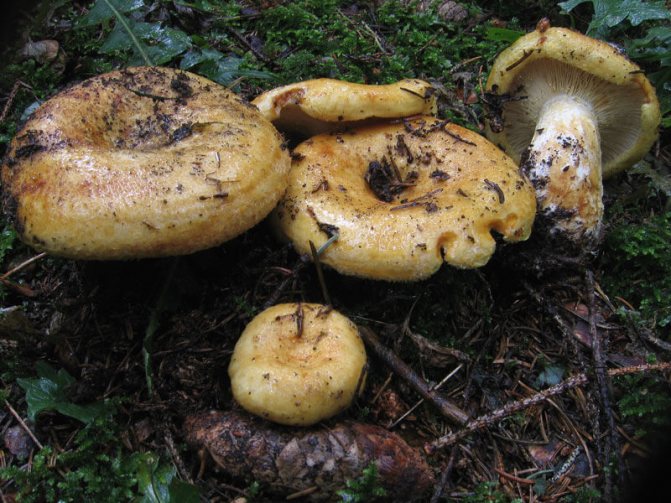
Pale toadstool is a very poisonous mushroom, poisoning with which is extremely dangerous for human life. It belongs to the genus of amanita and grows on fertile and well-lit soils of deciduous and mixed forests. Most often they are located in groups, but sometimes you can see that the mushroom grows separately, by itself. They can be found in late summer or early fall.

Pale toadstool is the most poisonous mushroom in the world.
Description of the distinctive characteristics of the pale toadstool
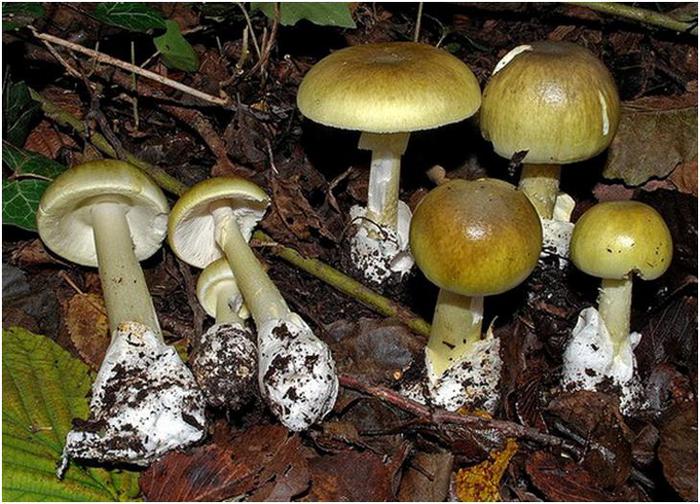
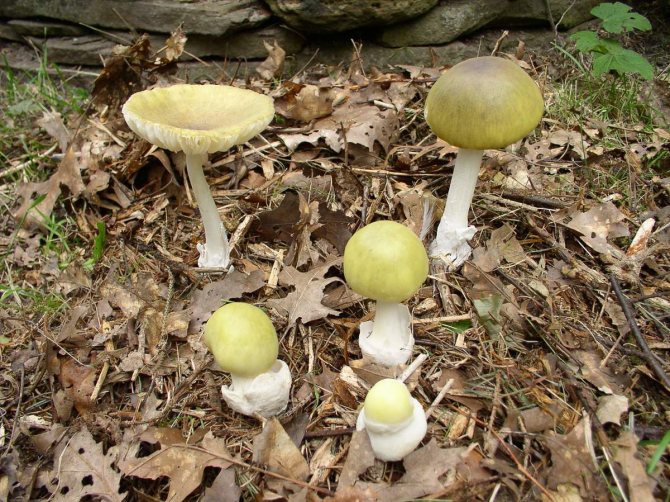
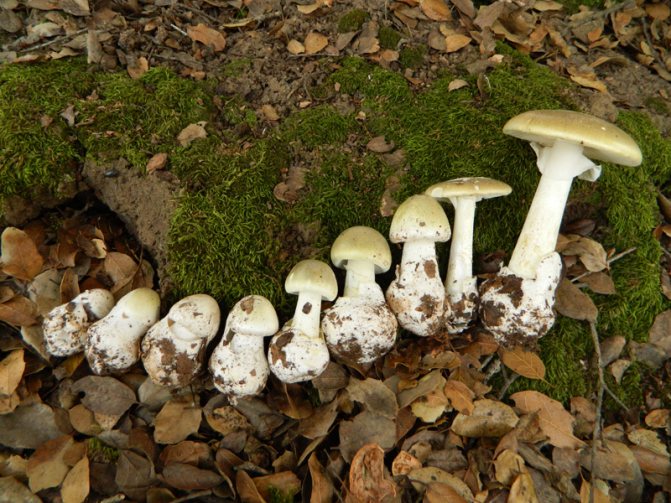
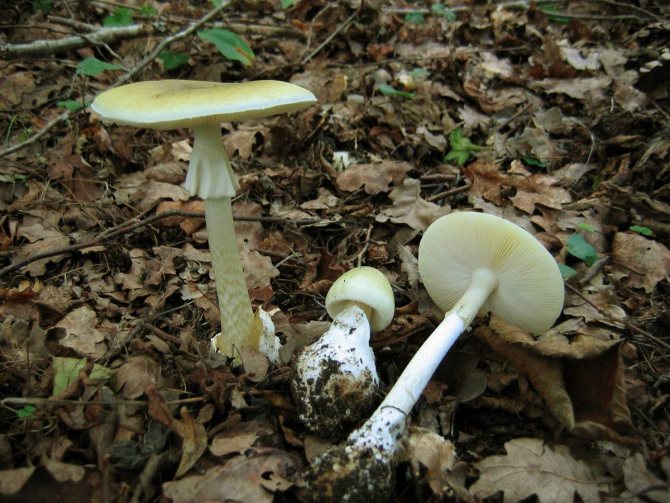
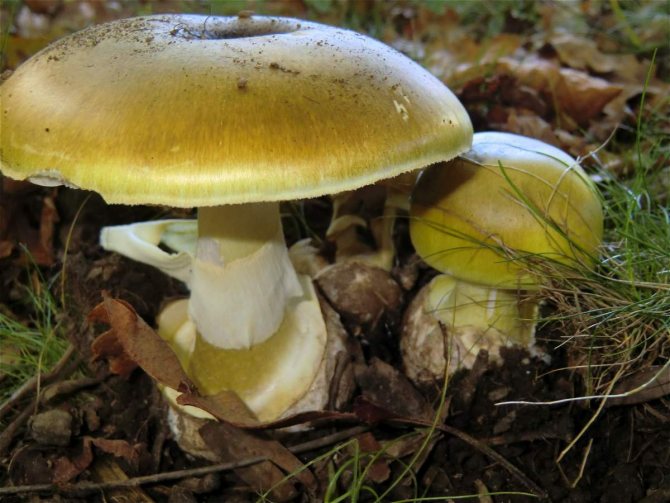
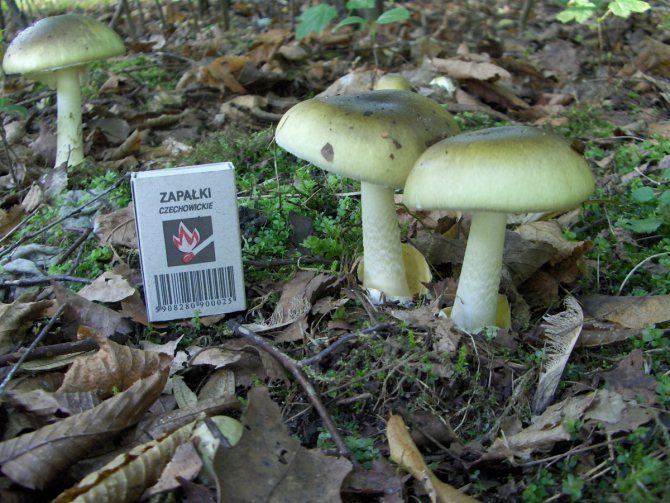
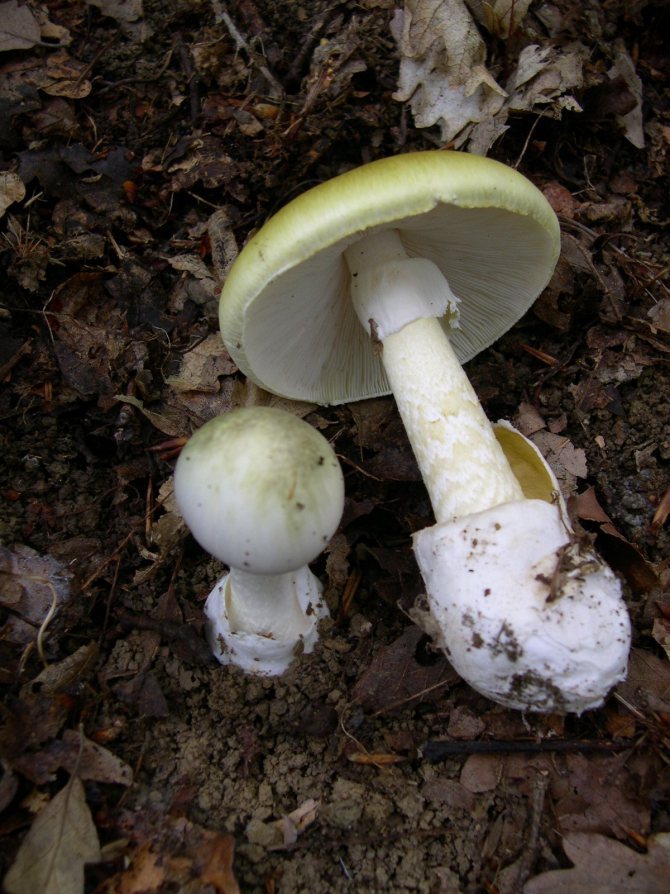
What does a pale toadstool look like? The body of this poisonous mushroom consists of a cap (its size ranges between 5 and 14 cm) and a leg (its length can be from 8 to 15 cm, and its diameter is from 1 to 3 cm).
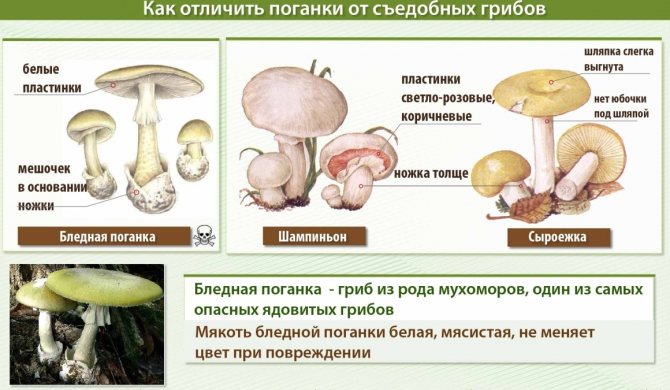

The difference between pale toadstool and edible mushrooms.
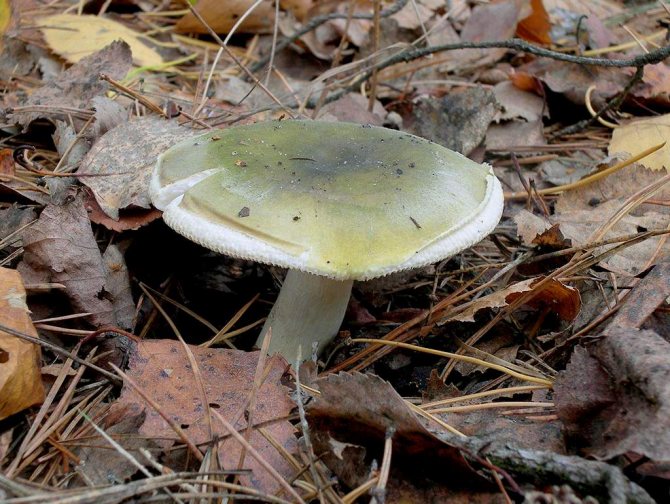
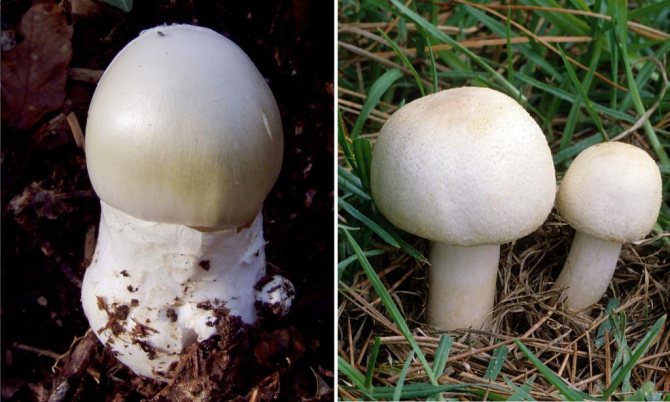
The young mushroom is usually covered with a film. The color of the cap can vary from grayish and greenish to olive, and its shape can be either flat or hemispherical, the edges are even. The pulp of the mushroom is white, juicy, its color does not change if the mushroom is damaged.
The toadstool tastes sweetish, the smell is not very pronounced. The leg of the mushroom is colored in the same way as the cap, there may be a moire pattern; shape - cylindrical, slightly thickened at the base.
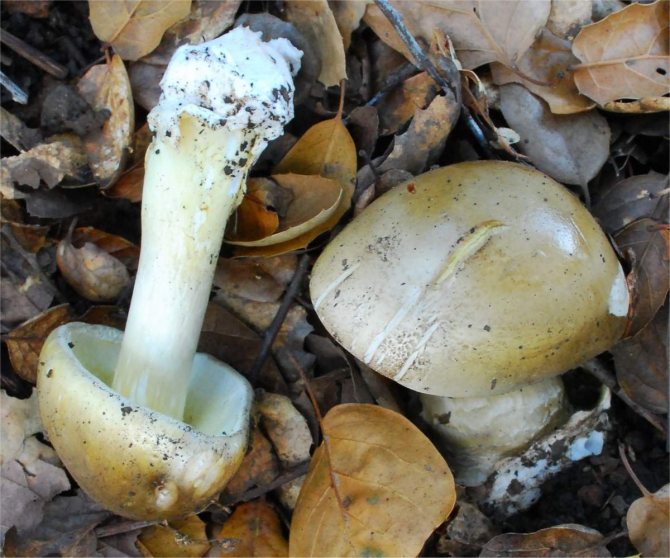
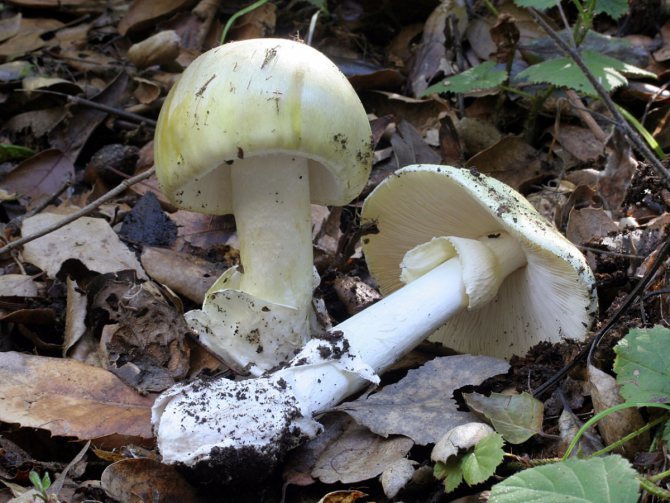
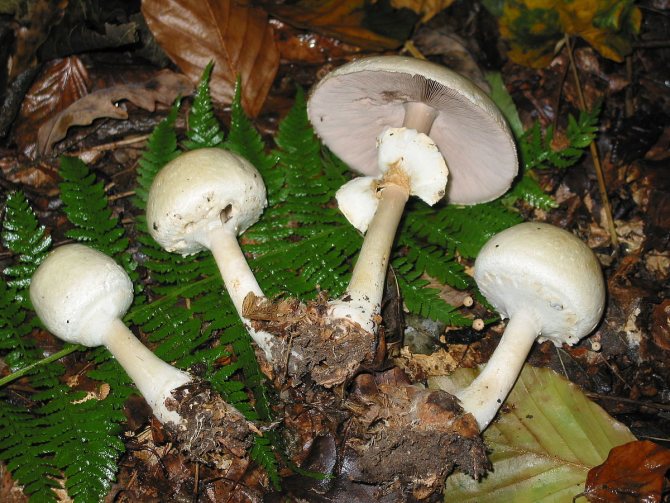
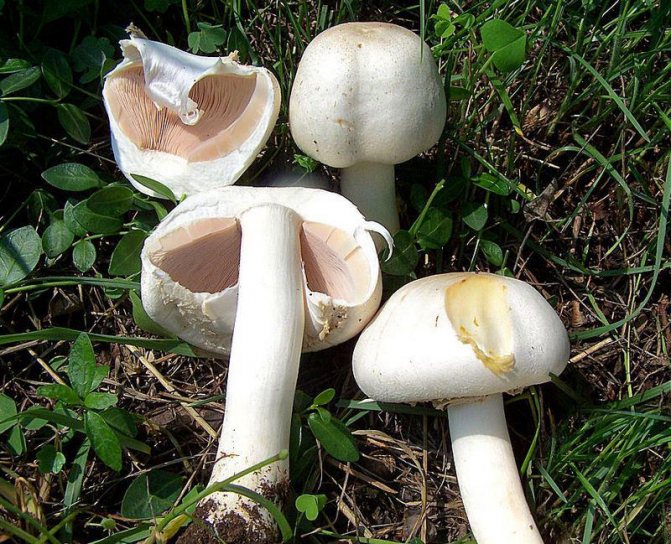
On the upper part of the leg, you can see a filmy ring, and in the lower part, where it is slightly thickened, there is also a film on the leg - already sack-like, it has a white or greenish color, its width varies between 3 and 5 cm. It is the presence of these films is the main characteristic by which you can distinguish the pale toadstool from other similar types of mushrooms.
Hat
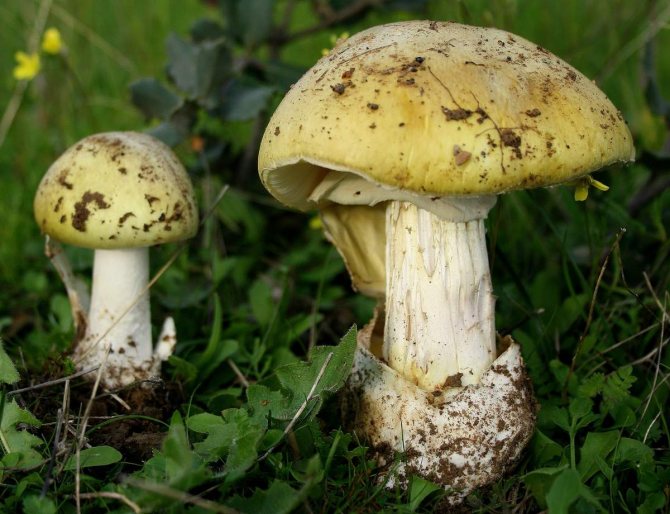
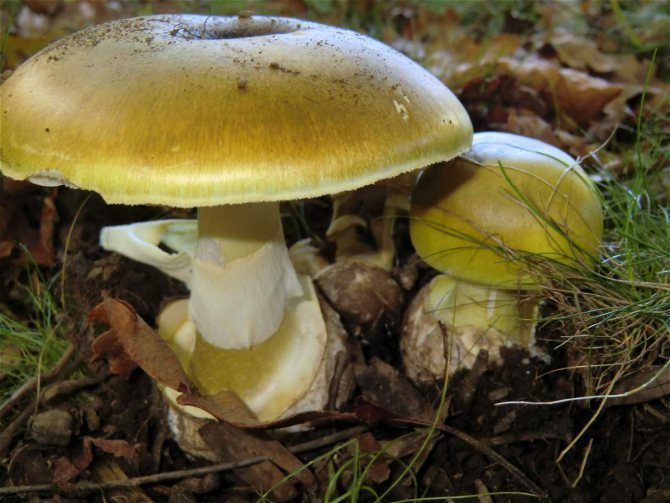
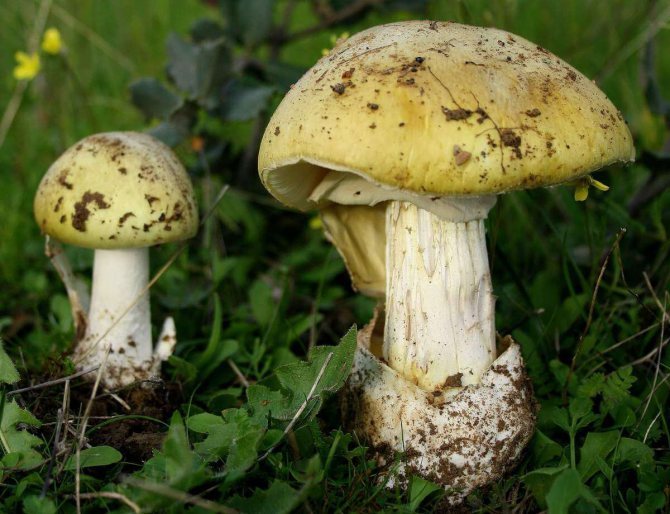
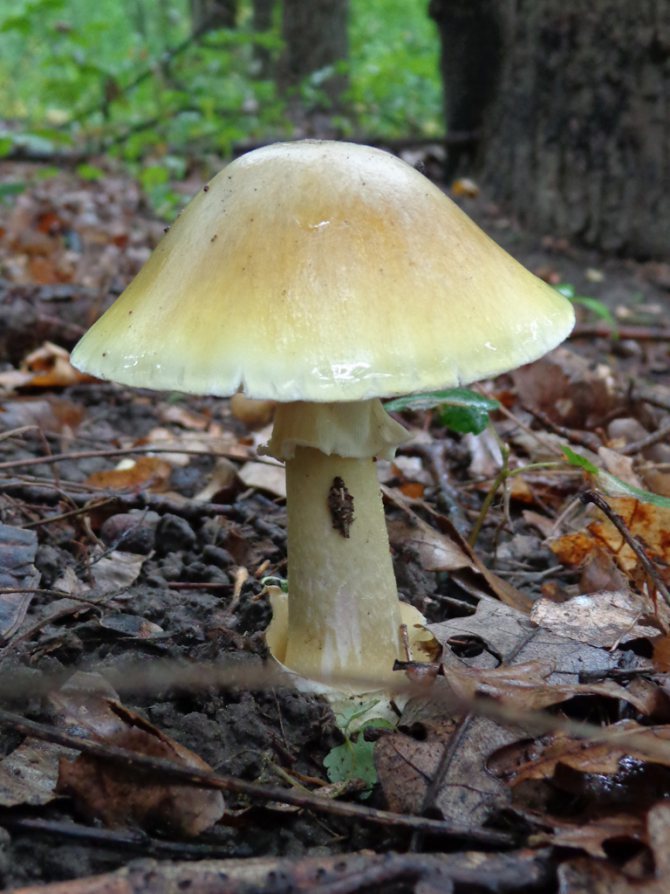
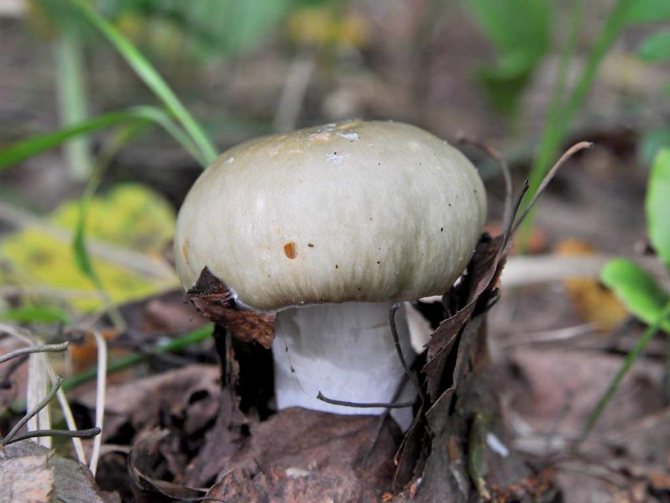
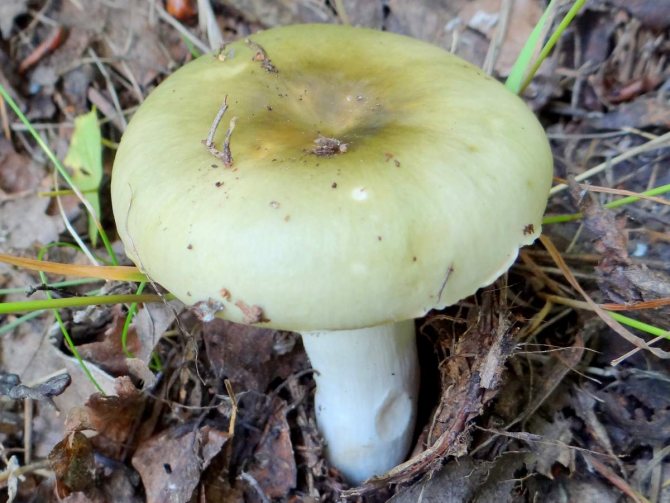
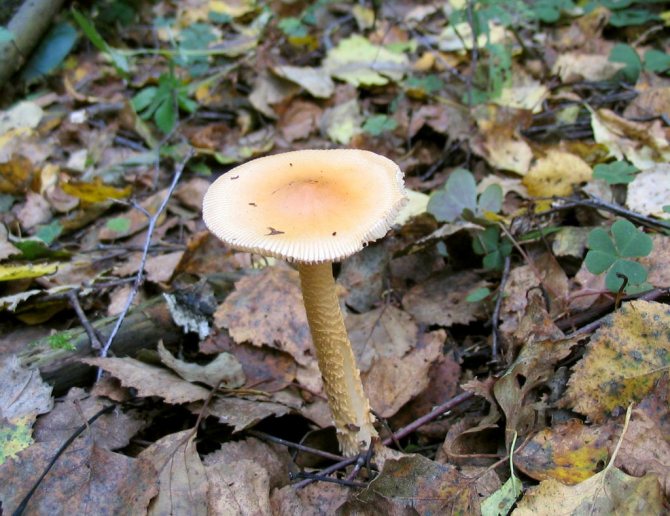
The color of the hat of the pale toadstool is white, beige, olive, grayish, yellow-green, and it itself has a convex shape, in young mushrooms it is bell-shaped, in adults it is hemispherical or flattened. The diameter of the cap is 4-15 cm. The edges have an even fibrous surface; in old mushrooms, the cap may have a ribbed edge. Small bumps can be located on the cap - the remains of a kind of blanket that covers very young toadstools.
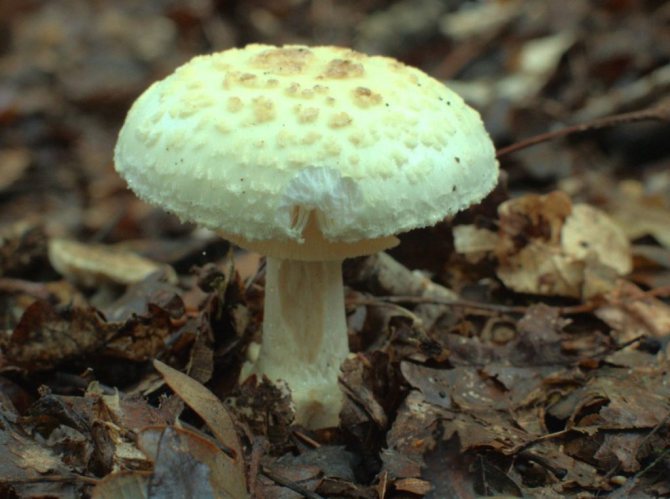


The bottom surface of the cap. The plates of the toadstool are exceptionally white, while those of the edible mushrooms are usually slightly pinkish. The increased width of the plates, as well as the lack of connection with the stem, can also speak of the toxicity of the fungus. In young toadstools, the plates are covered with a white film.
What edible mushrooms can be confused with pale toadstool?
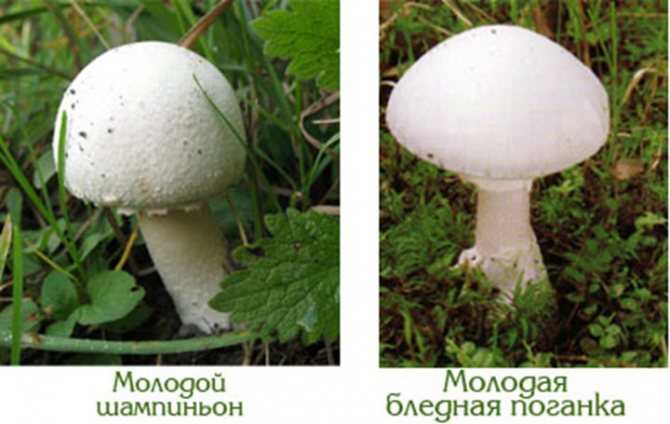
Pale toadstool is very similar in appearance to some types of mushrooms that can be eaten. These include champignons, green russula, greenish russula, russula with floats.
Important: filmy rings are the main distinguishing feature of the pale toadstool, since they are not found in the above types of mushrooms. That is why in no case should you cut them off under the cap when collecting mushrooms. You need to carefully examine the mushroom and make sure there are no filmy rings.
Symptoms and signs of pale toadstool poisoning


Description of the pale toadstool.
The pale toadstool is deadly poisonous. How does it differ from a number of other poisonous mushrooms? The fact that no processing, be it exposure to high temperatures or drying, can eliminate the toxic effect of its poison. In order for an adult to become poisoned, it is enough to eat only 100 g of the mushroom, that is, about a third of the fruiting body.Children are especially susceptible to the effects of the toxins of this poisonous mushroom. Tellingly, their symptoms of poisoning begin primarily with seizures; Another early symptom that occurs specifically in children is jaw clenching.
The peak of poisoning with this fungus, as a rule, is observed in August.
The severity of the symptoms of poisoning and the severity of the patient's condition depend on the amount of poison that has entered the body. The course of the disease can be divided into several periods.
The first period can last from 7 to 40 hours. It is called latent because no signs of the disease have yet been observed. This is the insidiousness of the pale toadstool: by the time the first signs of poisoning appear, a larger amount of poison has already entered the bloodstream and has begun to destroy the body.
The second period lasts from 1-2 to 6 days. Its symptoms appear suddenly and unexpectedly. These include:


Pain in the intestines and vomiting are the first signs of pale toadstool poisoning.
- severe diarrhea (first yellow-green, then - slimy and watery, sometimes with blood impurities);
- repeated severe vomiting;
- strong thirst: it is impossible to quench it, taking water leads to increased vomiting;
- severe cramps, abdominal pain, acute intestinal colic;
- severe dehydration, which leads to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, pallor of the skin, increased heart rate;
- blurry vision, dizziness, headaches;
- cramps, most pronounced in the calf muscles (this is the result of the body losing a lot of chloride due to vomiting and diarrhea);
- a sharp decrease in the amount of urine excreted or its complete disappearance (the reason is dehydration);
- thickening of the blood.
The third period is typical for poisoning with the poison of the pale toadstool. It is also called the stage of sham recovery. Its duration is about a day. The patient's state of health suddenly improves dramatically, however, if a biochemical blood test is done, liver dysfunctions can be seen. The patient suffers from severe drowsiness. Often after 10-12 hours, collapse suddenly develops and the person dies. This happens in the case of severe poisoning with the poison of the pale toadstool.
In the fourth period, poisoning of the internal organs develops. The symptoms are as follows:


In case of mushroom poisoning, you must first rinse the stomach.
- yellowness of the mucous membranes and eyes;
- pain in the liver (right hypochondrium), heaviness in the same place;
- resumption of diarrhea and colic;
- nephropathy;
- toxic hepatitis;
- acute heart failure (it develops in case of severe poisoning and leads to death).
Thus, a person usually dies during the action of the poison within 10 days. It all depends on the state of his heart and blood vessels. In the case of a mild degree of poisoning, the person recovers very quickly. In the case of moderate and severe poisoning, the patient requires long-term rehabilitation, the period of which can last from 2 weeks to several months.
As a rule, the body is able to fully recover: after about 2 weeks, jaundice passes, after which gradually both the liver and other organs resume their activity in full. However, do not forget that the likelihood of death with such poisoning is very high, since toxic hepatitis develops with lightning speed, and the signs of cardiovascular failure are very pronounced. Treatment, as a rule, does not work.
Inedible mushroom. Poisonous mushrooms in the forests of Russia
Mortality from poisoning with poisonous mushrooms reaches 90% in some cases! Poisonous mushrooms are especially dangerous for the child's body. The main distinguishing feature of poisonous mushrooms is the presence of deadly substances in them, and not the external resemblance or absence of any "normal" fungal trait. Therefore, when going on a mushroom hunt, it is important to become well acquainted with the representatives of poisonous mushrooms.
Poisonous Mushrooms - Pale Toadstool
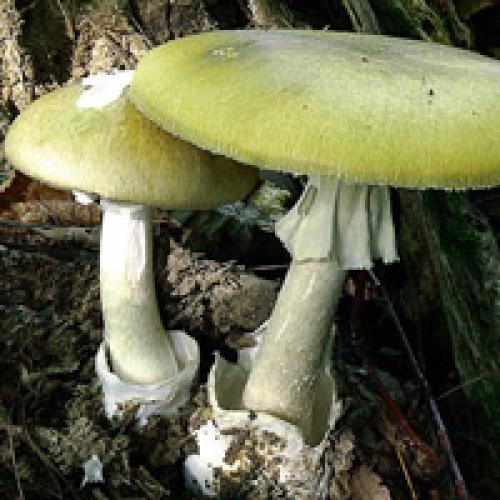


Pale toadstool - not the most poisonous mushroom! It is better to avoid poisoning with a pale toadstool! The appearance of this mushroom is practically not much different from other mushrooms growing in forests, so it is easy to quite easily confuse it with an edible mushroom.The color of the cap of this toadstool is yellowish-brown, pale greenish or greenish-olive. Usually the center of the cap is darker in color than the edges of the cap. The structure of this type of mushroom is rather fleshy, with cylindrical stripes of pale green color. On top of the leg there is a ring of a striped pale or white color. Pale toadstool forms mycorrhiza in deciduous tree species, growing in mixed and deciduous forests. Begins to bear fruit in late summer to late September. Pale toadstool (pictures) has a strong toxic effect.
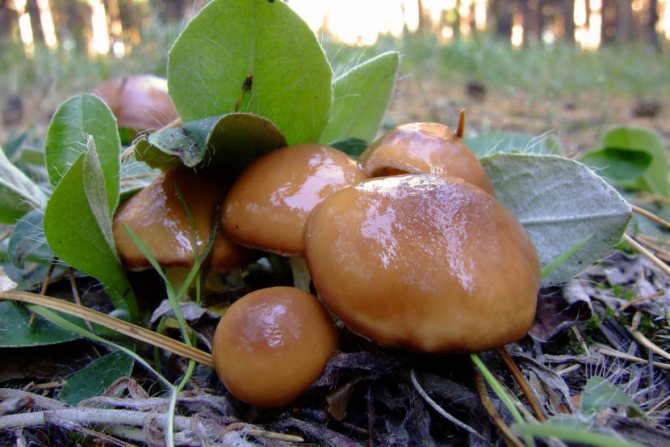
Poisonous Mushrooms - False Honey
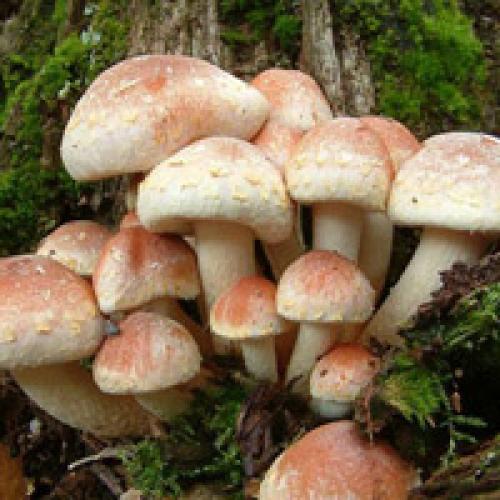


The mushroom has a convex head up to 5 cm in diameter. The color of the cap is predominantly yellowish with a red or orange tint and a darker color in the center. The mushroom has a thin, even, hollow, fibrous stem. The pulp of the mushroom is light yellow, has a bitter taste and an unpleasant odor. Falsefoam lives from June to October. Most often it can be found in fairly large groups on rotting wood. The fungus is poisonous and causes digestive upset. After 1-6 hours, signs of poisoning immediately appear: vomiting, loss of consciousness, nausea, excessive sweating. False foams are similar in appearance to autumn, winter, summer and gray-lamellar foams.
Poisonous mushrooms - False fox (orange talker)
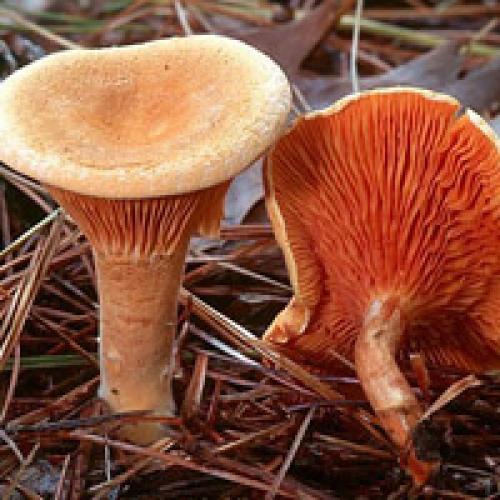


This poisonous mushroom has a bright orange-red to copper-red cap. The shape of the false chanterelle cap resembles a funnel with an even edge. The plates of the fungus are bright red, sinuous. The stem is about 10 cm long and 10 mm wide, often narrowed towards the base. False chanterelle mainly grows in the warm season from July to October, near real chanterelles. Also, this type of mushroom often grows in families, in rare cases alone. A false chanterelle can be easily distinguished from an edible chanterelle: A real chanterelle has a bright yellow color, a concave cap, smooth on top and wavy at the edges. The leg is dense and elastic, slightly darker than the cap. A characteristic feature of chanterelles is their pleasant fruity aroma. False relatives of the chanterelle are outwardly brighter, yellow-orange in color, with a hollow and thin stem. The edges of her cap are even, unlike a real chanterelle. And most importantly: the flesh of a false chanterelle has a very unpleasant smell.
First aid before the arrival of the doctor
Since the first symptoms of pale toadstool poisoning begin to make themselves felt only when a sufficient amount of time has passed after the poison has entered the body, first aid is ineffective, the result will be zero. It is necessary to see a doctor as soon as possible, ideally - to call an ambulance. In the hospital, the patient will undergo antitoxic therapy.
Important: it is necessary to treat each person from the same company that ate mushrooms.
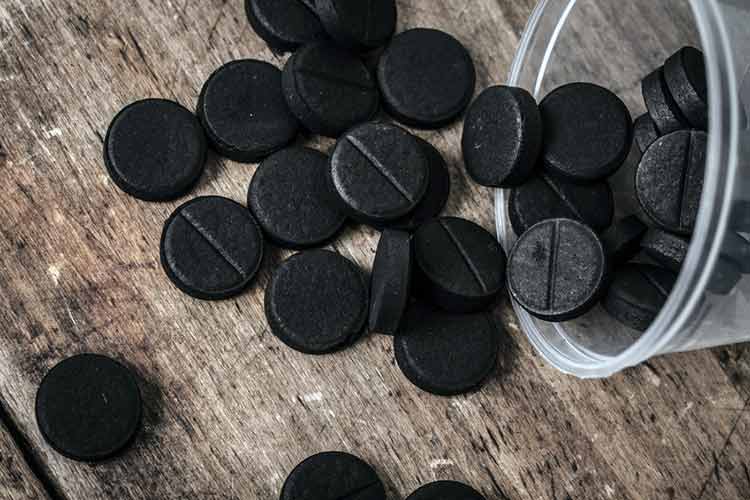
What can you do before the ambulance arrives? Everyone, in whose body a pale toadstool could get, needs to cleanse the stomach, after which it is necessary to take activated charcoal at the rate of 1 g per 1 kg of human weight.
Treatment of poisoning with a pale toadstool in a hospital
Since there is no antidote, poisoning with the poison of this mushroom is extremely difficult to treat, since at the time of going to the doctor it had long been absorbed into the bloodstream. Actions performed in the hospital:
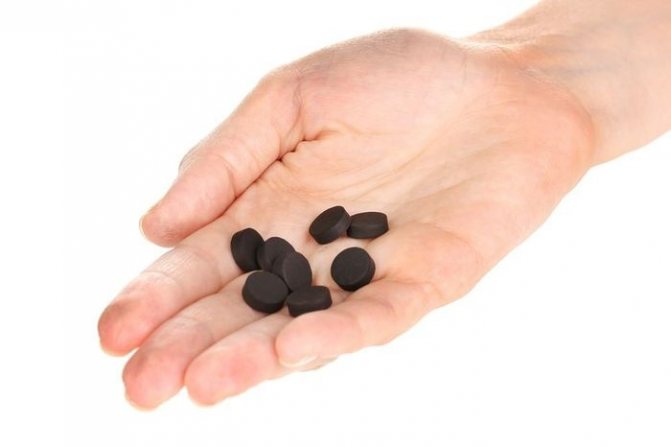


Immediately after washing the stomach in case of mushroom poisoning, the patient should be given activated charcoal.
- Gastric lavage. It is effective because food debris can linger in the gastrointestinal tract for up to 20 hours, so this procedure is carried out even if vomiting is present.
- Drug therapy (benzyl penicillin, silibinin, lipoic acid).
- To eliminate dehydration, intravenous administration of drugs such as "Trisol", "Acesol", Ringer's solution is carried out.
- To eliminate hypoglycemia, a glucose dropper is placed.
- Replenishment of chlorides (it can be done intravenously, or you just need to give the patient salt water).
- Hemisorption and forced diuresis, necessary to accelerate the elimination of toxins from the body.
- For the prevention of increased blood clotting, the use of proteolytic enzymes is shown.
- Prescribing cardiac medications.
- Hepatic therapy.
Unfortunately, the prognosis depends mainly on the amount of poison that has entered the body and the general condition at the time of poisoning.
Is it possible to use the pale toadstool for good purposes?
Interestingly, an antidote is currently being developed based on substances that are part of the most pale toadstool. They are able to neutralize both her own poison and the poison of the stinking fly agaric. Moreover, this mushroom, that is, its ultra-small doses, is used in homeopathy for the treatment of diseases such as diphtheria, Crumpy syndrome, gastritis, tenesmus, vertigo, visual disturbances due to damage to the eye muscles, collapse, cholera (with it, with the help of small doses of pale toadstools fought back in the Middle Ages), lethargy, etc.
Time and place of fruiting
Toadstool loves fertile moist soil, which is why it is so often found on the way of lovers of "quiet hunting". It can be found in forests, clearings and even parks, which makes it even more dangerous. After all, even edible mushrooms growing next to it become unusable.
Natural habitat - deciduous and mixed forests of Europe, Asia and America. The most common toadstool can be found near oaks, birches and hazel. But at the foot of coniferous trees, poisonous mushrooms almost never grow due to the poor quality of the soil around them.
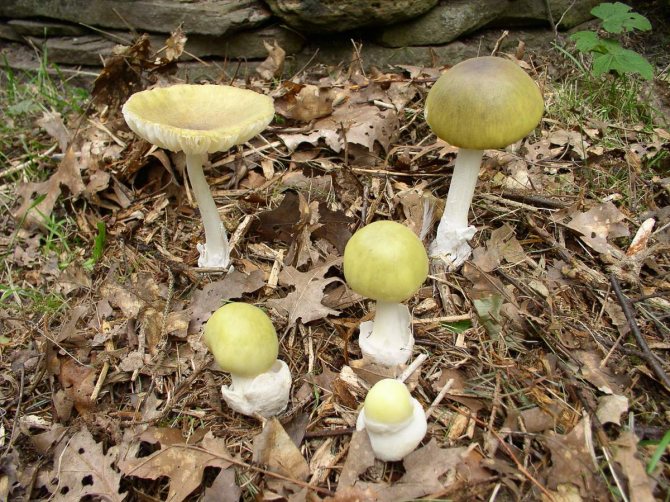


On the territory of Russia, forest fruits can be found in areas with a temperate climate and fertile, moist soil. There are frequent cases when toadstools grew in vegetable gardens and orchards.
The time of active fruiting of toadstools falls on the summer-autumn period, namely from August to November, due to frequent rains at this time of the year.
Prevention measures
First of all, you need to remember that it is very dangerous to take unfamiliar mushrooms in the forest, and just collect them without having the necessary experience for this. Also, in no case should you buy them from private individuals.
Toadstool poisoning, as a rule, occurs when accidentally mixing it with mushrooms, and this should also be remembered. If you suspect mushroom poisoning, it is necessary to urgently take measures to cleanse the stomach and detoxify for everyone who ate them.
Be attentive and take care of yourself and your loved ones!
First aid at home
If there is a suspicion of mushroom poisoning, namely, if vomiting begins a few hours after eating mushroom dishes, you should not hesitate and rely on "maybe it will pass by itself."
Having poisoned with mushrooms, you should not panic, you must immediately call an ambulance, and while she is traveling, you should rinse the stomach. How to properly carry out such a procedure can be found here.
After each gastric lavage, a saline laxative should be given. It is good to put an enema - for an adult, 1.2-1.5 liters is enough, for a child 0.25 liters of cool water. In case of convulsions, applying hot heating pads or mustard plasters to the calf is indicated. In case of loss of consciousness, care should be taken that the person does not choke on vomit.
The remains of the mushroom dish and vomit must be handed over to the emergency doctor for laboratory analysis. This will significantly reduce the time it takes to determine the exact cause of the poisoning and will help to start the appropriate therapy faster.












































