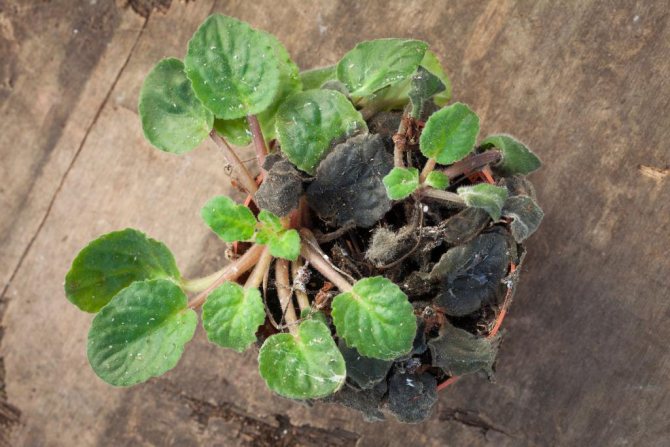
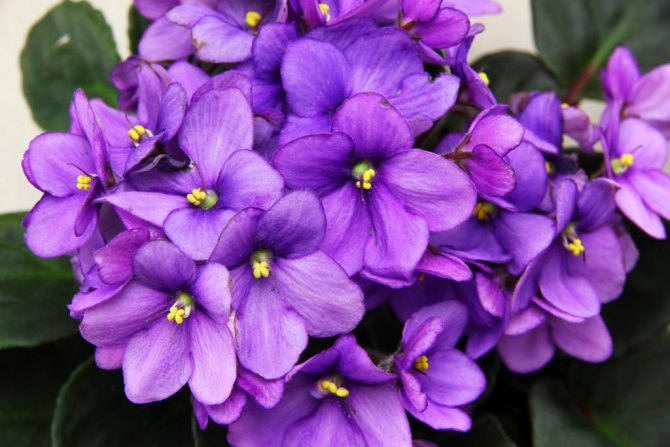
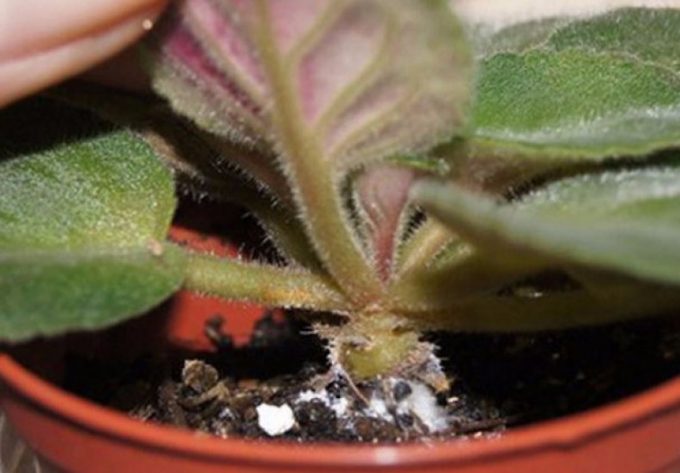
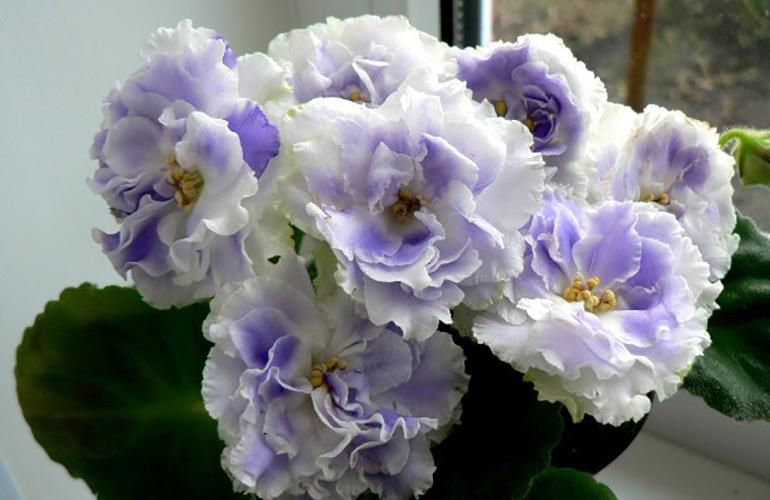
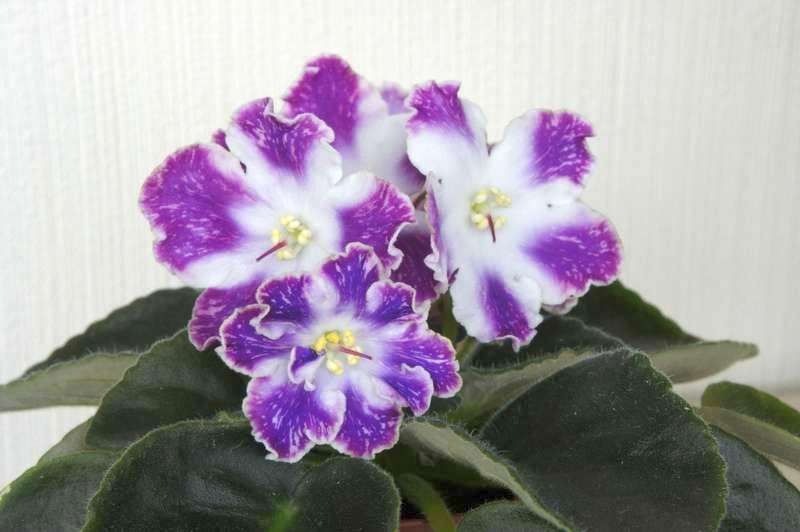
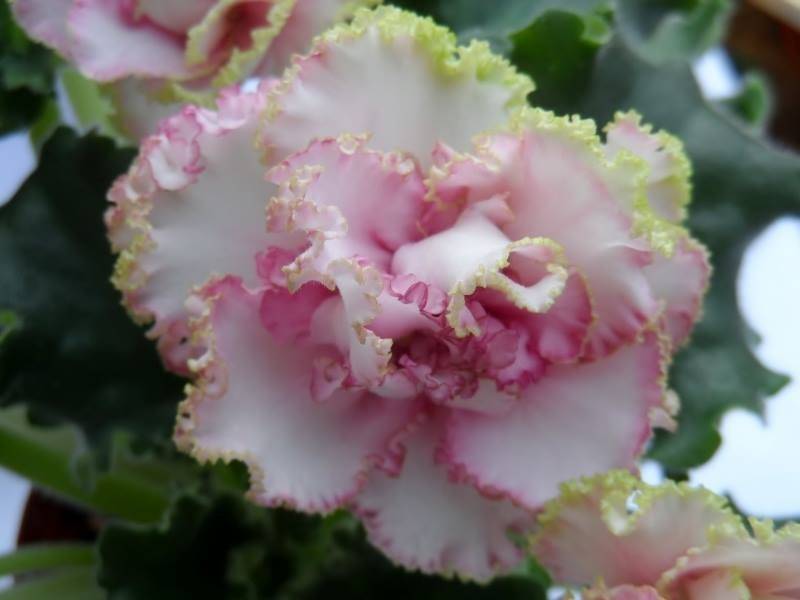
But it is this miniature flower that most often suffers from various diseases.
To successfully deal with them, you need to know the main signs of infection.
The causative agents of diseases are bacteria and fungi.
Thrips
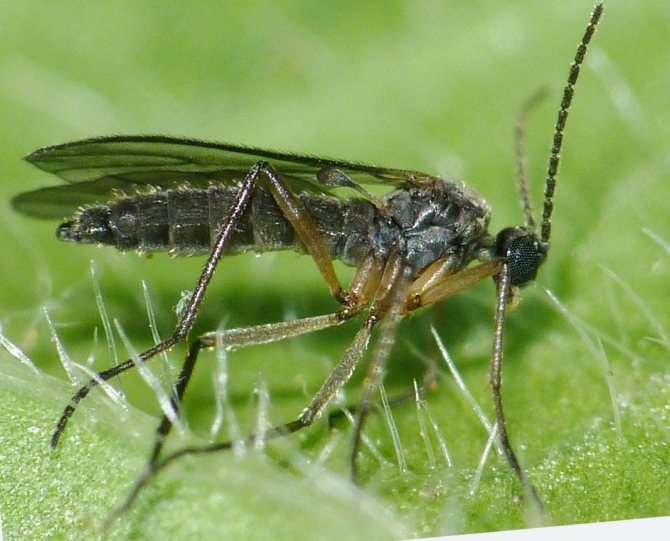
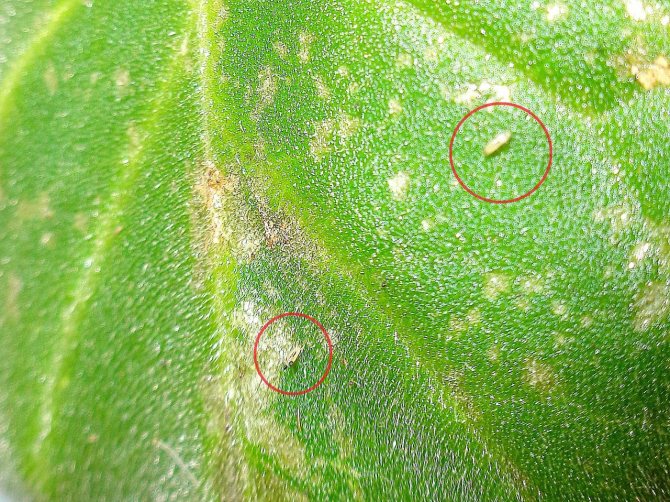
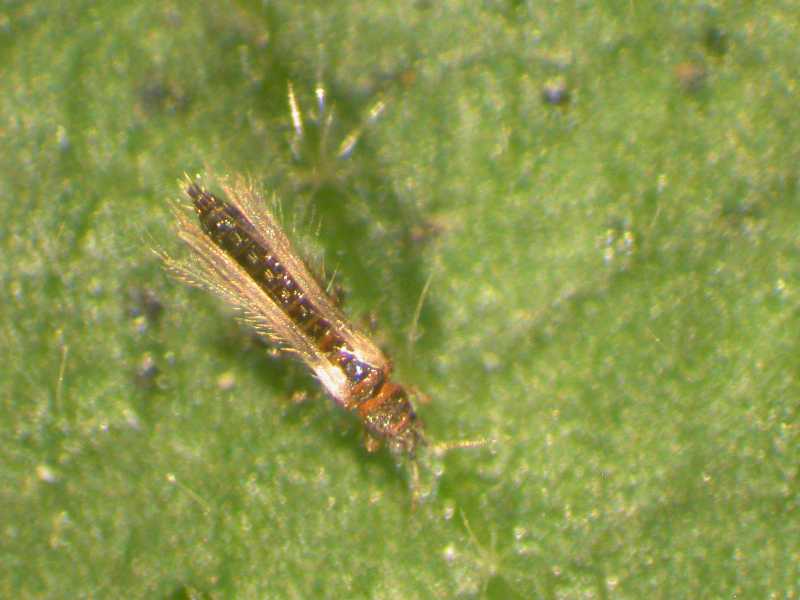
Start the list of violet pests with photos of thrips. The flower is attacked by both adults and larvae, feeding on its juice. The body length of the parasite does not exceed 1.5 mm, the back is colored black and brown, the larvae are yellow.
Adult insects are able to fly over short distances, so if timely measures are not taken to destroy them, the entire flower garden will soon be infected. Females of parasites lay eggs directly in the body of the plant - the pulp of the leaf plate. Moreover, in one clutch alone there can be about a thousand eggs. After a few weeks, larvae emerge from them, which turn into adults after about a month.
With the appearance of thrips, the leaves of plants change their color - clearly distinguishable whitish stripes and dots are formed on them. If young growth has already emerged from the eggs, then the flowers will begin to wither, and the plant itself will rapidly wither. At the same time, a colony of pests of violets can be found on the lower part of the leaf plate - it is there that they parasitize and multiply.

Thrips infect plants regardless of temperature conditions and seasons, giving one or two generations per quarter. Infection in most cases comes from garden flowers (chamomile, aster, chrysanthemum) that enter the house during the flowering period.
In order to get rid of thrips, you must first cut off all flowers and buds, and then treat the infected violet with Confidor. The soil is spilled with the preparation "Aktara". After 10 days, the treatment is repeated and over the next month they continue to remove the newly formed buds. In the future, it is very important to maintain correct farming practices.
Control methods and recipes of experienced florists
Folk remedies
Not in vain thrips is considered the most dangerous and difficult to remove pest on indoor plants.
Possessing several stages of development, moreover, occurring in different parts and places of the plant (green mass, flowers, earth), plus flying individuals, it is really very difficult to destroy.
Also fast enough adaptation to chemicals does not allow one-time removal of this parasite.
But, as they say, "in war, all means are good," therefore, in isolated cases, accidentally flown individuals or the small number of the colony, for a start, you can try various folk methods of struggle.
And although some growers claim that such methods are ineffective, experienced violet growers recommend in such cases to start the fight with safe, that is, folk recipes.
Infusions of marigold, garlic, celandine, or the use of liquid soap quite capable of scaring off a small group of pests or stopping its spread. But without modern insecticides, it will be problematic to cope with the destruction of the population. Therefore, we will consider how to deal with thrips using various techniques.
Advice! The use of folk remedies, coupled with chemicals, is the most effective method of dealing with thrips.
Katkova's recipe: bathing violets in a solution with the drug "Fufanon"
Quite often, at exhibitions and other events of violet growers, lovers of home floriculture turn to Violetta Katkova for advice on how to study her method of dealing with all kinds of pests. And not in vain. Participating quite often in exhibitions at which the risk of plant infection is quite high, her collection always remains clean and protected from parasitic insects.
What is her method? New purchases or violets that have returned from shows are being processed non-systemic organophosphate insectoacaricide "Fufanon".
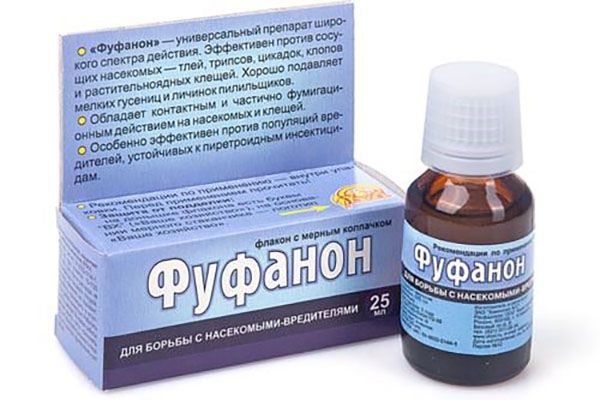

Fufanon.
For this procedure:
- A solution is being prepared: 1 ml of the drug per 1 liter of warm water;
- Before the procedure, the soil is dried;
- The container and the surface of the soil are covered with a plastic bag, and the above-ground part of the violet is covered for 10 seconds. dipped into the prepared solution;
- After dipping, the plant returns to its normal position, and the remnants of the solution from the aboveground part flow down to the surface of the dried soil;
- In this case, peduncles are not removed.
The positive aspect of this method is the absence of untreated areas, plus, in addition to prophylaxis, treatment is carried out against all sorts of pests.
Of the shortcomings, it can be noted only that unpleasant smell of the solution. But in a room with good ventilation, it is practically not felt. The method is fast, economical and somewhat ecological.
V. A. Konopatchenkov's recipe
Collector, breeder Vyacheslav Konopatchenkov applies his own method of processing the collection. A solution is prepared from:
- 5 ml (ampoule) insectoacaricide of biological origin with intestinal action "Akarin";
- diluted in ½ liter of warm water;
- one cap is added pet shampoo;
- the whole plant is sprayed.
The advantage of this processing is harmlessness of the drug and the removal of peduncles is not required.
And although Vyacheslav says that one treatment is enough, some experienced florists recommend 3-fold treatments with such a composition.
And even to guarantee the complete destruction of pests, it is advised to carry out the fourth treatment with the drug Aktara. But, apparently, a lot depends on the degree of population and neglect of insects.
Treatment with Iskra from T. A. Blinkina
The method to get rid of the thrips of the collector Tatyana Alekseevna Blinkina is based on the use of effective insecticide of natural origin "Iskra-Bio".


Iskra-Bio.
A solution with a concentration of 10 ml of the drug per 1 liter of warm water, with three treatments every 7 days. According to Tatyana Alekseevna and many violet growers, parasitic insects are completely destroyed.
Important! The action of Iskra-Bio is based on paralyzing actions and is not addictive to the substance.
Treatment with the drug "Spintor" according to the prescription of A. P. Kochetkova
Probably, one of the most effective thrips control methods from Anna Kochetkova. According to flower growers, plants treated with the latest generation insecticide "Spintor", even after a single treatment, completely get rid of pests. At least by spraying once a year, you can ensure that thrips do not appear during this time.


Spintor.
"Spintor" is highly effective and low-toxic. It affects a wide range of harmful insects, does not develop resistance, is compatible with other bio and chemical preparations in tank mixtures. Not phytotoxic, which is important in conditions of processing in closed, small rooms.
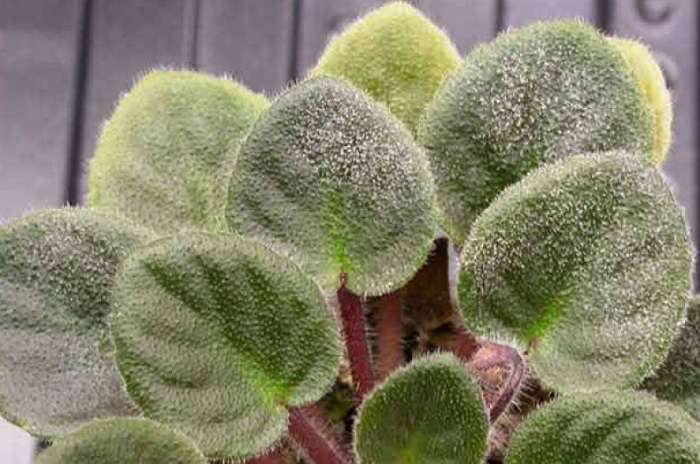
Mealybug
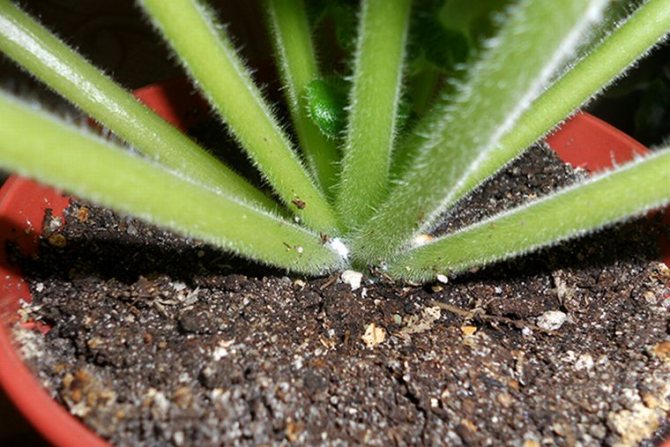
A small insect, the body of which is covered with a whitish downy, living in the axils of the leaves, as well as in young peduncles.The mealybug sucks out nutritious juices from plants and simultaneously secretes saliva, which, in turn, infects the flower and interferes with normal metabolism.
At the site of the bite, the leaves and flowers are deformed. Red-brown spots appear on them. When transplanting an infected specimen from the substrate, you can smell a specific mushroom smell. These pests of violets are very small, but since their body is covered with white fluff, it is quite possible to notice them upon a detailed examination of the plant.
In Saintpaulia, the mealybug moves from the garden plants brought home. If there are too many parasites, the attacked flower loses its decorative effect in a short time. In doing so, he becomes more susceptible to many diseases.
Pests of violets are destroyed using the drug "Aktara", "Fitoverm", "Mospilan" or "Aktellik". After 10 days, it is advisable to repeat the treatment. As testimonials testify, if you are not fighting the worms for the first time and are already reusing the "Aktara" remedy, then the parasites to it with a high degree of probability have already developed immunity. Florists recommend using different systemic insecticides each time, which will differ in their composition.
However, using an insecticide alone is not enough. The infected plant must be transplanted into a new substrate. It is also advisable to discard the pot in which the infection has occurred.
Scorms
For bugs that attack houseplants, including violets, a mealy bloom on the body is characteristic. This coating is protective and protects the pest from many pesticides. The sizes of adults are insignificant and range from 1 to 4 mm.
Among the mealybugs that parasitize Saintpaulia, the most common are the seaside and bristly mealybugs. These parasites hide in the folds and axils of leaves, as well as on young peduncles. Some of them can feed on the underground part of the plant. Mealybugs move, as a rule, together with water, which is in a common pan.
Symptoms
In those places where the pests fed, deformed areas appear, which eventually acquire a red or brown tint. A whitish bloom appears on the rhizome, whitish fluff can be found among the lumps of the substrate and on the lower part of the stem.
The leaves of the affected violet begin to fade. The plant weakens, looks sick and becomes vulnerable to infectious diseases. The soil takes on a sour mushroom smell.
Treatment
When Saintpaulia is infected with worms, the following measures are taken:
- we take the plant out of the pot, carefully clean off the spoiled substrate and transplant the specimen into fresh soil;
- additionally we treat the rhizomes with the preparation "Aktara", "Actellik" or "Fitoverm";
- in the process of transplanting, add the preparation "Bazudin" to the soil or spill it with the preparation "Mospilan", "Regent" or "Dantop";
- the last procedure is carried out 3 times at ten-day intervals.
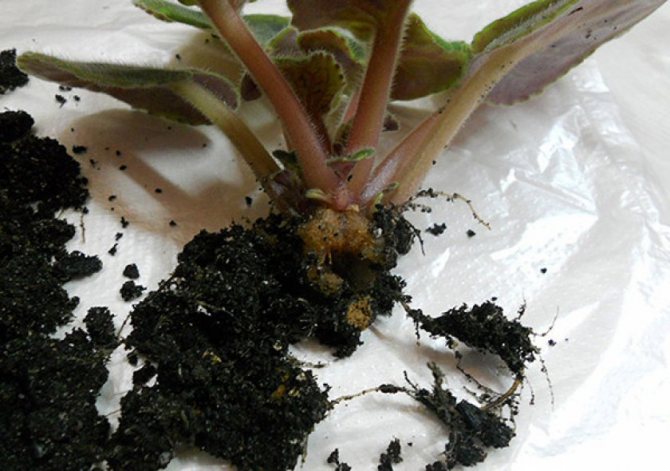
Root worm
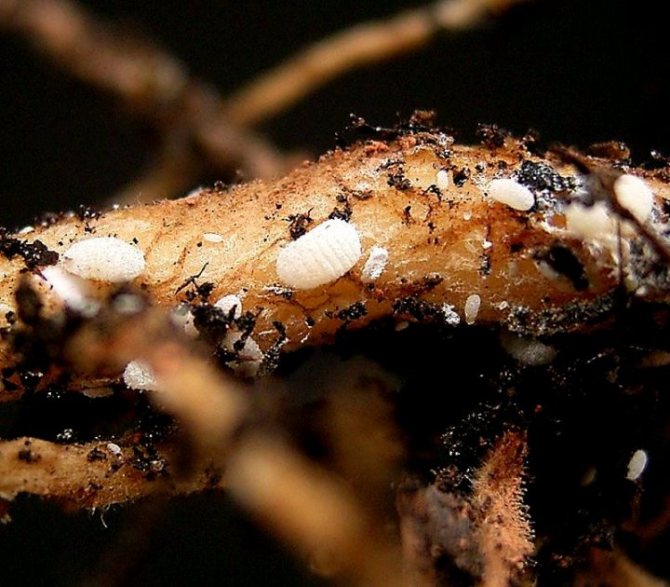


The rootworm is a close relative of the aforementioned parasite. They have similar names, but different taste preferences. This is a small insect that is a dangerous pest of the uzambara violet. If the mealybug attacks mainly the green part of the plant, then the root, as the name implies, leads an underground lifestyle, infecting the rhizome of the flower.
The root worm is dangerous because it is often found very late. By this time, the plants are damaged quite badly and the main symptoms are obvious: development stops, leaves become faded, flowers appear, but in small quantities. Over time, the flower loses its turgor, turns yellow. This suggests that a significant part of the root has been destroyed.And since the worm parasitizes underground, the florist simply does not see it. Below is an enlarged photo of the pests of violets.
The fight against them is carried out using one of the following drugs: "Regent", "Aktara", "Dantop", "Mospilan". The contaminated substrate is spilled with the chosen agent three times at intervals of 10 days. At the same time, the "Aktara" agent in the concentration recommended by the manufacturer often turns out to be ineffective. If, after the first treatment, a positive result did not follow, it is necessary to pick up another systemic insecticide. And remember that in the fight against mealybugs, contact-intestinal agents do not help.
Pests of violets - Sciarids, or mushroom gnats.
Sciarids - every lover of Saintpaulias is familiar with these pests of violets. Everyone knows the little flies that hover over pots of plants. Sometimes there are almost none, sometimes there are hundreds of them.


Sciarids do not cause significant harm to adult Saintpaulia plants with normal cultivation techniques. Sciarid larvae usually feed on rotting plant debris in the soil. In this case, the damage caused to the root system of Saintpaulia is few and is quickly compensated by the violet due to the growth of new roots. However, with mass reproduction of sciarids, they begin to actively feed on living tissues of plants, which allows them to be classified as pests.
It is not very difficult to cope with flies. One spillage of the soil by Aktara will solve this problem, but the very presence of these flies suggests that the soil is dense, prone to acidification, which is what happens. This is a serious signal that the root violets may well rot from waterlogging and from a lack of oxygen in the soil. This problem must be dealt with only by the selection of ingredients for the preparation of the soil. More rippers, less nutritious, dense soil. Take soils, if possible, without the presence of sand in them, which makes it difficult to "breathe" the soil.
Mites
Ticks continue the list of violet pests (with photos). Their treatment when infected with this parasite will be long-term, since the latter are so small that it is very difficult to detect them at the initial stages. They settle and reproduce, as a rule, in conditions of high humidity. On violets, cyclamen, red spider mites and spider mites are most often found. They live mainly in plant rosettes.
When mites appear on the back of the leaves, depressed marks appear, the plates begin to deform, become covered with red or brownish spots. After a while, these spots become entangled in a thin web. The plant takes on an unkempt appearance, as if covered with a layer of dust. Gradually, the infected violet lags behind in growth, new buds do not form, and those already released do not open, pollen spills out from the anthers. With a decrease in air humidity, the leaves begin to curl, dry out, the lower leaves are especially badly damaged.
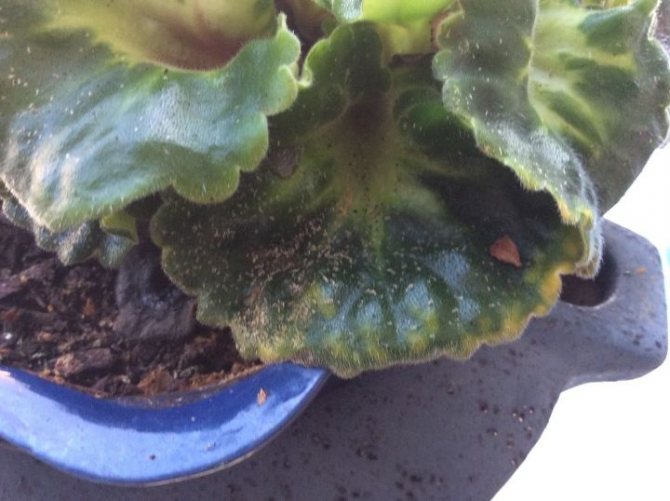


Violet pest control is carried out in several stages. First of all, it is necessary to thoroughly, but very carefully, rinse the infected specimens under running water (do not use cold water!). Thanks to this event, it will be possible to remove a significant part of the parasites. Treatment is carried out with acaricides. Sick plants are treated two to three times at weekly intervals. At the same time, the infected substrate is spilled with Fitoverm or Actellik preparations. If there are too many pests, it is better to use "Neoron" with re-treatment after 10 days. In the future, violets should be placed away from each other and periodically arrange water procedures for them, especially in hot and dry weather.
How to reduce the risk of parasites on a violet
Be sure to keep the purchased (or acquired in another way) violet in "quarantine" for two to three weeks.If you have any suspicions about her condition, treat the plant with Fitoverm and water the substrate with Fitosporin-M once a week for disease prevention for a month.
If you use ready-made soil for planting and transplanting Saintpaulias, be sure to sterilize it first, since the soil from greenhouses, greenhouses and flower beds is sometimes contaminated. Carry out an independent soil collection away from the city, somewhere in the forest. Wash and sterilize old pots well.
Do not allow a sharp decrease or increase in the temperature of the content, the room air is too dry - humidify, do not overdry the substrate and do not flood it. Provide sufficient amount of bright, but diffused light for the growth and flowering of Saintpaulias. Otherwise, your Saintpaulias will be weakened and vulnerable to parasites. Read more about the rules for caring for a violet here. The greatest harm to violets is caused by small pests. In this article we will tell you about each insect and how to deal with it in detail.
Nematodes
Another pest of indoor violets that damages plant roots. Nematodes are small, colorless worms with a body length of about 1.2-1.5 mm. In females, the body is pear-shaped, in males it is threadlike. Parasites multiply very quickly, in one clutch there can be 300-500 eggs. Small larvae in a short time move to neighboring plants, quickly infecting the entire flower garden.
With the appearance of nematodes, swellings are formed on the roots of violets - galls, which can have different sizes. In this case, the parasites themselves can be found inside these bulges. There they reproduce and parasitize. As a result of its vital activity, the pest sucks out nutritious juices from the plant and simultaneously injects toxic substances.
Symptoms of infection do not appear immediately. In order not to waste time and prevent the death of the plant, its roots must be carefully examined with each transplant. With severe damage to the root system, the aerial part of the violet also suffers: the growing point begins to dry out, new leaves appear in a modified form. The growth of the plant slows down, it looks weak and does not bloom, the green part begins to turn yellow. Gradually, the violet withers, its stem is deformed, the plant dies.
Unfortunately, in most cases the flower cannot be saved. The infected specimen is thrown away with the pot. If there is an urgent need to preserve the violet, pest control can be carried out in the following way: get it out of the substrate, cut off all damaged roots, treat the flower with a remedy to strengthen immunity and transplant it into a new land. The second way is to pick a healthy leaf and try to root it.
It is worth noting that it is much easier to ensure the prevention of the appearance of nematodes than after trying to save an infected flower. To do this, it is enough to use clean soil when transplanting violets. You can not take land either from a flower bed, or from a greenhouse, or from any other site where something is growing or growing.
Saintpaulia diseases with photos
Diseases that affect Saintpaulia can differ in the manifestation of symptoms, and therefore a novice florist cannot always understand the cause of the death or wilting of flowers. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you see photos of the most common diseases.
Quite often, indoor violets are affected by pests. How to recognize insects and cure plants, read the material at the link.
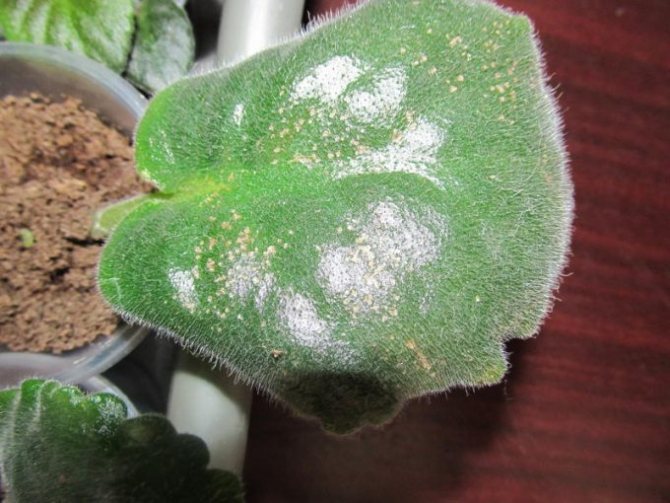
Powdery mildew
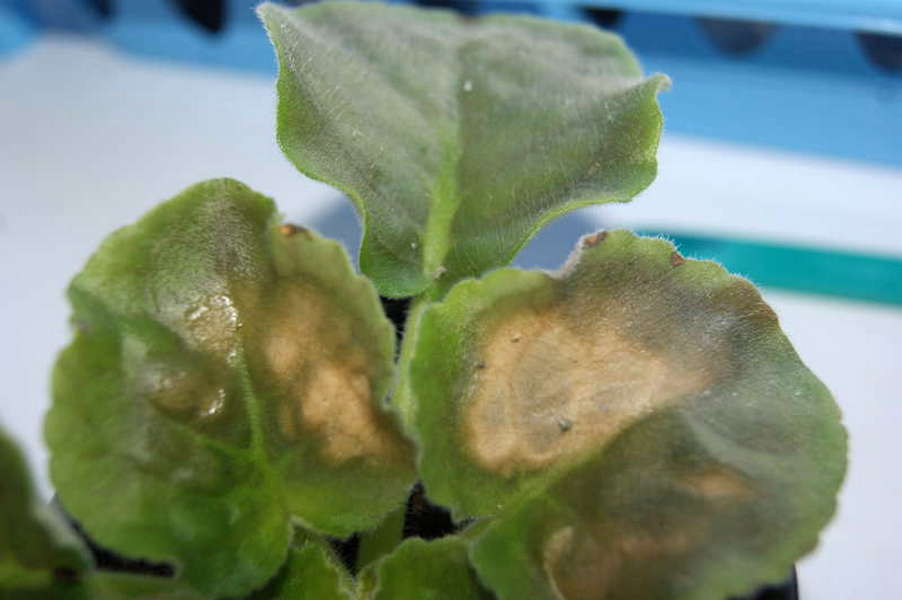
Powdery mildew is one of the most dangerous diseases that violets are exposed to. The source of the disease is fungal spores in the air.
There are many ways of infecting Saintpaulia - the fungus can get into a room with new purchased plants, with previously infected soil.Flowers that have strong immunity can easily withstand disease, while the likelihood of infecting a weakened plant is high.
The development of the fungus is provoked by factors such as:
- Increased level of air humidity;
- Low room temperature;
- Insufficient natural or artificial lighting;
- Accumulated dust on violet leaves and pot surfaces;
- Excess nitrogen in the soil.
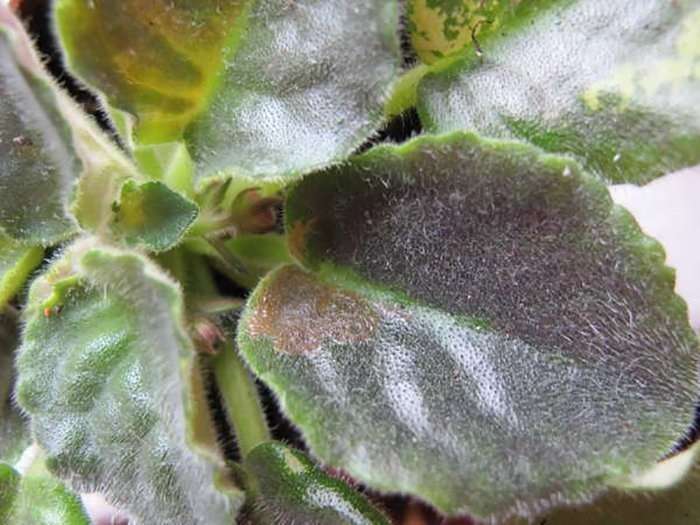
A sign of flower infection is the appearance of a whitish bloom on the leaf plates and stems. This white powder is the very spores of the fungus. There are two types of disease - real and false. Outwardly, they can be distinguished by the appearance of brown spots on parts of Saintpaulia, which indicates a false form of the disease.


Powdery mildew treatment is carried out using chemical compounds that can be purchased at a flower shop. Among them, the most effective are Topaz, Fundazol and Benlat..
Rust
In case of rust, Saintpaulia leaves are the first to suffer. They are covered with a characteristic bloom, yellow and brown bulges appear on the front and back sides of the leaf plate.... The causative agent of the disease is a fungus.
Under proper conditions of keeping Saintpaulias, they die in the fresh air, but when an optimal environment for reproduction is created, they begin to actively spread throughout the plant. This is facilitated by the high level of moisture and the elevated temperature in the room where the saintpaulia is contained.


IMPORTANT! The reason for the appearance of rust on the leaves can be an excess of fertilizers, so it is important to observe the proportions when feeding violets.
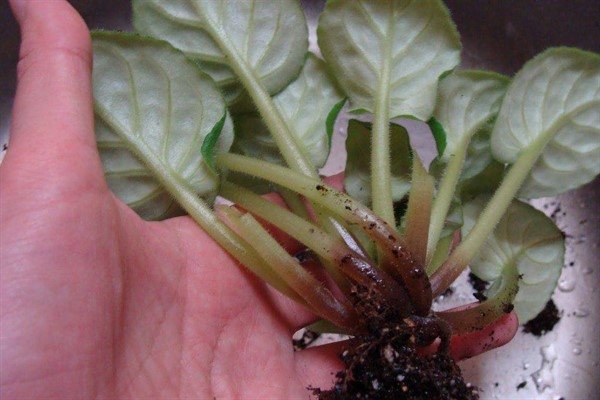
Root and stem rot
Symptoms of gray rot are characterized by the appearance of a powdery gray or brownish-white coating on the leaves and stems. The causative agent of the disease in Saintpaulia is the fungus Botrytis.
Gray rot affects the aerial part of Saintpaulia and the root system of the flower. In a short time, the violet withers, the lower leaves fall off, and the numerous stems become watery... Usually, the disease enters the ground along with roots and other debris from past flowers.


If there is a suspicion of this disease, then the infected flower must be urgently removed from other plants. The fungus spreads at a high speed and is able to destroy an entire greenhouse in the shortest possible time.
The diseased plant itself must be thrown away immediately. You cannot store the earth from this pot; you also need to get rid of it.
Expert opinion
Olga Nesterova
Land improvement specialist, master of landscape design. Indoor floriculture consultant
Prevention of the disease is a thorough preparation of the land when replanting Saintpaulias. The soil must be calcined in the oven or frozen for a while in the freezer. Extreme low or high temperatures will kill the fungus. You also need to establish a schedule for watering violets - excessive soil moisture provokes the growth of bacteria.
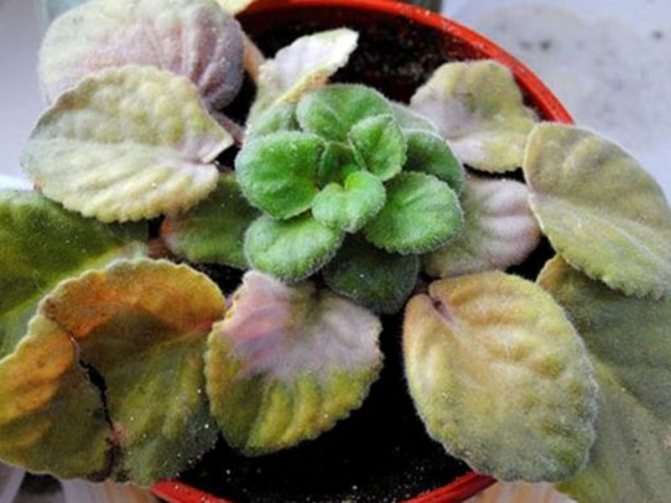
Bacteriosis
Bacteriosis most often occurs under the influence of high temperatures, that is, during the hot season. The lower leaves gradually die off, become covered with a thin layer of mucus and fall off.
Unlike diseases caused by fungal spores, bacteriosis can be cured.
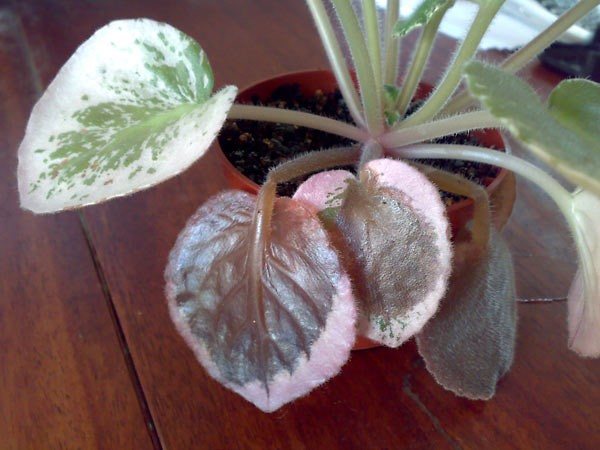


The affected violet must be moved to a separate place so as not to infect other flowers. Then the ground actively watered with antibacterial agents - foundation, previcur and immunocytophyte.
In order for the saintpaulia to release the leaves again, you need to adjust the temperature in the room and improve ventilation.
Do not forget! Until complete recovery, you cannot use the plant for propagation!
Late blight
This dangerous disease occurs due to the penetration of fungi into the body of the violet. Pathogenic bacteria enter the body of Saintpaulia through microcracks formed on the stems and leaves, root processes.
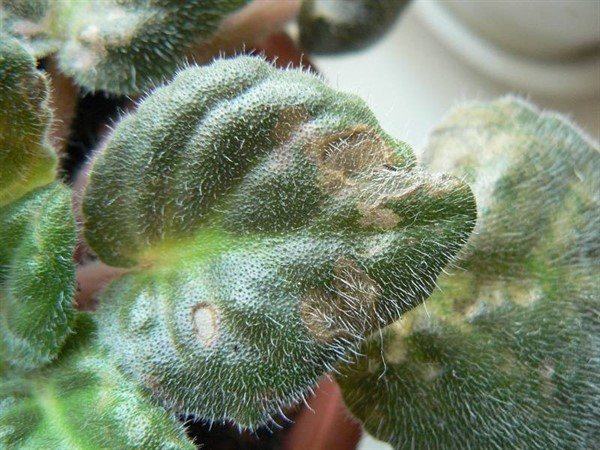


Some time after infection, the roots of the violet begin to rot, become watery and soft.
Signs of late blight is the appearance of brown spots on the leaves of Saintpaulia, their bending inward.
Due to the fact that the spores of the fungus can be in the ground for a long time and do not manifest themselves in any way until a favorable environment arises, it is better to get rid of the diseased violet.
The pot in which she was kept must be sterilized.... If it is made of clay, then the container can be baked in the oven.
Have your violets ever been sick?
Well no
Fusarium
Fusarium is a disease that affects both the aerial part of the violet and its root system. Under the influence of the disease in Saintpaulia, the roots rot, soften and gradually die off.
At the final stage of the development of fusarium, the infection spreads from the roots to the apex, spreading to the stems, petioles and lower leaves.
The main symptom indicating the appearance of fusarium is leaf wilting at the very base of the lower levels. In this case, the stems are saturated with excess liquid and gradually die off.
The death of a plant is accelerated by its weakness immediately after flowering, insufficient feeding or the introduction of the wrong type of fertilizer. At temperatures less than 16 degrees Celsius, roots die off faster.
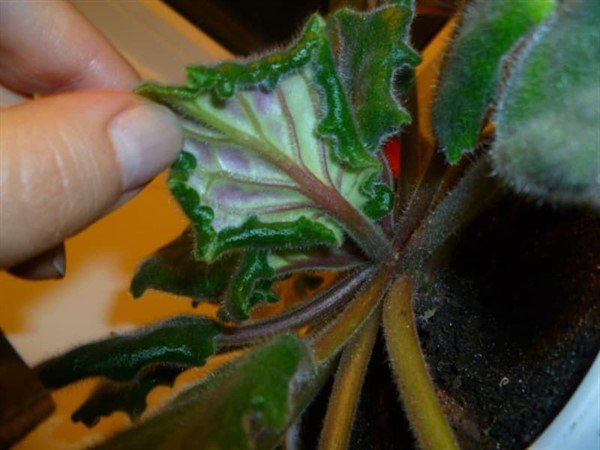


Fusarium can be prevented by removing the infected flower from the windowsill where other violets are kept. Such an instance is almost unrealistic to come out, and therefore it is destroyed along with the soil.
After that, the container, which contained the violet, is treated with copper sulfate or another disinfectant.
Prevention of fusarium disease is a solution of phytosporin. They need to water the violets monthly.
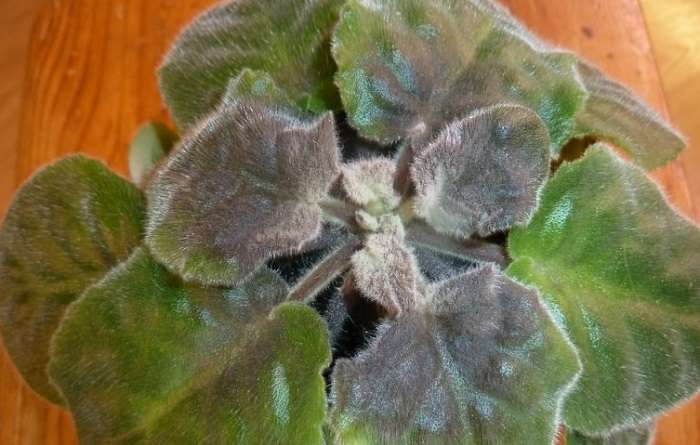
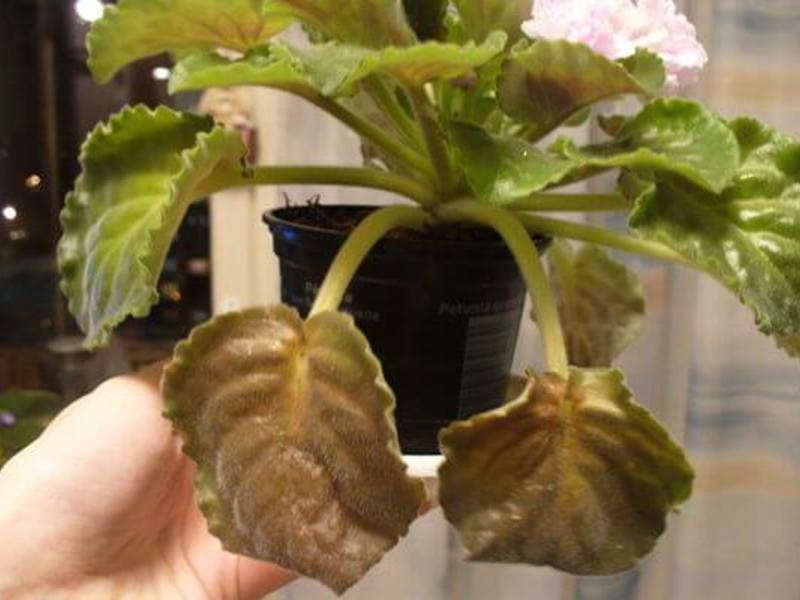
Bronze of leaves
The appearance of spots on the leaves is otherwise called bronze.
This disease is characterized by a change in the appearance of the violet, since under the influence of the disease the growth of the plant stops and its development is disrupted. The source of the bronze is a virus.
Because of him, the Saintpaulia ceases to bloom, and then grow altogether. New leaves and ovaries cease to appear in the flower.


In some cases, the bronzing virus provokes the appearance of brown and red spots on the surface of the leaf.
Aphids
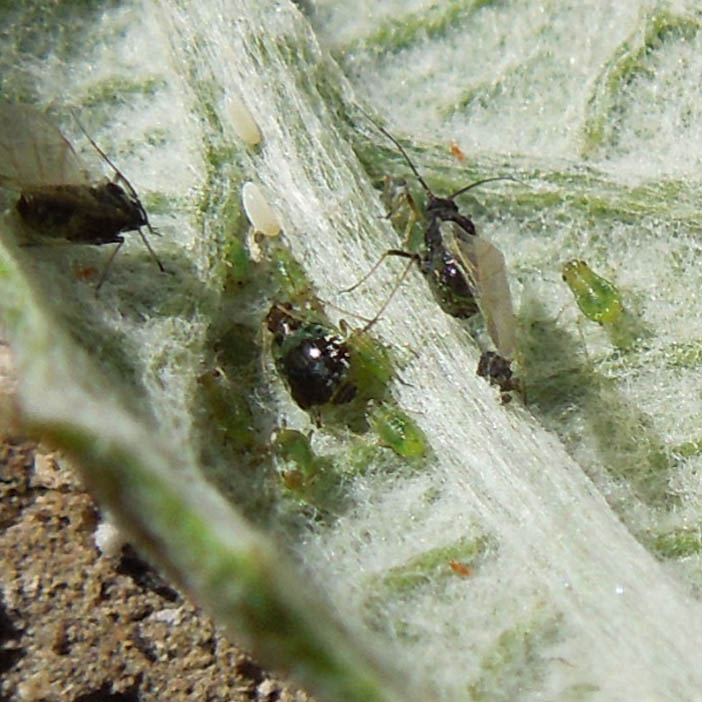


Aphids are pests of violets (in the photo you can see how they look), which can be either with or without wings. Their body length does not exceed two millimeters, while it is so soft that the insect can be easily crushed with your fingers.
The reproduction of aphids, and, accordingly, the infection of plants, occurs very quickly: about 150 larvae emerge from the eggs every 15 days. Small green pests settle on the back of the leaf plates. With a serious infection, a whitish sticky pad appears on this part of the leaves.
Aphid infestation of violets can be recognized by the appearance of buds and flowers. The petals begin to change their shape, the flowers wither, the buds do not develop. The leaves of the plant also begin to curl. Where there used to be a sticky pad, a sooty fungus grows.
How to treat violets from pests? An infected specimen can be cured with the help of special preparations: Fitoverm, Actellik, Mospilan, Intavir, Neoron. But before processing, the plant is carefully washed under running water, removing parasites from it. The rest are destroyed using the selected insecticide. A week later, the treatment is repeated.
Insect pests
Mealybugs
Mealybugs feed on young peduncles, can live in leaf axils and soil. They multiply actively, being saturated with plant sap, which is almost completely deprived of nutrients.
Related article: Keela plants, how to treat
Signs of damage to violets by mealybugs:
- discoloration of leaves to grayish or yellowish;
- leaf plates lose their shine, become less elastic;
- new leaves grow deformed and small;
- the plant stops growing;
- decay of roots and stems begins.
If you feel that the soil in the pot smells something like mushrooms, then it is infected with worms. By the way, you can even see these pests. They look like white fluff.
Treatment for mealybugs is insecticidal treatment.
Translucent insects with a black, green or red body are aphids. It feeds on the plant's intracellular sap, depriving shoots and leaves of food and causing them to die off. Aphids can be removed by washing all ground parts of the plant with soapy water, and then rinsing in the shower, preventing the soil from washing out of the pot.
There are several types of mites that can harm violets.
Cyclamen pliers almost invisible. Their appearance can be diagnosed by yellow traces on the plant. Leaves and young leaves are food for cyclamen mites.
Spider mites feed on the leaves of violets. In the place where the spider mites dined, reddish punctures with a thin cobweb appear.
The treatment for ticks is insecticidal preparations.
Mites can severely damage the plant. In addition, they carry various diseases.
Shield and false shield
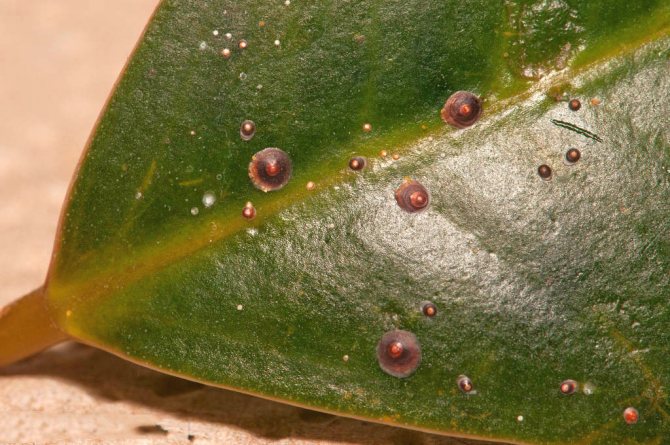
Very dangerous pests of violets, the treatment for the appearance of which is carried out in a complex manner. The presence of sticky drops on the leaves of Saintpaulia may indicate an infection with scale insects or false scale insects. In this case, the parasites themselves will certainly be immediately detected if a more detailed examination is carried out. These pests multiply very quickly, and therefore all copies of your flower collection will need to be processed.
Most often, the parasite settles on the leaves, stalks and rosettes of plants. The body length of an adult is about 7 mm, from above it is covered with a kind of shell or shield. At the same time, the shells of the pseudo-scutes are convex, in the scutes they are almost flat.
After pest bites, small yellowish spots appear on the leaves. Over time, the leaf turns completely yellow, curls and falls off. With a serious infection, the violet begins to wilt, sheds all leaves and dies.
To combat scabbards and false scabbards, the preparations "Aktara", "Aktellik", "Agravertin" are used. But before spraying, the flower must be washed under running water, then the detected violet pests are removed with hands or tweezers. In the future, saintpaulias are placed further from each other, change the frequency of watering and adjust the illumination.
Diseases of indoor violets and their treatment
Every year, professional breeders and amateurs bring out dozens of new varieties of violets. These are compact indoor plants that, with proper care, can bloom almost all year round. But there are people who fail to grow violets: they rot, then dry, then wither, then categorically do not want to bloom. The reason most often lies in improper care, but in some cases the flower dies due to diseases and pests, to which, alas, it is very susceptible.
Diseases of violets in most cases develop rapidly, so if you do not "diagnose" in time and begin to treat, these wonderful plants will turn into lifeless bushes.
Sciarids
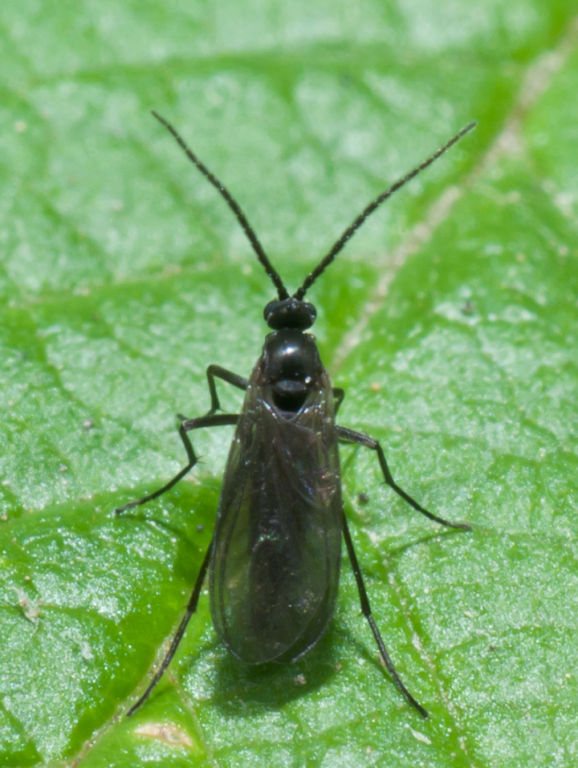


Mushroom gnats, midges - pests of violets (Saintpaulia), which destroy the root of the plant. At the same time, it is not adults who parasitize on flowers, but their larvae, which, due to their size and body structure, are able to easily penetrate into the substrate.
Sciarids simply penetrate into houses from the street, sometimes their larvae are brought in with the soil. These parasites prefer high humidity and settle where there is a lot of decomposing organic matter - in such conditions they multiply very quickly, and as a result of their vital activity, the root of the plant begins to rot.Subsequently, the pest moves to the lower leaves. With a damaged root system, the violet does not have the ability to restore strength, and therefore there is a risk of developing fungal diseases.
Violet pests are destroyed with the drug "Karbofos" or the soil is spilled with any other systemic insecticide. Quite good results in the fight against sciarid larvae are shown by "Regent". As a rule, 10 days after the first treatment, a second one is carried out. In the future, it is necessary to pay special attention to agricultural technology. If it is violated, the sciarids will certainly return.
Prevention of the appearance of insects that infect indoor Saintpaulia
To avoid the spread of insects to all your plants, it is enough to take simple measures:
- Have you treated Saintpaulias for pests?
- For all new violets, quarantine conditions must be created for 14-20 days. Spraying with chemicals is not necessary. If during the specified period of time no signs of insect activity are found, you can not be afraid to put the violet on the shelf along with the rest
- It is not recommended to put flowers plucked from a flower bed next to violets.
- In order to avoid insects from crawling from a sick violet to a healthy one, the plants should not come into contact with the leaves.
- Regular wet cleaning indoors is the key to the health of violets. This helps to maintain the desired humidity and does not allow insects to move along with the dust.
- Pots and trays must be disinfected before use
- Before transplanting, any soil, even purchased one, must be sterilized.
RegularlyNo
Garden soil cannot be used as a substrate for growing violets because of the presence of many microorganisms in it. Better to collect soil in the forest.
- From time to time, it is necessary to bathe the plant. This removes adult insects and their larvae from the violet leaves.
- Withered leaves and faded buds should be pruned in time
Saintpaulias don't bloom? There may be several reasons for this, detailed about them in our next material.
Failure to comply with the conditions for proper care (temperature, humidity, lighting), as well as frequent watering, weaken the plant.
It cannot withstand the attacks of parasites in this state.
Amateur flower growers always want to protect their plants from pests. Unfortunately, this is not always possible.
Therefore, it is very important to know the methods of dealing with uninvited guests. The tips in this article will help you combat the main insects that can kill the violet.
And in order not to have to use them, do not forget about preventive plant treatments and timely transplants.
Whitefly
Whiteflies are herbivorous insects that often inhabit indoor violets. A photo of the pest can be viewed below. Their body length is about 3 mm. Insects feed on plant sap, both adults and larvae.
Whiteflies hide on the back of the leaf plate, where they parasitize, leaving behind a sticky bloom. This pad becomes an ideal soil for the development of a sooty fungus. In addition, the larvae of the parasite are attached to the foliage and to the stems of the flower, parasitizing in this place for a long time.
The infected plant begins to weaken, lags behind in growth, and loses its decorative effect. The leaves wither, the buds do not open. With weakened immunity, the violet loses its ability to resist pathogens of bacterial, viral and fungal diseases.
In order to get rid of the whitefly, you can use the biological product "Aktofit". This bioinsecticide is often used in floriculture against a wide range of pests. Usually 2-3 treatments are carried out with 10-day breaks. Also very good results in the fight against whitefly show "Aversectin C" and "Avertin-N". They are especially effective for mass infestation of a flower by larvae.When this parasite appears, Akarin, Fitoverm and Aktofit are often used.
Preventive measures
They help to avoid the appearance of thrips on their delicate violets timely preventive measures and measures:
- conduct a close inspection of your indoor plants at least once a month;
- maintain the necessary humidity in the room, since thrips loves dry air;
- bathing in the shower on hot summer days;
- to keep purchased indoor plants in quarantine, isolated from the collection;
- avoid placing bouquets or wild cut flowers near indoor violets. It is better to completely abandon the presence of cut flowers in the room, especially greenhouse flowers.
Legs, puffs
In pots of Saintpaulias, representatives of the families Hypogastruridae and Entomobryidae are often found. As a rule, their sizes are insignificant - from 0.2 to 0.8 mm. These pests of the Usambara violet prefer places with high humidity, respectively, they start where the plants are watered too often. Dampness also promotes the reproduction of parasites.
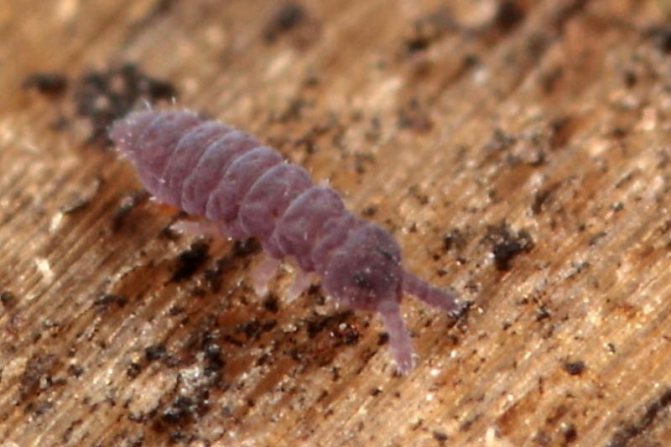


With a small number, these violet pests are unable to cause serious damage to the plant. However, with a mass accumulation, they begin to eat the young roots of indoor Saintpaulias, as a result of which the infected specimens weaken, wither and may die.
In the fight against suckers, it is necessary, first of all, to adjust the watering of the plants and remove the fallen leaves, since it is often under them that parasites prefer to hide. Having reduced the frequency of watering, pay attention to the composition of the soil: with an overabundance of organic matter, an increased reproduction of fungi and mold occurs. In most cases, these measures are enough to completely disappear springtails and podura.
If there are too many parasites, then it is recommended to transplant the violet into a new clean substrate. In emergency cases, the soil is treated with a solution of "Pyrethrum" or systemic insecticides are used, for example, "Aktaru" or "Mospilan".
You can also use "Bazudin". The preparation granules are scattered over the surface of the soil in a thin layer. This is quite enough to destroy all the parasites that live in the soil. The "Initiative" has a similar effect. In order for the insecticide to work, it is mixed with earth. The tool begins to work immediately - after a couple of hours, all the suckers and springtails will be destroyed.
Disease prevention
To reduce the risk of infection of violets with various diseases, the implementation of some recommendations for their care will help:
- The plants you just bought and brought home must be "quarantined" away from other colors.
- Do not reuse primerleft over from other plants.
- Before transplanting violets into a new container with soil, it is necessary sterilize soil - calcining or freezing.
- The most common causes of the growth of pathogenic bacteria are improper care. for saintpaulia - insufficient light, low temperatures, drafts and excessive watering.
- Don't use greenhouse soil with numerous types of flowers or greenhouses, as it can be infested. Better to take the land from the forest, away from the city.


The diseases that violets suffer from can be very dangerous. If treatment is not prescribed on time, then Saintpaulia and neighboring species can become infected and die.
They are especially demanding in terms of care and conditions - soil, temperature, feeding, etc. varietal violets, for example "Raisins" and "Chimera". They immediately stop blooming and, if not given proper attention, may die.
Woodlice
Woodlice complete the list of violet pests with photos. Their treatment when infected with these parasites must necessarily be complex.Woodlice is attracted to high humidity, and if the substrate in the pot is constantly waterlogged, then tiny crustaceans can be found in it over time.
Outwardly, woodlice are very similar to tiny armadillos. Having settled in loose moist soil, they begin to multiply rapidly. Larvae and adults mainly eat the roots of violets, but sometimes plant leaves also suffer.
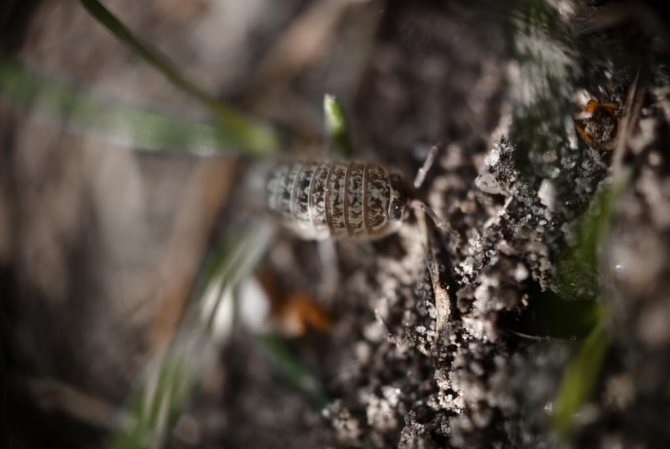


At the same time, young wood lice are considered the most dangerous for Saintpaulias. To combat them, acaricides are usually used. In this case, the treatment must be very careful: in parallel, the plants are sprayed and the soil is shed. As a rule, the treatment is repeated after 10 days.
Blooming violets can become a real decoration for your home. However, they will give you positive emotions only if you are able to provide them with proper care. After reviewing this list of violet pests and photos, it will be much easier for you to recognize the infestation in time and take the right steps to fix the problem. Remember, the earlier you start treatment, the more chances you have to save the best specimens of your collection from death.
Diseases of violets and their treatment
These indoor flowers are very vulnerable, so not everyone can successfully grow them. There are too many small nuances to consider when looking after these colors. In order to grow them all the same, it is important to properly organize the care of indoor violets in order to avoid their illness. This article is about it.
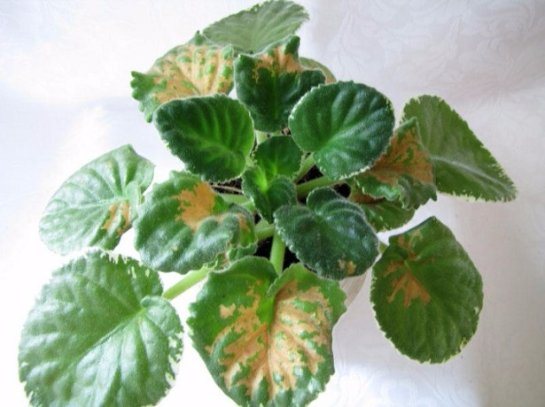


Fusarium violets
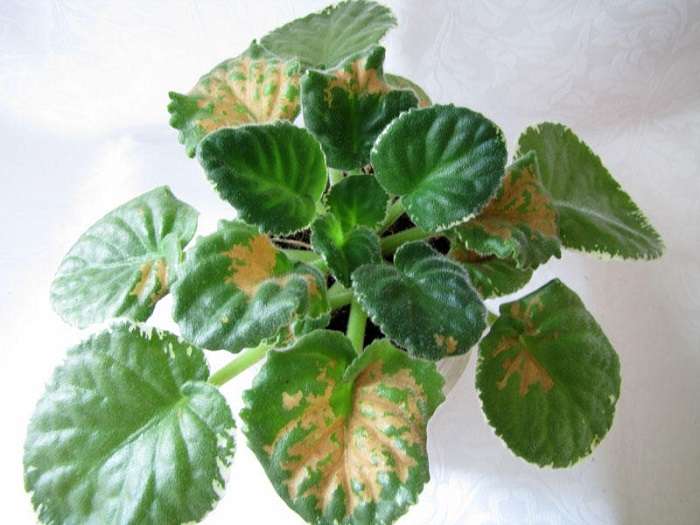
Speaking about diseases of violets with photographs and their treatment, one cannot fail to mention fusarium - a disease of violets, which is considered one of the most dangerous for them. It all starts from the very depths - from the roots of the plant. They are affected by decay, rotting, softening, becoming slimy; further the infection goes up the stem, affecting it too. The “end point” of Fusarium is the leaves that wither and die - just like the stem. The disease may not reach the upper part of the flower - this infection bears fruit quickly enough, so that we are mainly talking about infection of the lower leaves. The cause of the disease of violets (pictured) can be both the air temperature in the room where the flower stands, less than sixteen degrees with a plus sign, both an elementary lack of fertilizer, and the weakness of a newly flowered plant (after flowering they are in a very weakened state and their "immunity" is reduced significantly).


Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure fusarium. If the plant has undergone this misfortune, then the only way out to prevent the spread of fusarium to other flowers is to destroy the affected flower completely, along with the soil. It is urgently necessary to remove it from the rest of the flowers, destroy the plant itself, eliminate the soil, and thoroughly disinfect the pot in which the violet was located. This is done either with copper sulfate or any fungicidal agent available.
If we talk not only about the diseases of violets and their treatment (in the photo), but also about the prevention of these diseases, then you should know: you can try to prevent the occurrence of fusarium if you establish proper regular moisturizing of the plant, and also treat the violet with a phytosporin solution once a month.
Violet disease: bacteriosis
Finally, speaking about the diseases of violets and their treatment (with photo), it is necessary to say about bacteriosis - another common ailment. And not only widespread, but also no less dangerous than fusarium: it is also almost impossible to save the plant.
You can recognize bacteriosis by the following characteristic signs of this disease: brown spots on all parts of the flower - both on the petioles, and on the stem, and on the leaves; darkening of the leaves, and this process first affects the lower leaves, and only then rises up; softening of deciduous tissues.The last symptom is fatal: after that, the flower dies, and death occurs extremely quickly, in some cases in just two days. A diseased plant must be carried away from others so that the disease - it is contagious - does not spread to the rest of its "brothers". As flower growers note, bacteriosis attacks violets most often in July.
The causes of the aforementioned disease are usually improper care of the plant. Overdrying or transfusing a flower can lead to such sad consequences. To prevent such a result, you must follow simple rules: in the spring, transplant into new pots, using new soil; shade in the heat; at the beginning of summer - treat with special means.
Root rot
With root rot, the color of the plant becomes duller. This is due to the fact that the root system loses its ability to supply tissues with moisture and nutrients. The main reason for the development of this disease of violet flowers is waterlogging of the soil or its low acidity. Factors such as a dense, heavy substrate, a large amount of fertilizer, cold water used for irrigation, low air temperature, deep planting or too large a pot can also contribute to the appearance of the disease. When the earth is compacted, oxygen practically does not penetrate to the roots, and the underground part of the plant gradually rotts away.
Taking out the violet from the pot and removing the earthen lump from the root, you can find that this part has noticeably softened and acquired a brown tint. In this case, the activity of a harmful fungus is observed, the spores of which develop very quickly in a humid environment.
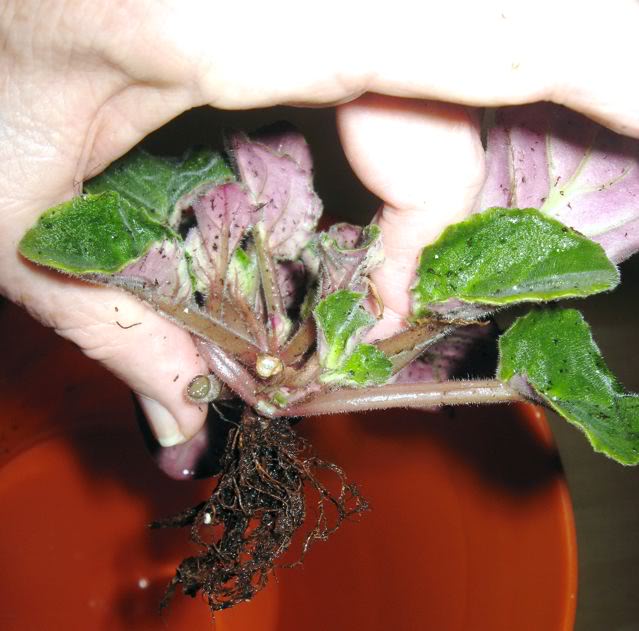


It is necessary to save the plant from root rot immediately. For this, the violet affected by the disease is treated with Fitosporin. Then it is transplanted into a new pot with fresh substrate. If you want to use an old container, then in this case it should be thoroughly washed and disinfected. At the same time, they are treated with a fungicide and then only individual leaves are rooted, which look absolutely healthy. The mother plant must be destroyed.
Diseases as a result of improper care
Some diseases of violets are not contagious, but they can kill a plant no worse than an infection.
Vascular bacteriosis
A multifaceted and insidious disease overtakes the violet at the height of summer and flowering. As soon as the heat passes over the 30⁰C mark, the plant begins to have problems with metabolism and moisture, and there is a "blockage of blood vessels". On the dead tissue particles, bacteria multiply intensively. Symptoms of bacteriosis are different - translucent brown spots appear on the inner side of the foliage plate, the petioles and stems turn glassy and turn into "jelly", the rosette rots and dies off quickly.
Since vascular bacteriosis appears due to heat, an effective way to combat it is to lower the air temperature and ventilation, but not a draft! The most reliable method is to install an air conditioner. If this is not possible, remove the violets from the windowsills to a more shaded place, on pallets with damp drainage. A diseased plant is recommended to be treated with a solution of trichodermin or trichopolum. It is also used for prevention.
Bacteriosis primarily affects weakened Saintpaulias, so focus on improving the immunity of flowers. And it strengthens:
- timely rejuvenation;
- spring (in May) transplant into a fresh substrate;
- treatment before stressful situations (heat is stress!) with immunomodulators, for example, Epin.
Proper care - healthy violet!
Basic rules of care:
- Indoor violets love diffused, not direct light. If there is not enough lighting, the plant will not bloom, from the direct rays of the sun - the leaves may turn yellow, wither, and the plant may die.
- The ideal temperature for plants is 20–22 ° C.
- Watering should be moderate.Excessive moisture leads to the appearance of putrefactive infections and the development of diseases, and a lack of moisture leads to the drying out of the flower.
- The soil should be loose, light, have enough nutrients, it is good to ensure air exchange and the outflow of excess moisture.
Site editors recommend that you read with a description of the varieties of domestic palms.
Bacterial diseases
Like all plants, violets are susceptible to bacterial contamination. Certain bacterial diseases can affect exactly violets, but most often they spread to almost all plants standing next to the window.
Rot
Most often, decay begins after the performed procedures of transplantation, division, circumcision. This is due to excess moisture or bacteria. The most difficult for Saintpaulia are the lesions of the root system and violet diseases.
With the development of brown rot, the turgor of the leaves worsens in the flower, the rosette loses its usual color, the plant withers and grows poorly. Flowers are treated radically, all diseased tissues are excised. A healthy rosette or leaves can be used to root a new plant. As a preventive measure, you can water the ground with phytosporin.


Gray mold also weakens the leaves and covers them with a shaggy coating of gray. The grower should cut off all affected tissues so that they do not come into contact with the soil. In order for the bacterial diseases of the room violet to develop less, it is not necessary to spray the flower rosettes from a spray bottle. The room should not be too humid. There should be no moisture in the pot. In addition, watering with Skor and Fundazol will help to resist bacterial infections.
Now read:
- Planting to decorate the site with three types of conifers
- A persistent, large harvest of cucumbers after planting for seedlings
- Effectively Get Rid of Whitefly Butterflies on Plants
- Delicate, easy-care coniferous bushes in garden plots
About
Leading Researcher of the Laboratory of Vegetable and Berry Crops, Yakutsk Research Institute of Agriculture, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
Prevention of diseases in violets
You can save your favorite flowers from diseases and pests by taking preventive measures and carrying out regular treatments with some drugs.
Useful Tips
There are preventive recommendations for amateur flower growers:
- Do not put new plants next to your home flowers, keep them in quarantine.
- Sterilize soil, even if purchased from a flower shop.
- Remove old leaves and wilted flower stalks.
- To avoid fungal infections, ventilate the room and do not place flowers too closely together.
- Do not bring fresh flowers from the garden into the house, with which pests and pathogens will get into the house.
Fitoverm treatment
Fitoverm treatment is used to combat plant pests. To get rid of violets from ticks, thrips, aphids, one ampoule of Fitoverm is diluted with 1 liter of water, you can add 1 tsp of flea shampoo, which contains permethrin, there. Treatment is carried out 4 times every 3 days by spraying violet leaves and flowers.
Potassium permanganate treatment
Potassium permanganate is used as an effective remedy for the control and prevention of diseases of violets - gray rot, fusarium, late blight, powdery mildew. For spraying violets with potassium permanganate, a slightly pink solution is used - 1 g per 5 liters of water. If you want to disinfect the ground, then you can dilute up to 3 g of powder with 5 liters of water.
Alcohol treatment
Treatment with a cotton swab moistened with alcohol is carried out before using insecticides in the fight against ticks, thrips, scale insects, mealybugs. It helps to remove immobile insects and the sticky plaque that they secrete.
Watering with Fitosporin
Fitosporin is a contact fungicide.Watering with Fitosporin is used to combat bacteriosis, rust, late blight, powdery mildew. For this, 5 g of powder is dissolved in 5 l of water for 30 minutes. After that, the solution is taken into a medical syringe and the soil in the pot is well moistened. Plants can be sprayed with Fitosporin M solution (10 g of powder per 1 glass of water).


How to care for a violet at home
Diseases are most often the result of improper care of indoor plants. After all, the wrong content of the flower most often leads to problems in its development. A person who does not know how to water and transplant a plant can make many mistakes that will be visible in its appearance very soon. Therefore, let's start with what should be the care of a violet at home. Diseases from the photo will be considered after that.
Most flowers need to be repotted periodically. Otherwise, they begin to grow poorly, do not bloom and simply wither before our eyes. The reason may be too tight a pot, which limits the development of the plant. Also, with a rare transplant, the soil can become covered with a white bloom. This means that it does not allow air to pass through well. In such soil, the plant can become seriously ill. If you notice pests in the soil, then a transplant is necessary. By changing the pot filler, you can get rid of unwanted microorganisms.
It is necessary to transplant the violet by the transshipment method so as not to damage its roots. The new land should be moderately damp. After transplanting, make sure that the soil does not sour and does not become salted. If you see such signs, immediately repot the plant again, it will not be able to live in poor soil: it will either rot or not bloom, which is also unpleasant.
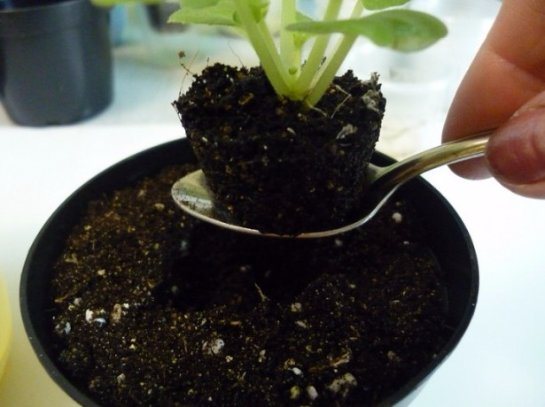


With a lack or excess of light, leaf diseases may appear. Violet reacts very sharply to light conditions. If too little sunlight reaches it, then it may simply not bloom. Too aggressive rays can provoke yellow leaves or even their falling off.
Watering the violet must be done carefully. Any drop falling on its leaves can provoke putrefactive processes. Also, do not give the flower too much moisture, otherwise the roots will start to deteriorate. The best way to add water to the pan, from there the flower will take as much as needed. The frequency of watering should depend on the indoor climate. If the soil in the flowerpot dries up too quickly, then you need to water more often, and vice versa.
If you have a lot of violets, then watering can be organized using a large bowl. Water is poured into it, and flowerpots with flowers are placed on top. After a while, they are returned to their usual place.
Watch also the humidity of the air. If it is too high, the violet may start to rot. The problem will start with leaves that cannot survive in too humid conditions.
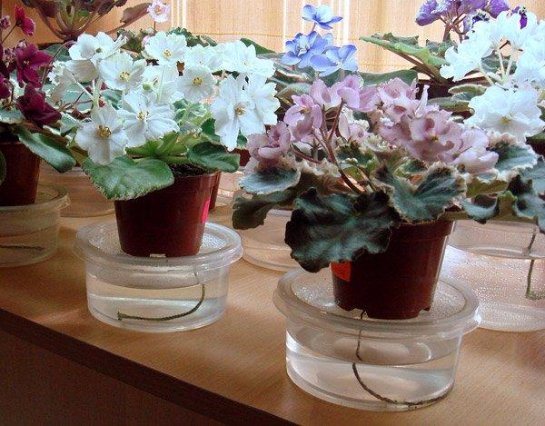


Fertilization is necessary, but here it is important not to go beyond measure. If you feed too often, the plant can be damaged. In such cases, leaf curling, lack of flowering is often observed.
Decay is generally characteristic of a violet. It can happen if you transplanted a flower and the soil does not fit. Also, putrefactive bacteria can appear on the leaves if the plant has not been watered for a long time, and then immediately received a lot of moisture. That is why these flowers are called delicate, because they can die due to the most insignificant reason.
Causes of the appearance of diseases in violets
Experienced flower growers know that it is possible to protect a plant from diseases by providing it with optimal conditions of keeping, close to natural ones. It is necessary to organize proper care at home.
Violets are heat-loving plants, they feel good at temperatures of + 20 ... + 25 ° С, they do not tolerate drafts and temperature changes. In a cold room, violets stop growing, and frequent watering under such conditions leads to rotting of the stem and roots.Heat also has a bad effect on the flower, weakening it, which leads to the disease of indoor violets.
When exposed to direct sunlight, the delicate leaves of the plant get burned, wither and turn yellow. Therefore, the light in the room should be diffused, dim.
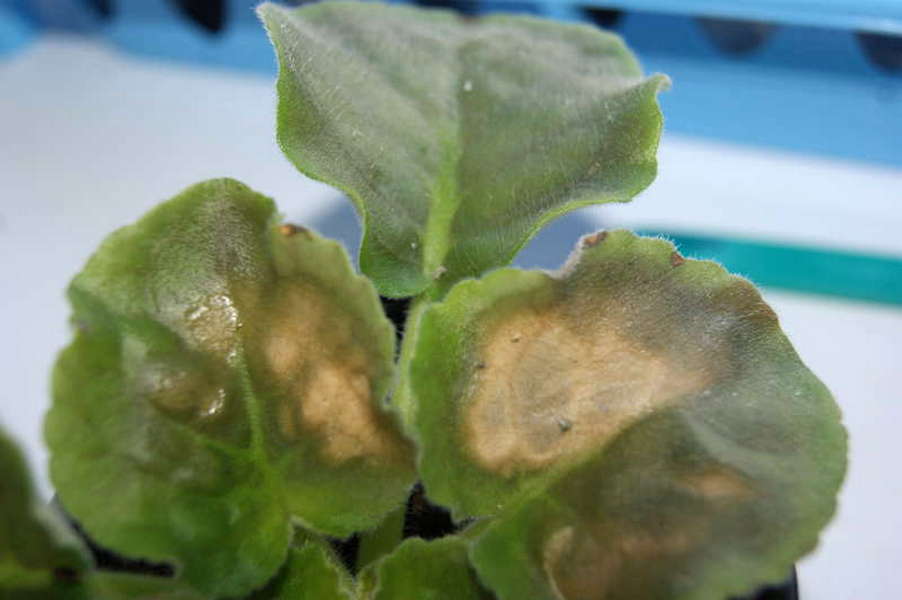


The soil should be free of pathogenic microbes and pests, so you should not take the land for violets from the garden. The soil for violets should be nutritious and light, providing air access to the roots and the outflow of excess moisture. Heavy, dense soil mixtures are not suitable for the root system of Saintpaulia, causing it to rot.
Violets like moderate hydration, not heavy watering, and cannot be moistened with cold water. To provide a guest from the tropics with optimal air humidity, the plant pot is placed in trays with moistened gravel or moss, or the air is refreshed using a spray bottle.
Dangerous pests
Diseases and pests of violets bring great damage to flower growers:
Insects can be brought in with garden soil, purchased plants, cut flowers. Therefore, the plants need to be regularly inspected, and when questions arise as to why spots and other symptoms of the disease appear on the leaves of the violet, immediately start treatment.
Ticks feed on the sap of violet leaves, their presence is indicated by the following signs:
- thin web on flowers or leaves that turn brown over time, dry and fall off (spider mite);
- young leaves in the center of the rosette turn yellow and thicken (cyclamen mite);
- the leaves of the plant curl inward, subsequently they wither and fall off, the plant may die (flat-calf mite).
To combat ticks, acaricides are used - Apollo, Neoron, Fitoverm.
The scutes and false scutes look like tubercles on the underside of the leaf, which are brown, green or yellow. Attaching to the leaf along its veins, insects suck the juices from the plant and produce a sticky secret, on which the sooty fungus multiplies well.
Adults must be removed from plants mechanically by wetting a swab in a soapy solution, since they are not susceptible to the action of chemicals. After their removal, the violet bush must be treated with solutions of Aktara, Bankol, Mospilan or other insecticides. It is necessary to treat the window sill, shelf, window glass with insecticides, on which the larvae of the scale insects may appear.
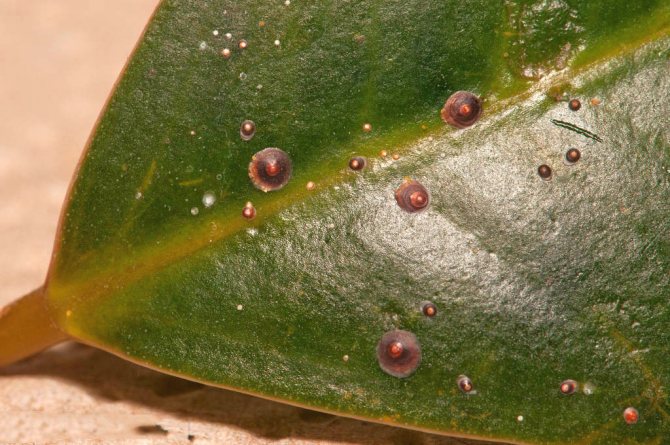


Thrips are small insects that look like elongated flies. They infect plants, not only feeding on their sap, but also transferring various diseases of flowers. Thrips are black, brown or gray in color and settle on the lower part of the leaves. After a while, on the upper part, you can see light dots and stripes, then the leaves are deformed and fall off, the flowers crumble.
Related article: Trichoseptoria plants, how to treat
In the fight against thrips, insecticides such as Fitoverm, Actellik, Confidor are used, which are applied at the root and used for spraying. Violet leaves must be rinsed well before processing. If thrips were seen on one plant, then all the specimens in the house need to be processed, because thrips migrate rapidly and infest flowers.
Nematodes are small, up to 2 mm, worms that live in the ground and feed on plant roots. Signs of root infestation with nematodes:
- roots are brown, black;
- the stem of the plant is elongated and thickened;
- petioles of lower leaves are short, upper leaves have none;
- leaves are compacted and dark green, curl inward;
- roots of brown, dark color with thickenings (galls).
There are no effective means that destroy worms, therefore, to prevent infection, peat or crushed dried flowers of marigolds are added to the soil. You can use an infusion of marigolds or peat for watering violets.
The mealybug, or hairy louse, is visible on the plant with the naked eye. Sucking sap from shoots, leaves, buds, parasites slow down the development and growth of the plant. The insect can be distinguished by its characteristic whitish waxy coating.A white bloom similar to cotton wool is visible on the plants, on which a sooty fungus multiplies.


If the plant is slightly affected, then with a cotton swab moistened with soapy water, you need to clean it of insects and their sticky secretions. It is necessary to prepare a solution of green soap (15 g per 1 liter of water), spray the violets, then repeat the treatment 2 more times after 7-14 days.
Aphids suck sap from plant leaves, slowing down their growth and inhibiting flowering. Aphid colonies are clearly visible, they prefer to settle on the back of the leaves. The danger of aphids is that they carry viral diseases, additionally infecting a weakened plant. To combat aphids at the very beginning of infection, it is enough to remove the damaged parts of the violet and wash it with warm soapy water.
The appearance of fusarium


This disease affects the plant completely, leaves, stems, root system, and this happens simultaneously and rapidly. The roots begin to rot, become soft, and dieback occurs. In the process of decay, the functions of the root system are suspended. Accordingly, the plant no longer develops, does not receive the necessary nutrition from the soil. Therefore, it dies off along with the roots.
The final stage of the development of the disease is from the root to the extreme top of the plant. The infection is simultaneously transmitted to all endings of the violet.
Symptoms of the appearance of the disease - the leaves begin to wither one after another from the base of the stem, the lower levels. The condition of the stems takes on a watery appearance. There is a gradual withering away. After the main flowering, the plant is most vulnerable, weakened and unable to fight the disease, it is this condition that will accelerate the death of the flower. Also, there is a lack of feeding, the untimeliness of this action or the wrong composition of fertilizers, which is necessary in a certain growing season. When a disease occurs and at the same time stably low temperatures in the room (below +16 degrees), the plant is also weakened and is not able to resist bacteria.
What needs to be done to prevent the disease? Isolate the plant from other flowers urgently. 98% of the plant cannot be saved, it is recommended to immediately destroy it along with the soil in which it grew. The pot must be processed, especially if you plan to use it in the future. For this purpose, use copper sulfate, you can replace it. The store will definitely tell you what is best to use. Having made the decision to grow such a delicate, defenseless flower, you must understand the importance of preventive procedures. To do this, use Fitosporin. Watering with a solution is carried out monthly, without disturbing the regularity.
General characteristics of violets
The uzambar violet belongs to the Gesneriev family. This flowering plant came to us from the mountainous regions of tropical Africa. You can also meet him in Japan and North America.
All types of flower, and there are more than five hundred, and according to some sources more than seven hundred, is very difficult to describe. White, sky blue, purple, light blue, pale and hot pink, cherry purple, dark purple blue, lilac pink, double and with petals corrugated along the very edge, large and small flowers please with proper care eyes up to nine months of the year.
It is a herbaceous perennial. Its oval or wide-oval dark green above and light, and sometimes reddish below, the leaves are covered with a soft, tickling, whitish down. They grow on long petioles and reach up to 8 cm in length. And the plant gives the first buds in the spring. These are solitary flowers with five petals, lanceolate or ovoid.


You may be interested in:
A few tricks and your violets will bloom for 10 months a year! More than 1500 species of indoor violets (Saintpaulia) are known. Hardly anyone will be left indifferent by miniature flowers of various ... Read more ...
Perhaps not many people know that violets are not only home decoration. They are widely used in medicine. This plant is used to treat allergies, at high body temperatures and as a diuretic.
Caring for a flower is simple, but you need to know the basic rules and adhere to them, since it is with improper care that the plant gets sick.
Stem rot
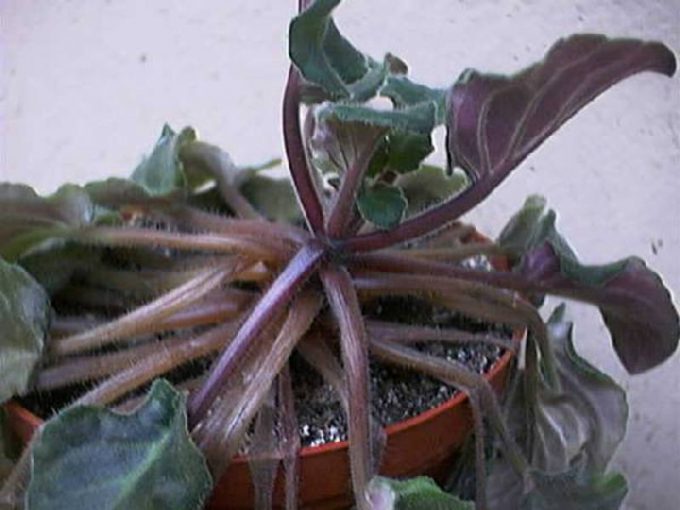
Violet stems are exposed to rot when the bush is divided into parts, when the leaves or the top are removed, which then goes on for rooting. Sources of infection in such cases are dirty tools that carry pathogenic bacteria into the body of the plant through small wounds. To avoid this, the sections must be treated with antifungal agents such as crushed charcoal or cinnamon powder. Another reason for the development of stem rot is waterlogging of the substrate after transplantation. Here, the weakened roots simply do not have time to absorb all the water. Violets and pests contribute to the development of this disease. They often grow on weakened plants, multiply rapidly and interfere with their growth.
You can identify stem rot by examination. At the initial stage, violet leaves suffer from the disease, and treatment should be started right now. The foliage begins to fade, its color fades, and the surface is covered with a dusty coating. At first glance, it may seem that the bush needs watering, but the earthen lump remains sufficiently moist. You can also notice the lesion on the stem during transplantation.
It is recommended to urgently re-root a diseased plant. To do this, cut off its apical part with healthy leaves and carefully examine the core. If no traces of rot are found there, the top is placed in water with the addition of an antifungal agent. Fungicides are ineffective in this situation. If the selected part does not take root, then it is also affected by the disease.
Violet leaf diseases: late blight
The aforementioned disease is unpleasant for violets in that the rosette (specific arrangement of leaves) can fade, which in especially advanced cases cannot be saved even with emergency measures. Late blight is the appearance of brown spots on the leaves of a plant, which appear suddenly and at first - in a completely small amount. They look as if they are drying up, and if you do not notice it in time and do not start taking treatment measures, these spots will very quickly spread over the entire surface of all the leaves. It is in this case that it will no longer be possible to save the outlet - it will fade, even if you start abundant watering, since the affected area will be very large. There is only one way out: destroy the outlet, and pickle all the flowers in the neighborhood with fungicidal agents for prophylaxis.
However, it also happens that the apical part of the outlet does not have time to be in the affected area and remains intact. In such a situation, it is not necessary to destroy it (in the sense of the top). It is enough to carefully cut it off and try to root it. Before doing this, the entire part affected by the fungus must be removed, and the healthy one, accordingly, must be carefully treated with any antifungal drug.
Leaf spot


Spotting or bronzing is a viral disease in which the appearance of the leaf plates changes. They become deformed and stained. Violet disease brings inhibition of growth and cessation of flowering. Penetrating into the plant's body, the virus infects all tissues and prevents moisture and nutrients from entering them.
The carriers of the disease are mainly insects, often thrips. The situation is aggravated by improper watering, washing with cold water and spraying - when drops fall on the leaves, and then they are burned by the sun's rays. In the cold season, the spread of the virus is caused by the cold air flow during ventilation.
At the initial stage of this disease, small stripes and white, yellowish or brownish spots of irregular shape can be found on the foliage of indoor violets. After a while, the violet loses its vitality, and it is no longer possible to save it. If spotting is found, remove the diseased plant from the shelf where other flowers are located as soon as possible, as the infection spreads rapidly.
Rust
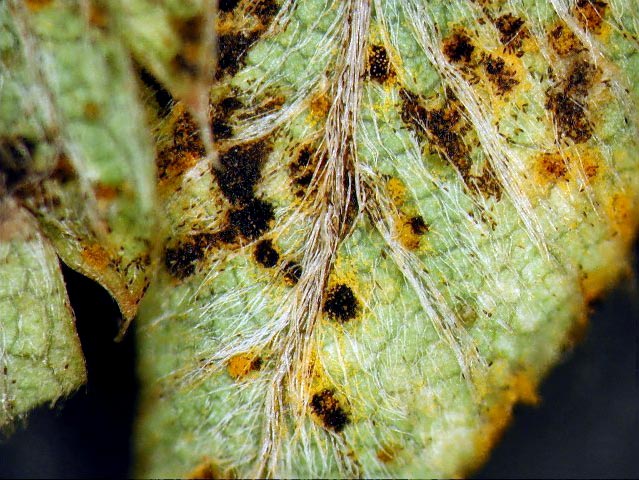


Fungal disease, the cause of which is high humidity at low air temperatures - less than +15 degrees. The main symptoms are orange tubercles on the upper part of the leaf plate and brown pads at the bottom. After a while, these places crack, releasing fungal spores onto healthy parts of the flower. As a result, the affected leaves die off. With increased humidity, fungal spores continue to spread.
For treatment, fungicidal preparations or a solution of Bordeaux liquid (concentration 1%) are used. Dusting with sulfur dust also shows good results.
The disease is considered quite rare and has very remarkable symptoms. But at the same time, it is often confused with a calcite burn.
What to do, if
Sometimes novice florists have questions, the answer to which can be given by their more experienced colleagues.
Drops appeared on the violet
The question is often asked why droplets of liquid formed on the violet, there are 2 answer options:
- if these are drops of water at the edges of the leaves and they appear in the morning, then high humidity can cause their occurrence (after watering, the plant releases excess liquid that accumulates in the form of drops);
- if the drops look like sugar syrup, then, most likely, scale insects have started on the plant.
The violet has lumpy leaves
When novice violet lovers buy a young plant, they see smooth, even leaves. After a while, you can see that the leaves have become hard, bumpy, the rosette has thickened strongly. This may be due to overexposure when the plant is near the window and a lot of the day is well illuminated by the sun. To eliminate this problem, the violet bush must be sent to the east window or something shaded.
Midges started
If you notice that midges have started over the violets, there may be several reasons:
- excess moisture due to excessive watering;
- high air humidity;
- the use of organic fertilizers such as humus, tea leaves;
- rotting old leaves;
- the use of garden (unsterilized) soil for the preparation of soil mixture.
The larvae of gnats, hatching in the ground, feed on rotting organic particles and damage the roots of the plant, causing considerable harm to it. If a midge appeared on violets, how to get rid of it:
- spray the flower with a pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- add wood ash to the ground;
- Dissolve 10 g of soap in 0.5 l of water, pour over the soil in a pot.
The origin of the violet
The Latin name for the flower we know as the violet is Saintpaulia. She owes them to one German botanist, who gave the name to the plant in honor of the German baron Saint-Paul. It was from Saint-Paul that the scientist received the seeds of the violet, which he later identified as a separate new genus. A little later, it will be told about what types of violets exist today, but for now we will add only that the first violet, the seeds of which were brought to his native country by Saint-Paul, in the area in which it was found, was christened Usambar. It happened in the nineties of the nineteenth century.
The whole African continent is called the homeland of the violet; as for a narrower definition of a particular country, doubts and difficulties arise with this. In addition to Africa, the plant can also be found in the Andes, Brazil, North America and Japan, Australia and New Zealand, Europe and Siberia - in general, in any places where the climate is humid enough and there is little shade (although violets and in an open area, so you can't call them particularly whimsical).
Late blight of Saintpaulia rosettes and treatment
Brown dry spots on the leafy part of the plant become a sign of late blight. The spots spread very quickly. In the shortest possible time, the plant tissue undergoes necrosis and the rosette fades.


If the top of the outlet is not damaged, then you can cut it off, treat it with a fungicide, cut off the damaged areas and root it.Individual leaves are also suitable for rooting.
The rest of the flower is destroyed. Neighboring flowers must be processed.
Common problems
Why did violets become small and dull?


If the flower lacks natural light, then new generations of leaves, compared to old ones, grow smaller and look dimmer. Their petioles are elongated, the edges of the leaf plates are curved upward. It is necessary to rearrange the flower pot on a windowsill illuminated by diffused sunlight. In the autumn-winter period, additional artificial lighting up to 12-14 hours will not interfere. Just protect it from direct sunlight and drafts. You will see that the violet will soon recover and return to normal.
Why do the leaves of the violet go up?


Ideally, violet leaves are located horizontally relative to the stem. True, some varieties of violets, for example, King's Ransom, Neptune's Jewels, Happy Feet, are prone to some raising of the leaves upwards. If you have a violet of a different variety, and its leaves suddenly began to rise and curl, there may be several reasons:
- Incorrect lighting... It should be neither weak nor redundant. On the southern sunny windowsill, there must be a light shelter in the form of curtains or blinds, otherwise the sun's rays will burn the delicate leaves of the violet and, in order to protect from the sun, it raises the leaves up. The western and eastern directions are the most preferable, and on the northern windows the violets will not have enough light. The cuttings will elongate, the leaves will stretch towards the light and stretch upward. The rosette becomes like a large spider with disproportionately tall and thin peduncles.
Move the violet pot to a suitable place, well lit by the diffused rays of the sun. In case of short daylight hours, arrange additional lighting up to 12 hours a day. Then the new cuttings will be of normal size, the leaves will spread out on the sides, as they should, and the rosette will gradually become beautiful and compact again. Just remember to remove the old leaves.
- Leaf rosette too thick... Many leaves suffer from a lack of light, reach for it and stretch out. The violet should be thinned out, and the extra leaves should be removed.
- Lack of humidity in the room... If the air in your room is too dry, the violet leaves will rise up and begin to curl. Try to increase the humidity of the surrounding air by all means.
- Heat from heaters... The leaves of the violets rise when the pot stands on the windowsill, directly under which there is a battery, from which powerful streams of heat emanate upward. Violet tries to protect itself from the heat and lifts up the leaves. It will be worse if the leaves begin to turn yellow and yellow-brown spots appear on them. It should be remembered that violets like a stable air temperature (18 - 26 degrees). Close the batteries, ventilate the room, but avoid drafts.
If you analyze possible mistakes and correct them, your violets will return to normal.
Why do violet leaves curl inward?


If the even leaves of your violet suddenly began to curl inward, look for the reasons in the following list:
- You may have gotten too carried away artificial lighting... An excess of light leads to the fact that in the center of the rosette the leaves begin to grow on top of each other, their shape is deformed. The reverse side of the leaves takes on a burgundy hue. The leaf plates become stiff, brittle and curl up into a tube. Peduncles are formed so short that they cannot get out from under the leaves, they also twist and, when touched, break off. If you do not reduce the duration and intensity of the violet lighting, you will get discolored leaves of the rosette, which will soon die.
- Excessive watering... The roots of the violet, being constantly in the water, suffer from oxygen starvation, begin to rot, the plant's entire metabolism is disturbed. Leaves are curling. Violet urgently needs to be saved. Take it out of the pot. Examine the roots. Remove all rotten and damaged ones. Treat with fungicides or crushed activated carbon. Transplant the treated plant into new soil (for Saintpaulias). The pot must be clean and disinfected. Check for drainage and drainage holes in the pot.
- Excess nitrogen fertilizers in the soil... The fragile violet is not able to assimilate the excess amount of nitrogen, so it twists the leaves. If you do not take action, do not transplant the flower into a soil that is suitable for its composition - the violet may die.
- The cause of leaf curling is sometimes a terrible and dangerous enemy of indoor plants - cyclamen mite... This parasite is so tiny that it is simply impossible to detect it without special equipment. The tick affects the underside of the leaves, which curl inward. The sheet itself is, as it were, covered with a layer of dust that cannot be washed off in any way. Over time, the cyclamen tick affects the entire plant, roots begin to rot, stems dry, leaves curl. It is necessary to remove all affected parts of the plant, then treat the flower with chemical agents (Agravertin, Neoron), and several times to consolidate the success and return the violet to a normal appearance and healthy state.
It may be interesting: Ehmeya - home care
Why do violet leaves wither?


If the beautiful violets suddenly began to wither the leaves, and the whole rosette is about to wither, you should hurry up and find out the reason for this disgrace. And there may be several of them:
- Banal violation of the content of the flower... Low or too high temperature, weak or too intense lighting, excess moisture, stagnant water in the pan, hard or cold water, burns of the root system due to exceeding the dose of top dressing, and others.
- Insect pests, which settled on the underside of the leaves and suck the juices out of them. Special drugs can help - acaricides. (See another article on pest control).
- Fungal diseases... The fungus can appear in the soil or get into the tissue of the violet through wounds in the stem or leaves, which appear mechanically during pruning, propagation or transplanting of violets. Below we describe the diseases of violets, which lead to the fact that its leaves wither and disappear.
Why do violet leaves turn yellow?


Perhaps you water it inaccurately - the water gets on the velvet violet leaves and spoils them. Yellow spots also appear from sunburn if the violet is in the sun. Ring spots can be from cold drafts during the winter season.
Why do violet leaves turn black at the edges?
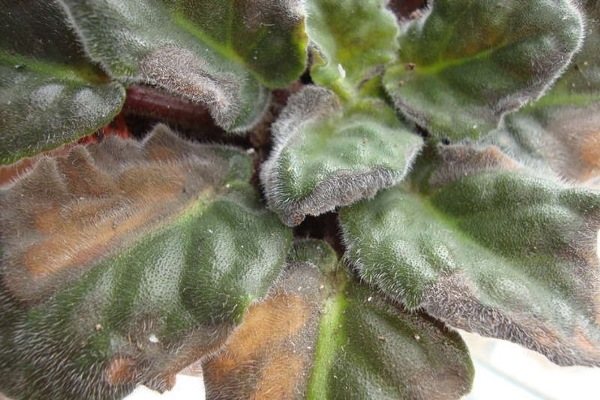


If the edges of the leaves began to turn black on the violet, it is necessary to find the cause of this phenomenon and eliminate it. Let's figure it out in order:
- The main reason for blackening of the leaves along the edges is excessive moisture of the substrate... Stop temporarily watering the plant, let the soil dry out. Feel the damaged areas - if they are soft, the root system may have begun to rot. Then we recommend removing the affected leaves, peduncles and stepsons. Remove the violet bush from the pot, examine the roots. Remove the brown ones. Treat the sections with crushed activated carbon. Transplant the violet into a new substrate according to all the rules, water and spray with phytosporin, and do not allow irrigation irregularities in the future.
- Delicate violet leaves do not tolerate drafts... Drafts can lead to light or brown spots on the leaves at any time of the year. But a few seconds in the cold air when ventilating the room in winter is enough for the green velvet leaves of the flower to begin to darken around the edges. Gradually, spots from the edges spread to the entire surface of the leaves.Violet in this case does not require treatment. Simply remove the damaged leaves so they don't ruin the flower's appearance.
- Lack of nutrients in the soil leads to the appearance of brown spots on the leaves of the violet. In the process of growth and flowering, the violet actively selects all nutrients from the soil. They should be regularly renewed by feeding the plant twice a month with special liquid fertilizers for violets (Saintpaulia). Also, do not neglect the annual transplantation of the plant into fresh substrate. If the flower is not transplanted for a long time, harmful salts accumulate in the soil, which interfere with the absorption of nutrients. Top dressing in this case will not be effective.
- The appearance of white bloom or spots of white or gray color on the leaves of Saintpaulia may mean any disease - fungal, bacterial or viral. We will talk about diseases of this nature later.
Why do flowers and buds of violets wither?
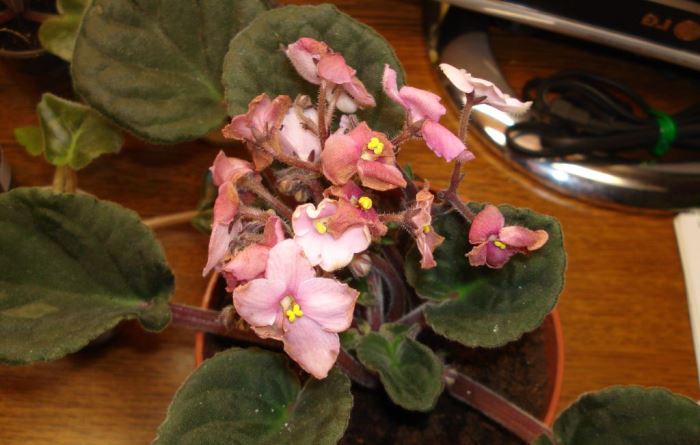


If the buds do not fully open, and the violet flowers dry out prematurely, you can sin for the following reasons:
- The room is too dry. It is necessary to increase the humidity of the air - the flower suffocates.
- The room is too hot. In the summer, the sun fries through the window pane, in the winter, the batteries are fried under the windowsill. There is no time for flowering.
- Not enough natural light. In winter, due to the short daylight hours, artificial lighting is required.
- Soil not suitable for violets, too acidic, with a pH below 4.5
- Excess nitrogen in the soil.
- Drafts. When ventilating, carry the violet away from the cold air currents.
Why doesn't the violet bloom?


If the violet refuses to bloom, it is worth analyzing all the possible reasons for this. Again, we will have to list all the conditions under which the violet will bloom for sure:
- First, different varieties of indoor violets bloom differently. There are violets that bloom all year round. But there are varieties that bloom for a very short time, but for this they also need comfortable year-round conditions of detention and long rest. If the violet is more than three years old, then, most likely, it will bloom rarely and reluctantly. Abundant flowering is usually observed on young rosettes, the age of which does not exceed three years. So, propagate your favorite varieties on time. You can tackle this winter by planting daughter rosettes or rooting leafy cuttings. By the spring they will grow up, adapt and, quite possibly, bloom.
- It is necessary to use a suitable pot for the violets. Young bushes grow well in 5x5 cm pots, medium rosettes need 7x7 cm pots, and adult specimens can easily fit in containers no more than 9x9 cm.If you planted a violet in a pot that is too large, the superficial violet roots will not be able to quickly master the entire space, they will grow ... Together with the roots, leafy rosettes will grow violently to the detriment of the formation of peduncles. In addition, excess soil in the back of the pot can acidify and provoke various infections.
- It is not advisable to allow a deficiency or excess of nutrients in the soil. For example, an excess of nitrogenous components will cause rapid foliage growth to the detriment of flowering. Excess potassium in the soil will cause the violet to stop growing and turn yellow. In order for the flowering to be abundant and colorful, phosphorus must be present in the dressings.
- It is very important for a blooming violet to grow in loose, light, slightly acidified soil. If you used soil from the garden or other, heavy soil that is not suitable for violets, then it will dry out for a long time, it is difficult to let air through. The roots will suffocate and rot. At this point, the violet is not up to flowering - it itself would not die.
- Use special soil for growing violets - light, breathable, nutritious. Observe the norms for transplanting into a new substrate, as even the best soil cakes over time and loses its nutritional value.
- In order for the violet to delight you with constant flowering, observe the norms of its watering during all periods of its life. Both the complete drying of the substrate and its constant waterlogging will not lead to anything good.
- Indoor violets are sensitive not only to the frequency of watering, but also to the method of watering. If you fill the growth point, the plant can get sick. If you get water when watering on velvet violet leaves, then the sun's rays through the window glass can leave ugly spots on them - burns. The violet will get stressed and refuse to bloom.
- The temperature of the water used is very important for the flowering of the violet. Due to clean, but cold water, light spots may appear on the leaf plates, and the root system can rot. The flower will get sick with a fungal infection.
- We do not recommend watering violets with tap water. Such water contains impurities, from which the soil will quickly become saline, becoming unsuitable for flower growth. Water the flower only with settled or boiled water at room temperature or even slightly warmer. Better evening. Use all the methods described by us in article about caring for violets, except for the top watering into the outlet (watering into the pan, immersing the pot in a container with water, drip irrigation and others).
- Lack of lighting is the most common reason violets do not bloom. If the flower pot is in the back of the room, the violet leaves will stretch towards the window, the flower stalks will not form, and the violet will turn into a bush of only leaves. For abundant flowering, violets need at least 12 hours a day of continuous lighting. In the autumn-winter time, we recommend using fluorescent lamps or phytolamps so that the daylight hours are at least 12-14 hours.
- But, if you put a pot of violets on a sunny windowsill, its leaves at noon can get sunburn, from which they become spotty, begin to dry out and fall off. This is another reason for the lack of flowering. Violets love bright, but diffused light for 12-14 hours a day.
- For the flowering of violets, high humidity of the surrounding air is needed. If the air in your apartment is too dry, especially during the heating season, it should be humidified by any means (pallets with wet expanded clay, containers with water for evaporation, spraying the ambient air, using household humidifiers and other tricks). Only at a humidity of 50 - 60% will a violet be able to live normally, develop, form peduncles and bloom for a long time.
- Gross violations of the temperature regime, its jumps, drafts can lead to the dropping of all flower stalks by the violet and even to the disease of the violet.
- In addition, the flower needs fresh air; in a musty room, the flower weakens and runs the risk of picking up some kind of infection or attracting sucking parasites. Ventilation of the room should be normal for you.
It may be interesting: Varieties of Medinilla are favorites among flowering
Brief information about the flower
Before talking about the diseases of violets and their treatment, you need to get to know this flower better, because suddenly someone really did not even see it with their own eyes. Meanwhile, the appearance of the plant actually captivates with its simple beauty without any frills. Violet flowers are common and terry - depending on the species, in the same way the plant can be painted in any color of the rainbow. There are blue violets, purple, yellow-blue, white-pink, burgundy and so on. Interestingly, the violet blooms for as much as nine months! Here's how long you can admire this plant.


There are usually several flowers on the stem, the size of which depends on the plant variety. It can be seven centimeters in diameter, or as much as forty. The leaves are oval or round, sometimes in the form of a heart (this also depends on the type of violet, as well as how the edge of the leaf turns out to be - even or wavy).In addition to the variety, violets also differ in life expectancy - there are both annuals and perennials.
Powdery mildew
Among the diseases of the uzambara violet, there is also powdery mildew - a disease in which the fungus is affected by harmful spores. This is one of the most common violet ailments, which most often affects either very young or very old plants, or those that have just been transplanted, or, finally, those that have just faded. It is not difficult to recognize powdery mildew: in this disease of violet leaves (pictured), flour seems to be scattered over the entire surface of both leaves and even flowers.


There is only one way to cure powdery mildew: by dressing the plant with a fungicide. As for preventive measures, it is possible to prevent the possible development of this disease on a violet if you water the flower correctly, feed it regularly and monitor the absence of sudden and severe temperature changes.
Vascular bacteriosis
They refer it to conditionally infectious diseases. Infection usually occurs in a hot period, when, due to a strong increase in air temperature and a violation of metabolic processes, a large amount of ammonia begins to be deposited in the leaves of the violet. The disease progresses and as a result, the plant poisons itself. The development and spread of pathogenic bacteria is very fast. They penetrate weakened tissues and damage the vascular system. And with their rapid growth, the violet can die for a day.
This disease of violets is characterized by such a symptom as the appearance of mucus on the lower leaves, due to which they quickly die off.
First of all, it is necessary to improve ventilation in the room and try to reduce the air temperature. To do this, pots with flowers can simply be lowered to the floor or placed between containers with frozen water. Just be careful - cold bottles should not touch the plants. Watch out for watering - the soil should not be waterlogged.
Treatment is carried out with drugs, the action of which is aimed at strengthening the immune system: "Zircon", "Immunocytofit". You can also use Previkur or Fundazol. These funds will help eliminate the risk of developing secondary fungal infections. In this case, it is advisable to act immediately, since if time is lost, the forecasts will be unfavorable.
Growing problems
Newbies starting to plant violets often have problems caused by improper care. The most common complaints:
- spots appeared on the leaves;
- leaves wither and dry;
- the root of the violet rots.
Violets - how to care to bloom
Spots on the leaves
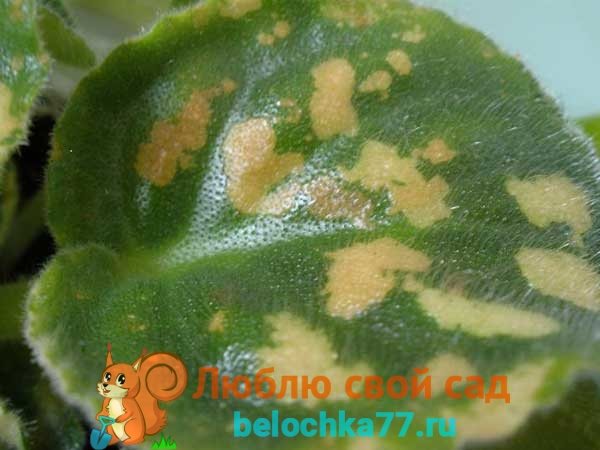


Why do yellow or brown spots appear on violet leaves? Most likely, direct sunlight falls on the violet, and the spots are sunburn. They save the violet in different ways: they stick the stained glass film on the glass, shade it with translucent roller blinds, and transfer it to the northern window sill. Ideally, the violet loves diffused, not bright light. Leaf spots can occur:
- due to dry (too humid) air;
- insufficient (excessive) watering;
- due to excess fertilizers, especially nitrogen;
- use of cold water for watering.
Elite varieties of violets should be grown on a rack equipped with an artificial lighting system.
Why leaves wither and dry
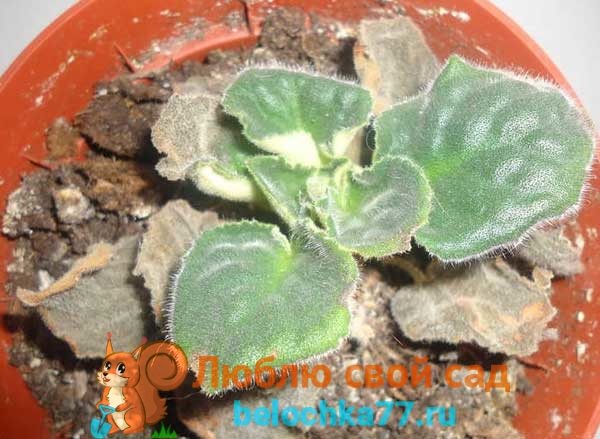


The edges of the leaves dry and darken for four reasons. The first reason is overflow. The second possible reason is a lack of nutrients in the soil. Reduce watering, water only when the top layer dries. If the matter is in poor soil, feed with any fertilizer for ornamental plants. The third reason due to which the edges of the leaves can dry is poor soil: dense, heavy, or when transplanting a flower, it was too tamped around the roots.The violet leaves are still drying from the draft, she categorically does not like him.
Violets: varieties with names and photos
The root is rotting
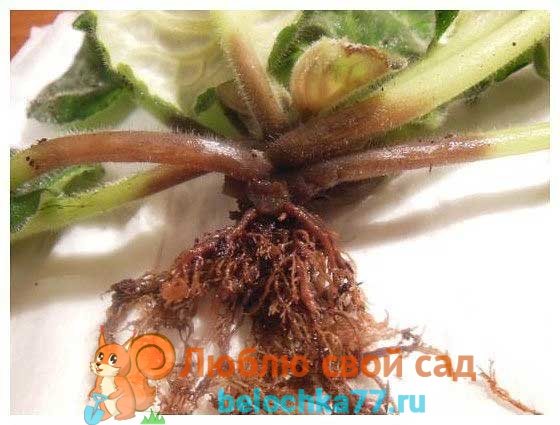


Usually in violets, the root rots due to overflow or acidic soil. Provide the plant with bottom watering. To do this, use pots with holes in the bottom, put them in a tray. Pour water only into the pallet; after 30 minutes, drain the water from the pallet. Use the soil purchased for Saintpaulias. Try to save the overflowing violet by re-root.
Most violet diseases are from improper care. If the conditions are optimal, the violet will bloom for most of the year. He loves oriental violet windows, artificial lighting in winter (10-12 hours), moderately humid air with a temperature of 18 to 24 ° C, a small pot (5-7 cm in diameter), light and nutritious soil.
Brown rot
Young rosettes and rooted parts of the plant are most susceptible to this disease. The disease can be recognized by the brownish brown base of the stem. It begins to soften, thinner and lose density. In this case, the substrate under the outlet is covered with a whitish bloom - mycelium. An infected plant cannot be treated - it must be urgently destroyed.


In order to prevent the spread of the disease, violets that are located nearby are irrigated under the very stem with the preparation "Fitosporin" or a chemical of a similar effect. At the same time, monitor the condition of the substrate - it must be loose enough to allow water to pass through. When violets are propagated, the separated leaves and cuttings should also be treated with a fungicide.
Botrytis (gray rot)
With this disease, the plant is completely covered with a gray bloom, which is why the process of decay begins. It develops very quickly. The movement of the fungus begins in the substrate as a result of improper watering. It often forms immediately on the leaves after being hit by drops of water. Due to the rapid spread of the disease, treatment of room violets is often not possible.
If the disease was detected at the very beginning of development, then it is recommended to cut off all affected parts and treat the plant with a fungicide. If the plaque has enveloped the entire flower, it is destroyed.
To prevent the disease, violets should periodically change the substrate. Before laying in a pot, it is frozen and spilled with a manganese solution. In autumn and winter, watering is reduced and no sudden changes in temperature are allowed.
Late blight
Late blight is a fungal disease. Infection occurs through microcracks in the body of the plant. As a result, the neck suffers first - it begins to rot. Then the disease spreads - spots on the leaves of violets appear very quickly. Their color is brown. Gradually, the foliage wilts and falls off. The cause of the development of the disease is hypothermia, insufficient lighting or excessive watering.
If the problem was identified at the initial stage, then it is quite possible to save the flower. It should be removed from the substrate, remove all damaged leaves, leaving only those that have a good turgor. Dead roots also need to be trimmed. Next, you need to prepare a pot, which will be smaller in size than the previous one, and pour the substrate enriched with perlite and vermiculite. Spill a small amount of the preparation "Fitosporin" and plant a healthy part of the plant. Then we build a greenhouse over it and leave it in this form until the formation of new leaves.
If the entire root system of an infected violet has died, then in this case you can try to do the following: cut the trunk transversely to healthy tissue and plant it in a new substrate according to the above scheme. It should be noted right away that with such a disease of violets, their treatment and resuscitation measures rarely bring positive results. In most cases, the flower is simply disposed of.
Disease treatment methods
If the disease is detected at an earlier stage and there is hope for the rescue of the violet, then a solution of any fungicide is urgently applied. These drugs have a spectrum of action - to destroy fungal spores and resist infection. But not only treatment with drugs is necessary for the plant.
In this situation, it is worth revising the growing conditions:
- be sure to lower the level of moisture, first of all, reduce the amount and frequency of watering; -the place for finding the pots with violets should be warm and well lit. The temperature is not higher than +22 degrees; - periodically remove the top layer of the soil, it is there that spores and bacteria are able to wait for the right moment for a long time.
There are a number of the most attractive, beautiful and popular varieties of violets: Duchess, Compass rose, Royal lace, Ice rose, Dance of galaxies.