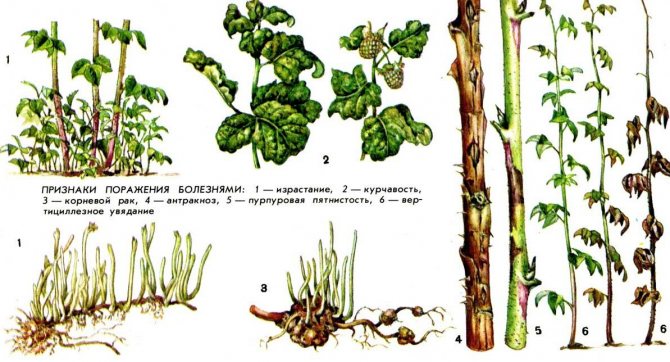
In the process of growth and development, raspberries are often affected by many diseases and pests. In order to grow raspberries and preserve them, it is necessary to carry out a set of works to protect the culture.
Raspberries are cultivated in almost every garden plot. It produces very sweet berries, endowed with a whole range of beneficial properties. However, this sweet product is annually attacked by various harmful insects, and besides, raspberries are susceptible to diseases. Today, pests and diseases of raspberries will fall into our field of vision, a description with photographs and methods of treatment of which will be the subject of our consideration.
Types of diseases of garden berries
Consider raspberry diseases and their treatment. The main types of diseases that raspberries are exposed to are viral infections and fungal infections. They can be simply called viral and fungal diseases of garden raspberries. Many varieties are susceptible to these diseases, although in modern catalogs there are quite disease-resistant species. But, completely immune do not exist yet. To protect planting from disease, you must:
- have a description of each ailment with photographs;
- know what they are being treated with;
- learn what preventive measures exist.
Let us dwell in more detail on each type of disease that garden raspberries are susceptible to. Consider common raspberry diseases, photos of their symptoms and how to treat each disease.
conclusions

Healthy raspberry. We are waiting for a good harvest!
Having familiarized yourself with the pests and diseases that most often affect raspberries, one should not forget that in order to reduce the risk of disease in berry bushes, it is necessary to observe agrotechnical measures, select varieties resistant to damage and carry out timely processing of plants.
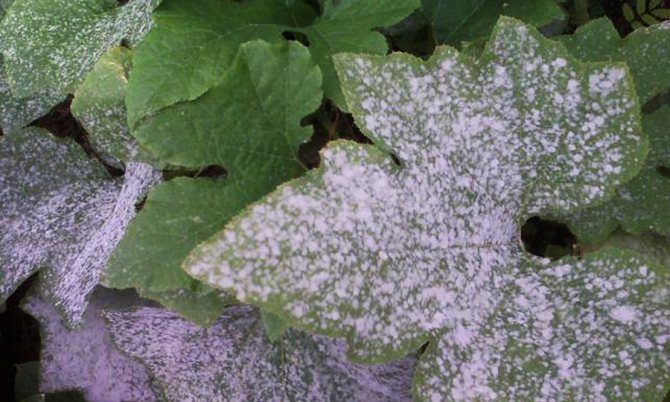
Diseases of fungal origin
These types of diseases can be classified as raspberry diseases. It is the berries that are more affected by fungal infections. Fungal diseases of raspberries are very common in plantings. Therefore, a description of their signs and control measures should be familiar to every gardener.
Rot gray (botrytis)


The most common disease. Small gray spots appear on the fruits, which grow and affect the entire berry. It begins to rot, becomes covered with a gray bloom, which contains the spores of the fungus. Spores spread with moisture and air, and are capable of infecting the entire raspberry tree. An outbreak of the disease is noticed during a period of rather cool days with high humidity.
The disease affects not only berries, but also leaves with shoots. Infected plants cannot stand the winter and die.
Important! Gray rot in raspberry beds spreads very quickly. You need to act immediately.
Disease control measures:
- bushes with signs of the disease are removed and burned;
- competently treat plants with drugs for protection;
- restore agricultural technology if there were violations.
To say in more detail - you should not process raspberry plantings just in case, and it is important to follow the berry planting scheme. All drugs that help fight the disease must be used before the berries ripen. If an overdose of chemicals occurs, the raspberries will be weakened and will not be able to withstand possible problems. In addition:
- The thickening of plants leads to the rapid development and spread of gray rot, so plantings are always thinned out. This makes it possible to ensure good ventilation and protection from disease.
- Diseased bushes are removed and burned, in the spring they clean the raspberry plantings well from the remnants of foliage and debris, and then they are treated with Bordeaux liquid.
Anthracnose
The second fungal disease that brings excitement to summer residents. In addition to berries, the disease also affects stems and leaves.
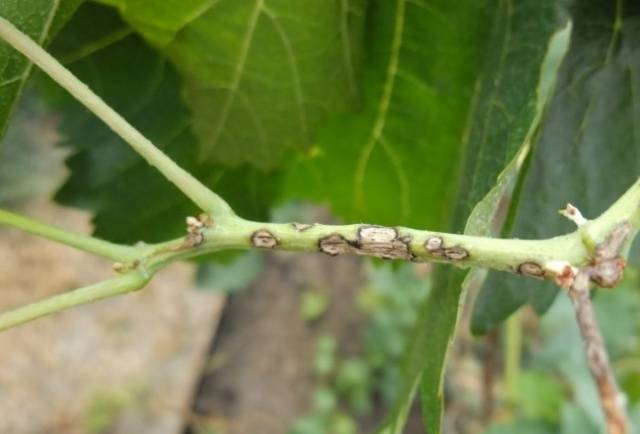


It appears as single spots on raspberry stems. The shade of the spots is grayish-white with a purple border around the edges. In places where stains appear, the fabric dries out. Subsequently, the spots merge, form ulcerative lesions. The bark exfoliates on the stems, and the leaves roll up and dry.


The main forces must be directed to:
- removal of diseased plants;
- spraying with preparations containing copper;
- reduction of planting density;
- ensuring good ventilation.
You will have to process raspberries from the disease at least three times per season. It is imperative to monitor plantings during rainy and high humidity periods. It is this weather that favors the spread of anthracnose.
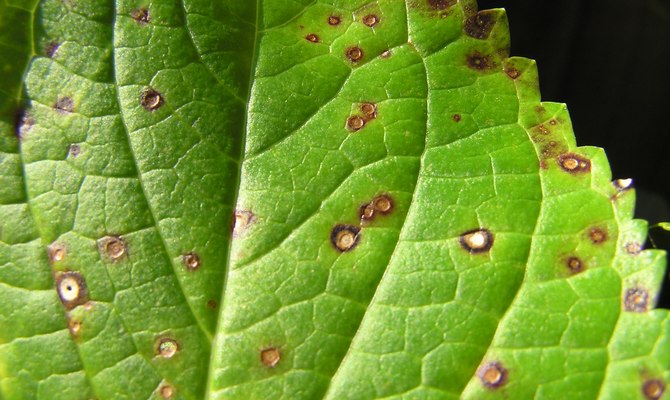
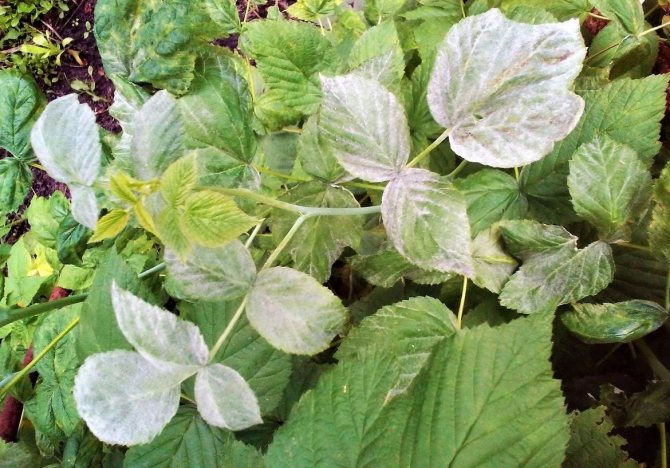
White and purple spotting
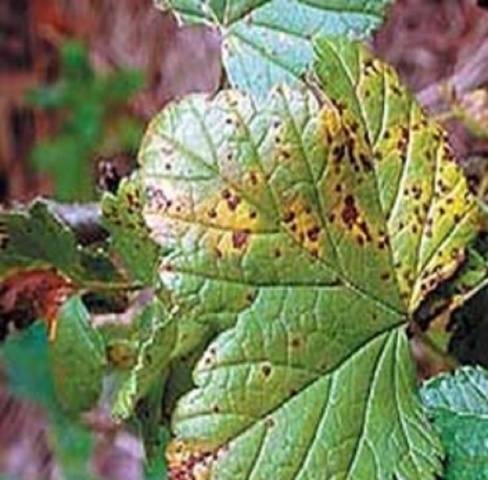


Common fungal diseases of raspberries. With the disease, leaves and stems are affected. White spot appears as brown spots, which gradually turn white, black dots are visible in them. With purple spots, they have a reddish tint. The main measures to combat the disease:
- plant only healthy material;
- thin out the plantings;
- treat with preparations containing copper;
- remove affected bushes.
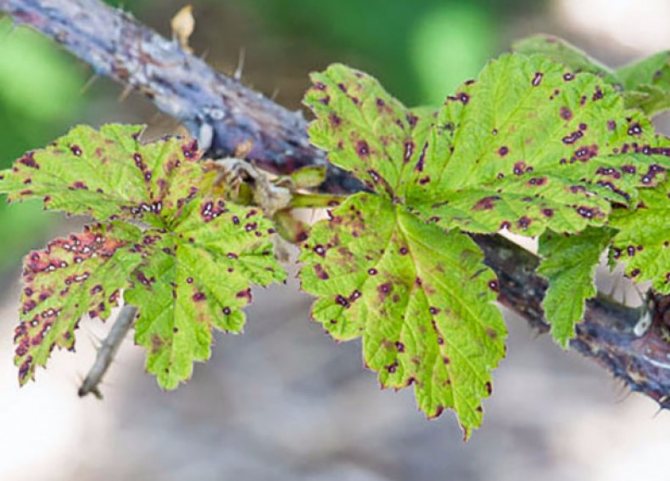
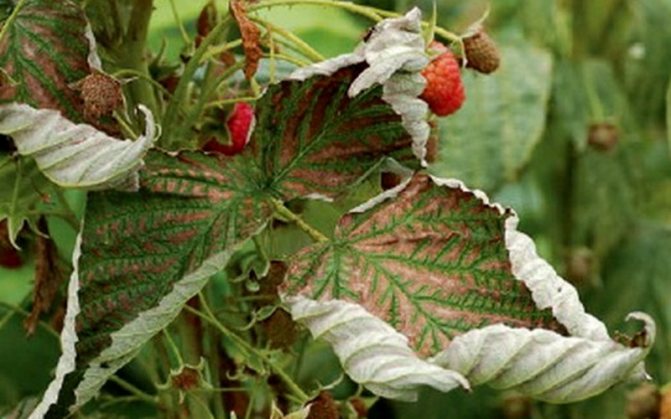
Raspberry rust


In case of illness, the stems and leaves of raspberries are affected. Yellow growths appear on them, which cause brittleness and drying of the stem, wilting of foliage. In spring, spores appear on the leaves; in summer, orange and dark mushroom cushions are noticeable on the underside of the leaves. They calmly endure the winter on loose leaves. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully remove the remnants of foliage from areas where raspberries are grown. During the wet period, the development of the disease continues until late autumn. Control measures are to collect and burn the leaves, dig deep aisles, spray the raspberries with Bordeaux liquid three times (1%).
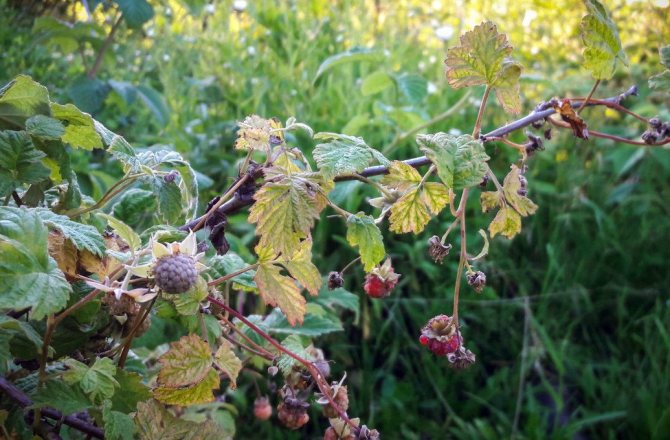
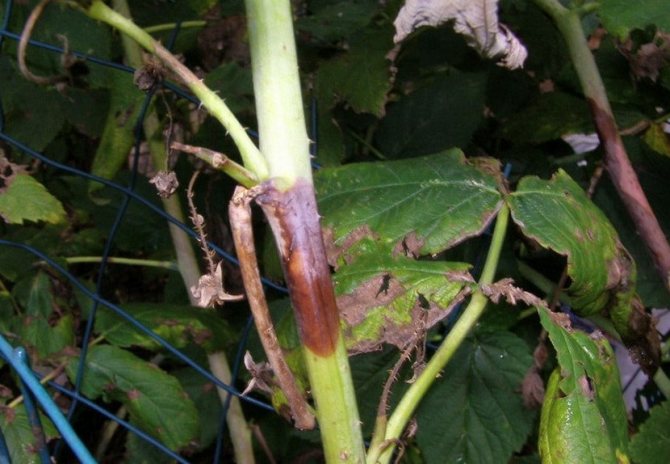
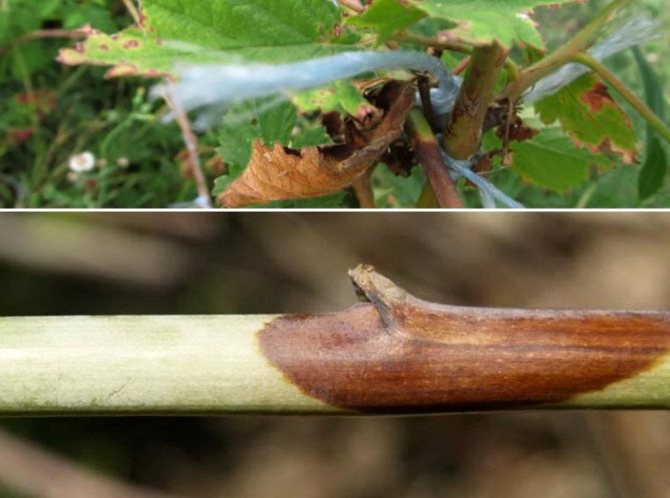
Purple spot
The disease attacks weak plants that have previously been injured by insects. Blurred purple-brown spots that appear near the adhesion of the leaves to the stem are a characteristic feature of the disease.
The spots grow over time. Slowly, merging with each other, they capture the entire stem. Manifestations in the form of necrotic spots are visible on leaves, petioles, twigs with berries. All this leads to drying out.


What can we counter this?
We cut off at the end of the harvest, without even leaving stumps, annual shoots that have been attacked. It is necessary to shovel the soil around and around the plant in late autumn or early spring with the simultaneous application of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
In the spring, before the very opening of the kidneys, we carry out the treatment with 1% Bordeaux mixture (10 liters of water - 50 g each of copper sulfate and lime). Or you can use it by taking 2 ml of Topaz powder per 10 liters of liquid. We do not forget to process with 1% Bordeaux mixture after harvesting the fruits.
Viral diseases of raspberry bushes
Another group of diseases that raspberries are exposed to. It is very difficult to treat viral diseases of raspberries, so every gardener should know preventive measures. They affect the root system, stems, leaves of the bush and lead to the death of the plant. These include:
Raspberry curl
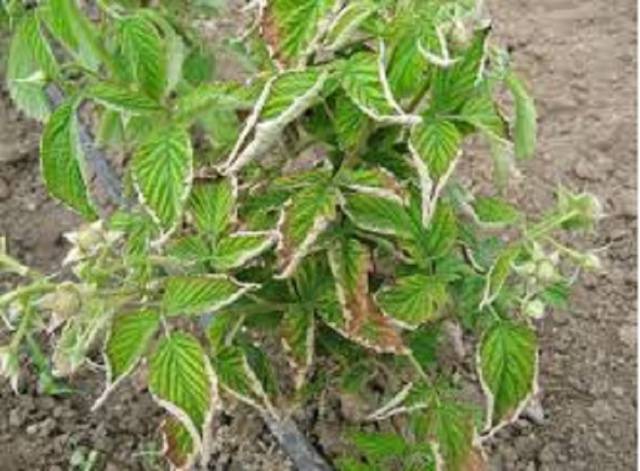


In case of illness, the leaves become tough, curl into a tube, and change color. First turn brown, then dry. The same result with berries. They become deformed and sour.The plant is not cured, dies after 2-3 years. You need to be especially careful when buying planting material. Otherwise, you can bring the disease into the planting and lose your favorite variety. Diseased plants are destroyed.
Mosaic
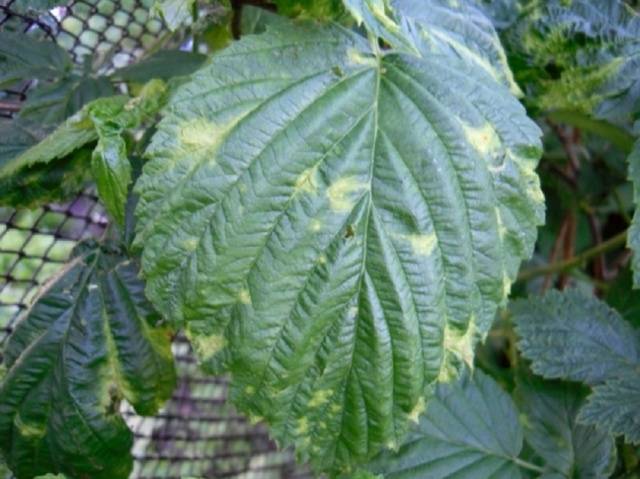


The main symptom is on the leaves. On them, areas of irregular shape are noticeable, which become speckled by the end of summer. The leaves become smaller, the shoots weaken, their growth slows down. The berries become woody, become unusable. Raspberries do not die, but it is completely impossible to cure the disease. Aphids are carriers of the disease.
Raspberry overgrowth or "witch's broom"
This is the name of mycoplasma raspberry disease. A lot of non-fruiting shoots are formed on the bushes. They are small, but the number can reach up to 200 pieces per bush.


It is transferred to other bushes very quickly, so the detected problem is immediately removed.
Important! Carefully select planting material and destroy pests - insects.
The disease is transferred to the site with cicadas and cannot be treated.
Preventive measures
To avoid the appearance of insect pests, preventive measures should be followed. After winter, it is recommended to prune off all wind-damaged, frost-damaged or mechanically damaged shoots. To get rid of gall midges at an early stage of the defeat of the bush, you should cut off the swollen branch and destroy.
After that, the shoots are treated with an insecticide. Wormwood or nasturtium can be spread around the raspberry tree. Effective protection - covering the soil with a thick layer of mulch. This prevents young insects from flying out.
Bacterial problems in raspberries
Pathogenic microorganisms, which include bacteria, cause diseases of the culture. There are diseases that are ubiquitous. Regardless of the region in which raspberries are grown, they can be affected by cancer.
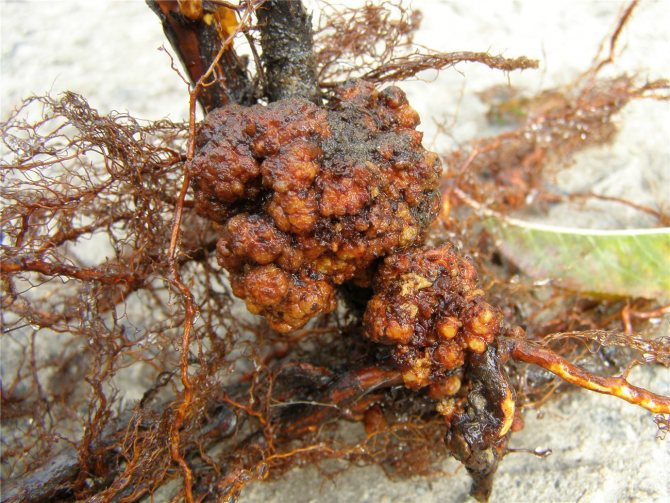
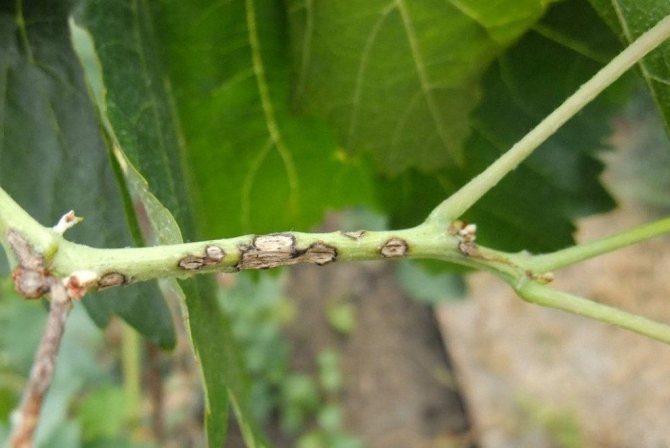
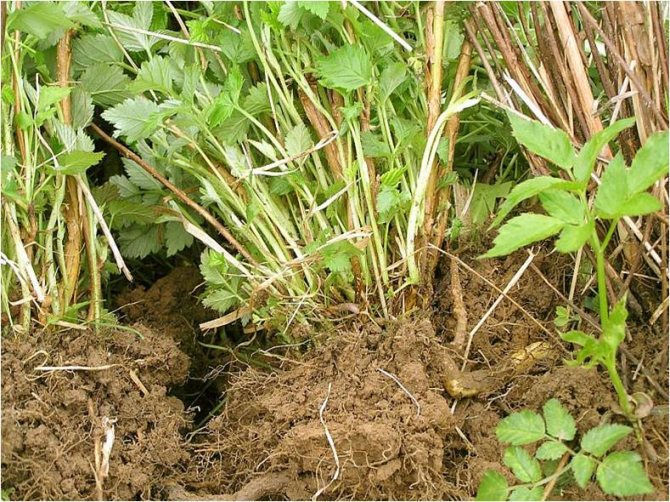
Stem and root cancer
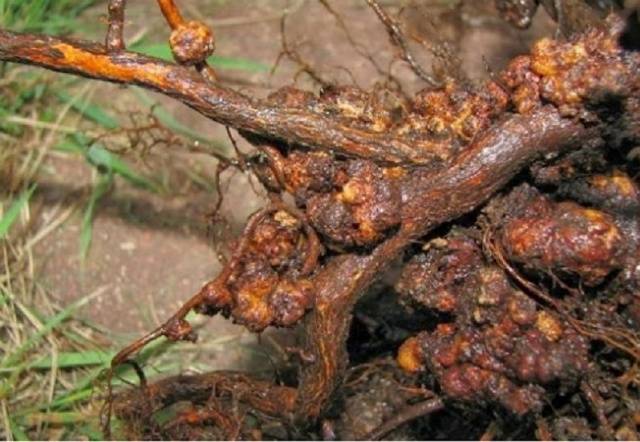


The main sign of infection is the appearance of small tumors (overgrown seals) on the roots. Gradually they merge and form a common lumpy surface with a rough crust. If such tumors affect the stems, then growing together, they break the bark. Bushes affected by this disease become weakened, do not tolerate winter frosts and die.
White spot
A signal for the presence of white spot is the appearance of small brownish spots on raspberry foliage. Then they take on a whitish shade with black dots. Stems attack blurry spots, which spreading along the stem, bring their bark to cracking. The result is not happy. Not only do the fruits lose their size, they also taste disgusting.
Rescue measures.
With the preparation "Energen" (liter of liquid - 20 drops) we process the area - 10 m² before the beginning of the flowering of the culture. After removing the last berry, it is necessary to spray 40 g of colloidal sulfur diluted in 10 liters of water or 2 ml of Topaz - 7 liters of water. For 10 m² there are 2 liters. Remember that we carry out the treatment when the weather is dry and warm.
Raspberry pests
Pests for planting raspberries in summer cottages
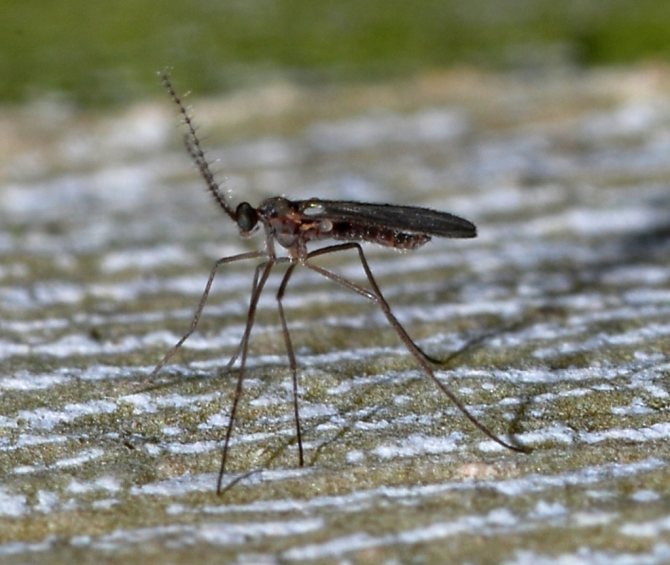
In addition to various diseases, raspberries are attacked by parasites and pests. How to process the planting to protect raspberries from damage? How to deal with pests that have already appeared? These questions are constantly worried about summer residents. Consider the main pests and parasites of raspberry plantings that annoy gardeners. It is better to get acquainted with the raspberry pests in pictures so that you know what they look like. The most unpleasant thing is that in addition to the harm caused by the parasites themselves, they are also carriers of many raspberry diseases.
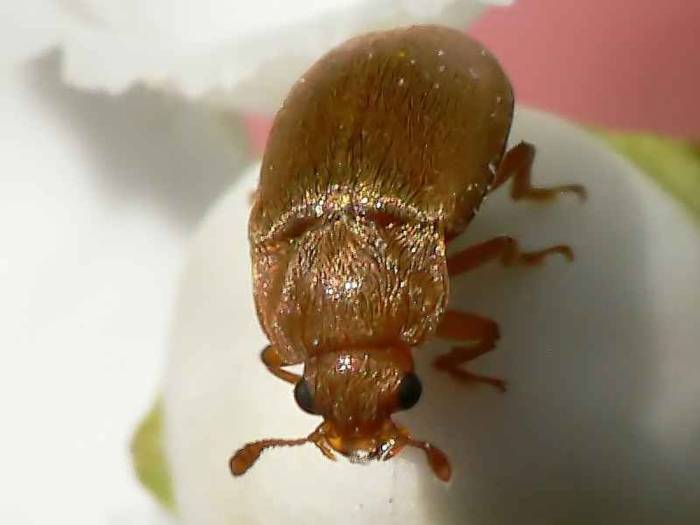
Crimson beetle


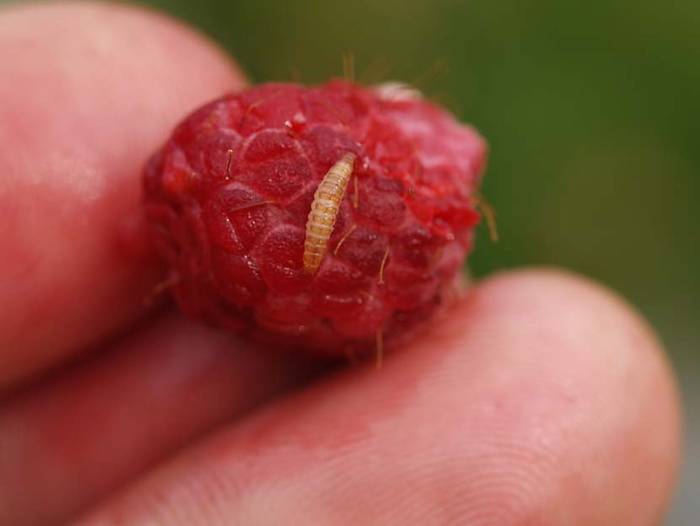
The pest hibernates in the soil at a depth of 10 cm, and when the soil warms up to 10-12 °, it comes to the surface. Until the buds appear on raspberries, the beetle feeds on the nectar of other plants.Then the pest moves to the raspberry bushes and begins to feed on the contents of the buds. As soon as the raspberry begins to bloom, the female raspberry beetle lay eggs and then the larvae continue their destructive work. When harvesting, the pest again goes into the ground for wintering. The beetle damages the buds, and the larvae damages the berry. What methods of control do gardeners use against pests? Firstly, the autumn digging of the soil in order to destroy the larvae of the raspberry beetle. Secondly, collecting beetles by shaking off the buds. Thirdly, the treatment of raspberries from pests in the phase of bud formation. In this case, karbofos helps well. At the time of picking berries, gardeners cover the containers with linen or waterproof paper. The larvae that have crawled out of the berries are immediately destroyed.


Raspberry stem fly


The larvae of the pest hibernate under bushes at a depth of 5 cm. After warming up the ground, they pupate, then flies appear. The harm from insects - pests lies in the fact that they lay eggs in the axils of the leaves and on the tops of raspberry shoots. The larvae of the pest feed on the core of the shoots, damaging the stems from the inside. Before the flowering of raspberries, they gnaw the stems and again go into the ground. To combat the pest, digging up the soil in the fall is used, before the raspberry blossoms, cut out and destroy the affected bushes. Spraying with karbofos during the summer of flies.
Stem raspberry gall midge
Very familiar to gardeners in central and southern Russia. A small insect (up to 2 mm) has transparent wings and a brown back.


The main harm of gall midge larvae is caused by raspberry stems. On the middle and lower parts of the shoots, characteristic swellings appear, which are called galls.


The larvae of the pest hibernate in them. In the spring, they feed on the contents of the stems, and in the raspberry flowering phase, an adult insect appears and lays eggs on young shoots. After a month, swellings are visible on them - the habitat of the pest larvae. Above the formation, the shoots dry out, then break off. On the galls themselves, the skin cracks and falls behind. If you do not take any measures, then a tiny gall midge can destroy up to 70% of raspberry plantings. How to stop a pest? First, in the spring and autumn, the plantings are thoroughly cleaned of damaged stems. They must be cut and burned.
Important! Cut the stem 3 cm below the bulge, but not to the ground.
On the rest of the raspberry can give a new crop. Treatments against the pest are carried out with the chemical preparations "Aktellik", "Fufanon", "Alatar", "Iskra-M". Spraying time is the laying of eggs by gall midges and the summer period of adult insects. The selected drugs must be alternated in order to achieve the desired result.
Raspberry walnut


Damage from this pest is similar to galls, only differing in size. The galls on the stems are about 3 cm long, and after the introduction of gall-milling larvae, swellings of 10 cm long appear. However, the measures to combat the pest are identical to the above.
Sprouting raspberry aphid


A familiar pest to gardeners in all regions. It is very harmful if the raspberry tree is located in a shaded place. It populates on inflorescences, ends of shoots, the pest forms whole colonies. As a result of damage by the pest, the leaves are curled, the shoots are bent and grow poorly, the flowers dry. A very small insect, but very harmful. In addition to damage to the shoots, it serves as a carrier of viral diseases of raspberries. More dangerous than aphids in dry years. It is necessary to fight the pest with the help of the chemicals listed in the section on gall midges.
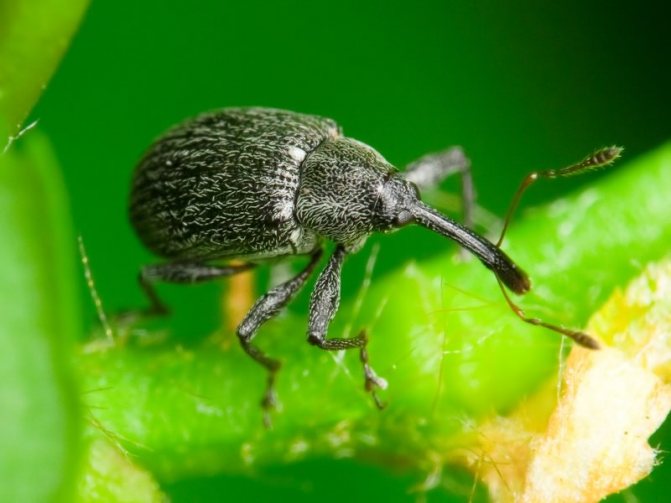
What other pests can be found on raspberry plantings? Plantings of raspberries are damaged by a beetle - weevil,


raspberry glass


and ticks.


The same drugs that are used against gall midge cope well with the weevil. And the glass bowl does not tolerate low cut of shoots and burning of damaged stems.Against the tick, use "Iskra-M", "Aktelik" or "Fufanon" for common varieties of raspberries.


Repaired ones are treated with "Garden Gray, Colloidal" or "Tiovit-Jet".
Pest preparations and their use
In early spring, when the buds are already bursting, it is necessary to process the raspberry bushes from pests. To do this, you can use the drug Aktar or the well-proven drug 30-B.
If the replacement shoot reaches 20-30 cm, the old stump must be removed. Raspberry protects against pests "Calypso", "Mospilan", "Karate", "Kung-Fu", and fungicides "Topsin M", "Switch" are also successfully used. Before flowering plants and in late autumn, raspberries are treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid or its analogue (Blue Bordeaux).
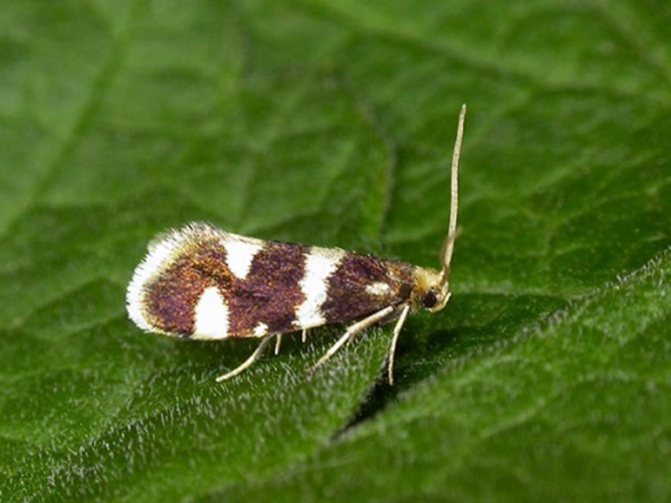
Raspberry glass
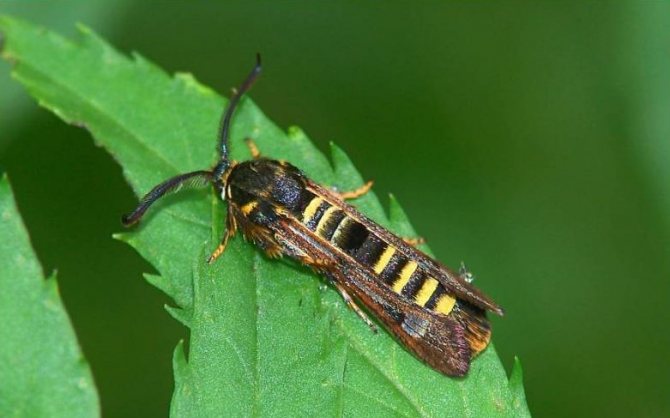


In mid-summer, butterflies lay their eggs in the soil at the base of the raspberry shoots.
The white caterpillars that have emerged from them begin to bite into the branches, which causes swelling. They hibernate and pupate right in the stems of the plant. The next year, the pupae turn into butterflies and the cycle repeats. Raspberry contaminated with glass withers and dries quickly.
In order to prevent the pest from multiplying, it is necessary to destroy the damaged shoots as soon as possible, and remove the old branches without leaving a hemp.
Raspberry beetle
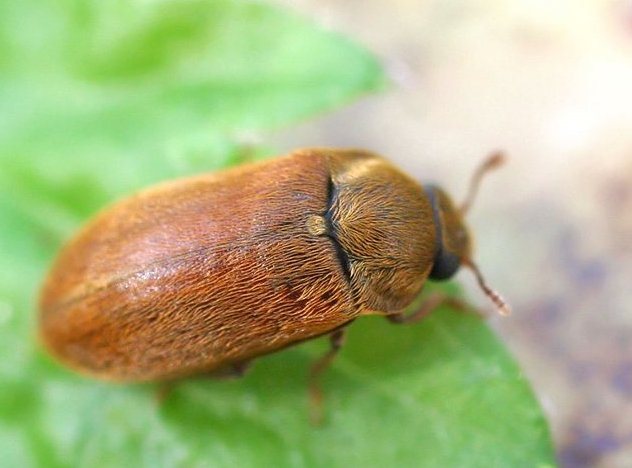


The insect hibernates at a depth of 5-10 cm in the soil.
In spring, it climbs on blossoming raspberry flowers, lays eggs, from which larvae develop, and eats the buds. The larvae return to the ground to pupate and turn into adult insects next spring. The cycle repeats itself.
In the war with the raspberry beetle, the following methods of struggle are used:
- digging up the soil under the plants and in the aisles during the formation of insect pupae;
- spraying with decis, confidor, karbofos.