places gradually darkens, dries up;
- as the disease progresses, the spot spreads throughout the leaf, expands, unites;
- diseased sheets dry out, fall off, darken;
- shoots, petioles, stalks are covered with small deep brown ulcers;
- diseased berries turn black, dry out, fall off.
In red currants, foliage quickly falls off, in black currants, the leaves first dry out, but hang twisted until the onset of autumn. Diseased plants lose nutrients, their resistance to frost and temperature changes is significantly impaired. The branches begin to die off, yield decreases, and the quality of berries deteriorates.
Black-fruited varieties are most often affected in the 20th of June, at a temperature of 27-30 ° C.The incubation period lasts 1-1.5 weeks. Red-fruited currant species become infected early - in late May - early June with warm weather 20-27оС. The incubation period lasts a week.