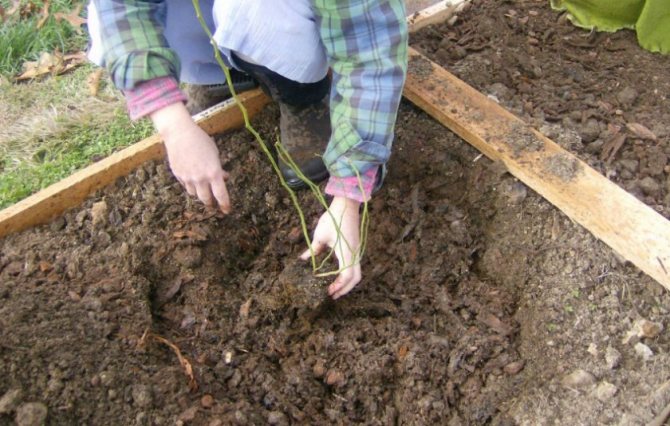
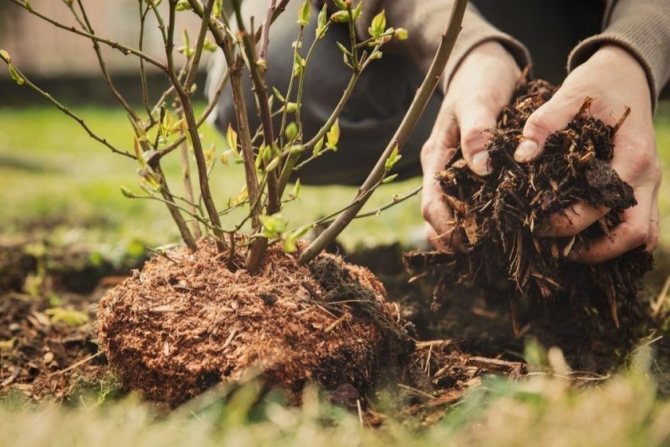
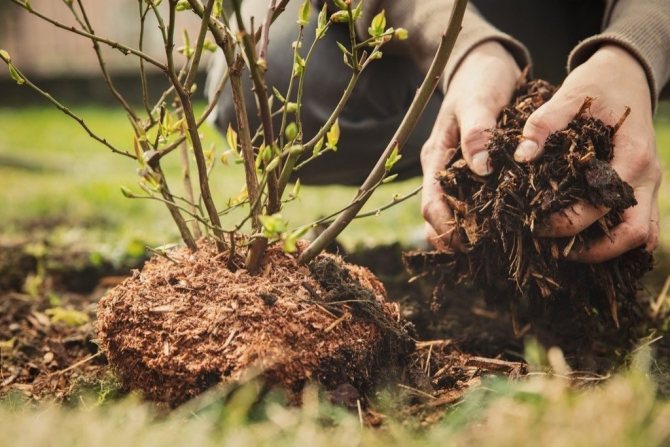
This procedure is sometimes carried out by gardeners on their plots. There are many reasons for replanting already formed plants to a new place: these are, for example, soil conditions (often together with the peculiarities of the climate). It happens that the place where the shrub has been growing for several years has been flooded with melt or rainwater, or the shrub has suddenly started to freeze annually. Or the conditions are purely domestic, when, for example, a neighbor has built a fence, and now your bush is in the shade, or the bird cherry tree has grown so much that the currant bush that grows nearby already does not have enough space.

Transplanting a currant bush. <>
One way or another, we are faced with the task of transplanting a shrub to a new place. And at the same time, you need to do this so that after transplanting the bush does not take root for too long and quickly re-fertilize.
At first glance, everything seems banal and simple: the bush needs to be dug up and re-planted, however, in fact, this is far from the case. Often, after such a transplant, shrubs simply die or get sick and take root for a very long time.
In order for everything to go smoothly, we will give general recommendations for transplanting in this article, we will give several important tips, and then we will analyze the transplantation scheme for each group of shrubs.
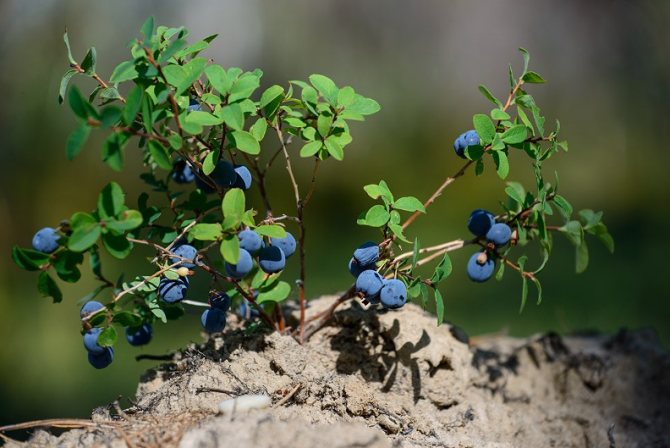
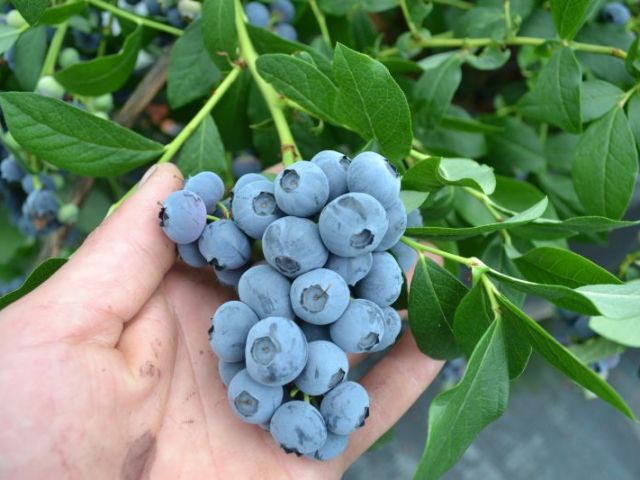
Delicious and healthy berry
Blueberries are a shrub that grows up to 1 meter in height. In high-altitude places it grows as a low shrub. Shoots are oblong, pubescent in the initial period of growth. Leaves are elliptical, slightly folded at the edges, bluish-green, matte on top.
Green or whitish flowers appear on the tops of the lateral branches. Blooms in May. The berries are spherical, purple-black, with a blue waxy coating.


The shrub grows in swamps, in swampy forests, on infertile soils containing little humus. In the mountains it grows at high altitudes. The berry has excellent taste and nutritional value and is rich in vitamins. It is important to know how to plant blueberries correctly, prepare the soil for planting, how to care for blueberries.
Growing blueberry seedlings
Blueberries take long enough to take root: at least 8 weeks. All this time, regularly moisten the soil in the bed with cuttings and periodically ventilate the greenhouse. Water once or twice a week until the leaves of the planting, and when the leaves bloom - several times a day (until the roots appear, the leaves on the cuttings of the blueberry should be constantly moist). Overheating or overcooling of the soil during the rooting period must not be allowed (the optimum substrate temperature is 18-21 ° C).
If you notice signs of disease on the cuttings, treat them with Azofos, Kuprozan, Topsin-M or Fundazol. To protect against pests, Ambush, Rogor-S or any other suitable insecticide can be used.
With the onset of the second wave of shoot growth, start feeding blueberries with Solution (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water), Kemira (1 tablespoon for 10 liters of water) or any other universal liquid chlorine-free fertilizer. In total, carry out 5 such dressings with an interval of 7 days, consuming at least 1.5 liters of solution per 1 sq. M. After each feeding, do not forget to water the cuttings with clean water from a hose to rinse the fertilizer from the leaves.
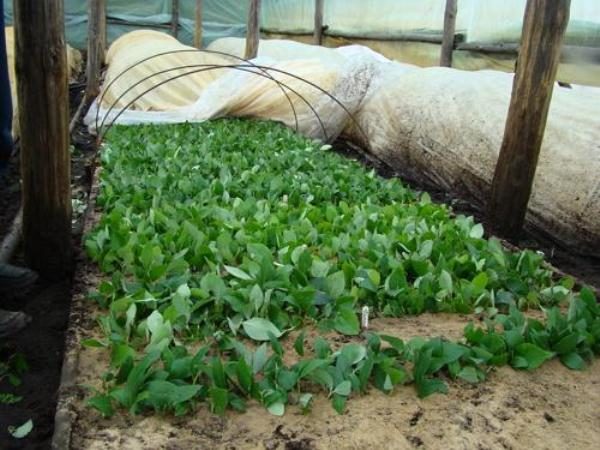
When the cuttings take root (usually after the second wave of shoot growth), start accustoming them to natural conditions: water less often and ventilate more often. In late August - early September, remove the film and spunbond altogether, and from the second half of September, reduce the watering of the seedlings so that when the cold weather sets in, the soil is not too wet.
At the end of summer or next spring, transplant the blueberries into containers with a volume of at least 1.5 liters, preferably 2 liters. Before the onset of cold weather, cover seedlings that will winter in containers with a 10-cm layer of wet (but not wet!) Sawdust or peat. And cover the plants remaining in the garden with spruce branches, after removing all the fallen leaves.
After 1-2 years, the grown blueberry seedlings will be ready for planting in a permanent place. Read about how to do it right in our article.
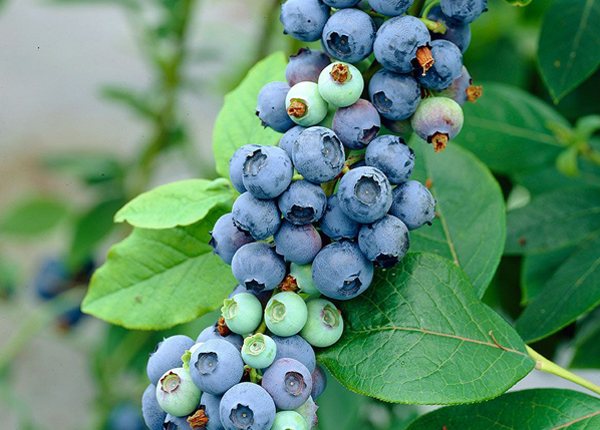
With proper care, up to 8 kg of berries can be harvested from one blueberry bush
Blueberries are not the easiest plant to grow. In order to propagate it by cuttings, patience and dexterity are required. But your efforts will be rewarded with a good harvest of delicate sweet and sour berries, which are also considered one of the healthiest in the world.
Landing rules
When choosing plants, you need to take into account the compliance of the variety with the agro-climatic conditions of the region. Selecting a site and preparing the soil is straightforward, but with just one blueberry variety, it is difficult to create the conditions for good quality cross-pollination. At least 2-3 plants of various varieties should be planted side by side. Bushes located nearby will lead to better fruiting and early ripening of the crop. It should be borne in mind that without insect pollination, blueberry fruits are smaller and have a thick skin. It is advisable to cultivate honey plants near the berry, which attract insects well.


Landing time
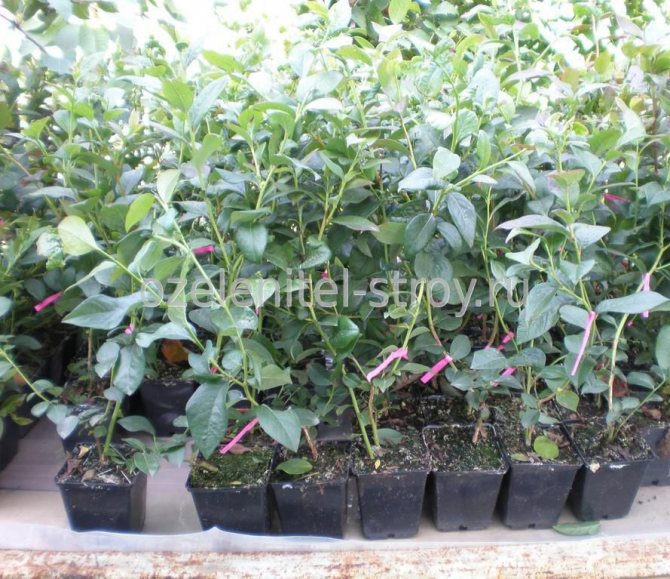
Varietal seedlings of fruit shrubs are always sold in plastic boxes or pots. This is the most comfortable planting material. Plants can be grown at home until the planting site is prepared. When planting blueberries is important to achieve good results. You can transplant a seedling to a permanent place throughout the growing season. Planting a closed-rooted garden blueberry is similar to transferring a potted plant from a smaller container to a larger container. A lump of substrate protects the roots from damage, which allows a 2-3 year old seedling to quickly adapt to new conditions.
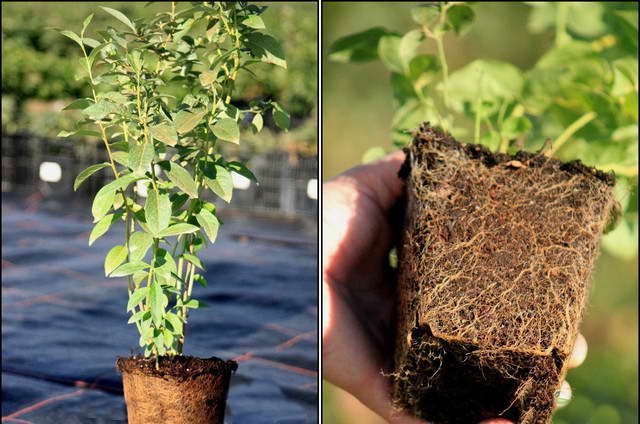


It is better to transplant adult bushes in the fall, after leaf fall. A planting pit or trench is prepared in advance, filled with a prepared substrate so that the soil has time to settle.
Soil preparation
Well-drained, light, peaty-sandy, loamy soils are favorable for the berry. The acidity of the substrate is from 3.5 to 4.8 units. All heather crops grow well only on acidic soils, neutral, and even more so alkaline environment is unfavorable for plants. This feature is due to the fact that the fibrous root of the plant functions in symbiosis with the fungal mycelium.
Important! Mycorrhiza is a form of symbiosis of plants with fungi, in which there is an interchange of nutrients. Fungal mycelium actively develops only in an acidic environment.
The soil mixture is prepared from:
- peat;
- sand;
- sawdust;
- fallen leaves, needles;
- tree bark.
The components are mixed by adding 40-60 g of sulfur.
Also, a solution of citric, acetic, malic acid helps to bring the acidity of the soil to 3.5-4.5 units. A cheaper option is battery electrolyte, 5 ml of which is diluted in 1 liter of water. The preparation of the pit will require 1.5-2 buckets of solution.
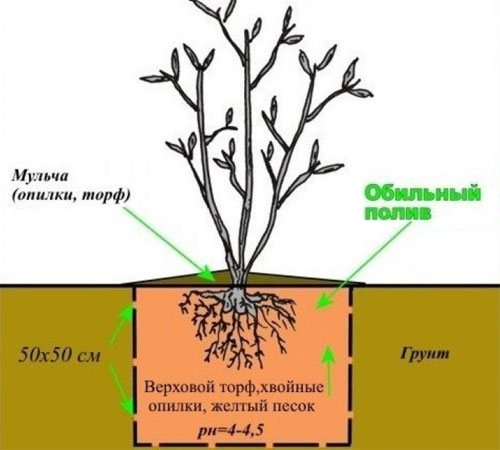

Planting in spring
A place for blueberries is chosen sunny, on a hill, it is desirable that the land in this place be fallow for several years. In addition to lighting, the level of groundwater should be taken into account.In areas where flooding and stagnation of water are possible, drainage is mandatory. The feeding area for tall varieties should be 1.5-2 sq. m. When planting several plants, planting holes are dug at a distance of 1.2-1.5 m from each other, with a diameter of 60 cm and a depth of 40-50 cm. The bottom is lined with a thick layer of rotted leaves, prepared soil is laid on top.
The seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place after a couple of weeks, when the soil settles. Previously, containers with seedlings are placed in a container with water for 15 minutes. A well-moistened lump is easier to reach without damaging the small and thin blueberry roots. It is advisable to gently straighten the pressed roots in order to change the direction of their growth in the horizontal direction. The seedling is placed in a dug hole and sprinkled with the removed soil. The earth is slightly compacted, watered and mulched with sawdust with a layer of 5-8 cm.


Important! With insufficient light, the berries become smaller, fewer flower buds are laid, which affects the next year's harvest.
Planting in autumn
In the fall, when part of the site is completely vacated, you can transplant the blueberries to a new place or plant a new variety on the old bushes. It is advisable to prepare the soil in advance and fill the landing pits with it. The work must be done on time - this is the main feature of planting blueberries in the fall. Plants must settle in a new place before the onset of a stable cold snap, and for this they will need 30-45 days. For adult plants, leaf fall is a signal of readiness for transplanting. For the winter, plantings are mulched and covered with spruce branches.


Sapling planting process
Procedure:
- A pot of blueberry seedlings is soaked in water for 30 to 60 minutes.
- Take the seedling out of the pot and gently straighten the roots so that they hang freely.
- A mound is made in the planting pit, so that the root collar of the seedling placed on it is flush with the ground.
- The place around the roots is covered with prepared soil, compacted and watered.
- The landing site is mulched with coniferous litter.

Correct planting of blueberries is carried out without deepening the root collar
Growing garden blueberries
Blueberries are quite unpretentious, at the initial stage, after planting, caring for blueberries is reduced to timely watering and weeding. In subsequent periods, when the plant takes root and starts growing, additional care will be required, which will include annual pruning, protection from pests and diseases.


Watering
The upper, root layer of soil under fruit bushes should always be kept moist.
- Water the blueberries abundantly - 1-2 buckets of water per bush, twice a week.
- In hot weather, it is advisable to spray blueberries to reduce the stress of the leaves from overheating.
- Adequate watering of mature bushes is especially important during the period of fruiting and bud formation.
In case of drought and lack of watering, blueberry fruits become shallower, the yield of this and next season decreases.


Top dressing
The plant is not demanding on fertility, however, the use of mineral fertilizers for blueberries replenishes the nutrients washed out of the soil during irrigation.
On soils with acidity from 3.5 to 4.8, it is recommended to use:
- ammonium sulfate - 90 g;
- superphosphate - 110 g;
- potassium sulfate - 40 g.
The rate is calculated for 1 fruiting bush. Top dressing is carried out twice during the growing season, every 6-7 weeks.
When growing in a garden, it is advisable to use a simpler feeding method using complex mineral fertilizers.
Important! When feeding blueberries, it is completely forbidden to use any organic fertilizers.
Pruning
A technique such as pruning seriously affects the growth and development of the bush. It can be used to change the quality of blueberries and the amount of harvest.
Features of the reproduction of garden blueberries in different regions
The difference in climatic conditions affects planting, growing, wintering. The methods and rules of reproduction by region are identical, some nuances differ. In the harsh conditions of Siberia and the Urals, frost-resistant blueberry varieties are grown. Short summers and long winters presuppose the use of greenhouses, hotbeds, warm beds, the principle of which is based on the release of heat by compost embedded under the fertile layer.
In the south of Russia, blueberries do not grow or multiply. In the North Caucasus, it is impossible to find acidic peat soils and mycelium of fungi necessary for the development, fruiting and reproduction of a culture.
In Central Russia, meteorologists note sharp jumps in temperature, frosty winters, thaws. The growing season for blueberries begins in April. At this time, planting is organized, greenhouses are opened, seedlings are taken out into the street, which were planted with seeds a year ago. At the end of October, the plants are prepared for wintering.
Blueberry propagation
Blueberries are propagated vegetatively or by seed.
- Seeds are collected from ripe berries and immediately planted for germination, or dried and stored in paper bags. The seeds do not lose their germination for about 12 years, but before planting they must be awakened by keeping them at a temperature of 3-5 degrees in wet sand for about three months. Seeds are sown in pots with well-moistened peat and placed in a warm, bright place. With the appearance of 5 true leaves, the seedlings are transplanted into a greenhouse. In the summer, the seedlings are fed with mineral fertilizers, keeping the soil moist. In October, plantings are mulched with peat and covered with two layers of spunbond for wintering. In the spring, plants are transplanted to a training bed or containers.
- Vegetatively, blueberries are propagated by cuttings or layering. Lignified cuttings are harvested from December to March, semi-lignified cuttings - in summer, from late June to mid-July. The cuttings are rooted in the greenhouse, processing them before this means for better root formation. In small greenhouses, the soil is constantly kept moist. By the end of August, the film is removed from the greenhouses. In October, plantings are mulched with peat and from the first days of November they are covered with spunbond. In the spring, seedlings are transplanted into pots, boxes for further cultivation.


- In the garden, blueberry bushes are also propagated by layering. To do this, the side shoot is pressed to the ground and sprinkled with sawdust and soil. After a couple of seasons, roots form at the base. The branch is separated from the bush and grown in a nursery or container. Since blueberries do not take root well, the process takes a long time and produces a small amount of planting material.
Obtaining seedlings from seeds is a lengthy process, while the signs of the garden blueberry variety are not preserved. It will be possible to identify the advantages and disadvantages of the plant only after the first harvest is obtained, which may take 5-6 years. This method is suitable for amateurs of breeding work. It is much more convenient for the gardener to propagate the plant he likes by cuttings, while the varietal characteristics are fully preserved.
Is it possible to propagate blueberries
Garden blueberry with a low calorie content (39 kcal) contains a rich set of vitamins and minerals. Removes radiation, relieves fever, improves blood composition. In the off-season, fruits support the body's immune defenses. Thanks to its beneficial properties, the culture is becoming more and more popular.
Amateur gardeners are interested in whether it is possible to cultivate blueberries with their own hands, without purchasing plants in specialized nurseries or through intermediaries. Subject to the rules and recommendations, the task is quite feasible. The berry crop reproduces in the same way as other fruit bushes.
Pests
Insects that eat leaves and buds and feed on plant sap can cause minor harm to tall blueberries.
- pine silkworm caterpillars;
- leaf rollers;
- scabbards;
- aphid.
Chemicals are used against insects; it is enough to collect the caterpillars by hand.
More damage can be caused by birds that attack berry growers during the ripening period of the crop. For protection, the blueberries are covered with a fine mesh, shiny objects are attached to the branches, and sound cannons are installed.


How to properly propagate garden blueberries?


Blueberry propagation is a great way to complement a garden's berry collection or to rejuvenate an obsolete plant. Wherein it is important not only to increase the number of bushes, but also to maximize the preservation of genetic traits... This is possible only with vegetative reproduction, which must be carried out correctly and in a timely manner.
Diseases
The most common and similar in appearance is stem cancer and drying out of branches. Also, blueberries are affected by such a common disease as gray rot. To combat fungal diseases, three times spraying of plants is used before and after flowering with a 0.2% solution of topsin or euparen. All damaged branches must be cut and burned in a timely manner.
Diseases of a mycoplasma or viral nature pose a great danger to varietal blueberries. These include red and necrotic spotting, dwarfism, mosaic. Such diseases are extremely rare, but when they are diagnosed, the plants must be destroyed.
Preventive means of combating pathogens that cause blueberry disease are elementary agricultural techniques. Thanks to regular weeding, soil mulching, timely watering and feeding, the plant will fully develop and be able to resist diseases.
Blueberries are a perennial that attracts with their beautiful bell-shaped flowers and delicious berries. The fruits are used for canning, freezing, eaten fresh, and the shrub itself emphasizes the unusual landscape design. In order for a crop to bear fruit and maintain productivity, it must be transplanted correctly. The works are carried out in the autumn or spring season. According to agronomists, transplanting garden blueberries on your own to a new place is effective in the fall. Experts recommend choosing the right material, preparing the soil and following the planting scheme.
How to transplant a bush of grapes, actinidia, lemongrass and other vines
It is better to replant grapes and vines in autumn. The signal to start the transplant is usually the complete fall of the foliage. This means that the plant has entered a dormant stage. The main thing here is to have time to transplant the plant to a new place at least a week before the start of serious frosts, and of course, to prevent damage to the root system. In the event that winter was early and you did not have time to transplant grapes and vines, then it is quite possible to wait until spring. The main thing here is to have time to finish the transplant ten days before the start of bud break.
Transplanting both grapes and lianas, as well as currant bushes, usually begins with the preparation of a hole for planting, like a hole for currants and similar crops. When the planting hole is ready, you can start preparing the plants for digging. To do this, the vines and grapes, three days before transplanting, stop watering, then the grapes will need to leave a couple of sleeves with young vines, a year or two old. In this case, the uppermost shoots must be cut off into two or three eyes, and all sections must be covered with garden pitch. Only after that, the grape bush can be dug, stepping back 45-55 cm from the center, and removed from the soil like digging a currant bush.
As for the vines, you can leave two or three of the youngest shoots with them, located as well as possible, the rest can be removed. When digging, you can move away from the center, in the case of vines, by 35-40 cm, the rest of all actions are exactly the same.
Later, after planting grapes and vines, after compaction of the soil, watering and mulching, it is necessary to remove all flowers at the first flowering in order to allow the plants to fully develop in a new place. For the next season, it is necessary to remove part of the inflorescences: for grapes, about half, and for vines - by a third. Do not forget to provide the plants with sufficient moisture and nutrition during this period.
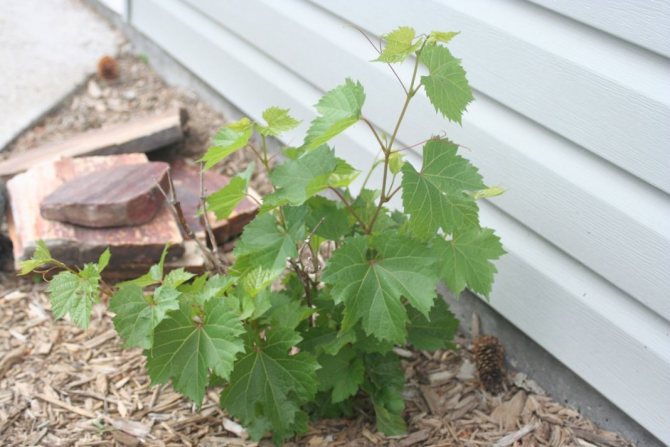


Young bush of grapes. <>
Planting material: selection and preparation
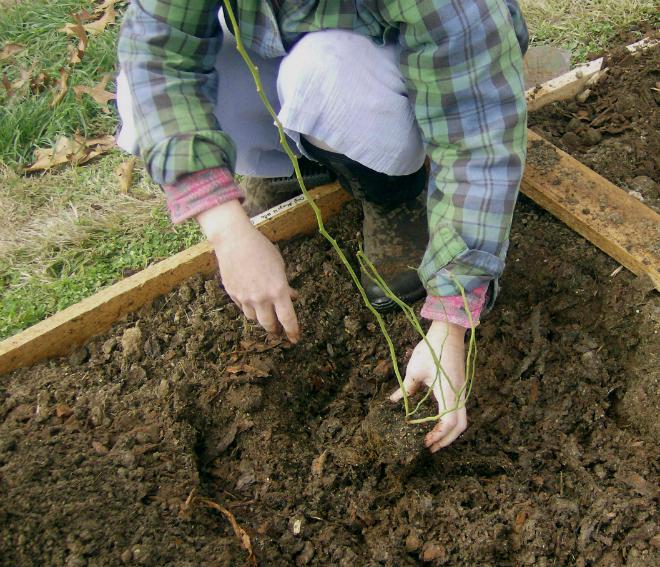
It is best to move blueberries to a new site in early September. So you can eliminate the risks of freezing of seedlings, increase their survival rate in frosty weather. For high-quality cultivation of a shrub, it is worth choosing its type, taking into account the climatic conditions and the time of fruit ripening.


The boggy Russian form grows in natural conditions. It is almost impossible to cultivate it, since the plant prefers acidic peatlands of coniferous forests. However, at home they take root:
- tall American uniform. Berries are compared to blueberries, but the bush is not resistant to weather factors and temperature extremes;
- Bluecrop, Patriot, Weymouth - species with early and middle ripening periods. Suitable for the middle lane.
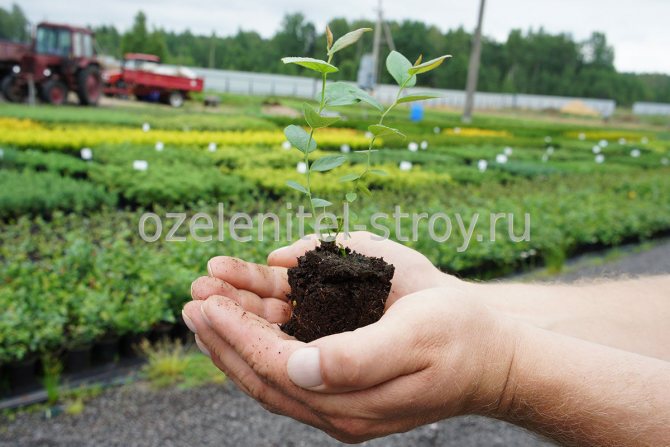
The full survival of the shrub is guaranteed only by high-quality material. It can be purchased at stores or nurseries. Seedlings with roots covered with soil, which are in pots and containers, are of good quality.
Blueberry breeding methods and optimal timing
There are quite a few ways to breed garden blueberries. Each of them has certain pros and cons.
Cuttings
Blueberries reproduce well by cuttings. They are usually harvested in the summer. In the fall, the planting material should be prepared for storage, and in the spring, transplanted into the ground.
Green cuttings
This is the most commonly used blueberry breeding method. It is recommended to start harvesting green cuttings at the end of June. To do this, it is worth picking up high-quality shoots that do not have defects. Gardeners advise cutting branches that have at least 5 buds.
After cutting the material, it is worth preparing the ground. To do this, it is recommended to mix sand with peat in a ratio of 1: 3. Cuttings should be planted in the prepared mass. It is important to follow the 5x5 centimeters scheme. Cutting is recommended to be carried out in a container. It is covered with foil.
After a couple of months, the cuttings take root. In winter, it is recommended to cover blueberries with peat and sawdust. In the spring, the cuttings are planted in a greenhouse and watered.
This method has significant advantages:
- it is possible to preserve the varietal characteristics that the mother plant has;
- seedlings develop stronger roots when compared with other varieties;
- the bushes are characterized by excellent endurance.
However, this method also has certain disadvantages. The key disadvantage is that blueberries take root in August, and therefore they may not be ready for the upcoming frost. Therefore, culture needs to create optimal conditions for the winter period.
Root
This method is not suitable for tall plants as they do not produce underground root shoots. Therefore, this method is used for marsh, twig-like and undersized blueberries. Its shoots produce good material that takes root easily.
To carry out the procedure, it is recommended to do the following:
- Prepare a bed in a shaded area of the site. Needles, peat, sawdust need to be added to the soil. In addition, it is recommended to use a compound fertilizer.
- Expose overgrown roots in selected adult crops. At the same time, it is recommended to cut off long fragments from them.
- Cut the resulting material into cuttings 10-17 centimeters long. It is important that a large kidney is present on each of them.
- Form furrows on the bed. Their depth should be 10-12 centimeters. The indentations are made with an interval of 15 centimeters.They should be watered well.
- Arrange the cuttings in the grooves. It is recommended to point the kidney up.
- Sprinkle the cuttings with earth and water again.
- Place a shelter of arcs above the bed and cover it with spunbond. It needs to be removed in a month. By this time, the sprouts should appear. If this does not happen, you can suspect the appearance of problems. The cuttings could dry out or, conversely, rot. They are also often affected by soil pests. To determine the causes, it is worth digging up a few roots and assessing their condition.
- From the moment of planting until the beginning of autumn, the soil must be systematically watered. It is important to ensure that it does not dry out.
- By the end of the season, it will be possible to get ready-made seedlings. It is recommended to transplant them to a permanent place or leave them in the garden. This should be done before spring. Pre-mulching with peat and cover the area with spunbond.
Growing blueberries at home from seeds in a pot
Blueberries can also be grown at home. But this is a long process that requires a lot of patience. To harvest the seeds, you need to pick ripe berries. Go through them, separating the planting material. You can knead the berries with your hands, and extract the contents from the pulp.
How to check seed germination?
The grains are lowered to the input. Those that fall to the bottom are ideal planting material. Selected seeds are well dried.


How to dry blueberry seeds?
The seeds are spread on a layer of wet sand or moss and kept for about 3 months. Seeds are planted in a pot or box in the spring. For planting from into a container, it is necessary to prepare a peat soil mixture. The planting material does not need to be deepened into the ground, it is enough to place them on the surface and cover them with a small layer of sand or sawdust on top. Then it should be covered with transparent polyethylene or glass that allows the sun's rays to pass through.
Blueberry seed
Seed propagation is a very interesting, but also time consuming way:
- Seeds can be bought in a store in your city, ordered over the Internet, collected by yourself from berries, either your own or bought on the market.
- The soil is sour peat, it can be mixed with coarse sand and rotted sawdust. Peat tablets are great.
- Sowing dates are easy to calculate. Stratification for blueberries lasts up to 90 days; it is advisable to get seedlings in March, when the sun begins to illuminate our windowsills well. Therefore, it is necessary to start working with blueberry seeds already at the beginning of December.
- Sowing is carried out superficially without deepening. Blueberry seeds are very small, the seedlings will not have enough strength to break through even through loose soil. Moisten the substrate before sowing, if you water it after, the water will pull the seeds deep into the soil. You can sow in rows in the seedling box or individually each seed in a peat tablet or glass.
- Cover crops with glass or wrap in a plastic bag and place on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for 3 months. Once a week, you need to take out, ventilate and moisturize if necessary.
- In March, transfer crops to a light and warm windowsill. Shoots should appear in 1-3 weeks. Grow them like normal seedlings. But do not forget to take a special acidic soil from peat for a pick without adding earth, humus and other components familiar to us.


Blueberry seeds and loose substrate
Video: stratification rules in the refrigerator and in the garden under the snow
The choice of soil for planting
Blueberries are not a purebred culture. This is a bush from the lingonberry family, from the blueberry genus. There are two main types found in nature:
- swamp Russian blueberry growing in peat soil in the forest zone. The plant does not lend itself to cultivation and is a "wild" berry. Found in deciduous-coniferous forests;
- tall American blueberry. This variety is difficult to tolerate temperature extremes, but it is a garden plant. It multiplies easily and pleases with an excellent harvest on the plots.
When choosing garden blueberries for planting on your site, you need to select and prepare the soil for planting a shrub. This allows you to avoid problems with the root system and get an excellent harvest next season.


Determination of suitable soil
There are several recommendations for the selection of the optimal place and soil for plant cultivation:
- blue berry is a light-loving culture. The optimal place for planting shrubs is an area that is illuminated by the sun throughout the day. The lack of ultraviolet light is bad for the yield;
- the site must be fenced off from drafts and cold winds;
- for planting in the garden, preference should be given to early maturing varieties that tolerate frost well. Such species quickly adapt to new conditions and easily tolerate any changes in the weather;
- the soil is suitable only with drainage, i.e. it should not retain surface water. Waterlogging of the soil leads to decay of the root system;
- blueberries do not tolerate drought. In the summer, the bush must be well watered. It is also not recommended to plant a crop next to other fruit trees;
- the ideal soil for growing black berries is a drained, peaty soil with a small layer of their rotted leaves;
- clayey terrain is not suitable for cultivation.
Taking into account the recommendations of experts on choosing the optimal place for planting blueberries, you can achieve excellent results in growing berries. Every year the bush will bring a good harvest of delicious fruits.


Propagation by cuttings
The methods of harvesting, rooting of green and lignified cuttings have differences and similarities.... Regardless of the planting material, the gardener must carry out the procedure with minimal disruption to the biological characteristics of the plant.
Harvesting green cuttings
With this method of reproduction, compliance with the optimal timing is of particular importance. This is the period from June 20 to July 10 .
Cuttings from insufficiently ripe shoots often suffer from drying out, are affected by diseases and fungal spores. The leaves of such cuttings are underdeveloped and cannot supply the stem with sufficient nutrients. With a later harvesting of cuttings, nutrients enter the growth points, which leads to their loss, affects the formation of roots.


Green blueberry cuttings
Shoots ready for grafting have springy, unbreakable stems and a dark green leaf color. For cutting cuttings, strong shoots of the first and higher orders of branching with a height of 6-12 cm are chosen ... They are broken off by hand with a part of the wood and bark of last year's growth (heel).
Cutting preparation:
- processing of the lower part of the cutting (removal of exfoliated bark);
- removal of 2-3 lower leaves (1/3 of the length);
- trimming the remaining leaves by 1/3;
- treatment of the cuttings with growth stimulants
Cuttings are planted on a prepared ridge in greenhouse conditions.
Harvesting lignified cuttings
For harvesting cuttings, last year's shoots that are completely ripe and not damaged by frost are chosen formation or replacement with a diameter of 0.5-1.2 cm. Cuttings of a larger diameter root poorly, and smaller ones are given by weak plants. Shoots with a large number of flower buds are not suitable for reproduction, and their removal does not give positive results either.
Branches cut in winter are stored in boxes filled with peat or sawdust and openings for aeration. The boxes are placed in a dark, well-ventilated room at an air temperature of 0 ° С- + 5 ° С ... Cuttings are cut at the end of March or in April. The lower parts of the branches are distinguished by the best root-forming ability.


The easiest way to propagate blueberries is lignified cuttings.
How to plant blueberries with seedlings in the fall?
Planting blueberries by planting cuttings is easier than, for example, growing a crop from seeds. In the autumn, when all the leaves fall, cuttings from an adult shrub are cut. They are cut off at the very roots and twigs with a length of at least 12 cm are selected. It is important to remember: the thicker the cutting, the faster it will grow roots.
Ensuring the survival of the material
In order for the seedling to quickly take root in the ground, it must be kept in a cool room for a day. After that, it is transplanted at an angle into prepared soil with peat and sand in a container. When the seedling is buried in soil, another layer of peat is poured on top, about 3 cm.When the stalk takes root, they are washed and cut with a pruner. Pruning will allow an additional branch of the root system to start up. Now the young sprout is ready for planting in a permanent place.


How to transplant blueberries to a permanent place?
The need to transplant a blueberry bush is associated with an increase in fruiting and the exclusion of plant diseases. The culture should be planted in a new place at the same depth. Also, the procedure is performed for adult bushes.
Breeding methods and timing
Blueberries can be successfully cultivated using seeds, parts of the bush. The first method takes a lot of time, requires considerable effort and does not guarantee that the seedlings will retain their economic and genetic properties. To preserve the qualities inherent in varietal blueberries, a vegetative propagation method is used by cuttings, layering, and root shoots.
The modern achievement of biologists is the microcloning of biological tissue taken from a plant.
The choice of the breeding method depends on the region, the age of the bush, the variety, and the choice of timing depends on the type of planting material. In autumn and spring, blueberries are bred with ready-made seedlings, root shoots. Sections of shoots, stratified seeds are planted only in spring.


Features of cuttings
A popular way of breeding blueberries is rooting of green, lignified or rooted cuttings, starting with the selection of quality material.
Lignified
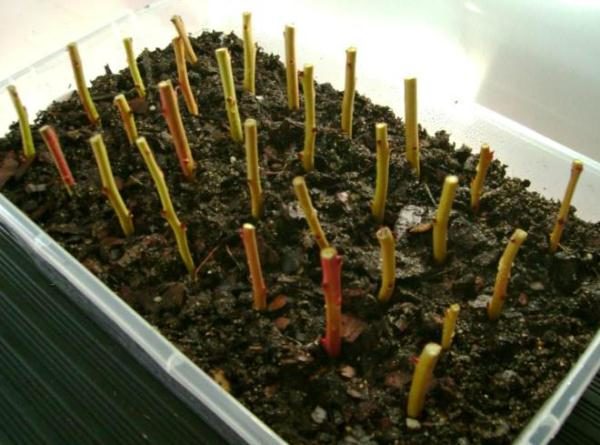
From December to March, shoots are harvested from young annual plants, which are stored, tied in bunches, at a temperature of 0-4 ° C. If the blueberry is low-stemmed, the branches are cut into pieces 10 cm long, in high-stemmed varieties - 15 cm. The lower part ends with an oblique cut under the kidney.
The top is cut horizontally, leaving 2 cm to the upper bud, preventing the growth zone from drying out. Before planting, the bottom of the cutting is powdered with Kornevin or dipped in a solution obtained from a liter of water and 1 g of a substance that stimulates root formation for 2-7 days.


At the end of March or in April, the cuttings are planted in a greenhouse, having prepared a box filled with peat substrate in advance. A part of the plant with two buds is left above the ground. You can dig in immediately on the garden bed, covering it with a film, spunbond, stretched over arcs. Planting scheme - from 5 to 10 cm between plants and rows. The rooting period is from two months.
Green cuttings
Cutting blueberries in summer is more effective. A larger amount of planting material takes root, the rooting period is shortened (1.5 months). In summer, from the last days of June to the end of July, a new growth or branching shoots are selected. Areas that form inflorescences are unusable.
See also
How best to keep fresh blueberries for the winter at homeRead
When harvesting, the green shoots are separated with a sharp jerk down so that a section of last year's stem bark remains on them. The lower part is freed from foliage, treated with a root formation stimulant. The remaining leaves are thinned out so that after planting semi-lignified cuttings in the greenhouse, they do not touch.


Favorable conditions for rooting - regular moistening of the soil, as an indicator of which is the state of the leaves, the temperature in the range of 18-22 ° C.
Root
Bushes with a developed root system are dug in, exposing the roots.Sections of rhizome shoots are separated, which are cut into 20-centimeter cuttings with buds.
Before planting the branches, make and moisten the furrows in the garden bed. Cuttings in an inclined position are covered with earth, watered again. Cover with a film stretched over arcs. After rooting the garden blueberry, the protective material is removed. In winter, the culture is left in the same place, having previously taken care of insulation.


The root cuttings method is used to propagate low-growing varieties that form underground shoots.
Breeding by layering
The method is used in late spring. Flexible healthy shoots, previously placed in a solution of a chemical rooting stimulator, are suitable for reproduction.
After trying on, a shallow groove is dug, along which a branch is laid, and covered with earth. If you press the shoot only at the base, you get one layer. With full burial, several new plants may appear no earlier than 2 years later. After separation from the bush, the planting material is grown in greenhouse conditions for another 1-2 years before planting in the berry.


The method of propagation of blueberries by layering is long and not the most effective, since the result is not guaranteed.
Seeds
Seedlings are grown from self-collected or purchased seeds at home. Cold stratification is preliminarily carried out. 3 months before planting, the seeds are placed in a container with a wet coconut substrate or moss, the container is closed, and placed in the refrigerator.
Algorithm for growing blueberries from seeds:
- An acidic substrate is poured into the container, moistened. Or they have rows of pre-soaked peat tablets.
- Planting material is sown on the surface without deepening. Sprinkle on top with sand, peat or sawdust with a layer of no more than 2-3 mm. Cover with glass, place on the windowsill.
- Monitor soil moisture. A spray bottle is used for watering. Ventilate at least once a week.
- The glass is removed 7–20 days after the first shoots appear.
- In the three-leaf phase, blueberry seedlings require more nutrients. Each plant is transplanted into a separate glass or pot.


From spring to autumn, seedlings are kept outdoors in natural conditions. For the winter, they are brought into a closed unheated room, insulated with a covering material. Seedlings are planted on the garden bed two years after the seeds are planted.
Root shoots (partial bushes)
For propagation by partial bushes, young healthy specimens of low-growing varieties of blueberries are used. The main condition is a developed root system that forms stolons. The growth zones located on the shoots form young shoots. To isolate it from the mother plant, a blueberry bush is dug up. Separation takes place in spring or autumn. Planting in separate containers or immediately to a permanent place is allowed.
See also
How to properly store fresh blackberries, drying berries and shelf lifeRead


By dividing the bush
The method is used for old plants for the purpose of rejuvenation. The bush is dug up, divided into parts, each of which includes several branches and a root from 5 cm. The resulting cut is planted immediately to a permanent place. Begins to bear fruit in the fourth year.
Reproduction by means of cardinal pruning
Planting material is obtained by total pruning of the bush. The event is held in early spring. After removing the shoots, a double rate of mineral fertilizers is introduced under the root, the blueberries are covered with a 30-centimeter layer of sawdust on top.
A greenhouse is built over the formed elevation, which protects the cut bush from unfavorable weather conditions, and retains moisture. On the new shoots that have appeared, after 2 years, roots appear above the original root system on the parts covered with sawdust. The structure is removed, young plants are separated from the mother bush, grown or planted in a garden bed.


Micropropagation of garden blueberries
The method related to vegetative propagation is used to improve the culture, the rapid multiplication of blueberries from a piece of biological tissue (meristem).
Growing stages:
- The mother plant is selected for genetic or economic qualities.
- A piece of the trunk, bark, leaf plate is cut out. If the laboratory is faced with the task of obtaining a large number of cuttings in a short time, then the tops of the shoots are used.
- The sterilized biomaterial is placed in a nutrient medium based on agar-agar with the addition of hormones, micro and macro elements. 5-9 shoots are obtained from one point of growth.
- Further, they are separated with a scalpel in distilled water.
- Prepare a fresh nutrient medium different from the first in the ratio of hormones.
- In cuttings placed in sterile conditions, the root system begins to develop rapidly.
- When the plant reaches the desired parameters, the blueberries are transplanted into the greenhouse.


The advantages of blueberry micropropagation are the absence of dependence on climatic conditions, the possibility of growing new varieties.
Sapling planting scheme
For different varieties of blueberries, different planting schemes are used, differing in some features:
- Tall blueberries are placed in holes 50 cm deep, 60 cm apart.
- Low varieties are planted at a distance of 50 cm.
- Medium and tall varieties need free space. A distance of about 1m should be observed between adjacent plants. The optimal width between the rows can be considered 3-3.5 m.
The final stage of shrub planting is surface mulching. To do this, use straw, sawdust, pine needles, peat. The thickness of the mulch layer must be at least 12 cm.


Planting cuttings in a greenhouse
Cut the prepared shoots into 10-15 cm pieces each. If you are propagating undersized blueberries, cuttings 7-10 cm long will suffice. Just make sure that each cut has at least 3 well-developed buds. In this case, it is extremely important that the bottom cut of the blueberry is exactly oblique, and the top one is flat and horizontal. Make the lower cut just below the kidney, and the top one 1.5-2 cm above the last kidney.
Plant blueberry cuttings on the garden bed according to the 5 × 5, 5 × 7, 5 × 10 or 10 × 10 cm pattern. The choice of the pattern depends on how soon you plan to plant the seedlings in open ground. The later this happens, the greater the distance between the plants should be. Cut the cuttings into the substrate about 2/3 of the length, but at the same time make sure that there is at least one bud on the surface.
Blueberries are very reluctant to root. To help her, before planting, treat the lower part of the cuttings with a special heather rooting or Kornevin.
Now it remains only to water the garden bed, install arcs over it and cover them first with polyethylene, and then with spunbond.
In farms, blueberry cuttings are sprouting right in the fields
Specificity of agricultural technology
Agricultural technology of blueberries involves loosening the soil on the walls and bottom of the hole before planting the seedling. This facilitates the passage of air and the development of the root system. The pit is filled with an acidic substrate, consisting of the following components: needles, sawdust, sand, sulfur 50 g and high moor peat. There is no need to apply organic fertilizer. At the bottom of the pit, the substrate becomes denser, a young plant is lowered into it, the roots are well spread, and covered with earth. If the seedling is less than a year old, after planting in the ground, you should cut off the damaged branches. Young blueberries over 2 years of age do not need additional processing.
Garden blueberries: propagation by cuttings, layering, sowing seeds


How to propagate blueberries?
Tall, or garden, blueberries win the hearts of more and more gardeners, summer residents and farmers. And of course, many people have the question of how to get seedlings in sufficient quantities, while maintaining the features VARIETIES OF BLUEBERRY
.
Breeds GARDEN BLUEBERRY
generative and vegetative ways. Each of them has certain advantages and disadvantages, therefore, how to propagate garden blueberries must be decided, weighing all the pros and cons.
Vegetative propagation of garden blueberry
It is not for nothing that garden blueberries bear other names, such as blueberry tall or blueberry tree. Unlike their relatives - common blueberries and Swamp blueberry
, it has other morphological features: the plant almost does not form root shoots. Or it forms so little that it is problematic to reproduce it in this way.
It should be noted that garden blueberries are classified as plants that are difficult to propagate vegetatively. This is due to the fact that the plant has poor root-forming abilities. However, with vegetative propagation, the plant retains all varietal characteristics.
► Blueberry Diseases
Of the popular vegetative propagation methods for garden blueberries, it should be noted: - cuttings; - reproduction by layering; - root shoots.
Reproduction of garden blueberries with green cuttings
One of the most successful, quick and effective ways to get young blueberry seedlings is to root green, non-woody shoots. These shoots differ in their growth rate and in more active metabolic processes in tissues, which allows them to root several times faster than woody shoots. And the percentage of rooted planting material is 2 to 4 times higher.
When propagating blueberries by green cuttings, one must take into account the following feature - green shoots on different parts of blueberries are physiologically different from each other. For rooting, it is better not to use flowering branches.
Green cuttings are obtained from late June to mid-July - so that on the one hand they have time to accumulate a sufficient amount of nutrients, and on the other hand, they would have time to put down roots. The shoots that will be used for rooting should be free of spots or chlorosis, the leaves should have a pronounced dark green color, and the shoots should be firm and not brittle.
Green cuttings for propagation of garden blueberries are not cut, but broken off with a part of the bark, which is then removed. The resulting material is kept in a fungicide solution (10 - 15 minutes), and then parts of the leaf blades are cut off, leaving only 2/3 (the bottom sheet can be cut even more, leaving 1/3). The length of the cuttings is 8 - 12 cm. When planting cuttings, it is imperative to use a rooting agent (according to the instructions).
Cuttings are planted in: • prepared beds on the ground; • in cassettes with cells, which are placed on racks; • in the substrate, which is poured on the racks (usually it is fenced with borders, 10-15 cm high); • in plastic transparent boxes with a lid (in this case, blueberries can be rooted even in an apartment).
► Reproduction of chokeberry
► Reproduction of cherries
The substrate for rooting may be different: the opinions of experts in this regard differ. Sometimes the cuttings are planted in wet sand, sometimes in pure high-moor peat. But a mixture of sand and peat (50/50), or sand, peat and rotten pine sawdust (in equal parts) is preferable. After planting, the cuttings are covered with a film to maintain air humidity, which should be kept at a level exceeding 90%. The film should not touch the leaves - the distance from it to the shoots is 20 - 50 cm.
The air temperature during the development of roots should be 20 - 25 degrees. Gradually, as the root system forms - that is, after 4 - 5 weeks, the film must be lifted in order to accustom the seedlings to dry air. During this period, you need to spray the leaves less, reducing the relative humidity to 82 - 85%.
Depending on the conditions and quality of the planting material, the cuttings form a root system within 2 - 3 months.By the end of this period, the film (or glass) must already be removed, and the seedlings should feel normal with an air humidity of 40-50%. Young plants can be fertilized with ammonium sulfate.


Reproduction of garden blueberry lignified cuttings
This method is similar to the previous one: cuttings for rooting will need similar conditions and a similar substrate. Unlike green cuttings, woody shoots take root less well. Even under optimal conditions and the use of a rooting agent, the percentage of established seedlings is from 20 to 35% (and in the absence of such, the percentage of rooted plants may be only 2 - 3%). On the other hand, some gardeners consider this breeding technique to be the most successful.
Shoots for seedlings must be harvested in advance: • the material is cut only when the blueberry is dormant (from the end of November to March); • annual shoots harvested in autumn or winter should be stored in a cold, humid place, with a temperature of 1 - 5 degrees, not allowing them to dry out (in a refrigerator, in a cellar, or in glaciers designed for storing shoots); • the optimal time for cutting shoots is spring, before the beginning of the growing season (approximately March-April, depending on the region and weather conditions); • the length of the cutting for tall varieties should be 11 - 15 cm, and for low ones, slightly less (8 - 10 cm); • the lower part of the cutting is cut at an acute angle to increase the surface of contact with the substrate, and the upper cut, which should be 2 cm above the bud, is usually made horizontal.
► Reproduction of currants by cuttings
► Reproduction of black currant by layering
Before planting, the cuttings are soaked in a fungicide solution for 10 - 15 minutes, and then, the lower part is dipped in a rooting agent (usually it is in the form of a powder). And then, they are planted in a prepared substrate (see composition above). In addition to standard rooters (such as Kornevin), a special rooting agent has now been developed for plants from the Heather family (which includes blueberries).
For rooting, it is important that high humidity is created in the room where the cuttings are located - the optimal indicator is 90 - 95%. To maintain this indicator, water mist sprayers are used. An easier way is to cover the seedlings with a transparent film with holes made in it for air circulation. The height from the film to the substrate surface is 40 - 50 cm. In this case, the sprayed water falls not only on the cuttings, but also on the film, and the desired microclimate is created. The presence of a film over the seedlings avoids temperature fluctuations and gradually adapts them to drier air.
The advantage of the blueberry seedlings obtained from lignified cuttings is that after rooting and adaptation, they are already quite ready for planting in the ground in a permanent place.
Reproduction of blueberry garden layering
As already noted, it is difficult to get tall blueberries to take root, therefore, reproduction by layering can take a couple of years. In order not to damage the plant, the soil around it is loosened, and next to the shoots intended for rooting, a furrow 7 - 8 cm deep is made, which I spill with water. Then, a shoot is laid in the furrow, having previously cut off the leaves on its lower part (that is, where the branch will be covered with earth).
The shoot must be fixed with wooden or metal hooks, and then sprinkled with wet coniferous sawdust and peat (or a mixture of sand, peat and needles). The sprinkled shoot must be kept moist, preventing the substrate from drying out.
In-vitro propagation of blueberries
This method of vegetative propagation, which allows you to get hundreds, thousands and even hundreds of thousands of blueberry seedlings, while free of any viruses and infections. Its only drawback is that this method requires special laboratory conditions and knowledge of technology.
This method is used by some domestic research and production enterprises and nurseries. In the USA, Canada and some countries of Western Europe, where large-scale cultivation of this berry has been established, in-vitro propagation of blueberries makes it possible to obtain seedlings on an industrial scale for growing on blueberry plantations.
Generative reproduction of garden blueberry
Seed, or generative, propagation of blueberries is used, most often, by breeders to obtain new varieties and forms of this plant. The main drawback of the method is that blueberries can lose varietal characteristics: the resulting seedlings will differ greatly from the mother, and it is not a fact that for the better.
► Reproduction of garden strawberries
Another disadvantage is the length of time it takes to grow. More than ten years can pass from the moment of sowing to active fruiting. Overripe berries are chosen for reproduction, from which seeds are obtained. The seeds are washed, dried and sown in wet peat (or peat with sand). Sowing can be done immediately, or you can leave the seeds until spring. Grow seeds in greenhouses or closed containers to maintain moisture. When growing seeds in plastic containers, holes must be made in them for ventilation.
► RETURN TO SECTION
| <Previous | Next> |
Bush care
Transplanted blueberries will need proper care. It is as follows:
- Periodic watering. Depending on weather conditions, the shrub needs to be watered several times a week in spring and summer. In the fall, soil moisture can be excluded.
- Mulching the earth. Rotted sawdust and needles are used as mulch.
- Top dressing. In the spring, mineral fertilizers are applied under the bush.
- Pruning. Pruning is done in the spring, before the buds are ripe. The procedure is carried out a year after planting the seedling.
- Spraying the leaves. Moistening the leaves of the bush must be done on hot days in the evening.
Garden work is recommended to be carried out in a comprehensive manner and strictly observe their frequency.


Reproduction by layering
Also, as mentioned above, blueberries can propagate by layering. This method is used for propagation of young bushes that have few shoots for propagation or for varieties that are poorly rooted during propagation.
Before that, the trunk circle under the mother plant is loosened. Pick up strong and healthy shoots. Opposite the selected branches from the base of the bush, a furrow is formed with a depth of 6-8 cm and a length equal to the length of the shoots... Sprinkle with water.
Annual branch growth is shortened by 1/5 and placed in the furrow. Each section of a branch with two developed buds is fixed to the soil with wire hooks. The furrow is sprinkled with sawdust.
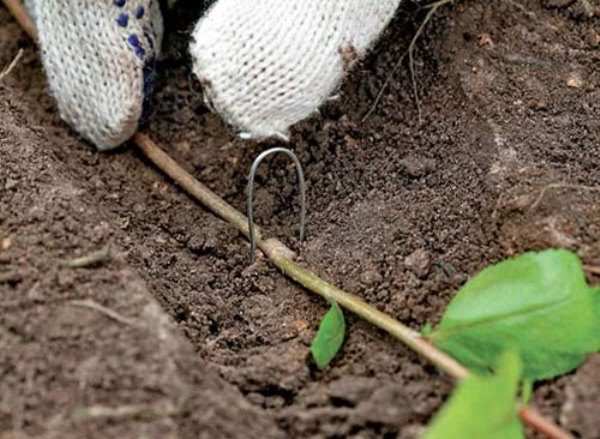


To obtain a full-fledged blueberry seedling, the branch is laid in the furrow and fastened with a crochet
After vertical shoots reach a height of 8-10 cm, they need to be earthed up to half the height... For this, a mixture of peat and sawdust (1: 1) is used. This procedure is repeated 2-3 times as the shoots grow back. Throughout the summer, the soil is kept moist and loose. The shoots that have grown in the current year will form a full-fledged root system in 2-3 years, after which they are transplanted to a permanent place.
Blueberries are a relatively new crop in Russian horticulture, the agricultural techniques of which are not fully mastered by gardeners. The secrets of successful cultivation are based on the correct selection of varieties that are highly adaptable to the harsh conditions for this crop.... By planting varieties suitable for the region, it is possible to maintain home blueberry plantations for many years, propagating them vegetatively.
Many gardeners are interested in how to properly propagate blueberries. Today, there are many ways to carry out this manipulation. You can get a new plant by cuttings. Also, the culture is propagated by seeds, layering, root shoots.Each method has certain advantages and disadvantages. In order for the manipulation to give the desired results, you must strictly follow the recommendations for its implementation.
Preparing for winter
Also, preparation for wintering is included in the stages of caring for blueberries. The plant must be prepared without fail for the arrival of cold weather. For this, the following activities are carried out:
- bush branches are straightened;
- then the branches are pressed to the ground with staples;
- in severe frosts, the shrub is wrapped in burlap or host to prevent freezing.
You can open the bush and release the branches after the onset of spring. These activities help to protect blueberries in winter from cold weather and strong winds. Blueberry is a shrub with beautiful berry color and spreading branches. The plant has a lot of useful properties. Leaves and fruits are used in folk medicine and are eaten. The correct transplanting of delicious blueberries to a chosen new location in spring or autumn will help you get high yields of healthy berries every year.
Transplanting blueberries to a new location in the fall is an important and crucial step. The further development of the bush depends on its implementation. So that the plant does not suffer during transplantation, it is important to find a suitable place for it and prepare the substrate. A shrub will adapt more quickly to new conditions if you provide it with good care.
Propagation by horizontal layers
In the spring in early summer, choose strong, flexible branches that you can lay on the ground. If it is only possible to bend them in an arc, then the seedling will turn out to be one with roots at the point of contact with the ground, and if you manage to dig in most of the branch, then several bushes will grow. The easiest and most reliable way is to propagate blueberries with horizontal layers:
- Try on a branch where you want to dig it in, and make a shallow (5–7 cm) groove in the ground.
- Scratch the side where the branch will come into contact with the ground with at least a fingernail and moisten with a preparation that enhances root formation.
- Attach the branch to the ground with wire pins and sprinkle with earth. If the branch does not fit, is curved and touches the ground in only one place, you can dig it in and press it down with a brick or stone. In any case, the top of the rooted branch should be outside, above the ground.
- Keep the soil moist throughout the summer.
- Next spring, you can dig up our branch, cut it off from the mother bush and divide it into seedlings. But according to the experience of gardeners, it is known that rooting of blueberry branches has to wait 2-3 years.
Video: rooting with a ditch and air layers
When do you need to transplant blueberries to another place?
In nature, a blueberry bush grows in one place for up to 100 years. Cultural forms, planted in a summer cottage or personal plot, bear fruit within 50 - 60 years. However, the plant does not always take root well in a new place. Then it is necessary to transplant a bush.
The need to transplant blueberries to another place often appears in the following cases:
- external factors (overgrowth of neighboring trees and shrubs, changes in landscape design, etc.);
- depletion of the soil;
- shrub rejuvenation;
- reproduction of culture.
Gardeners have to replant garden blueberries if the wrong site has been chosen for them. For example, when planting, the substrate was not prepared, and the plant does not develop well. In addition, the site can be flooded by melt water in spring, which leads to the death of the shrub.
Blueberries can be damaged by external influences. If the nearest crops grow rapidly, then they inhibit the development of other plants. As a result, blueberries do not receive enough light and nutrients.
Important Tips
Transfer time. For these purposes, it is better to choose late autumn or early spring, but if you transplant very large shrubs, then this can be done in winter.In the summer, replanting plants, even with a clod of earth, is very risky, especially if you cannot provide the shrub with sufficient moisture and nutrition after planting. By the way, about nutrition: those fertilizers that we gave in the example (with the exception of ash) are best applied in a form dissolved in water.
Try to replant shrubs as quickly as possible. Remember: the sooner the bush is back in the soil, the more chances it will quickly take root in a new place. Usually, most of the time is spent on digging up the bush, while planting is carried out, as a rule, in a matter of minutes. It is imperative to take this into account and allocate time correctly.
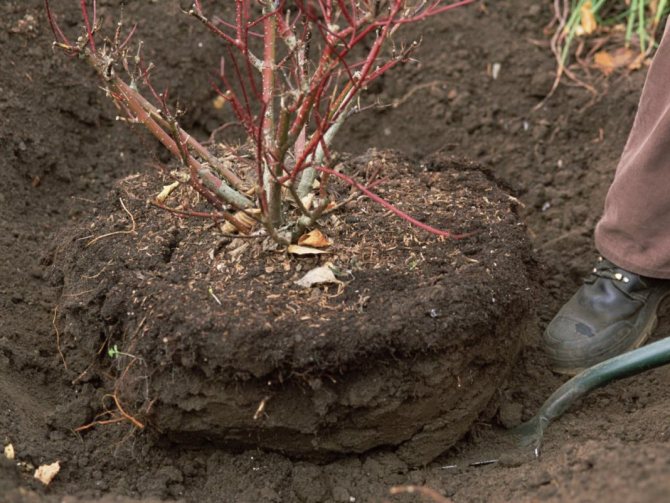


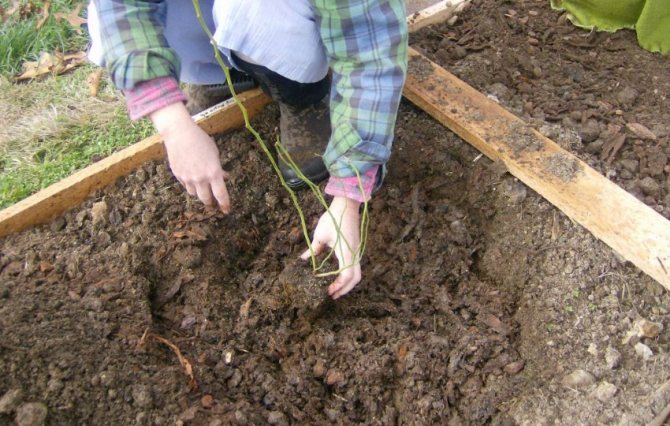
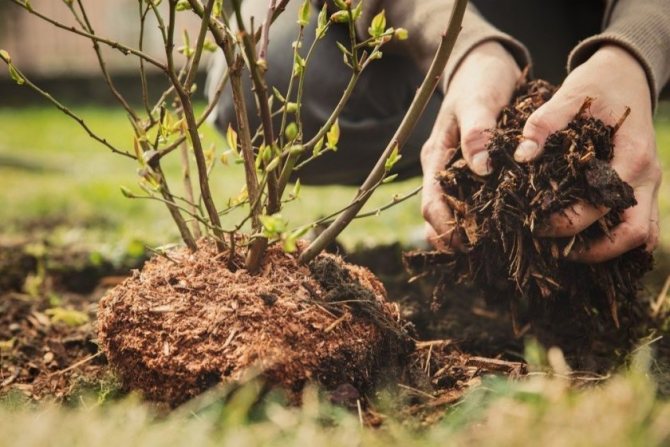
We take out a bush with a clod of earth.
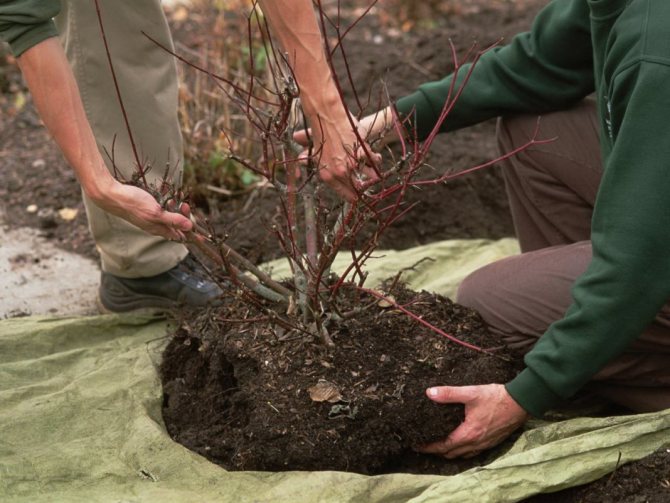


We transfer the bush with a lump of earth to a new place.
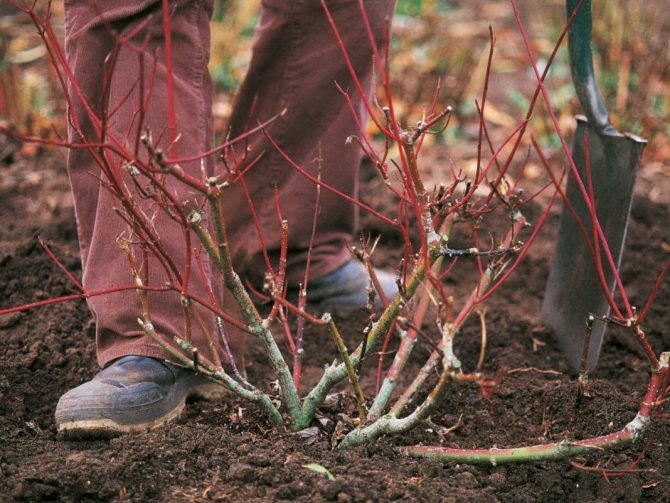


We plant the transplanted bush in the planting pit.
When is the best time to transplant blueberries
There are several options for replanting blueberries to another location. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are taken into account before starting work. Specific dates are chosen taking into account weather conditions and the condition of the bush.
Transplanting is most preferable in early spring or late autumn. During such periods, the plant tolerates changes in external conditions best of all. Transplanting in the summer is also possible, but it has a number of restrictions.
For a spring transplant, a period is chosen when the snow melts and the soil warms up. It depends on the climate in the region and weather conditions. In the south, work is carried out until the end of March, in the middle lane - in April. In colder climates, transplanting is done in May.
Without restrictions, you can transplant blueberries in the spring in the middle lane, in the North-West, the Urals and Siberia. It is recommended to complete the work before bud break. If you are late with the deadlines, it will take more time to adapt.
Benefits of planting shrubs in spring:
- manage to adapt to a new place;
- there is no risk of cold weather;
- the ability to care for the shrub during the season.
Spring planting has several disadvantages:
- the growing season may begin earlier than suitable weather conditions;
- if spring frosts are predicted, then work will have to be postponed until autumn or a shelter should be built for the shrub;
- the plant is provided with full care: watering, feeding, mulching.
Summer shrub replanting is not the best option. If you disturb the plant during the growing season, this will disrupt its life rhythm. The procedure is especially dangerous during the period of flowering and ripening of berries. If it is necessary to transplant the bushes in the summer, then the harvest is completely removed first.
Summer transplantation is best tolerated by young bushes that have not yet begun to bear fruit. Usually on the bushes of the first berries ripen 2-4 years after planting. If you transplant a five-year blueberry in the summer, then the plant will direct its forces to adapt to new conditions. It is highly likely that next year the yield will be minimal.
The main advantages of a summer transplant:
- the berry will not suffer from frost;
- suitable for working with plants in containers.
Cons of transplanting blueberries in summer:
- the growth and development of the bush is disrupted;
- the plant needs more strength to adapt.


Autumn transplantation is practiced in the south. Work is carried out in November, 2 - 3 weeks before the onset of cold weather. In other regions, the bushes are replanted in October. At the same time, they wait until the end of the growing season, when leaf fall will pass. If frosts are predicted in the region, then it is better to postpone the transplant until the spring. There is a high probability that blueberries will die under the influence of cold.
In autumn, the plant goes into a dormant period and tolerates transplantation well. At the same time, the root system continues to grow in blueberries. Therefore, by the beginning of winter, she manages to adapt to new conditions.
Benefits of transplanting blueberries in the fall:
- high survival rate of bushes;
- the adaptation period will take place in the fall, and in the spring the blueberries will immediately begin to grow;
- after transplanting, plants require minimal care: enough watering and shelter for the winter.
Disadvantages of an autumn transplant:
- blueberries can suffer from a sharp cold snap;
- in winter, the bushes are more often damaged by rodents;
- provide shelter for the young bushes for the winter.
Features of the autumn planting of blueberries
Blueberries are planted both in spring and autumn, or even in summer if the seedling has a closed root system. Spring planting seedlings take root best of all, but if blueberries are grown in a pot, then they can be planted in autumn.


For planting in the fall, choose seedlings with a closed root system.
A feature of the autumn planting of blueberries is the pruning of shoots from one-year-old seedlings. After planting, all weak and broken branches are cut off, and strong shoots are cut in half. Despite its winter hardiness, it is better to cover the autumn plantings of blueberries with thick non-woven material or spruce branches. Please note that it is not worth just throwing covering material on the bushes, you need to make a low support for it (arches, boxes) and already lay the covering material on them.
How to transplant blueberries correctly
When transplanting blueberries, it is important to consider a few nuances. A suitable place is chosen for the culture, after which the substrate is prepared. The order of work does not depend on the season and remains unchanged.
Site selection and soil preparation
The blueberries are transplanted to a sunny location away from large trees, buildings and fences. In the shade, the bush slowly grows, its yield drops, and the berries do not gain sugars. Areas in lowlands where moisture and cold air accumulate are not suitable for transplanting.
Particular attention is paid to the pH level of the soil. The optimal indicator for the culture is from 3.5 to 5. It is measured using a special device. If the acidity of the soil is insufficient, a special substrate is prepared.
After transplanting, blueberries grow well in sour peat. Litter from coniferous forest, wood chips, rotted sawdust, coarse sand are added to the substrate. A hole is dug at the chosen place. Its size depends on the size of the bush. Usually, a pit 60 cm deep and 1 m in diameter is suitable for transplanting. The pit walls are insulated with polyethylene or tin sheets.
If the site has dense soil, then it is required to create a drainage layer. Crushed stone, expanded clay, broken brick are suitable for him. Drainage is poured into the bottom of the planting pit. As a result, a layer 10-15 cm thick is obtained. Then the prepared substrate is transferred into the pit.


How to transplant blueberries
To transplant blueberries to a new location, follow the instructions:
- Prepare the planting pit and substrate. The bush is planted on a small hill or ridge.
- Blueberries are examined, old or dry shoots, young shoots are removed. The remaining branches are cut in half.
- They retreat from the center of the bush by 20 cm and undermine it from all sides.
- The plant is removed from the ground. There is no need to pull on the shoots: this can seriously damage the blueberries.
- To protect the roots, they are wrapped in tarpaulins.
- The shrub is transferred to the prepared pit.
- The bush is placed on a ridge, its roots are covered and watered abundantly.
- The land is mulched with peat.
Blueberries are also transplanted into containers. They are placed on a veranda, gazebo or terrace. In this case, a large ceramic container or wooden box is prepared for transplantation. Be sure to make drainage holes and pour small stones on the bottom. Sour peat is prepared for the culture. After transplanting, the plant is watered, and rotted coniferous litter is poured into the trunk circle.
Preparing for autumn planting
Blueberries are considered to be quite a demanding crop, and several factors affect how the bush will grow and bear fruit.
Choosing a landing site
Blueberries love to grow in a sunny location. It is best if this area is protected from the wind. The level of occurrence of groundwater is also of great importance.Despite the fact that in nature, blueberries prefer to grow in a swamp, they do not like stagnant water, so you should not plant blueberries in lowlands, which are flooded with water in spring.
Preparation of planting holes
Separate and very great attention should be paid to the preparation of the planting holes. Blueberries develop well and bear fruit only on acidic soils, with an acidity of 3.5–5 pH, so be sure to do a soil acidity test before planting.
Remember that plants such as bumbleweed and horse sorrel are not indicative of the acidic soil of the site.
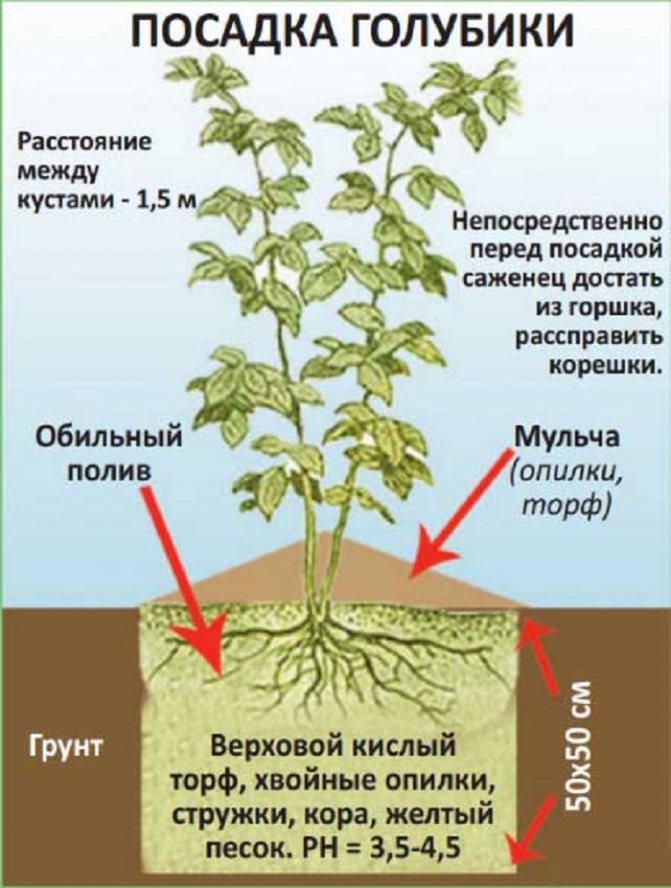
Landing holes are dug large: 40-60 cm deep and 60-90 cm in diameter. The more room with comfortable soil is provided to the roots, the better the blueberry bushes will grow and bear fruit.


A planting hole is made at least 60 cm in diameter, and if you need to plant several blueberry bushes, then the distance between them is made from 1 meter to 1.5 meters
If the soil at the bottom of the planting pit is dense, clayey, then drainage must be provided: expanded clay, broken bricks, large crushed stone.
You can dig not individual planting holes, but a trench or a small corner pit, in this case they do not need to be made very deep, since the root system of blueberries is superficial.
It is better to isolate the walls of the planting pit (trench) from the external soil by covering them with a thick film, linoleum, and curb tape.
The planting pit is filled with acidic soil. It is recommended to pour 1 bag of acidic soil into one planting hole, but in this case the plant will look depressed. Each large hole takes 10 to 20 buckets of acidic soil.
In order for the earth to settle, the planting pits are prepared 2 weeks before planting the seedling.
Where to find acidic soil
Of course, sour peat is sold in garden shops, and is the most preferred for planting blueberries. But it will be very expensive. You can replace part of the sour peat with soil taken from a pine forest, with rotted coniferous litter, or at sawmills, where the bark of coniferous trees is rotting. When preparing the soil for blueberries, you can add a couple of buckets of sand (if the planting hole is very large).


When buying peat, be sure to look at the acidity declared by the manufacturer
The closer the soil acidity is to 3.5–4.5 PH, the better the blueberry will grow.
Video: preparing a planting pit with soil for blueberries
Blueberry care after transplant
If the transplant took place in the fall, then the plant is no longer watered or fed. The intake of moisture and nutrients stimulates the development of the bush. Before the onset of cold weather, it is prepared for winter: they spud and mulch with peat. A frame is erected over the young blueberry, to which any non-woven fabric is attached.
If the blueberry is transplanted to a new place in the spring, then it is provided with good care. Watering and top dressing is started in 2 - 3 weeks. During this time, adaptation to new conditions takes place.
In the future, the bush is watered 1 - 2 times during the week. At the same time, they do not allow the soil to dry out and moisture stagnation in the soil. Mulching the soil with peat or pine needles helps to maintain an optimal level of moisture.
After transplanting in spring, blueberries are fed with ammonium sulfate or urea. Add 10 g of fertilizer to 10 liters of water. During flowering and fruiting, they switch to potassium sulfate and superphosphate. A large bucket of water requires 30 g of each substance. It is convenient to use complex fertilizers for crops that contain all the necessary substances.


Transplanting an adult bush
To transplant an adult bush to a new place, you first need to equip a planting pit. It is important to transplant quickly so that the root system of the plant does not begin to fade under the sun's rays. It is best to carry out work in the evening, after sunset.
The hole is dug up to 50 cm deep, 40-50 cm in diameter (depending on the size of the shrub and its root system). For good survival, it is advisable to correct the soil composition: a small layer of a mixture of high-moor peat, sand and coniferous litter is poured into the planting pit (5: 1: 2).


It is necessary to fill the hole with the same composition after planting. You can slightly fertilize the soil with a useful mineral composition - 40 g of ammonium sulfate, 100 g of superphosphate and 30 g of potassium sulfate are added for 1 planting.
An adult bush to be transplanted must be dug from all sides, and then uprooted with a shovel. The procedure must be carried out carefully in order to minimize damage to the root system, which extends 30–40 cm deep. Also note that the stems are easily detached from the rhizome, so there is no need to pull on them when trying to pull out the bush.
The shrub, together with the earthen clod, is transferred and placed in a new planting pit, sprinkled with soil composition. The planting should be watered abundantly (8-10 l) and mulched.


Next, you should follow the necessary care rules: regularly water the bush (2 times a week), weed the soil from weeds and do not forget about preventive treatments for diseases and pests that contribute to the cultivation of healthy strong crops.
Garden blueberries are a great alternative to many berries, such as blueberries, which can only be harvested in forested areas. Its berries are not inferior in the complex of biologically active substances useful for the human body. By carrying out a periodic transplant, you can save the plant from exhaustion and disease, provide it with good yields for many years.
How to plant blueberries correctly
In nature, blueberries grow on swampy acidic soils. It is these nuances that should be considered when planting a shrub on your site. It is also important to take into account that the culture absolutely does not tolerate stagnant moisture at the roots, since this can cause rotting of the root system and the death of the seedling. In addition, the area for placing shrubs should be well lit by the sun. If the crop is in partial shade, the harvest will be small, and the berries will be small.
Despite the fact that the planting technology as a whole remains the same, there are still some peculiarities in planting blueberries. Firstly, it should not be planted in lowlands due to the risk of waterlogging at the roots and the accumulation of cold air currents. Secondly, each hole must be completely covered with special nutritious soil, and only after that it will be possible to make a depression in the center of the hole and plant a plant in it.
There are certain rules to consider when planting blueberries:
- Soil acidity: should be in the range of 4-5.5 units. You can measure the acidity of the soil on the site using special testers that are sold in gardening stores (Figure 1). If the acidity is within the limits indicated above, you can safely plant blueberries. However, if the soil is not acidic enough, it should be watered with a weak solution of sulfuric acid.
- Soil composition: Peat-bog or peat-sandy soil is considered ideal for blueberries, since it is good for water and air. Unfortunately, such soil is rarely present in an ordinary household plot, therefore, when planting, a nutrient mixture consisting of high peat and sand in equal proportions must be added to each hole. For additional acidification, a little sulfur can be added to the soil mixture (100 grams of substance per bucket of soil). It is advisable to prepare the planting holes several months before the direct planting of seedlings.
- Compliance with growing conditions: Blueberries are very sensitive to temperature changes and soil moisture levels. In order to prevent stagnation of moisture at the roots, the soil should be drained, and it is advisable to mulch the trunks. In addition, it is advisable to plant shrubs in areas protected from drafts and strong gusts of wind.


Picture 1.Tester for checking soil acidity and selection of a site for a shrub
These recommendations are general, although it is on them that the success of growing a shrub depends. However, there are other nuances that should also be considered when cultivating a plant. Let's consider the main ones in more detail.
When is the best time to plant
It is believed that it is possible to plant blueberry seedlings in open ground not only in spring, but also in autumn. During these periods, the plant is in a state of relative dormancy, and will survive the transplant more successfully.
Seedlings sold in closed-root containers can be planted at any time of the year (Figure 2). However, experienced gardeners still agree that the procedure is best done in the spring, especially if you live in a region with a cold climate. Only with spring planting will the probability of plant survival in a new place significantly increase. If you bought a seedling with a closed root system, but did not have time to plant it in the ground in the spring, you can easily keep it until next year in a dark, cool room.


Figure 2. Quality seedlings with a closed root system
However, if you want to increase the crop's chances of adaptation, planting is still best done in the spring, before the buds swell. So you can be sure that the plant will completely take root in a new place before the onset of the winter cold. But young seedlings, like adult plants, must be covered for the winter to prevent freezing of the roots and tops of young shoots.
Where to plant blueberries
When choosing a site for blueberries, you need to pay attention not only to the acidity of the soil, but also to the features of the future bed itself.
First, the site must be well lit by the sun. Blueberries not only do not take root well in the shade, but also yield much less harvest. Even if you manage to grow a healthy shrub in a shaded area, there will be few berries on it, and they will be small and watery.
Secondly, you cannot plant shrubs in the lowlands. Such areas accumulate currents of cold air, which can adversely affect the health of the plant. It is better to choose areas on a hill for blueberries.
It should also be borne in mind that the soil in the garden bed should not be too wet. Stagnation of moisture at the roots can provoke rotting of the root system and fungal diseases.
Diseases and pests of blueberries
Blueberry bushes are often affected by diseases such as flower rot, moniliosis, phomopsis, anthracnose and red spot. All these diseases can be divided into viral and fungal. They appear, in most cases, from poor-quality care of shrubs.
The main procedure for the prevention of diseases includes the following measures:
- take care of the plants regularly (watering, weeding, removing weeds);
- in spring water the bushes with boiling water (temperature from + 80 ° С to + 90 ° С);
- at the end of March, spray the plants with copper sulfate (10 g per 20 l of water).
The symptoms of flower rot include drying of the shoots and yellow foliage. Over time, ulcers appear on the branches, which lead to the death of the plant. In the fight against the disease, they use "Euparen"(100 g per 5 liters of water).
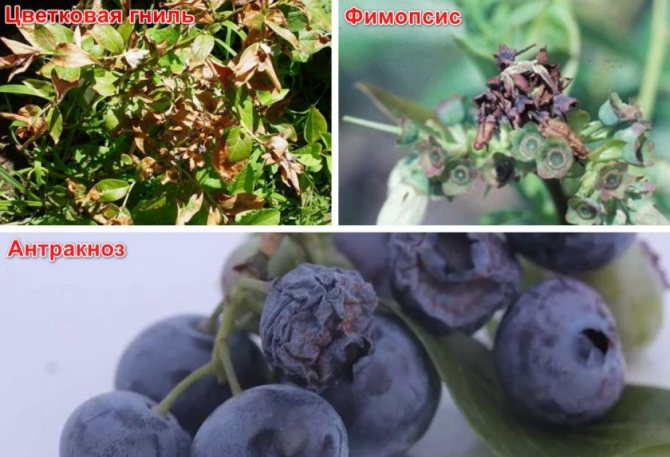


Signs of phomopsis appear in brown spots (1–1.5 cm in diameter) on the leaves. For treatment, spraying with a solution of "Fundazol" (50 g per 4 l of water) or "Toxin"(50 g per 3 liters of water). Moniliosis manifests itself in the yellowness of the top of the bush and brown spots on the leaves and berries. A solution is used against this disease "Karbofos"(100 g per 5 liters of water).
Symptoms of anthracnose include orange dots on the berries. The fight against the disease lies in the treatment of bushes "Fufanon"(20 g per 5 liters of water). Signs of red spot are crimson and light brown spots on the leaf blade. Treatment is carried out bordeaux liquid (30 g for 4 liters of water).Spraying is carried out once a month until the symptoms are completely eliminated.
Common pests that infect blueberry bushes include aphids, beetles, leafworm and flower beetle.... The main procedure for the prevention of parasites is the timely removal of weeds.
- A solution is used against aphids "Oxychoma"(30 g per 3 liters of water).
- In the fight against beetles, they use "Endured"(2 ampoules for 5 liters of water).
- Eliminating the leaflet consists in processing "Soon"(40 g per 5 liters of water).
- Spraying "Tridex"(100 g per 4 l of water) help fight the flower beetle.
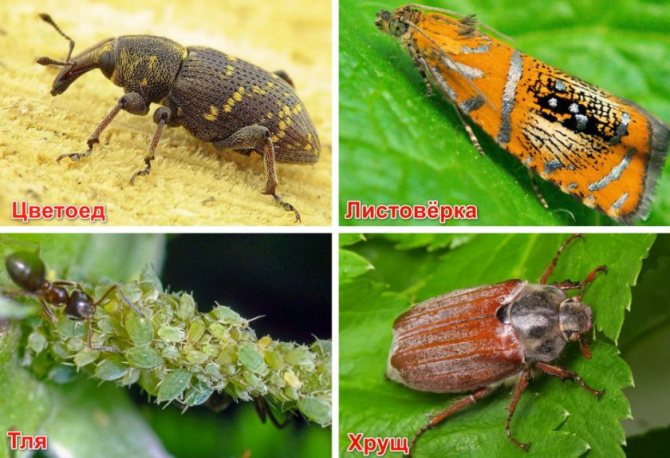


All treatments are carried out at intervals of 21 days.
So now you know how to plant blueberries in the fall. The process of planting a crop is simple, so it does not require a lot of time from the gardener. After immersing the seedling in the soil, do not forget to properly care for it - not only the harvest depends on this, but also the health of the entire shrub.


Distinguish between garden and forest blueberries. Garden blueberry grows into tall, powerful bushes with large berries. Forest blueberry is a shrub from 30 to 100 cm, its yield is smaller and less in quantity, but the berries themselves contain more vitamins. Therefore, many gardeners want to grow garden blueberries on their site in order to get unusually tasty and healthy berries.
Fertilizing garden blueberries
The capriciousness of blueberries is expressed not only in special requirements for soil conditions, temperature and lighting, but also in feeding an adult shrub.
Note: It is forbidden to feed blueberries with organic matter. Any organic fertilization makes the soil alkaline, which is absolutely not suitable for the culture and the shrub may die. In addition, compost, humus or manure can contain weed seeds, pathological microorganisms or pest larvae that can negatively affect the health of the shrub.
Ammonium sulfate is best suited for blueberries, as well as complex mineral fertilizers, and preference should be given to preparations for heather crops (for example, azalea). It is these preparations that contain all the substances necessary for blueberries.
In the spring
Spring is the most important time of the year for blueberries. The correct care during this period will determine how abundant the harvest will be.
Spring feeding of blueberries is carried out even before bud break. For this, it is recommended to use ammonium sulfate. It not only saturates the soil with the necessary nutrients, but also acidifies the soil, which is extremely important for the normal development of culture and the growth of green mass. In order for the fertilizer to be absorbed into the soil faster, it must be applied in liquid form. It will be enough to add 70 grams of the drug to a bucket of water and pour the bush with the mixture.
It should be borne in mind that spring feeding begins from the second year of planting, since annual plants have enough nutrients that are in the peat-sand mixture added to the holes during planting.
In summer
Summer feeding is carried out twice: the first time a month after the first fertilization, and the second - during the formation of the ovaries. Unlike spring feeding, special complex fertilizers for azaleas should be used in summer (Figure 4).


Figure 4. The best mineral fertilizers for the crop
The nutrients contained in such preparations have a beneficial effect on plant health and increase yields.
In autumn
The main purpose of autumn feeding is to saturate the soil near the roots with nutrients that the plant will use for winter nutrition. Superphosphate and potassium sulfate are best suited for this purpose. It will be enough to add 100 and 40 grams of the drug under each bush, respectively.
It is important that liquid fertilizers are not used in the fall. In order for top dressing to evenly dissolve in the soil in the cold season, they must be added to the soil in a dry form.To do this, a hole is dug near the bush, no more than 10 cm deep, fertilizers are placed in it and sprinkled with soil. Dig the hole carefully so as not to accidentally damage the superficial root system of the blueberry.
After fertilizing the soil, the soil around the shrub should be watered with a bucket of water, covered with a fresh layer of mulch and the plant should be prepared for wintering. To do this, you need to bend the shoots to the ground, fix them on the surface of the soil and cover them with any mulching material. Agrofibre or burlap, covered with a layer of dry leaves or spruce branches, is best suited for this purpose. It is necessary to cover for the winter not only young, but also adult plants, since the roots and tops of the shoots of the culture are sensitive to cold and can freeze without shelter.
How the timing depends on the region of cultivation
Blueberries are successfully bred in different countries - in Russia, central regions of Belarus, Kazakhstan. The natural conditions of Belarus are ideal for growing crops. Therefore, it is bred throughout the territory.
Severe frosts are typical for Central Russia. Therefore, planting work is recommended in April. The culture is sent for wintering in the second half of October or November.
A rather harsh climate is observed in the Urals and Siberia. Therefore, in these regions it is worth growing special frost-resistant varieties. When breeding, it is recommended to use tunnel greenhouses or greenhouses.
Blueberries are propagated in a variety of ways. The most effective method is considered to be cuttings. For this, you can use green, rooted or lignified cuttings. The use of other methods requires serious skills from the gardener.
Choosing a landing site
The berry can be of different varieties, tall shrubs have a large number of fruits, and low-growing plants are highly resistant to frost. Planting and caring for different types of blueberries is carried out in the same way.
The planting site should be well lit by the sun; blueberries should not be placed under the crowns of trees or tall bushes, which will form a shade. In a shady area, the plant will develop poorly, give small and sour fruits, while the bark does not have time to ripen.
The soil should have sufficient moisture, but not excessively, it is better to choose an area with soddy soil, and a deep passage of groundwater, where no fruit trees have grown before. Blueberries are planted so that the bush is not blown by the winds, not far from the fences.
Important! The plant does not take root well after planting in an open area, therefore, at first, the shoot is grown in a pot, and then, along with the ground, is moved to a prepared place. The roots remain dormant and adapt quickly. The shoots for planting must be at least two years old, then a rich harvest can be collected in the third year.
Planting culture
Every gardener should know how to properly plant blueberries in order to get a good harvest in the future. The shrubs should be planted in rows extending from north to south. This is necessary for the culture to be saturated with sunlight. The row spacing varies depending on the variety:
- undersized bushes - about 60 cm;
- tall - 1-1.5 meters.
If the cultivation of the crop is for industrial purposes, then it is better to make the aisle of 2 meters so that the special equipment can drive without problems.


Planting of garden blueberries is carried out in recesses, the size of which is 60x60 cm. The depth of the pit reaches half a meter. The distance between low-growing bushes is 50 cm, between medium-sized bushes - 1 meter, between tall bushes - 120 cm. The bottom of the depression and its walls must be loosened so that air can freely pass to the root system. Before planting, an acidic substrate is laid out in the pit, which is prepared as follows: peat is mixed with needles, sawdust and sand, after which 50 grams of sulfur is introduced into the composition for oxidation.In no case should you add organic matter at this stage, because it alkalizes the soil. Now you can do the landing directly. To do this, the seedling is lowered into a hole, its roots are straightened and it is sprinkled with earth. In this case, the root collar should be underground at a depth of 3 cm from the surface. After planting, young shoots are watered with warm water, and the soil around them is mulched. To do this, mix bark, straw, add coniferous sawdust and straw and cover the plant with this composition from all sides.
How to choose a blueberry seedling
An equally important role is played by the selection of high-quality planting material. The seedling should be strong and healthy, and the priority should be given to two- or three-year-old plants. By this age, the plants have already matured enough and developed a full-fledged root system, therefore, they will take root much faster in the new area.
Note: Experienced gardeners recommend buying seedlings in special containers with a closed root system. Such plants receive all the necessary nutrients from the soil of the container and are characterized by increased survival rate.
It is also best to buy seedlings from specialty stores or nurseries. So you can be sure that the plant has been properly processed, and there are no larvae of pests or pathogens on its roots or aerial parts.
Making planting holes for blueberries
One of the common mistakes when planting blueberries is the fact that the seedling is simply placed in regular soil. Under such conditions, the likelihood of a quick survival of the seedling on the site is significantly reduced, but even if the plant takes root, its fruiting will not be high enough.
It should also be borne in mind that this culture has a superficial root system, but it grows in width, therefore, planting holes must be prepared taking into account these features (Figure 3).
Planting pits for blueberries are prepared as follows:
- The hole should be 40 cm deep and 80 cm wide. A drainage layer of pine bark, needles and cones should be placed on the bottom of the hole. This layer should be about 10 cm.
- To strengthen the walls of the hole, slate or boards are placed around the perimeter. They will prevent the growth of the root system beyond the pit with acidic soil.
- The seedling is placed in a bucket of water for 30 minutes. This will help to easily remove the plant from the container without damaging the roots.
- The planting hole is completely filled with a special nutrient medium for blueberries. It can be bought at a gardening store or replaced with a mixture of ginger peat and sand in equal proportions. You need to fill the entire hole with soil, carefully tamp the soil, and to acidify the earth, sulfur must be added to it (about 50 grams per plant).
- A small depression is made in the center of the hole and a seedling is placed in it. The roots need to be spread in width, but it is important to make sure that they are not outside the hole. Sprinkle the root system with soil and water the shrub abundantly.
When planting, it is advisable to bury the seedling 5 cm more in the ground than it grew in the container. In addition, after planting, the trunk circle must be mulched with coniferous needles. This will prevent rapid evaporation of moisture and prevent the rapid growth of weeds.


Figure 3. Technology of planting culture and preparation of planting holes
Organic fertilizers do not need to be applied when planting, as they are completely unsuitable for blueberries.
Immediately after planting, a small formative pruning of the plant is carried out. You need to choose 4-6 strongest shoots and shorten them by a third of the length. All other branches that look weak are cut at the root. This procedure helps not only to speed up the adaptation of the seedling in a new place, but also allows you to form a suitable bush crown.
Alternative planting options for garden blueberries


Given that the plant prefers acidic soil, peat is the best option for planting it. However, if a different type of soil prevails on the site, then planting blueberries is possible without it.
Landing without the use of peat
We plant garden blueberries without peat as follows. We fill the planting hole with soil from the garden plot and acidify it. For this we use oxidizing agents. Pour the powder into a 15-20 cm pit and mix it with the planting soil, while adhering to the dosage described in the instructions. The product will dissolve during watering and oxidize the soil.
Acids such as oxalic and citric acids can be used as folk oxidation methods. We prepare a solution at the rate of 1 tsp / 3 l of water. When using vinegar (9%), take 100 ml / 10 L of water. We water the plant with ready-made mixtures 2 times / year: after the end of frost and before preparing the winter culture.
Culture pests
If planting and caring for seedlings are carried out properly, in accordance with the rules of agricultural technology, then the shrubs will grow healthy. But sometimes even a healthy plant needs help and protection. The crop most often suffers, as birds encroach on it. As protection from winged lovers to feast on berries, a regular mesh with a small cell, which is neatly stretched over the bush, is suitable.
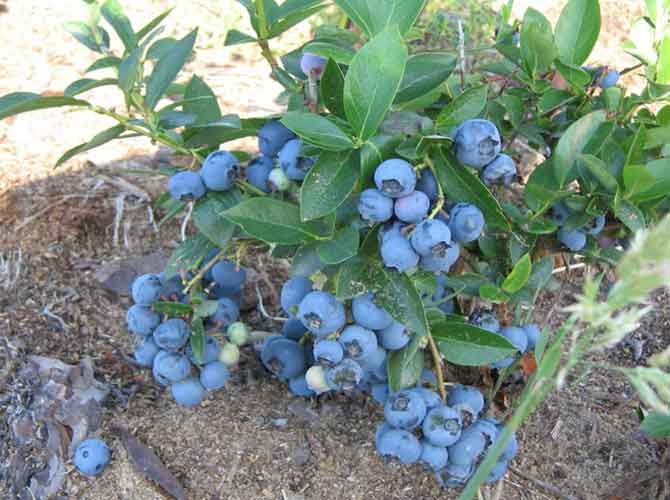


Culture suffers from insects much less often than from birds. Sometimes in the spring you can observe a deplorable picture of the invasion of May beetles and beetles for a gardener. They devour the leaves and flowers of the bush. The roots of the bush suffer from beetle larvae. In addition, the caterpillars of the pine silkworm, scale insects, as well as aphids and leafworms can cause great harm. It is constantly necessary to inspect the culture for the presence of insects and their larvae. After the collection of pests, it is necessary to drown by adding salt to the water. It should be remembered that spraying is an excellent tool in the fight against insects. For this, drugs such as Karbofos and Actellic are suitable. It is best to spray twice a year as a preventive measure: in spring and autumn.
How and when to plant blueberries in the fall: features and step-by-step instructions
Autumn planting is carried out in early October. First, you need to dig holes, the dimensions of which are 50 × 60 cm.The distance between the rows is determined depending on the size of the planting material. If you plant low-growing bushes, then 60 cm is enough. Planting medium-sized plants is carried out at a distance of 100 cm between rows. For bushes with a high growth rate, 130 cm will be required.


Optimal planting times
Planting blueberries with an open root system is carried out in early autumn - it is better to start after harvesting so as not to lose it next season. The optimal planting dates are selected based on the growing region. It is necessary that the soil has cooled to + 5 ° C, and then you can start planting the culture.
If we consider the detailed landing dates based on the weather conditions of different regions, then the following features are noted:
- in the middle zone of the country - mid-October;
- southern regions - early November;
- the northern part is in mid-September.
Pick-up location
Blueberries are planted in well-lit areas. The place should be open, without fruit trees and other shrubs growing nearby. If blueberries are planted in the shade, the berries become smaller and taste sour. It is forbidden to land in the lowlands. In such places, a large amount of water accumulates in the spring (rain, melted snow), which increases the risk of diseases such as root rot.

The optimum depth of groundwater is 3-4 m.
If on your site there are only lowlands, then you can create an artificial hill: you need to bring black soil 4-5 months before planting (about 3 tons)... During this time, it will settle and create a fertile layer for planting blueberries.
Features of blueberry cuttings
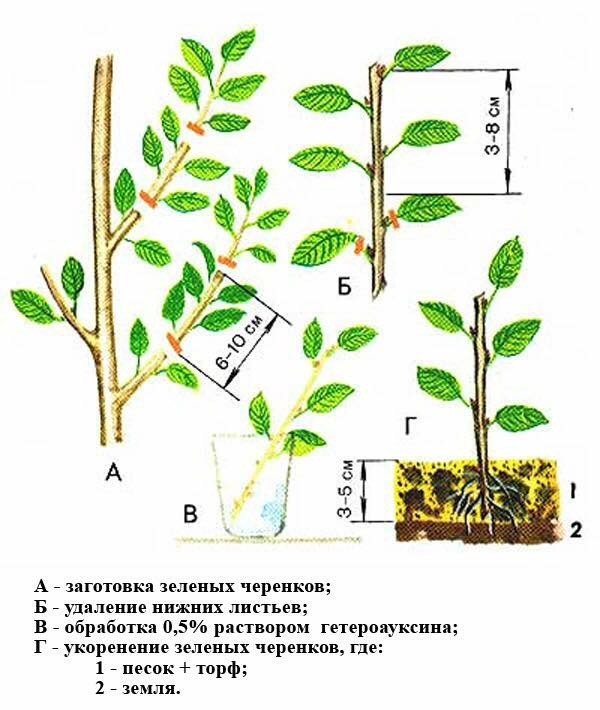

Blueberry is a plant, although it is not capricious in rooting, but it does not take root very willingly. To successfully reproduce it by cuttings, you need to know exactly what, when and how to do it right. Blueberries are propagated by both lignified and green (semi-lignified) cuttings.
Propagation by woody cuttings
Woody blueberry cuttings are harvested from December to March, when the plant is at rest. When harvesting cuttings, it must be borne in mind that the longer the cutting is stored, the more difficult it will be to root. Therefore, it is best to harvest woody cuttings of garden blueberries at the end of March.
For cuttings, one-year shoots are chosen, well-formed and ripe. Smooth or weakly branched cuttings 1.5-2 cm thick and 20-25 cm long are best suited for rooting.
Such shoots are cut off, bunches are formed from them and placed in storage until the moment when it will be necessary to start rooting the cuttings. Professionals use special glaciers to store blueberry shoots.
But in domestic conditions, you can use any suitable place with a temperature of 3-5 ° for these purposes: a refrigerator, a cellar, if it is cold enough, or simply sprinkle them with snow.
During storage, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the cut shoots: if they begin to dry out or they show signs of disease, they are ruthlessly removed - they are no longer suitable for further grafting.
Before rooting, cuttings are harvested from cut shoots. For tall varieties of blueberries, the optimal length for the cutting is 10-15 cm, for the undersized varieties - 7-10 cm. At the bottom of the cutting, immediately under the bud, an oblique cut is made, and at the top, the cut is made horizontal, retreating 1.5-2 cm above the bud.
To increase the root-forming ability of cuttings, immediately before starting rooting, the lower cut of the cuttings is treated with Kornevir or a special root-forming preparation for rooting heather crops. Rooting of woody cuttings lasts at least 2 months.
Propagation by semi-lignified cuttings
Blueberries are also propagated by semi-lignified (green) cuttings. They are harvested from late June to mid-July, while the plant is in summer dormancy. The raw material for harvesting cuttings are young growth shoots or the same young branching shoots.
The process of harvesting semi-lignified cuttings is quite peculiar. Young shoots are not cut off, but are torn off from the stem with a sharp downward movement, so that a "heel" remains at the lower end of the cutting - a strip of last year's bark.
If, when the shoot is torn off, a long strip of bark comes off from the stem, it is shortened by cutting off the excess with a sharp knife or pruner. Then the lower part of the torn off shoot is freed from the leaves, and treated, like woody cuttings, with a root-stimulating drug. Depending on the size of the harvested cuttings, the leaves are removed from 1/4 to half of their length.
1/3 of their area is removed from the remaining leaves, after which the bottom of the cutting is treated with root-forming growth stimulants. Like lignified, semi-lignified cuttings are planted in a greenhouse on specially prepared beds. They are planted in such a way that the leaves remaining on them do not touch, let alone overlap each other.
For normal rooting of semi-lignified blueberry cuttings, it will take at least 1.5 months. All this time, the beds with planted cuttings need to be regularly watered and ventilated. The signal about the need for the next watering is the state of the leaves - they must always remain fresh. They cannot be allowed to fade.
Also, when rooting semi-lignified cuttings, nitrogen fertilization cannot be applied, otherwise they will continue the growing season, do not have time to completely woody by the beginning of winter and die.
Preparing the beds for rooting cuttings


Both lignified and semi-lignified cuttings are rooted in a greenhouse or greenhouse in specially prepared beds. They equip such beds in 2 ways:
- A wooden rectangular frame with a height of 20-25 cm is made, and it is filled with a previously prepared soil substrate.
- The top ball of soil is taken out to a depth of 20-25 cm, and the resulting niche in the ground is filled with a prepared soil substrate.
To prepare the substrate, high-moor peat is mixed with sand, crushed bark and rotted sawdust. You can also use pure high-moor peat for rooting.
Blueberry cuttings are most often rooted in unheated greenhouses or greenhouses. When the average daily temperature inside such a structure reaches 20 °, the cuttings can be planted for rooting. In most regions, this occurs in early or mid-May. In heated greenhouses, rooting cuttings can be planted in late March or early April.
There are several schemes for planting woody cuttings on a bed:
- 5X5 cm;
- 5X7 cm;
- 5X10 cm;
- 10X10 cm.
The choice of scheme depends on when you plan to plant the rooted cuttings in containers for further growing them. If you plan to keep them in the garden until next spring, then you should choose the widest planting scheme.
Before planting the cuttings, strong wire arcs are equipped over the prepared beds, and immediately after disembarkation, first a plastic film is laid on these arcs, and then also a spunbond.
Such a shelter allows you to shade well the planted cuttings, as well as maintain a high level of humidity inside the greenhouse, which is necessary for their successful rooting. All the time while the cuttings are in the greenhouse, it must be regularly ventilated, preventing air stagnation, and the planted cuttings must be regularly watered and treated against diseases and pests.
Also, it is important to carefully monitor the slightest changes in the temperature regime in the greenhouse - both overheating and strong cooling are equally detrimental to the planted plants.
Woody cuttings are planted, deepening them by 2/3 into the soil substrate, but at the same time leaving 1-2 upper buds free. When planting semi-lignified cuttings, they are buried in the substrate for the entire length at which the leaves were torn off.
Usually, the process of rooting cuttings (both lignified and semi-lignified) lasts until the end of August. In the last days of August, covering material is removed from the greenhouse or greenhouse so that the rooted cuttings acclimatize in the fresh air and prepare for winter. All the time before the start of preparation for winter, beds with rooted cuttings should be regularly watered and fed.
In areas with a temperate climate, rooted woody cuttings of blueberries can already be planted for growing at this time. But in areas with cold autumn and early cold weather, it is better to leave them to overwinter in a greenhouse. For semi-lignified cuttings, there is no choice - they are left in the greenhouse for the winter.
To prepare for wintering, depending on weather conditions, in early or mid-October, the rooted cuttings are carefully sprinkled with a 5-7 cm layer of sawdust. If there is not enough sawdust, you can use horse peat for dusting.
At the beginning (if the weather is warm, then in the middle) of November, beds with rooted blueberry cuttings are covered with spunbond and left to winter. In the spring, as soon as the soil thaws, the rooted seedlings are planted in special containers for growing.
Features of care for cuttings planted for rooting


Cuttings planted for rooting require constant care and maintenance.First of all, it is important to observe the temperature regime: the soil temperature must be maintained at 18-21 ° throughout the rooting period. If the soil is too cold or overheated, the weak and delicate little roots that release blueberry cuttings are doomed to die.
Also, it is important not to miss the beginning of the development of diseases or the appearance of pests on the planted cuttings. If signs of disease are detected, plants should be immediately treated with Fundazol, Kuprozan, Azofos or Topsin-M. Insecticides, for example, Ambush, will help to cope with pests.
Cuttings planted for rooting should be watered regularly, maintaining a high humidity level in the greenhouse. Usually, until the cuttings are fully rooted, two waves of their growth pass.
With the beginning of the second wave, the planted cuttings are fed with complex fertilizers. Most often, Solution or Kemira is used for dressing, diluting 1 tablespoon of the drug in 10 liters of water, but in principle, any liquid chlorine-free fertilizer is suitable for feeding.
The seedlings are fed, consuming 1.5 liters of nutrient solution per 1 m² of the garden. Usually, 5-6 such dressings are carried out, observing an interval of 1 week between them. After each feeding, it is imperative to water the plants in order to wash off the fertilizer residues from them.
At the end of the 2nd growth wave, when the blueberry seedlings are already well rooted, they slowly begin to prepare for life in the field - they reduce the frequency and intensity of watering and more often ventilate the greenhouse.
Planting blueberries in the fall: choosing seedlings
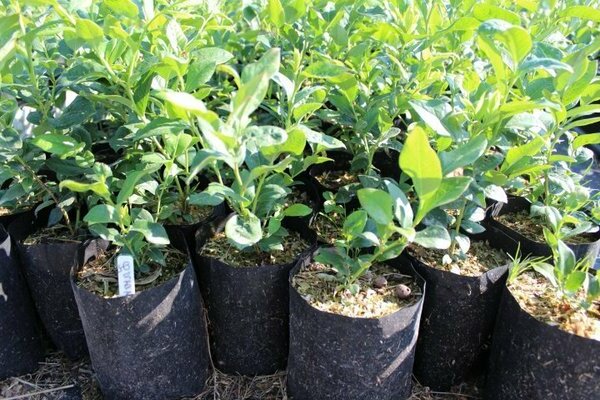


Selection of seedlings
Seedlings for planting can be purchased in specialized stores. The most profitable warrant is to purchase 3 bushes, but you should pay attention to the berry variety, given the climate in your region. For example, for Siberia, it is required to choose varieties that can survive rather low temperatures.
Seedlings that are in containers must be watered during planting, thereby preparing them for further planting in the ground. The roots are hidden there, you need to be careful when pulling out a clod of earth. When planting, they must be straightened and directed downward so that they occupy all the space in the previously prepared hole.
We plant in the autumn During the autumn planting, special attention should be paid to the plant, since on the eve of winter it must have time to pass the adaptation period. It depends on how correctly the landing was made.
If the seedlings are of an average size, then we prepare a hole of 50 by 50 cm. For lands that are prone to acidification, you need to choose a special planting method using a plastic barrel with a volume of 200 liters. We place it at the bottom of the prepared hole, then pour drainage (10-20 cm), and the next layer is the nutrient mixture. The next step is to plant the seedling in the hole, then season it with nutritious soil and tamp it. A distance of 1.5 m - 2 m should be left between the bushes, since the roots do not grow down, but in width.
We advise you to mulch the soil after watering, and for this you need to choose an acid filling: pine needles bark, peat, rotted needles sawdust. This mixture will protect the soil from freezing, moisture loss and weeds.
The main methods of breeding


There are three ways to propagate garden blueberries:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- layering.
Each of them has its own pros and cons. For example, obtaining blueberry seedlings from seeds is a long, laborious and very specific process, therefore it is used only by breeders to obtain new varieties of blueberries.
Reproduction by layering is also a rather lengthy process, in addition to high-quality planting material, it gives little. But the problems with rooting new plants are incomparably less than when rooting blueberry cuttings.
How to cut blueberries and at what time
For propagation of garden blueberries with lignified cuttings, the harvesting of planting material is performed in early spring or at the end of winter, in regions with a warmer climate. Cutting cuttings is often combined with general shrub cutting. The main rule when collecting lignified cuttings is that the mother plant is in a dormant period. To obtain planting material, annual shoots that are well ripe are cut off.
A video about the propagation of garden blueberries with green cuttings shows that planting material is collected in the middle of summer. Harvesting time is limited to a few weeks during the dormant period of the plant. Depending on the region of cultivation and the weather conditions of the current season, the collection of green cuttings begins at the end of June. At this time, the first wave of shoot growth is completed, and the next has not yet begun.
Planting material in the case of green cuttings of blueberries is collected from the growth shoots of the current year or branching shoots.
How to propagate blueberries with woody cuttings
Sliced lignified shoots are tied in bunches. Before planting, they must be stored in a refrigerator or a specially constructed glacier, where the cuttings are left in an alternating layer of snow and sawdust. The temperature during storage should be about + 5 ° С. Cuttings during this period must be periodically inspected to prevent them from drying out or the appearance of mold.
For propagation of blueberries by cuttings at home, a place in the greenhouse is prepared in advance. An acidic substrate is poured into a separate box. A mixture for planting is prepared from 3 parts of high-moor peat and 1 part of river sand. With a direct planting in a greenhouse bed, the soil is removed from it to a depth of 20 cm and replaced with a suitable one for growing heather culture.
Depending on the equipment of the greenhouse, the planting of cuttings is carried out in the spring one month after storing them in the refrigerator. From the video about the propagation of blueberries by cuttings, you can see that the prepared shoots are shortened for tall varieties of blueberries up to 10-15 cm and for undersized varieties up to 7-10 cm.The lower cut is made obliquely under the bud, the upper cut is even, 1.5-2 cm above kidney.
Depending on the expected time spent in the greenhouse, the cuttings are planted on the garden bed more densely or sparsely according to the scheme 5 by 5 cm or 10 by 10 cm.The cuttings are stuck vertically into the soil mixture and watered. To create the necessary microclimate above the bed, arcs are installed and the planting is first covered with plastic wrap, then with any non-woven material. In the greenhouse, it is necessary to maintain a high air temperature in the range of + 26 ... + 28 ° С and constant humidity. Watering is carried out by sprinkling.
With the method of reproduction of blueberries by lignified cuttings, rooting takes about 2 months. At this time, the plants need constant care. The greenhouse is regularly ventilated, maintain a constant temperature of the air and soil without sudden changes. Seedlings are watered and treated for diseases.
After the cuttings take root, the shelter is removed. Before planting in a permanent place, seedlings are grown for several years. With good care, the results of propagation of blueberries by cuttings can be obtained after 2 years.
Blueberry propagation by green cuttings
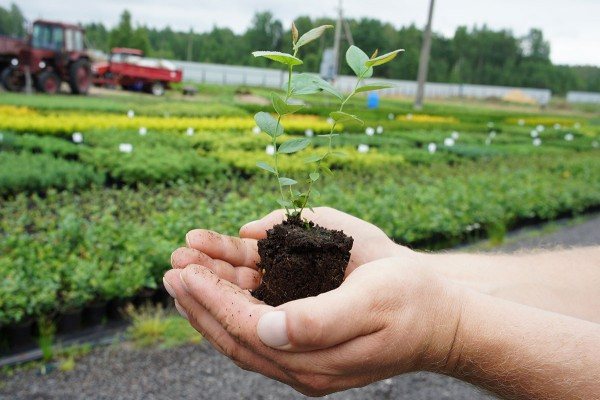


With the method of green cuttings of garden blueberries, the planting material is harvested early in the morning to prevent dehydration of the stem. The lateral shoot is clamped with the thumb and forefinger at the base and cut off with a sharp downward movement so that the "heel" remains at the shoot - a part of the bark from the main branch. Too long a strip of wood is cut off with a disinfected sharp knife or pruner. The length of the cutting should be about 10 cm. The lower leaves are cut off, leaving only a few upper leaves, which are shortened to half.
For the cultivation of green cuttings, high-moor peat and rotted coniferous litter are mixed in equal parts.The planting material is placed in a prepared substrate in a greenhouse. The cuttings are placed in a common planting container or cassettes so that the leaves do not come into contact with each other. When caring for plantings, it is important to maintain a high temperature of the air and soil. When blueberries are propagated by green cuttings, their leaves should always remain moist; for this, frequent spraying is carried out or a fogging system is installed.
Advice! Chlorinated water is not used for watering blueberry seedlings.
In the case of propagation of blueberries by green cuttings in a greenhouse, additional shelter is not required in the summer. With proper care, cuttings take root in 4-6 weeks. In autumn, young plants are sheltered or transferred to a cool room. In the spring of the next season, the sprouts are transplanted into larger containers for further cultivation.
The survival rate of blueberry propagation by green cuttings is somewhat lower than lignified ones. But harvesting green cuttings is easier and does not require storage space during the winter. Lignified cuttings are recruited from formation shoots, which are less on the bush than branching shoots from which planting material is taken for green cuttings.
The cuttings method is one of the only possible methods of propagation of tall blueberry varieties.
How to root a blueberry stalk
Blueberries take root for a long time, so before planting the cuttings, the lower cut is dipped in a special powder that stimulates the formation of roots. For heather crops, which include blueberries, root growth accelerators based on indolylbutyric acid are also used. If all growing conditions are observed, the average survival rate of sprouts when grafting blueberries is about 50-60%.
Description of the plant
The culture is a shrub with erect branches covered with dark gray or brown bark. Small leaves, reaching a length of 3 cm, are painted in a bluish-green tone. Their edges are slightly bent downwards. The bush grows up to a meter in length, but there are varieties that reach two meters. The fruits are oblong. Greenish flesh is hidden under the blue skin. Blueberry is a deciduous type of shrub. In nature, it is found in the Northern regions, where a cold and temperate climate prevails. For our latitudes, it is better to choose plants of an early or medium ripening type, since late varieties do not have time to ripen completely.


Blueberries - Pruning at Planting
Pruning blueberries during planting is mainly aimed at producing more buds and branching. However, care must be taken that there is no thickening of the crown. Young plants are pruned to create the correct shape. The shrub should grow upright and have small branches. Too much branch density can interfere with the penetration of sunlight, which will significantly affect the yield.
In the future, you can trim the ends of the shoots to increase yields, as well as carry out preventive and sanitary pruning. To do this, remove weak, frozen and diseased branches. If the blueberries are well formed, then there is no need to prune them at all.
Proper care and creation of favorable conditions for the plant will allow you to pick tasty and healthy berries.
Propagation by lignified cuttings
When using the propagation method using lignified cuttings, mature one-year shoots will be required. In autumn, the blank material is cut from the bush and stored until spring at low temperatures (+ 3 ... + 6 ° C). A cellar or refrigerator is well suited for these purposes. Rooting can begin in March if planting is carried out in a heated greenhouse with a temperature of + 20 ° C, or in late April - early May in a greenhouse without heating.
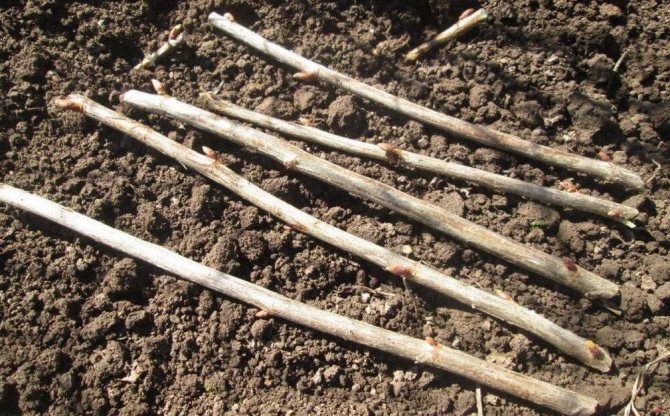


The process itself consists of several stages:
- The prepared shoots are cut into pieces, the length of which is 12-15 cm for tall varieties and 8-10 cm for low-growing ones. The lower cut is made oblique and it is located immediately under the kidney. Cut from the top at a right angle at a distance of about 2 cm above the kidney.
- For rooting cuttings, pre-prepared cassettes filled with peat or a mixture of equal parts of peat, sawdust, sand and bark are used.
- Cuttings, which were given pre-lignification, are planted according to the standard scheme: at a distance of 5 × 5, 5 × 7 or 10 × 10 cm. A wire is pulled over the beds, and covered with plastic wrap on top.
Video: Cutting blueberries with lignified cuttings
Rooting of lignified cuttings takes up to 7-8 weeks, during which the shoots need frequent watering and regular ventilation... You should also pay special attention to the temperature regime - overheating or hypothermia of the planting material should not be allowed.
Important! Since blueberries belong to crops that are difficult to root, it is recommended to treat all cuttings with a growth biostimulant before planting.
Proper care in the autumn
If we talk about leaving, then for the autumn planting it is required several times less than in the spring-summer period. But it is worth paying maximum attention to feeding and watering.
Always check soil moisture during the adaptation period - it should be moderately moist. The frequency of watering depends on the weather outside the window. If it is constantly raining and cloudy, do not water it again, so as not to flood the roots with water. If the weather is dry, then watering should be daily and about 10 liters of water for each bush.
In the fall, with a lack of minerals, it is customary to add potassium nitrate and potassium sulfate. The granules are poured into the soil and dug up. It is worth abandoning nitrogen-containing mixtures in the fall and waiting until spring, when they are needed.
In the fall, when leaving, the planted bushes should be trimmed: we cut them out completely, if there are weak and damaged branches, and good branches are cut in half.
Planting blueberries in different regions
Wild blueberries are common in Belarus, Ukraine, as well as in some regions of Russia, for example, in Siberia and the Urals.
In the Moscow region, we recommend planting the following varieties of blueberries:
Garden blueberry varieties differ not only in terms of ripening, but also in the height of the bush. So, in the northern regions, we recommend planting:
Such varieties as "Northland", "Bluetta", "Weymouth" and "Northblue" are distinguished by their higher adaptability to cold weather, various diseases and pests. If the region is distinguished by sharp temperature changes, winters with little rainfall, we recommend choosing low and medium-sized varieties for planting that can withstand temperatures down to -34 ° C.
Reproduction of blueberries is a delicate, but rewarding business


Mass plantings of blueberries can be found mainly in natural conditions, but in horticulture this culture is still a novelty. Not every amateur is taken to grow it due to the exacting nature of the plant. In addition, blueberries have their own nuances and reproduction, because they are one of the shrubs with a low root-forming ability. Not only is the rooting rate of cuttings not more than 40%, but also young specimens develop rather slowly. A surprise will also come from blueberries from seeds. Cherishing seedlings for 2-3 years, you can get a completely different variety from which the planting material was taken.
Nevertheless, the vegetative method remains the most affordable for gardeners. It allows you to significantly reduce the waiting time, moreover, it preserves the varietal characteristics of the plant, in contrast to blueberries grown from seeds.
We cover for the winter
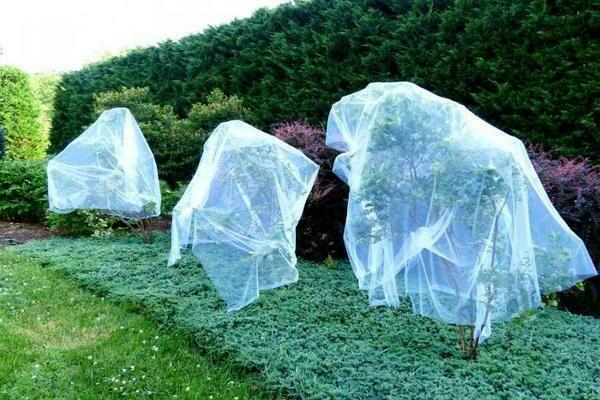


Shelter for the winter
If you decide to grow blueberries, then you should think about how to protect them in the winter.First of all, it must be covered, regardless of the variety.
Preparation for winter begins in the autumn after planting and consists of several stages: • First you need to provide abundant watering - in this way, we create the necessary amount of moisture for the winter period, which will nourish our plants.
• Next, you need to add mulch to the soil. Thanks to this, we keep the warmth and moisture of the soil, and the roots from freezing.
• The next step is to acidify the soil, but this should be done in warm autumn. If the weather still does not work out, then this procedure is postponed to the spring.
• Bushes are pruned every fall. In the spring, the bushes grow more actively, and in the winter they are not susceptible to freezing if the pruning is done correctly.
The material for the shelter must be dense and breathable, otherwise root rot will begin. For this, agrofibre or burlap is best suited.
Each plant should be tied with material, while using nylon threads and secured with additional oppression.
Adult shrubs must be bent to the ground in advance so that they can be lowered and not spoiled during strapping. If the branches lie on the ground without help, then they are covered with material, they are strapped and boards are placed on top for the best fixation.
When the snow has fallen, and the temperature is below zero, you can additionally make snow decks on top of the sheltered blueberry bushes. This will keep the berries from freezing in winter. Thus, the preparation for winter is over!
When spring comes, the snow must be removed in advance before the thaw period begins. Then all additional floorings are removed when the temperature stabilizes above 0 degrees.
Propagation by green cuttings
To use propagation by green cuttings, you will need a previously prepared area with uterine bushes, from which you can take blank material. The optimal time for the procedure will be the middle of summer. (late June - early July), and the most suitable shoots are young growth that has grown over the spring or one-year shoots left after pruning.
The choice of raw materials should be taken seriously - the quality of future bushes will depend on this.... The selected shoots should be strong and well developed, covered with healthy leaves. It is the foliage that will help to replenish the stalk with a margin of safety before the appearance of the rhizome, feeding it with moisture and minerals.
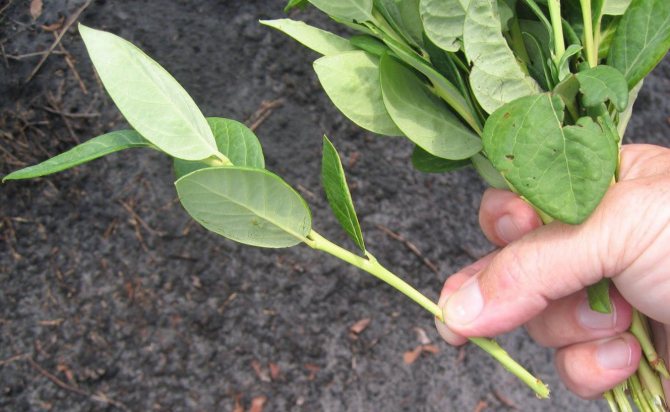


The grafting process is as follows:
- The shoots are cut to a height of about 6 cm, after which they are soaked in water or a fungicidal solution, which will act as a disinfection.
- A special soil is prepared, consisting of acidic peat mixed with micronutrient fertilizers, which are designed for long-term release of useful substances.
- The soil is poured into cassettes, carefully compacted and moistened. Cuttings are planted (to a depth of about 4–5 cm), and the containers with cuttings themselves are placed in a room (for example, a greenhouse) with certain conditions.
Video: Green blueberry cuttings
Conditions for rooting cuttings:
- the floor covering on which the cassettes will be displayed must consist of drainage. As drainage, a gravel mound, 10 cm thick and a layer of sand 5 cm thick, is most often used. From above, everything must be covered with any durable material (you can use agrotechnical cloth);
- the humidity in the greenhouse must be kept constant at 100%. This result can be easily achieved with the help of special foggers, the principle of which is to spray water throughout the room to the size of microdroplets. In addition to the humidity level, such equipment also maintains the required temperature regime;
- the temperature regime should be at the level of + 20 ... + 24 ° С.In case of persistent summer heat, it is recommended to use additional shading of the greenhouse with nets.
In conditions of adherence to all recommendations, rooting of cuttings occurs in the fourth week after planting.... After that, the seedlings gradually begin to adapt to the usual greenhouse conditions, and then the containers with the plants are transferred to the open air area.
Important! The whole process of preparation, rooting and adaptation of cuttings takes from 1.5 to 2 months.
Planting time for blueberries in autumn
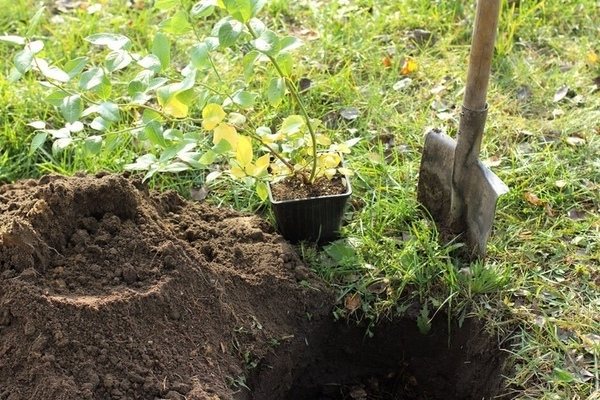


Planting time for blueberries in autumn
For a timely planting date, you should choose a warm autumn day closer to the end of September or the beginning of October. The calculation also depends on the climatic region in which the plantation is located, and before the first cold weather below zero, it should be approximately 30 days. This period is considered the most optimal for normal plant adaptation.
Blueberry diseases
Most often, fungal diseases of various types can be observed in a plant:
- stem cancers;
- double spotting;
- gray rot (botrytis);
- drying of branches (phomopsis);
- physalsporos;
- white spot (septoriasis);
- monoliosis of fetuses.
Stagnation of moisture provokes the appearance of a fungus, which accumulates around the root area. The main causes of formations are as follows:
- improper watering;
- poor soil permeability.


For preventive purposes, shrubs should be treated with Bordeaux liquid twice a year (in early spring and after harvesting the fruits). If the disease could not be avoided, then when it is detected, a double-triple treatment is carried out with a weekly break with the following drugs:
- Topaz;
- Bordeaux mixture;
- Fundazol;
- Topsin.
Often, garden blueberries suffer from viral or mycoplasma diseases, which include: mosaic, filamentous branches, dwarfism, as well as red annular and necrotic spotting. These types of diseases do not respond to treatment. The infected bushes are dug up and burned.
How to propagate blueberries by dividing a bush
You can propagate blueberry seedlings by dividing an adult bush. With the method of dividing the bush, the mother plant is dug out completely. Several independent plants are obtained from one adult shrub during reproduction.
Important! The division of the bush is not carried out during flowering.
The root system of blueberries is shallow, so digging up the bush is easy. After removing the bush from the soil, shake the ground, examine the roots. Only a completely healthy plant is suitable for transplanting. Damaged or dry roots are cut. The bush is divided by hand in such a way that on each independent part - the cut - there is a well-developed root, more than 5 cm long. 3-4 cuttings are usually obtained from an adult bush. After separation, the roots are sprayed with disinfecting compounds, as well as root formation stimulants.
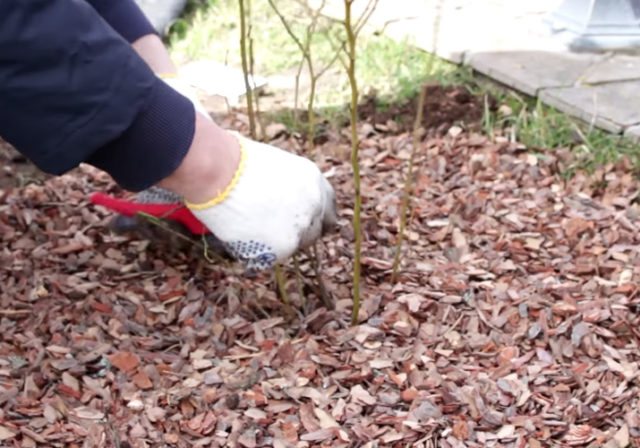


When propagating by dividing the bush, it is important to prepare a place in advance for transplanting new plants. When planting, the roots are straightened so that they are evenly distributed in different directions, otherwise the plant will not take root.
How else can you breed blueberries
For planting and breeding blueberries, you can use not only saplings. We use the following methods for plant propagation:
Seeds
This breeding method is the most laborious. In autumn, we get the seeds from ripe berries, dry them and sow them into the soil for seedlings to grow. The most suitable conditions for growing seeds:
- air temperature within 23-25 ° С;
- air humidity at 40%.
After planting, we regularly water the seeds, loosen the soil and remove the emerging weeds.
Cuttings
Cut the cuttings in the fall after the bushes have dropped the leaves. We use cuttings of 8-15 cm in size for breeding, which are at the root. We plant them in a peat-sand mixture (1: 3) at an angle.
Bends
Branching of blueberries is not always successful.We select the longest branch and incline it to the ground, sprinkling with sawdust. The branch will take root after 2-3 years and only after that we separate it from the main bush.
To properly plant blueberries and grow a healthy fruiting plant, you need to adhere to the basic rules for choosing a "planting material", planting site and soil preparation. Also, don't forget to follow our step-by-step instructions for planting a plant.
Distinguish between garden and forest blueberries. Garden blueberry grows into tall, powerful bushes with large berries. Forest blueberry is a bush from 30 to 100 cm, its yield is smaller and less in quantity, but the berries themselves contain more vitamins. Therefore, many gardeners want to grow garden blueberries on their site in order to get unusually tasty and healthy berries.
Reproduction of garden blueberries by cardinal pruning
A method in which the bush is completely replaced with several new plants. All shoots are cut in the spring. A complex mineral fertilizer is applied under the remaining root in a double dosage. Sawdust from coniferous trees is poured on top. The sawdust layer should be about 30 cm.
A small greenhouse is installed above the growing area in order to maintain the necessary humidity and growing temperature, as well as to protect young plants from a sharp cold snap. In place of the cut shoots, new ones will soon appear. But the development of their own roots will take place within two years. They are formed above the original root system, in a poured sawdust layer.
After 2 years, young shoots with their own root system are separated from the mother bush and planted separately. With the method of pruning the bush and growing new shoots of replacement, the bush is grown for several more years to get the first berries.


























