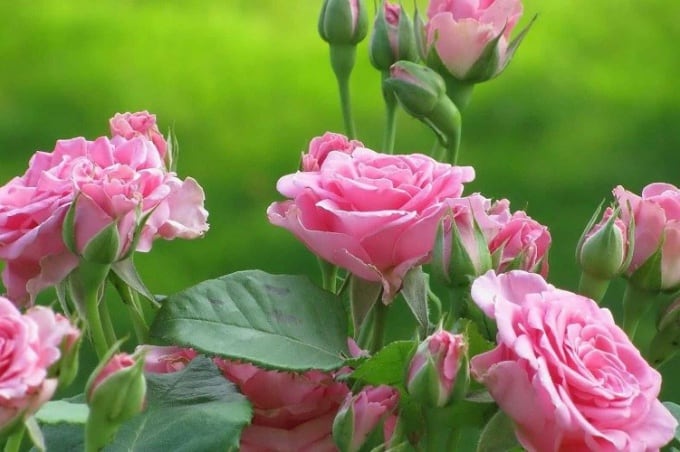
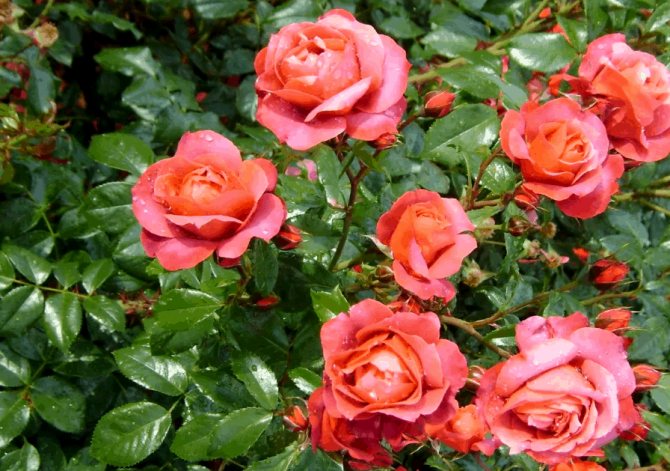
Of course, it is best to plant a rose bush once, and then just take care of it and enjoy the magnificent flowers and wonderful aroma. But sometimes the flower needs to be moved to a new place in order to clear the area for a new building, swimming pool or playground. It happens that we plant a rose in unsuitable conditions, where it cannot develop normally and bloom profusely. Many landscape projects are initially designed to be dynamic and require regular redevelopment. Transplanting roses to another place in the fall can be both a forced measure and a planned one - not all owners want to enjoy the same landscape from year to year.
Perennial flower groups
Perennial flowers are classified into two groups. Firstly, these are thermophilic crops that cannot winter in our climate. They have to be dug up annually in the fall, stored at positive temperatures and under special conditions, and planted in the spring. This group includes many tuberous and bulbous flowers. For example, flowers of gladiators and gladiolus warriors, or cheerful dahlias.

The second group consists of frost-resistant rhizome flowers that winter right on flower beds and in flower beds. These perennial flowers do not need to be replanted annually, because many of them can grow in one place from 4 to 10-12 years. But even these flowers after a while will require transplantation, dividing the bush.
Why is it necessary to divide the bushes of perennial flowers
Because during the years of vegetation, the root system of the plant grows in width and upward. Roots and rhizomes interfere with each other, compete for food. Old, dying roots interfere with young developing ones. The roots come to the surface, which can cause them to freeze. To enable the young parts of the plant to develop, perennials are transplanted and divided.


Care after transplant in the fall


Daylily is a fairly frost-resistant plant
At the first time after transplanting daylilies, soil moisture is maintained for better rooting, but the plants are not flooded much. The planting site is mulched with wood chips, crushed bark, hay or dry peat.
General recommendations for care:
- Shrubs transplanted in autumn are fertilized in spring and summer, after flowering, when buds are laid for next year.
- Flowers do not like scanty and frequent watering - it is better to water once a week, but abundantly, so that the roots receive moisture at depth.
- When treating the garden in the fall from fungal diseases and pests, do not forget about daylilies. Plants are sprayed with fungicides and insecticides for prophylaxis.
Daylilies tolerate winter cold well and do not need special shelter.
When to divide perennials
You can determine that the plants need a transplant by looking at the “bald” center of the bush. If the flowering has become scarce, and the flowers are crushed. As a rule, the division of perennials is carried out every five to six years. Experienced gardeners annually rejuvenate, divide or transplant two or three perennials in a flower bed. Thus, the overall decorativeness of the flower garden is not disturbed.
The division of the bush and the transplantation of perennials is carried out in early spring, before the foliage grows, and in the fall, a month and a half before a steady cold snap. Perennial flowers blooming in late summer and autumn are transplanted in the spring.So that before flowering they have time to take root, recover and bloom in due time.
In autumn, perennials are transplanted, which have faded in spring and early summer. They should take root in a new place before the cold weather and get stronger, preparing for winter.
Perennial flowers that are transplanted in early fall
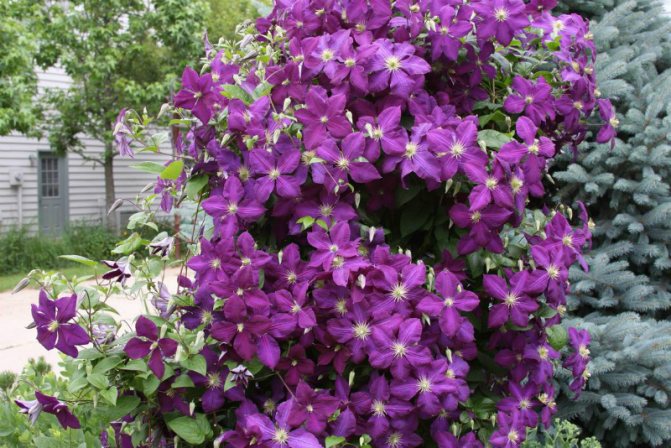
In September, unpretentious astilba is transplanted, this beauty of a shady garden. However, this plant easily tolerates a transplant in any phase of the growing season. Brunner, herbaceous peony, delphiniums and lupins are planted and divided in early autumn. Transplanted hosts, irises, clematis, phlox take root well at this time.
As a rule, new varieties of these plant species can be planted at the same time.


Advantages and disadvantages of an autumn transplant
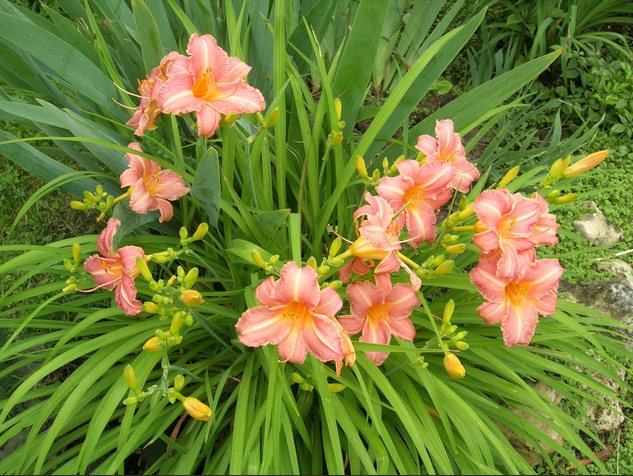


When transplanting daylilies, you need to follow some rules.
Daylilies can be divided and transplanted both in spring and autumn, but if the spring transplant is late, there is a risk of not seeing flowering in the current year. In rare cases, flowers are transplanted in the summer by the transfer method, without dividing the mother bush into divisions.
The plant tolerates an autumn transplant more easily than a spring or summer transplant - this is its main advantage. There is no scorching sun from which you need to cover young seedlings, it rains, and there is no need for frequent watering.
Harsh snowless winters and short autumn can harm flowers transplanted before winter. It is necessary to complete the planting work in the garden a month before frost - then the daylilies will have time to take root and winter safely.
Perennial flowers: the rules for dividing the bush
It is better to start dividing and transplanting a bush on a cloudy day. The day before transplanting, the plant must be watered abundantly. So that the leaves and roots have a good turgor and easier to bear stress.
Also, a day before transplanting, planting pits are prepared, filling them with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers or autumn complex fertilizer. Wood slag can be added. Nitrogen fertilizers should not be applied in the fall. Because they can provoke the growth of new shoots. Which will not have time to ripen before the cold weather and will die, thereby weakening the bush.
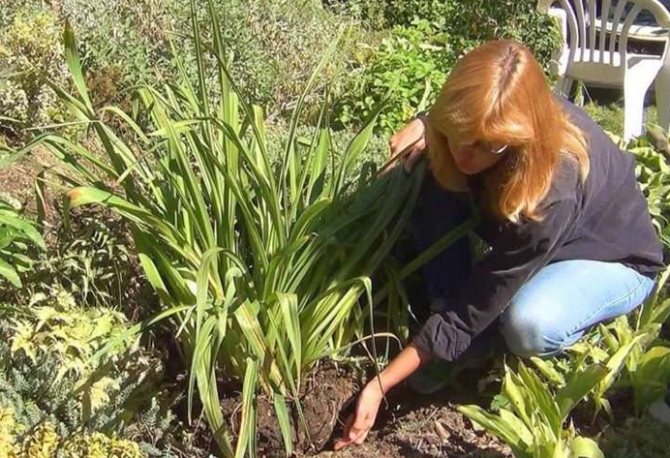
The transplanted bush is widely dug in, trying not to damage the root system. Carefully removed from the soil. Shake off the ground. Carefully examine the roots, remove dead, sick and rotten ones with a sharp knife.
Then determine the places of incisions into divisions so that each has at least three healthy kidneys. Divide the bush with a shovel, knife or pruner.
Delenki are treated with a fungicide solution, for example, "Maxim" or a pink solution of potassium permanganate. Then it would be nice to dust the roots and cuts with ash.
The planted cuttings are watered abundantly, the soil under them is mulched with mowed lawn grass, high-quality compost, and chopped straw. The plantings are covered with spunbond from the hot sun rays.
The technology for planting new plants is exactly the same. It is only important not to miss the optimal landing dates. Because the plants planted at a later date will not have time to adapt and take root. As a result, they will die in winter or come out of wintering extremely weak. And full bloom in the new season should not be expected.
The timing of the autumn transplant of daylilies to another place


Transplant times depend on weather and climatic conditions
It is possible to carry out the autumn division and transplantation of these plants in central Russia from the end of August to the end of September, and in more southern regions until mid-October. It is advisable to do this in cloudy weather so that the plant suffers less from overheating.
Recommendations by region:
- In Siberia and the Urals, daylilies are transplanted in August.
- In the Moscow region, the best time for transplanting flowers is early September.
- In the Leningrad Region, planting work is carried out in late August or early September.
- In Belarus and Ukraine, plants are dug up and moved to a new location in September.
- In the south of Russia, you can carry out the procedure in October.
According to the lunar calendar for 2019, daylilies can be transplanted: 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31 August and 18, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 26, 27, September 28, 29.
Auspicious days fall at the beginning and first half of the lunar month, when all the activities in the garden related to planting work are successful.
Perennial flowers: features of transplanting individual crops
Perennial flowers are very diverse and each culture has its own characteristics.
Peonies
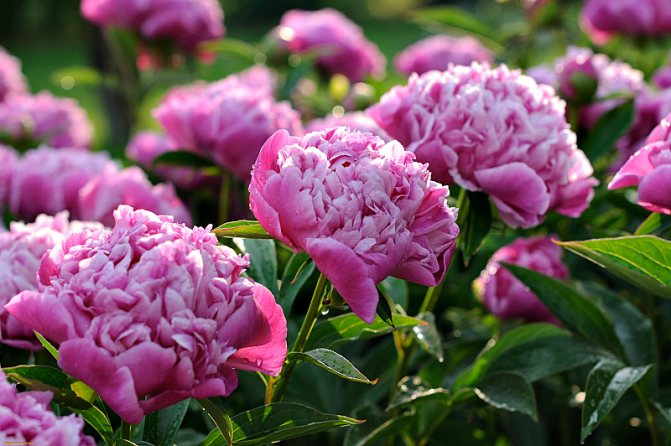
We already talked about how to transplant peonies in the article Peonies in August: we prune, divide, transplant. These luxurious flowers can grow in one place for up to twenty years. But so that the flowering is plentiful, and the flowers themselves do not shrink, they are transplanted every 5-6 years. And this should be done at the end of August and the very beginning of September. So that the peonies have time to settle in a new place and prepare for wintering.
The peculiarity of planting peonies is that they cannot be buried. If the upper bud is more than 1.5 centimeters in the ground, then you will get a bush with abundant luxurious foliage. But you won't get flowers. If the upper bud is left above the soil level, it can freeze out.


Irises
The cultivation of irises was described in the article Irises in the garden: we care properly. Irises require transplanting at least once every three to four years. Otherwise, they grow to form a "bald" center of the bush. Lateral roots go deep into the soil and flower buds do not form on them.


Astilba
This plant is best replanted after flowering. It tolerates transplanting well and easily adapts to a new place. It is only important that at least a month remains from the transplant before frost. By the way, if there is high soil moisture in the shady corners of your garden, feel free to plant astilbe there. She is able to drain stagnant areas.
Phlox
Foam caps of these uncomplicated flowers can beautify any garden. For more information on growing phlox, see the article at the link.
Phlox is transplanted in the second half of September. They easily tolerate the division of the bush and take root well in a new place. Phlox bushes should be transplanted and divided at least every five years. In addition, phloxes need to be hilled every year in the fall.


Hosta
We already talked in detail about the peculiarities of growing hosts in the Host's article - emerald greens and sun glare ...
This queen of the shade does not tolerate transplants and bush division very well. But in one place it can grow and increase decorativeness up to two to three decades. That is why the choice of the landing site should initially be approached with all seriousness.
The host is transplanted no later than the first half of September, so that it has time to grow new roots.
In addition to the listed perennials, daylilies are transplanted in the fall, they are also called the flowers of an intellectual lazy person, dicentru, or a broken heart, adonis. If the division of the bushes and the transplant is carried out in a timely and correct manner, then the perennial flowers will winter well and in the new season they will delight you with a magnificent view.
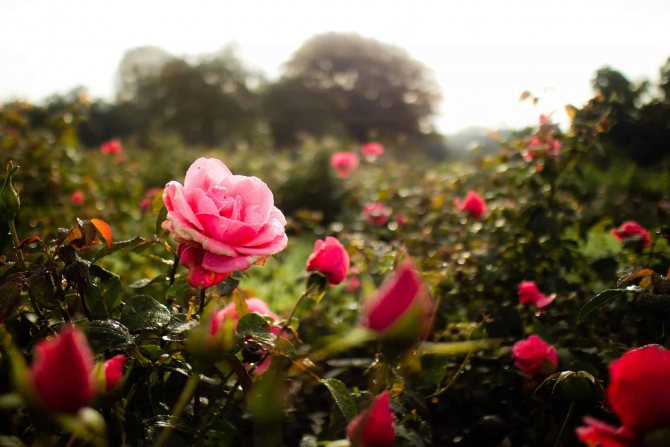
Rose transplant
The easiest way to transplant roses is at the age of 2-3 years. But sometimes it is necessary to move an adult, well-rooted bush. It is difficult to do this, but it is quite possible. We will tell you how to transplant a rose in the fall, correctly and without spending extra effort.
Seat selection
Roses are best planted in an open, well-lit area in the morning. It is then that increased evaporation of moisture by leaves occurs, which reduces the likelihood of fungal diseases affecting the bush. It is good if the plot has a small, no more than 10 degrees slope to the east or west - spring melt water in such a site does not stagnate, and the risk of damping out is minimized.
Before transplanting roses in the fall, study their lighting requirements - many varieties cannot stand the midday sun. Under the scorching rays, they quickly fade, the color fades, the petals (especially dark ones) burn and lose their attractiveness. Such roses are transplanted under the cover of large bushes or trees with an openwork crown, placing them at some distance from them so that the roots do not compete for moisture and nutrients.


Comment! In the northern regions, rose bushes need to be planted in the most lighted areas - the sun gives less ultraviolet radiation there, and it is barely enough for the growing season and flowering.
For a flower, you need to provide protection from the north and north-east wind, and not place it in a deep shade. You can not transplant the bushes to a site where Rosaceae have already grown - cherry, quince, Potentilla, Irga, etc. for 10 years or more.
Almost any soil is suitable for this flower, except for swampy, but slightly acidic loams with a sufficient humus content are preferable.
Comment! If your soil is not very suitable for growing rose bushes, it is easy to improve it by adding the necessary components to the planting hole, and in areas where the groundwater is high, it is easy to arrange drainage.
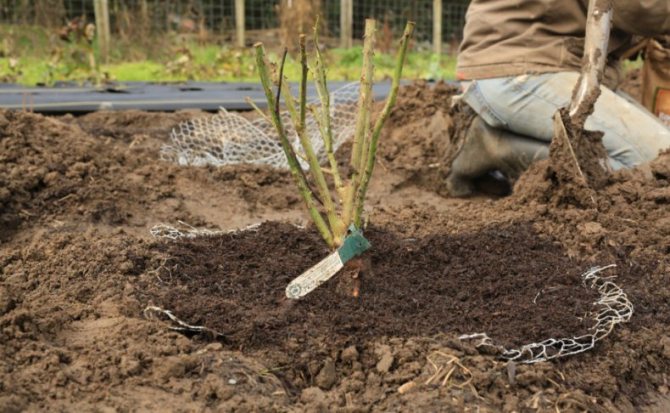
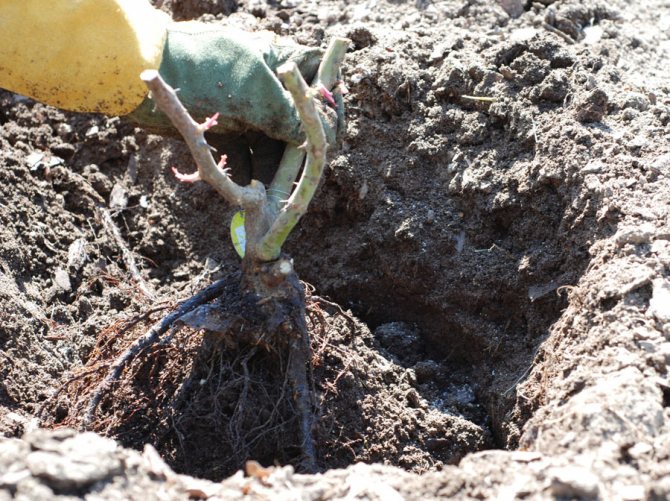
Digging and preparing roses for transplanting
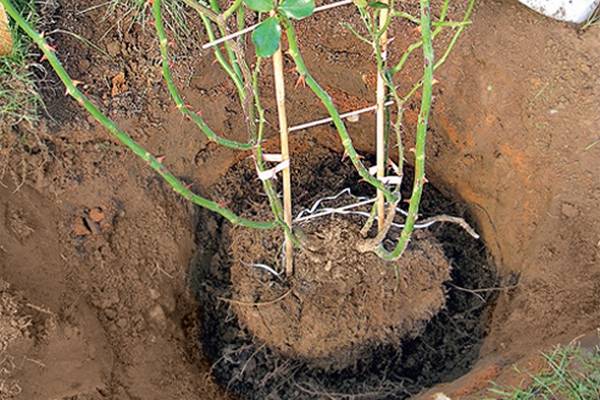


Before replanting roses in the fall, they need to be watered abundantly. After 2-3 days, dig out the bushes, stepping back from the base about 25-30 cm.Young roses will be easy to get out of the ground, but you will have to tinker with the old ones. First, they need to be dug in with a shovel, then loosened with a pitchfork, cut off the overgrown roots, and then transferred to a tarp or into a wheelbarrow.
Attention! Adult rose bushes grafted onto rose hips have powerful taproots that go very deep into the ground. Don't even try to dig them out completely without damaging them.
When transplanting in autumn, the shoots are not touched at all or only slightly shortened, all leaves, dry, weak or unripe twigs are removed. The main pruning of the bush will be done in the spring.
But it happens that a rose has been dug up, and the planting site is not yet ready for it. Is it possible to somehow save the bush?
- If you postpone transplanting for less than 10 days, wrap an earthen ball or bare root with a damp cloth, or better with wet burlap or jute. Place it in a shady, cool place with good air circulation. Check from time to time to see if the fabric is dry.
- If the transplant is postponed for more than 10 days or indefinitely, the roses need to be dug in. To do this, dig a V-shaped moat, lay the bushes there obliquely, sprinkle it with soil and compact it slightly.
Important! If you are replanting roses with an open root system, immediately after digging, remove all broken and diseased roots and place the plant in a container with water, adding any root-forming agent.
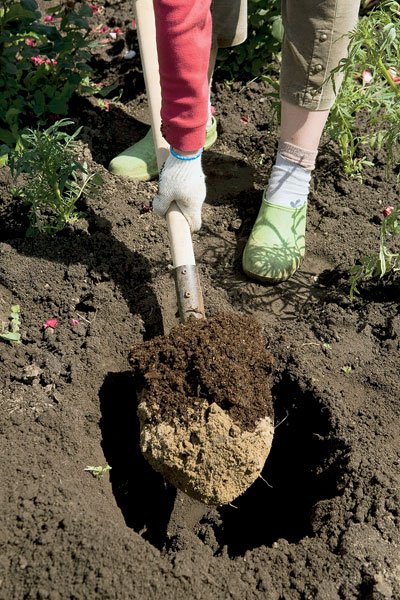
Preparation of planting holes
It is best to prepare holes for the autumn transplantation of rose bushes in the spring. But, frankly, you do this very rarely. Try to prepare the site at least two weeks before transplanting.


If your plot has good black soil or loose fertile soil, dig holes to the planting depth, adding 10-15 cm.On depleted, stony or unsuitable soils for growing roses, a deepening is prepared with a margin of about 30 cm.Prepare the soil for backfilling by mixing in advance:
- fertile garden soil - 2 buckets;
- humus - 1 bucket;
- sand - 1 bucket;
- peat - 1 bucket;
- weathered clay - 0.5-1 bucket;
- bone or dolomite meal - 2 cups;
- ash - 2 glasses;
- superphosphate - 2 handfuls.
If you do not have the opportunity to prepare such a complex composition, you can do the following:
- turf soil - 1 bucket;
- peat - 1 bucket;
- bone meal - 3 handfuls.
Fill the pits completely with water the day before transplanting.


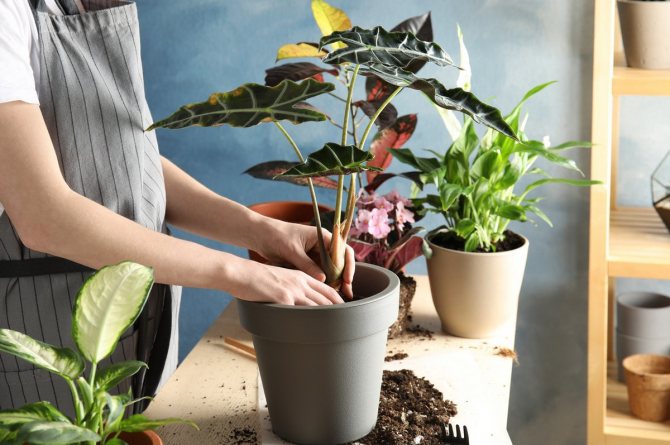
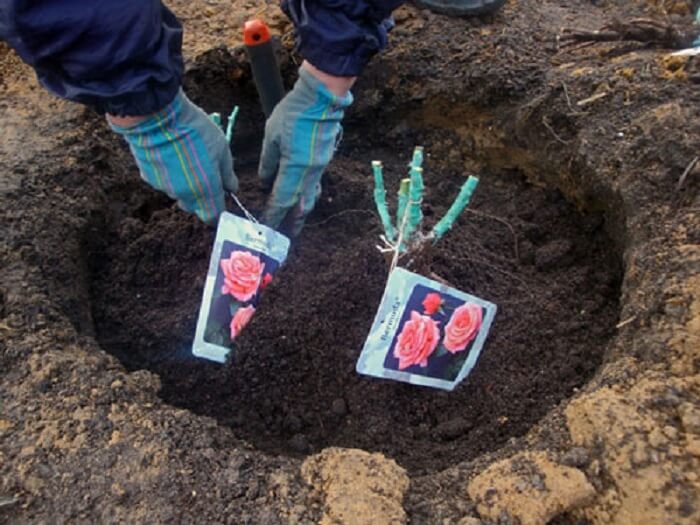
Transplanting rose bushes
A good time to start work outdoors is a warm, calm, cloudy day.
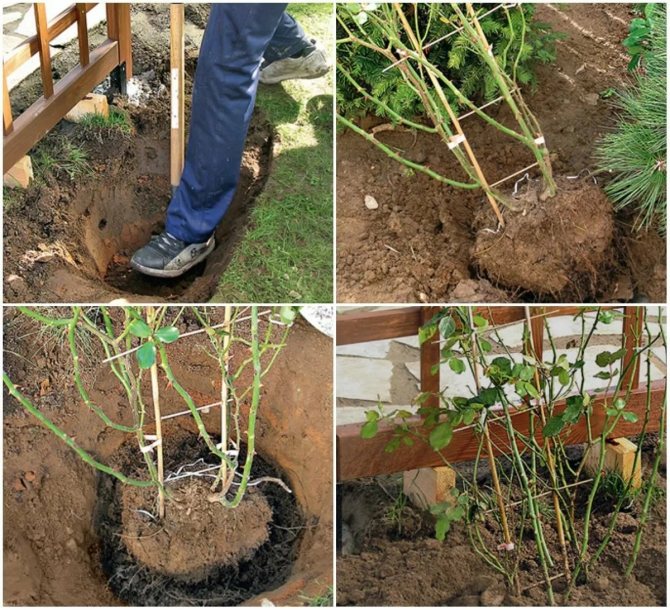
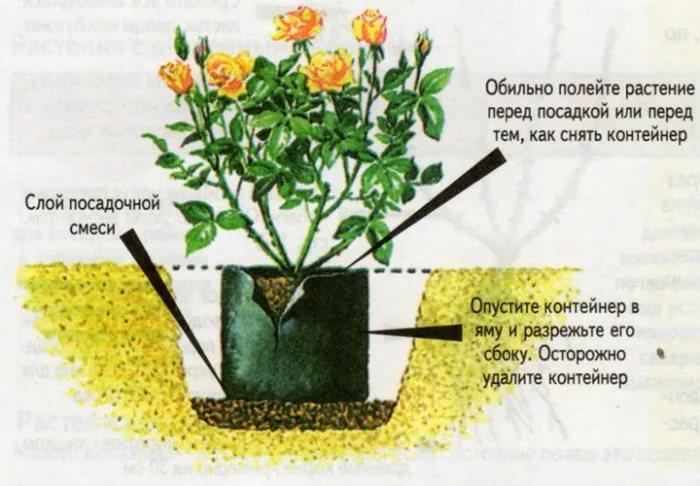
Transplanting roses with an earthen ball


Pour a layer of the prepared mixture at the bottom of the planting pit. Its thickness should be such that the earthen lump is located at the required level. The planting depth is determined by the grafting site - it should be 3-5 cm below the ground level for bush and ground cover roses, and for climbing roses - by 8-10. Own-rooted plants do not deepen.
Fill the voids with the prepared fertile soil up to half, gently apply it and water it well. When the water is absorbed, add soil to the edge of the hole, tamp it lightly and moisten. After a while, repeat watering - the soil under the transplanted rose should be wet to the full depth of the planting pit.
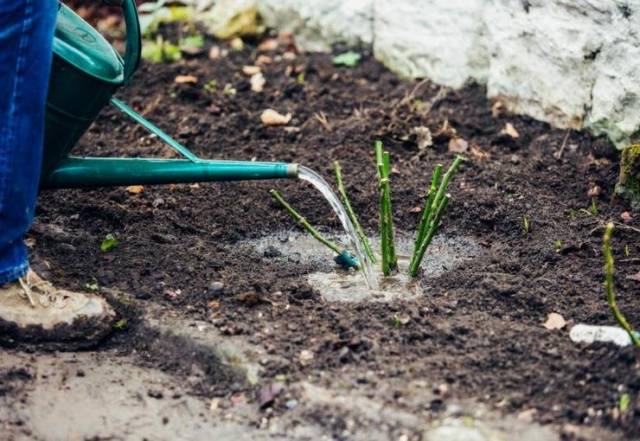


Check the graft site, and if it is deeper than necessary, gently pull the seedling and add soil. Spud the rose to a height of 20-25 cm.
Transplanting bare-root roses
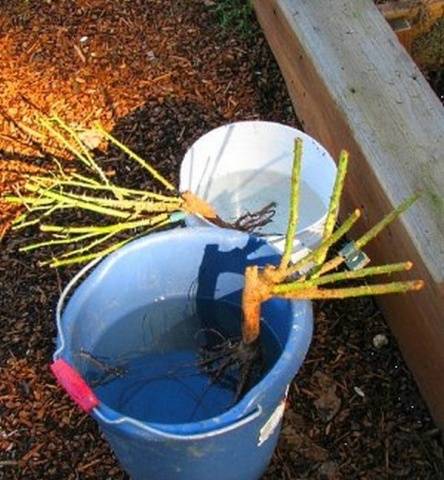


Of course, it is best to replant shrubs with a lump of soil. But, perhaps, friends brought the rose to you, dug up in their garden, or it was bought at the market. We will tell you how to properly transplant a plant with bare roots.
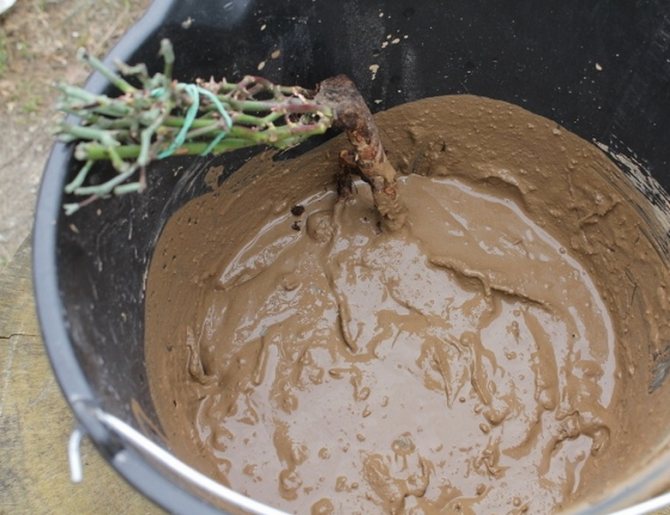
If you are not sure that the rose was dug 2-3 hours ago, be sure to soak it for a day in water with the addition of root-forming preparations. The bottom of the bush should also be covered with water. Then dip the root into a mixture of 2 parts clay and 1 part mullein, diluted to thick sour cream.
Comment! If the rose root, protected with a clay mash, is immediately wrapped tightly with cling film, the bush can wait for planting for several days or even weeks.
Pour the required layer of soil on the bottom of the planting hole, make an earthen mound on it, on which you place the rose. Gently spread the roots around the elevation, not allowing them to bend upwards. Make sure that the planting depth of the bush corresponds to that indicated above.
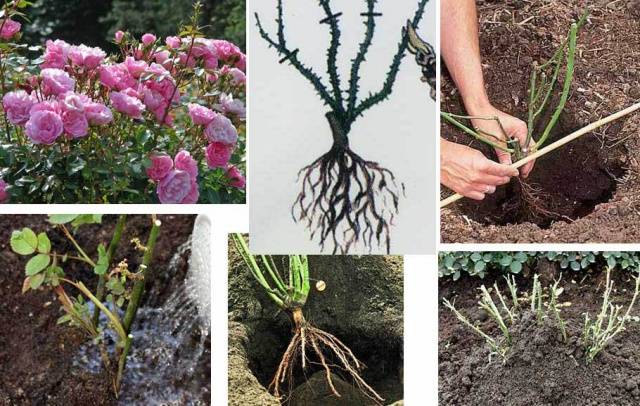


Gradually cover the roots with prepared fertile soil, gently crushing it from time to time. When the rose is planted, tamp the edges of the hole with a shovel handle, and gently press down inside the planting circle with your foot. Water abundantly, check the location of the root collar, add soil and spud the bush by 20-25 cm.
Pit preparation for planting
Usually, a hole for a new bush is prepared three weeks before planting. In size, it is not inferior to the pit from which the rose bush was extracted. The pit is usually 60cm in diameter and 45cm deep.
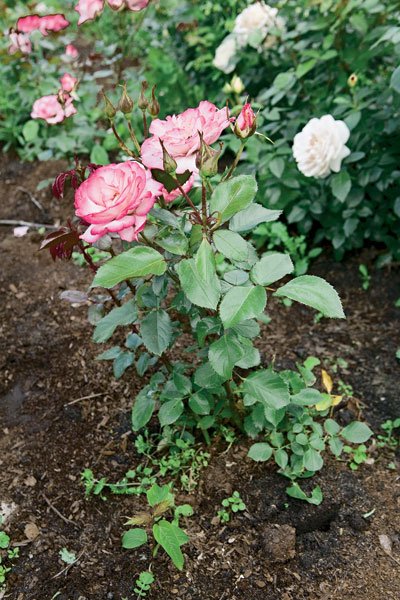


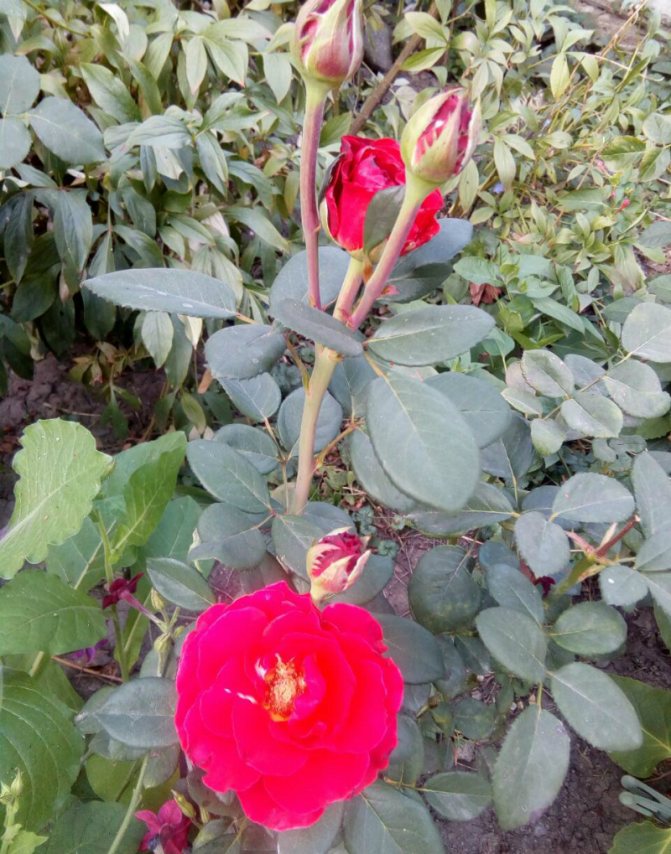
A rose transplanted according to all the rules will give you a wonderful flower that will become a real decoration of your garden
Loosen the bottom and sprinkle the soil with compost. On top, sprinkle with ordinary soil to avoid burns of the roots of the bush. Before direct disembarkation, the pit must be thoroughly shed with water.
Variants of using the vacated space
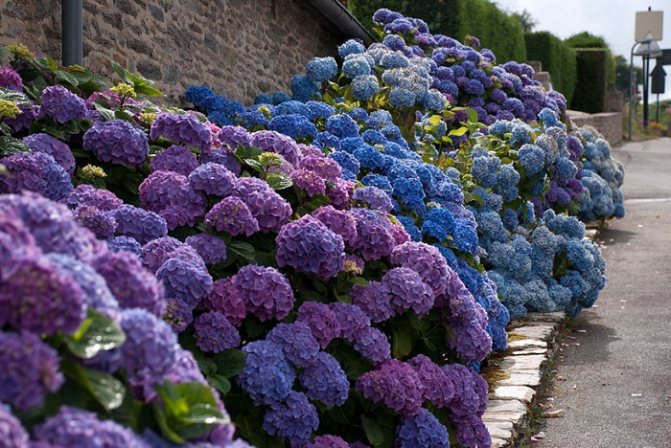


On too acidic soils, destructive to the rose, hydrangea will bloom most luxuriantly, acquiring the blue tint of the inflorescences.
The place where the rose bush used to grow can be used to plant any annual flowers. The hole formed after digging the bush is covered with fresh fertile soil and a small flower bed is formed. The choice of the type of annuals depends on the parameters of the soil and the illumination of the site.
If the rose was transplanted due to the increased acidity of the soil, the vacant space can be occupied by rhododendron (azalea). This is a magnificent ornamental plant - a lover of acidic soils and shady places.
On a low, damp area, after a rose, heather will feel good. However, when planting this melliferous shrub, you need to take into account that it, like a rose, needs a lot of sun.
Landing place
The modern rose has its roots in tropical plants, and therefore loves good light and sunny places. In the shade, roses cannot bloom normally.If the place is shaded and the humidity is high, there is a risk of fungal diseases of the culture.
The place of growth should not suffer from an excess of moisture, the level of groundwater should not be close to the surface. If necessary, drainage is done in the planting pit. Soil requirements are not critical - you can always fill the planting pit with a substrate of the desired composition.
Soil for roses should have a slightly acidic reaction (5.5-6.5 pH), therefore, when using peat, it is imperative to add deoxidizers (lime, chalk, dolomite flour).
Important: already in August it is necessary to exclude nitrogen from the list of fertilizers. It causes the growth of green mass, including shoots, which, not having time to form, will die in the winter cold, which can lead to the death of the entire plant.
At the same time, feeding with potash fertilizers is a good preparation for winter.


Instructions on how to transplant a large or old rose
How to transplant adult roses - in principle, this is already clear, based on the previous description of the spring plant transplant. You can transplant an old rose in the usual way: a pit is prepared, lined with drainage, filled with good soil and left to settle for two to three weeks.
Further, the bush is dug out according to the projection of the crown, and all activities are carried out in the same way. A small crowbar is a good help in the case of a very old bush with an extensive root system. It can be used as a lever by pulling out the rose by placing the tool under the base of the plant.
When to replant roses: in autumn or spring
Each of the flower growers at heart considers himself a landscape designer, and the concept of a flower garden can change almost every year.
How to make your dreams come true without harming your blooming pets and at the same time not limiting the flight of your imagination? Let's talk about transplanting adult roses, they are the ones who most often suffer when changing a design project.


Replacing a dead bush with a new one
Usually, an empty space is not ignored, and a new adult is planted where the old bush grew. Of course, it is advisable to select the same variety of roses that grows around or grew in this place. Flowers should match in color, and bushes in size. If you plant a bush capable of strong growth among smaller and much more modest fellows, then most likely it will simply overshadow and suppress them with its size.


The size of the hole for a new bush (when replacing an old bush with a new one) should not differ from the one from which the old bush was removed
Replacement of bushes is done in spring in April or in autumn in October. In this case, we are considering a spring transplant. Be that as it may, the land in the place where the old bush grew must be completely replaced at a depth of 50 cm and within a radius of 30 cm.
So that neighboring bushes do not interfere with high-quality work, it is recommended to pre-cut them.
For better survival of the bush in the first year, you need to remove all nascent buds from it.
Indications for transplantation
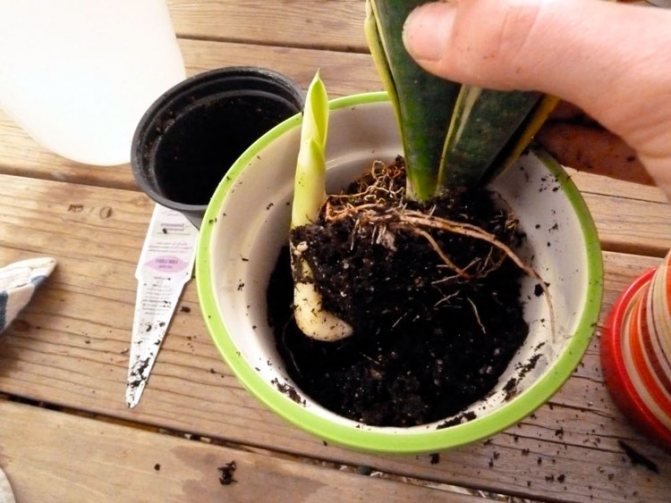
- The earth ball dries up very quickly. This is a signal that the root system has grown, there is not enough water for it, which is placed in the pot.
- The plant looks sick, withers, although the soil is moist. A possible reason for this is overflow and the appearance of root rot. The measure of control is the transplantation and healing of roots.
- The flower is healthy in appearance, but grows poorly. The soil is compacted, it does not allow oxygen to pass through well. Replacement of soil is required.
- The pet's crown has grown, it has become unstable - change the container to a larger one.


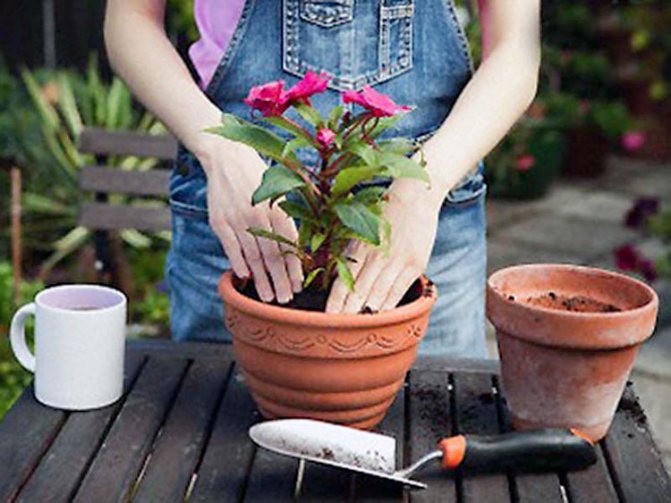
Disembarkation rules
For the rose garden to grow well and bloom profusely, the place chosen for planting flowers is of great importance. These are light-loving and heat-loving plants, they need a sunny place without drafts, as protected from the wind as possible.With a lack of heat, the accumulation of nutrients necessary for the normal development of the plant slows down.


Planting a rose
Roses are not planted in excessively moist soils. Long stay of roots in water leads to their decay and death. Also, wet soils are cooled more, so the plant can freeze out.
The thickened plantings make it difficult to care, the bushes of densely planted roses are poorly ventilated and illuminated. This leads to disease and pest attacks, poor growth and flowering. The planting density is determined depending on the size of the mature shrub. Low-growing roses are planted at a distance of 35 cm, tall roses at a distance of 50 cm or more.
Spring planting of seedlings in open ground is carried out in late April - early May, when the soil warms up to + 10-12 ° C. Also, an autumn planting is carried out, in rare cases - a summer planting.
Note! A pit for planting is prepared in advance, of such a size that the roots in it are located freely. Fertilized with organic and mineral dressings for the favorable formation and development of the root system.
Cut off the top by 15 cm. Cutting off the vegetative part of the seedling reduces evaporation and allows the plant to take root better. The roots are cut, dry areas are removed, leaving a rhizome 30 cm long. Then the roots are immersed in water for several hours so that they are saturated with moisture.