Why does a cow's udder swell
Prenatal and postpartum edema occurs due to changes in hormonal levels, insufficient movement of the animal and the presence of a large amount of acidic feed in the diet of the cow. If the edema has arisen in a different period of time, then the reasons for a hard udder can be:
- kidney problems;
- diseases of the heart, blood vessels and circulatory system;
- excess of salts, potassium, magnesium in the diet;
- lack of food with coarse fibers;
- bite, trauma, contusion.
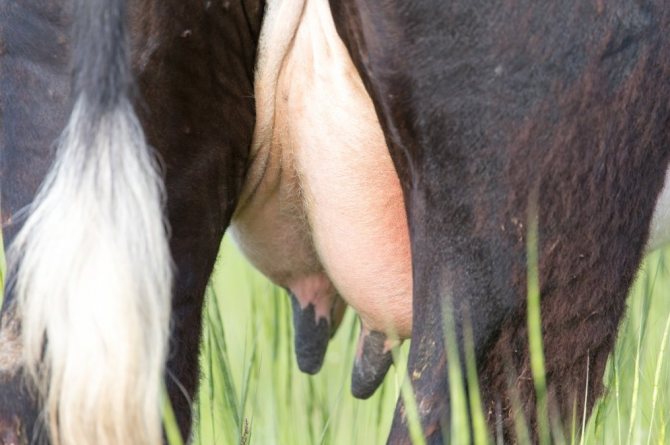

The causes of serous (congestive) edema include impaired blood and lymph flow during pregnancy and after calving.
To graze separately from the herd
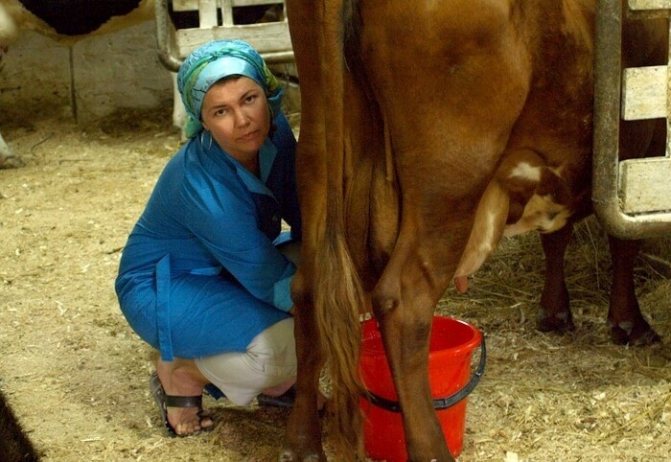
If the swelling of the udder has not gone away within 4-5 days after calving, intensive treatment should be started. To restore skin elasticity, massage with pihtoin ointment is performed. 7-10 grams of calcium is added to the feed every day. To remove excess fluid from the body, use disalunil or urodiacin, following the instructions.
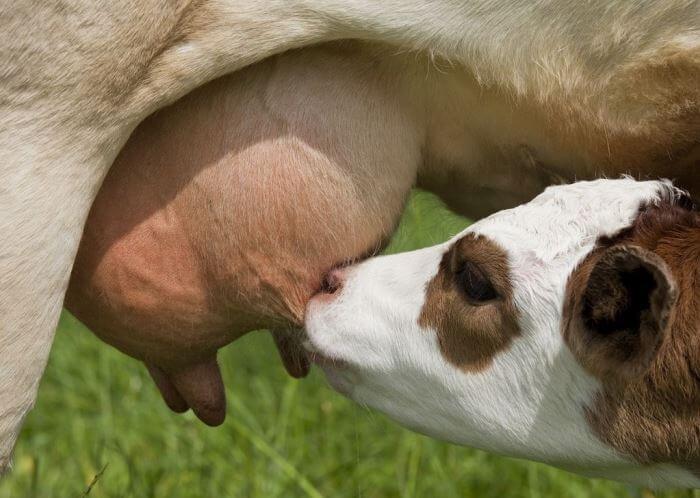
Results should be visible five days after using these treatments. If they are not there, then there are stagnant areas in the udder. This type of edema is called serous, which indicates inflammation of the connective tissue layers and the further development of the disease. The main help is frequent milk withdrawal and massage to restore blood circulation. Calves sucking milk have a beneficial effect.
You can then use the mixture to lubricate the nipples before you start massaging them. The direction of movement is from the udder to the abdomen.
External signs
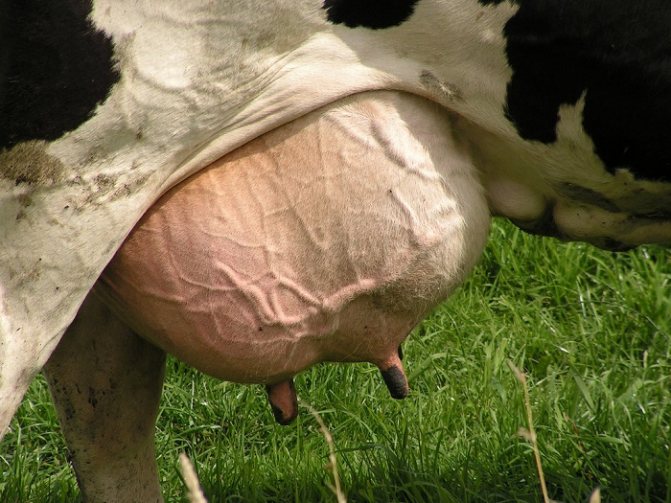
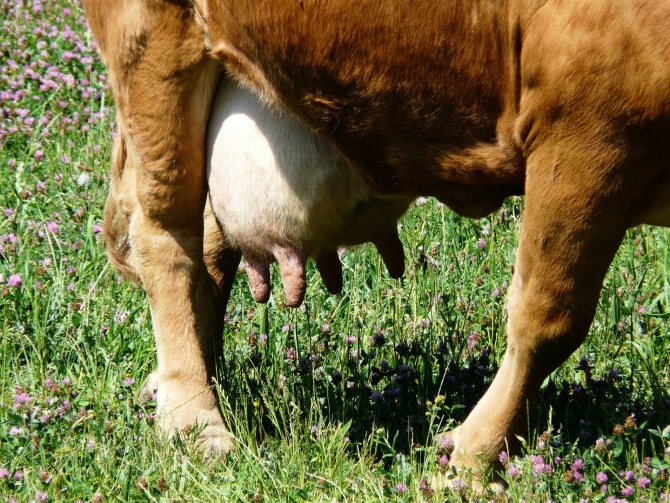
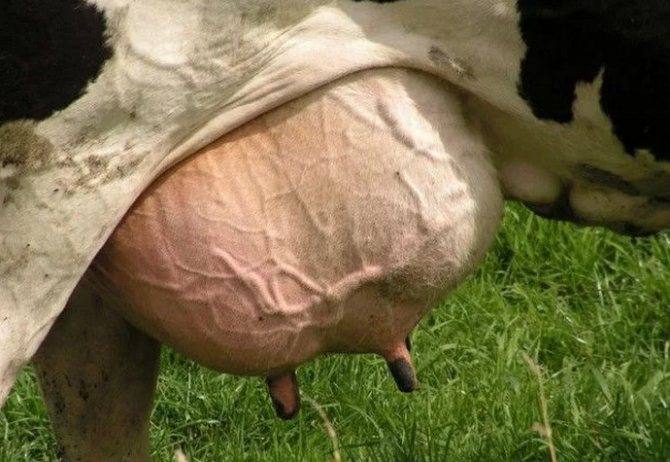
Timely solution of the problem minimizes the loss of milk production of the cow or can completely reduce them to zero. Therefore, it is very important for farmers to monitor the condition of their cows in order to understand in time why the changes are taking place after the first symptoms are detected. Signs of udder swelling are:
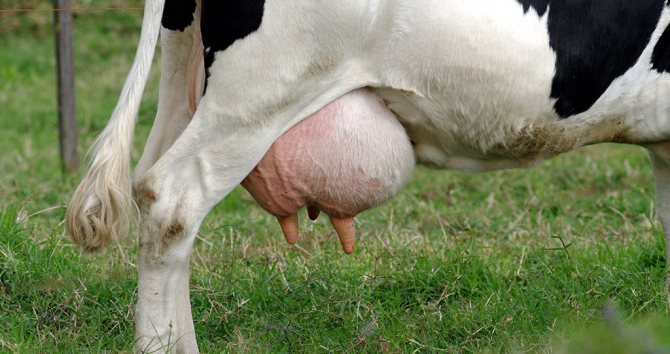
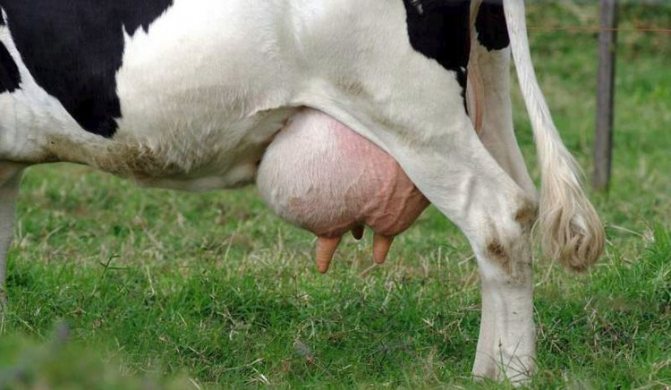
- an increase in the size of the organ;
- thickening of the skin and the appearance of dents after pressing on the organ;
- the udder in the place of edema feels like dough to the touch;
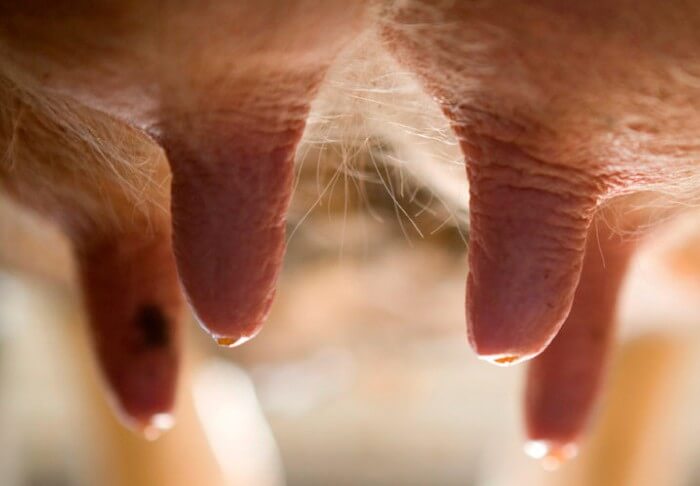
- shortening of swollen nipples;
- tension and tension of the skin on the mammary glands, the appearance of a shiny bluish tint;
- sometimes more watery milk and a gradual decline in milk yield;
- the animal does not have a painful reaction to organ palpation.
Did you know? In order for a cow to produce 50 liters of milk, she is forced to pass 25 thousand liters of blood through the udder.
Symptoms
Signs by which you can determine the disease:
- Udder enlargement.
- Organ deformation.
- One back or front nipples are shorter.
- Dough-like structure of the udder (when pressed, a dent remains, which does not disappear for a long time).
- The organ is cold to the touch, the skin is pale.
- Milk from a sick cow is watery.
Important! In severe cases, the swelling turns into mastitis.
Treatment of udder edema in cows
When a farmer notices a change in the udder of a cow, he immediately gets the idea of how and how to treat the animal. But don't panic right away. Perhaps nothing critical happened. It is necessary to compare all the facts. If changes occurred before calving (shortly before) or after, then a few days after delivery everything should go away on its own.
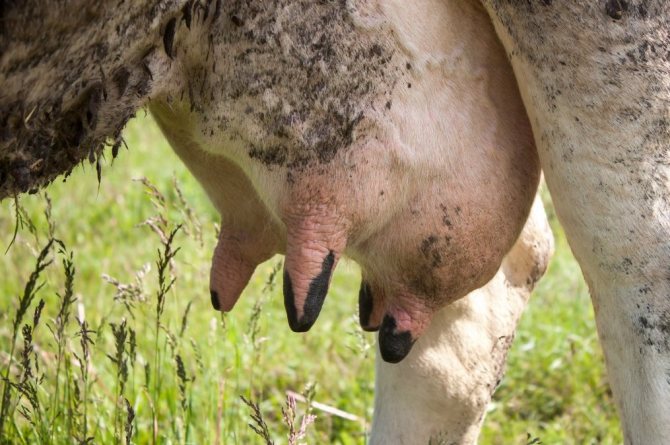


It will be enough just to correct the diet and increase the mobility of the cow, as well as to carry out milking in a timely manner. If the swelling does not disappear and even increases, or the reason for its appearance is not related to pregnancy, then treatment should be started.
Diet changes
In any case, regardless of the cause of the onset of the disease, the animal's diet first of all changes. High-calorie, juicy feeds are excluded from his menu, less salt, concentrates, protein supplements are given. The diet is based on high quality cereal hay. The menu should be individual.
Important! It is impossible to take a sick animal to pasture in a common herd.
Physiotherapy
In order not to stagnate milk and cause mastitis, it is necessary to milk the cow 5–8 times a day at the same time interval. If the swelling appears during the pregnancy period, then milking should be done once a day. If the udder sags heavily due to edema, it is advisable to support it with a special bandage.
Light massage helps to relieve swelling. It should be carried out without ointments several times a day. With smooth movements, the mammary glands are rubbed from the bottom up.
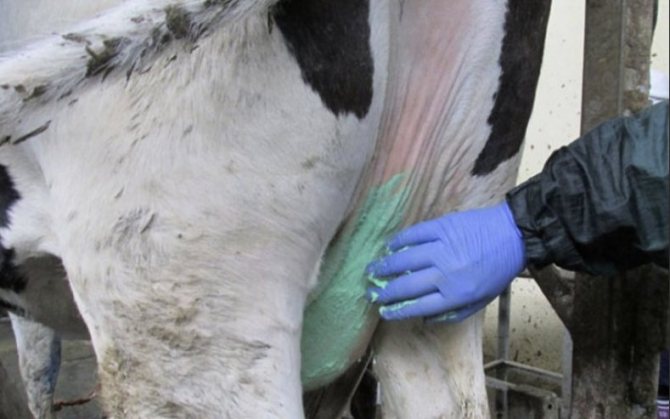

For warming, paraffin compresses and ozokeritotherapy are used. It is extremely rare to treat with ultraviolet and ultrasound.
Medicines
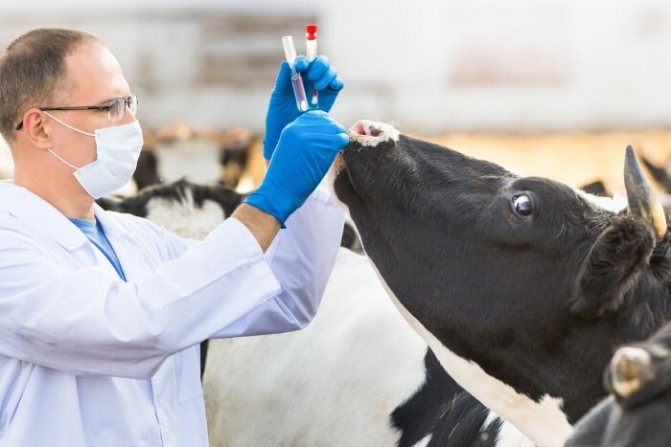
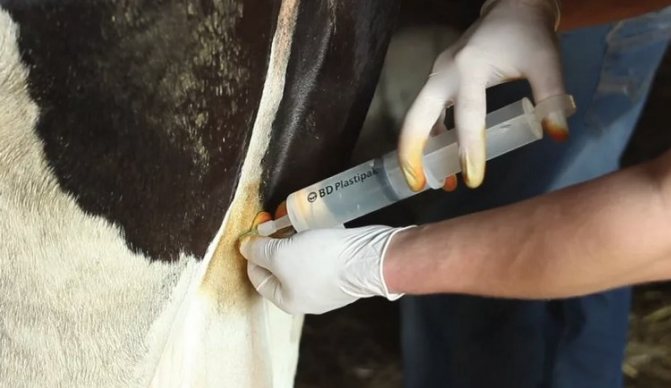
Drug therapy is usually rarely used, mainly if the edematous process is delayed and changes in the diet did not give the desired result. To begin with, they seek help from a veterinarian. He will tell you what to do after diagnosing, and will write down the dosage of the necessary drugs. As a rule, they apply:
- calcium chloride or gluconate (intramuscular injection to normalize blood flow);
- caffeine benzonate solution 20% (subcutaneous injection supporting the nervous and cardiovascular systems);
- dexamethasone (intramuscular injection for bites);
- ointments (Rigefen, Pikhtovitin, Troxerutin in order to relieve edema).
Important! Drug therapy is carried out only after calving.
Folk ways
Traditional medicine is more often used in the early stages of the development of the disease or in combination with drug therapy to accelerate the arrival of a positive effect. As a diuretic, infusions and decoctions are used:
- juniper berries - 50-100 ml, birch buds - 10-40 ml, field horsetail - 15-30 ml;
- on a bucket of boiling water 15-20 tbsp. l. insist dill or fennel for three hours and drink 1-2 buckets a day for three days;
- if the edema is prolonged, then the dill broth is given for 10 days.
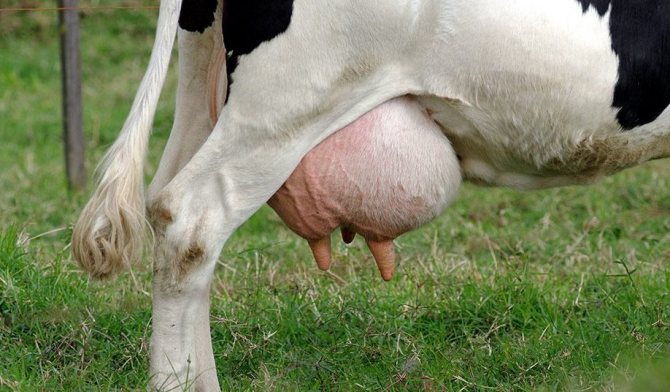

You can prepare ointments and lotions yourself.
- Recipe number 1: 1 tbsp. vegetable oil, 40 g of paraffin or beeswax, mix in a water bath, cool.
- Recipe number 2: 2 tbsp. l. potato starch, 1 tbsp. l. mix vegetable oil to a creamy consistency.
- Recipe number 3: Rice starch is diluted with water to a state of thick sour cream and, putting it on cheesecloth, is applied to the swollen area for three to five hours.
- Recipe number 4: Milk, rye flour, butter. The amount of ingredients is determined by eye. You should get a cake that can be applied to the swelling for two to three hours.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of a life-threatening disease in animals, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of asepsis and antiseptics when performing various manipulations:
- surgical intervention;
- castration;
- trimming the tail;
- ear circumcision;
- removal of horns;
- a haircut.
All wounds must be treated with antiseptic drugs in order to avoid their contamination and the development of a pathological process in the damaged area. It is also important to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene. To prevent the development of malignant edema, it is imperative to perform antiseptic treatment of hands and instruments, helping the animal during labor or treating lesions on the skin.
If the birth of a cow is too difficult, the discharge of the placenta is delayed, the doctor prescribes intramuscular injections of antibacterial drugs. The genital tract is irrigated with concentrated disinfectants. The procedures are performed only after the appointment of a doctor.
Those rooms in which sick animals were kept, as well as equipment and all items must be sterilized.
Edema in primiparous cows
Edema in primiparous cows is not much different from those who become pregnant not for the first time.
Udder edema in first-calf heifers after calving
We have already said that the occurrence of udder swelling after childbirth is quite normal and, if all the rules for caring for the animal are observed, it is not fraught with serious consequences. If you start it, then the immune system of the cow begins to weaken, so the animal can easily pick up any disease. Also, advanced edema leads to mastitis, and if the birth process was complex, then more serious problems may arise.
Did you know? Pregnancy in cows lasts as long as pregnancy in humans - 9 months.
Postpartum edema in first-calf heifers is relieved by frequent milking (two hours apart) and intense but gentle massage. You need to continue the procedure for 2-3 days. Then, when the swelling has passed a little, switch to milking four times a day. If the udder greatly increases in size, then it is necessary to apply ointments.
Swelling in heifers before calving
Nature has laid down an increase in the size of the udder in pregnant cows 2-3 weeks before delivery. The reason for this is low mobility and improper diet. It is enough to increase the duration of absenteeism, and adjust the diet. If the mammary glands have greatly increased in size and prevent the animal from standing normally on its feet, it is necessary to give less water, exclude juicy and combined feed from the diet, and apply a supporting bandage. After calving, the swelling should go away on its own.

Prophylaxis
Compliance with the recommended parameters for keeping and feeding cows is considered as preventive anti-edema measures. An animal free from a leash will not suffer from adynamia. If the recommended zoohygienic parameters are observed, the cow is provided with a full exercise, dry clean bedding, and a moderate content of harmful gases.
The main preventive measure against diseases of the udder and genitals is the correct organization of feeding during dryness, as well as during the transition period, limited to three weeks before and after childbirth. Timely launch, two months before the expected date of calving, ensures the renewal of the udder tissue, its preparation for the new lactation.
In addition to reducing the number of milking, the cow is provided with a special diet. In the wild, ruminants calved in early spring, when there was no grass in the pastures. Therefore, they ate dried up vegetation. This approach is also justified for farm animals. Therefore, the cow is deprived of succulent feed and concentrates and transferred to hay. It should be cereal to prevent excess protein and calcium. Three weeks before the expected birth, the microflora of the proventriculus begins to prepare for the upcoming lactation - to introduce concentrates, protein supplements, silage or haylage in small quantities.
It is necessary to pay increased attention to the quality of feed. Check the food of cows for the content of microtoxins, prevent violent fermentation in the rumen by pretreating the grain - by crushing or extruding it.


Feed intake by the cow is constrained by rumen pressure on the calf. And after giving birth, the animal's appetite will be poor for a long time. This time due to the pressure of the scar on the uterus that has not recovered from childbirth. Therefore, dietary changes must be made gradually.A cruel joke with livestock breeders can play literal adherence to the norms of feeding from reference books. A pregnant cow needs one diet, a lactating cow needs another. But a cow is a ruminant animal, its microflora needs a gradual change.
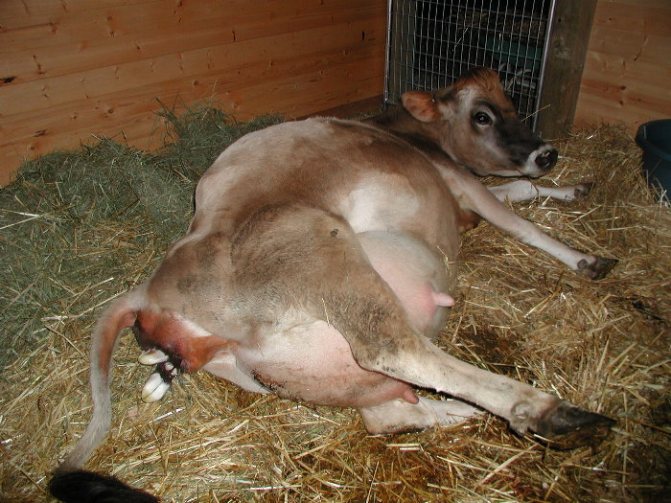
After calving, the cow has swelling on the abdomen
It is also normal for a cow to develop swelling on the belly after calving. Most often it occurs in highly yielding individuals. Such animals are limited in liquid and succulent feed. You can additionally apply decongestant ointments. After a few days, everything should return to normal, if suddenly the appearance of a "bump" on the abdomen is not associated with the onset of an inflammatory process that has arisen against the background of a protracted and difficult labor or after an injury. You can establish the abnormality of the swelling by the following signs:
- The "bump" is hot to the touch, increases in size;
- a crisp sound is heard on palpation;
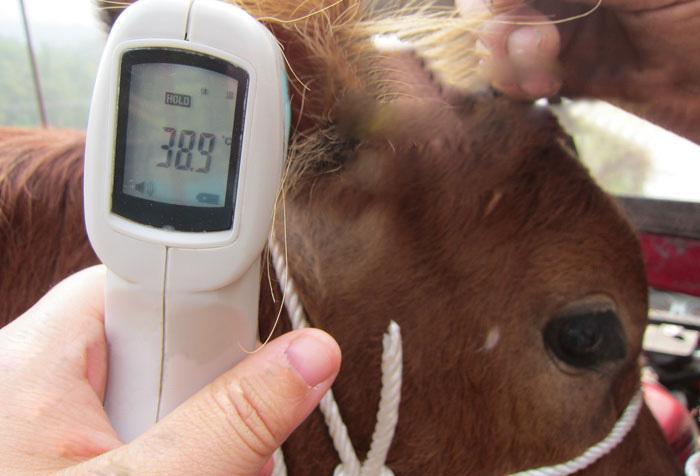
- the temperature of the animal jumps to 40-40.5 ° C;
- swelling of the labia;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- inflammation captures the perineal area;
- the oppressed state of the animal;
- refusal of food;
- change in the rhythm of breathing.
Important! If the edema is abnormal, call your veterinarian immediately.
Classification
There are three forms of malignant edema:
- emphysematous;
- edematous toxic;
- mixed.
With the emphysematous form, there is an abundant and rapid gas infiltration, which appears in the affected area, quickly spreads to damaged areas and to healthy tissues.
In the edematous-toxic form, a painful and hot swelling first occurs. The epidermis is hyperemic and reddened. After a while, the seal becomes cold, sensitivity is lost.
A mixed form of edema is most often diagnosed. It is characterized by the features of the previous two forms.
What is the danger of edema
Earlier it was mentioned that a running edematous process can lead to mastitis. It affects milk conditions and milk yield. It comes in different forms. If it goes into a purulent stage, it can lead to adverse consequences, up to lethal.
In addition, breast disease can signal the presence of problems in the functioning of the kidneys and heart. As a result, the protective functions of the body are weakened and any infection can attack the animal unhindered. Therefore, as soon as there is an edema of the udder, not associated with pregnancy, or from a mild form to a more severe form, it is necessary to urgently conduct a diagnostic examination of the animal.

The method for treating breast edema in a cow will depend on the stage of the disease. At an early stage, it is enough to correct the diet, increase mobility and isolate the animal from the herd. With a running version, you will need the help of a veterinarian.
Prophylaxis
First-calf heifers require great attention, because prolonged udder edema is most often observed in them. There are a number of specific actions that can be taken to help prevent swelling.
Conditions of detention
It is recommended to keep the animal off a leash. A pregnant cow should have dry bedding and no harmful gases in the room. Burenka must be provided with the correct exercise.
We must not forget about proper nutrition. Two or three months before calving, juicy and concentrated feeds are excluded from the diet. It is best to switch the cow to hay, preferably cereal, to maintain calcium and protein levels in the body.
Sanitary standards must be observed in everything. Before the winter stall period, disinfection of the stall is mandatory.
Drug prophylaxis
There are no specific medications to prevent swelling of a cow's udder. At the first symptoms, it is worth calling a veterinarian for an examination.