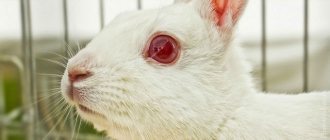
Rabbit breeding is a popular household branch. After all, these domestic animals are highly fertile, and their meat is of high value. However, breeding does not always go as smoothly as we would like.
Many rabbit farmers know that these animals are susceptible to diseases that lead to serious consequences. One of the dangerous diseases that often occurs in these animals is myxomatosis.
If the appropriate treatment is not provided on time, then as a result, all livestock may die. In this article, we will analyze the symptoms of myxomatosis in a rabbit, find out how to treat the disease and whether it is dangerous for humans.
What is myxomatosis in rabbits
Viral infection myxomatosis affects only lagomorphs - hares, rabbits, pikas. It is caused by various strains of the Myxomatosis cuniculorum virus. It originally originated in South America and was used in Australia in the 1950s to biologically control the vast population of rabbits on the continent. It was then used to combat the invasion of wild rabbits in France. These experiments ended with the virus spreading across Europe.
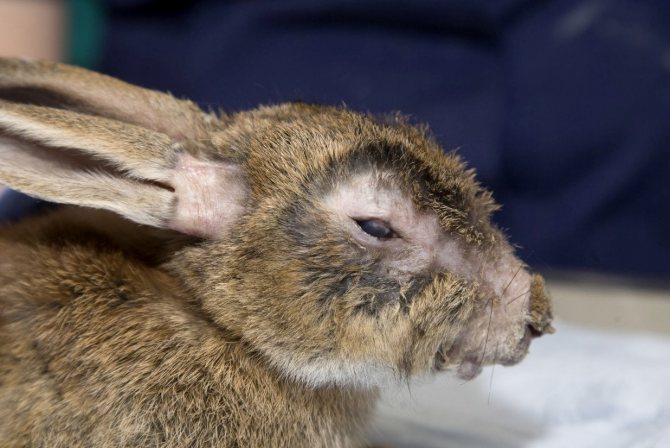
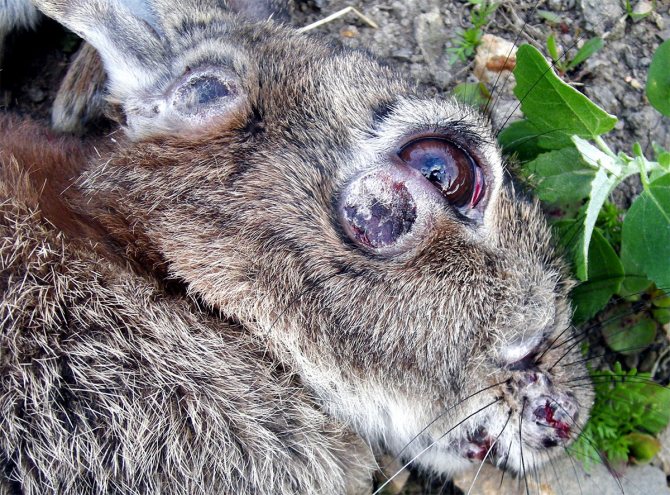
The disease is characterized by acute conjunctivitis and the formation of tumors on the genitals, neck, anus. After the pathogen enters the skin tissue, it begins to multiply on the mucous membranes and then penetrates through the lymph into its nodes. There, the second stage of reproduction begins. The incubation period of the disease lasts up to seven days, and after a maximum of forty days the animal dies. The percentage of deaths from myxomatosis reaches 100%.
Did you know? The rabbit has very wide eyes. If he wants to see what is happening from behind, he does not even need to turn his head.
Nodular form
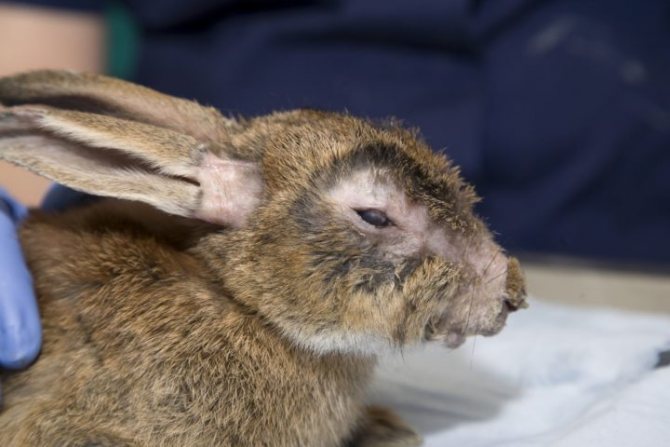
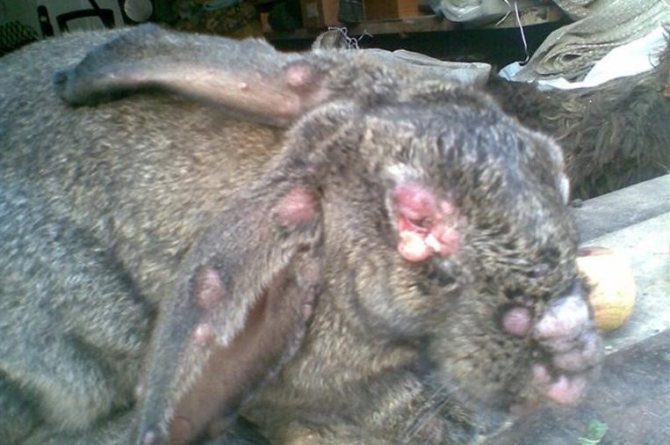
Myxomatosis in a nodular form in rabbits lasts from 30 to 40 days. This form of the disease is considered the mildest, and it is characterized by the appearance of small nodules in the greatest number on the head and ears. Later, there are signs of conjunctivitis and runny nose.
For the treatment of myxomatosis in this form, it is necessary to start immediately after the first days. Usually, antibiotic drugs, vaccination and treatment of wounds with iodine solution are used to treat this form. The survival rate after this form is almost 70%.
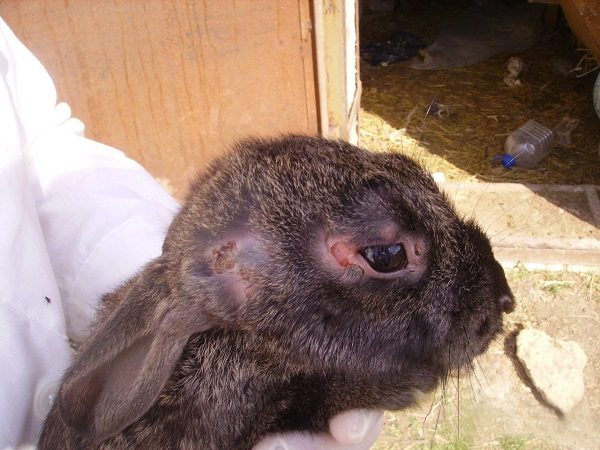

Nodular form of myxomatosis
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of myxomatosis are pronounced already on the third or fourth day after infection. The following symptoms occur:
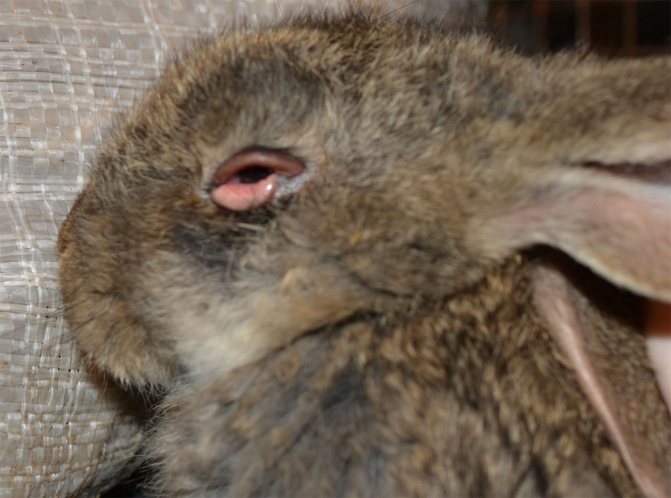
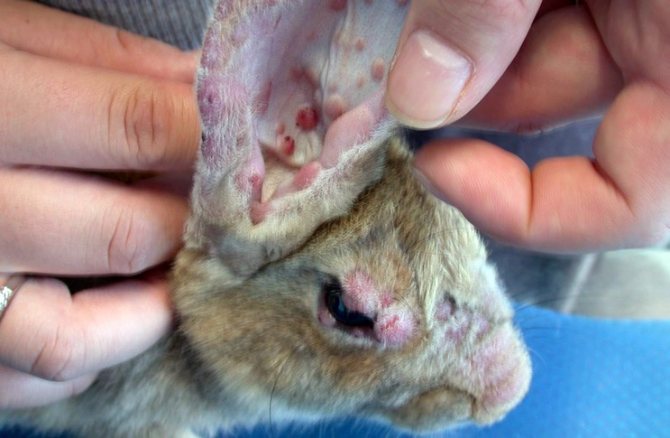
- the whites turn red first, then similar spots appear around the eyes, and later skin nodules become visible in the ears and near the eyes;
- acute ocular conjunctivitis;
- mucus is secreted from the eyes first, and then pus;
- eyelids swell and stick together;
- there is severe swelling, especially near the genitals, anus, head;
- the animal is lethargic, inhibited;
- body temperature is very high, sometimes it can exceed 41 ° C. The animal is very hot to the touch;
- the condition of the coat is rapidly deteriorating - it loses its shine and color, the hairs fall out if you easily stroke the rabbit;
- lips, nose, ears swell to very large sizes;
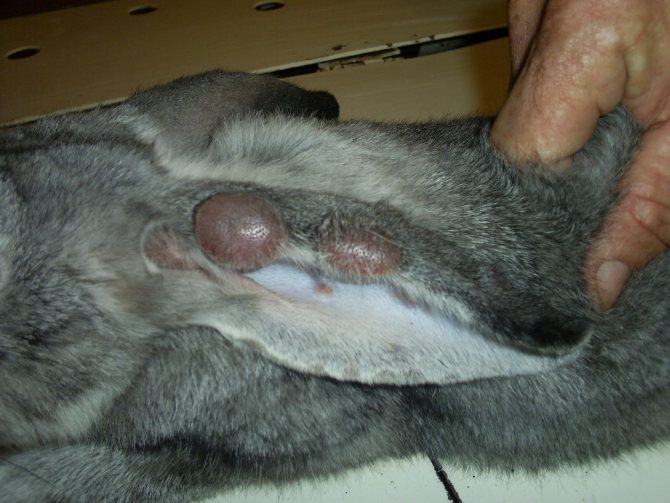
- fibrous nodes form on different parts of the body;
- at the apogee of the disease, the rabbit, as a rule, is in a coma.
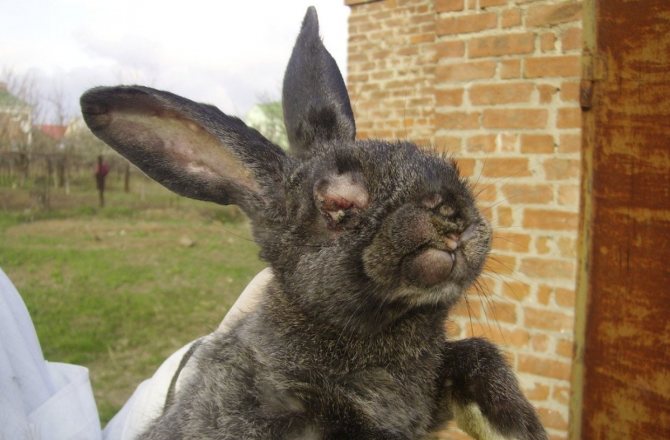


Sometimes the disease is too fleeting - the animal can die in 48 hours.It depends on the strain of the virus.
Video
The farmer shares his personal experience of combating myxomatosis in rabbits in the following video:
A loving husband and a caring father. A versatile person who is interested in literally everything. Gardening theme is no exception. I am always glad to discover something new and share it with other people. It is of the opinion that nature is the second home for every person, therefore, it should be treated with respect.
Found a bug? Select the text with the mouse and click:
In Australia, scientists have begun experiments to clone several grape varieties from colder regions. Climate warming, which is predicted for the next 50 years, will lead to their disappearance. Australian varieties have excellent characteristics for winemaking and are not susceptible to diseases common in Europe and America.
Humus - rotted manure or bird droppings. It is prepared like this: manure is piled in a heap or pile, sandwiched with sawdust, peat and garden soil. The collar is covered with a film to stabilize the temperature and humidity (this is necessary to increase the activity of microorganisms). The fertilizer "ripens" within 2-5 years - depending on external conditions and the composition of the feedstock. The output is a loose homogeneous mass with a pleasant smell of fresh earth.
It is believed that some vegetables and fruits (cucumbers, stalk celery, all varieties of cabbage, peppers, apples) have a "negative calorie content", that is, digesting more calories than they contain. In fact, the digestive process uses only 10-20% of the calories from food.
The novelty of American developers is the Tertill robot, which weeds in the garden. The device was invented under the guidance of John Downes (the creator of the robot vacuum cleaner) and works autonomously in all weather conditions, moving on uneven surfaces on wheels. In doing so, he cuts all plants below 3 cm with the built-in trimmer.
"Frost-resistant" varieties of garden strawberries (more often simply - "strawberries") also need shelter, as well as ordinary varieties (especially in those regions where there are snowless winters or frosts alternating with thaws). All strawberries have shallow roots. This means that without shelter, they freeze out. Assurances of sellers that strawberries are "frost-hardy", "winter-hardy", "endure frosts down to -35 ℃", etc., is a deception. Gardeners should remember that the root system of strawberries has never been changed.
Tomatoes have no natural protection against late blight. If late blight attacks, any tomatoes (and potatoes too) die, no matter what is said in the description of varieties ("varieties resistant to late blight" is just a marketing ploy).
Compost - rotted organic residues of various origins. How to do it? Everything is stacked in a heap, a hole or a large box: kitchen leftovers, tops of garden crops, weeds mown before flowering, thin twigs. All this is interlayered with phosphate rock, sometimes with straw, earth or peat. (Some summer residents add special composting accelerators.) Cover with foil. In the process of overheating, the pile is periodically ted up or pierced for the flow of fresh air. Usually compost “matures” for 2 years, but with modern additives it can be ready in one summer season.
Convenient Android applications have been developed to help gardeners and gardeners. First of all, these are sowing (lunar, flower, etc.) calendars, thematic magazines, a selection of useful tips. With their help, you can choose a day favorable for planting each type of plant, determine the timing of their ripening and harvest on time.
The homeland of pepper is America, but the main breeding work on the development of sweet varieties was carried out, in particular, by Ferenc Horvat (Hungary) in the 20s. XX century in Europe, mainly in the Balkans. Pepper came to Russia from Bulgaria, therefore it got its usual name - "Bulgarian".
Infection routes and risk factors
The disease is carried by all insects without exception, which can bite through the skin of an animal. These are:
- fleas;
- midges;
- mosquitoes;
- flies;
- lice;
- mosquitoes;
- ticks.
Cases have been reported of birds carrying infection on their claws and infecting rabbits upon contact. If one animal falls ill, then the rest of the livestock can become infected from contact with it.
Read on to learn how to rid your rabbit of ear mites.
Infection occurs through:
- direct contact with an infected individual;
- common drinkers and feeders;
- the virus can be on the clothes and tools of the breeder;
- can get into the feed and through it - to the animal.
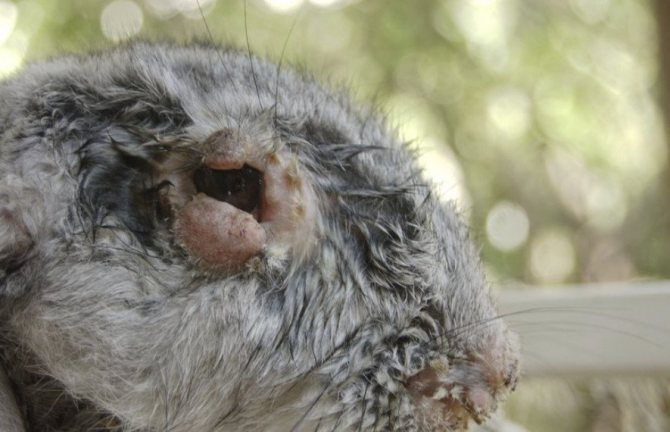


The risk of infection increases significantly in the summer with high humidity. It is at this time that blood-sucking insects become active. The degree of infection of the entire livestock is high if there are many animals in one cage.
It should also be borne in mind that a rabbit that managed to recover from this disease is still able to carry the infection and infect other animals.
Important! If you notice any signs of malaise in your rabbit, you need to immediately isolate it to avoid infecting other pets as much as possible.
Features of the virus
Myxomatosis was first described at the end of the 19th century. The disease was observed in Uruguay in rabbits imported there from Europe. The spread of the virus to other continents began half a century later. It was brought to Australia specifically for the purpose of exterminating and limiting the uncontrolled growth of the rabbit population, which had no natural enemies in nature and caused huge losses to farmers. In the 80s of the last century, the virus reached European countries, including the USSR - outbreaks of the disease were noted in Russia, Belarus, Ukraine.
The causative agent of myxomatosis is highly resistant in the external environment: in animal corpses it can persist for a week, in skins dried at 70 ℃ for several hours, and at 20 ℃ for several months. The frozen virus is active for two or more years. This is why frozen meat and raw skins from infected animals pose a great danger to other rabbits.
The virus is also resistant to a wide pH range. It can be destroyed by heating at a temperature above 60 ℃ for an hour. A 3% solution of formaldehyde and caustic alkali, trypsin, ether and formalin are capable of inactivating the pathogen.
Propagation paths
Today myxomatosis is considered the main infectious disease that has a direct impact on the rabbit population.
Virus spreads mainly by blood-sucking parasites: mosquitoes, lice, fleas. It is localized in the salivary glands of insects, where it can remain active for a long time (a rabbit flea remains a carrier of infection for more than 100 days, a mosquito for 7 months), and when bitten it enters the blood of animals.
The pathogen can be transmitted through direct contact from an infected individual to a healthy person, through household items, and also by some species of waterfowl.
To the virus all breeds of rabbits are susceptible... In affected individuals, it is found in the blood, skin, subcutaneous tissue, parenchymal organs.
Diagnosis of myxomatosis
Only a veterinarian should diagnose myxomatous infection. He studies the rate of spread of the disease, symptoms, clinical signs, takes samples of biomaterials for research.In the role of the latter, areas of affected tissues and animal feces can act. The material is sent for histological examination to the laboratory - there they confirm or deny the diagnosis originally made by the doctor.
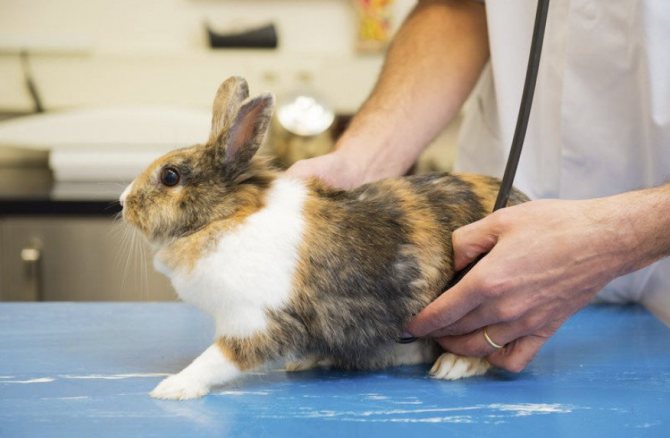

Home treatment methods
Treatment for myxomatosis can help with early detection of the disease. Most rabbit breeders believe that it is impossible to cure myxomatosis, and therefore often the entire livestock is cut out. However, there are recommendations on how to treat the animal in order to give it a chance to survive.
Medication
Experienced rabbit breeders vaccinate young animals. This does not protect the animals from infection, but in case of infection, the disease is less painful. In addition, the mortality threshold is significantly reduced.
Find out what to do if your rabbit's eyes are festering.
Vaccination takes place in several stages:
- the first vaccination is given to rabbits after seven days from the moment of jigging from the rabbit;
- at two months young animals are revaccinated;
- all manipulations are performed with disposable instruments;
- after vaccination, the animal is strictly monitored for 20 days.
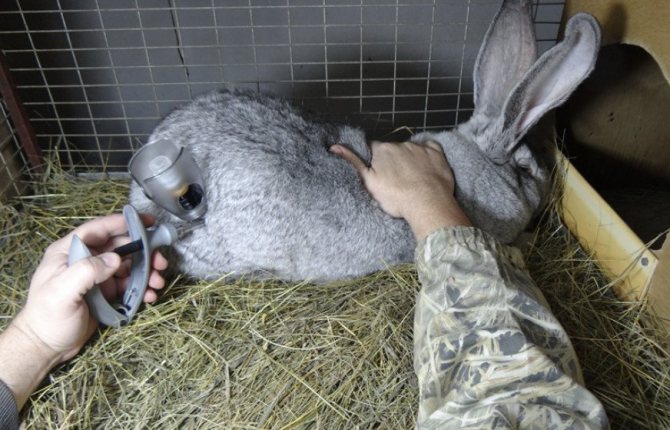


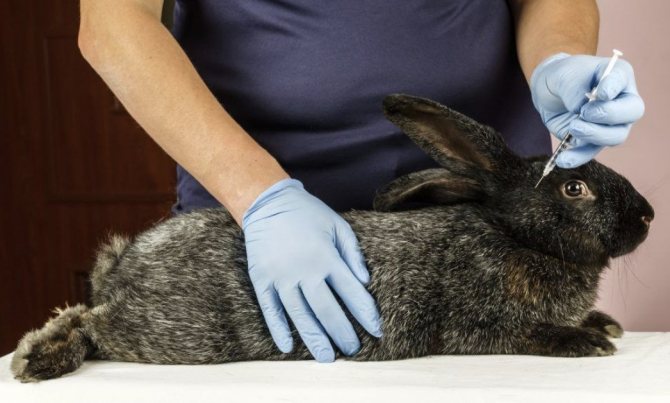
The vaccine against myxomatosis is valid for 9 months. If it is injected subcutaneously into the femoral region, then half of its dose and the same amount of solvent are used per individual. In total, this is 0.5 milliliters in volume. The dosage for intradermal injection into the ear area is one-fifth of a milliliter of the finished product. For its preparation, the medicine is diluted with a solvent in the proportion: 0.2 ml of solvent for one portion of the vaccine. For more information on how to dilute the vaccine, see the instructions for its use.
Important! Only healthy rabbits can be vaccinated. Otherwise, the vaccine will not be effective.
Medication to facilitate the course of myxomatosis can be as follows:
- every day sick animals are given injections of Gamavit under the skin in the amount of a fifth of a milliliter or Fosprenil in the amount of 1 milliliter. They are placed until complete recovery;
- vitamin B is introduced during the week to maintain immunity;
- a week sick individuals are given Baytril to drink. It is added to water based on the proportion: 1 ml of the product per 10 kg of animal weight;
- it is recommended to treat eyes with Ofloxacin in the form of an ointment or drops;
- eyes are washed with furacilin solution or simple saline solution;
- it is advisable to rinse the nasal cavity with Aquamaris or sea water;
- if there are open wounds, they should be treated with healing and antiseptic agents.

Folk remedies
It is impossible to cure and prevent the disease with folk remedies, you can only alleviate its symptoms. There are several recipes that, according to experienced rabbit breeders, help the animals recover faster:
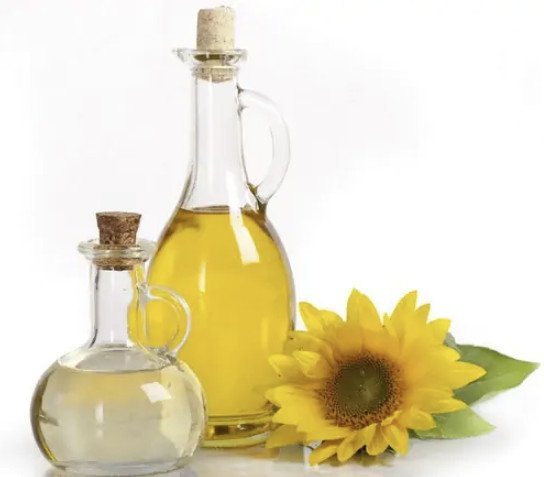


- vegetable oil is fried in any container for twenty minutes. After that, the eyes of the animal are smeared with it;
- it is advised to inject a solution of camel thorn into the leg area to sick animals. Adults need five milliliters of it, and young animals need half as much. It is prepared like this: fill any suitable container with the actual thorns, pour boiling water over them, let stand for three hours and strain;
- collect some urine in a container and let it stand in open sunlight for a couple of hours. Then apply the liquid to the tampon and lubricate the wounds of the rabbits;
- in the early stages of the disease, feeding parsley, spruce and raspberry branches helps well.
Skeptics question the effectiveness of these methods. However, many agree on one thing - animals have an increased chance of survival if, during illness, conditions are created that will strengthen their general condition.
Prophylaxis
To prevent outbreaks of infection, vaccinations are carried out and the rules for keeping animals and disposing of carcasses of dead animals are carefully followed. The best preventive measure is to administer a vaccine.
Stable immunity is also formed in the surviving rabbits. Youngsters born from those who have had myxomatosis are resistant to infection for up to 5 weeks, since they receive antibodies to the virus with breast milk.


The best way to prevent myxomatosis is to vaccinate.
Vaccination
If the likelihood of infection is high, then from 4 weeks of age a monovaccine is administered, and after 3 and 6 months the vaccination is repeated.
Monovaccine is a drug designed to develop immunity against one disease. When vaccinated with a single vaccine, the strongest immunity is developed.
To protect against myxomatosis, monovaccines are produced:
- Lapumin Mix (Ukraine);
- Miksovak (RF);
- Live vaccine B-82 (RF);
- Miksoren (Czech Republic).
With a low risk of infection, rabbits are vaccinated with a polyvaccine from 1.5 months. Polyvaccines are used to prevent several diseases.
Rabbits are injected with a polyvaccine against myxomatosis and hemorrhagic disease:
- Associated vaccine (RF);
- Pestorin MorMix (Czech Republic);
- Lapumin Gemiks (Ukraine).
After the introduction of the polyvaccine, tense immunity against Myxomatosis cuniculorum is formed on the 9th day and remains at an increased level for 9 months. Rabbits are vaccinated in early spring, when there are no mosquitoes - the main carriers of poxivirus.
The vaccination is done once a year. The procedure provides immunity from disease and allows you to get healthy offspring, resistant to poxivirus in the first 5 weeks of life.
Disease control on farms
When breeding rabbits in a home farm, you must strictly follow the instructions for keeping animals. It is necessary to sanitize not only animal cages, but also the territory adjacent to the area where rabbits live and walk.
The food must be fresh, drinkers are thoroughly washed and filled with clean water. All animals should be regularly treated for parasitic insects. In May-June, when mosquitoes become active, mosquito nets are installed to protect the animals from blood-sucking flying parasites.
If signs of myxomatosis are found:
- Quarantine is established for 2 weeks.
- Disinfect the territory and buildings.
- The farm is treated from insects.
- Sick animals are isolated or killed. Carcasses, litter of killed animals are burned.
- Healthy rabbits in contact with sick are treated or slaughtered for meat.
- Animals that have not been in contact with sick animals are vaccinated.
The quarantine is removed 2 weeks after the last registration of an infection on the farm. For the next 2 months, new rabbits should not be imported so as not to expose them to the risk of infection.
Preventive measures
It is very difficult to protect yourself from myxomatosis, but there are still preventive measures, namely:
- vaccination of animals according to the schedule;
- maintaining cleanliness in cells;
- ensuring sufficient air flow to habitats;
- disinfection of cages and equipment;
- restricting access to pets for strangers;
- during periods of greatest risk of infection, it is necessary to treat animal habitats with repellents.
Did you know? The rabbit can jump three meters in length.
Description of the disease
Myxomatosis is a highly contagious, acutely ongoing disease of an infectious nature. Fur-bearing animals, in particular rabbits, are ill with it. Among the obvious symptoms:
- Serous-purulent conjunctivitis;
- Swelling on the head;
- Swelling of the genitals;
- Formation of nodules on the body.
Penetrating into the body of the animal, the virus is localized in the layers of the epidermis, blood and in the perchymal organs. Such widespread distribution leads to rapid disruptions in the work of internal organs. Myxomatosis is highly dangerous for rabbits; mortality as a result of this disease is 85-100%. A great difficulty in treatment is the fact of transferring the virus - an infected individual can infect others.These reasons are sufficient reason for the farmers to know as much as possible about this disease.
Recovery and care of rabbits
If the pet has survived myxomatosis, it needs to be provided with improved living conditions. This is done due to the fact that the animal has a very weakened immune system after an illness. It will be useful:
- protect animals from heat and cold, while it is important to avoid drafts;
- ensure the constant availability of your favorite food. It is better to use foods that do not contain a lot of protein;
- make sure that drinking water is always fresh;
- regularly remove the litter from the cages and feed residues;
- add vitamins and minerals to food, which help to strengthen the immune system.


Quarantine measures
The economy, settlement or district is declared unfavorable for myxomatosis in cases of outbreaks of infection and confirmation of the diagnosis. Quarantine is declared on their territory, veterinary and sanitary measures are carried out as provided for by law.
All infected livestock are destroyed on the spot and burned along with the skin. Waste products of animals, litter, feed residues, and low-value inventory are also subject to disposal. Places where sick rabbits are kept, work clothes and shoes are disinfected. To do this, use a vapor-formalin chamber, 3% formalin solution or boiling for 1 hour.
Also, measures are being taken to eliminate the breeding places of mosquitoes and other blood-sucking insects.
Healthy rabbits are subject to an extra vaccination. However, it should be noted that combination (polyvalent) vaccines are not suitable for use in disadvantaged areas. Under quarantine conditions, the animals are vaccinated exclusively with a single vaccine.
15 days after the slaughter of all sick and suspicious animals, as well as the necessary veterinary and sanitary measures, the quarantine is lifted. After that, the import of new rabbits is allowed no earlier than 1-2 months later. All imported individuals are subject to mandatory immunization against myxomatosis on the territory of the supplying farm 2 weeks before shipment.
Is it possible to eat the meat of a sick rabbit after vaccination
Many are interested in the question of whether the virus that causes myxomatosis is dangerous for humans. Virologists say there is no such danger. The pathogen dies at temperatures above 55 ° C in a minute, so the meat of a sick and vaccinated rabbit can be eaten after significant heat treatment. However, some advise against doing this for moral reasons. In addition, the sight of a sick animal causes disgust and therefore most often the corpses are simply disposed of.
So, opinions differ on the advisability of treating rabbits for myxomatosis, primarily because a recovered animal remains a carrier of infection for a long time. However, in many cases, animals recover and become immune to the disease.
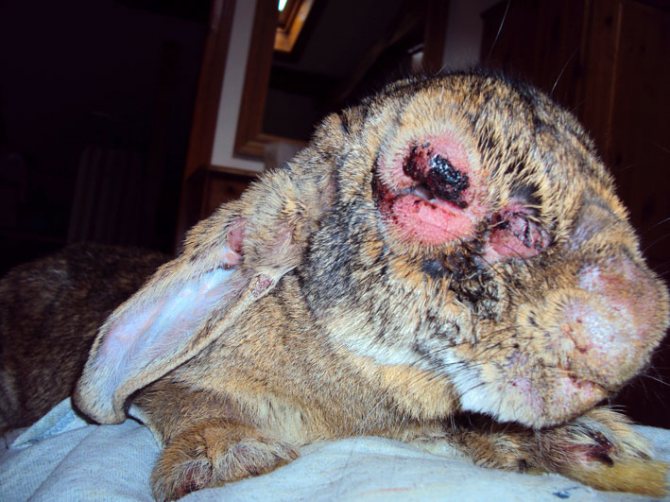
Edematous form
The edematous form or the classic form of myxomatosis in rabbits is considered the most severe. Its duration ranges from 4 days to 15 days. It usually ends in death.
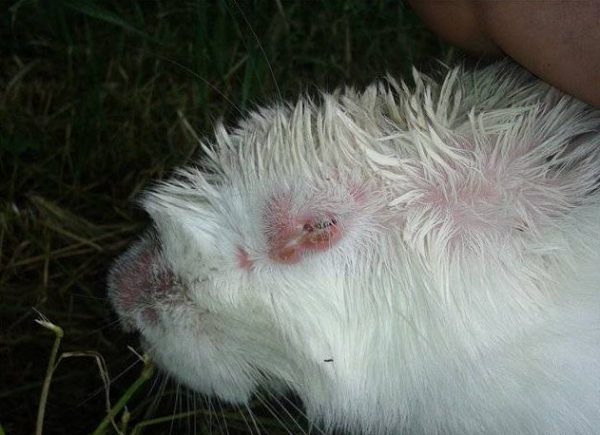

Edematous form of myxomatosis
The main features of this form:
- Redness occurs in the form of spots or bumps on the surface of the skin around the eyelids and on the auricles;
- Lesion of the mucous membrane of the eyes, conjunctivitis manifests with purulent discharge from the eyes;
- Severe swelling of the eyes;
- Bonding eyelids;
- The appearance of liquid nasal discharge;
- Difficulty breathing.
Treatment of miskomatosis in edematous form is not carried out, because it does not give results. If individuals develop myxomatosis in an edematous form, then they should be slaughtered. Meat after slaughter cannot be consumed in food.