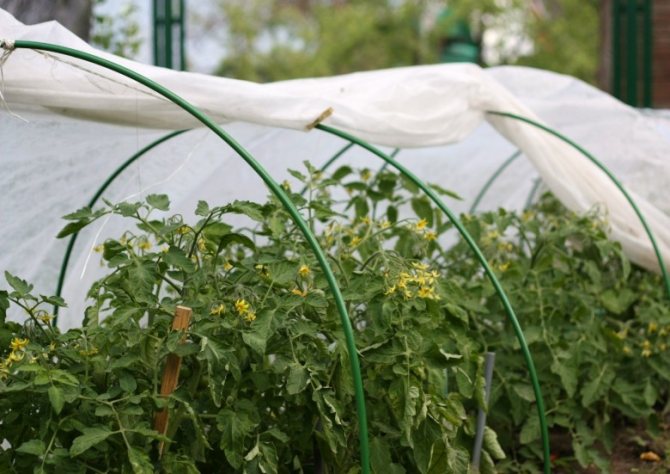
What is tomato cladosporium disease?
Cladosporium is a fungal disease of plants, otherwise it is popularly called brown spot, which is found on tomato leaves. It usually appears on bushes planted in a greenhouse, or in a greenhouse, that is, in closed ground.

This fungal disease is quite difficult to remove, since it continues to function even with drought and a strong drop in temperature for 10 months.
The plant can become infected from any source, as this fungus spreads in the form of light dust. Therefore, the mushroom can be transferred with work equipment, on shoes, or with an ordinary gust of wind.

In addition to all this, it hibernates well in the soil, without dying from its freezing, and then infects fresh seedlings.


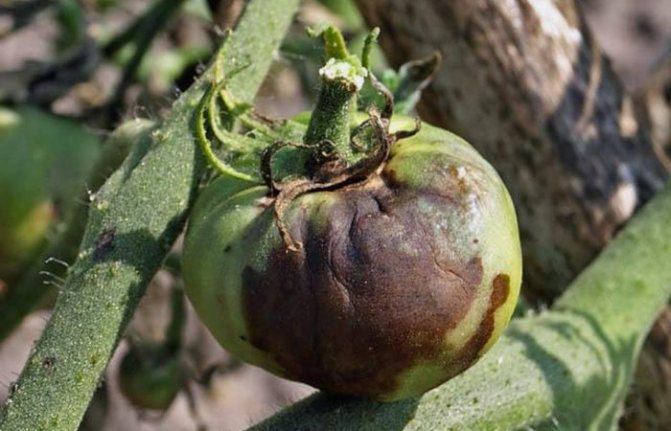
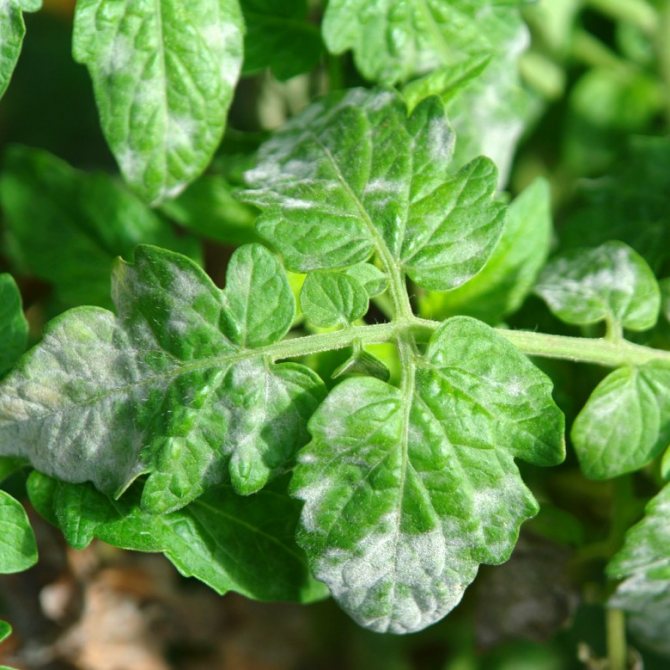
In conditions of high humidity, fungal conidia renew and increase their activity. At the beginning of flowering and formation of tomato fruits, as can be seen from the photo of tomato cladosporiosis, primary signs of damage appear.


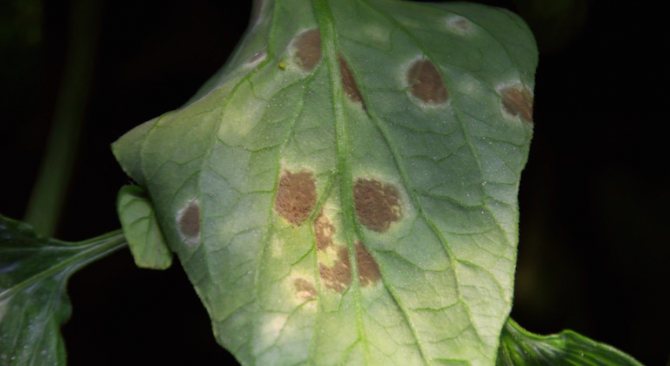
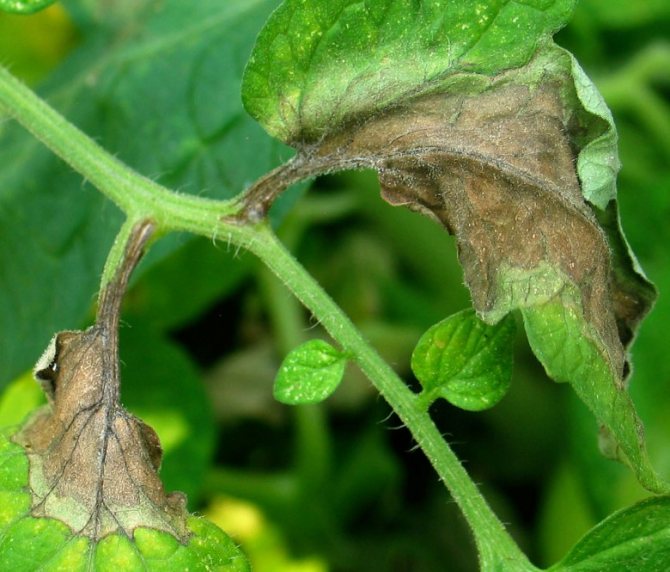
So, around July, a sick plant shows spots on the leaves of a yellow hue, which are simply impossible to overlook. After a certain time, spots of various sizes take on a brownish brown color.
With the germination of conidia, the surface of the leaf is compacted and becomes, as it were, velvety to the touch. If you do not start the processing and treatment of the culture in a timely manner, the weakened leaves will turn yellow completely and fall off. And having lost foliage, the plant loses photosynthesis, which provokes a negative effect on the formation of fruits.


It is important to know that one bush infected with a fungus can destroy all other tomato plantings! The only advantage is the fact that the symptoms of brown spot can be discerned visually. Therefore, it is reasonable not to wait for the spread of the disease, but to start processing the bushes that have changed their parameters in a timely manner.


Signs of defeat
An important factor in the successful treatment of tomato bushes affected by the fungus in the greenhouse is the timely identification of this disease.
The first signs of the appearance of cladosporium are:
- the appearance of gray-brown spots on the inside and small yellow-green spots on the outside of the leaves during the period of active growth and flowering of seedlings;
- delayed fetal development;
- drying of leaves on the bushes.


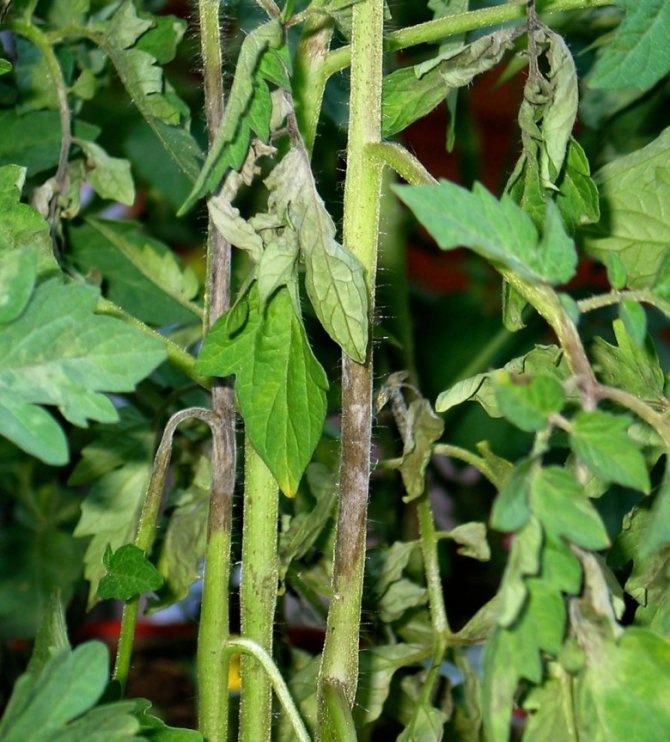
The second stage of the disease is characterized by the cessation of access to the stem and roots of nutrients, as a result of which the growth of the bushes slows down.
At the last stage of the disease with brown spot, such irreparable changes occur with tomato:
- color change of fruits, they acquire a brown tint;
- rotting the bottom of the sheets;
- drying and curling of leaves.
Preventing the appearance of cladosporia
Experts recommend in advance to carry out the prevention of tomato cladosporiosis by various methods of struggle and drugs.


So you do not have to process the ripe tomato crop itself with hazardous chemicals, risking your health. And the prevention itself is rather easier than the fight against the onset of the disease.


The main task is to create favorable conditions for seedlings:
- regulate humidity in a greenhouse or greenhouse;
- adhere to a temperature of no more than 25 degrees;
- thoroughly clean the planting area from winter debris and old crops;
- the frame of the greenhouse should be treated with a special compound;
- do not get carried away with frequent abundant watering of plants.


It is also recommended to use tomato varieties resistant to this disease for planting. All of the above methods must be used in greenhouse conditions, since the plants in the garden do not suffer from this ailment.


Recommendations for growing tomatoes in a greenhouse
To achieve a high yield of tomatoes in a greenhouse and minimize the appearance of brown spot and other diseases, it is necessary to adhere to some recommendations:
- Prepare the beds 5-7 days before transplanting the seedlings into the greenhouse. They should be 60–90 cm wide and 25–30 cm high. It is also necessary to make passages between the beds, the width of which will be about 70 cm.
- The soil should be clay or loamy, humus, peat and sawdust must be added to it in equal parts. For 1 m² of land, you need 3 buckets of mixture.
- At the time of planting seedlings, the ground should be warmed up, and the height of the bushes should reach 30–35 cm. It is better to plant seedlings in early May.
- Two weeks after planting, the tomatoes need to be fed. To prepare fertilizer, you need to add 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska and 500 ml of liquid mullein to 10 liters of water.
- Water the tomatoes every five days. It is necessary to control the temperature of the water for irrigation, it should be + 20 ... + 22 ° С.
Which varieties tolerate brown spot well?
Experienced gardeners and gardeners recommend immediately using tomato varieties resistant to cladosporium for planting in a greenhouse. These types include:
- Sort "Delicacy" with juicy pinkish fruits.
- Vezha variety of Belarusian tomatoes.
- The variety “Nasha Masha F1” is famous for the most excellent quality harvest.
- Space Star tolerates pre-spraying against cladosporia well.
In addition to these types, there are many other options that are most resistant to this ailment. Among other things, science does not stand still and breeders are developing more and more disease-resistant tomato varieties.


Useful tips for the gardener
When growing tomatoes, it is necessary to carefully examine the bushes of this vegetable crop at different stages of its development in order to notice the signs of cladosporium disease in time. Indeed, at the beginning of the disease, it is easier to fight it, and the plants will suffer less damage.
All preventive measures should also be taken to prevent the appearance of the causative agent of this disease in garden ridges or in greenhouses. It is especially important to observe the irrigation regime, to prevent an increase in humidity when growing tomatoes in greenhouses, to grow mainly those varieties of tomatoes that are highly resistant to cladosporium disease.
When the infection with cladosporiosis is at an initial stage, and the damage is focal, tomatoes can be saved with the help of changes in agricultural technology:
- Reduce the moisture content of the soil and air in the greenhouse. For several days, do not use sprinkler irrigation for watering, and also reduce the volume of water.
Increase the air flow to the bottom of the plants, from where leaf spot begins to spread. Shoots close to the soil should be cut and burned. The use of contaminated or suspect compost greens or grass for animal feed is not permitted.
If brown spot is found in dense plantings, part of the plants should be removed. It is necessary to thin out the tomatoes until the distance between the bushes increases to 50-60 cm.
Chemicals
When the brown spot on tomatoes has spread or infected a large area of the vegetable garden, the chemicals are most effective at controlling the fungus. Suitable for the treatment of fungus:
- Bravo;
- Hom;
- Ditan NeoTek 75 VDG;
- Captan;
- Abiga Peak;
- Acrobat MC;
- Quadris;
- Poliram;
- Tsineb;
- Polycarbacin;
- Azophos;
- Mancozeb.
Each drug has its own characteristics, which are reflected in the instructions for use. For an effective fight against cladosporia, it is necessary to follow the instructions exactly, not to use products with an expired shelf life, and also not to purchase substances with an unknown composition.
Treatment with chemicals acts on the fungus faster than other methods. However, do not use fungicides in anticipation of fruit ripening: 4 weeks should elapse between the last treatment and harvest.
Biological agents
A more gentle method of treating brown spot is considered to be the treatment of tomatoes with biological agents. The main component of such drugs is live microorganisms that can kill fungal spores.
Known biological agents against cladosporia:
- Fitosporin;
- Fitolavin 300;
- Strobe;
- Alirin;
- Pseudobacterin-2;
- Trichoderma veride;
- Effekton-O;
- Gamair.
After applying the products, leaf mold and brown spots stop growing, and infection of neighboring plantings stops.
The substances in the composition are safe for plants, do not harm animals or humans, and also do not affect the composition or quality of the soil.
Biological methods of combating cladosporia are suitable for tomatoes in the stage of active fruiting. Tomatoes can be harvested and eaten 2-3 days after processing.
Folk remedies
At the initial stage of cladosporia, or with a small number of leaves with brown spots, you can use folk remedies:
- Garlic infusion. In 20 liters of water, 30 drops of ordinary iodine are dissolved, a pound of peeled garlic or arrows is added. It is enough to withstand the mixture for a day, and then apply to the leaves with a spray bottle.
- The whey-based product is the easiest to make. The aqueous solution is prepared in a ratio of 1:20. All tomatoes and neighboring crops must be densely sprayed with the prepared mixture.
- Long-term treatment is possible by alternating weekly watering of tomatoes with potassium permanganate and ash, diluted in water.
- Milk iodine solution is also effective against brown spot. For 20 liters of water, 2 liters of fresh milk and 60 drops of iodine are enough. The product is ready to use immediately after mixing the components.
Cultivation of land after cladosporium
After the destruction of the pathogen of brown spot on tomatoes, you need to disinfect the soil in a greenhouse or greenhouse. If the plants are still growing, the best option is to use biological agents.
After harvesting the last crop and removing bushes from the beds, the land can be cultivated more thoroughly. In addition to biological products and ordinary steep boiling water, the following are used for soil disinfection:
- 3% Bordeaux liquid solution;
- copper oxychloride not higher than 4%;
- Oxyhom in accordance with the instructions.
Since cladosporium or brown spot is resistant to frost and can activate after 10 months spent in unfavorable conditions, the soil sterilization procedure should be repeated in the spring, before preparing the site for planting tomato.
Cladosporium-resistant tomato varieties
If there is a high risk of brown spot infestation, it is recommended to plant tomatoes with good resistance to fungal infections. When buying seeds, you should carefully study the description, where information about the immunity or resistance of the variety should be present.
Among the tomatoes resistant to cladosporia, it is worth noting hybrids for growing in a greenhouse or greenhouse:
- Marissa F1;
- Bohemia F1;
- Vezha;
- Opera F1;
- Doll Masha F1;
- Delicacy;
- Charisma F1;
- Pink Paradise F1;
- Opera F1.
In the open field in the garden, they are protected from brown spot:
- Our Masha F1;
- Fast and Furious F1;
- Blitz;
- Red Arrow F1;
- Crunchy F1;
- Titanic F1.
In regions where the climate and weather conditions contribute to the development of the disease, it is worth growing hybrids:
- Ural F1;
- Konigsberg;
- Olya F1;
- Space Star F1;
- Vologda F1.
Prophylaxis
In order not to think about how to get rid of cladosporiosis on tomatoes, you should take care of timely preventive measures.
At a permanent growing site, you need to completely change the soil every 2 years.
Brown spot will not be able to develop indoors, where there is a possibility of regulating temperature and humidity.
The main activities required to grow healthy tomatoes in a greenhouse or greenhouse:
- mulching of the root circle and aisle;
- use of quality seeds;
- regular ventilation;
- compliance with the tomato planting scheme;
- standardized or drip irrigation;
- disinfection of garden tools and tools;
- pest control;
- weeding and destruction of plant residues.
It is easier to avoid infection and treatment of brown spot in the open field, since the free circulation of air in the lower part of the plants prevents the development of disease. It is enough not to thicken the plantings, keep them clean and comply with watering norms.
Regular prevention and adherence to the rules of agricultural technology will help protect tomatoes even from such a dangerous disease as cladosporia.
Knowing what to do at the initial stage of the disease, there is a real opportunity to get rid of brown spot and completely preserve the tomato harvest.
Cladosporium resistant tomatoes
Growing tomatoes involves not only competent care and pleasure from the harvest. Summer residents have to study the diseases that are inherent in tomatoes and how to eliminate them. Cladosporium is a rapidly spreading disease, especially during periods of high humidity. The second name of the disease, which is more familiar to summer residents, is brown spot. It affects tomato beds in greenhouses and in the open air. Therefore, the fight against fungal disease is a hassle for all gardeners.
It is very easy to notice the signs of cladosporium disease. Light spots appear on the inside of the leaf, which gradually turn brown and the foliage begins to dry out.
It may not be possible to wait for the fruits on such bushes, they simply do not ripen. A spot is found at the place where the stalk is attached. Compared to late blight, this fungal disease is less dangerous for tomatoes, but leads to the loss of leaves on the bushes. In plants, photosynthesis is disrupted and productivity is sharply reduced. However, rotting of fruits, as with late blight, is not observed. You can eat tomatoes, but they are much smaller than their healthy counterparts. After all, the nutrition of the fruit is provided by the leaf mass, which suffers from cladosporia.
What will help keep the planting of tomatoes from cladosporiosis
Cladosporium is rarely seen in dry, warm climates. Therefore, in order to reduce the risk of plant disease, it is necessary:
- Reduce humidity (especially in greenhouses) and provide tomatoes with sufficient temperature for development. For this, regular ventilation is carried out. In the open field, they try not to violate the tomato planting schemes, so that thickening does not lead to excessive moisture. If the humidity is below 70%, then there is no need to be afraid of the appearance of a formidable disease.
- Reduce watering during periods of mild drought. Tomatoes that are severely ill with cladosporia are best removed. On the rest, cut off leaves affected by brown spot and process.
- Thinning plantings. If the rows of tomatoes are not thickened, then cut the lower leaves to a height of 30 cm from the soil. This is also necessary with an excess of organic matter in the soil. Then the leaf mass is very powerful, which is the reason for poor ventilation of tomato beds and the rapid spread of cladosporium disease.
- Choose tomato varieties that are resistant to cladosporiosis. This is the most important factor for summer residents. Modern breeders develop varieties of tomatoes with certain properties. Disease resistance is the most requested parameter. On the packaging, instead of "resistant" may be indicated "tomato tolerant" to KS.
- Grow tomato seedlings on your own. Viruses and fungi can already be found on young tomato seedlings. Therefore, by growing your own selected variety and observing all the care requirements, you will provide yourself with protection against cladosporiosis.
Cladosporium tolerant tomato varieties
Hybrid tomatoes are in great demand among summer residents. Hobbyists do not always collect their own seeds, so they are satisfied with the set of characteristics of hybrid varieties.
Several varieties for greenhouse cultivation. Well suited for regions with cool climates requiring shelter of tomato beds.
Charisma F1
A hybrid that is resistant not only to viral diseases, but also to low temperatures. The fruits grow to a weight of 150 grams each. They are planted according to the 50x40 scheme with a density of 1 sq. m no more than 8 plants. Mid-season, cladosporium and tobacco mosaic resistant, which makes it popular with greenhouse tomato lovers. Suitable for any kind of use - fresh, pickling, canning. The bush grows in height from 80 cm to 1.2 meters, depending on growing conditions. The yield from one bush reaches up to 7 kg.
Bohemia F1
A stunted representative of hybrids that can successfully grow in open field. Plant height no more than 80 cm. Fruits are medium - about 145 g, red. Disease resistance is high. The planting density is maintained at 50x40, the density of the placement of bushes per 1 sq. meter - 8 plants. The yield is lower than the previous variety, only 4 kg from one bush. It is not capricious in leaving, requires loosening, weeding, fertilizing with mineral compounds.
Opera F1
A taller tomato for greenhouses - 1.5 m in height. Resistant to cladosporium and other diseases. The fruits are smaller, with an average weight of 100 grams. Early ripe, yield - 5 kg per bush. Fruits of excellent taste, suitable for pickling, canning and fresh dishes. They have a red tint and a rounded shape, there is no spot at the stalk.
Vologda F1
Clustered greenhouse tomato resistant to brown spot. Fruits are smooth and round, weighing 100 g. In addition to the named disease, it resists fusarium and tobacco mosaic well. Average ripening period. Productivity withstands up to 5 kg per plant. Looks beautiful with whole-fruit canning. Fruits are even, not prone to cracking. High product characteristics. The planting scheme is classic for greenhouses - 50x40, but the number of plants per 1 sq. m in total 4 pcs.
Ural F1
Cold-resistant and resistant to common tomato diseases. A large-fruited hybrid, the mass of one tomato can be 350 g, which is very beneficial for greenhouse tomatoes. Although the area of use is limited, it is best used in salads for fresh consumption. With a 50x40 planting scheme, only 4 plants are planted per square meter. The height of the bush in the greenhouse is more than one and a half meters.
Spartak F1
Mid-season and tall hybrid with excellent taste characteristics. Suitable for fresh use and blanks. Very high commercial characteristics - uniform, rounded fruits. Cultivation in the open field with the formation of a bush is possible. It responds well to nutrition with mineral fertilizers, regular weeding and loosening.
Olya F1
An early ripening hybrid that can withstand low temperatures.Bushes form. Simultaneously forms three cluster inflorescences at the place of the bookmark. Each cluster has up to 9 fruits. The fruits ripen very quickly, the total yield is up to 26 kg per 1 sq. m. advantages of a hybrid:
- does not react to heat and low temperature;
- develops well in low light;
- resistant to cladosporiosis, HM virus, nematode.
Designed for use in salads.
Moving on to varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to cladosporia and grown in the open field.
Red arrow F1
Reputed to be a very reliable hybrid among gardeners. It copes well not only with cladosporia, but also late blight. Early ripening and fruitful, with excellent taste and aroma - the dream of every summer resident. The bushes are undersized and slightly leafy, so there is no need for pinching. The fruits are fleshy, even in shape with a rich red tint. Brushes are arranged through 1 leaf; in total, up to 12 brushes are formed on the bush. In addition to resistance to formidable diseases (cladosporium and late blight), it is not affected by nematodes and pathogenic bacteria. It stands out for its excellent transportability.
Our Masha F1
According to summer residents, it is the best variety of all medium early and resistant to cladosporiosis. The first inflorescence forms above the 10th leaf. Productivity is recorded up to 10 kg per 1 sq. m of area (4 plants) with a planting scheme of 50x40. Also suitable for greenhouse cultivation. The fruits are cuboid, very fleshy, weighing 185 grams. The advantages of the variety include:
- resistance to cladosporium disease and extreme weather conditions of cultivation;
- commodity characteristics;
- stable yield;
- large-fruited.
Titanic F1
Tomato, beautiful in fruit shape, resistant to cladosporium disease. Large-fruited is another indisputable plus for lovers of large tomatoes. Medium early, with a tall bush, requiring the formation of one stem and the timely removal of stepsons. The foliage is good, the skin of the fruit is thin, so the tomatoes should be transported in a container in one row. Suitable for shelter and outdoor cultivation. In greenhouses, the tomato yield is 18 kg per 1 sq. m, and in the open field up to 35 kg from 1 sq. m.
Fast and Furious F1
Early ripening with excellent taste. Resistant to
diseases (cladosporium, verticillium wilting, fusarium, apical rot and powdery mildew). Great for preparing meals and preparations. The weight of one fruit is 150 g, the shape slightly resembles a plum. It is highly appreciated by gardeners for its resistance to heat and transportability. There are few stepsons, the brush is simple and compact.
Crunch F1
An excellent late-ripening hybrid with a long shelf life.
In addition to the original color, it has a melon-like aroma. The fruits really have a crispy texture that attracts many fans of unusual tomatoes. The features of the hybrid are:
- shade tolerance;
- unusual color;
- density and uniform color of fruits.
Tomato bushes are tall, leafiness is medium. The fruit is harvested when the olive color begins to take on a slightly yellow tint. The harvest is stored in the dark and at a temperature not higher than 17 ° C. Such conditions will ensure the safety of the tomato until the end of February.
Conclusion
Among the popular varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to cladosporiosis are o, "Eupator" and "Funtik". "Swallow F1", "Paradise Delight", "Giant", "Business Lady F1" received good reviews from summer residents. All of them show good cladosporium resistance and yield. Therefore, for gardeners there is a decent selection of varieties that can withstand diseases for growing on the site.
Causes of the appearance, signs and treatment of tomato cladosporium disease in the greenhouse and in the open field. Brown spot prevention measures
July begins. Fruits are poured on powerful tomato bushes that have gained strength.
But it's worth taking a closer look at the bright, green foliage.Perhaps a villain has already lurked there, capable of destroying this splendor in a couple of weeks.
This article describes the measures for the prevention of cladosporiosis on tomatoes.
What it is?
Brown spot, olive spot, leaf mold, cladosporium are the names of the same common tomato disease. The causative agent of the misfortune is the ancient mushroom Cladosporium fulvum cooke, or otherwise Fulvia fulva.
Further in the photo you can see what the disease looks like on tomatoes:
Reasons for the appearance
Spores of the fungus spread very easily, just a little breeze. The main danger is diseased plants and their non-destroyed remains.
Transferred with dust or successfully survived the winter, pathogens of the disease fall on healthy tomatoes. The presence of damage to the plant is not necessary. The main conditions are high humidity and a comfortable temperature. It takes 12-14 days from infection to the appearance of the first signs of cladosporium..
Signs
The disease begins on the lower leaves and rises to the top. Passing by the plant, you may not notice that the tomato is already affected by brown spot.
If you miss the first signs of cladosporia, the disease will quickly spread to all tomatoes. It will be extremely difficult to save the plants. The period from infection to death is only 30 days.
In order to detect the disease in time, it is necessary to regularly examine the leaves of the lower tier.
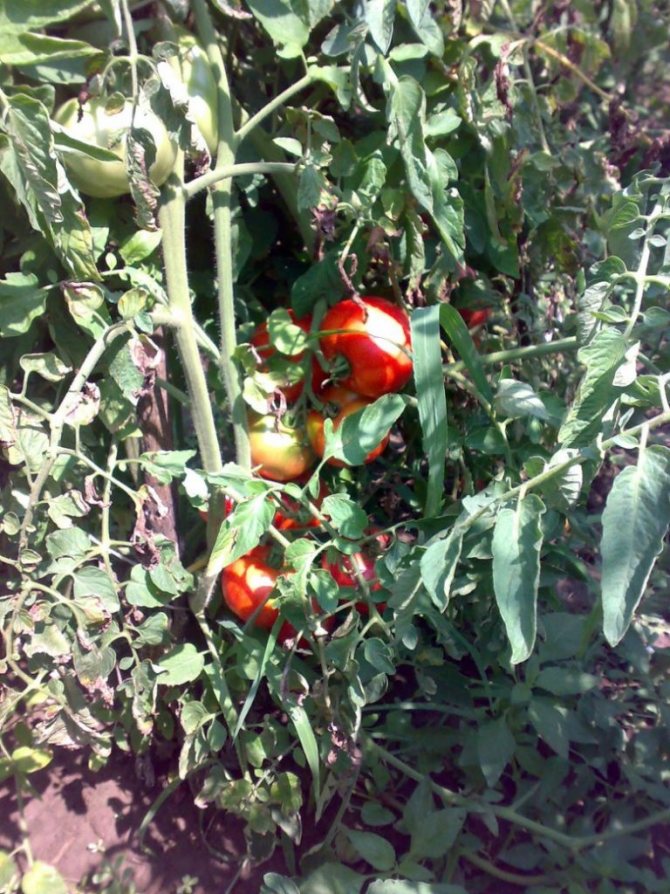
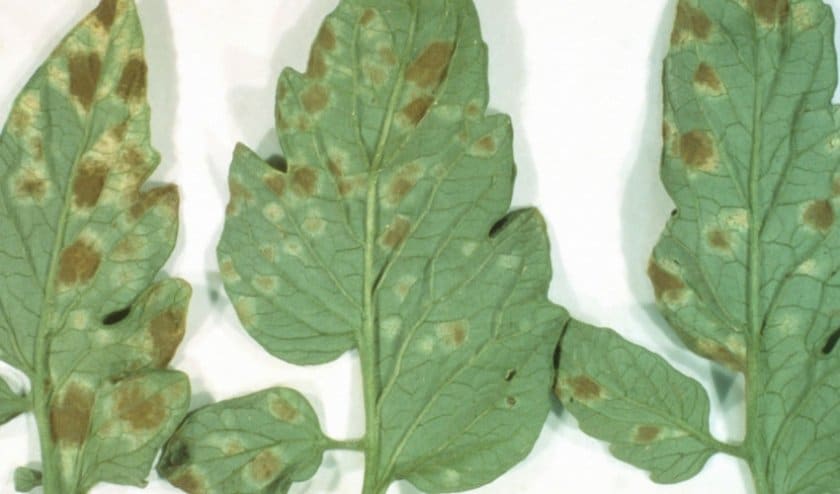
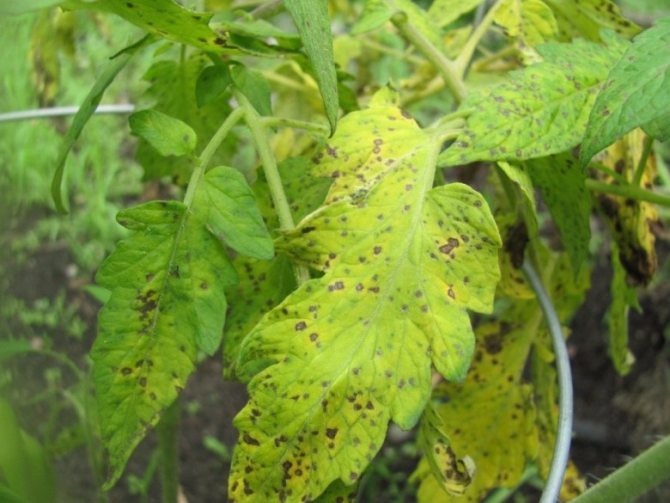
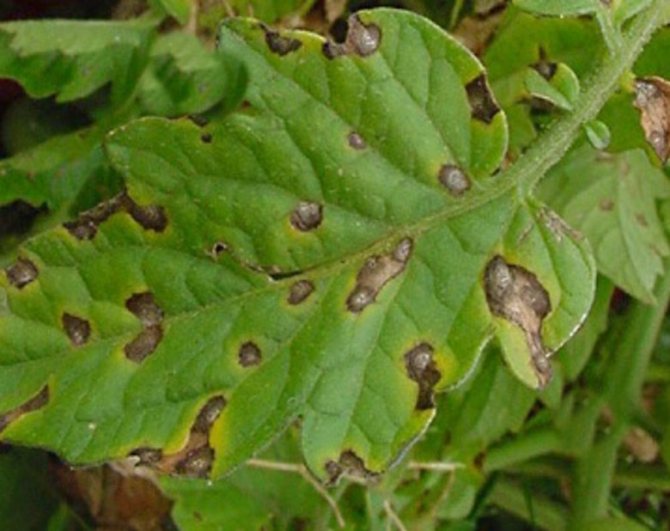
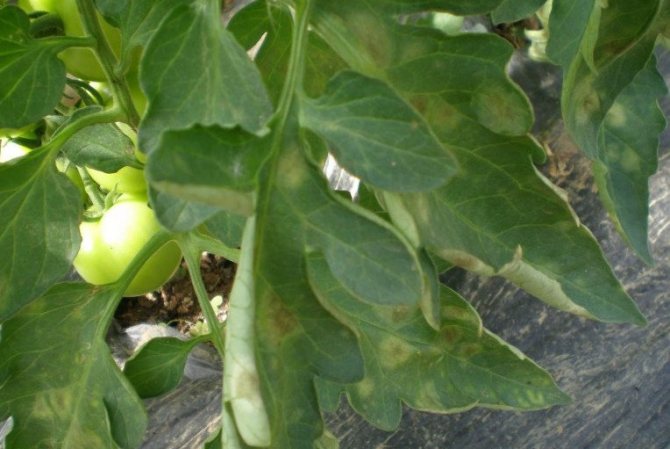
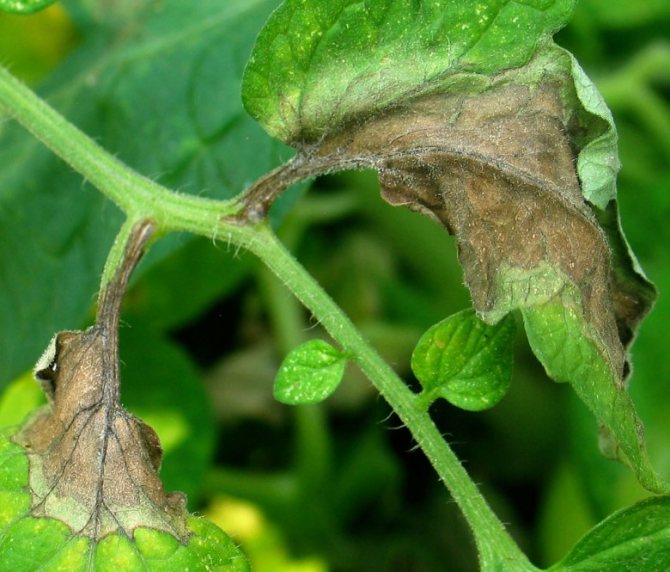
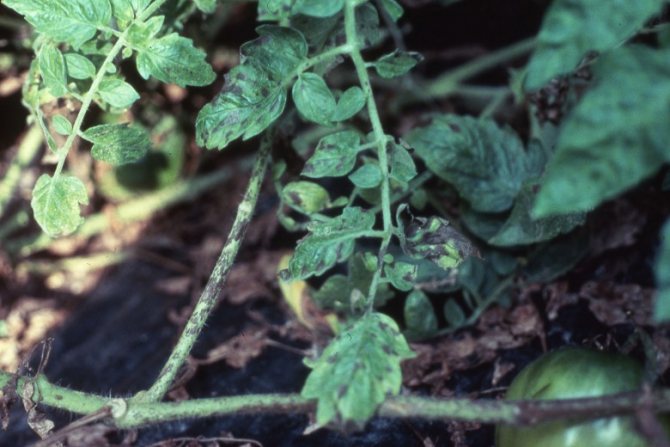
On the upper plate of the affected leaf, light specks of olive color appear. Chaotically located and few in number, they stand out little against the general background. This is the initial stage. A neglected disease is characterized by extensive brown spots on the leaves, with a silvery bloom on the back of the plate.
Cladosporium is often confused with late blight.... With late blight, on the outside of the leaf, rounded brown spots are immediately formed, scattered around the edges, after a few days the fruits are affected. The infection manifests itself anywhere in the bush and begins in August, when the temperature drops to 10⁰C.
How does olive spot develop?
A small speck forms at the point of introduction of the parasite. The more resistant the plant is, the smaller its size. A dense velvety formation forms on the back of the leaf at the site of the lesion.
As it spreads, cladosporia spreads over an ever larger area of leaves. Yellow-green spots merge, turn yellow and turn brown. Affected leaves dry up and die off. The disease moves up to the next tier. Mass infection leads to damage to flowers and ovaries. The taste of the fruit deteriorates.
Ways to fight
Various methods of controlling cladosporium disease are more effective at an early stage of the development of this disease.
Agrotechnical methods
- Reduce humidity if possible. Avoid over-watering, do not use sprinkler irrigation.
- It is very important to mulch the soil around the tomato. The disease starts from the lower leaves due to the moisture in the soil under the bush. It is good to use cut grass or hay. Under the mulch, in the form of white mold, a useful hay bacillus develops, which inhibits the development of cladosporiosis.
- Provide ventilation for the plant and its lower tier. You need to carefully break off the lower leaves and carefully place them in a bucket or plastic bag. Do not put the leaves in the compost; it is better to remove them from the garden or burn them. Next, carry out preventive treatment of tomatoes with copper-containing or biological preparations.
- To grow other crops and green manures on the site of the tomato bed over the next two years. Cereals and corn are ideal.
Folk remedies
They are ineffective for treatment. Well suited as a preventive measure.
- Add 3-4 ml of iodine to one liter of milk and bring to 10 liters with water.Spray generously on the lower layer of leaves, especially on the back. After 10 days, repeat the treatment.
- Make a natural preparation against fungus, which is additionally a microfertilizer. Collect weeds: nettle, quinoa, burdock. Chop finely, fill the bucket by a third. Add a glass of wood ash, cover with water and put in the sun. After 3-4 days, a strong fermented infusion is obtained. Dilute one liter of infusion in 10 liters of water. Process the tomatoes at least 3 times in July.
- Mix whey with water 1:10. Spray after 10 days.
Chemicals
If the plant is already heavily affected, fungicides cannot be dispensed with.... Before use, you must carefully read the instructions. Preparations suitable for the destruction of the fungus:
- Bravo;
- Ditan-neotek 75 EDC;
- Abiga Peak;
- Poliram;
- Captan;
- Tsineb;
- Kurzat R;
- Mancozeb;
- Consento.
Acrobat MC - local systemic fungicide... Valid for 2 weeks. It affects the fungus in a complex manner. Penetrates tissue and destroys the surface. Prevents the formation of spores.
Dilute 20 g of the drug in 4 liters of water. Prepare the working solution before use and store for no more than 3 days. Carry out processing in dry, calm weather. If the leaves of the middle layer are affected, repeat the spraying. The price of 20 g of the product is 40 rubles.
The Swiss drug Quadris is highly effective against cladosporium. For personal subsidiary plots, it is produced in ampoules of 6 ml, worth 68 rubles.
Biological preparations
The basis of biological products is made up of live microorganisms that destroy the pathogens of cladosporiosis.
The most common drug Fitosporin... Available in powder and soft plate.
Prepare stock solution: dilute 100 g of product in 200 ml of water.
- for prevention, it is enough to dilute 1 tablespoon of the prepared mother liquor in 10 liters of water;
- with the initial signs of brown spotting, the dose can be increased to 2 tablespoons per 10 liters.
Process the plants very carefully. Wet the lower leaves liberally from the inside. The droplets should be small, in the form of a fog. Spray once every 10-14 days. In humid weather, shorten the interval between treatments to a week.
Similar drugs: Trichoderma veride, Gamair, Alirin. Alirin and Gamair work well together and enhance each other's effectiveness.
Features of treating ailment in a greenhouse
In the open air, tomatoes are rarely affected by brown spot. Limited space, high temperature and humidity, and accumulation of condensation on the ceiling and walls create a favorable environment for the pathogen in greenhouses. To avoid high humidity it is necessary:
- The soil surface is kept practically dry. Tomatoes should be watered no more than once a week. The need for watering is determined by a slight wilting of the leaves.
- The greenhouse must be regularly ventilated.
- Maintain temperature no higher than 25⁰C.
- Carry out preventive measures.
We offer you to watch a video about the treatment of tomatoes for cladosporiosis in a greenhouse:
Prevention measures
It is impossible to create unbearable conditions for the mushroom while growing tomatoes, therefore preventive measures are very important to combat cladosporia.
The parasite develops well at a humidity of 58%, in a temperature range of 5⁰C-30⁰C, at a PH of 2 to 10, in any light up to 23,000 lux. At the same time, the oldest inhabitant of our planet is constantly mutating and adapting.
- Improving the soil. Composting and organic matter. The nutrient-rich, breathable soil grows stronger plants that can resist infection.
- Regular irrigation schedule, without overdrying and waterlogging.
- Crop rotation. Many bacteria and fungi live in the soil for years. To get away from cladosporiosis, you need to grow tomatoes in the same place no more than 1 time in three years. Other nightshades on the territory of the former tomato planting are not worth planting.
- Sowing cereals after harvest, better than winter varieties, leave them until spring.
- Regular processing of tomatoes with biological products from the seedling stage on the shelves.
- Soil cultivation.
- Thorough cleaning of areas from old debris and crops. Destruction of the remains of infected plants.
- Disinfection of walls, ceilings and frames of greenhouses with a pharmacyod.
- Selection of resistant varieties and hybrids.
- Soil solarization. In the hottest, sunny period of summer, place the infected area under a film for 6-8 weeks. For the fungus, prolonged exposure to bright daylight, more than 23,000 lux and UV radiation is detrimental.
Tillage
In autumn, carefully collect all old plant residues and destroy. Dig up the soil.
The most preferred way to improve the soil is to use drugs that contain beneficial microorganisms. Effective drugs Baikal EM-1 and Baikal EM-5... 3 weeks before the autumn frosts, the soil is shed with working solutions. Suitable biological products:
A teaspoon of the product is added to a bucket of water. Repeat the treatment in the spring. Biologics do not work well when the temperature drops below 15⁰C.
In advanced cases, chemicals are effective.... You can cultivate the soil:
- 3% Bordeaux liquid solution;
- 4% - copper oxychloride;
- 2% Oxychom solution.
Chemicals destroy not only pathogens, but also beneficial microflora. Therefore, it is worth resorting to their use only in extreme cases.
Disinfection of planting material
- Prepare a solution. Dissolve 1.5 g of dry Phytosporin powder in 100 ml of water. Let stand for an hour and a half to activate natural bacteria.
- Soak tomato seeds in Fitosporin solution for 2 hours.
Are there varieties that are resistant to the disease?
Varieties and hybrids that are resistant to cladosporium disease and, at the same time, according to reviews, have good taste:
- Our Masha;
- Vezha;
- Pink magic;
- Pink Paradise;
- Pink Bush;
- Delicacy;
- Ira (cherry);
- Paradisaic delight.
What to do with the seeds and fruits of diseased tomatoes?
The disease is not seed-borne. But spores of cladosporium persist for up to 10 months and can get on the seeds from the surface of the fetus. It is not recommended to use such seeds to avoid contamination. Fruits not directly affected by cladosporium do not pose a health hazard.
Gardener Tips
- Do not thicken the tomato planting in the greenhouse. Form plants into one stem.
- Disinfect the frame and the inner surface of the greenhouse with Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate.
- Freeze the soil in the greenhouse in winter. To do this, open the doors and remove the side walls, if possible.
- Once a year, disinfect the greenhouse with a sulfuric checker.
- Grow only genetically resistant tomato varieties.
- Use biological products at all stages of growing, starting with seeds.
It is not easy to get rid of cladosporiosis. But if you use the entire arsenal of available tools and measures, you can restrain its development and grow a full-fledged crop. The most important thing is prevention and early diagnosis.
What varieties of tomatoes are resistant to cladosporium disease and how is the disease treated?
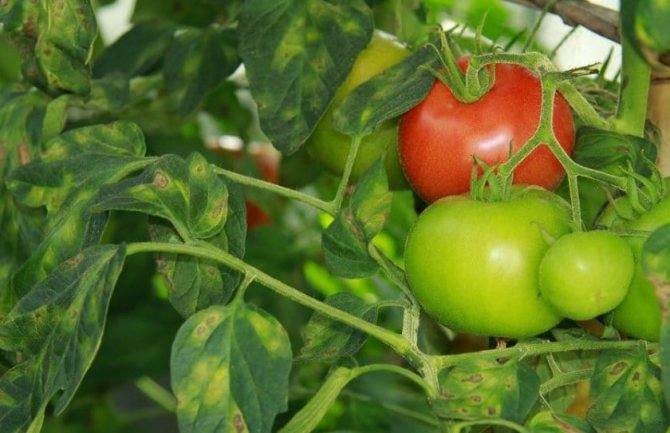
Cladosporiosis of tomatoes is a fungal disease of plants that develops mainly in greenhouse conditions. Brown spotting of tomatoes appears as small yellow-brown spots on the leaves of the plant. Then the spots can go to the stem. In the affected areas, there is a violation of the process of photosynthesis. As a result, the fruit does not receive the necessary nutrients, which affects its taste and nutritional value.
Treatment of tomato cladosporium disease takes a long time, since fungal spores can be transmitted from one plant to another through watering and carried by insects. The disease most often occurs in areas where the correct crop rotation is not observed.
In addition to the aforementioned, brown spotting of tomatoes is characterized by other features:
- The disease manifests itself first on the leaves of the lower layer.
- Light yellow small spots may appear on the outside of the leaf. Then they increase in size, darken and turn reddish-brown.
- After the appearance of spots, a gray or brownish velvety coating forms. In this plaque, fungi settle, so the disease spreads.
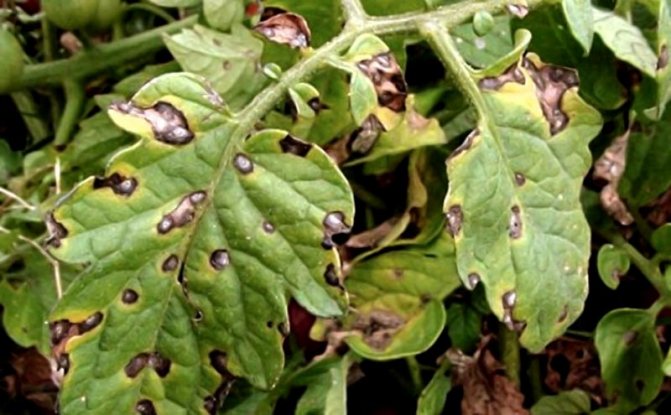
- With a severe form of the disease, tomato leaves begin to dry out and curl, and subsequently simply disappear.
Cladosporium disease in tomatoes is caused by a fungal pathogen. Its particles - conidia - are unicellular organisms of a round or oval shape, located in the tissues of the stem and other parts in bundles. In greenhouse conditions, spores can live up to 10 years due to the ability of the microorganism to evolve.
At the same time, if tomatoes resistant to cladosporiosis are grown together with already affected hybrids, mutation of the harmful gene is possible: later it will be able to infect previously unresponsive species.
As mentioned earlier, spores can be spread by water, air, people and animals.
The harmful gene is viable for one to two months, and its conidia may remain in the soil until the next planting season. For ten months, fungal organisms are able to survive in conditions of low temperatures and low humidity.
Fruit resistance is the dominant trait inherited from one plant to another. Genetic engineering has identified 24 such dominant genes to date. At the same time, the pathogen is also capable of mutating, and today there are already more than eight varieties of the pathogen.
As a result of mutation of the pathogen, two genes - Cf1 and Cf3 - have already lost their resistance to the pathogen. Therefore, today breeding work is carried out with the dominant genes Cf2, Cf9, Cf4, Cf6.
There are species that have several genes for resistance to harmful fungi at once. However, when planting bushes that do not have this property, additional use of fungicides may be required.
The main question that interests all gardeners is how to deal with brown spot on tomatoes.
The main measures can be summarized as follows:
- Since the most favorable conditions for the development of the fungus are the air humidity of more than 80 percent and the air temperature from 20-25 degrees, it is necessary to change these parameters in the greenhouse.
- It is necessary to frequently ventilate the greenhouse.
- To avoid the spread of spores from diseased to healthy bushes, it is enough to reduce the intensity of watering.
- Old and stained leaves must be removed in a timely manner.
- To destroy the infection, you can steam and disinfect the soil with special means.
All agents used in the treatment of fungal infections can be divided into chemical and biological. Among the chemicals used are: Abiga-Peak, HOM, Poliram. Biological remedies include Fitosporin-M.
Brown spot of tomatoes can be cured not only with fungicidal agents, but also with folk remedies.
Basic folk recipes:
- Sprinkle the stems with a solution of iodine chloride. Pour diluted iodine into the soil to a depth of 10 centimeters.
- Dilute milk whey with water and treat all necessary areas with the resulting liquid.
- Prepare a tincture from 500 g of garlic arrows or the same number of cloves and one bucket of water. Add 20-30 drops of iodine solution to it and start processing.
- Add 500 ml of milk and 20 drops of iodine to five liters of water. With the resulting product, process the greenhouse and soil.
- You can prepare two tinctures at once and spray the soil and vegetation alternately. To prepare the first, dissolve potassium permanganate in water.For the second tincture, boil 300 g of ash for 25 minutes, and dilute the resulting broth with 10 liters of water.
- The soap solution added to the soil, due to the potassium content in its composition, also kills fungal organisms well. However, this method is best applied before planting.
In order to avoid the reappearance of the disease after chemical or biological soil treatment, you can plant hybrid varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to fungal diseases. These include:
According to people's reviews, some vegetable hybrids are completely resistant to cladsporium disease. Breeders are constantly on the lookout for new varieties that are resistant to newly emerging types of fungus.
In the new planting season, agro-industrial companies offer a number of new varieties, including:
- Casper. The plant is resistant to fungi, the bush is tied quickly, the tomatoes are oval in shape. The average weight of a ripe fruit is 100 grams.
- "Brother". The variety yields a harvest within 60-70 days after germination, it is grown indoors. The bush is very compact, grown at home in small pots. Weight - 50 gr.
- "Gigantissimo". Possesses high resistance to the pathogen, the weight of a mature vegetable often reaches almost one and a half kilograms. The bushes are tall and spreading (height - 180 centimeters). The ripening period is 80 days from the moment of disembarkation.
- "Terek". The hybrid is early maturing, grown indoors. The ripening period from the moment of planting is approximately 90 days, the weight of a mature vegetable is 15-19 grams. The fruit has a juicy sweet taste.
- "Pepper". The fruits are oblong, reminiscent of bell peppers. The height of the bush is up to one meter, the ripening period is 100 days from the moment the first shoots appear. The weight of a ripe tomato is 70 g.
- “Red red”. The hybrid is one of the most disease resistant varieties. Each brush yields 6-7 vegetables. The mass of a ripe vegetable is from 200 to 500 g.
- "Curiosity". The fruit looks like a cherry variety. The mass of one mature vegetable is 20 grams, it has a red-brown color. They ripen best in greenhouse conditions. The fruiting period is June-October.
- "Red Guard". Ripens quickly, the first crop can be harvested at the beginning of summer. Fleshy fruits, weighing from 150 to 300 g.
Proper care of plants and adherence to planting techniques will help protect the crop from fungal diseases. If the spores of the fungus still managed to penetrate the soil, in the early stages of the development of tomato cladosporiosis, it is recommended to use folk methods of struggle. In more severe cases, it is necessary to resort to the use of fungicides. To prevent the further appearance of the disease on new plantings, it is recommended to choose the above varieties with a dominant gene.
Cladosporium disease in tomatoes: causes of the disease and treatment methods
Among the diseases affecting tomatoes, one of the most common is cladosporiosis. This disease is quite difficult to cope with, since the fungi through which it spreads can withstand both severe frost and drought. That is why it is worth taking preventive measures in a timely manner in order to save the harvest.
What is tomato cladosporium disease
Brown spot is a disease that appears on the leaves of a plant. However, it can infect flowers and young shoots that are only set. More often this disease affects vegetables growing in greenhouses.
The disease is spread through the fungus Cladosporium fulvum Cooke. They retain the ability to survive for 10 months, and are also able to hibernate in the ground. After wintering, new young seedlings are infected through the infected soil.
The plant pathogen is light dust, so it can be carried by clothing or shoes, gardening tools, soil, or even a gust of wind.Thus, tomato infection can occur in many ways, even without negligence on the part of the gardener.
With an increase in humidity, the conidia of the fungi come to life and the disease manifests itself. This occurs at the beginning of flowering and fruit formation. Somewhere in the middle of summer, yellow spots appear on the leaves of the tomato, which can already be seen. In the future, they acquire a brown tint. When the leaves begin to fall off, the plants will lose their ability to photosynthesize, which means that the formation of fruits will slow down. If you do not take any action, then gradually the disease will progress, and in the last stages it will directly affect the fetus.
One bush affected by brown spot is capable of infecting all the others. Therefore, if a disease is detected, treatment should be started immediately.
So that the course of the disease does not affect all tomato seedlings, it is necessary to identify cladosporium in the early stages. To do this, you need to find out exactly how it manifests itself.
Symptoms and external signs
The external signs of brown spotting in tomatoes, which appear one after the other, respectively, include the following:
- The disease begins to manifest itself in the middle of the growing season. The leaves of plants begin to become covered with spots of various shapes and sizes. At first, they are usually small and highlighted in yellow. On the inside of the leaf, something similar to a bloom of a light gray hue appears.
- Then the disease begins to progress, spreading to an ever larger leaf area. Gradually, uninfected leaf plates no longer remain on the seedlings. But the stems and fruits have not yet been affected.
- Then the spots turn brown, in full accordance with the name of the disease. On the reverse side of the sheet, this color is especially noticeable. This is the germination of the conidia of the fungus - the carrier of the infection. Leaf blades, drying, curl and die off.
- The plant begins to wilt, as the process of photosynthesis, which provides oxygen, is disrupted. A plant that has lost its leaves can no longer be saved.
- Tomato fruit can also be affected by brown spot, although this is rare.
Causes of the spread of the disease
The main causes of cladosporiosis include the creation of conditions for the development of conidia of the fungus: high humidity and temperature. Greenhouses fall under these criteria.
Already at an air humidity of 80%, the infectious agent is capable of vital activity. At a temperature of + 25 ° C, together with high humidity, optimal conditions are created for the spread of the disease.
This is relevant if tomatoes that were already infected were planted in greenhouses before the new planting, or the soil was not fully cultivated after the transferred cladosporiosis.
Disease spores are especially dangerous. The range of possible sources of infection is wide, and the fungus itself is tenacious. Therefore, to prevent the spread of brown spot, the soil should be carefully cultivated after the previous harvest.
The causative agents of the disease can change. Even if we are talking about resistant varieties of tomatoes, they can become infected with a new strain of the disease.
Cladosporiosis treatment
Methods of dealing with the disease can be divided into groups: folk remedies, biological and chemical preparations.
Folk remedies
Iodine and milk have proven themselves well. The proportions are as follows: for 0.5 liters of milk, you should take 15 drops of pharmaceutical iodine. Add the resulting solution to 5 liters of water and spray the plants. Tomato leaves must be carefully processed from the underside.
Iodine chloride is actively used in the fight against disease. Its solution is sprayed from a spray bottle not only on the leaves, but also on the soil. Thus, the soil will be disinfected. The depth of penetration of the medicinal solution should be at least 10 cm. The composition of the mixture for treatment includes 40 drops of iodine and 30 drops of potassium chloride.
Another remedy in the fight against brown spot is a solution made from potassium permanganate with the addition of a decoction made from ash.
This medicine is valuable in that it cannot cause any harm to health. Even during the ripening of the fruit, this solution is safe for humans.
The product is prepared as follows: boil about 300 g of crushed ash in a small amount of water. Hold on the stove for 20 minutes and dissolve the resulting medicine in 10 liters of water. Potassium permanganate is diluted so that the liquid is slightly pinkish.
When processing tomatoes, it is advisable to alternate funds, using the first week - one, and then another 7 days - another.
Another effective method in the fight against cladosporiosis is the use of milk whey, which is dissolved in water in a 1: 1 ratio.
Folk methods are recommended to be used at the beginning of the manifestation of cladosporium.
Biological agents
This category is either safe or less hazardous than chemicals. This is due to the fact that such drugs have an effect on the surface of the plant, without penetrating inside.
Biological agents are washed off by rain or during irrigation, which is why it is better to carry out the treatment in clear weather so that the work is not in vain.
The following substances are used:
- The drug "Fitolavin 300", harmless to tomatoes. Use by diluting 20 ml of the product in a bucket of water and spray on the affected plants.
- "Strobi" - is a fungicide, but does not harm animals and insects. Not completely safe, but less harmful than other chemicals. You need to use it strictly according to the instructions.
- Another medicine of biological origin useful for brown spotting is "Fitosporin". The drug is used at the rate of 5 g per bucket of water
- Another remedy is Pseudobacterin-2. It is able to fight many diseases, it is used according to the instructions.
Chemicals
If traditional and biological methods for treatment were in vain, then you should go to chemicals.
Fungicides are one of the widely used agents. These drugs are broad-based. These include, for example, "Bravo", "Hom", "Tsineb" or "Neo Tek".
Chemicals are powerful. Therefore, the solution must be prepared strictly according to the instructions, not exceeding the recommended dosages. Otherwise, you can burn the tender leaves of the seedlings.
It is recommended to carry out 2 treatments with fungicides. The first time this is done to destroy infected leaves. The second time, you need to carry out the treatment after a couple of weeks to get rid of the remaining spores that are carriers of the infection.
A mixture of polycarbacin, copper sulfate, and colloidal sulfur has proven itself well. To prepare the medicine, you need to stir about 3 tbsp in 10 liters of water. l. sulfur and 1 tbsp. l. polycarbacin and copper sulfate.
If the cladosporium is at an advanced stage, then it is worth adding in addition to this solution, another liquid soap.
The resulting product is used to treat the seedlings, carefully spraying them on the underside of the tomato leaves. It is advisable to spray and soil to kill the infection.
Cultivation of the land after a disease
In order to prevent the further spread of infection after the tomatoes have had brown spot, the soil should be disinfected. After all, carriers of the disease could remain in it.
Antifungal agents are used to destroy the pathogens of cladosporia. Biological ones are the safest ones. One of the most effective is trichodermin. It is used for soil for seedlings, as well as for steamed or sterilized soils. It is permissible to use the preparation in planting holes.
If the soil is not cultivated, the chances are increased that the next year the new seedlings will also suffer from cladosporiosis.
Another way to cultivate the land is to use the Fundazol solution. Copper sulfate and potassium permanganate are also used.
When using "Fundazol", you should read the instructions, since the drug is used strictly in the recommended doses. Otherwise, when applied to the soil in high dosages, a toxic effect may appear.
Preventive measures
Although the external signs of cladosporia are easy to discern with the naked eye, it is necessary to carry out prophylaxis of the disease in advance so that the harvest does not suffer in the future.
Prevention of cladosporiosis includes:
- Destruction of infected plant residues that have survived the disease. It is best to burn any infected stems, leaves, and other debris.
- If the tomatoes were grown in greenhouses, then it is imperative to carry out special processing. It lies in the fact that after harvesting, all the components of the greenhouse are disinfected with Bordeaux liquid. Then the room is fumigated with a sulfuric checker. The surface of the earth is disinfected, or simply removed, replacing with a new layer.
- Soil processing after plants that have undergone diseases.
- Compliance with the rules for planting tomatoes: avoiding overcrowding of seedlings, adherence to the feeding schemes recommended for each variety.
- Compliance with modes of optimal humidity, as well as temperature. It is especially important to regularly ventilate the areas where the plants are located.
Additional measures include the processing of seedlings during the ripening period with the help of "Effecton-O". The drug is sprayed on plants, having previously diluted 2 tbsp. medicines in 10 liters of water. So the immunity of tomatoes will increase.
Brown Spot Resistant Tomato Varieties
Among the variety of tomatoes, you can choose varieties that are not initially prone to this disease. They are divided according to the place of cultivation.
Tall varieties are more suitable for greenhouses:
- Pink Paradise F1. Mid-season tomatoes with a bountiful harvest. The tomatoes themselves have pink flesh, weigh up to 150 g.
- Marissa F1. They are distinguished by increased productivity. The fruits weigh 150 g.
- Spartak F1. Mid-season tomatoes.
- Opera F1. The variety is mid-season, the fruits weigh about 100 g.
Charisma F1 can be attributed to stable average height. The variety is resistant to low temperatures, and also gives an excellent harvest. The fruits weigh about 150 g.
Suitable undersized varieties include Bohemia F1. It does not bear especially many fruits, but it can withstand the vagaries of the weather very steadfastly and is unpretentious in its care.
Suitable for open ground:
- Red arrow F1. Differs in fast ripening of fruits.
- Our Masha F1. Medium early and unpretentious variety in care. The fruits are fleshy, weighing from 150 to 180 g.
- Titanic F1. Medium early tomatoes. The fruits are large and fleshy.
- Fast and Furious F1. Early variety. The fruits weigh about 150 g.
- Crunchy F1. The tomatoes are yellow and have a melon aroma. The consistency of the tomato is crispy.
For areas with unfavorable weather conditions, resistant hybrid varieties are suitable:
- Olya F1. Early variety. Resistant to heat and low temperatures.
- Ural F1. Differs in large tomatoes. Resistant to frost.
- Vologda F1. Mid-season, disease-resistant variety, with small fruits.
Brown spot disease in tomatoes, with timely treatment measures, may well be cured, and the crop will be saved. It is also very important to observe preventive measures to prevent the spread of cladosporiosis and closely monitor the growth and development of tomatoes.
Cultivation of the land after a disease
For soil disinfection, there are various antifungal agents. The safest of them are biological agents. The most popular is Trichodermin. It is used in soil cultivation for growing seedlings, for sterilized or steamed soils and directly into the holes.
In order to increase the effectiveness of the drug, soil mulching is practiced on tomato plantings. Apply according to the instructions.
The soil is also spilled with solutions of "Fundazol", copper sulfate or potassium permanganate.
Final part
Using various methods of combating cladosporia, you need to remember about safety precautions, especially when fungicides and other toxic drugs are used. It is preferable to choose a method of treatment with folk remedies, but if you still had to use chemistry, you need to carefully study the instructions for use. When treated with chemistry, adult plants will absorb some of the chemical components in any case.
In order not to poison your loved ones, you need to wait at least 3 weeks before eating processed fruits. For processing, only broad-spectrum fungicides should be used. It is important to observe safety precautions during the processing itself. If infected plants are found, it is best to immediately destroy them, and treat healthy bushes with a manganese solution.
Varieties of therapy
It is better to start treatment of the disease at an early stage, then there is a very high probability of maintaining the yield and getting rid of the fungus completely. When the humidity drops to 60%, new symptoms of the disease appear rather rarely. It is better, of course, to choose hybrid tomato varieties that are resistant to fungal infection for planting in greenhouses. The methods of struggle involve several types of treatment:
- agrotechnical;
- folk remedies;
- using chemistry.
Treatment methods should be selected depending on the variety. Even the most resistant tomato varieties are not susceptible to a particular strain of cladosporium disease. You need to start fighting the disease when you find the first symptoms. To a large extent, the spread of tomato disease is influenced by the correct care of crops; without favorable conditions, disputes will not germinate. First of all, you should remove the affected leaves or plants completely, and also change the strategy of caring for them so that you do not have to use fungicides in the future.
Agrotechnical method
Agrotechnical methods of control involve the removal of all affected leaves, frequent ventilation of the greenhouse and a reduction in the frequency of watering. Plants need to be watered about 1 time per week. To reduce the risk of the spread of the fungus, you need to cover the soil between the plants with dark plastic wrap, and also remove all leaves on which the borax is visible.
Infected leaves must be removed with extreme care to prevent contamination of surrounding plants. To do this, take a plastic bag and carefully put it on the affected area, and then pinch off. Ideally, the affected plant should be removed completely and burned to prevent the spread of spores. The thing is that the spores of the fungus are very similar in appearance to dust, and when they get on the leaves, under favorable conditions, they begin to actively germinate, blocking the processes of tomato photosynthesis.
Traditional methods


You can fight the disease with folk methods
To fight the disease, if the previous method did not fit, you can use folk remedies. Such methods are much safer than using fungicides, but their effectiveness will depend on many aspects. Tomato cladosporium has been terrorizing gardeners for many years, so people have long learned to fight it. One of the most common methods of fighting folk remedies is watering and spraying with an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate. The watering solution should be pale pink in color.
The most versatile remedy is garlic. He is good in the treatment of human diseases and will help plants effectively get rid of fungal infections. To prepare the solution, you will need: 0.5 kg of garlic, 30 drops of iodine per 10 liters. water.With such a composition, it is necessary to process all bushes, both affected and healthy. Treatment should start with healthy plants.
In combination with watering and spraying with potassium permanganate, it is recommended to use parallel watering with ash decoction. 10 liters. water you need to take 300 g of ash and boil it for 15 minutes. An effective remedy is considered baby or laundry soap, which should be added in a small amount to water for irrigation and spraying.
Chemical Compositions
If the fight against cladosporiosis turned out to be in vain, you will have to resort to radical methods and use fungicides - chemical preparations of a wide spectrum of action. One of these drugs is Bravo. The treatment started on time gives great efficiency, that is, when there is a possibility of infection, the drug should be introduced, even at the planting stage, when the infection has not yet occurred. If the drug is used at a time when the symptoms of the disease have already begun to appear, then precautions must be taken because the drug has a rather high toxicity for animals, bees and birds, it is also prohibited to use fungicides of this type in the immediate vicinity of water bodies.
The dosage of the drug is calculated depending on the area of the planted crops. Another effective drug for getting rid of fungal disease is Ditan Neo Tek. It belongs to a wide spectrum of fungicides. Shows the greatest efficiency when treated before infection with a fungus. It is important to observe the interval between treatments in 7-10 days, so that there is no infection of the new growth.
The presented fungicides of the new generation continue their action, even after precipitation, the main thing is that after processing, moisture does not get into the ground for 3-6 hours. Processing should be carried out after the plants have dried out from dew or precipitation. Prevents the emergence of resistance in pathogen strains. For the treatment and prevention of the disease, several more drugs can be used:
- Pseudobacteria 2;
- Phtosporin;
- Abiga Peak.
For all the effectiveness of drugs, fungicides are quite toxic. This method is not suitable for everyone, so many gardeners are trying to cope with the disease with folk remedies. The main measure to combat the disease is timely prevention and proper care.