Almost all gardeners will agree with me that chrysanthemums are the ideal inhabitant of a personal plot. These are beautiful plants that have a large number of varieties and varieties, do not require serious care and are suitable for both landscape design and cutting. The only problem is diseases and pests that can infect plantings, and in advanced cases, they can hopelessly ruin the appearance of flowers or completely destroy them. To prevent this from happening, you need to identify the disease as soon as possible and get rid of it, and today I want to talk about the first signs
Chrysanthemums have good immunity, so they get sick if there are favorable factors for the reproduction of fungi and pathogenic microorganisms. The most common causes of chrysanthemum diseases are violation of growing and care conditions:
- high density of plantings;
- poor air permeability of the soil;
- improper soil composition (high concentration of nitrogen, acidity);
- untimely watering;
- lack or excess of nutrients.
Accordingly, in order to completely get rid of the disease, it is necessary not only to treat flowers, but also to identify and correct errors in planting care.
Treatment of fungal and viral diseases
Chrysanthemums have relatively strong immunity, so timely prevention will help to avoid problems. But, if the flower is still sick, it is useful to know what the chrysanthemum diseases and their treatment are.
The most common fungal infections of chrysanthemums are caused by thickening of plantings, and in this regard, poor ventilation, also heat, high acidity of the soil, excess nitrogen in the soil. Fungi of various origins on chrysanthemums are effectively dealt with with the help of fungicides - Bordeaux liquid, copper oxychloride, colloidal sulfur, Fundazol.
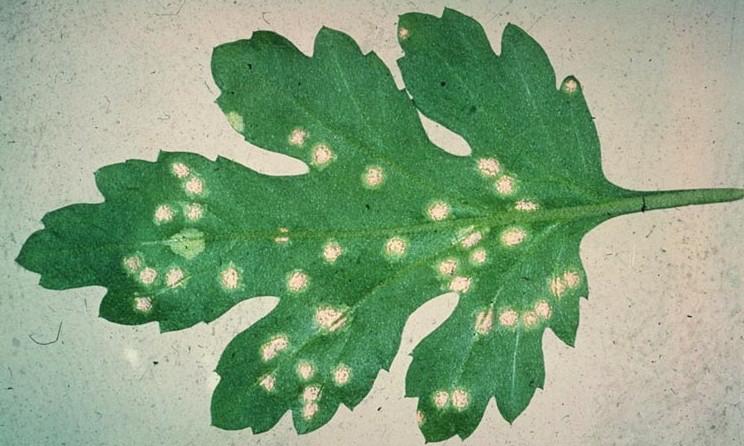
Chrysanthemum leaf septoria
Why do the lower leaves of chrysanthemums dry? Often this is a sign of septoria, which makes itself felt by the appearance of yellow spots, as a rule, it is on the lower leaves of chrysanthemums closest to the surface of the earth - the spots darken, acquire a brown tint, then turn black, spread over the surface, as if healthy greens are burning out.
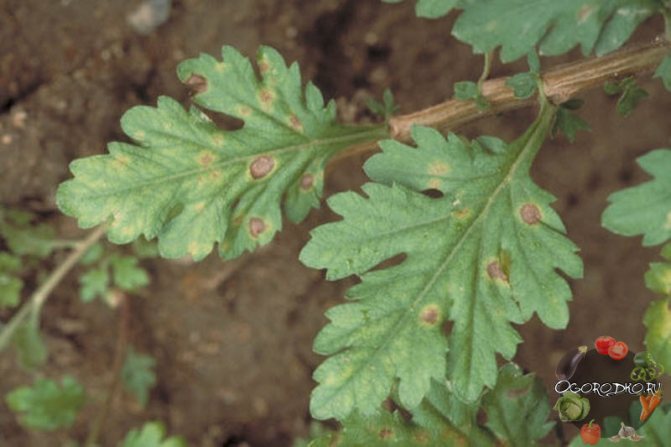

Chrysanthemum leaf septoria - pictured
What to do:
- Darkened vegetation is plucked and burned
- Infected specimens are sprayed with fungicides
- For prophylaxis in flower beds and in general on the site, withered vegetation should be removed in time
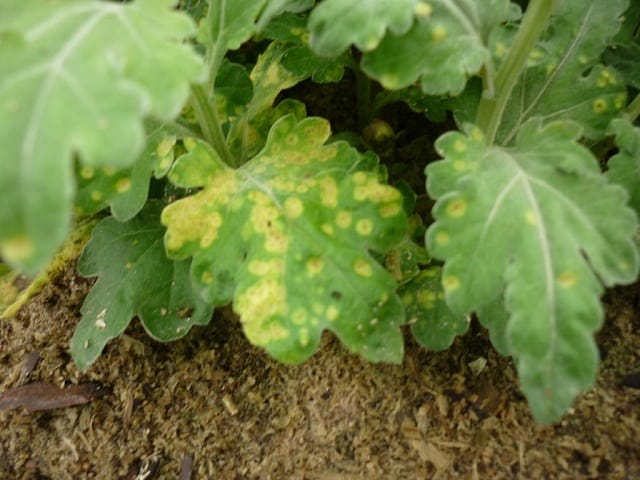
Rust
On the outside of the leaves of chrysanthemums, pale spots appear, and on the inside they are powdery orange, rust reduces the intensity of flowering, since it takes a lot of effort to fight infection.
What to do:
- Infected leaves are immediately removed
- Bushes are treated with fungicides
- Landings are thinned to improve air circulation
- Watered strictly at the root, water should not fall on the foliage
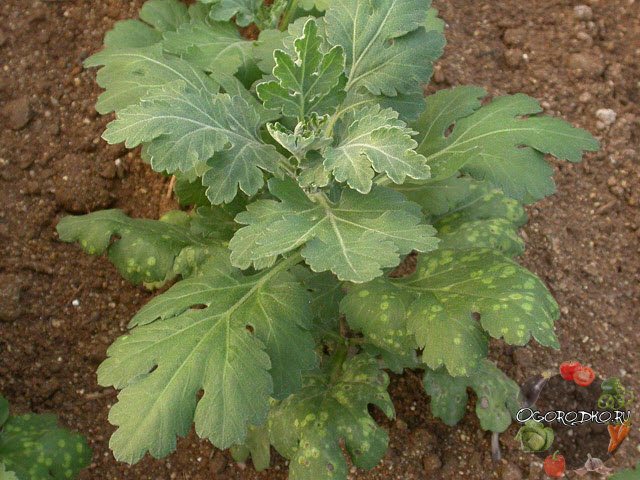


chrysanthemum rust - pictured
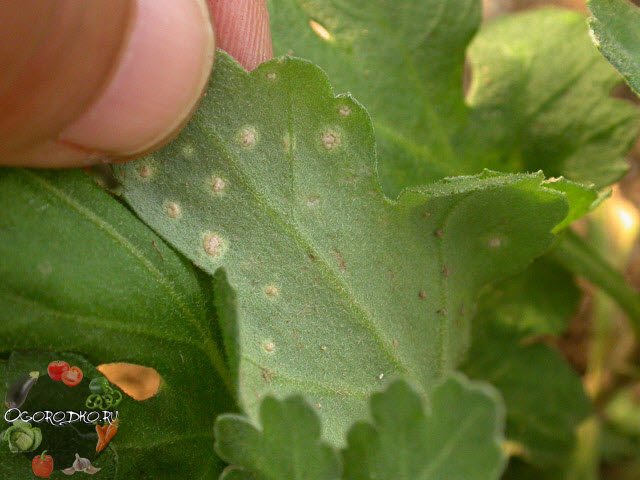


spots on chrysanthemum leaves - in the photo
Fusarium wilting
If the leaves of a chrysanthemum turn yellow, this may be the first sign of fusarium wilting, a disease caused by the fungus Fusarium. A sick flower experiences an acute lack of moisture, since the fungus infects the roots and prevents the flow of water necessary for the growth of the chrysanthemum.In affected specimens, development slows down, they noticeably lag behind in growth, and often it never comes to flowering.
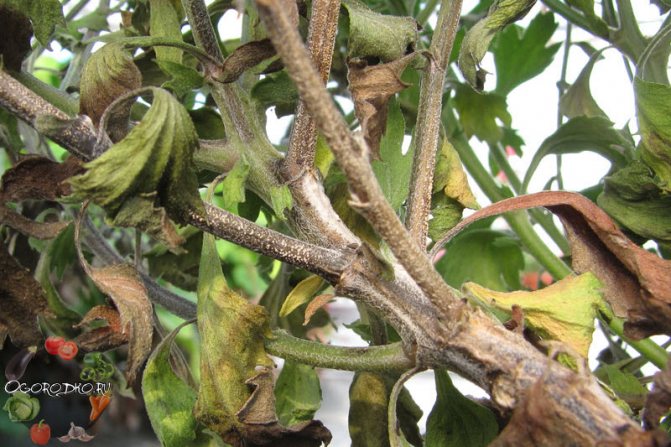


Fusarium wilting of chrysanthemum - in the photo
What to do in such cases:
- Infected bushes are completely removed
- Choose varieties with increased resistance to fusarium
- The soil should be slightly acidic or neutral, with a pH level of 6.5 - 7.0
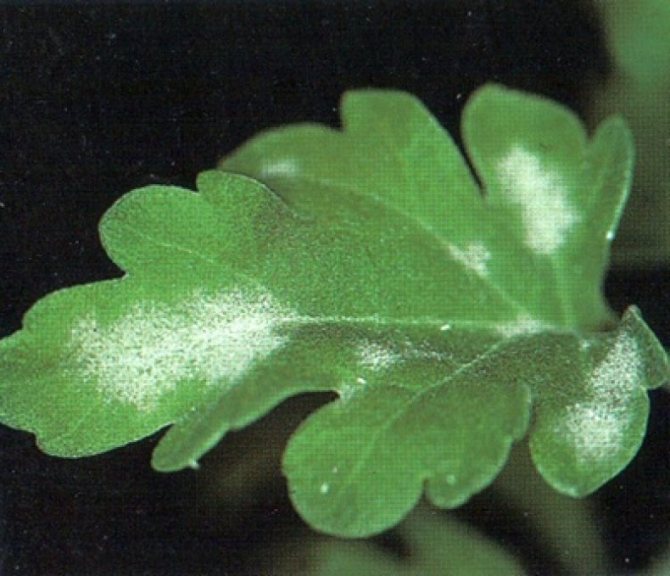
Powdery mildew
A symptom of this fungal disease is a dirty white powdery bloom on chrysanthemums, often occurs in a humid environment, therefore it spreads widely in wet rainy weather.
How to help the plant:
- Infected parts are removed
- The bushes are carefully treated with fungicides
Mosaic
In total, at least two dozen viral infections are known to which the autumn beauty of chrysanthemum is susceptible - these are aspermia, dwarfism, white spot of flowers, rosette and others. One of the most dangerous viruses for chrysanthemum is mosaic, the specimens affected by it lag behind in development, grow poorly, their foliage turns yellow, and the flowers become smaller.
What to do:
- Sick bushes completely destroy
- The site is regularly cleared of weeds
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of diseases and pest attacks on domestic or garden chrysanthemums, just follow a few simple rules.
- Thoroughly weed and loosen the soil. This will avoid stagnation of root moisture, provide good growing conditions.
- Avoid applying fresh manure. It can cause burns to the roots, severely damage the plant.
- Water with extremely moderately warm water, it is better if it is at room temperature.
- Apply potash and phosphorus-based fertilizers regularly. Top dressing should take place in liquid form every 10 days. No fertilizer is applied during the flowering period.
- Observe the distance when landing, when it comes to growing chrysanthemums in the garden. It is not necessary to thicken them, otherwise the risks of developing diseases will be significantly increased.
- Carry out preventive spraying with Bordeaux liquid 10 days after planting. Before sending to the ground, cuttings must be treated with a solution of "Fundazole" to prevent fungal infections.
- Indoor chrysanthemums up to 3 years old need to be replanted annually. At an older age - once every 2 years.


Be sure to thoroughly clean your garden in the spring and fall. It is in the fallen foliage that pests live, capable of causing serious harm to plantings in spring. Under the chrysanthemums themselves, you also need to remove the fallen parts of the plant.
How to grow and treat chrysanthemum, see below.


Chrysanthemum is a perennial plant that can grow in one place for a long time without transplanting, therefore, the likelihood of disease and pest damage to bushes increases. But even young, newly planted plants need to be regularly inspected for signs of disease and pests, and immediate action is taken.
Chrysanthemum problems are often caused by care errors. And although they have a fairly high immunity, diseases and pests of chrysanthemums can be dangerous if there is insufficient watering, high air temperatures, intensive vegetative reproduction and prolonged storage in an enclosed space.
Pests and the fight against them
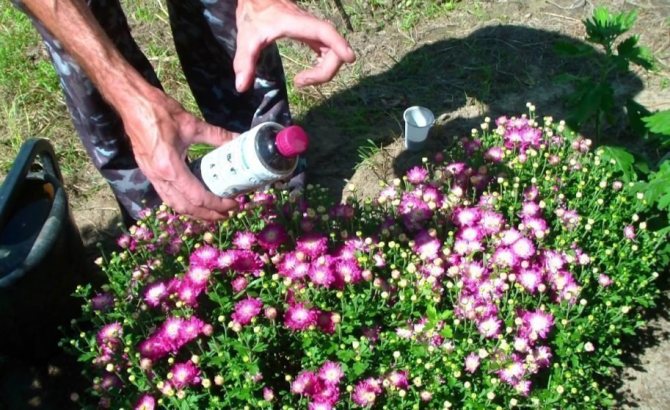
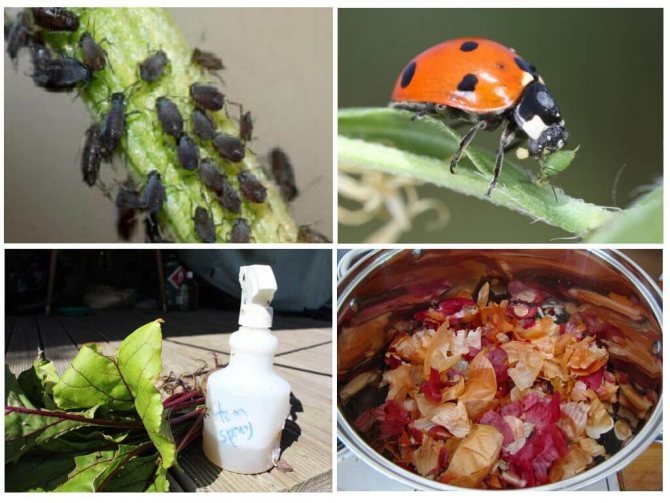
Diseases of chrysanthemums and their treatment consist in the destruction of not only infectious agents, but also pests - with aphids, spider mites, meadow bugs, slobbery pennies, tobacco thrips, leaf nematodes, they fight mainly with the help of insecticides.
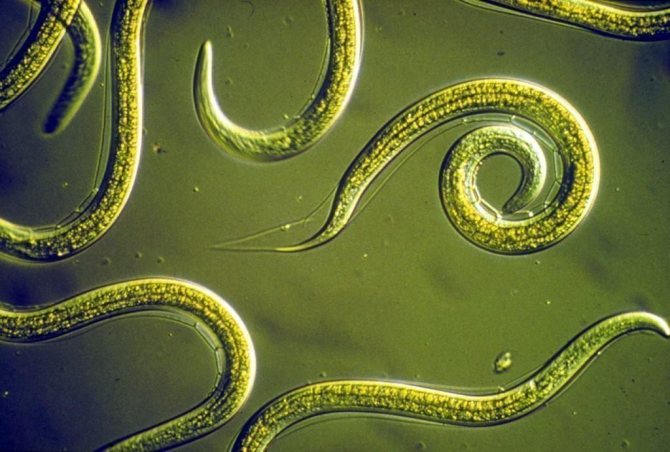
Leaf nematode
Nematodes are tiny worms that infect not only chrysanthemums, but also many other flowers and shrubs, they often hibernate in the beds, in the remnants of vegetation, so they must be removed in autumn.
On the leaves of the chrysanthemum, which the nematode has reached, yellow-brown spots appear, which gradually occupy the entire leaf, and it dies, first the foliage at the bottom of the stem dies off, then the pest spreads higher and higher along the trunk. If you do not take action, the entire bush dies.
What to do:
- Destroy not only the diseased specimen, including the roots, but also the surrounding soil
- In the spring, the ground around the flowers is mulched - this prevents the appearance of a nematode
- When watering, water should not fall on the foliage; 4. At the initial stage, you can apply a leafy spray, which contains green soap - an organic insecticide that includes potassium salts of fatty acids and vegetable oils
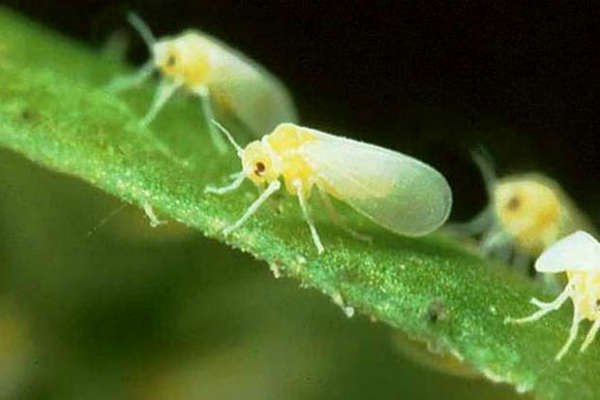
Aphid
Greenhouse aphids and brown aphids inhabit chrysanthemums. The first, green or pink, settles on the seamy side of the leaves, on the buds and flowers, and feeds on their cell sap. Brown aphids live in inflorescences without damaging them, but polluting them with their waste products.
What to do:
- The bushes are sprayed with any of the insecticides - Actellik, Bi-58 new, Karate
- A solution is also prepared from copper sulfate (20 g) and liquid soap (200 g) per 10 liters of water
Other pests are also fought with the help of insecticides, but the symptoms of insect damage are different:
- slobbering penny, or leafhopper, absorbs the juice of the chrysanthemum flower, while covering the plant with foam
- meadow, or field bug deforms the leaves, chrysanthemum buds and flowers, interfering with the flowering of plants
- a spider mite weaves webs on the underside of chrysanthemum leaves, which turn yellow and wither. Hot weather contributes to the spread of the pest. The spider mite easily adapts to drugs, so you need to use different pesticides in turn, alternative methods are also used - spraying with an infusion of henbane, dope, yarrow, garlic, onion
Powdery mildew: chemical treatment
If powdery mildew has appeared on your flowers, the fight against it is most effective with the help of modern fungicidal agents. They have a detrimental effect on the fungus, stop the harmful processes in plant cells, protect and treat it. Spraying is carried out 1-4 times with an interval of 7-10 days (depending on the selected drug).
Powdery mildew chemicals work quickly and effectively


The most effective preparations for powdery mildew:
- Fundazol;
- Topaz;
- Acrobat MC;
- Previkur;
- Speed;
- Vitaros;
- Amistar extra.
A well-known fungicidal preparation is phytosporin, the active ingredient in which is a concentrate of bacteria Bacillus subtilis in powder from chalk and humates. Despite the fact that phytosporin is considered a remedy, it is practically useless against the existing powdery mildew. However, as a prophylactic agent, it will work flawlessly.
As you know, chrysanthemums have natural immunity to various pathogenic factors. With good weather and adherence to agricultural technology, they grow healthy and do not cause much trouble. However, both climatic changes and constant vegetative reproduction can create favorable conditions for the development and spread of certain diseases and pests.
Sometimes chrysanthemums are also affected by pests. The leaves and flowers can be devoured by caterpillars of various scoops, leaf rollers, slugs. However, these pests do not pose a serious threat and cause significant damage only during the years of mass reproduction. Spider mites, aphids and meadow bugs are much more dangerous for chrysanthemums.
Powdery mildew appears on the leaves and stems as a whitish powdery coating, which is the mycelium of the fungus. Affected leaves turn yellow and die, which leads to a general oppression of plants. The fungus hibernates on regeneration shoots and dried leaves. In a humid and warm environment, it develops rapidly and affects the entire plant.
Read next: Garden perennial varieties of bush chrysanthemums: growing and care of Chinese varieties of photo plants
Control measures. When signs of disease appear, it is recommended to treat the plants 2-3 times (with an interval of 10-14 days) with one of the following solutions: copper-soap liquid (20-26 g of copper sulfate and 200 g of soap per 10 liters of water), soda ash and soap ( 40 g of soda and 40 g of soap per 10 liters of water), zinebom (0.5%), phthalan (0.5%), foundazol (0.2%) or benlate (0.2%).
Gray rot affects all aerial parts of the plant, on which brown blurred areas with a fluffy mouse-colored bloom appear. Sometimes, growing, they ring the shoot, which can cause the death of all parts of the plant located above. The fungus remains on plant debris. The development of the disease is facilitated by cold rainy weather, increased acidity of the soil, excess nitrogen, too dense planting.
Gray rot poses a serious danger to rooting cuttings - the pathogen easily spreads when spores hit uninfected parts of plants, which can lead to their mass death. Having noticed the first signs of the disease, all infected leaves and even cuttings should be carefully removed. Perceptible harm is caused by gray rot during storage and transportation of cuttings.
Control measures include spraying plants 2-3 times with one of the following preparations: soapy liquid, copper oxychloride (0.5%), Bordeaux liquid (1%), captan (0.5%) or foundation.

Septoriosis causes the appearance of brown or black spots on the leaves, lighter towards the center, which can merge and occupy most of the leaf blade. Over time, small foci of sporulation of the fungus are formed on them, which are a source of infection for new plants. Sick specimens are weakened, bloom poorly, they have
Control measures. When the disease manifests itself, it is necessary: to regularly collect and burn all the affected parts of the plant, loosen and weed the soil in a timely manner, periodically change the planting site, since the spores remain in the soil for several years. Copper oxychloride, cuprozan (.0 5% ", funzazol.
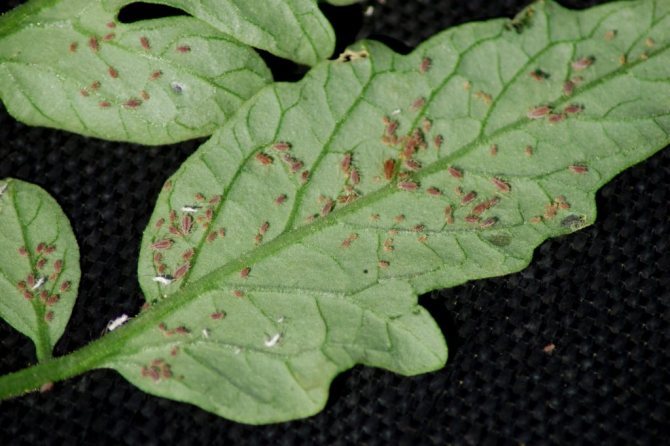
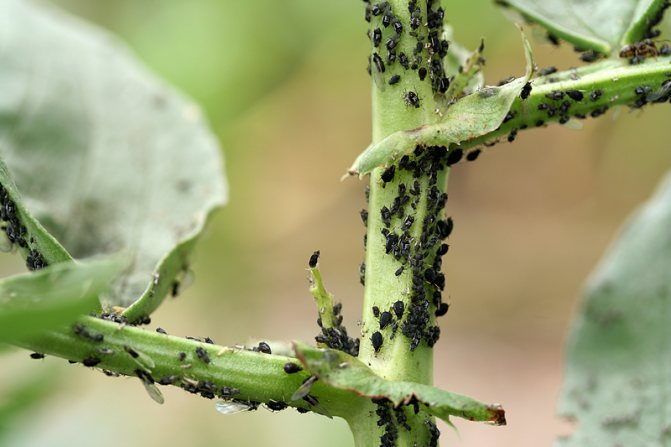
Aphids do great harm to chrysanthemums. Plants are mainly affected by two types of aphids. green - peach and black - bean. Aphids feed on plant sap, causing growth retardation, deformation and spoilage of buds. Insects develop most actively at a temperature of 14 -19 ° C and an air humidity of 90%.
Control measures. To destroy aphids, you can use karbofos (0.2%), rogor (0.1%), metaphos, actellic and other insecticides. They are also used: infusion of makhorka (100 g of makhorka is poured into 1 liter of water, insisted for two days, boiled, filtered and diluted 2-3 times with water with the addition of 40 g of soap); infusion of dandelions (40 g of fresh dandelion leaves are infused in 1 liter of water for 2-3 hours); infusion of celandine {amp} lt; 300 g of blooming celandine insist.
The spider mite is a greenish-yellow or red insect, 0.3-0.5 mm in length. Sometimes you can only see it with a magnifying glass. In the open field, ticks appear in the second half of June. The optimal conditions for their development are dry and hot (25 ° C and above) summers. Mites settle on the underside of the leaf blade and suck out cell sap.
The affected leaf is covered with cobwebs, light, and subsequently yellowish spots are visible on it. Such leaves die off prematurely. Mites overwinter under plant debris and in the surface layer of the soil, therefore, preventive measures include timely burning of plant debris and deep autumn digging of the soil. During the growing season, it is recommended to periodically spray the underside of the leaf with water.
Control measures include the use of pesticides: acrex (0.1%), metaphos, actellik, karbofos. Of natural preparations, the following are effective: infusion of onion scales (6 g of scales are poured into 1 liter of water and insisted for 7 hours in a closed
dishes, filtered ;: yarrow infusion (80 g of dry crushed plants are steamed with boiling water, added to 1 liter and insisted for 48 hours).
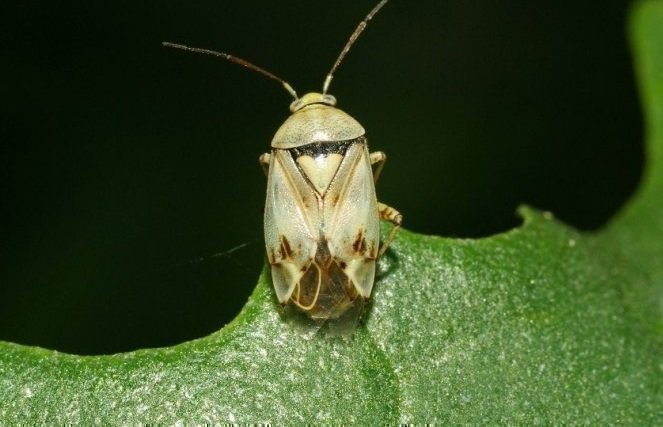


Meadow (field) bug is a light green or green-yellow insect with dark dots on the back and a body length of 6-7 mm. The eggs are laid in the petioles or leaves of plants. Two generations develop during the summer. It moves quickly on sunny days and is easier to spot early in the morning. Larvae and adults feed on the sap of leaves, stems, buds, causing their strong deformation. Leaves curl, buds produce ugly inflorescences or do not bloom at all. Bedbugs hibernate under plant debris.
Control measures are the same as for aphids. The treatment is repeated after 10 days. From herbal preparations, an infusion of onion or yarrow husks is used, sometimes the plants are pollinated with ash.
How to recognize aphids
Aphids are small (up to 2 mm) insects that live in colonies and multiply rapidly. The reason for her invasion of indoor plants can be only one female, which flew in through an open window or was brought in with a bouquet.
Most often, aphids settle on unopened buds, young leaves (on the lower side) and tops of shoots. These insects are easy to spot by carefully examining the plant.
The first signs of plant damage are:
- curling or gluing leaves;
- flower buds do not bloom, but over time dry up and fall off;
- blooming flowers are irregular in shape;
- the appearance of liquid, sugary clots, in the place of which a fungus can develop.
All this happens because the insect sucks nutritious juices and minerals from the plant. In addition, aphids infect the plant with harmful bacteria and viruses that can lead to death. That is why you need to get rid of it immediately.


Aphids suck nourishing juices from chrysanthemum
Watering the plant
Chrysanthemum is usually referred to as disease and pest resistant flowers. But they are also not 100% insured against harmful insects. Aphids are one of the most unpleasant misfortunes. These are insects up to 2 mm long, which prefer to live in colonies in order to capture the largest amount of food. For this reason, getting rid of aphids is sometimes a long process that requires patience.
Aphids live both on chrysanthemums growing on the street and on domestic specimens in pots. Indoors, there are black or white insects. On the street, including in greenhouses, there are pests of brown shades. Certain types of aphids often choose specific varieties of chrysanthemums.
Aphids are dangerous because of their speed of spread. She instantly passes from a sick plant to a healthy plant, threatening the death of all chrysanthemums in the area or in the house.
Aphids can be recognized by their mucus marks. The change in the appearance of flowers should also alert:
- buds do not bloom or deform;
- leaves dry, change color and fall off;
- shoots dry up or curl.
This harmful insect has such an effect on chrysanthemums in the process of sucking out nutrients from it. The consequences can be catastrophic and lead to the death of chrysanthemums, as a result, fungi and bacteria settle on them, so pest control should be started immediately.
Aphids appear on domestic chrysanthemums in different ways:
- when transplanting, it hides in the ground - it moves from one plant to another in this way;
- with flowers or fruits that have fallen into the room;
- from a plant next to it, which has appeared recently.
Watering is a must. Chrysanthemum loves high humidity, so growers recommend regularly spraying it with a spray bottle. This will help create optimal conditions for keeping.
The plant needs regular watering. Do not allow the earthen coma to dry out, as this can cause the root system to dry out. Watering indoor chrysanthemums should be moderate. There should be no water in the pan. If it has accumulated after watering, then it is better to drain it. During periods of active growth, the plant must be watered up to two to three times a week so that the soil is always moderately moist.
Chemical methods of aphid control
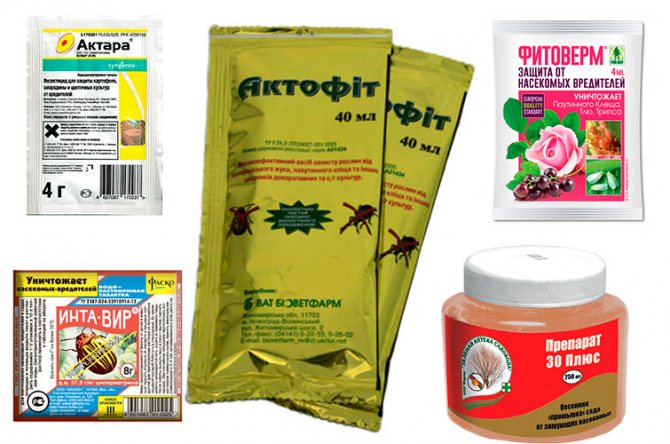
The most effective and fastest way to combat harmful insects is to use insecticides (chemicals from the pesticide group). These are Aktellikom, Intavir, Agravertin, Fitoverm, Neoron.
Before processing with chemicals, it is better to wash the plant. This will help get rid of a lot of pests. Treatment with chemicals is carried out by spraying or applying them to the soil. This is done in several stages. The first spraying is carried out when signs of infection appear. The plant is treated a second time after a few weeks, in order to prevent the appearance of new insects. After processing with these agents, the plant needs to be covered with a film for some time.
Let's summarize
- To protect the planting from death, treatment of chrysanthemum diseases should be carried out immediately after the first signs of infection appear.
- Weakened plants are most susceptible to pathogenic microorganisms, therefore, along with treatment, they must be provided with proper care.
- You can fight diseases with the help of folk recipes or chemicals - among the most effective are Maxim, Fundazol, Bordeaux liquid, funds containing copper.
- Plantings should receive a sufficient amount of nutrients, and you should not get carried away with preparations containing nitrogen and organic fertilizers (especially fresh manure), as they contribute to the development of diseases.
Folk remedies against aphids
Traditional methods of fighting insects are not so effective, but when used together, with constant and proper care of the home chrysanthemum, they give a good result.
Soap solution
The leaves and shoots of the infected plant are sprayed with soapy water. Prepare it in a ratio of 1 part soap to 6 parts boiled water. The prepared solution is sprayed or carefully washed all the leaves. Repeat the procedure several times until the pests are destroyed.
You can use potash green soap. A small piece of such soap must be grated and dissolved in 1 liter of ordinary water. Rinse the affected flower with the resulting solution. Do this carefully so that the solution does not get into the ground and destroy the root system.
Tobacco broth
To get rid of pests, tobacco broth helps. For its preparation, tobacco (it can be removed from any cigarettes) is poured into 1 liter of slightly heated water and insisted for 2 days. After that, the broth is boiled, allowed to cool and filtered. When processing flowers, cover the soil in the pot with a film or newspaper.


Decoction tobacco can be removed from any cigarette
Citrus peel
It is necessary to pour 200 g of orange or lemon peel with 1 liter of boiling water, insist in a warm place for three days. Then spray the affected plant abundantly with this infusion.
Treatment with pesticides
Let's make a reservation right away: folk remedies for powdery mildew are effective as a prophylaxis or at the initial stages of the spread of the disease. If the destructive process was launched a long time ago, more than 5-7 days ago, it is already useless to fight in this way. It may be possible to stop the development of the disease, but not completely eliminate it.
1. From soda ash and soap
25 g of soda ash is dissolved in 5 liters of hot water, 5 g of liquid soap is added. Plants and topsoil are sprayed with a chilled solution 2-3 times at weekly intervals.
Read next: Indo-duck breeding maintenance care
A protective drug against powdery mildew is prepared from soda ash and liquid soap (best of all household soap)
2. From baking soda and soap
Dissolve 1 tbsp in 4 liters of water. l. baking soda and 1/2 tsp. liquid soap. Spraying is performed 2-3 times with an interval of 6-7 days.
3. A solution of potassium permanganate
2.5 g of potassium permanganate is dissolved in 10 liters of water, used 2-3 times with an interval of 5 days.
4. Whey solution
The serum is diluted with water 1:10. The resulting solution forms a film on the leaves and stems, which makes it difficult for the mycelium to breathe. At the same time, the plant itself receives additional nutrition with useful substances and improves its health, which affects the improvement of its appearance. Treatment with a whey solution is carried out in dry weather, at least 3 times, with an interval of 3 days.
5. Horsetail decoction
100 g of horsetail (fresh) is poured into 1 liter of water, kept for a day. Put on fire and boil for 1-2 hours. Filter, cool, dilute with water at a concentration of 1: 5 and spray the bushes. The concentrate can be stored in a cool, dark place for no more than a week. Horsetail spraying can be carried out regularly to prevent powdery mildew in the spring and summer. In the fight against an already existing disease (in the initial stage), 3-4 times spraying with a frequency of once every 5 days is effective.
6. Copper-soap solution
This remedy for powdery mildew is distinguished by a high degree of effectiveness, due to the inclusion in the composition of a well-known fungicidal preparation - copper sulfate. In a glass (250 ml) of hot water, dissolve 5 g of copper sulfate. Separately, 50 g of soap are dissolved in 5 liters of warm water. After that, the solution with vitriol is carefully poured into the soap solution, in a thin stream and with constant stirring. The resulting emulsion is sprayed on plants 2-3 times with an interval of 6-7 days.
7. Mustard solution
1-2 tablespoons are mixed into 10 liters of hot water. dry mustard. The cooled solution is good for both spraying and watering.
8. Ash soap
In 10 liters of heated (30-40 ° C) water, 1 kg of ash is stirred. The solution is insisted, stirring regularly, for about 3-7 days. After that, the liquid component (without ash suspension) is poured into a clean bucket, a little liquid soap is added, poured into a spray bottle and processed. Plants are sprayed every day or every other day 3 times. Add 10 liters of water to a bucket with ash particles that have sunk to the bottom, stir and use it for watering.
9. Infusion of rotten manure (better than cow)
The rotted manure is poured with water in a ratio of 1: 3, insisted for 3 days. Then the concentrate is diluted in half with water and sprayed on the bushes.
10. Infusion of garlic
25 g of garlic (chopped) is poured into 1 liter of water, kept for 1 day, filtered and sprayed on the collection.
The modern chemical market offers a whole line of effective means to combat this parasite. The most effective are systemic insecticides - Aktellik, Aktara, Intavir, Agrovertin, Mospilan and Neoron.
No less effective is the double spraying of the plant crown with preparations - Fosfamid-10, Metaphos-20, Tsimbush-10, Karbofos-20. Instructions for use are indicated on the packaging of the chemical.
To get rid of aphids on a home or street chrysanthemum, it is necessary to carry out several such treatments. First, the plant is washed with a warm shower to wash off some of the parasites. Then, after the flower dries, the crown and soil are sprayed at the first signs of damage. The second treatment is carried out two weeks after the first to prevent the appearance of new insects. After each treatment, the crown is covered with a film for 2 hours. In greenhouse conditions, the likelihood of the death of all pests increases.
Insecticides are more suitable for treating outdoor plants, since they are less dangerous to humans.
Home culture can be treated with less potent agents:
- Liquid for washing glasses with the addition of ammonia. Processing is carried out twice with an interval of 10 days.
- Washing powder. The foamed substance is applied to the surface of the entire crown, thereby blocking the access of parasites to oxygen. As a result, they die.
Before using insecticides, you must wear protective equipment - gloves and a respirator to prevent contact of active substances with mucous membranes. After processing the plant, you should thoroughly wash your hands with soap, and dispose of all items used in the treatment.
If you have children and pets in your home, it is better to use harmless homemade products to treat an infected bush.
Soap solution
To prepare such a product, you will need 1 part of soap (household or liquid) for 6 parts of warm boiled water. The solution is sprayed on the soil and crown of the plant. The treatment is carried out until the parasites are completely destroyed. During treatment, the interval between treatments should be observed - once every 5 days.
Ammonia
This affordable product is highly effective against sucking insects. It is necessary to dilute the ammonia with warm water in a ratio of 1:10. Pour the solution into a spray bottle and process the crown, having previously covered the soil with film or paper. Spraying is carried out several times at intervals of three days.
Folk remedies: soap, oil, ash, onion infusion
To prepare tobacco broth, you need shredded tobacco (you can take it from regular cigarettes). Pour it with a liter of warm water (60 °), insist for 48 hours. After the time has elapsed, put the infusion on the stove, bring to a boil, cool to room temperature, filter.
Before processing, the soil around the plant is covered with foil or paper. In order for the destruction of the parasite to be successful, spraying the crown is carried out in two stages - at the first signs of the appearance of insects and 10 days after the first treatment.
For 1 liter of boiling water, take a glass of chopped lemon or orange peel. Close with a lid and insist for three days, then filter and spray the affected specimens 2 times. In case of severe damage, the number of treatments is increased up to 4-5 times.
Garlic infusion
Getting rid of aphids is carried out using garlic. The head of garlic, peeled and chopped on a grater, is poured with a glass of warm water. Insist for 40 minutes, then bring to a volume of 1 liter with warm water. Stir, filter and use to spray the crown. Processing is carried out every 3 hours during the day.
Folk remedies: soda, soap, ammonia, horseradish, celandine
Onion broth
This folk remedy helps to quickly and effectively exterminate the parasite. For 100 g of onion husks, 1.5 liters of water are required. The liquid with the husk is boiled for 10 minutes, then infused under the lid for half an hour, filtered and used to treat bushes. This tool can be used at any time of the year.
Pelargonium
The Pelargonium plant exudes a specific aroma that aphids simply cannot tolerate. If you put it next to a home orchid, the insects will disappear in a couple of days.
In a flower garden to scare away aphids next to garden chrysanthemums, you can plant parsley, dill, marigolds.
Spicy crops will repel the pest with their rich smell.
Why does house aphid appear
Before proceeding with active actions, it is worth determining the source of the appearance of the pest. Without identifying the cause, you run the risk of wasting your energy: individuals will reappear, if this cause is not eliminated first.
There are two main factors of infection:
- Irregular watering of the soil and, as a result, its dryness.
- Warm environment.
Analyze the situation: whether the watering of indoor flowers or garden beds occurs often enough, whether the plantings are in a too warm microclimate.
But in order to get to the foliage of crops, the parasites need to find a way to get to it. Let's consider the main paths:
- An insect can enter the apartment through an open window during ventilation.
- A plant can become infected from another plant.
- Ants are famous for "breeding" aphids, they transfer it to neighboring crops.
- The planting in the garden may be contaminated through the soil or some garden tools.
Knowing the main ways of spreading pests, you can prevent their parasitism in the garden.


Causes and diagnosis of the appearance
When small black, green or white insects appear on a chrysanthemum, the owner should sound the alarm.
Aphids penetrate the closed ecosystem of the room in the following ways:
- with fresh flowers brought from the street;
- with contaminated soil;
- through the open window - with a winged female who laid the larvae in pots of indoor plants.
After breeding, numerous insects spread along the flower, mainly affecting the back of the leaves, young shoots and buds.


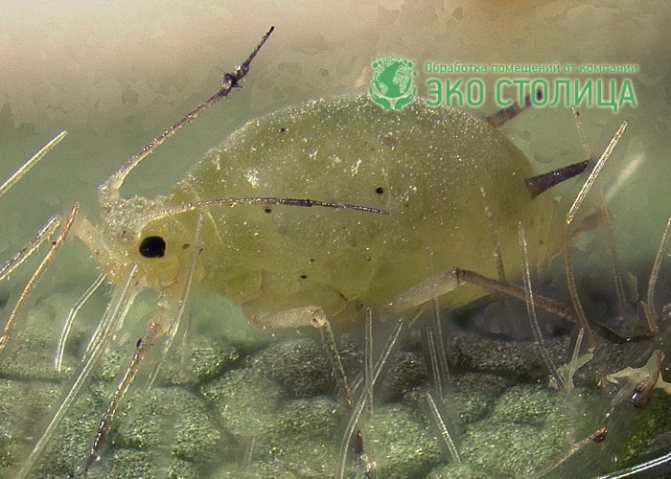
The presence of aphids is recognized by the following features:
- curling or sticking foliage;
- drying of unblown buds, cessation of flowering and general lethargy of the chrysanthemum;
- irregular shape and ugly outlines of flowers;
- the accumulation of a sticky sugary liquid on the plant.
In addition to signs of pest activity, the insects themselves and the remnants of the cocoons of the larvae adhering to the leaves and buds of the flower are clearly visible.
Parasite control methods
Pest control methods are conventionally divided into three groups:
- Folk methods. Folk aphid control methods involve the use of any available means to scare away and destroy the pest.
- Chemical methods. This is the most radical way, requiring the attraction of chemicals of various concentrations.
- Biological methods. In order to cope with the problem, you can try to use the laws of nature itself to your advantage. In their natural habitat, insects, like any other creatures, hunt each other. Therefore, you can use ladybirds or riders that will destroy aphids.
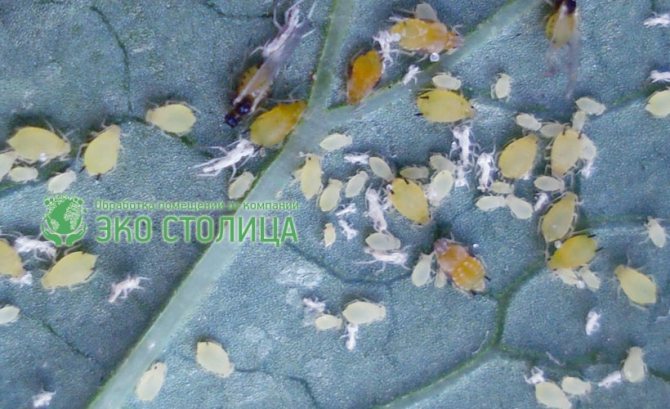


How to get rid of indoor aphids with chemicals
This insect annoys people for a long time. Therefore, today many folk methods of struggle have been invented. In addition, pest control chemicals have been developed.
To achieve a long-term effect, it is necessary to use chemicals. It should be borne in mind that those products that are intended for home use have a weaker concentration, therefore, are harmless to the environment. Among such drugs are Knimix, Fitoverma, Aktara and others. Most products are based on fatty acids and vegetable oils.
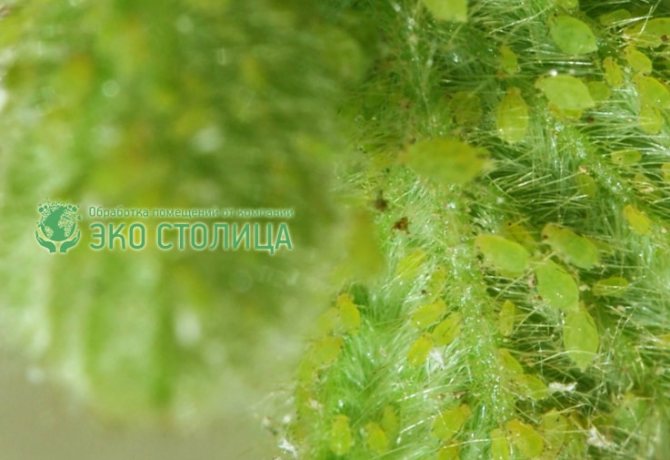


The pest control procedure is not as simple as it seems at first glance. The fact is that insects have the ability to develop immunity. That is, buying a product, a person has no guarantees of a positive result. You may have to try a number of drugs before the effect appears. If it is noticed that the purchased product does not act on parasites, it should be replaced immediately.
There is also such a situation: the chemicals gave a result, and the population began to decrease, but after a short time, the effect began to disappear. This suggests that during this period, individuals were able to develop strong immunity. In this case, you should also switch to another tool.


Absolutely all plants in the house should be processed, not just the affected ones.
To avoid wasting money and time, we recommend that you consult with a specialist about which remedy is best for your situation.
How to get rid of house aphids - an eco-friendly method
This section is intended for those who shy away from handling chemicals and prefer to cope with improvised means.This is, indeed, a more sustainable path, but not always effective. It all depends on the degree of damage to the territory.
The procedure is performed in the following stages:
- First you need to find all the affected areas of the foliage and apply a soap solution to them. All individuals should be washed off the plant using a shower or jet.
- In the case of few pests, it is best to prune the affected area carefully.
- The next step is to treat the foliage with an oil-based product. It is harmless to humans and vegetation. The substance should be sprayed evenly, being especially careful in the area of buds and flowers.
- To reinforce the effect, place a repelling object next to the flower. Pelargonium fragrant has an excellent deterrent effect, just place it next to the pot.
After about 2-3 days, the parasites should disappear. If this did not happen, check out other extermination options.
What harm can aphids do?
The parasite is most dangerous for young immature crops. The pest feeds on cell sap from stems, buds and leaves. Together with this juice, the plant loses nutrients and moisture.
What is the danger of aphids:
- The leaves and tops of infected plants begin to deform, and new shoots do not grow. The result is wilting and death during a massive attack of aphids;
- The insect secretes a viscous liquid - pad. It covers the leaf plate, stops the process of photosynthesis;
- Aphids carry bacteria and fungi - the causative agents of dangerous "garden" diseases.
REFERENCE: The pest is distinguished by fertility and rapid reproduction. A new generation of 100-150 individuals appears every 2-3 weeks. For 1 season, aphids can have up to 18 new generations.
Traditional methods
As a rule, tinctures and decoctions of herbs are most often used, which are complemented by intensive care of the vegetation.


The basis for such decoctions are herbs that have a repellent effect on insects, as well as fruits and vegetables.
The first and very important stage is the obligatory transplantation of the plant: this will allow you to change the land and avoid those individuals that can hide in the soil.


Consider a few recipes:
- Onion. You will need 40 grams of onion heads. Chop them (adding onion husks will only be a plus), leave in water (about 1 liter) for 6 hours. Then grate a few grams of laundry soap and add to the infusion. Strain and bring to a liter.
- On potatoes. Take a kilogram of potato tops (it should not be damaged by anything), grind and infuse in 8 liters of water for 4 hours. If dried tops are taken as a basis, then less will be needed - about 0.7 kilograms.
- Garlic. Take 300 grams of garlic heads and chop. Pour 1 liter of water and leave unopened for one week. The concentration should be 20 milliliters per 8 liters.
- On oranges. You need 100 grams of orange or tangerine peel. Fill them with a liter of warm water and leave for 4 days.
- On tobacco. Grind tobacco leaves in the amount of 300 grams and pour 6 liters of water for 3 days. Then bring to a volume of 12 liters, strain.
- On pine needles. Get 1 kilogram of pine needles and fill with 5 liters of water. Insist one week, stirring every day. After that, spray the infusion, following the concentration one to one.
- On a camomile. There are two recipe options here. First: take 200 grams of dried common chamomile, fill it with a liter of water and leave for 15 hours. Add crushed laundry soap at the rate of 5 grams per liter of infusion. Spray the resulting infusion in a ratio of one to three.
Prevention tips and tricks
To prevent diseases in chrysanthemums, you need:
- water them moderately with water at room temperature;
- make timely potash and phosphate fertilizers;
- plant bushes at an optimal distance from each other;
- spray with a solution of Bordeaux liquid after planting chrysanthemums after 10 days;
- loosen the soil after watering and rains;
- weed the flower beds in time.
Growing chrysanthemums is successful only if the rules of plant care are followed.
Rules for the use of decoctions
To get rid of aphids and avoid unwanted consequences, follow these rules:
- Processing of fruit crops from aphids should only take place at the stage of bud formation. This period begins after flowering and ends on average one month before harvesting.
- Processing of vegetable crops is not allowed later than a month before harvest.
- You cannot immediately start processing the landings. First of all, it is necessary to check the influence of the infusion on the culture. Therefore, start by treating a small area and, only after making sure of the effectiveness and safety of the method, use the recipe throughout the garden.
- As for the berries, these crops can be processed before flowering and continued after the berries are harvested.
Non-communicable and infectious diseases
Non-communicable diseases develop if the conditions for growing flowers do not meet the standards, if the diet and watering regime, soil, and air temperature are not suitable for them. In this case, flowers will not need treatment, you just need to fully comply with the cultivation technology.
* Non-communicable diseases affect individual specimens or all flowers at once, but in any case they are not transmitted to healthy plants. Their danger lies in the fact that they inhibit the growth and development of chrysanthemums, weaken their immunity and increase the risk of contracting infectious diseases - viral, fungal, bacterial.
So, on heavy, floating soil that does not have a drainage system, chrysanthemums can experience the so-called "root suffocation", during which their oxygen supply deteriorates, and they are unable to absorb nutrients from the soil to supply them to plants. As a result, the flowers begin to ache, the leaves turn yellow, the roots rot, the plant dies.
Excess moisture upsets the balance between the absorption of it by the roots and evaporation of the aerial part of the plant. It is not able to get rid of excess moisture and a transverse crack appears on the flowering stem, due to which the stem breaks together with the bud. Sometimes the stem remains intact, but the inflorescence is deformed. Lack of moisture is also harmful to chrysanthemums. They become lethargic, the leaves turn yellow, the flower petals crumble.
Low temperatures during flowering cause yellowing or reddening of leaves along the central and longitudinal veins.
Non-infectious diseases of chrysanthemums also arise from an excess or lack of minerals. A plant that is constantly on a "starvation diet" weakens and cannot resist pathogenic organisms.
It harms chrysanthemums and the introduction of fresh manure, it burns young roots, and they become a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi, which also causes the death of the flower.
Chrysanthemum infectious diseases, as well as human infections, are transmitted from sick individuals to healthy ones. In a flower affected by an infectious disease, negative physiological changes occur, which are reflected in their appearance. They have reduced photosynthesis, water absorption, metabolic processes slow down. Outwardly, this is manifested by wilting, growth retardation, rotting roots, dying off of shoots, leaves and buds, powdery bloom on the leaves, and malignant neoplasms. What infectious diseases are chrysanthemums susceptible to?
Chrysanthemum white rust
The first signs of the disease are round yellow spots on the leaves 5 mm in size. First, spots appear on young leaves, gradually they become larger and larger, change color to light brown.At the same time, round "pockmarks" appear on the underside - sporangia containing tleitospores. It is noteworthy that the leaves affected by the disease do not fall off.


White rust of chrysanthemums.
Tellytospores germinate and form spores of a new species - basidospores, which are carried by the wind. In conditions of high humidity, they easily germinate on healthy leaves and infect the flower, as a result, most of the plants are affected by the disease and lose their presentation. For this reason, chrysanthemum white rust is recognized as a quarantine pathogen.
The fight against the disease consists of a whole complex of measures. Diseased flowers are removed and sprayed with fungicides. Which ones - you should ask the specialists. The fact is that the fungus that causes white rust has already developed immunity to some fungicides, so it is quite difficult to fight the pathogen. Plants can be treated with miclobutanil, azoxystrobin, difenoconazole, kresoxim-methyl, or tebuconazole.
Gray rot of chrysanthemums
Gray rot of chrysanthemums - develops in cold and damp weather, during prolonged rains, or when transporting cut flowers. Brown watery spots appear on the petals. Then the spots grow, and the inflorescence turns into a rotting mass. Gray rot affects both mature plants and cuttings during rooting.
White rust


The symptom of the disease is spots of a yellow tint, which first affect young leaves, after which they spread to other parts of the plants and acquire a light brown color. It is noteworthy that diseased leaves do not fall off, but the plants quickly lose their decorative appearance.
White rust is one of the most dangerous diseases of chrysanthemums, as its pathogens quickly spread and infect healthy specimens. In addition, they develop immunity to chemicals, therefore, before processing the plantings with any means, you need to consult a specialist. Some of the most common fungicides used to control disease include:
- Difenoconazole;
- Miclobutanil;
- Kresoxim-methyl;
- Azoxystrobin;
- Tebuconazole.
All infected plants should be removed and burned, and the rest should be carefully examined - if there are characteristic spots on the leaves, they should also be cut off and destroyed.
Harmful insects
Chrysanthemums also have insect pests - mites, aphids, meadow bugs, tobacco thrips, spider mites, and drooling pennies. For example:
Greenhouse aphid
Greenhouse aphids are greenish or pinkish in color. It settles on leaves, from the lower side, in whole colonies. Aphids are a sucking insect that affects peduncles, shoots and buds. As a result of the "work" of aphids, the leaves are deformed, and the buds remain unblown.


Greenhouse aphids.
Brown chrysanthemum aphid
Brown chrysanthemum aphid - black-brown color. Inhabitant of greenhouses, settles in inflorescences, but does not damage them, but pollutes with excrement and residues from larvae.


Brown chrysanthemum aphid.
These pests are destroyed by the preparations "Bi-58 new", "Aktellik", "Karate", diluted in water in accordance with the instructions.
Spider mites
Spider mites - these pests of indoor and greenhouse flowers, settle on the underside of a leaf, and braid it with cobwebs. As a result, the leaf turns yellow, dries up and falls off. Ticks reproduce well in dry, hot weather, except for chrysanthemums, they can damage other plants in the greenhouse. In one season, ticks give 3-4 generations, and if you do not fight them, you can forget about the quality of flowers. Females of ticks hibernate under plant debris, so they cannot be left in the greenhouse for the winter, in addition, they can overwinter in the upper soil layer.


Spider mites.
Folk remedies are powerless in the fight against ticks, so chrysanthemums must be treated with Actellik or Fitoverm preparations.
Pests
Chrysanthemum bushes look sick when harmful insects attack them.Most of the parasites are sucking species. They make the plants look messy. Leaves and inflorescences especially suffer from the attack of insects.
Greenhouse aphid
A small sucking insect the size of a pinhead is green or pink in color. Usually, aphid colonies are located on the back of young leaves, which is why they warp and dry out. The female aphid lays eggs several times over the summer, which leads to a complete defeat of the plantings of chrysanthemums.
Spider mites
Small spiders with four pairs of legs attack plants in early spring and autumn. It is difficult to notice the insect, but as a result of damage to it, the foliage on the stems turns brown and dies. Fertilized female ticks overwinter in plant debris, under clumps of earth. To stop the invasion of the pest, it is necessary to remove and burn garbage in time in the fall, dig up the soil.
Helps fight ticks by dusting the shoots of chrysanthemums with sulfur powder or spraying with a solution of colloidal sulfur (100 grams per bucket of water). When processing, the underside of the leaves, where the mite nests, is especially carefully sprayed. The procedure must be carried out three times with a break of 10 days.
Leaf nematode
Filamentous worms infect the entire aerial part of chrysanthemums, becoming more active during the rainy seasons. The consequences of nematode damage are:
- the appearance of brown spots on the leaves;
- twisting and withering them away;
- lack of flowering;
- growth retardation.
After wintering in fallen leaves, nematodes continue to harm chrysanthemum plantations in spring.
Bushes infected with nematodes should be destroyed, and the remaining plants should be treated with Heterophos solution.
Meadow bug
Damage to leaves, buds and flowers is caused by bugs. They feed on plant tissues, which is why the leaves curl and deform, and the flowers fall off. It is necessary to process chrysanthemums with insecticidal preparations in order to destroy the pest.
Chrysanthemum fungal diseases
Chrysanthemum fungal infections are most often caused by poor air circulation, high soil acidity, excess nitrogen fertilizers and high temperatures.
Leaf spot, or septoria, chrysanthemum
The disease manifests itself in the form of spots on the leaves, which are yellow at first, and then gradually turn dark brown and black (and can grow in size). First of all, the lower leaves are infected.
| Prevention and treatment 1. The first step is to cut and destroy the affected leaves. 2. In order to prevent it, it is necessary to regularly remove and destroy the remains of dead plants in the garden. 3. If the disease spreads, it is worth using fungicides. |
Rust
The infection manifests itself in the form of pale areas on the surface of the leaves, as well as powdery orange spots on the underside of the leaves. Severely affected plants weaken and no longer flower properly.
| Prevention and treatment 1. Urgent removal of diseased leaves. 2. Thinning bushes for better ventilation. 3. When watering, avoid getting moisture on the plants. 4. If the disease has seriously spread, you need to switch to the use of fungicides. |
Withering chrysanthemum leaves
The first symptoms of fusarium wilting are yellowing and browning of the leaves. Infected plants are stunted and often unable to flower. The fungus enters plants from the soil through the roots and blocks the flow of water into the tissues of the chrysanthemum.
| Prevention and treatment 1. Removal and destruction of all infected plant parts. 2. Planting wilt-resistant varieties. 3. If there is already a Fusarium fungus in the soil that causes wilting, then the soil pH should be increased to 6.5 - 7.0. |
Powdery mildew
The leaves are covered with a whitish ash-gray powdery bloom. Spores of the fungus love a humid atmosphere; this is favorable for their growth and reproduction.
| Prevention and treatment 1. Removal of the affected plant material. 2. Use of fungicides. |
To fight fungal infections, copper oxychloride and Bordeaux liquid, Fundazol, as well as 1% colloidal sulfur are most often used.
Correct flower feeding
The lack of nutrients in the soil can lead to a deterioration in the general condition of chrysanthemums, the appearance of brown spots on the leaves and stem. Most of all, organic matter is suitable for feeding flowers - humus, wood ash, compost. Take your time and pay special attention to this process.
The color of the foliage will help to guess that the flower suffers from a lack of trace elements. In chrysanthemums, which lack nitrogen fertilizers during the period of active flowering and growth, they turn from dark green to whitish. If the buds of the flowers are crushed, and the leaves are curled, then the plant needs to be fed with potash fertilizers.
The minerals needed by flowers are added several times a year. During planting, in addition to organic fertilizers, superphosphates are added under the chrysanthemum bush. After 20 days, the procedure is repeated. After the plant begins to form buds, the chrysanthemums should be fed a third time. For 1 sq. m. of land will need 30 g of phosphorus and 40 g of potassium. A prerequisite for fertilizing is abundant watering of plants with water at room temperature.
Chrysanthemums will bloom magnificently only if the soil contains all the necessary trace elements
Read more: Indeterminate and determinant tomato varieties contrast
Dangerous for chrysanthemums and an excess of mineral fertilizers. From this, the leaves of the plant turn red, curl up, and then fall off. It is important to adhere to a clear schedule for the introduction of organic matter. During the year, the plant fertilizes no more than 3-4 times. If you notice that you are mistaken in the dosage, and this is reflected in the condition of the bushes, reduce the amount of minerals and take a break in feeding.
Planting a plant in good soil allows the bushes to develop correctly initially. However, chrysanthemums quickly draw out all the nutrients from the ground, so they need to be fed regularly. Fertilization is an indispensable element of plant care. Chrysanthemums respond well to minerals. Untimely application of potassium and phosphorus can lead to later flowering. It is for this reason that it is desirable to apply complex fertilizers.
Mature shrubs can be fertilized once every ten days during the growing season. Florists recommend using liquid organic matter. Top dressing is applied until the buds appear. Fertilizers are also a good prevention of disease.
The fight against powdery mildew is an integrated approach. First, you need to put in order the cultivation techniques of the affected plant. It means:
- watering only after the top layer of the soil has dried;
- during the fight against powdery mildew - completely abandon spraying;
- if possible, take the affected specimen to a brighter, sunny place until the moment of cure from powdery mildew;
- thin out thickened plantings, tear off old leaves that touch the ground;
- for the period of remission - less nitrogen fertilizers, more phosphorus-potassium (in case of illness - no fertilizers at all).
All care errors must be corrected without fail, otherwise powdery mildew will appear regularly. Now let's talk about direct treatment.