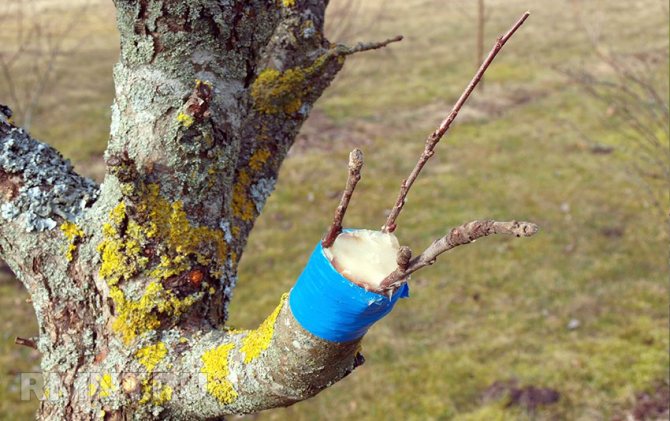
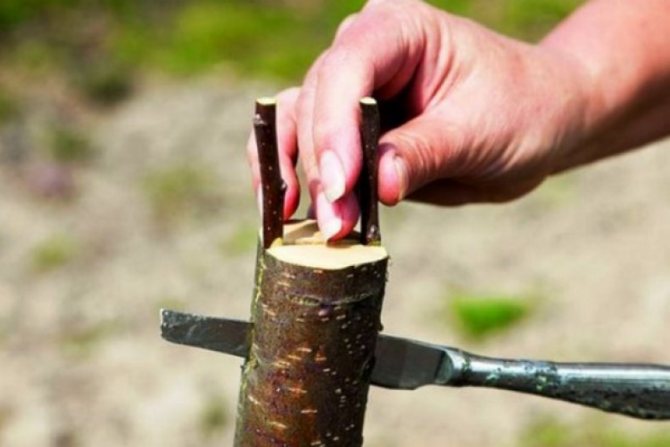
When vaccinated, the gardener transfers part of one plant to another, and they grow together.
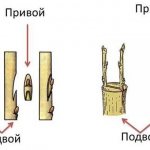
Rootstock and scion are needed for grafting.
What is a rootstock and a scion.
- Rootstock - this is a seedling or an adult tree to which we are grafting.
- Graft - a small part of the cultivar, which we grow to the stock.
The cells of the cambium, located directly under the cortex, grow together. Wood tissue (without cambium) does not grow.
Why budding is carried out
- The procedure is carried out in the absence of plants of the desired variety on sale.
- Budding fruit trees allows you to increase the winter hardiness of the grafted variety.
- Budding makes it possible to replace low-value tree varieties or wild animals with better ones in the garden. Or keep the variety you like.
- Allows you to reduce the waiting time for a new harvest. Grafting on an adult tree or a three-year-old seedling allows you to enjoy the harvest in a few years. Whereas trees grown from seeds or seeds bear fruit no earlier than 5-6 years later.
- Grafted different varieties on one tree will diversify the number of fruit crops and save space on the site.
- Budding will help to get the desired varieties of fruit trees, but not adapted to your conditions.
Rootstock selection

Rootstock.
Optimal stock is considered a one-two-year-old shoot that has grown from a seed. Varieties:
- Anise.
- Chinese woman.
- Antonovka.
Initially zoned, resistant to local diseases and climate... Their minus is that fruiting occurs 4-5 years after vaccination.
Dwarf and semi-dwarf rootstocks more early maturing and bear fruit for 2-3 years, but require constant additional care: watering, feeding, pruning.
Advantages of budding
- Almost any well-formed bud can produce a new plant with all the benefits of the original variety.
- The procedure is very fast.
- Small grafting area allows for minimal trauma to the stock.
- Inoculation in the same rootstock can be repeated if budding was unsuccessful.
- Budding of fruit trees requires a minimum of rootstock material. This is true if there are only one or several cuttings of the desired variety.
Advantages and disadvantages
Many processes in our life have their pros and cons, including vaccination. Budding fruit trees has its own characteristics, for some it is not suitable. For example, evergreen trees cannot be grafted. So, let's talk about the advantages of this procedure:
- Ideal for propagation of various fruit plants that cannot vegetatively divide.
- Promotes better branching.
- Promotes more active tree growth.
- Cuttings are cut at the place of fruiting.
- The grafted plants begin to bloom and bear fruit earlier.
- High reproduction rate.
Vaccination also has its drawbacks:
- Large expenditures of time and effort for leaving;
- For some plants, grafting shortens life. For example, red-flowering chestnuts gradually die after this procedure.
- Sometimes there is a physiological incompatibility.
- Ornamental plants often deteriorate in the quality of the planting material.
- Plant growth slows down.
Despite the many disadvantages, it should be remembered that summer budding of fruit trees is important. Sometimes this is the only way for plants to reproduce.
What are the grafting of fruit trees
Methods of grafting fruit trees by type of scion are divided into several groups:
- with an eye, when one kidney is inoculated, which is called budding;
- cuttings, the so-called copulation;
- a plant - the most difficult method of reproduction, called ablation.
Grafting of fruit trees according to the technique is divided into:
- inoculations in the butt;
- lateral incision grafting;
- wedge vaccinations;
- direct and improved copulation;
- inoculation in the split;
- bark vaccinations;
- flute vaccinations;
- budding in the butt;
- budding into a T-shaped shield.
The listed methods are the most common. In practice, gardeners use a maximum of five.
The methods of grafting fruit trees according to their location on the rootstock can be divided into those that are made into the root, into the trunk, into the branches of the crown, into the stump. And also grafting can be horse and side. Horse grafting requires cutting off the top of the rootstock, with the scion subsequently forming the top of the tree. Lateral grafting is done on the side of the trunk, without cutting off the top of the stock.
Application practice
The budding method is convenient and efficient.


Small-fruited apple and mountain ash are similar in growth rates. Budding an apple tree on a mountain ash increases the winter hardiness of the seedling. In addition, the mountain ash rootstock can reduce the growth of the usually tall Chinese women.
Grafting large-fruited apple trees on mountain ash is short-lived.
Having studied the ways how apple and pears should be inoculated with an eye (budding), you can significantly expand the capabilities of your orchard.
The difference between vaccinations by timing
Spring grafting is carried out during the period of intensive movement of juices. The graft should be harvested at the end of autumn or at the very beginning of spring, but it should still be in a dormant state. Spring grafting is done in April or May, the buds should not swell yet.
Summer vaccination occurs in the second half of the summer. The buds and shoots that have developed well during the current year become a graft. The timing of grafting trees in summer starts from the 20th of July and ends at the end of August.
Winter grafting is often done indoors. The seedling grows together in the winter months, and in the spring already grafted trees are planted in the ground. Can be grafted into the trees in the garden in winter, if the air temperature has not dropped below + 2 °.
Budding in the spring and summer is considered the most productive, since it is during these periods that the bark of the trees leaves the trunk well, the cambium divides intensively, facilitating the procedure and ensuring good bud survival.
Inoculation"
Budding fruit trees with an “eye” is one of the most common breeding techniques. In this case, a single kidney becomes the admission. In the spring, a bud of a cultivated plant, formed last summer, is grafted. It is taken from a cuttings harvested last fall or at the end of winter. In the same season, the grafted bud will grow and give a new shoot, therefore, spring budding is called "grafting with a sprouting eye".


Summer budding is done by a bud that has matured in the current season. It will grow into growth only next spring, so the summer vaccination is called "sleeping eye budding."
Timing
The specific time for summer vaccination depends on on the climate of the region and the weather of the current season... There are standard guidelines, but experimental gardeners sometimes violate them.
When budding (kidney grafting)
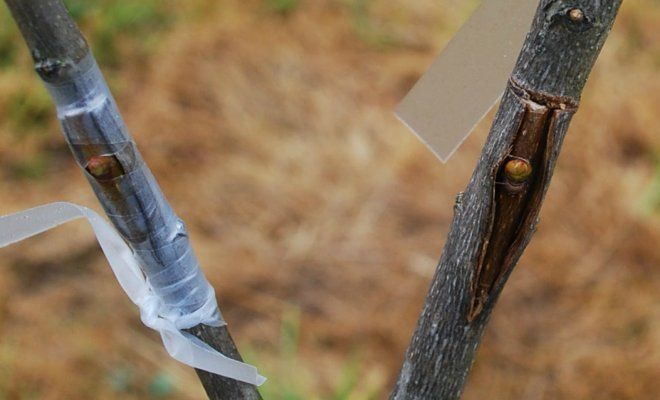


The timing of budding depends on the region where the apple tree grows.
Budding from mid-July to mid-August is carried out in Central Russia, in the North-West region, in the Urals, in Siberia.In this time interval, the second (after the spring) active sap flow of the apple tree occurs. Young shoots are already partially lignified, and the buds on them are ripe and are dormant until the next season.
In the southern regions, apple trees are usually inoculated from mid-August to early September.
Optimal days for budding are when the incised bark easily lags behind the wood, and the cuts shine with moisture... The best clues are the plants themselves, although sometimes gardeners prefer to focus on the growing moon and zodiac signs.
Scientists and enthusiastic gardeners have experimented with an earlier summer budding time - June, first decade of July... In this case, the bases of the young shoots of the scion should already be semi-lignified, with fully formed buds. It is more difficult to carry out operations - because of the poor separability of the bark, but the stock and the scion grow together normally.
Summer grafting with green cuttings
For northern regions, the recommended dates are no later than June, for central regions - no later than July, for southern regions - any summer months are suitable.
Shoots grow from established cuttings, and they must have time to woody before the winter cold. Sometimes in the south they practice grafting on aging apple trees in late summer and early autumn; the buds wake up next spring.
Scion harvesting
It is advisable to cut the cuttings immediately before grafting or budding.
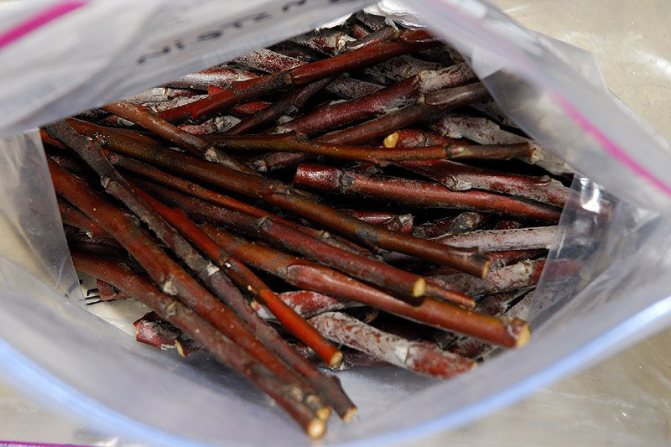


It is important not to let the cuttings dry out.
We immediately remove the leaf plates from them (leaving the petioles). If the operations are postponed for several hours, then we put the branches in a container with a small amount of water and place them in the shade. For several days, the cuttings can be stored in a damp cloth, but then the effectiveness of the vaccinations will be lower.
If the role of the stock is played by an apple tree of a cultivated variety, then we select the scion with close ripening times.
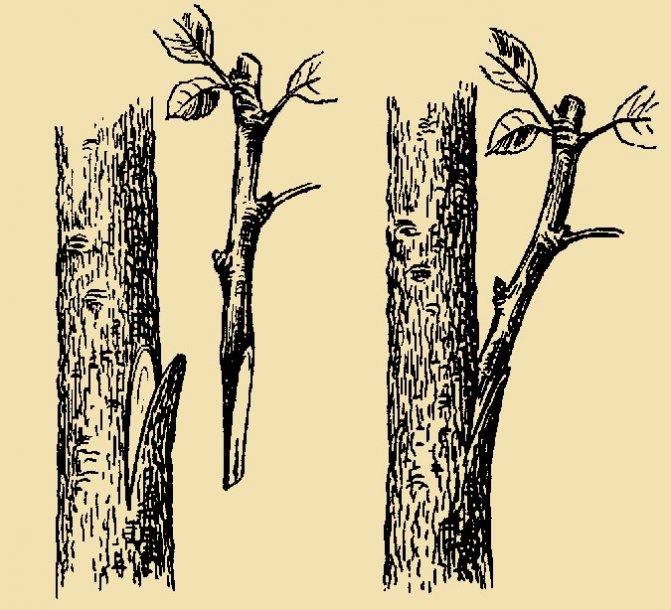
Method of budding in the butt
This is a fairly simple method of grafting fruit trees. To carry out the grafting, the rootstock must first be wiped from dirt and dust and a sharp knife and tape must be prepared for dressing. Further:
- On the rootstock with a sharp knife we cut shallowly along the shoot by 2.5 cm. We make a "tongue". About half of the tongue, but no more, should be cut off.
- The scutellum with the bud is cut from the cuttings of the selected plant. Its size should be the same as the cut on the rootstock.
- Scutellum with kidney. It should completely coincide with the cut on the rootstock, or they should be aligned so that one edge coincides well with the cut of the bark and the cambium.
- The budding site is tightly bandaged with a prepared tape, while the kidney should remain outside. After a couple of weeks, the results of the vaccination can be expected.
The shoot over the grafted bud during spring budding is not cut off until it is completely fused. The next spring, a cut is made of the shoot above the budded bud, which has gone into growth if the vaccination was summer. This method, which does not require peeling off the rootstock bark, makes the grafting period wider.
Method of grafting with a flap in a T-shaped cut
It is for this method of budding that the movement of the juices is very important, since the scion is oculated directly to the cambial layer. So:
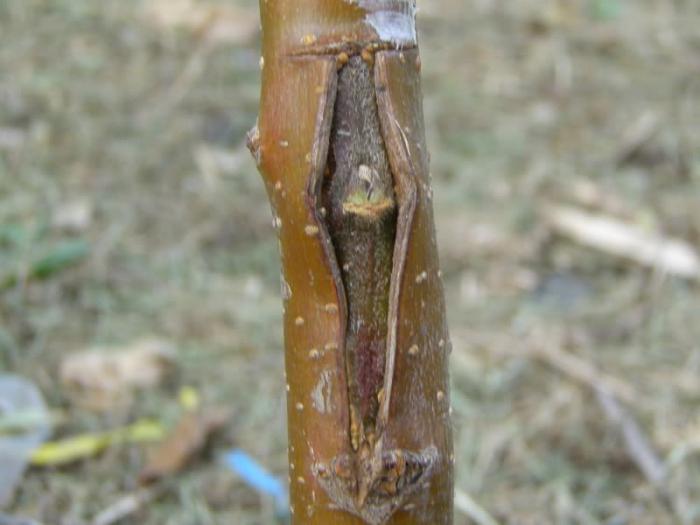


- The bud for this grafting method should be cut off along with a thin layer of bark and wood. The length of the flap - the so-called cut - should be 2-3 cm, width - half a centimeter. When making budding in the summer, a stalk should be left above the selected bud, for which it will be convenient to take a shield. During the spring inoculation, the flap itself should be cut off with a margin from above, which can be removed after inserting the flap into the pocket.
- A cut is made on the rootstock, trunk or shoot, corresponding in size to the shield. First a horizontal incision, then a vertical one. The edges of the vertical cut are gently folded back to form a pocket.
- The kidney shield is inserted from top to bottom into the pocket. The bottom edge of the flap will be fixed with the base of the pocket, and the top, if it is larger, should be cut off with a knife.
- The graft is tightly fixed with tape.The dressing starts from the bottom and tightly presses the scutellum to the cambial layer of the rootstock plant.
The budding of apple trees is carried out precisely with the help of the T-shaped cut, since it is simple and highly productive. The average air temperature should be 8 ° C.
Scion preparation


Preparation of rootstocks.
Cutting of the desired grade it is more convenient to take when pruning an apple tree in summer. For this, annual lignified branches with a length of 30-40 cm are suitable, which must be removed.
For vaccination use growth buds, more elongated in comparison with flower buds. They are located in the middle of the annual growth rate.
On a note! On the lighted side of the tree, the buds are most viable.
4-5 cm of the tops are cut from the harvested shoots, leaves and stipules are removed. It is advisable to leave the leaf stalks for the convenience of further work and as an indicator of survival rate.
It is good if the grafting material can be taken in a neighboring garden and start budding on the same day.
If this is not possible, cuttings with buds must be protected from drying out - wrapped in a damp cloth or transported in a plastic bottle wrapped in wet paper.
How to bud a sweet cherry
Cherries are grafted mainly on cherries. This allows you to increase its frost resistance and yield. Moreover, the cherry is chosen bushy, which makes the cherry flexible and compact in shape. Piping cherries on a tree cherry will make the cherries powerful, and it will be problematic to cover them for the winter. Vaccination begins in the spring, in late March-early April, before the start of the movement of juices. For this, a two-year-old cherry shoot is selected, onto which a sweet cherry is grafted at a height of 20 cm from the soil. Cherries take root on cherries with difficulty, so you need to act carefully and carefully. An improved copulation with an incision length of at least 3 cm will be the best way. For this, short cuttings with two buds are prepared. In mid-July, the bandage around the vaccine is loosened slightly. At the same time, a stronger growth formed from the kidneys is retained and the second is removed. A part of the cutting above the lower growth is cut into a ring.
Gardening Tips
- The most suitable for budding will be trees whose crown branches will not be thicker than 11 mm. If the thickness of the branches exceeds 15 mm, it is better to use grafting with a cuttings.
- Budding on the south side of the trunk or branch can be unsuccessful as the sun can dry out the bud.
- Good survival can be ensured by budding with several buds at once from different sides of the rootstock branch. Only the distance between the eyes should be at least 15 cm.
- At a distance of 30 cm from the fork in the trunk, the last peephole should be located, if there are several of them.
- The use of putty for budding is optional.
- Budding in the rain is prohibited.
- An unsuccessful inoculation can be repeated if the bark on the rootstock is still separating.
- It is possible to bubble in the spring and on cloudy summer days at any time. In the summer heat, the procedure is best done in the morning or in the evening.
- Summer budding in dry weather requires abundant watering several weeks before the procedure. This will provide intensive sap flow.
- The best eyes will be those in the middle of the shoot.
- Only mature buds are suitable for budding. You can check by simply bringing the kidney to your ear and pressing lightly on it. If the sound is squeaky, then the "eye" is mature.


Fruit tree budding is suitable for propagation of any cultivated tree or shrub. Having mastered the technique of grafting, any gardener can acquire a garden with his favorite varieties, and not only with those that can grow in specific climatic conditions. However, you should not rely solely on advice to gardeners, calendars, television programs or country horoscopes.Consider local climatic conditions and listen to seasoned gardeners in your area. And then the garden of your dreams will not keep you waiting long.
Harvesting cuttings
Cuttings are used as a stock:
- Annual shoot at least 30 cm long;
- With a cut diameter of 5-6 cm;
- Well ripened;
- Having a characteristic color for the variety;
- Not damaged by pests;
- No signs of disease.
It is better to procure material from the south side of the treeremoving competing branches so as not to harm the mother plant.
Shoots are very elongated, with too long distances between the buds and have a light green color may not be ready enough or weakened.