Is it difficult to grow and care for walnuts? How to do it right?

Despite the fact that the walnut is a rather unpretentious species and it is not very difficult to care for it, there are some features that must be taken into account. Adhering to simple tips, you can easily grow an excellent fruiting walnut tree, which will delight you with a wonderful harvest of incredibly useful properties - walnuts!
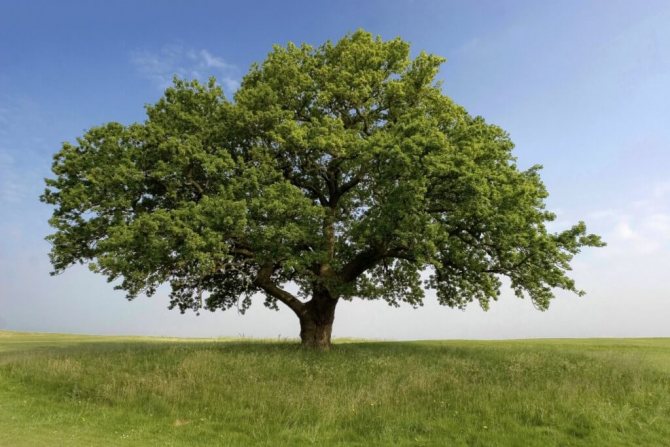
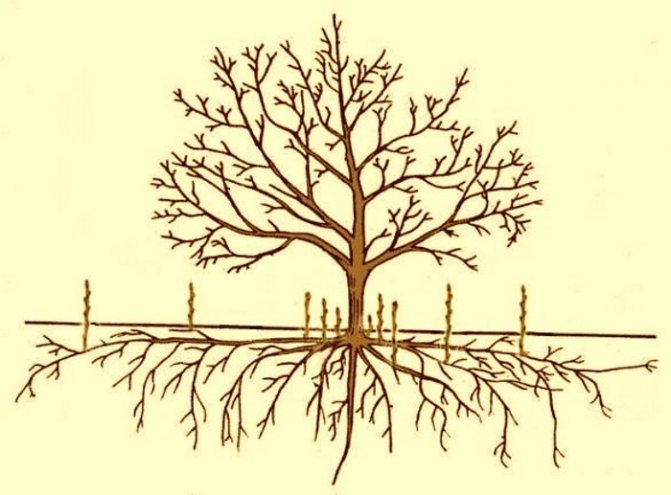
Before growing any tree, it is necessary to choose the right place for planting it - this is a well-known fact. As for the walnut, its cultivation must take place in a spacious area, with good ventilation and lighting... The open areas of your garden area are perfect for this. So that the trees do not "interfere" with each other, mutually reducing the yield, it is not recommended to plant them closer than 10 meters from each other.
How to choose and prepare the right soil? How to plant a walnut?
Soil is also a very important issue. Optimal for growing walnuts will be loam, without strong drops in groundwater level... Initially, having planted a walnut in the soil that suits it, you will not have to take care of it in a special way and constantly monitor its composition - the walnut is not at all capricious in this regard. One thing is for sure: marshy soils are absolutely unsuitable for growing walnuts, where groundwater levels are high.
Before planting a walnut, it will be better to properly prepare the soil and fertilize it in advance with a mixture of manure, ash and superphosphate (ammophos). It should be remembered that the pit in which you are going to grow the pre-selected seedling must be covered with polyethylene (pieces of slate or brick) for the root system to develop in the correct way. And do not forget about the introduction of humus at the time of planting the seedling, the root collar of which, in the end, should remain at ground level. Next, we mulch the soil near the seedling with peat chips or sawdust.
Possible reasons for restricting access:
Access is limited by a court decision or on other grounds established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The network address that allows you to identify a site on the Internet is included in the Unified Registry of Domain Names, Pointers to Pages of Internet Sites and Network Addresses that allow you to identify sites on the Internet that contain information, the distribution of which is prohibited in the Russian Federation.
The network address that allows you to identify a site on the Internet is included in the Registry of domain names, page pointers for sites on the Internet and network addresses that allow you to identify sites on the Internet that contain information distributed in violation of exclusive rights.
How to care for walnuts?
Now let's answer the question: "how to care for walnuts?" First, let's divide into three areas:
- pruning and shaping the crown;
- watering and watering the tree;
- fertilization and feeding.
Tree pruning and crown shaping serve to improve fruiting and increase the resistance of the tree to various external influences.Growing a healthy fruiting walnut without observing this condition is problematic. It will be important during the first years of life to correctly start the formation of the crown: the shoots are cut off until 6 or 7 skeletal branches are formed. In fact, the gardener himself makes a kind of skeleton for the future head of the tree. Subsequently, it will be necessary to take care of the crown minimally, it will form mostly on its own. Thus, you can grow a beautiful and well-bearing tree.
Further, in fact, only sanitary pruning is made, when damaged or dried branches are removed, and branches that grow inside the crown.
Walnut is a very moisture-loving plant. It is necessary to take care of your garden, be sure to take this circumstance into account. Watering the garden from walnuts should be sufficient and regular. As such, it will rightly be considered abundant watering at intervals of 3 times a week. As practice shows, the most important period in terms of regular watering is the spring period. In general, seasonal watering should be stopped in the fall, after foliage has fallen.
Mulching, which we mentioned in passing above, in order to grow a good walnut is a desirable condition, but in general it is not necessary. The soil well covered with mulch will not have a tendency to dry out, which means that watering will be more efficient, which will ultimately have a very favorable effect on the state of the tree's root system.
What fertilizers are needed for a tree?
To fully disclose the question of how to care for a walnut, consider some of the nuances of fertilizing and feeding a walnut. Once a year, it is necessary to fertilize trees - this procedure is not difficult and not too troublesome. When is the best time to do it? In general, it is believed that the best time to feed is autumn. But in early spring, it is also quite possible to carry out these procedures.
There are specificities in how to perform this procedure, depending on the season. In the process of fertilizing in the fall, the soil is loosened to a depth of about 20 cm.When feeding a tree during the growing season in spring, the soil is not dug deep - no more than 10 cm.
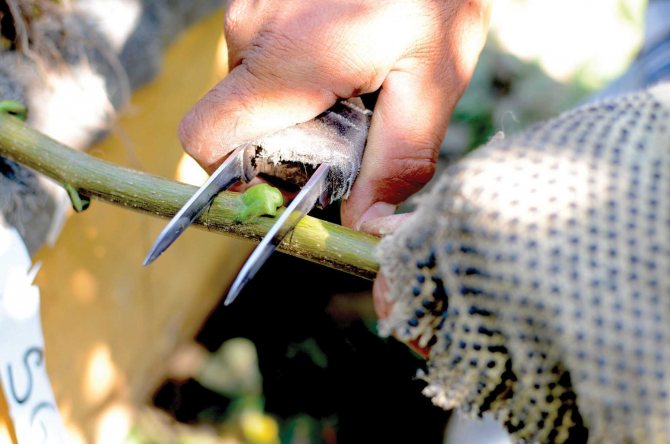
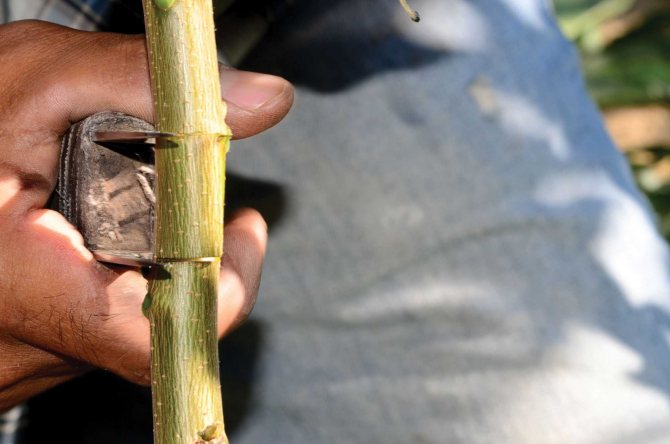
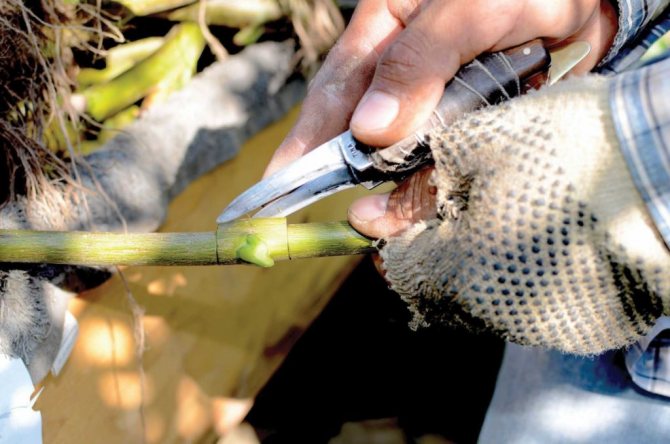
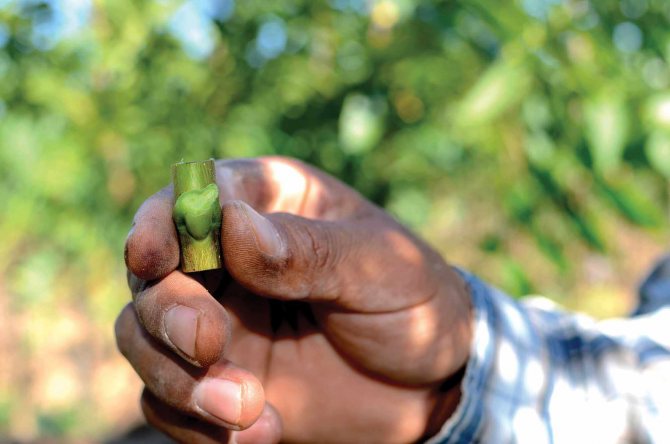
Preparation for vaccination
Walnut grafting is carried out for several reasons:
- in order to accelerate the receipt of fruits;
- to preserve the maternal qualities of the nut;
- if it is necessary to obtain a new variety of fruits, while preserving the garden plot.
The vaccine can be carried out at any time of the year, but each season has its own characteristics.
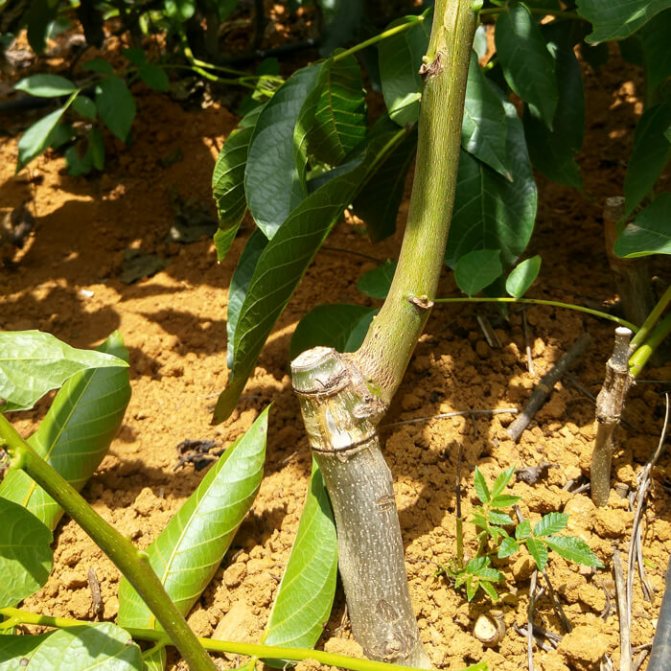


Difference of seasons
Winter
How to grow walnuts at home?
As follows from the above, growing a walnut at home and caring for it is not at all a difficult task that does not require any special skills or expensive resources. A summer cottage or garden plot, as a rule, meets all the requirements and allows you to grow a small fruitful walnut plantation on it. Following the simple rules and techniques listed above, you will be able to take good care of and regularly have a good harvest of walnuts, with which you can fully meet the needs of your family.
How do you care for walnuts?


Some gardeners, having planted a nut on the site, immediately forget about it, believing that the nut will grow without their participation, and after a dozen years they wonder why there is no harvest. Of course, the nut is one of the most unpretentious garden centenarians, but it also requires a certain amount of attention. Otherwise, over time, instead of a large tall tree with a sprawling crown, a lopsided screech with small fruits will grow.
Walnut care is simple and includes:
- regular watering;
- periodic feeding;
- pruning;
- treatment against pests and diseases.
Watering mode


The frequency of watering directly depends on the frequency of precipitation and the age of the tree. Young walnut seedlings, from spring to autumn, need very abundant watering 2 times a month. However, if the summer is rainy, additional moisture is not needed so that the roots do not rot. In the absence of autumn rains, a young hazel tree needs water-charging irrigation for a good winter.
Large nuts, the height of which exceeds 4 meters, practically do not need watering (excluding prolonged drought), since their powerful roots are able to take moisture from the depths of the earth.
As for loosening the near-trunk circle after watering, it is often not necessary to do this, so as not to damage the roots. Enough two loosening per season and autumn digging. The nut generally does not like excessive interference, and in order to protect the soil from the formation of a dry crust, it is better to use mulch.
Preparatory work before landing
Walnut seedling is undesirable to purchase from random sellers. Special nurseries offer high-quality planting material. When choosing a tree, pay attention to factors:
- Buy an adapted tree from the nursery in your region.
- The taproot of a well-developed seedling should be strong.
- The bark on the stem, branches must be healthy, without signs of damage.
The seedling is planted in fertile loose soil. The planting hole is dug just before disembarking. The ground must remain moist. The size and depth of the pit correspond to the size of the plant and the length of the root. Approximately 50X50 cm.A pillow made of broken bricks, gravel, construction debris with a layer of 25 cm is placed on the bottom.


Then a layer of compost, humus, ash (only 5 kg). Or take ash 400 g and 200 g of superphosphate.
An excess of fertilizer is not allowed, so as not to stimulate the intensive growth of the ground part of the tree.
Features of nut fertilization


Nut dressing begins from the fourth year of life. This applies to those seedlings, when planting which substances necessary for the development of the tree were introduced into the planting pit. Their nuts usually last for the first three years.
Starting from the fourth year after planting, nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium nitrate) should be applied in the spring, and in the fall - mineral preparations, which include potassium and phosphorus (potassium salt, superphosphate).
Early forms
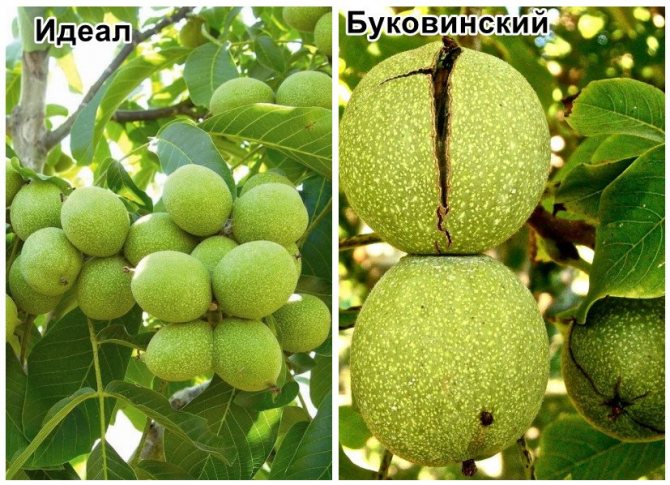
Early-fruiting forms have an undeniable advantage, a short period of entry into fruiting. If an ordinary and large-fruited nut begins to bear fruit at the age of 6-7, then the first nuts on the tree of the early-growing variety will appear twice as fast. This variety of nuts was discovered by scientists less than 80 years ago in the Tashkent region. They bloom in the third year, enter fruiting, and the next year they already give a tangible harvest.
The flowers of this variety are collected in a brush, on which several nuts are tied and ripen. And 12 days after the first phase of flowering, the second occurs. If during the first flowering up to four fruits are formed on the seed, then during the second - more than ten. In other forms, this feature is absent.
Nut trimming
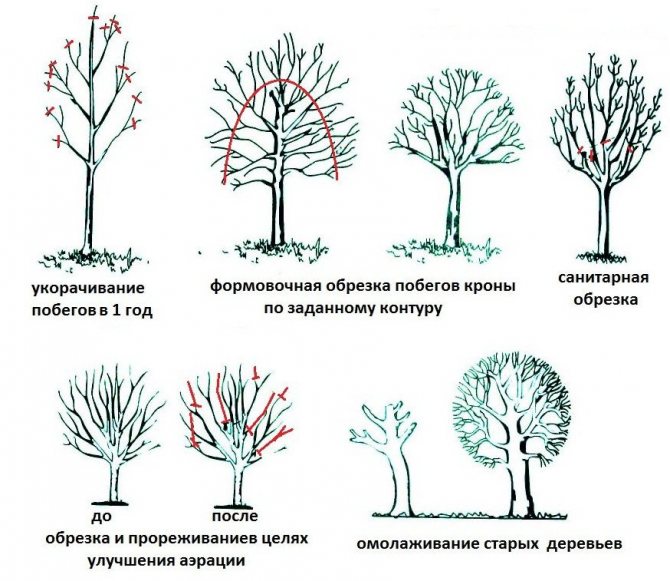

During the first five years of the life of the nut, the crown of the tree is formed:
- choose and leave the strongest shoot in the tree nut, which will become the main one, and pinch the tops of the remaining branches;
- in the future, the lateral shoots must be cut off until 6 to 10 skeletal branches are formed on the tree (they are pinched).
When the contours of the crown are formed, then the nut will cope on its own. It remains only to carry out sanitary pruning, cutting out damaged and diseased shoots, as well as those branches that go inside the crown.
Formative pruning is best done in spring and sanitary pruning in fall.
Growing walnuts at home
Not everyone knows how to grow a walnut at home, however, like any other fruit crop, it is not difficult to grow it, it is enough to plant the plant correctly and take regular care of it. Growing in tubs or large pots has its advantages: it is easier to protect a thermophilic plant from severe frosts and gusty winds, as well as to provide it with the soil mixture it needs. A walnut, planted in this way, grows in the form of a small shrub, and due to its small size does not give large yields. The fruits of the home tree are somewhat smaller, and their peels are stronger than those grown in the open field. It should be noted that with proper care, the quality of the fruit can be quite high.
Reproduction
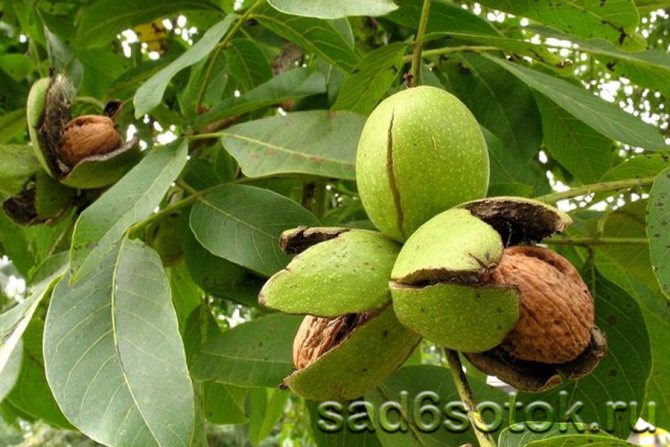


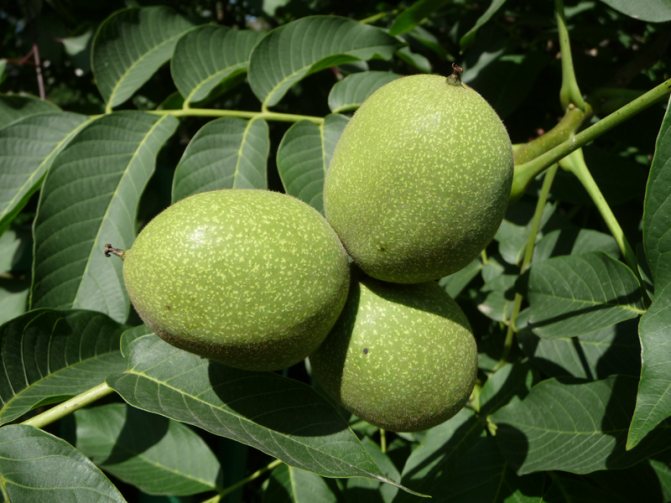
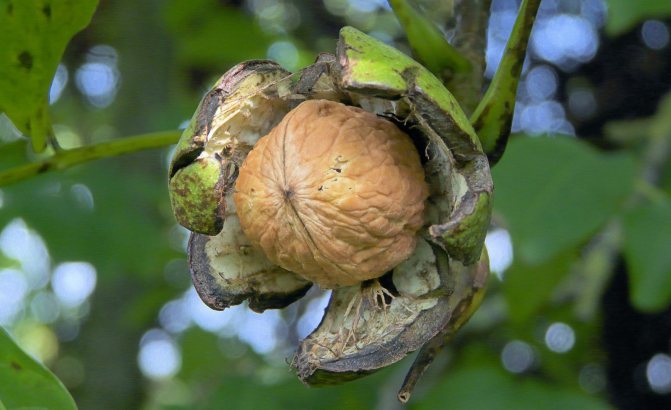
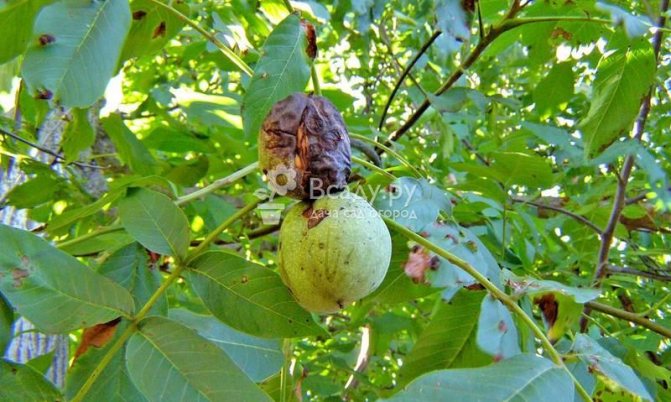
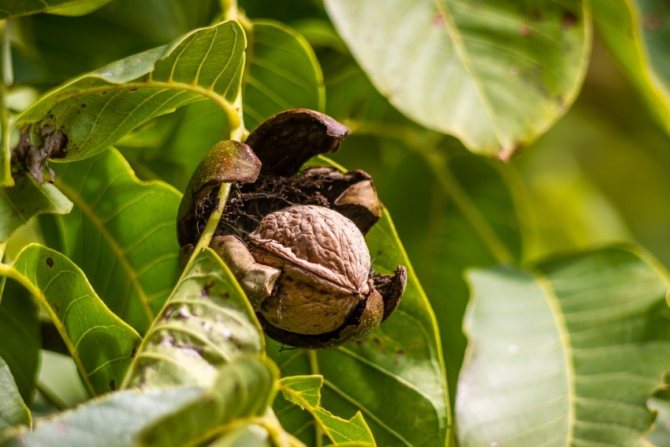
Ripening of walnut fruits
You can get a new plant seeds, vegetatively, grafting.
Seed propagation
Before planting, the seeds are soaked in water, and then in the growth preparation "Zircon" for 3 days. Planted in April, when the soil warms up to 10⁰C in a fertile soil prepared in advance. Planting depth - 10 cm.
When planting, we do not throw the nut, but set it sideways on the edge. Under the "open sky" growth is slow, seedlings grow much faster in film greenhouses. Interestingly, they can surpass the mother plant in their qualities.
Walnut at home - choice of capacity
Before planting a walnut at home, you need to choose a container where it will grow. Any deep container with good drainage will do. The first vessel for a young tree should be 25-30 cm in diameter and deep, that is, such that the root system can freely fit in it. When grown in a tub, the plant is limited in growth, therefore, 1-3-year-old seedlings must be transplanted annually, picking up a pot 8-9 cm in diameter larger than the previous one with each transplant.
How can you grow walnuts at home?
At high air temperatures, wrap the pot with a damp thick cloth to cool the roots.
In the spring, in order to protect the walnut from frost, it is covered with burlap or brought indoors. In the same way, you can save the tree from birds (in winter - buds, in summer - fruits). Winter frosts are detrimental to this culture, therefore, for the winter, the pot is buried in drained soil or transferred to a shelter (in a greenhouse, winter garden, on a loggia).
When growing walnuts at home, in the spring they mulch the soil with a layer of peat, moss or rotted manure. The mulch layer is renewed annually.
Homemade walnuts are practically not affected by diseases and pests. When brown leaf spot appears, it is sprayed with Bordeaux liquid.
Top dressing is applied during the growing season, when additional nutrients are very important for the plant. For this, liquid mineral fertilizers with potassium content are used. Top dressing is applied every 14 days from the beginning of the growing season, and then every 7 days until the fruits are fully ripe.
Walnut at home - transplanting and molding
The transplant is carried out in the fall, carefully removing the tree from the tub, 1/10 of the roots are cut off, and its aboveground part is cut off in the same way. Repotting is necessary until the nut reaches its final size.
A tree growing in a tub can be given any shape. The first years of his life, the formation of the crown is combined with the removal of some of the flowers in order to prevent abundant fruiting. In summer, weak thin shoots, excess and dry branches are removed.
Walnut grows well and bears fruit in our region.
And it seems that there is no trouble with him. Unless you choose a suitable variety - large-fruited and thin-bored. But in order to keep a tree healthy for a long time (and a nut lives for about 300 years!), You need to take care of it.
Firstly, dry, damaged and thickening branches are cut out from an adult tree, elongated shoots are shortened. But they do this not in autumn or spring, as in fruit trees, but in the second half of summer.At this time, the leaves of the nut are well developed and the roots work intensively, which will help it quickly restore the loss of juice, heal the cuts.
Secondly, many believe that the nut does not get sick and does not have pests. Unfortunately, over the years, it often happens that the fruits crumble ahead of time, and most of them are empty or rotten. The reason is plant diseases and pests. The most harmful diseases of the walnut are bacteriosis, brown spot.
Bacteriosis is the most common nut disease. There are practically no varieties resistant to this disease. The disease affects all aboveground organs of the tree: buds, leaves and their cuttings, male and female flowers, one- and two-year branches, shoot growth points, fruits at different stages of their development. On non-lignified shoots, as well as on leaves, elongated brown spots are formed due to the disease. In rainy weather, the shoots dry out and bend.
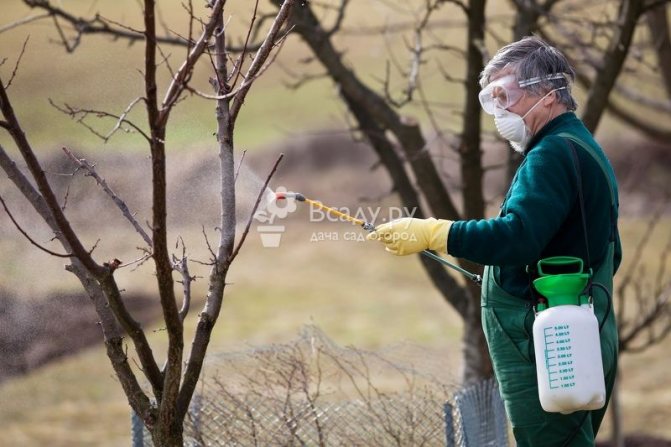
Plant diseases and their treatment
Treatment of plant diseases:
- Marsonia - fungal, anthracotic lesion of walnut foliage. The surface of the leaves begins to become covered with reddish-brown spots, which grow and destroy the entire area of the leaves, the disease can spread to the fruit. The cause of the disease is excessive rainfall.
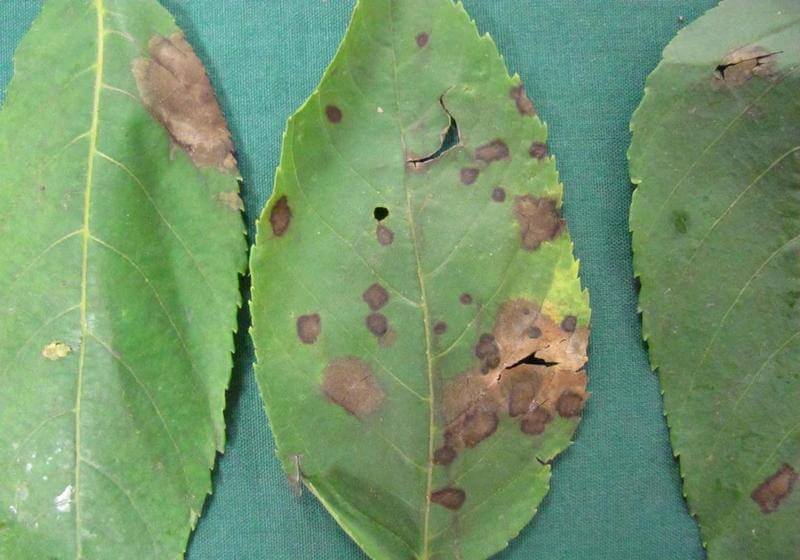


Disease prevention - three times spraying the crown of a tree with a mixture of quicklime and copper sulfate, in a ratio of 1 to 1, diluted with water. In the spring, in April, the swelling buds of a walnut are sprinkled with Strobi and Vectra. The stained leaves are harvested and burned. - Bacteriosis - damage to leaves and fruits, leading to deformation and shedding. The reason is frequent rains in spring, excessive watering and feeding with nitrogen-containing agents.
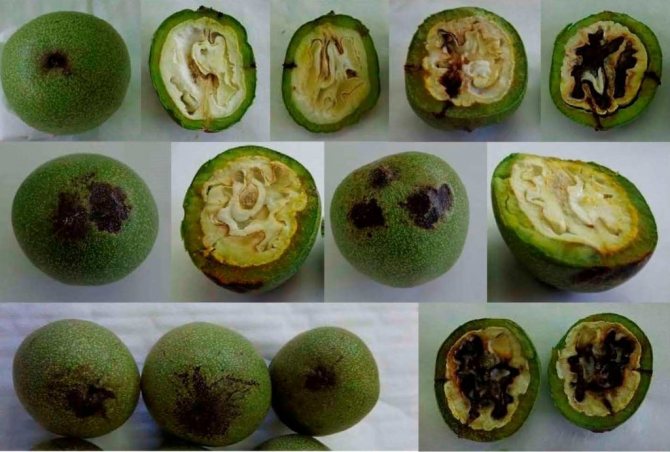


Disease prevention and treatment: three times processing of walnut with a mixture of marsonia, carried out before the flowering period. Leaves and fruits contaminated with bacteria are harvested and burned. - Root system cancer - stopping the growth and development of the plant. Cracks in the stem and roots are overgrown with bumpy formations, as a result of which the tree cannot receive nutrients and water from the soil and begins to die.
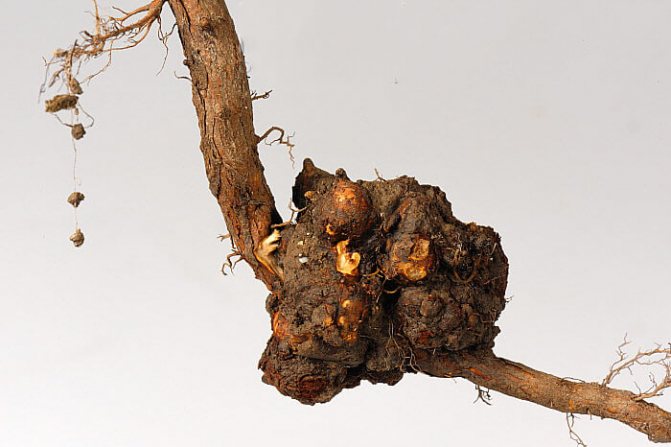


Treatment - the growths are cut off, the cut points are moistened with liquid caustic soda and washed with water.
A properly planted walnut will begin to ripen and pollinate after a few years. The yield of trees depends on the correct selection of varieties, planting seeds, prevention of nut disease, control over the volume of spring pruning, harvesting pollinators, and the maturity of a fruitful plant.
How to plant walnut walnut in autumn
Infection hibernates on the bark of diseased branches. In the spring, it enters the leaves through the stomata, and into other organs of the tree through mechanical damage. Large doses of nitrogen fertilizers in plantings increase the development of the disease. Varieties with thin-peeled nuts are more susceptible to disease than thick-peeled ones.
Brown spot, or anthracnose, of a walnut affects leaves, shoots, fruits. Numerous round or irregular spots appear on the leaves. This usually occurs in early or mid-July. In years with high air humidity, these spots grow very strongly, the leaves dry out prematurely and fall off. At first, small spots are formed on the shoots, sometimes ulcers, the shoot is bent. Damaged fruits remain underdeveloped. At a young age, they fall off, at a later period they remain hanging, due to spots they have an irregular shape. In damaged fruits, the skin of the kernel becomes dark.
Now, in the fall, measures to combat bacteriosis, anthracnose and the main pests of walnuts (walnut moth, aphid, tick, nut moth) are the same: collection and burning of leaves, damaged branches of fruits and residues.
Thirdly, like all fruit-bearing trees, walnuts need feeding.If, when planting seedlings, the recommended organic and mineral fertilizers were added, then the nut will be provided with the necessary substances for the next 3 to 5 years. In the future, organic (3 - 6 kg of rotted manure or humus), phosphorus (5-10 g) and potassium fertilizers (3 - 8 g) are introduced (per 1 sq. M.) Once every 2 - 3 years in the fall, embedding them in soil (usually in grooves along the perimeter of the crown) to a depth of 10 - 20 cm.Nitrogen (10-15 g) - annually in the second half of April in the form of a solution or dry to a depth of 3-4 cm. trace elements (boron, manganese, magnesium, etc.). Especially if signs of their lack in the soil are noticeable - the death of ovaries, yellow spots on the leaves, weakening of growth, etc. Doses are the same as for other fruit trees.
What to do if there is no harvest
To eradicate the reasons why walnuts do not bear fruit, you can use the following methods:
- At high crown density, part of the branches and shoots are cut off.
- If the soil is depleted, then it is dug in with a pitchfork, 3-4 buckets of humus are introduced, and covered with mulch.
- In dry weather, the plant is watered abundantly, but the volume does not exceed 100-150 liters.
- With an excessive concentration of organic matter in the soil, feeding and watering is stopped until the indicators come back to normal. The roots should be trimmed if necessary.
- If the tree is not self-pollinating, a plant of the opposite sex is planted nearby for the pollination process.
- Pollination is carried out mechanically: a branch with ripe pollen is shaken over non-pollinated flowers.
- Pollen is harvested in advance: the earrings with the formed pollen are ripe, they are collected, dried in the sun for 24 hours, after which they are collected in a gauze bag and manually pollinated the tree, shaking the bag over the flowers.
- To accelerate fruiting, the tree is grafted with an "eye" of a walnut, similar in flowering period. Inoculate the crown, cuttings and roots.
- The presence of such parasites as wart mites, walnut moths, white butterflies, apple moths are eliminated by manual collection of pests and their larvae, as well as sprayed with special solutions. Spraying during flowering and ripening is prohibited.
- Plants affected by diseases - marsonia, bacteriosis, root cancer - are treated.
Read also Beautiful landscape designs of small areas
Growing walnuts at home
For its culture, they usually choose areas with sufficiently fertile soil, where fertilizers are not needed in the first years of plant life. Thus, it is possible to apply fertilizers to enhance the growth of walnuts only in very limited conditions, for example, when growing it on poor, marginal soils (sandy slopes with highly washed out soils, etc.).
Enhancing the growth of walnuts by applying fertilizers on sufficiently fertile soils can lead to undesirable consequences. Excessive growth of shoots will cause prolonged vegetation, their wood will not ripen in time and the plant will be killed by the winter cold. This danger of a decrease in the winter hardiness of the walnut must be taken into account when fertilizing. VM Rovskiy (1970) emphasized the need to use fertilizers to increase the growth of walnuts in nurseries only on insufficiently fertile soils (gray soils, etc.).
Fertilization of walnuts in gardens in order to enhance the fruiting of its trees is necessary and has long been used. This was mentioned in our country by N.I.Kichunov in 1931.
A. A. Richter proposed for young walnut orchards of the Crimean region. in the first 10 years after planting, annually apply on nutrient-depleted soils the following fertilizers per 1 m2 of garden area, g: ammonium sulfate 60, ammonium nitrate 35, superphosphate 80, potassium salt 15. In the absence of mineral fertilizers, apply to the same area 3-4 kg of manure, and with the combined application of mineral and organic fertilizers, the rates of both are halved.Nitrogen fertilizers are applied in spring, the rest in autumn, to a depth of 30 cm.
PP Dorofeev for the conditions of Moldova advises to apply fertilizers in walnut orchards growing on marginal soils in the following amount per hectare of area, q: ammonium sulfate 3, superphosphate 2 and potassium salt 1. In the absence of mineral fertilizers, you can apply half-rotted manure in the amount of 30 t / ha.
In experiments on the fertilization of fruiting walnut trees in Gorny Bostandyk (Uzbekistan), 1.5 kg of ammonium nitrate at the rate of 50 kg / ha of pure nitrogen was applied under each tree before the beginning of the growing season, and in October - November 4 kg of superphosphate at the rate of 75-80 kg / ha phosphoric acid. Fertilizers were applied for 3 years - from 1964 to 1967. Already a year after the fertilization, fruiting began to increase. Initially, the yield on the fertilized plots exceeded the control by 4-5 times, and in 1967 even more than 10 times. The average weight of fruits also increased under the influence of fertilizers (Butkov and Talipov, 1970).
Studies have also shown that the addition of ammonium sulfate, as well as superphosphate and potassium salt, reduces the incidence of walnut fruit by the moth.
According to N.A.Tkhagushev (1970), in the Black Sea regions of the Krasnodar Territory, it is necessary to apply a complete mineral fertilizer under a fruit-bearing walnut orchard at 1200 kg / hectare. or 1 t / ha of manure and 60 kg / ha a.c. NPK. The same amount of NPK is required in the conditions of the Kuban fruit zone.
According to A.K. Kairov, in Kabardino-Balkaria, the main fertilizer for walnuts is applied for autumn plowing. Manure is given once every 4 years at 20 t / ha. Superphosphate and potassium salt are applied annually, respectively, 5-8 and 1-1.5 centners / ha. For top dressing, ammonium nitrate is used at the rate of 1-1.5 c / ha during the second cultivation.
Walnut seedlings in nurseries need fertilizers. The use of nitrogen and phosphorus at 60 kg / ha increases the growth of seedlings, the yield of large-sized planting material, and improves the water regime.
In Bulgaria, when creating a walnut orchard for deep plowing (30-40 cm), holes for trees are dug every 12 m, measuring 0.6X0.6X0.6 m, with finer plowing, the size of the holes is larger, 1X1X0.6 m. the top layer of the soil and a mixture of 15 kg of well-rotted manure, 300 kg of superphosphate and 80 kg of potassium fertilizer is added to it per area of 0.1 hectare. In school branches of the Bulgarian nursery, the soil is fertilized (20-30 t / ha of manure, 6 centners of superphosphate and 2 centners / ha of potash fertilizer), spud at least 5 times, 2 times a summer fertilized with ammonium nitrate (50 kg each time) and regularly watered (Bonev, 1967).
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.