A plentiful and high-quality harvest of tomatoes and cucumbers can be obtained only if all the rules of cultivation and care are observed. One of the important components of care is the timely application of fertilizers and top dressing. They contribute to abundant flowering, the formation of ovaries and fruits, high quality of the harvest and the duration of its storage, increase the immunity of vegetable crops.
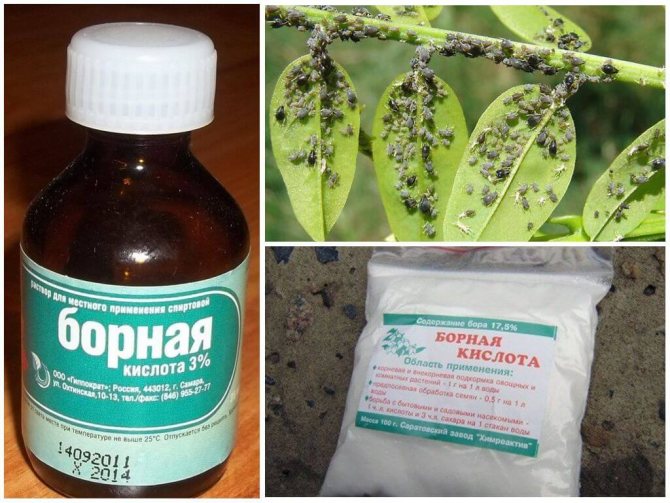
Among the wide variety of fertilizers, many gardeners prefer to choose those that are both very effective and safer than conventional chemicals. We are talking about a simple and affordable drug for everyone - boric acid.
Boric acid composition and properties

The chemical formula of boric acid (acidum Boricum), or Lewis acid, is H3BO3. In the natural environment, the substance is part of sassolin, a mineral that is present in free form in hot springs and some mineral waters. A substance of low acidity is obtained by mixing borax with acids or by a hydrolysis process.
Boric acid is produced in the form of a white powder, tasteless and odorless. In medicine, the drug is used as an antiseptic. In the middle of the last century, the Ministry of Health limited its use as an ineffective means. In household plots, boric acid is used as an insecticide and for feeding plants with boron deficiency.
Important! Boric acid is dangerous if used uncontrollably. The lethal dose for an adult is 15 - 20 g, and for a child - 4-5 g.
The value of boron for tomatoes
Boric acid for cucumbers
Tomatoes experience a severe boron deficiency in the first weeks of cultivation, when roots, flower brushes, buds are formed, flowering and an ovary is forming. The introduction of boron during this period stimulates the growth of young roots, due to which young plants take root and take root faster.


Why fertilize tomatoes with boron
On older plants, the substance has the following effects:
- stimulates the growth of flower brushes and increases the number of buds in them;
- prevents shedding of the ovary;
- increases the level of tomato resistance to the main fungal diseases (powdery mildew, leaf spot, late blight);
- activates the flow of carbohydrates into fruits, thereby increasing their sugar content;
- promotes friendly and abundant flowering;
- increases the ability of tomatoes to synthesize and assimilate the substances they need;
- reduces the risk of developing rot in wet weather;
- stimulates the rapid ripening of the crop.
Tomatoes need boron in a relatively small amount, but the lack of this trace element immediately negatively affects the state of the plant. With a deficiency of a substance with a culture, the following negative changes occur:
- chlorosis develops, which initially appears on old foliage, and then affects new foliage;
- a powerful growth of lateral shoots is activated, which dry out very quickly;
- grow brown and black, and subsequently the growth points die off;
- petioles and stems become brittle and hollow;
- foliage on seedlings and young tomatoes becomes purple;
- the number of buds is decreasing;
- flowering rate decreases;
- the ovary falls off;
- the yield decreases, the fruits turn out to be small, often deformed.


Boron deficiency
Boron deficiency is least noticeable on clay and loamy soils. Boron deficiency is usually most pronounced on the following soil types:
- sandy soils;
- calcareous alkaline soils;
- acidic soils after liming;
- poor sandy loam;
- swampy soils.
An excess of boron is no less dangerous for tomatoes than a lack of it. In such a situation, necrosis begins on the lower leaves, they acquire a yellow color and fall off. Subsequently, the defeat passes to the foliage of the middle tier. The plant gradually withers, the yield is significantly reduced.


Excess boron
This microelement is present in the composition of various fertilizers, however, boric acid is the most common among gardeners and summer residents. It is produced in the form of borax or powder, in which the boron content is 11.3 and 17.5%, respectively. The substance is most common in horticulture and horticulture, since horticultural crops consume more boron than cereals.
The effect of boric acid on tomatoes


For the development of plants, in addition to the main components, microelements are also needed. Tomatoes are especially demanding on boron at the stage of development of the young parts of the plant. Thanks to boron:
- A healthy root system is being formed.
- The number of buds and individual flowers increases.
- The assimilation of useful micro- and macroelements improves.
- The process of nitrogen assimilation is improved, which activates the development of green mass.
- Increases immunity to the development of fungal diseases.
- The process of fruit ripening is accelerated.
- The sugar content of the fruit increases.
Boron does not accumulate in soil and fruits even with excessive use.
The role of boron in plant life
Boron is an essential trace element for the life of all plants. It is needed in a small amount (in comparison with the main nutrients). But its biological role is great.
Boron is an active participant in the development of the meristem (educational tissue). The trace element stimulates cell division in vigorously growing parts of the plant. These are points of growth, tips of roots, young leaves, parts of reproductive organs and cells of vascular tissue.
Boron improves the production of carbohydrates, especially sucrose, in plant leaves. Accelerates their distribution to the roots and fruiting organs. Stimulates pollen germination and prevents ovaries from falling off.
Boron promotes better absorption and utilization of calcium in the metabolic processes of the plant. The trace element normalizes the production of nitrogenous substances and increases the level of chlorophyll in the leaves.
Boron deficiency causes the depressive state of plants. They are often affected by diseases and pests.
Boric starvation does not lead to the death of plants, but significantly reduces the speed and coherence of the processes of their development. Ultimately, crops produce low and low-quality yields.
How to determine the lack of boron in tomatoes
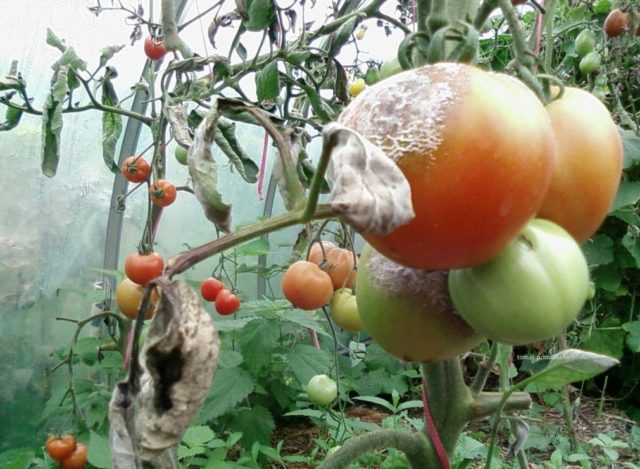


Boron deficiency in the soil affects the condition of tomato bushes and, as a result, the quantity and quality of fruits. Plants grown on clay soils have the least demand. In dry and hot climates, boron lasts longer in parts of tomatoes. The lack of a substance is easy to notice from the state of the plants:
- Change in leaf color (chlorosis).
- Growth points yellowing.
- Activation of growth and rapid dying off of lateral shoots.
- The fragility of the stems increases.
- The number of flower brushes is reduced.
- Flowers are falling.
- The formation and growth of fruits slows down.
- The ugliness of the tomatoes appears.
If you do not feed with boric acid in a timely manner, then the harvest will turn out to be meager.
What soils is boron deficient
First, it is necessary to determine on which soils the boron deficiency is most common. The fact is that the symptoms of boric calcium deficiency are very similar. In both cases, dying off of the top is observed, that is, the growth point does not develop, dies off.The trace element belongs to those species that are not able to move inside the plant, therefore, the situation is better in old leaves than in young ones.
If the soil at the site is swampy, acidified, then it is more likely that the lack of boron will manifest itself brighter.
Signs of an overabundance of boron
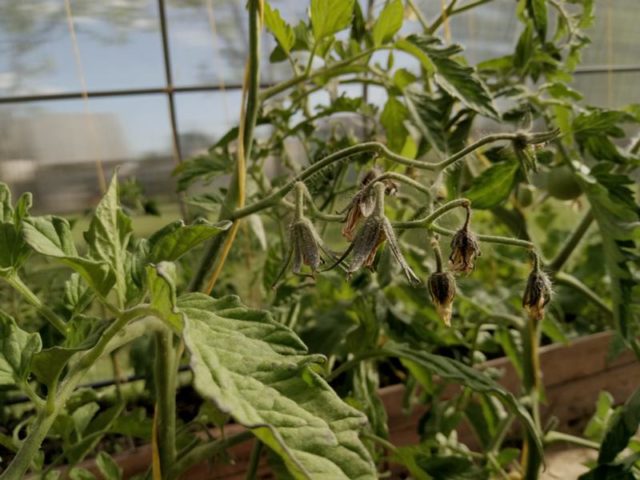


Compliance with the proportions of boric acid when feeding a tomato with a solution is mandatory. An excess of a trace element inhibits the growth of bushes and the formation of fruits. The first signs of excess boron are leaf necrosis and domed leaves. Plants gradually turn yellow and dry out. In this case, urgent measures are required to remove excess boron from the site.
How to dilute and prepare a working solution?
An important question is how to dilute boric acid for spraying tomatoes. To dilute the powder mass, take only warm water. If crystals remain, burns will occur. After dissolving the ingredient, wait for the liquid to cool, and then start spraying.
There are 2 options for how to dilute boric acid for spraying tomatoes.
The solution will be slightly more or slightly less concentrated:
- To preserve inflorescences, leaves and ovaries, you need to take 1 g of boron and dilute it in a liter of water. This recipe is also used to accelerate growth and increase yields.
- To cope with some diseases of tomatoes (with late blight, etc.) and strengthen the immune system, 1 teaspoon of powder dissolved in a liter of water will help.
In order to process a plot of 10 sq.m. planting, you will need about 1 liter of ready-made solution.
How to properly dilute boric acid
For feeding tomatoes, I use an aqueous solution of boric acid as an independent agent or in combination with other fertilizers at all stages of development.
Boric acid is poorly soluble in water. The solution is prepared in 2 stages. First, the required amount of powder is diluted in a small volume (100-150 ml) of hot water until it is completely dissolved. The liquid temperature should be at least 50-60 ° C. Otherwise, the powder will precipitate. The solution is cooled and diluted to the required volume for feeding.
Solutions for feeding cucumbers


For pre-sowing treatment, a solution is prepared from one liter of hot water and 0.3 grams of boric acid powder. It is advisable to soak cucumber seeds a day before planting, for twenty-four hours.
Step-by-step processing of cucumbers with boric acid, iodine and manganese (as with tomatoes) can also be used, but only without exceeding the dosage. Excessive volume will only harm vegetables.
Low Pollination Cucumber Nutrient Solution, for plants after transplanting from a greenhouse to open ground, they are prepared from five liters of hot water, two teaspoons of boric powder and three hundred grams of sugar. Top dressing is used cold. This "medicine" helps cucumber bushes adapt to a new place, get used to new living conditions, and also helps to accelerate the growth and development of crops and increase yields.
For spraying before fruit ripening the solution is prepared from ten liters of water, ten grams of boric acid, fifty grams of baking soda, two grams of potassium permanganate, four grams of iodine solution, two large spoons of sugar and sixty grams of potassium humate. This top dressing is suitable not only for cucumbers, but also for many fruit vegetable plants.
Read more in the article: Top dressing of cucumbers in the open field during flowering and fruiting
Methods and scheme of feeding tomatoes
Boric acid is added to the soil before planting crops or a solution is prepared for soaking seeds and spraying seedlings and adult tomato bushes. The proportions of the solution depend on the stage of development of the plants that need feeding.
Seed soaking
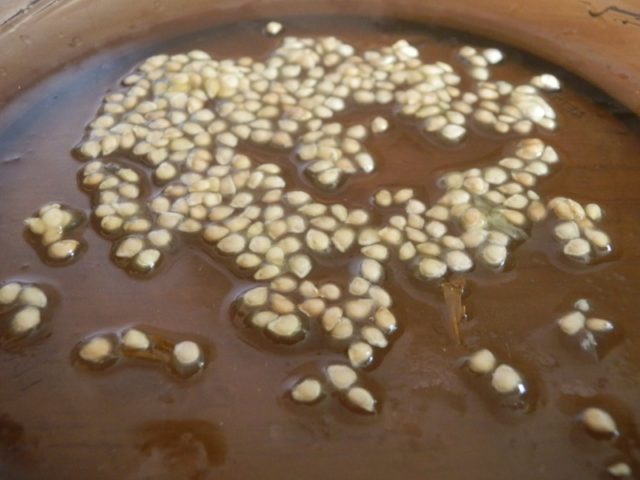


Before sowing tomatoes, it is recommended to soak the seeds in a boric acid solution to disinfect and stimulate germination. The composition is prepared at the rate of 0.5 g of powder per liter of water. The seeds are poured into a small container, poured with a solution of room temperature and left for a day in a warm place. Then the seeds must be rinsed with running water and sown in the usual way.
Soil pre-treatment
Boric acid is introduced into the soil before planting seedlings in open ground or a greenhouse. The product helps to protect young tomato seedlings from fungus and harmful insects. Experts recommend pre-processing the site if the soils are sandy, peaty or very wet.
Important! Boric acid must not be added to the soil in dry form.
To prepare the soil for planting, boric acid is diluted at the rate of 10 g per bucket of water. The consumption of the nutrient fluid is minimal. For 1 sq. m, a liter of solution is enough, which is applied by direct irrigation.
You can add boric acid directly to the wells when planting tomato seedlings. In this case, the prepared planting hole is poured in 2 liters of water, into which a glass of working solution is added.
Root dressing
The introduction of a boric acid solution under the root is required with obvious signs of a deficiency of a trace element. Such feeding is carried out once a season. And only if absolutely necessary, if the soil is too wet and trace elements are quickly washed out of the roots of plants, top dressing under the root can be carried out a second time.
For root top dressing, boric acid is diluted in a proportion of 10 g of powder per bucket of water or 1 g per liter. About 1 liter of the mixture is poured under the bush. Watering tomatoes is necessary in the evening when solar activity drops. Otherwise, accidental contact with leaves or stems will cause severe burns to the plant.
With the correct introduction of a boric acid solution under a tomato bush, you should not be afraid for the condition of the root system. The low acidity of the solution will not harm the roots of the plant.
The effect of root feeding becomes noticeable after a while, in contrast to the foliar method of fertilizing tomatoes with boric acid.
Foliar dressing
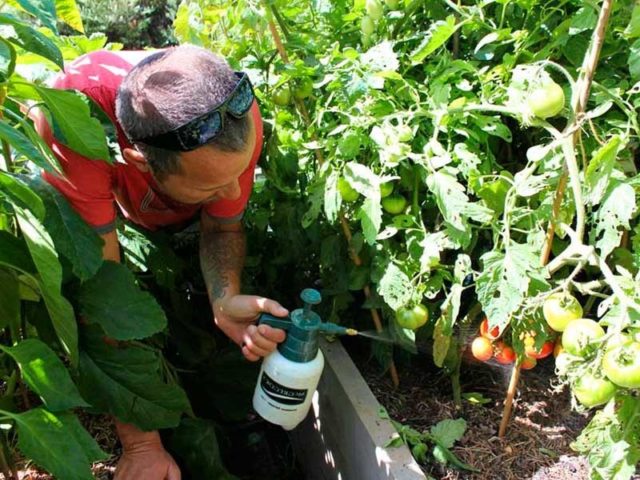


As a prophylactic agent against fungus and as a fertilizer for tomatoes with boric acid to replenish the deficiency of a trace element, plants are sprayed over the leaves. Vegetable growers consider this method the most effective. Boron is almost immediately absorbed through the pores of the leaf plates, improving their condition and affecting the plant as a whole.
Experts recommend spraying tomato bushes, paying special attention to the underside of the leaves. To do this, the spray head is directed upward and the cylinder is held at an incline. Top dressing is carried out in calm and dry weather in the evening or early morning.
The solution is prepared at the rate of 1 g of boric acid per 2 liters of water. To prolong the effect of the drug and prevent the nutrient fluid from being washed off from the vegetative parts of tomatoes, a small amount of laundry soap or a special agent to improve adhesion is added to the water.
For the prevention of fungus, boric acid is enhanced with iodine. Plants need a natural antiseptic not only as a protective agent, but also as a useful trace element.
For high-quality processing of tomato bushes, the spray nozzle must be set to fine spray. The consumption of the working solution for feeding one bush should not exceed 100 ml.
Useful Tips
First of all, try to spray correctly and avoid common mistakes:
- Do not increase the dosage: using 2 times more of the drug, you will not make the tomatoes better, but simply get a different effect - for example, instead of strengthening the ovaries, you will kill pathogenic microflora or pests.
- Apply the preparation where impact is required: feeding with boron from the roots can rise to the leaves, but never vice versa.
- Expand the range of drugs you use. When people hear that a drug is good, they assume that there is enough of it for a good harvest, but combinations of drugs and processing methods give a much better effect.
Video: Processing tomatoes with boric acid to increase the yield
How often do you need to feed
Foliar dressing is carried out no more than 3 times during the entire growing season of tomatoes. Regardless of whether the soil was fertilized with boron before planting the tomatoes in the ground, the plants should be sprayed for the first time during the budding period. This activates the development of strong peduncles, increases the number of flowers on the brush and accelerates the formation of ovaries.
During the period of mass flowering, a second foliar feeding with boric acid of tomatoes is required. In the greenhouse, it is especially important due to the high humidity and temperature. According to biologists, self-pollination stops if the air temperature rises above 30 degrees Celsius. The reason lies in the drying out of the pistils of tomato flowers. Foliar dressing helps plants cope with adverse external conditions.
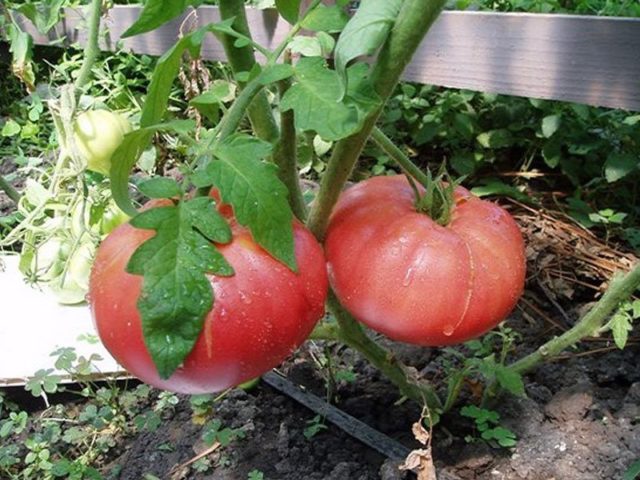


The last dressing of the season is carried out during the ripening period of tomatoes. During this time, tomatoes are especially sensitive to the availability of nutrients. Boron promotes the absorption of nitrogen compounds and affects the movement of carbohydrates in the cells of the fruit. Tomatoes, which are fed with nutritious liquid, ripen faster, do not get sick with late blight and other diseases of fruits and vegetative parts. Fruits fed in a timely manner are distinguished by increased taste. In addition, the keeping quality of tomatoes increases, which is especially important when transporting vegetables.
Processing time
To determine how many times you need to fertilize tomatoes, you need to find out how important boron is to them. The first watering must be carried out in the budding phase. In this phase, boron actively affects the formation of ovaries, their strengthening and fertilization. If signs of boron shortage are found, then after 10-14 days, during active flowering, you need to carry out a second feeding. It is the signs of micronutrient deficiencies that determine how often they need to be added.
It is also easy to notice when boron needs to be reapplied. Heavy clayey, acidified soils often need to be reapplied with the mineral, since plants cannot fully assimilate the substances in the soil.
Also learn how to properly feed tomatoes with iodine and boric acid.
3 dressings with boron are considered classic for the entire growing season:
- during the formation of ovaries;
- during active flowering;
- during the ripening of the fruit.
Between them should pass at least 10-14 days. But you don't have to stick to this pattern, as too much boron is just as bad as too little.
Any dressing is recommended to be applied in the morning or in the evening. This is because spraying under the influence of sunlight can burn tomatoes. The exception is cloudy days, but the absence of precipitation and wind is important, otherwise spraying will not give the maximum result. Each farmer decides for himself what time of day it is best to feed, but it is usually recommended to do this in the evening.


Security measures
Boric acid is not poisonous. With careful use, no negative consequences for human and plant health have been identified. Redness and itching on the skin can be caused by an individual intolerance to the drug or increased skin sensitivity.
Important! In the 60s of the last century, the USSR Ministry of Health prohibited the use of boric acid as an antiseptic for the treatment of children under 12 years of age, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
The drug can be dangerous if the powder is taken by mouth as a solution or undiluted. Signs of poisoning when working with boric acid are:
- vomiting;
- redness and itching of the skin;
- general weakness;
- tremor.
If symptoms of internal poisoning appear, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with a weak solution of soda and immediately consult a doctor.
In case of irritation of the skin or mucous membranes with boric acid, be sure to rinse the affected parts of the body with plenty of water with the addition of baking soda.
To avoid accidental misuse of boric acid, store it in standard packaging away from food.
When working with the drug, it is necessary to use respiratory protection.
Recommendations for combating late blight
The main problem of most summer residents is late blight. This fungus can destroy the entire plant and quickly spread to other healthy specimens. Rainy weather is especially detrimental to infected crops, as water contributes to the rapid destruction of all plant cells. In the middle of summer, the activity of the fungus increases due to an increase in air humidity.
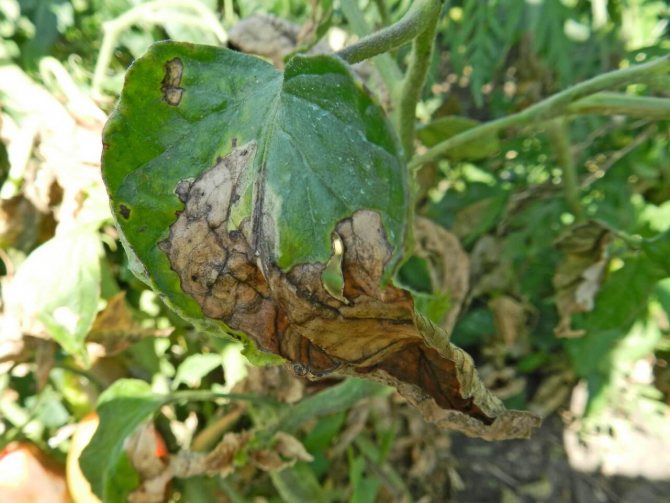


Of course, this disease is transmitted in other ways: through the soil, seeds, damaged plant surfaces. Therefore, timely harvesting of rotten plant debris, weeds and regular feeding will increase cellular immunity.
Important! If it rains after spraying, the event must be repeated in good weather.
And as practice shows, boric acid is a very simple and effective enemy against this fungus. Sick bushes with rotten leaves and spotted fruits must be ruthlessly thrown away, and all efforts must be directed to healthy plants in order to protect them and protect them.
Phytophthora is also dangerous because it can be in an inactive state for a long time, therefore, preventive measures for tomatoes are extremely necessary. Effective recipes for phytophthora with boric acid:
- 1 tsp is added to a bucket of water. powder;
- 1 g of copper sulfate and 0.5 g are dissolved in 1 liter of water;
- 1 liter of whey, 5 g of acid, 20 drops of iodine per 10 liters of water.
All of these recipes are suitable for spraying foliage, stems and tomato fruit.
Gardeners reviews
The advantages of an affordable source of easily digestible boron have been noticed for a long time and are successfully used in the cultivation of various garden crops. For better assimilation of boric acid, it is recommended to use urea before feeding the tomatoes with monofertilizer.
The introduction of dressings with the presence of boron improves the palatability of the fruit pulp, which becomes more aromatic and sweet. The substance is well tolerated by different varieties of nightshade and the prolongation of their fruiting period. Compliance with the proportions when dissolving a chemical element makes it useful for tomatoes.
Features of feeding with boron
Top dressing of the soil with fertilizers, and in the future, the processing of foliage, will saturate the plants with useful substances, which will help to improve the yield. The use of boric acid will allow the first fruits to be obtained at the end of June. You just need to correctly and accurately apply fertilizer.
If suddenly, after the first feeding, the seedlings began to look bad, you need to stop using this tool. The dose may have been accidentally exceeded. If the plants have tolerated the first feeding well, re-treatment should be carried out only after 10 days, not earlier.
It should be noted that a violation of the dosage, excessive use of boric acid can harm this vegetable. In addition, health problems may appear after consuming vegetables, since the substance is poorly excreted by the kidneys and can accumulate in the body.


Therefore, the use of such dressings should be carried out with caution and adherence to dosages.Tomatoes are treated with boric acid in the morning or evening hours or in cloudy weather, when the sun is not shining, there is no rain or wind. It is necessary to spray using fine spray spraying devices.