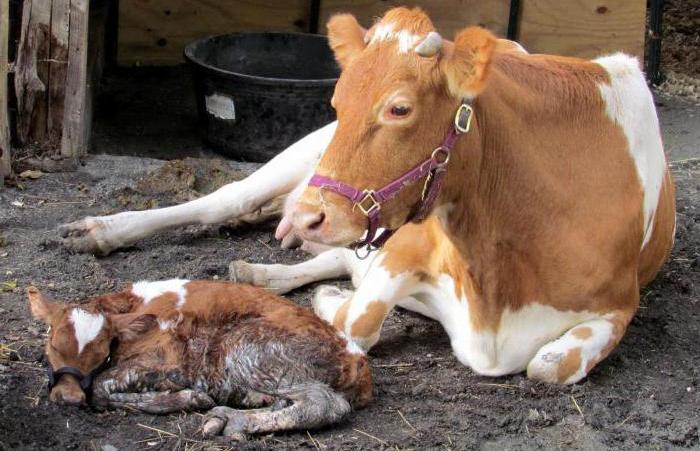
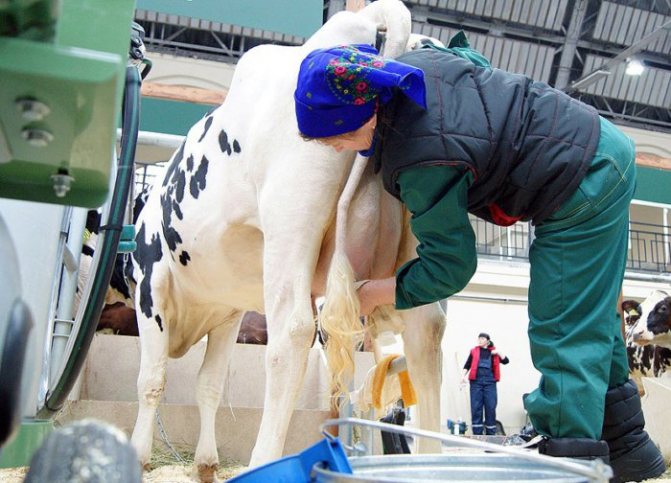
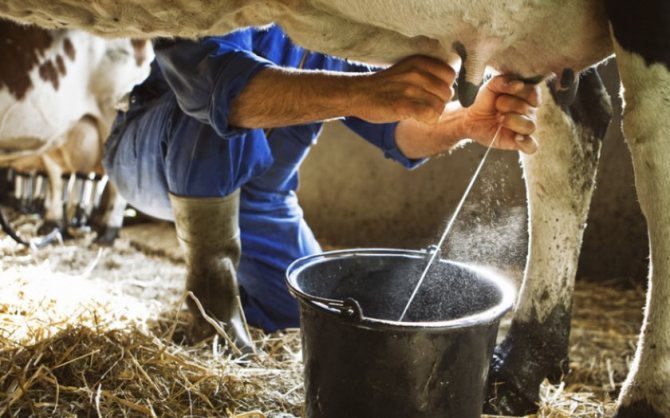
The owner should pay a lot of attention to calving animals. How to milk a cow after calving? First of all, the female needs to provide rest. After the heifer has rested, you can begin to milk the first milk. Not many people know how to properly milk a cow. But it is imperative to know this, because the improper milk production of cows after calving can lead to a number of diseases and problems with the udder of your wet nurse.
What is calving
Calving is giving birth to a cow. The calf birth process begins with contractions during which the cervix opens. Further, attempts arise, in which the fetus is expelled from the uterus and goes out through the birth canal. The duration of the entire process depends on several factors:
- having calved earlier - firstborns calve longer;
- the general state of health of the cow - a weakened animal gives birth longer than a completely healthy one, properly prepared for childbirth;
- fetal size - a large calf takes longer to hatch than a small one;
- number of calves.

Newborn calf with cow
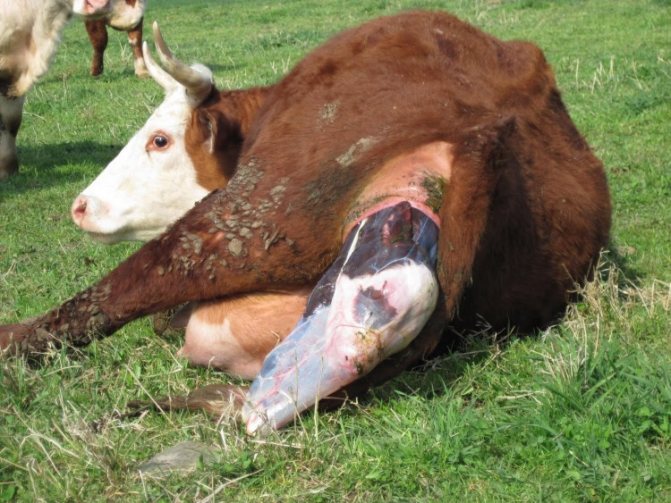
Typically, a cow gives birth within a few hours. From the moment of development of attempts to give birth to a calf, it takes about an hour. In primiparous, this lasts longer. The need for veterinarian help can be said if labor in a re-giving birth cow did not end within 10 hours, and in a primiparous - within 12 hours.
Reception of a calf
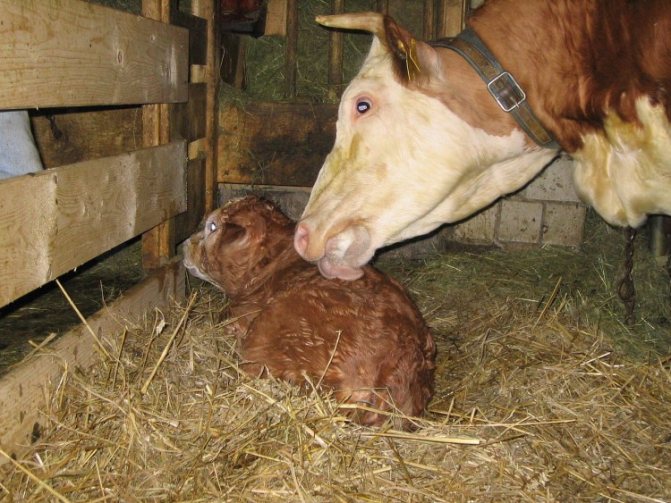
The baby is born, and you need to meet him correctly. Reception of the calf is carried out only on a clean cloth or sheet. His nose and eyes are cleared of mucus. You can entrust this job to a cow, but first-calf heifers sometimes get scared and do not know what to do with the baby. Tie the baby's umbilical cord with sterile threads and cut off the remaining edge with scissors. Treat the wound with any antiseptic, such as hydrogen peroxide or alcohol.
If a cow has calved normally, then she usually copes on her own. If childbirth was difficult, then the nurse often does not have the strength to take care of her baby. In this case, milk the cow and feed the calf its colostrum. This must be done no later than 60 minutes after its birth. After the calf is placed in a separate pen or left under the cow.


What is watering
Correct milking of the cow is extremely important, as it allows to ensure its high milk productivity. Preparation for it begins in advance by increasing the amount of feed immediately after mating. Such enhanced nutrition allows the animal to accumulate the necessary valuable microelements and prepare for calving.
Breeding continues for three months after calf hatching and consists of increased feeding, udder massage and regular milking.
At first, sometimes up to a month, the number of milkings should be 4–5 times a day. The udder of the cow is quite sensitive, so it should be massaged gently. This will help to establish lactation, and special ointments will protect the skin from microtraumas.
Important! To distinguish colostrum from mature milk will allow it to be heated at a high temperature. In this case, colostrum will necessarily curdle, but fresh milk will not.
Particular attention is paid to "primiparous" young animals, unaccustomed to the milking process. With such individuals, you should be more careful and patient.
In most individuals, hunting after calving begins in 30 days.A deviation up or down by 10 days is allowed. However, during this period, a cow with a bull should not be brought together, since she needs time to recover. The minimum allowable period after which insemination can be carried out after calving is 3 months.
Razda is a set of measures aimed at increasing milk production. The postpartum period is a particularly important step for the farmer.
Milking preparation is advisable immediately after starting the cow and preparing for her calving. Milking duration is three months after calving, before lactation. During this time, the cow needs to be provided with advanced nutrition. Based on the milk yield obtained, feed is given more than required. Remember that animals do not immediately respond to premiums. Also, during the milking period, competent milking and udder massage are organized.
During the entire milking period, the heifer should accumulate a supply of nutrients for lactation and at the same time not be overweight. First heifers are additionally taught to the milking process. At the same time, it is not recommended to milk before calving itself - this can cause unwanted early appearance of the calf.
Immediately after calving
Half an hour after calving, the animal is rested and should be given a bucket of warm salted water. It is permissible to offer the animal oatmeal swill if the udder is not inflamed. This will quench your thirst and at the same time whet your appetite, and besides this, it will relieve the delay of the placenta. Then they put plenty of legume-cereal hay in the feeder, but only of high quality.
After an hour and a half, the cow needs to be milked, and the calf should be fed with colostrum. The second time he is fed after 6 hours.
In order to prevent paresis during the first milking after calving, it is necessary to leave some of the milk in the udder (sometimes in the first few milking if the animal is susceptible to the disease).
Power features
In the first days, together with colostrum, and then milk, more nutrients are excreted from the body than comes with the feed.
Hay and mash, with some addition of easily digestible concentrates, are given to the cow approximately 1-2 days after calving. Then succulent feed is gradually added to the diet. Now you can increase the amount of concentrate. Monitor the condition of the udder and intestines at all times.
It is undesirable to feed the cow abundantly from the first day - often the animal does not eat all the food, loses its appetite, and may even refuse food altogether. Intestinal function is disturbed when overfeeding, the udder can become inflamed and milk yield will fall. This is especially true for well-fed, high-yielding cows - moderation is important. Always pay attention to the quality of your feed and try to give only the best.
They drink at least three cows a day with warm water, give water - how much they drink.
If everything is in order with the udder and the cow is healthy, from the 8th-12th day, you can transfer it to a full diet. If the udder is inflamed, the increase in diet should be slowed down (wait up to 20 days), and milk should be milked more often.
The need for calving cows for feed depends on their weight, productivity and milk fat. The diet must include: high-quality hay, succulent feed, spring straw. If you give the animal a large amount of succulent food, take the trouble to diversify them with silage, sugar beets, potatoes and other root vegetables.
Beets should be fed carefully so as not to cause the formation of nitrites and subsequent poisoning (no more than 25 kg per day for a dairy cow and no more than 10 kg for young animals over a year old). Diets with a lot of concentrates are high in protein. This can cause stomach problems and even barrenness.
For each heifer, it is better to keep a separate control record of milk yield (every 10 days). The higher the milk yield and its fat content, the more feed the cow should receive.For young cows of the 1st and 2nd calving, an increase in growth is made to the norm, and if the heifer is emaciated - to restore body condition.
During the milking period, the feed supply must be uninterrupted. Otherwise, heifers will reduce milk yield, and it will be much more difficult to increase them.
It is advisable to observe how the cow eats the individual feed. Those that eat willingly, add more. During the milking period, you need to create a proportion between concentrates and bulk feed in a ratio of 40:60.
Milking and massage
In the first days after calving, a highly productive cow can be milked 4-5 times a day. It is possible to replace part of the milking process 1.5 hours after the main one. At this time, the animal has the highest milk production. In this case, milk should be strictly at certain hours and at regular intervals.
The transition to intermediate milking three times a day depends on the condition of the udder and the amount of milk. In high-yielding cows, a spontaneous flow of milk may begin - the udder will become coarse from this and may become inflamed. Finally, when the cow began to give no more than 10 liters of milk per day, you can safely switch to the usual two-time milking.
In the first few days after calving, a cow's udder needs special care. At this time, it is hard and low-elastic. To bring the udder back to normal as quickly as possible, you should combine thorough milking with massage. Edema, which most often occurs in high-yielding cows and first heifers, decreases after about 5 days, and completely disappears by the 10th day.
Significant edema requires a reduction in drinking, disposal of succulent feed, and massage of the udder. It is produced from the bottom up, along the blood and lymph vessels, to the base of the udder. You can apply emollient ointments (bismuth-zinc and others) to restore skin elasticity and speed up treatment.
Milking a cow means a whole range of measures for keeping, feeding and milking. Its goal is to obtain maximum milk yield throughout the entire lactation period. Correct breeding of a cow consists of:
- Advance feeding,
- Regular massage of the udder,
- Competent first milking,
- Day mode organizations.
READ White-headed cows: Kazakh white-headed cow breed
The entire lactation period consists of four stages:
- For the first seven days, colostrum is secreted, which is only suitable for feeding the calf,
- The second stage is flogging,
- The third stage is lactation,
- The fourth stage is old-fashioned milk, which is not drinkable.
Colostrum contains a lot of protein, immune bodies and various enzymes, and is intended for feeding calves.
The cow's milk, habitual for humans, appears only seven to ten days after the cessation of colostrum excretion.
There are some basic rules on how to milk a cow after calving. The first is regular massage of the udder, as well as expressing the first streams of milk to identify blood clots and foreign bodies in it. This is necessary for early detection of mastitis and other infectious diseases. Before the massage, the udder is washed with warm water or wiped with disinfectants.
Very often, newcomers to breeding ask themselves the question - when does a cow start giving milk?
In a cow, colostrum begins to be produced immediately after calving, and the first milking should be carried out within an hour and a half after the calf is born. The first colostrum does not need to be milked completely, otherwise paresis cannot be avoided. But with subsequent milking, it is already possible and necessary to completely milk the udder. If milk remains in the udder, this leads to mastitis and a decrease in productivity.
How to milk a cow after calving
The special term “milk supply” used by livestock breeders means the formation of the lactation process in a newly calfed cow.The subsequent productivity directly depends on how correctly it will be carried out. It is important to know that these activities do not begin after calving, but at least two months before it.


During this period it is necessary:
- provide the animal with additional nutrition according to special schemes so that the cow does not spend internal reserves for bearing the fetus, but receives everything she needs with food;
- first heifers should be taught to the milking process with the help of light massage, and the milking of adult cows should be completely stopped.
If all the necessary conditions for the cow have been created, the birth of the calf should take place without complications and, therefore, it is possible to start shearing.
In order for lactation to be established quickly and to be as productive as possible, during the milking period it is necessary:
- to provide the animal with the so-called advanced (enhanced) nutrition, at the same time being careful to ensure that the heifers do not gain excess weight;
- carefully monitor the condition of the udder, especially during the first days after calving, to prevent swelling, milk stagnation, hardening;
- keep animals warm and protected from drafts;
- pay special attention to the cleanliness of the litter - the main source of dirt and microbes on the udder;
- very strictly observe the milking regimen, in the first days combining it with massage (it is equally important to observe the daily regimen in general);
- give the cow as much liquid as possible, since without it, milk production is physically difficult.

However, the last rule requires special caveat. The fact is that in first-calf heifers, as well as in animals of highly productive breeds, the udder very often swells after calving, and this can lead to the development of various pathologies. The critical period in this case is the first five days, then the swelling gradually subsides.
In order to alleviate the condition of the animal, the amount of liquid consumed by it should be reduced, and this applies not only to drinking as such, but also to juicy feed. But massage, on the contrary, should be done more often, moving along the blood and lymph flow - from the nipple to the base of the udder.
If such procedures do not help, you can use emollient or absorbable ointments, but it is important to know that some of them are categorically contraindicated during the period of milk production, therefore, a preliminary consultation with a veterinarian must be carried out.
Of particular importance is the observance of the milking regimen in primiparous heifers. In general, it is carried out according to the same rules that apply to adult animals, but requires more attention and care. Therefore, in large farms, newly calved young animals are usually housed separately from the main herd for at least three months.


Here, the following activities are carried out in relation to animals:
- during the first two to three weeks, the heifers are fed in a slightly limited amount so as not to provoke udder edema, mastitis, gastrointestinal upset or other postpartum problems;
- only after it becomes obvious that the animal has recovered from childbirth, do they switch to enhanced feeding using compound feed and root crops;
- additional feeding is introduced gradually, as milk yield increases, and stops when stable lactation is established;
- 10 days after the start of receiving fixed milk yields, the daily portion of feed is also gradually reduced to the usual rate;
- every 10 days during the entire period of milking, a control milking is carried out in order to check the amount of fats and proteins in milk;
- if it is impossible to graze freely, they must feed the heifers with green fodder;
- at the end of the milking process, the productivity of each cow is assessed according to a certain set of indicators (the amount of milk per day and for the period, the rate of its return, the condition of the udder, etc.) and a decision is made on its further use.
For both first-heifers and adult cows, breeding is considered complete at the moment when the amount of milk dispensed during each milking and in just one day becomes stable and makes it possible to clearly predict milk yield for the next period. At this moment, the animal is transferred to a regular diet and is kept without any additional requirements.


Stages of fetal development
With the development of the fetus in the uterus, there is a significant monthly increase in its weight. By the time of birth, the calf weighs from 30 to 40 kg, and in large breeds it is not uncommon to weigh about 50 kg. In the first month after fertilization of the egg, the weight of the embryo is 1 g. At the end of 2 months of pregnancy, the weight of the embryo is already about 40 g. Further weight gain is more active, and by the end of 3 months the fetus weighs 400 g, and at the end of 4 months 2.5 kg ...

Fetal position before calving
When 2 calves are formed in the uterus, then at the time of birth their weight turns out to be slightly less than the standard one when 1 fetus is formed. Such offspring are somewhat weaker than a single calf, but with proper care, two calves quickly reach their usual size and do not lag behind in development.
What to do if a cow beats (kicks) during milking
Not all animals like the milking process, so they can beat and kick. Usually this applies to first years who are not accustomed to it, which means that the owner will have to establish contact with the wayward animal. At a minimum, try to always bring some kind of delicacy with you in the form of vegetables or at least bread, in order to distract the cow from your actions for a while and calmly engage in the milking procedure.
Some housewives also practice the "cold towel" method, when a piece of cloth soaked in cold water is spread on the back of the cow. This solution is very important in the summer, since it not only cools the cow, but also drives away annoying midges from it. In winter, a wet towel can only be used in a heated barn.
A calf will also help a little to calm down the nurse and make her release milk. He will switch her attention to himself, and the owner at this moment will be able to calmly return to milking. As a last resort, if you cannot agree with the cow and you fear for your health, you can tie her leg to the fence using a long cord that will not allow reaching you during the pumping process.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: We build drinking bowls for chickens at home
For safety reasons, when milking, we tie the cow's leg to the fence. A correctly performed milking procedure will not only allow you to get a large amount of tasty milk, but also protect the animal from unnecessary suffering, which in turn will reduce your worries. If the task cannot be completed the first time, do not be discouraged, the skill will definitely come with experience.
Cow diet
Correct and organized feeding directly influences how soon milk will appear and what quality it will be. Ten days after calving, the cow is transferred to an enhanced diet, which is called advance. If you start feeding intensively before this period, there is a threat of mastitis and intestinal diseases.
After calving, Burenka must be given time to rest, recover and normalize the work of the mammary glands. Advance feeding lasts approximately one hundred days. During the entire period, it is necessary to constantly increase the daily portion of food until the cow begins to decrease the daily milk yield. Then the proportion of vegetables and concentrates is gradually reduced.
Advance feeding looks like this:
- 16% of the daily ration is hay,
- 14% - haylage,
- 18% - silage,
- 12% vegetables
- 40% - concentrates.
If the cow is high-yielding, and gives more than thirty liters per day, then the proportion of concentrated feed should be at least 50%.
When feeding the cow after milking, certain rules must also be observed:
- Do not overfeed the cow, especially in the first days after calving,
- Overeating can cause problems with the udder,
- Water must be constantly available and clean,
- Succulent feed must necessarily include silage, fodder and / or sugar beets, potatoes,
- Mandatory addition to the diet of feed yeast and eggs,
- In hot months, more than half of the feed is given at night feeding,
- Food should be kept in the trough at all times.
The amount of feed eaten by a cow depends on its weight. For good milk yield per day, a cow should eat about three kg of concentrates for every hundred kilograms of her weight. Juicy feed for every hundred kilograms of live weight is given about ten kilograms, and rough - about two kilograms.
Milking features
During labor, there is a high risk of infection for both the cow and the calf. Therefore, childbirth should be done in a clean, well-ventilated area and using sterile instruments.
An hour after calving, you can begin to milk the animal. On the first day after calving, a suction milk system is used for first-calving heifers - a calf is allowed to the nipples. This is because the young animal is scared and for the first time may not let the owner come in. After several such feedings, the hostess begins the first milking of the first heifer.
Do not donate all milk, otherwise it will provoke postpartum paresis.
If the animal has a weak immune system, milk is not completely milked several times in a row. Individuals that belong to dairy breeds are handed over 5 times a day with an interval of 2 hours. Particular attention should be paid to the care of the udder of the cow. To prevent the development of mastitis, it is massaged after each milking. This procedure increases milk yield.
How many days does a cow walk before calving
Milking and massage
The duration of bearing a calf is influenced by a number of natural factors, due to which the process can be somewhat lengthened or shortened. Such deviations are considered normal and do not require veterinary intervention. A pathological change in the duration of pregnancy is also possible, when the birth of a calf occurs too early or with a strong delay, and then it is necessary to call a veterinarian to assess the situation and prescribe treatment if necessary.
Fine
Most often, calving occurs on 285 days, but in most cases it is not considered a deviation and the appearance of a calf in the period from 240 days to 311. Early birth of offspring is noted in 6%, and no more than 10% of cows walk over the period. How many days a burenka walks, one cannot say with absolute certainty.


Pregnant cow
Early birth of calves occurs if the fetus is large, and the care of the female is poor, in which she suffers from vitamin deficiency and stress.
Cows can move after the standard date of birth for 26 days. If the 311th day of pregnancy has passed, and signs of childbirth are not observed, an urgent appeal to the veterinarian is required, since this condition is pathological. If possible, an examination of the animal by a specialist to monitor the condition should be carried out already when walking in 10 days. The phenomenon is most often observed if the female has a hormonal failure.
Why the cow doesn't milk
This is a problem often faced by budding farmers and small household owners. There can be several reasons for the absence or insufficient amount of milk, as a rule, they all boil down to improper care of the animal before and after calving.
By observing all the above recommendations, the lactation process can be established, however, if this still fails, you should also pay attention to other factors that could affect milk production. Let's try to highlight the most typical of them.


| Second | hay or grass in the same amount, the rate of bran or oatmeal in a chatterbox is doubled |
| Third fourth | a mixture of flaxseed meal, bran and oats - 1.5 kg; |
| Fifth - sixth | the rate of the previous day with an increase in compound feed by 0.5 kg per day (up to 2 kg) |
| Seventh - tenth | the rate of the previous day with an increase in compound feed by 0.4 kg per day and the gradual addition of silage, pumpkin and other juicy feed |
| The reason for the lack of milk in a cow | Possible remedies |
| The animal does not want to give milk, instinctively leaving it for the calf | The calf should be kept out of the udder and fed with milk from the bottle. At the same time, it is recommended to keep the baby separately from the mother, then the animal quickly forgets about parental feelings. |
| The milk is too fat and therefore difficult to drain. | During the milking period, the cow should not be overfeeded or given excessive amounts of high-calorie food. |
| The milk ducts are narrowed | This symptom may indicate adrenal disease and increased production of adrenaline. But everything can be explained in a simpler way, for example, the shock that the first heifer experienced from touching her udder with cold hands or from being injured by unskillful movements. |
| Mastitis, edema and other diseases of the udder | Caused by improper care, hypothermia, injuries, infections. They require timely diagnosis and proper treatment. |
| Emotional stress | As in humans, lactation in animals is largely dependent on the emotional state. The fear experienced can easily lead to a blockage of oxytocin synthesis and, as a result, to the loss of milk. |
| General disease | There are many diseases that adversely affect milk production, so it is very important to carefully monitor the health of the animal and recognize the characteristic symptoms of the disease in time. |
| Late start-up and other irregularities in the lactation cycle | Overexploitation inevitably leads not only to a decrease in milk yield, but also to a reduction in herd life expectancy. |
| Individual features of the structure of the muscles of the nipple and hereditary factor | Not all animals are equally productive, even the breed is not a guarantee of high milk yield. |
Breeding a cow after calving is a very important stage in dairy farming. Here, as in the process of growing a crop, the general rule applies: what you sow is what you reap. It is necessary to start preparing a heifer for lactation even during pregnancy (pregnancy), and the process can be considered complete only when the average daily milk yield has completely stabilized, the animal does not lose weight and feels well.
The owner should pay a lot of attention to calving animals. How to milk a cow after calving? First of all, the female needs to provide rest. After the heifer has rested, you can begin to milk the first milk. Not many people know how to properly distribute a cow. But it is imperative to know this, because improper milk production after calving can lead to a number of diseases and problems with the udder of your wet nurse.
Calving date determination
It is important for the cattle owner to know exactly the expected date of birth. This will allow you to determine whether an early or normal calf is born, as well as how much the pregnancy has passed. How to find out when a cow will give birth is well known: it can be calculated in two ways. It is convenient to use any of them to determine the date. The choice depends only on the personal preference of the owner of the animal.
Using the formula
Calculating the estimated calving date using a formula is a fairly simple task. The formula looks like this: D = (H 11) (H-3). D - date of the alleged calving; H - the number when the mating occurred; H is the month in which the cow was covered. To understand how to determine the calving date using a formula, you need to consider an example of such a calculation.
A special calendar is also kept to determine the calving date. This is a calving chart of cows, in which the month and day of insemination and calving are marked.In such a calendar, 5 dates are usually allocated in each month (1,5,10,15,25). Also in it, breeders mark the launch date of the cow before calving, so as not to get lost and not to miss this period. This table is especially useful for cattle if the farmer has several cows.
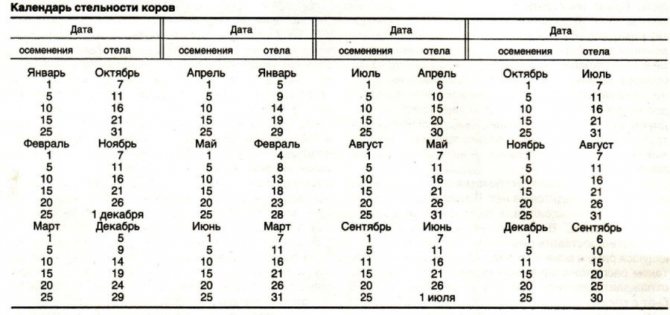

Cow pregnancy calendar
Milking frequency
Most novice owners are interested in the question of how many times to milk a cow per day? The answer to this question depends on many factors. First of all, it depends on when the cow calved, the first days you need to milk the cow about 4-5 times a day, then the frequency decreases.
Special dairy breeds need to be milked more frequently. In the household, the daily regimen includes morning and evening milking. Experts advise to milk the animal 3 times a day. When a cow goes to run, she cannot boast of a large milk yield and it is enough to collect milk 2 times a day.
Milking of first heifers with milking equipment
The video describes in detail how and what to feed a calving cow, and how to milk it correctly in order to get high milk yield in the future.
READ How to feed a cat after anesthesia. How to take care of a kitten after surgery? A cat has constipation after surgery: solving the problem
You can milk cows by hand or using special machines. If the farm contains only one animal, it makes no sense to buy a special apparatus, but for two or more individuals it becomes a necessity. Milking equipment significantly saves time and effort for the farm owner or staff caring for the herd.
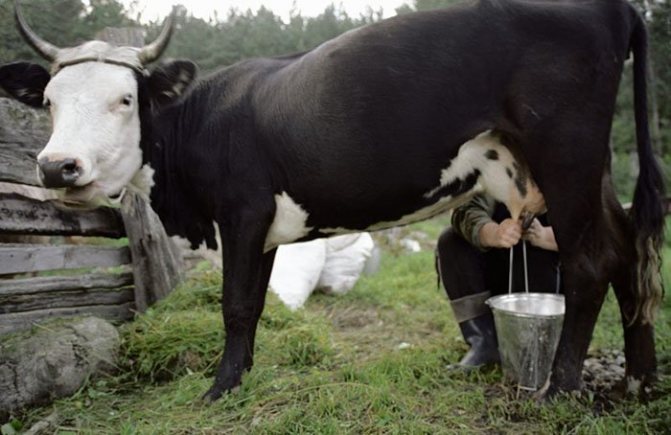
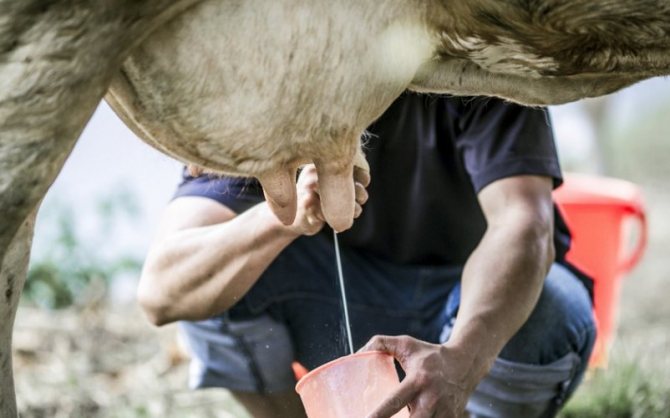
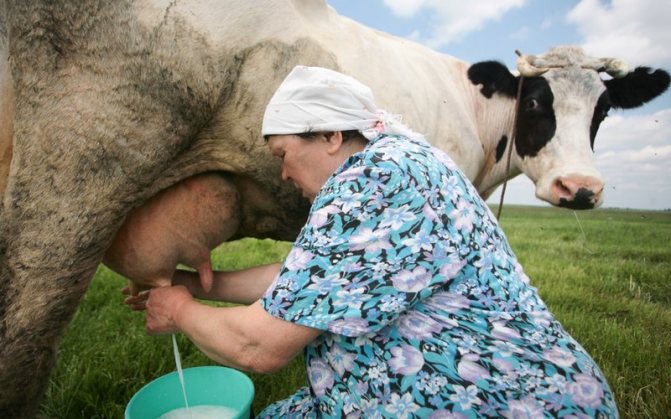
Manual milking method
You need to know how to properly milk the animal so that the milk flows out quickly and evenly, and in the process the udder is completely cleared of milk.
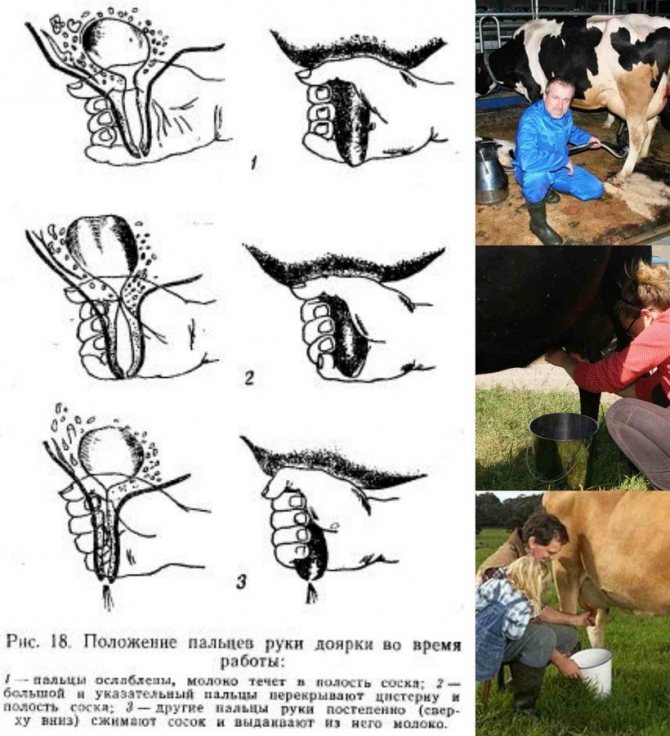
To learn how to properly milk a cow with your hands, you need to do the following:
- You can correctly grab the nipple as follows: place all fingers on the nipple so that the index finger is under the thumb, and the little finger is from the outside of the nipple;
- Squeezing a fist, it is necessary to ensure that the nipple does not wry, and the pouring milk should not come into contact with the hands;
- In order for milk to pour out of the nipple in a stream, not all fingers are squeezed at once, but from top to bottom: first the thumb and forefinger, gradually going down to the little finger. This technique improves milk flow.
- After that, the fist is unclenched, but the fingers are not removed from the nipple.
- When squeezing of the ring finger and little finger begins, the rest of the fingers should be squeezed so that the milk does not go up. Then the sequence of actions is repeated.
The fingers need to be squeezed frequently so that the milk flows out in a continuous stream (about 80 squeezes per minute). Milking too slow has a negative impact on milk yield. Figure 3 shows a schematic of the technique of hand and machine milking.
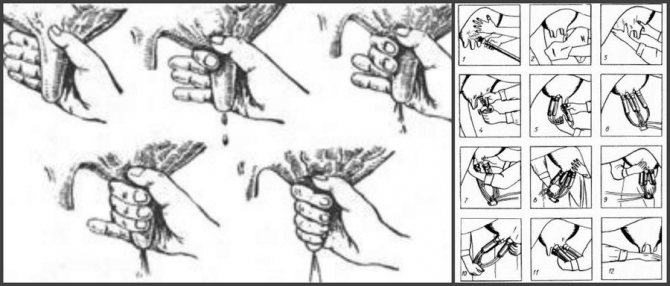

Figure 3. Schematic of manual and machine milking
It is best to milk the front two teats first and then the rear two, as squeezing milk out first from the right and then from the left lobe may result in insufficient milk evacuation from the back. This is because one part of the udder will be milked with a stronger (right) hand and the other with a weaker one.
Fist milking is only impossible if the animal has very short teats. This happens in young first-calf heifers. In this case, you need to milk very carefully with your fingers, being careful not to pull the nipple down too much. How to milk a cow is shown in the video.
It is not enough just to know how to milk a cow correctly; you also need to prepare the apparatus and the animal itself for the procedure.
We will tell you how to milk a cow with a machine correctly. To do this, you need (Figure 4):
- Thoroughly wash your hands and udder, dry the animal with a clean towel (preferably disposable).
- Massage and turn on the milking machine so that it builds up the necessary pressure.
- Put the suction cups of the device on the nipples so that the minimum amount of air gets inside.
- Set a milking routine suitable for the individual.On average, it should last no more than 7 minutes, the pulse frequency should be from 45 to 60 cycles per minute.
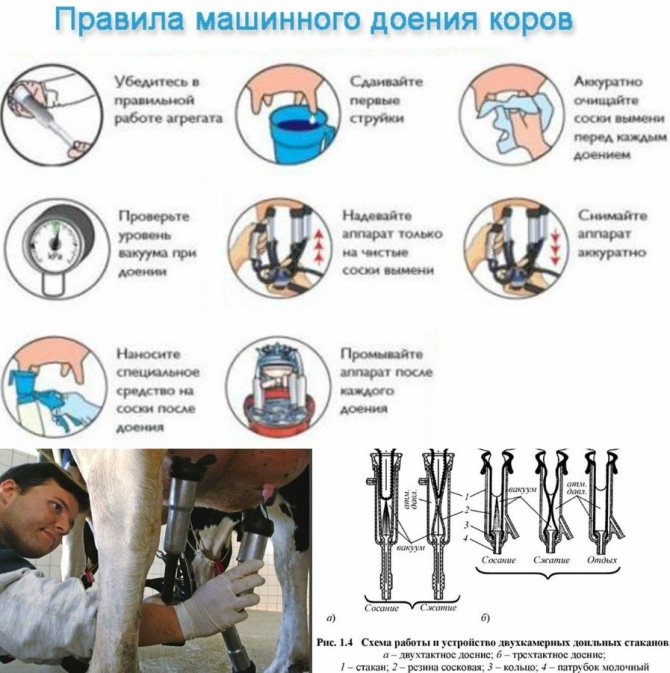

Figure 4. Milking with a machine
When the milk flow stops and the udder becomes soft, carefully remove the apparatus. The device is washed immediately after use to increase its service life.
Usually, during the first lactation, young cows give on average 25% less milk than adult animals, and cows begin to give the greatest amount of milk only from the fifth lactation year. It is very important to understand how to milk a first heifer, because the performance of a cow throughout her life depends on the correctness of the first distribution.
With manual milking, the cow begins to be taught to the milking process two to three months before calving. The process begins with a gentle massage of the udder, training in wiping and washing. It is recommended to carry out these procedures at the expected hours of the future milking - this way the cow will develop a reflex, and she will get used to a certain regime. When the cow gets used to the manipulation, you can imitate the milking process with your fingers - squeezing and releasing the nipples.
How many times a day to milk heifers depends on the filling of the udder. Usually in the first week, milking takes place three to five times a day, at the same time. Some owners prefer to replace full milking with a milker. It is carried out an hour and a half after the main milking - this allows you to get more milk. And after a week, the first heifer can be transferred to the usual three-time milking.
When choosing a machine method of milking, it is necessary to start accustoming the cow to the machine in advance. Training begins with washing the udder and drying it off with a dry towel. Then the udder is massaged and the nipples are stroked.
When the animal calmly endures all the manipulations, the milking machine is placed in the stall. It is recommended to turn on the device during feeding - this will allow the animal to react more calmly to the noise of the machine. It usually takes several days for the animals to stop responding to the noise of a working device. It will take a few more days for the animal to get used to the teat cups. It is also recommended to wear them during meals. An animal keen on food will react more calmly to external stimuli.
During training, it is recommended to cheer the animal up with treats, and at the first sign of dissatisfaction, stop the action. The first milking with milking equipment after calving can be carried out in one and a half to two hours. It is necessary to milk the first week as the udder is poured, and then milk, depending on the milkiness, two or three times a day.
Not all cows can be milked with a milking machine: suitability for machine milking is determined by the shape and size of the udder. If the udder shape is cup-shaped, then the milk is evenly distributed, and there will be no problems with milking with the milking equipment. If the cow has a rounded udder, then there is no necessary uniformity in the distribution of milk, and milking with a milking machine will not be as effective.
If the cow has a more developed back of the udder, then it is better not to use machine milking - the machine will not be able to milk the cow completely. It is easier and easier to milk such a cow by hand - it does not produce much milk. Some cows refuse to be milked by the machine, and show aggression towards the machine even after a long period of time - in this case, only manual milking is also recommended.
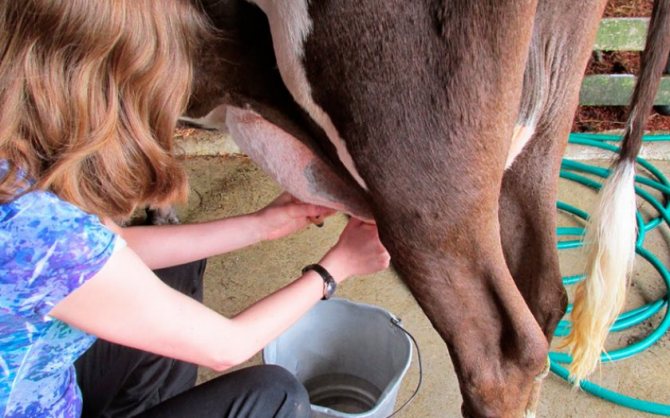
When to start milking a cow after calving
As a general rule, a cow should be milked one and a half to two hours after calving. However, before this, it is very important to restore the water and electrolyte balance in the animal's body, as well as prevent possible postpartum infections, since the compliance with this condition largely depends on how much milk the heifer will give in the future.
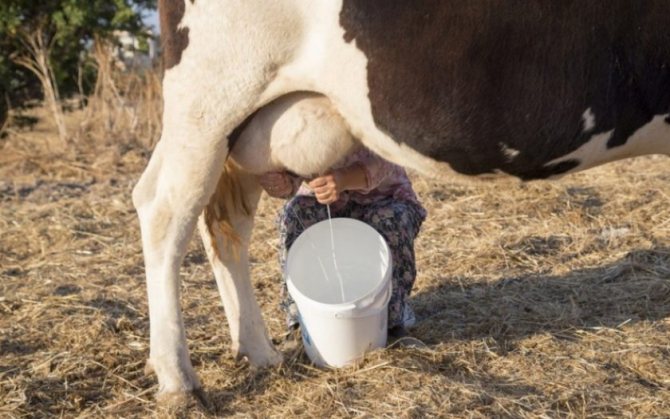


To do this, before the first milking begins, very simple but necessary emergency measures should be carried out:
- Intensively rub the back of the animal's body with a hard massage brush (you can use a homemade improvised product by twisting dry hay or straw into a dense ball). Such a procedure will accelerate the contraction of the uterus, ensuring the outflow of blood from it.
- Carefully rinse the udder, vulva and surrounding areas of the skin with a disinfectant (you can use furacilin or a weak solution of potassium permanganate) and wipe dry with a soft cloth.
- To drink the animal with one and a half buckets of water heated to the temperature of a human body, in which 150-200 g of ordinary table salt is preliminarily diluted (according to another technology, instead of salt, sugar is added to the water at the rate of 0.5 kg per 10 liters).
The cow is then fed a small amount of fresh, high-quality hay and, if desired, a liquid mixture of oats and bran or steamed oatmeal swill. An hour after the animal has eaten, it can be milked. The described rules apply to a situation when the birth was successful and the cow feels well.


If the animal has developed mastitis (the udder is swollen and hardened, this process usually manifests itself even before calving), the cow should be milked immediately after the end of labor, and you need to try to empty the udder completely.
The resulting colostrum is destroyed, it cannot be given to the calf in order to avoid the infection or medications that were used to treat the mother from entering the baby's body (both the bacteria that cause mastitis and antibiotics get into the milk and can cause serious disorders and even the death of the calf).
For the same reason, the baby is not allowed to milk a cow with mastitis, although it is the calf that is able to develop the swollen udder as safely and intensively as possible. An even more serious complication after childbirth is paresis, or, as it is also called, a coma of dairy cows.
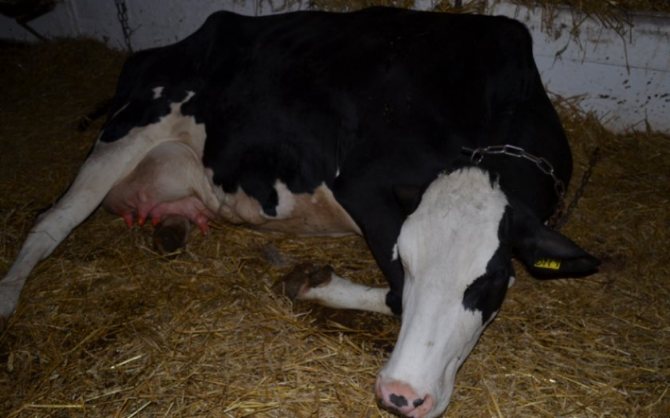


Paresis in a cow This disease is of a nervous nature and is manifested by severe tremors in the limbs, staggering and even paralysis, accompanied by fainting. If a fresh cow shows such signs or lies, characteristically arched neck, she needs urgent help.
For this purpose, as a rule, a special technology is used for pumping air into the udder, leading to the receipt of the "correct" impulse in the brain. If the procedure has helped and the animal has risen steadily to its feet, they begin to milk it after two hours. Otherwise, the treatment is continued.
Running a pregnant cow
Launching a pregnant female is required so that she can gain strength before calving, and the volume of milk that will be formed after the calf appears, was sufficient to feed it. Milking is completely stopped 2-3 weeks before the birth of the cub. The launch begins 2 months before the expected calving. Proper care and maintenance allow you to get full-fledged offspring and prevent the negative consequences of childbirth for the cow.
First of all, the cow's diet is changed. A few days before changing the milking regimen, the following are excluded from the cow's diet:
- green herbs;
- silage;
- concentrates;
- roots;
- juicy feed.
The animal should receive only hay. The volume of water given to the cow also decreases. This reduces the amount of milk produced.


Starting a cow correctly before calving
To stop lactation, the number of milkings is reduced. Udder massage is stopped. Gradually, milking is brought up to 1 time per day. Milking of beef cows is completely stopped when the volume of milk per day is not more than 1 liter, and milk - when the volume is about 4 liters.
Sometimes running a cow is required with medication. They are administered by injection. Only a veterinarian can determine the need for such a method after examining the animal.This method is used when it is impossible to carry out a normal launch using the soft method.
Milking technique and mode
Breeding a cow after calving will be successful and productive if you follow the regimen and technique of carrying out:
- High productivity of the cow will be ensured if you develop a habit in her. With a milk yield of 16 to 20 liters, milking is carried out no more than 3 times a day.
- Feeding is carried out 1.5 hours before or after milking. So the animal will not be distracted by food. In addition, milk obtained during milking will not contain feed odor.
- Before each milking, the udder is washed with warm water, then wiped dry with a towel.
- It is better to put the first trickles into a separate vessel, since they contain admixtures of dirt and microbes.
- Distribute begins with the back nipples, and ends the process with the front ones. To eliminate the risk of injury to the nipples and udder, the nipples are completely wrapped in a fist.
- Intensive milking has a positive effect on increasing milk yield up to 15%. For 5-7 minutes, you need to try to milk the entire portion of milk.
Weekly readiness
A week before the expected calving of the cow, constant monitoring is required, since it is impossible to accurately determine the day on which the calving will take place. The owner must also fully equip the stall in which the cow will give birth and in the future stay with the calf. It is advisable to carry out such preparation in advance, even a month before the expected calving, so as not to face a problem if it happens early.
Feeding a week before giving birth needs a special one. Nutrition needs to be balanced. Hay feeding is stopped as soon as lactation stops. In order to understand how well a cow is eating, she is weighed. A week before calving, she should gain about 65 kg. If more than 75 kg of weight is gained, then this means that the animal is overfed, which will negatively affect the process of giving birth to a calf.
READ Stress and Aggression Cats Sedative
A week before the expected calving, the cow should be washed with warm water and her hooves should be treated with a 2% strength creolin solution. The animal must be kept as clean as possible.
Stimulating labor in a cow
There are situations when a veterinarian recommends to induce (artificially induce) labor in a cow. This is done only for special medical reasons and only by a veterinarian. in case of danger to the life and health of a cow or calf.
Important(!): You do not need to try to make the cow calf faster using domestic (folk) methods. This will only harm you. Calving stimulation is a risky procedure that can only be prescribed and carried out by a specialist with experience.
An example of such a situation would be weak labor in a cow. The veterinarian medically causes an increase in contractions, but only after making sure that the fetus is located correctly (!).
You can independently find out how the fetus is located already in childbirth - manually, feeling the calf (the head of the calf lies exactly on the front legs, or the fetus goes with exactly two hind legs).
The master's task, when the cow is walking, monitor the condition of the mother and fetus and, in case of unwanted symptoms, call a veterinarian.
How to prepare for childbirth
Preparing for the birth of a calf includes not only starting the cow, but also arranging the premises, purchasing the necessary materials and medicines. You also need to be able to immediately call a veterinarian in case of complications.
In the room in which the cow will give birth, the owner should have the following at hand:
- dense threads that can be used to tie the umbilical cord;
- scissors;
- iodine;
- diapers or waffle towels;
- laundry soap;
- latex gloves (disposable at the pharmacy);
- warm boiled water (brought directly during calving).
It is advisable to find an assistant who, if necessary, will assist.Normally, an animal gives birth on its own without human help, but at the same time, the development of complications cannot be ruled out, even in an individual that has already calved more than once.
The room in which the calf will be born must be warm and dry. The floors and walls of the barn must be washed with a chlorine solution. Then clean, necessarily soft hay is covered, which must be changed daily. The burenka should be in the prepared room already 5 days before the expected calving time. There should be no rubbish in the stall. The house is completely cleaned before the cow calves.
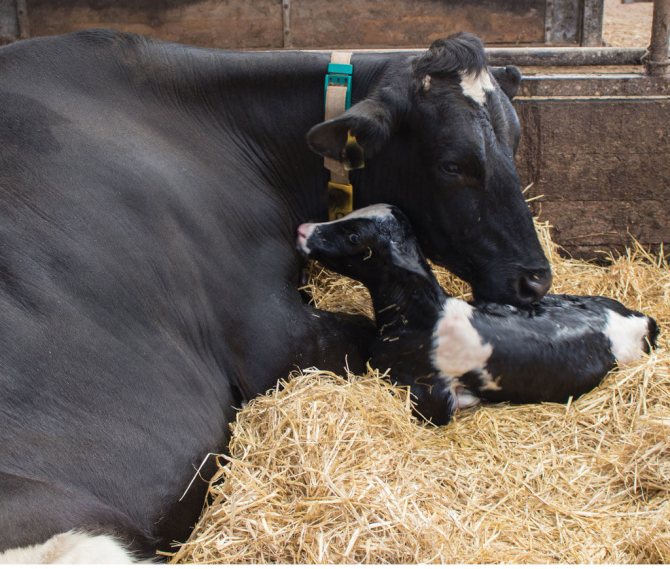


Cow with a calf in an equipped stall
The area for the cow and calf needs to be large enough so that they can feel comfortable in the future. The cow should give birth in a pre-prepared room, as this greatly reduces the risk of developing complications of calving.
Before calving, the feeding of the animal is changed. The volume of food is increased by 20%. 4 days before the expected calving, forage is excluded from the diet of the cows. Meals should only consist of good quality hay and small amounts of green grass. They stop grazing the animal a week before calving. How to feed the cow before calving will be determined by weighing, as overfeeding should not be allowed.
Preparing for the milking process
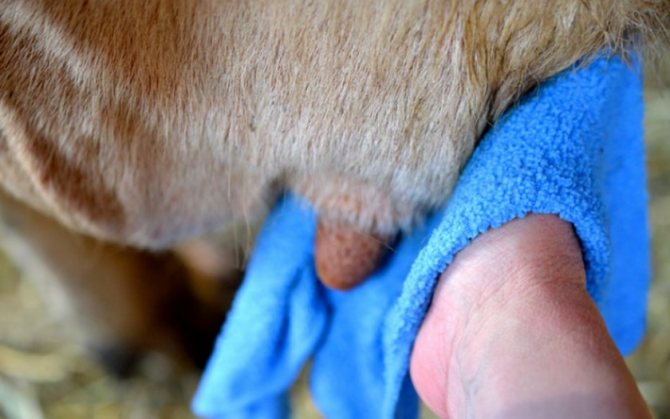
Before you milk a cow with a machine or manually, you need to prepare the udder. It is cleaned of dirt, washed, disinfected and dried. In milking parlors, special aisles are intended for cleaning the udder, where the legs, abdomen and udders of animals are washed.
In private farms, the udder is processed as follows:
- a warm soapy solution is prepared: water is diluted with laundry soap;
- wash the udder;
- rinse with clean water;
- wipe with sodium hypochlorite or other antiseptic;
- nipples are dried with a disposable towel;
- teat cups are put on dry teats.
Operator's hands must be clean. To improve milk production and for the cow to give it better, massage the udder. All 4 lobes of the mammary gland are kneaded. The procedure is especially important for heifers and cows with high milk production. Milk residues can accumulate and cause mastitis.
The operator carefully examines the udder, checks it for mastitis or cracks. If no pathologies are found, then they proceed to milking. The first drops of milk are decanted into a separate bowl. Examine the liquid. If it contains cheesy flakes or blood clots, then the animal is examined by a veterinarian.
The equipment should be checked before milking. If the device operates with a hiss, then the pump passes air. The installation is turned off, the malfunction is eliminated. A ringing sound indicates a problem with the motor or pump. If the pump is oil-lubricated, moving parts may need lubrication.
Before considering different ways of milking cows, you need to understand how to prepare the animal for this process. Any animal feels affection very well, so you shouldn't shout at a cow without a reason, let alone beat her. If your cow is especially shy, you need to approach her so that the animal can see you.
For tethered housing, first you need to prepare the room, for this, clean it of manure and bring some fresh bedding, if necessary. The animal needs to be tied, quite rarely the owners milk the cow when she is just standing there. It is rather difficult to predict the actions of the cow, she may just walk when you are sitting under her. Some representatives even have one hind leg fixed if the cow likes to kick up.
Immediately before milking, you need to tie the tail to the hind leg, the animal will try to drive away insects with it, it can accidentally hit the milker with it. Tied with a special thin rope or with the hair itself at the tip of the tail.
Milkmaid preparation
It does not matter whether the cows are automatically milked by the machine or hands must be thoroughly washed by hand. The hands of the person who is milking should be warm. The area around the udder should be wiped with a dry cloth, and the udder should be washed with warm water, temperature from 40 to 45 ° C. Then wipe the udder dry. In this way, you can not only get rid of the dirt on the milking, but also give a little massage to make the cow milking easier.
Massage before milking
Additionally, you can do a real massage, which lasts no more than a minute. This will not only speed up the milking of the cow, but will also provide good milk yield. The massage consists in stroking the udder, if this is not done, the milk will not be fully milked out, over time its amount will decrease, which sometimes ends with the development of mastitis.
Udder problems
Mastitis
The most common problem for both young cows and those for whom calving is not the first. One of the first causes of the disease is cracks in the skin of the udder and teats, which are formed during illiterate milking. The first symptoms of mastitis are udder swelling. It becomes hard and hot, any touch on the inflamed area is painful.
Lack of milk
Another common problem is the lack of milk after calving. There are several reasons for this:
- Improper feeding
- Reflex disorder
- Ketosis,
- Mastitis.
If the cow does not produce milk within a few hours after calving, it is best to call your veterinarian to determine the exact cause. The first two problems can be easily eliminated by restoring the balance of feeding and medications that activate the process of milk production, as well as eliminating the source of stress.
It is not enough to know how to milk a cow; you also need to massage the animal correctly. The udder is kneaded before and after each milking, moving from top to bottom (along the lymph nodes and blood vessels). During the massage, you can use special emollient ointments.
Massage plays an especially important role after calving. In such animals, the udder is too stiff, and without massage, milk stagnation or mastitis can begin. To prevent this from happening, the number of milkings is increased, accompanied by a gentle massage.
The lactation of cows does not always go like clockwork, sometimes there are some difficulties. The most common of these are low milk yield, complete absence of milk and swelling of the animal's udder.
Small milk yield
Hypogalactia or low milk production is usually caused by inappropriate milking or malfunctioning of the animal.
In this case, the following rules will help to increase milk flow:
- strict adherence to the milking schedule will allow the cow to enter the rhythm;
- massage of the udder of a cow before each milking;
- compliance with sanitary rules during milking and in the barn itself;
- introduction of feed stimulating lactation into the diet (2 hours before milking).
If compliance with these rules did not increase the amount of milk, then perhaps the reason is in the state of the animal's health. In this case, you need to seek advice from a veterinarian.
Lack of milk
A more difficult situation is when the cow calved, but lactation has not begun. This phenomenon is called agalactia. It can be caused by inflammatory diseases, impaired milk flow reflex or malnutrition.
The fact is that during and after pregnancy, many complex physiological processes take place in the animal's body, which weaken the body and make it vulnerable. And some health problems appear during this period.
Important! If the reason for the lack of milk is in the state of the animal's health, then only a qualified specialist will help here, who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medications.
The solution to the problem of lack of lactation can be the organization of good nutrition and improvement of the conditions for keeping the animal.Burenka are given more succulent feed, vitamin and mineral supplements and preparations to activate lactation. You should also protect the animal from stress as much as possible.
Swelling of the udder
Sometimes the circulation of blood and lymph in the udder of a cow is disturbed, as a result of which edema occurs. The primary reason for this may be the predominance of juicy and acidic feed in the diet of the cow, as well as low physical activity. In cows, alternating half-edema is common.
Due to the constriction of tissues and blood vessels with edematous fluid, inflammation of the udder can occur, as well as its compaction as a possible complication of mastitis.
If the udder edema persists within a week after calving, you should contact your veterinarian for appropriate treatment.
It is now known that milk can be drunk about a week after the calving of a cow. And its amount directly depends on the diet, conditions of detention, breed, age and health of the animal. Be attentive to your cows, and they will certainly delight you with excellent milk yield.
Postpartum care
Taking proper care of your cow after calving:
- immediately after giving birth, her litter is changed;
- wash the birth canal with warm soapy water;
- 40 minutes after calving, the animal is allowed to drink slightly salted water to quench its thirst.
If the animal is bleeding, it is worth giving quick help. To induce contraction of the uterus, the back of the body is rubbed with a bunch of hay. This will stop the blood flow and facilitate the rapid release of the placenta. Cleaning the birth canal after calving is carried out using warm water.
Taking proper care of an animal after the birth of a calf involves ensuring good housing conditions - the animal needs a warm, draft-free environment. In the morning and in the evening, the procedure for washing the vulva is carried out. A weak solution of potassium permanganate is used for washing. They are washed until the bloody discharge stops.
After the first and second milking, the udder is thoroughly washed with warm water and soap, then wiped dry with a towel. To restore all body functions, the animal is given a special Energetik drink, which includes prebiotics, probiotics, vitamins, minerals and polysaccharides. If the animal is not cared for, the risk of developing many diseases is possible.
How to recognize the approach of calving
The owner's ability to correctly recognize when calving is approaching avoids many of the problems associated with an unexpected onset of labor. The fact that the animal's body has begun to prepare for the birth of a calf can be understood by external signs. The female's behavior clearly indicates that calving will take place soon. Preparing a cow for calving, such as washing her back with an antiseptic, begins with the first symptoms of labor.
Before the birth of a calf, a cow undergoes certain changes that will be noticeable even to a novice livestock breeder. The following signs indicate the approach of calving:
- swelling of the genitals - the genital gap looks swollen;
- discharge of milk from the nipples;
- swelling of the udder;
- the opening of the genital slit and the secretion of mucus from it - the discharge from the cow before calving - this is the outgoing plug.
When such external changes appear, observation of the animal should be constant, since the birth of a calf will occur within the next few hours.
The behavior of the animal before calving also changes. Signs of cow calving appear with the onset of labor. Burenka becomes restless and constantly tries to lie on her side. This is an indicator that there are 3-4 hours left immediately before calving. If the animal is on grazing, then before calving, it begins to look for a quiet place away from the rest of the herd.
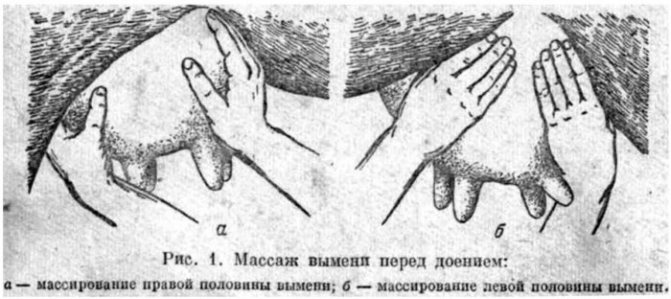
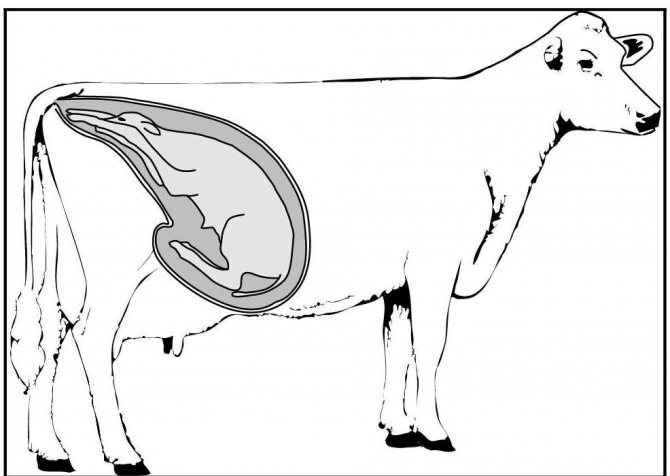
Why do udder massage
The process of secretion and accumulation of milk in a cow takes place in the so-called alveoli - tiny cavities, from which the nutrient mixture then flows through special ducts into the milk tanks, and from them into the nipple. This movement does not occur in the form of a free current, but under pressure provided by the contractions of the muscle cells surrounding the alveoli.
The "command" to contract the alveoli is given by the brain in response to stimulation of the udder (in natural conditions - when the calf begins to suck on it) by the production of a special hormone - oxytocin, secreted by the pituitary gland.
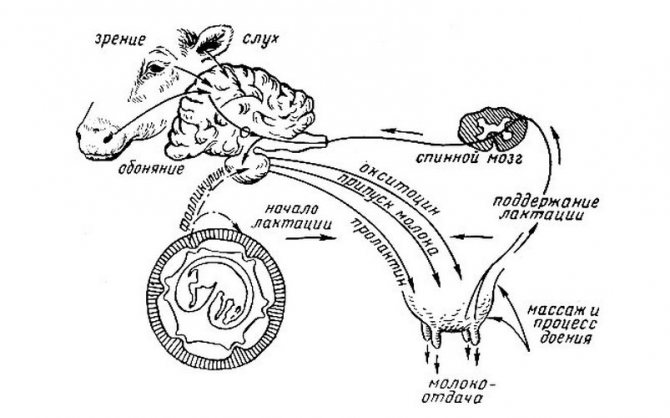

The process of milk secretion Before milking, up to half of the milk produced is already in the milk ducts and cisterns and is ready to stand out at the slightest touch, but at least the same amount remains in the alveoli. To extract this very second half, it is necessary to stimulate the production of oxytocin. It is known that from the moment of the first touch of the udder to the beginning of the flow of milk from the alveoli into the milk ducts, approximately 45-60 seconds elapse.
If the milking process is organized incorrectly, then after the cisternal milk has been milked, the milking process goes “idle” for some time until the liquid from the alveoli enters the nipple. Such a break is very harmful to the health of the animal and, moreover, leads to significant losses in productivity, sometimes up to 30-40%.
The stimulation of the udder by means of a gentle massage ensures uniform and continuous milking, when milk from the milk tanks is smoothly replaced by the alveolar milk. Udder massage in a fresh cow is also the best prevention of edema and mastitis. However, so that the animal does not get nervous, the procedure should be started even before calving.
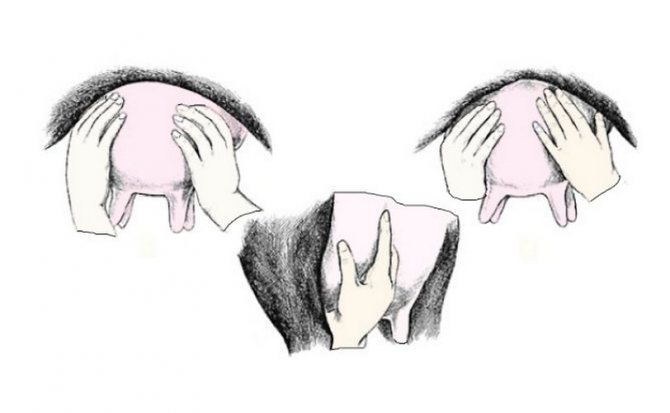

Cow Udder Massage This primarily applies to first-calf heifers, for whom stimulating the udder creates new and incomprehensible sensations. A few days before the expected onset of labor, massage should be discontinued, since it, like full-fledged milking, can cause early labor.
To avoid vasospasm and emotional stress, touch the udder only with warm hands. The procedure is carried out very carefully and does not last long, no more than thirty seconds. It consists in gently stroking first the right and then the left half of the udder with active, but at the same time not rough movements.
Important! When performing the massage, both the udder and the hands of the person performing the procedure should be perfectly clean and dry.
How and what to feed
You need to feed the cow with hay or fresh grass, give a talker with light concentrates. After 2 days, they begin to add juicy feed, while the amount of concentrates in the diet should not be reduced.
Important! It is not necessary to feed the cow excessively from the first days: she cannot finish the feed, her appetite decreases, the activity of the intestines is disturbed, and inflammation of the udder is possible. Milk is rapidly declining.
If everything is in order, the cow is healthy, the udder is in good condition, then on the 8-12th day, you can give a full feed ration. There is another way of feeding: the first days only hay is given, and after a week a full diet is introduced.
The feed rate depends on the following factors:
- weight and fatness of the animal;
- the amount of fat in milk;
- calving month (in winter the diet will be different);
- the amount of milk.
The higher the milk yield and fat content, the richer the diet should be, with a large amount of nutrients: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins. After the first and second calving, the diet is gradually increased for the further growth of the young heifer. An increased diet is also recommended for malnourished cows.
The more milk a cow gives, the more feed she is given.


With proper care and milk production, the amount of milk after calving gradually increases, reaching a peak by the end of the first month, the maximum milk yield is maintained throughout the second month, sometimes even the third. Then the milk yield starts to drop.