Fungal diseases of the plum and the fight against them
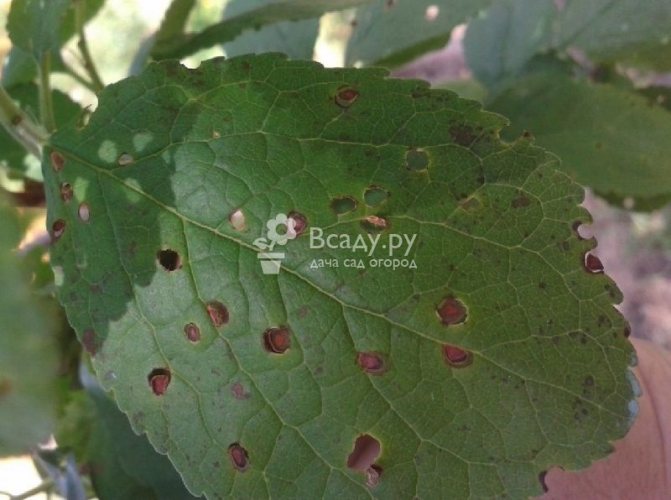
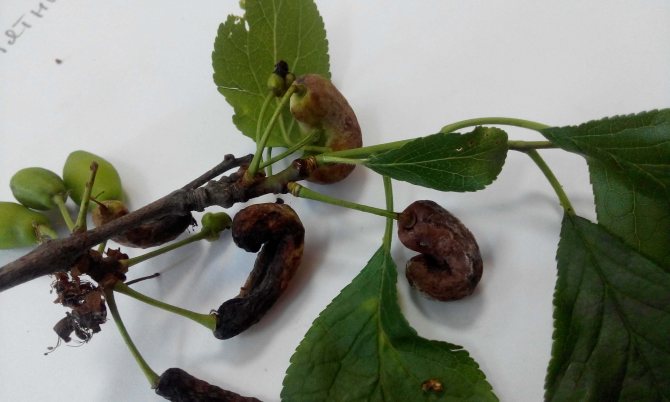
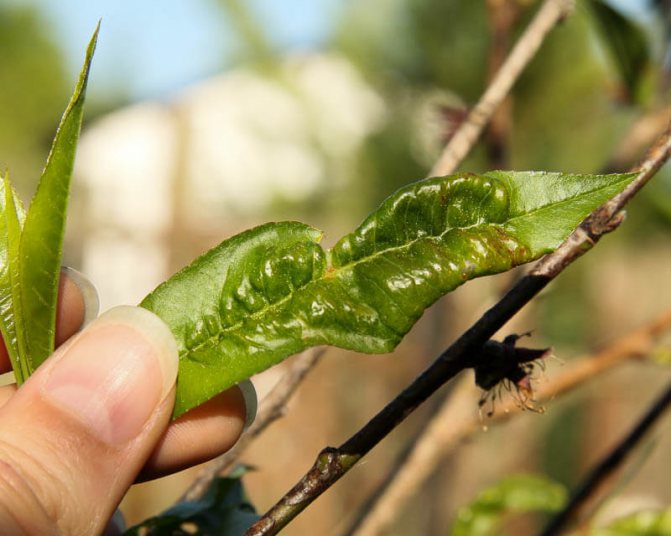
Clasterosporium disease, or perforated spot - a disease that affects the crown of the plum, that is, branches, leaves, shoots, flowers and fruits. The disease can be determined by brown spots with a reddish border that appear on the plum leaves. Over time, tissue from the middle of the spots falls out, and holes remain on the leaves. Small depressed spots also appear on the fruits, which swell with the development of the disease, and gum flows from them. Both fruits and leaves affected by clasterosporium wither. As a result of the defeat of the perforated spot on the plum, winter hardiness and productivity are reduced.

Fungal diseases of the plum and the fight against them
Control measures. As a treatment for perforated spotting, spraying the tree with one percent Bordeaux liquid five times per season is used: during the period of sap flow, during the appearance of buds, immediately after flowering, two weeks after the end of flowering and three to four weeks before harvesting. In case of severe damage, when shoots have suffered from the disease, after leaf fall, another treatment is carried out, but the composition should be three percent.
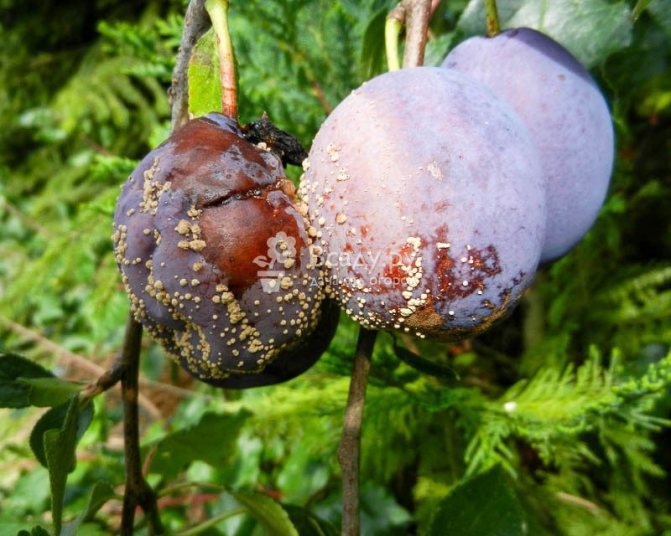
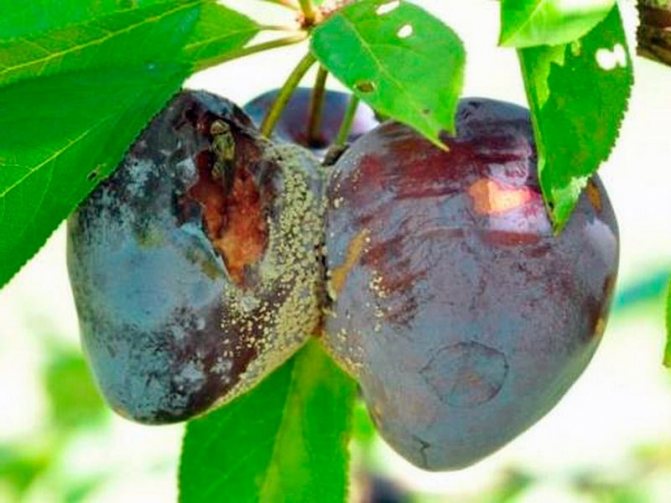
Moniliosis, or monilial burn, or fruit rot, or gray rot, looks really like a burn: the affected branches dry out, as if a fire was made under them, the fruits rot, but not all fall off: some of the diseased plums remain hanging on the tree. With the beginning of the new season, the fungus that has overwintered in the fruits is activated and begins its destructive work.
Control measures. Affected fruits and leaves must be removed and destroyed from the tree, and the plum must be treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, copper or ferrous sulfate in the same mode as for clasterosporium disease.
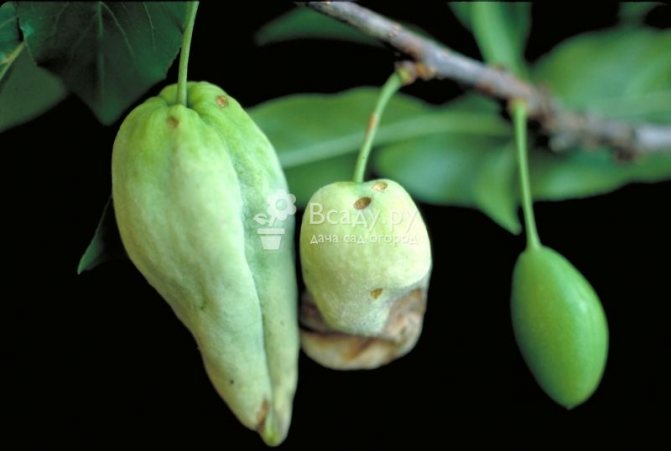
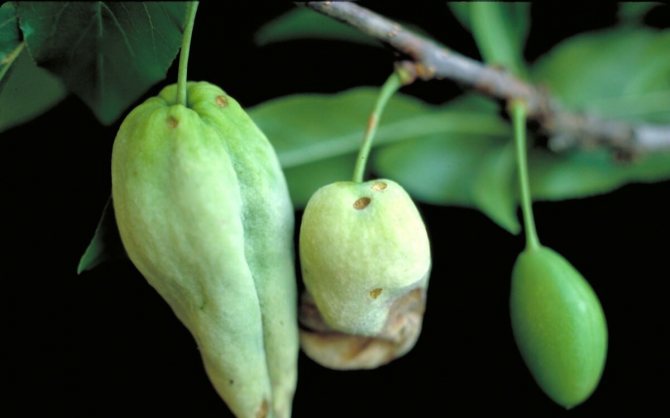
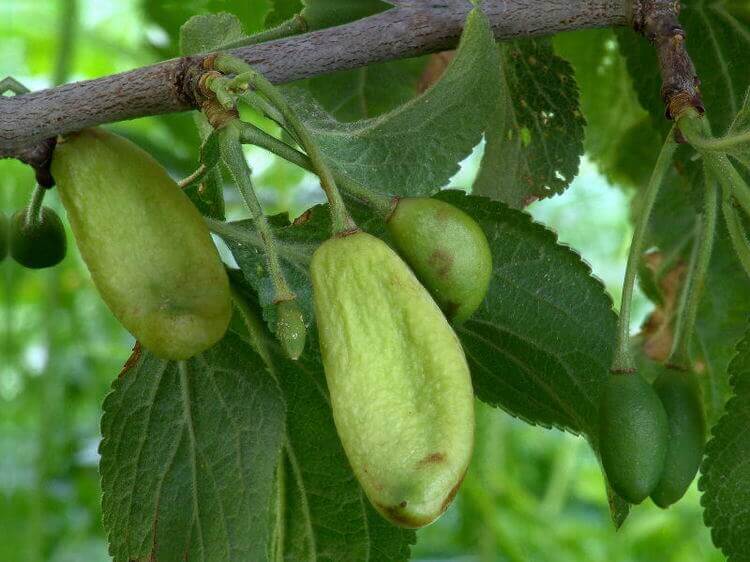
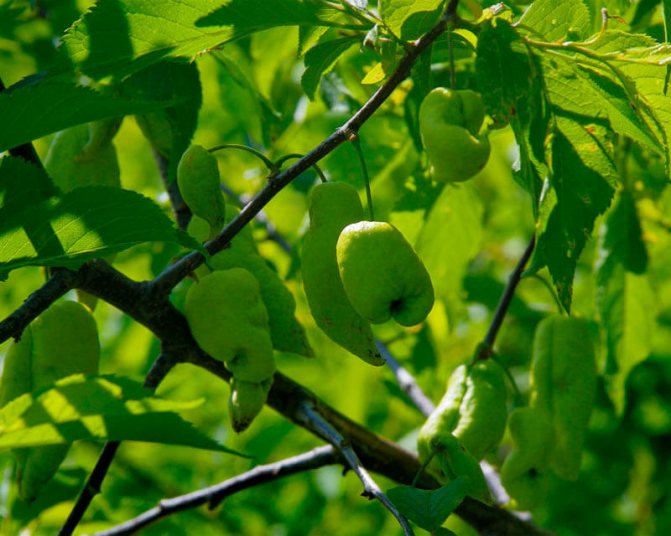
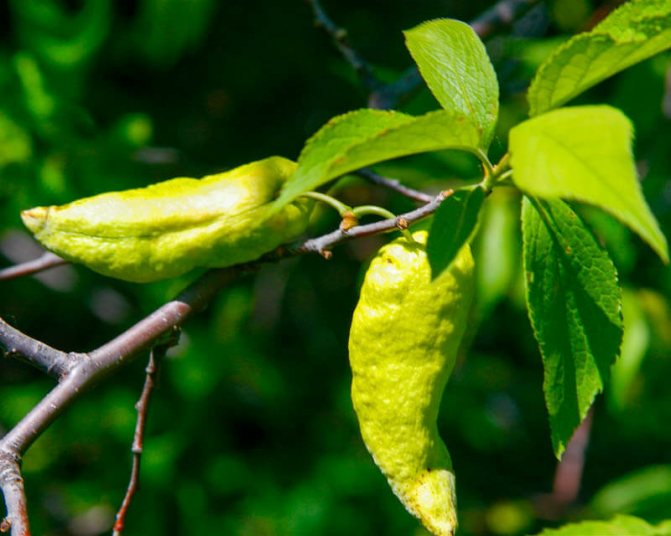
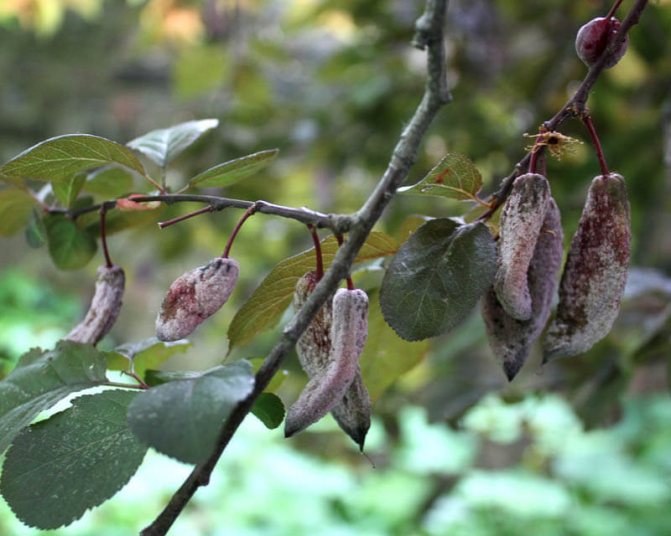
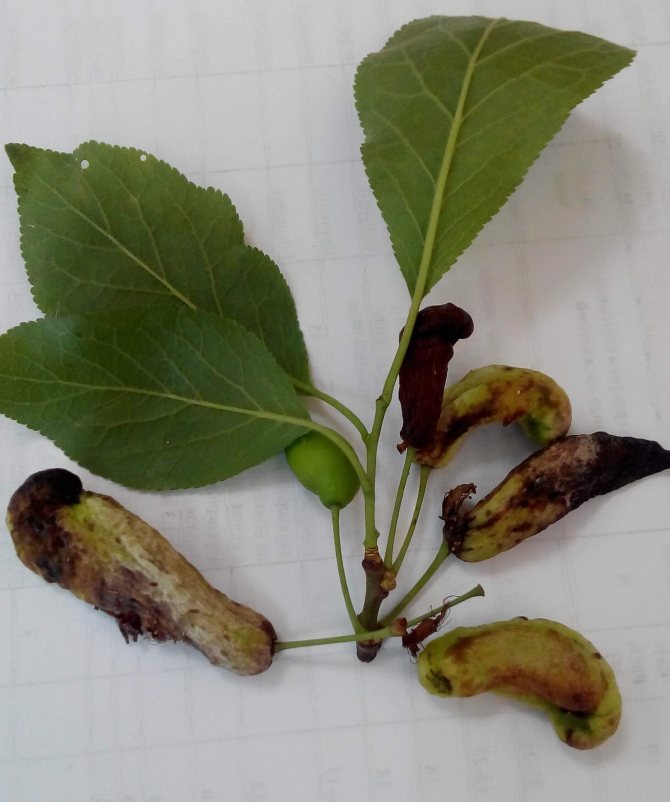
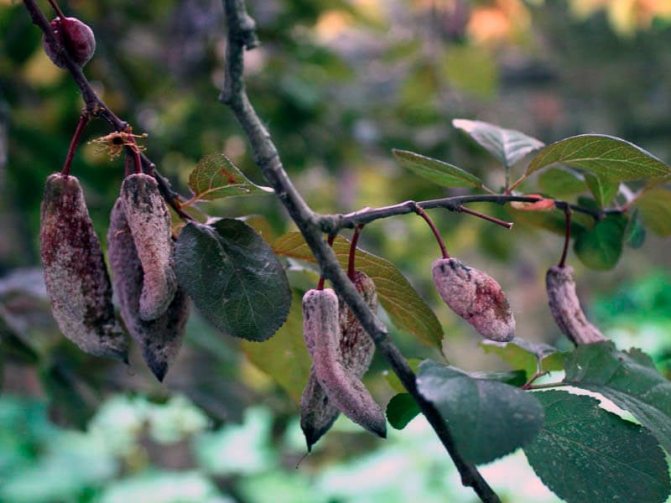
Plum pockets, or marsupial disease, gives the fruits a strange look: they stretch out like empty sacs, since the seeds in such fruits are not formed. Diseased fruits can reach a length of five or more centimeters, they remain green for a long time, then turn brown, dry out and fall off. After overwintering under bud scales or in cracks in the bark, pathogens infect plum flowers in winter.
Control measures. In early spring, before bud break, the plum is sprayed with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid, and after flowering, it is re-treated, but with a 1% Bordeaux mixture.
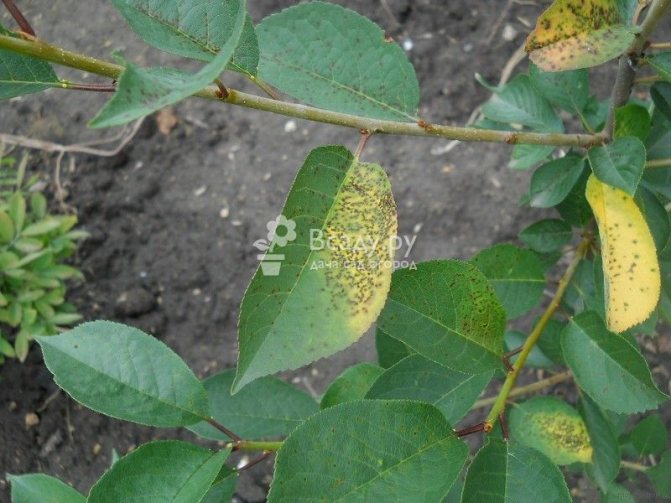
Coccomycosis affects fruits and leaves: small red-violet or brown spots appear on the leaves, then they grow, merging with each other, until they cover the entire leaf plate. The underside of the leaves is covered with whitish tubercles with fungal spores. Leaves fall off, fruits become deformed and unfit for food. The disease reduces the winter hardiness of the tree, and young plums are more vulnerable to coccomycosis than adults.
Control measures. The plant and the soil in the near-stem circle are treated with a solution of copper-containing preparations 4-5 times in the already described mode.
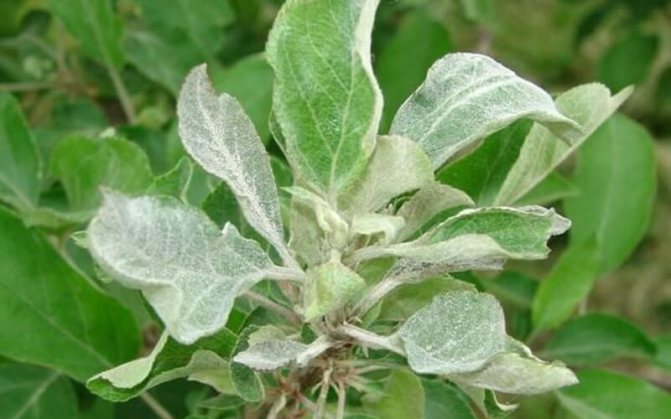
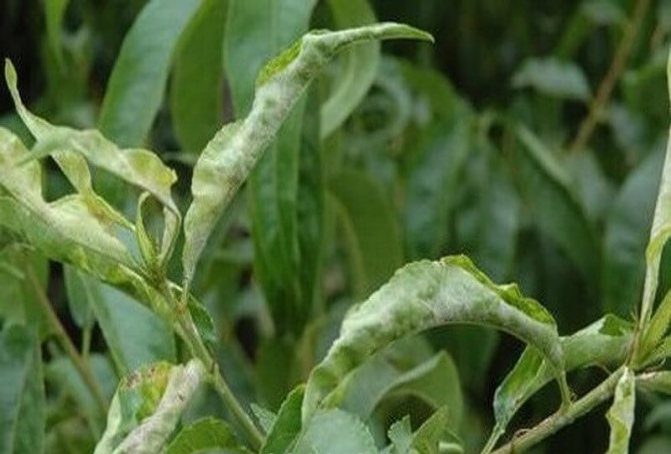
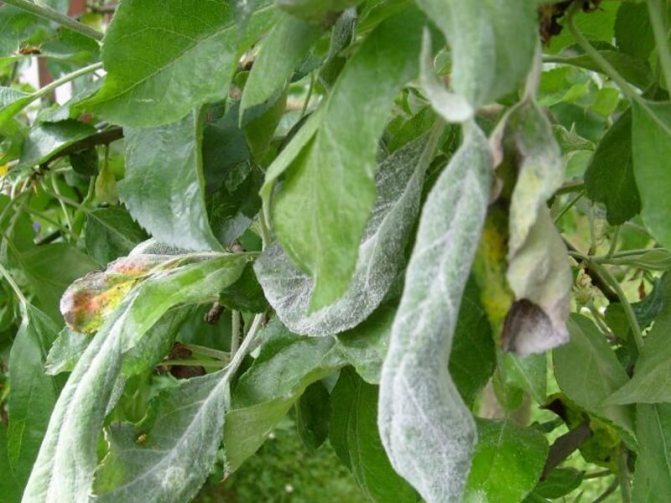
Milky shine - an incurable disease that often affects plum trees: the leaves are covered with a silvery-white bloom, and air bubbles and even whole cavities form in their tissues. The terminal border of the leaves and veins die, dark spots appear and grow on the trunk and branches, the bark on which peels off in stripes with the development of the disease. The leaves dry up and the tree dies.The disease progresses in conditions of high humidity.
Control measures. This disease cannot be cured, so it is better to immediately get rid of the affected tree.
Polystygmosis, or red spot - also a burn, but only a mushroom one. Blurry pale spots appear on both sides of the leaves, which gradually turn red, and the surface of the plate becomes glossy and convex. These spots are denser to the touch than the leaf tissue. In wet weather, the disease develops quickly, and the leaves begin to fall off in the summer. If summers are dry and hot, the leaves can stay on the tree longer, and dark formations with spores appear on their surface.


Plum bacterial diseases
Control measures. In early spring, plums are abundantly treated with a 1% solution of the drug DNOC, fungicides Switch, Horus or a 7% solution of urea, starting from the uppermost branches. If necessary, during the season, additional spraying of plum trees is carried out in the same terms that have already been described.
Curliness - a disease from which the plum leaves are deformed, become as if corrugated, turn yellow or turn red, gradually thicken, become covered with bloom, the shoots are curved, the fruits become ugly, and their pulp is inedible. The winter hardiness of the plum is reduced so much that the tree may die even in moderate frosts. The disease begins with kidney damage.
Control measures. In early spring and after leaf fall, the plum is treated with copper-containing preparations: Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate or a mixture of sulfur and lime. Solutions are prepared in accordance with the instructions.
Rust it is more common in areas with a warm climate: reddish-brown spots appear between the veins on the leaf plate, by the fall, pads with fungal spores form in their place. Affected leaves fall off, and winter hardiness decreases in a weakened tree. The original host of rust can be a nearby juniper or a garden flower anemone (anemone). Plum varieties that are absolutely resistant to this disease do not exist, but Renklode green and Anna Shpett are less likely to be affected by rust.
Control measures. Copper-containing fungicides such as copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, HOM and Oxyhom are used against the rust pathogen. Treatments are carried out in early spring and after leaf fall. As needed, you can treat the plum from rust and during the growing season, however, the last spraying should be carried out no later than three weeks before harvesting.
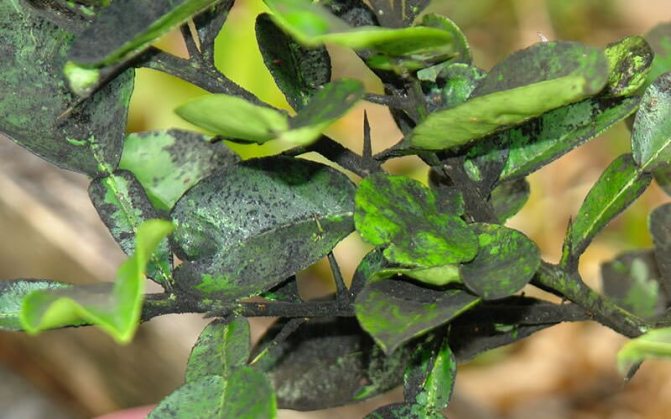
Sooty fungus covers the fruits and leaves of the plum with a black bloom, which disrupts air exchange and the formation of chlorophyll in the leaves. Most often, the disease affects plants occupied by pests: aphids, scale insects, whiteflies and other harmful insects leave honeydew on the leaves and fruits of plums, or sticky excrement, which is a favorable environment for the development of this fungal infection.
Control measures. Plaque of soot fungus is easily erased, and any antifungal preparation containing copper can be used to destroy the pathogen.
Moniliosis
This disease affects flowers, ovaries, fruits, young branches and annual shoots of plum. The causative agent is a fungus. There are two forms that affect the plum (diseases and treatment are described in the article):
- monilial burn in spring;
- fruit rot in summer.
Despite the fact that the causative agent of these forms is the same, the number of affected flowers and fruits is completely different. It is the fruits that are most susceptible to disease, especially if the air is characterized by high humidity. The causative agent of monoliosis can overwinter without losing its viability in mummified fruits, as well as in the tissues of affected branches.
The manifestations of the disease are as follows: pronounced rot appears on the fruits, after which they dry out.The lesions are pads about 0.5-1.5 mm in size. It is in these places that disputes accumulate. Rotten fruits can either fall or remain on the tree until spring.
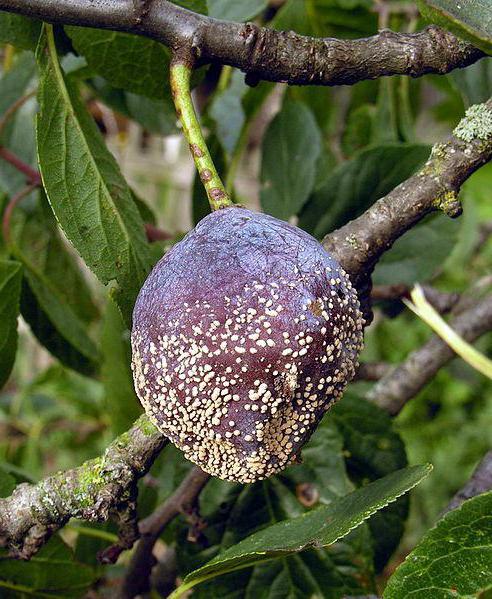


In the case of fruit rot, it is better to carry out timely prevention than to treat plums later. It is necessary to carry out thinning pruning in time, to destroy all fallen leaves, since among them there may be rotten fruits, affected shoots.
If the plum (diseases and treatment are described in this article) is already affected by moniliosis, then the trees must be treated with Bordeaux liquid at a concentration of 3-4% during the green cone period and at a concentration of 1% during the period after flowering. As a fixing treatment, spraying is carried out three weeks after the last procedure. During wet summers, the number of treatments should be increased.
Plum viral diseases
Plum pox, or sharka, manifests itself on the leaves of the tree as chlorotic spots in the form of rings or convolutions. If you do not fight the disease, the leaves acquire a marble color, spots and stripes are also formed on the fruits, their flesh becomes too dense, reddish-brown and inedible.
Chlorotic annular spot most often affects those parts of the crown that are in the shade, and manifests itself in the form of light green or yellow stripes and rings on the leaves. Loss of fruit yield from chlorotic spotting can be up to 50%.
Necrotic ring spot affects young plum leaves and resembles a hole in the spot, but without a red border around the spots. The tissues in the affected areas begin to crumble and gradually fall out, leaving holes.
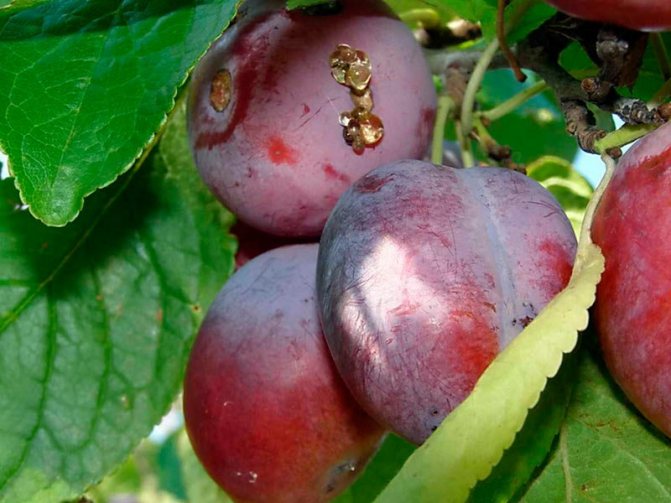


Linear pattern: This virus "decorates" the leaves along the veins with a yellow border, forming a pattern that resembles the outline of an oak leaf. Infection occurs primarily during pruning or vaccination. Insect pests can also carry the virus.
Control measures. It is impossible to cure these viral diseases, and the diseased plant will have to be destroyed. But you can try to prevent the infection of plums with viruses, for which you should regularly destroy weeds on which sucking pests parasitize - carriers of viral and bacterial infections. You need to plant only healthy material, holding it for a quarter of an hour in water at a temperature of 45 ºC before planting in order to destroy the viruses. In addition, every autumn, after leaf fall and sanitary pruning of plums, it is necessary to remove from the trunk circle and destroy all plant residues, and deeply loosen the soil in the root zone. In early spring and before the onset of frosts, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of trees with one percent Bordeaux liquid.
Root cancer
This disease is very common not only on such a tree as plum (diseases, photos of which can be seen in the article, are curable), but also on other fruit crops. Root cancer is caused by bacteria in the soil. They are able to penetrate the root of the plum if there is even minor damage on it. As a result of the disease, the plant stops developing, and the seedlings simply die. This disease is especially pronounced during periods of drought and in the case of growing on slightly alkaline and neutral soils.


Treatment options are as follows:
- choose areas where this disease has not been noticed;
- when digging up seedlings, the root must be processed, namely, to remove the noticed growths and disinfect with copper sulfate;
- in case of severe damage, the seedling is subject to destruction;
- you need to process all gardening equipment in order to avoid contamination of healthy plants (a procedure is performed using chloramine of 0.5% concentration or formalin).
Plum bacterial diseases
Bacterial spot at the beginning of development looks like small rounded spots on the leaves. Gradually, the spots lose their roundness, a dark broken border appears around them, and in the center of the spots the fabric dries up, crumbles and falls out. On the fruits, raised black tubercles with a white edging are formed, they gradually increase, become brown and scaly, with a depression in the middle. The disease greatly reduces the yield and winter hardiness of the tree.
Control measures. Bacterial diseases, like viral ones, are almost impossible to treat. You can save the garden from them only by preventive measures: in early spring and after leaf fall, you need to process the plum with one percent Bordeaux liquid.
Witch's broom - mycoplasma disease, in which on the plum begins a violent growth of thin sterile shoots, thickening the crown and taking away food from the fruiting branches. Leaves on such bunches are covered with bloom on the underside.
Control measures. Mycoplasma formations must be cut out to healthy tissue and must be burned, and the wounds must be disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate and painted over with oil paint on drying oil.
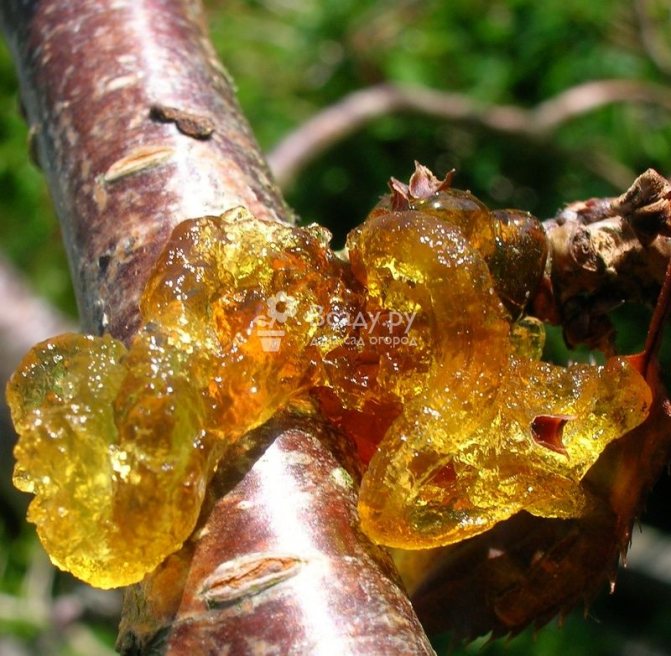
Hommosis, or gum flow
Gommosis is affected not only by plums, but also by other stone fruit cultures. Frozen trees or those that are already affected by the fungus are susceptible to this disease. In addition, there are factors that increase the risk of the disease. These are high soil moisture and a large amount of applied fertilizers.
It is quite easy to recognize gommosis: gum is released from the trunk and branches. After release, this substance solidifies, a transparent drop is formed at this place, the size of which can be absolutely any.
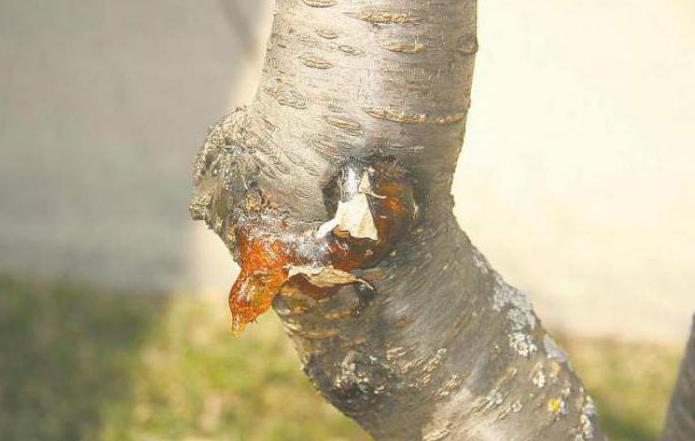


It is also necessary to fight this disease. First of all, it is necessary to comply with the basic rules of plum care. If any damage occurs, they must be treated with a solution of copper sulfate or garden varnish. If the lesion with gommosis is too strong, it is better to remove the diseased branch.
Plum non-communicable diseases
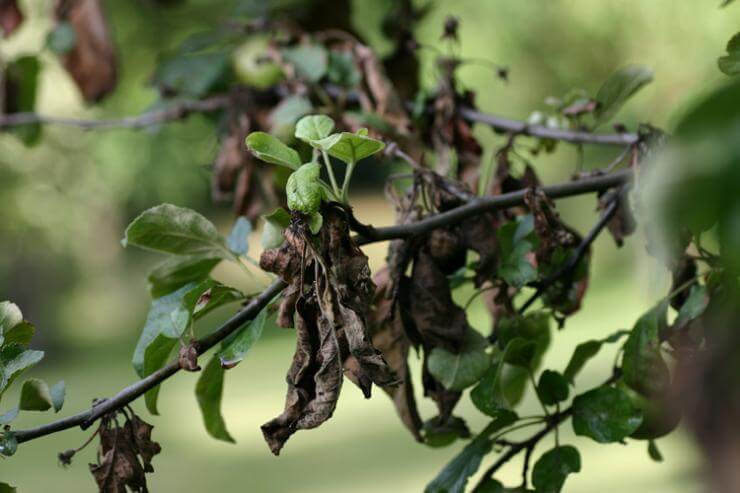
Hommosis, or gum flow, characteristic of all stone fruit trees: from a wound on the trunk or skeletal branch flows transparent, like amber, solidifying liquid. In this way, the plant tries to heal tissue damage. Responsibility for these "tears" rests entirely with the gardener: the cause of injury can be untimely or careless pruning, uncleaned and untreated wounds and cracks in the bark, hollows and frost holes. Gum therapy weakens trees, since it cannot heal serious wounds, and an infection can get into them at any time. Trees flowing with gum lag behind in development, their strength is depleted, and they may die.
PHOTO4
Control measures. Clean the damage on the tree immediately, treat the wound with a fungicide solution and cover with garden varnish with mullein.
Shrinking... The reason for this phenomenon, which can lead to death in a plum literally in a month, is non-compliance with agricultural technology:
- the plant is wet and dries up, because it was planted in an area with a high groundwater table;
- the soil on the site is excessively salty, acidic or alkaline;
- the superficially located root system of the plum is exposed to freezing, since it is not protected from frost;
- the plant was cut too much in the fall and did not have time to recover by the beginning of frost;
- the plant ran out with gum and became very weak.
What can a tree get sick with
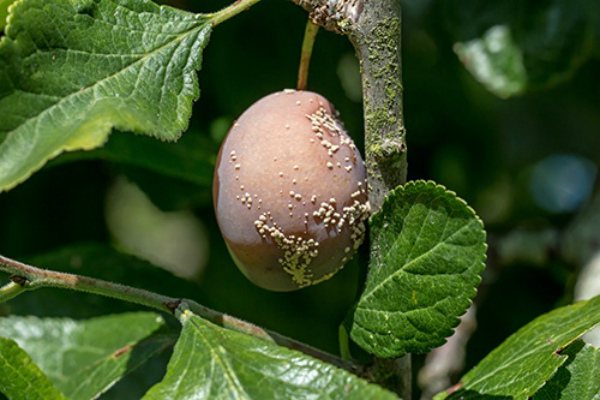


The plum tree is prone to diseases that fall into 3 main categories:
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- viral.
Attention! There are also non-infectious diseases of stone fruit trees that can lead to shrinkage.
If the gardener did not recognize the plum disease in time and did not take adequate measures to treat it, then there is a high probability of losing all the stone fruit trees in the garden.
Preventive drainage care
Plum is a crop that requires more careful maintenance than other fruit trees, especially in unfavorable conditions for it. But if, when planting, you chose the optimal site for it and fulfill all agrotechnical conditions, then to maintain the health of the plant, it is enough to perform several simple preventive measures:
- in early spring, before the start of sap flow, the tree should be abundantly treated with a 1% Bordeaux liquid or a 7% urea solution;
- all agrotechnical measures must be carried out strictly and in a timely manner;
- they begin to fight pests and diseases immediately, at the first sign of a problem;
- in the fall, when the plum sheds its leaves, they carry out a sanitary cleaning of the crown, collect and destroy plant residues - carrion, fallen leaves, cuttings of branches - and burn them, and loosen the soil in the near-trunk circle.
Rust
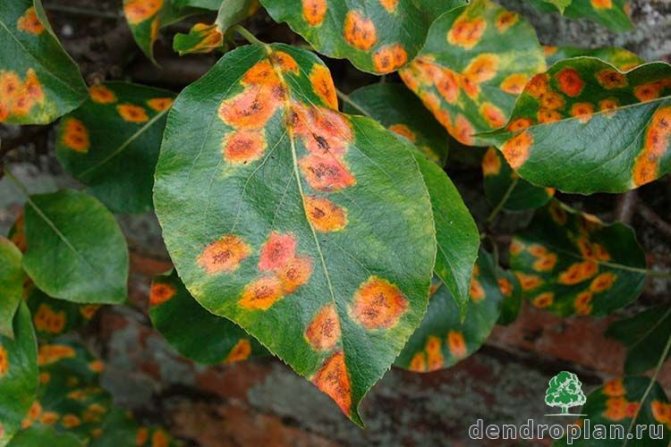


Symptoms Fungal disease affecting leaves, the disease is especially active in July. On the outside of the plum leaf, rounded swollen "rusty" spots are formed, which tend to gradually increase in size. Infected trees weaken quickly, leaves fall off ahead of time, and resistance to cold winter is significantly reduced.
Control measures. It is necessary to destroy the fallen leaves in a timely manner. Even before flowering, the plum must be sprayed with copper oxychloride (40 g per 5 liters of water, use 3 liters per tree), and after harvesting, the tree must be treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid.
Milky shine


Symptoms The disease is widespread, affects fruit crops and can lead to the death of the tree. Leaves become whitish-silvery, voids are formed in them. The leaf tissue gradually dies off, and the bark becomes dark. The disease mainly affects trees exposed to frost.
Control measures. Autumn whitewashing of the trunk, increasing the winter hardiness of the tree, spring feeding, timely removal and destruction of branches damaged by the disease.
Care calendar for disease prevention and control
Diseases and pests cause significant damage to the plum crop and can weaken the tree so much that it will not withstand even a mild winter and will die. To prevent this from happening, gardeners need to apply some agrotechnical measures and, in the most extreme case, chemical preparations.
- Early spring (before bud swelling). Damaged branches are cut and destroyed. Frost cracks, cuts are covered with garden pitch. They dig up the soil. The plum is sprayed with 3% nitrophene (60% paste).
- Flowering period. Chemical spraying is not applied during this period. A flowering plant is treated with a solution of honey (30 g per 10 l of water) with the addition of micronutrient fertilizers (1 tbsp. Spoon or 1 tablet per 10 l of water).
- Post-flowering period (before ripening). Chemical spraying is carried out with a solution of 0.2% chlorophos, 0.5% copper oxychloride and 0.4% vitriol.
- Ripening period. The collection and destruction of diseased ovaries is carried out. Tin cans, flags and halves of onion heads are hung to scare away birds.
- After harvest. All items to scare away birds are removed. The tree is examined for broken branches and diseases, wounds are treated and sprinkled with a garlic-mustard solution with ash broth, with the addition of 50 g of mineral fertilizers and 1 micronutrient tablet per 10 liters of water.
- Autumn-winter period. All weeds are carefully removed, the fallen leaves are raked up and destroyed, the boles, scraps and sunburn spots are whitewashed and the soil is dug around the tree.
- Late fall. The boles are whitewashed again, which are then wrapped with roofing material, spruce branches, roofing felt or white transparent film.
Photo gallery
If the slightest deviations in the condition are revealed, decisive measures should be taken without delay. Minimal delays in treatment can cause not only the death of a diseased plant, but also contamination of neighboring plants.
Photo gallery
To prevent this in your own area, use a cleaned and disinfected garden tool for working with plants, and also organize timely pest control that feeds on tree sap.
The exuberant growth of small branches on a tree is not always the result of improper pruning of the crown. Often this is nothing more than a disease of mycoplasma nature, called the "witch's broom". On the branches that are affected by the disease, a huge number of thin shoots are formed, located very densely. Peduncles do not appear on them, and the leaves are covered with white bloom and crumble prematurely.
Landing rules
Cistena seedlings are planted both in spring and autumn, but in the middle and northern lane it is recommended to perform the procedure only in the warm season, immediately after the winter dormancy of the soil. In this case, the plant will have time to get stronger before the onset of winter and will definitely survive it.
Planting holes begin to be prepared two weeks before the intended planting of seedlings or even in autumn. First of all, you need to dig up, loosen and level the selected area, and then dig a hole 70 cm in diameter, with the same depth. Performing the procedure, the extracted upper layer of the substrate must be thrown aside, mixed with peat and humus, and drainage from broken bricks or small stones must be laid on the bottom of the pit (especially important for swampy areas). A small mound of fertile substrate should be poured over the drainage layer and the hole should be left until planting.


When preparing seedlings, it is useful to place specimens with an open root system in a container with water for several hours, and then immediately move them into the prepared holes, placing them exactly in the middle of the soil mound (the roots are carefully distributed over the entire mound).
Important! When buying seedlings, carefully examine them and make sure that you are in front of the variety of interest. The shoots of the Cistena plum are always red and burgundy, and of course they should look strong and healthy.
Closed-rhizome plums (sold in small containers) can be planted together with the earthy clod in which they are located, after moistening the soil well for easier extraction of the plant.
When filling the seedlings with a nutritious substrate from the upper layer, the procedure is performed so that the root collar remains 4 cm above the ground surface, and there are no voids between the individual roots. At the end of the process, all that remains is to water the seedlings and mulch them with a layer of peat or sawdust.


The main methods of breeding
The described bush plum can be propagated in several ways at once, and the choice of a particular option depends more on climatic conditions and personal preferences of the gardener.
Important! Whichever method of reproduction you choose, all parts of the mother plant taken for it must be absolutely healthy, without the slightest signs of rot or damage by pests. Dried cuttings are also not suitable, especially if they are used for rootstock.
Possible ways include:
- Propagation by bones... Basically, the seed option is used to obtain a rootstock for grafting other varieties, since when growing an adult plant "from scratch" there is a possibility that it will receive a limited number of varietal characteristics of the mother shrub. For the procedure, only seeds from fully ripe fruits are suitable, which, after stratification and pre-planting disinfection in a solution of potassium permanganate, are planted in pots with nutrient soil (usually in spring).In the future, care comes down to regular watering, fertilizing and airing the sprouts that have appeared, and as soon as they get stronger, they are transplanted into a greenhouse. During the year they are in a greenhouse, after which they are transplanted to the site or used as a stock.


In March, the seeds are planted in pre-prepared planting pots, which are filled with nutritious soil. - Propagation by root offspring... Plum trees and shrubs form a lot of root growth, so it is not surprising that this particular method is considered the easiest. Only a strong and well-developed offspring, located at a distance from the donor plant, is suitable for rooting. At a distance of 20 cm from the stem, it must be separated from the shrub and the cut sites must be treated with garden pitch. The material ready for planting is planted in the prepared place in the usual way.
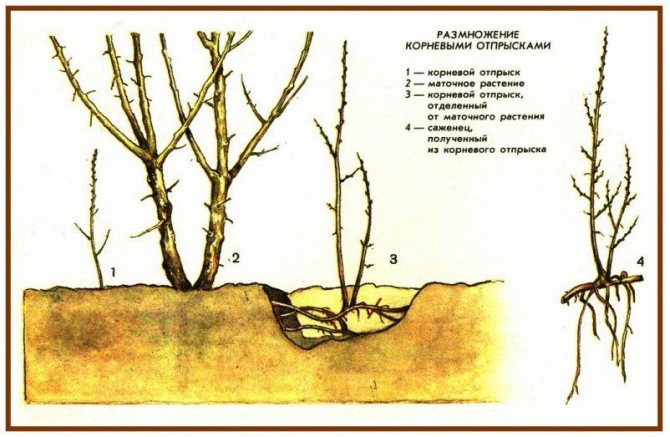

This breeding method is considered the most common, as plum trees produce a large amount of growth suitable for reproduction. - Propagation by green cuttings... Cutting plums is a simple process involving cutting healthy cuttings, 30-40 cm long. Before planting, the resulting parts are immersed in water, kept in a root formation stimulator (for example, "Heteroauxine"), and then rooted in a mixture of sand or peat. It is important to leave at least 5-7 cm of free space between adjacent cuttings, and the segments themselves are deepened into the substrate at an angle of 45 degrees. Further care for the cut parts is based on regular watering and fertilization with nitrogen-containing compounds (introduced into the soil about a month after planting the cuttings). Before winter, the rooted planting material is dug up, the roots are covered with moss and wrapped in a film, after which they are sent for storage in a cool place. The next year, with the arrival of spring, you can plant cuttings in a greenhouse and grow in such conditions for two years.


This method of propagation is also often used by gardeners, as it gives a good positive result of the survival of young seedlings. - Reproduction by grafting. This method of obtaining new plants is no less relevant than the previous one and is used just as often, and the gardener only has to choose one of two possible methods of grafting: by bud or cuttings. In the first case, a healthy kidney with a part of the bark is cut from the selected scion and placed in a T-shaped incision of the rootstock, tightly fixed with tape. In the second, an incision is made on the stock with a sharp knife (2.5 cm in length) and the lower cut part of the cutting deepens into it. For the tightness of the connection of the two parts, it is worth wrapping them with an eyepiece film.
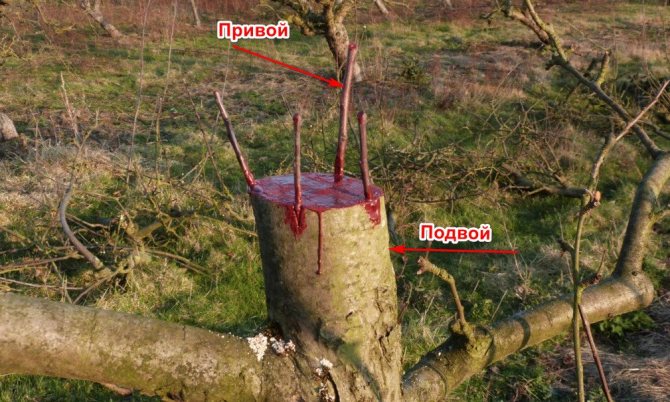


This variety of plum is often grafted onto stems to produce a slender Cistena plum tree.













































