Origin story
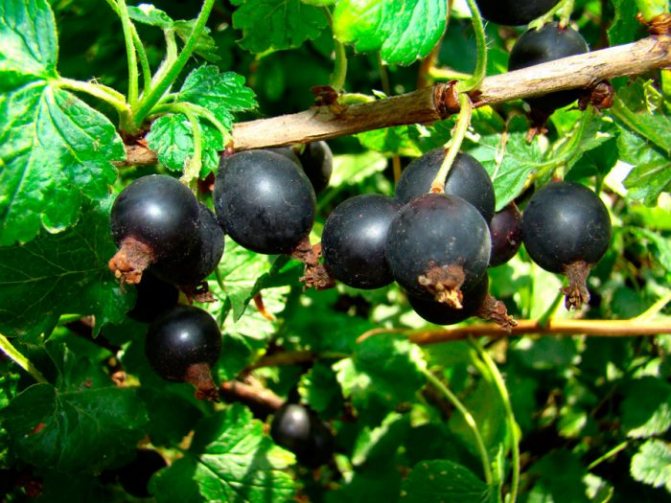

Yoshta (esta) is a cultivated fruit and berry plant. Derived as a result of hybridization of common gooseberry and black currant. For the first time, the shrub was bred by the German breeder Rudolf Bauer; as a garden plant, the hybrid has been grown since 1989.
The name of the culture is derived from the first syllables of the German words Johannisbeere and Stachelbeere, which translates as currants and gooseberries, respectively. In Russia, yoshta is not very popular, but it is widespread in European countries.
Possible contraindications and harm to yoshta
There are not many of them, but they are:
- If gooseberries or black currants cause an allergic reaction in a person, then this is a sure sign that he should not use yoshta in any case.
- Those who have a tendency to form blood clots should also be very careful about this berry.
- Individual intolerance to ascorbic acid signals that yoshta is not your product.
- In the presence of colitis, peptic ulcer, gastritis and other disorders in the digestive tract, it is not recommended to eat yoshta, since the use of berries can only aggravate the situation.
Important! Women in an "interesting position" should be wary of taking yoshta. It is best to consult your doctor regarding the use of these berries.
- Measure is needed in everything. This "golden rule" applies to any situation. Remember, excessive consumption of yoshta berries can cause an allergic reaction.
Similar publications:
Description and features
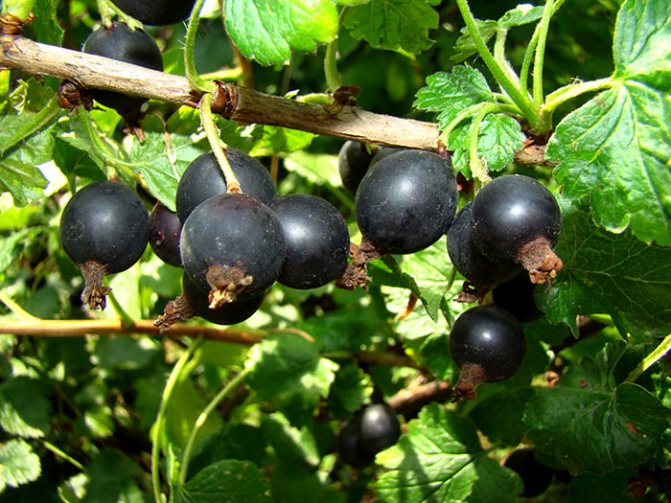
Outwardly, yoshta is represented by a powerful and spreading shrub. Shoots can grow up to 1.5 m. The root system is developed, it goes into the ground by 40-50 cm. Unlike gooseberries, it does not have thorns on the branches, which simplifies plant care. The crown grows up to 2 m in diameter.
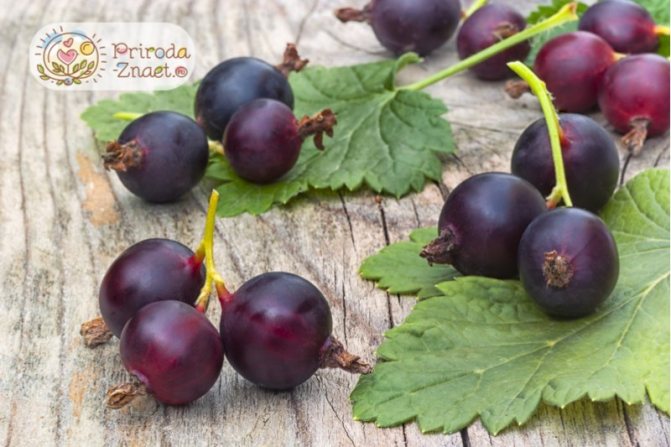
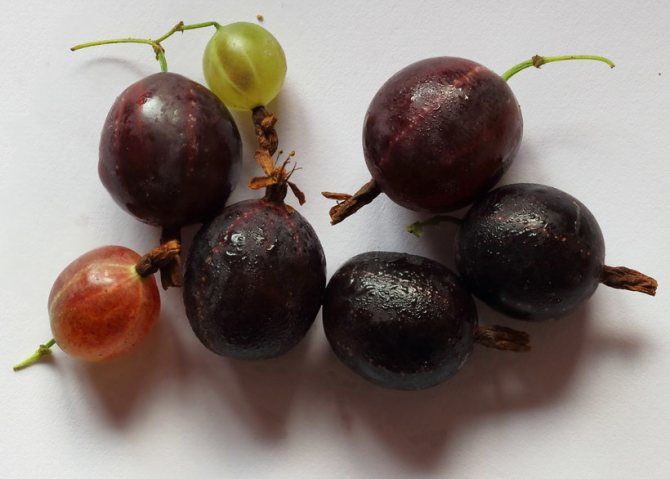
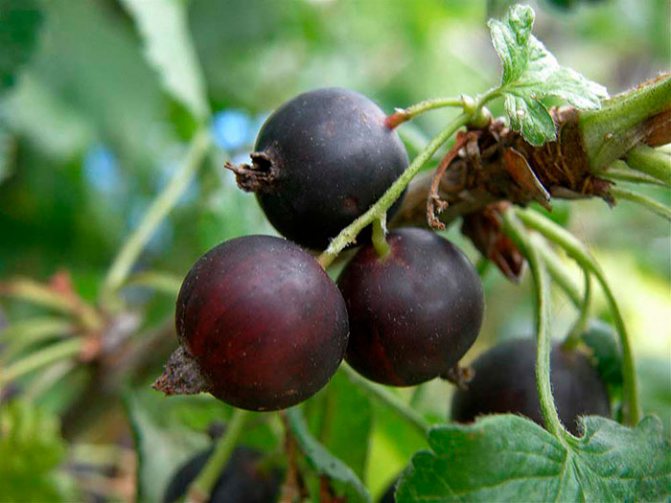
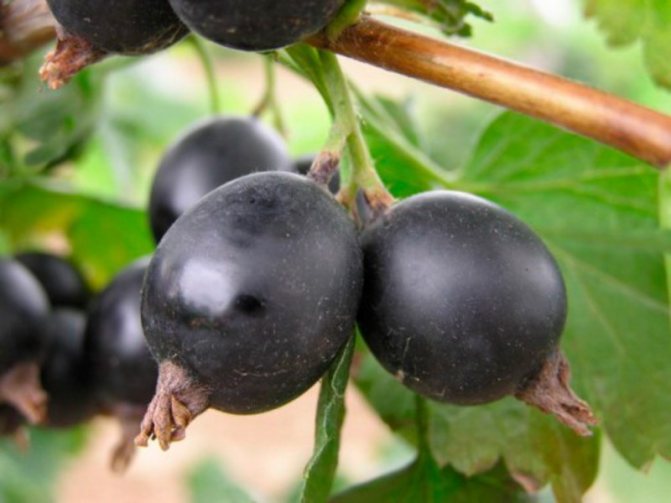
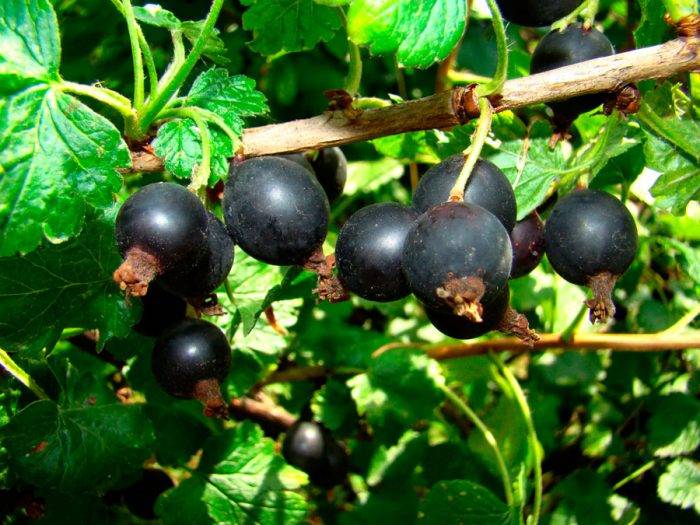
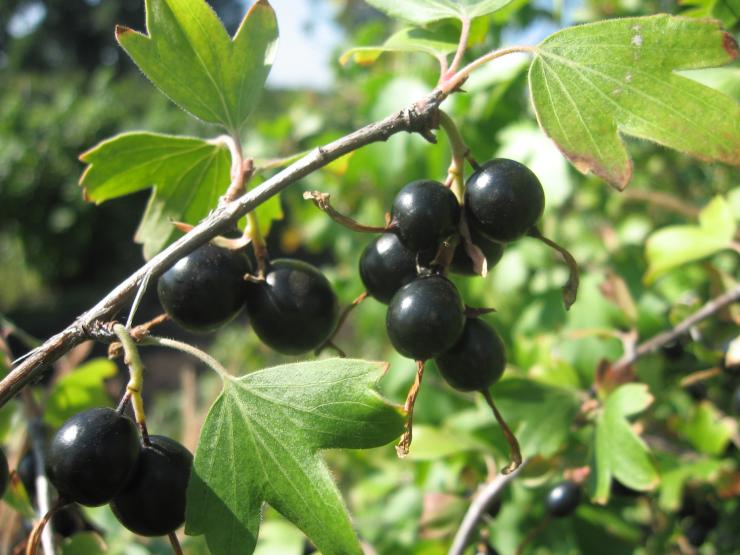
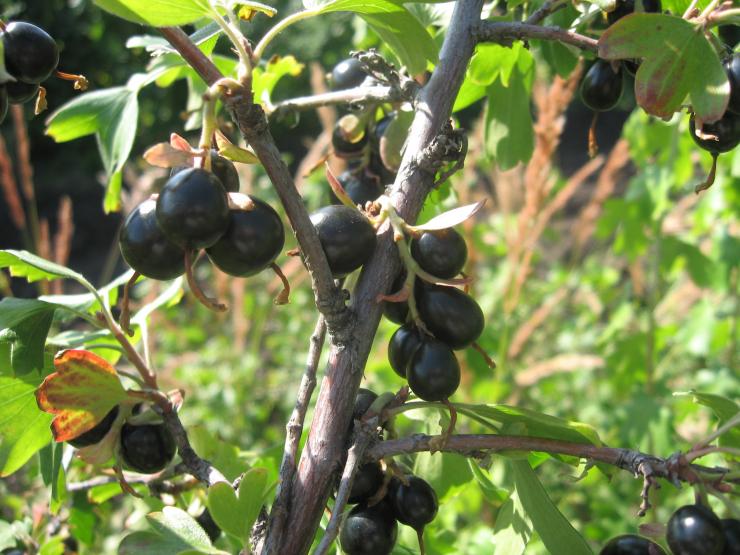
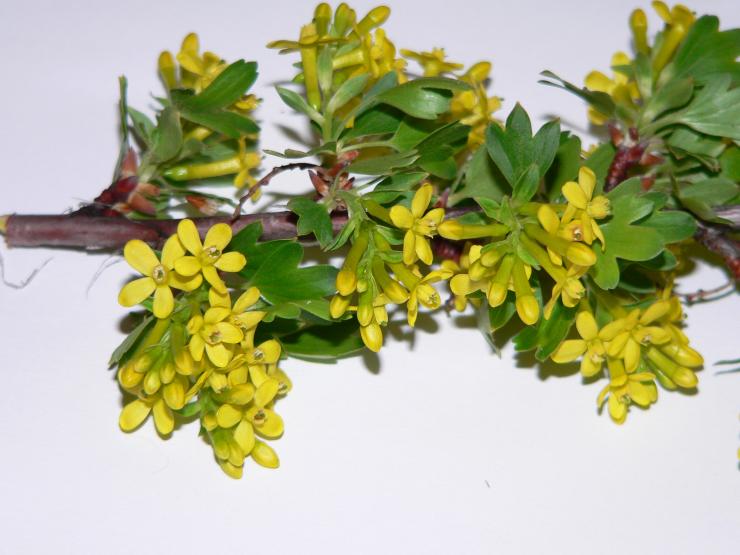
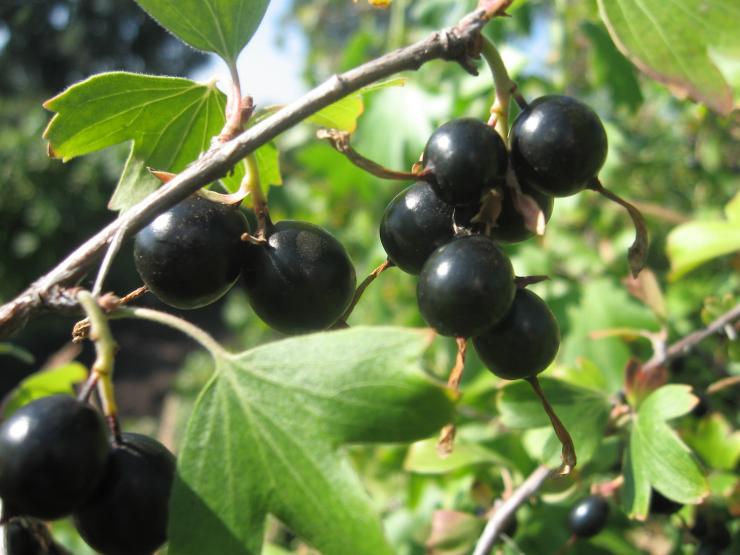
Leaves are dark green. They remain on the bush until late autumn. The flowers are large, after which the berries are formed. They have a sweet and sour taste, and the skin is purple in color. Berries are collected in a bunch of 3-5 pieces. Fruiting is possible from 2 years of growth.
Yoshta has resistance to frost, strong immunity to pests and diseases. It can grow in one place for more than 20 years without the need for a transplant.
The yield, as well as the health of the shrub, directly depends on quality care and adherence to agricultural cultivation techniques.
Yield


With proper care from one bush, you can collect from 5 to 10 kg of fresh berries in one season. The fruits do not fall off the stalks, they sit firmly on the bush. After harvesting, they retain their taste and presentation for a long time.
Suitable for the preparation of various blanks, used fresh. Storage is possible as part of preserves, juices or frozen.
Harvesting and transportation
The first fruits of yoshta begin to ripen in the second decade of July, while the ripening of berries is uneven - for 2-3 weeks. With a shortage of time, you can wait for all the fruits to ripen and collect them at the same time, since they do not fall off the bushes. Harvesting is carried out in warm dry weather, in the morning or in the evening. The plucked berries are placed in a small wooden or plastic container.
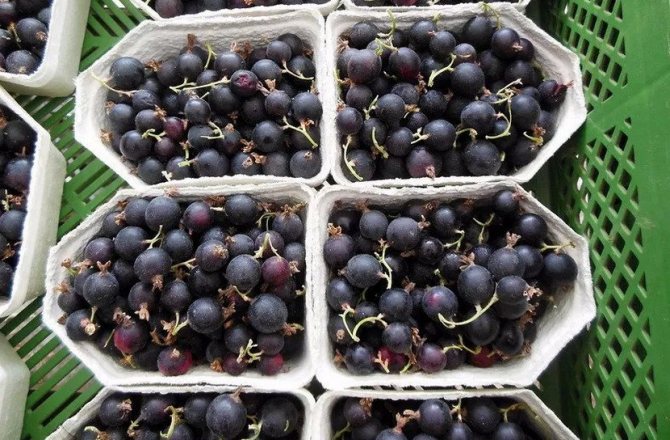


The fruits of the hybrid are characterized by the presence of a dense peel not prone to cracking, due to which they have excellent keeping quality and can be transported over long distances without losing their presentation.
Yoshta is great for fresh consumption, as well as for cooking canned food, compotes, jams and preserves. For long-term storage, the fruits are frozen. Subject to the optimal temperature regime, which is –16 ° C, the shelf life of berries can reach one year.
Find out when to plant gooseberries and currants, planting scheme, rules of care.
Every year yoshta more and more wins the hearts of domestic gardeners. The culture fell in love for its unpretentious care, ease of cultivation, strong immunity, great taste of berries and their excellent keeping quality. Today, more and more farmers are thinking about growing the plant commercially - on an industrial scale.
Suitable region and climate for growing
The plant actively grows and bears fruit in temperate climates. Gardeners practice planting in cold areas, but the quality and quantity of the crop is reduced. Against the background of a short summer, the berries are formed small, have a sour taste.
Yoshtu is recommended for planting in central Russia, in the Central and Northwest regions. For abundant fruiting, a long daylight hours are required, as well as a stable temperature in the range of 15 to 25 ° C throughout the growing season.
Benefits of consuming yoshta
Beneficial features:
- The use of yoshta during epidemics of infectious and colds (as a rule, this occurs in autumn and early spring) will save you from such ailments due to the fact that there is a significant increase in the protective properties of the body.
- The presence of iron in yoshta makes it extremely beneficial for those who suffer from anemia. The hemoglobin level can be significantly increased by eating berries. But, at the same time, do not forget that this must be done in conjunction with other means that help with anemia.


- Yoshta is a fairly effective product that has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antifungal effects due to the presence of phytoncides in the berry.
- Those who have been diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease can eat similar berries along with other medications. The presence of pectins in the product helps to normalize gastric motility and improve intestinal microflora.
- Yoshta helps to eliminate harmful substances such as lead, mercury, strontium and radionuclides from the body. Also, berries stimulate the excretory system to get rid of toxins. That is why yoshta is called the "orderly" of the body.
- Berries normalize the activity of the digestive tract and central nervous system.
- They have a beneficial effect in the case of any indigestion such as diarrhea or constipation.
- Yoshta is used in dietetics, since the product contains a small amount of sugar, and the berries are low in calories. In addition, anthocyanins contribute to the acceleration of metabolic processes: as a result, there is a rapid breakdown of fats (that is, their burning). Therefore, the berries are shown to people suffering from obesity or who want to lose weight.


On a note! Nutritionists advise to consume 550-650 g of fresh berries every day to bring your weight back to normal. The course of admission is one month. In this case, it is necessary to abandon high-calorie foods.
- Berries improve the blood circulation process.
- Normalize the functioning of the heart muscle.
- They help to lower blood pressure (it is better to use berries in combination with honey).
- Strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
On a note! Saturating the body with minerals and vitamins, yoshta has a general strengthening effect on the human body.Therefore, in order to cure this or that pathology, it will not be enough to use only berries only: treatment in a complex is necessary. [/ Su_note]


Hybrid varieties


Yoshta is a spreading berry shrub covered with dark green leaves in the shape of a gooseberry. After the discovery of the hybrid, breeders began to cultivate the plant and develop new varieties that would be adapted to the climate of a particular region.
So such varieties became known as:
EMB
This is a fairly well-known variety of Yoshta, which was bred in England.
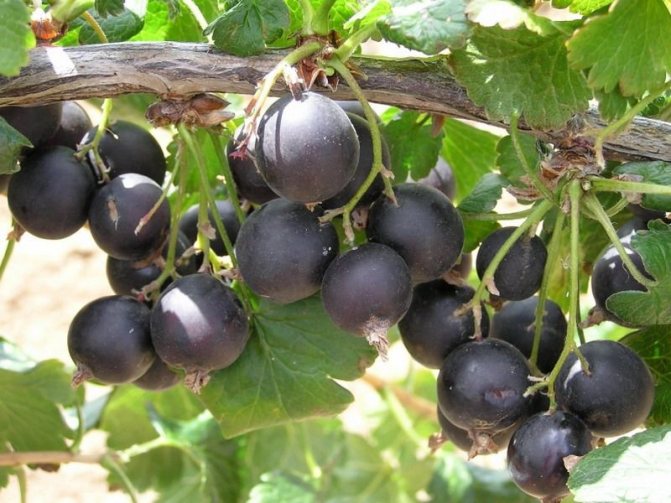


The features of this shrub include:
- It reaches a height of up to 1.6 m, and the crown diameter can be 2 m.
- The branches are strong and durable, do not require a garter.
- The leaves and berries are large in size, the average weight of a berry is 5 g, sometimes they grow up to 12 g.
- The yield is high - 5-10 kg per bush.
The EMB variety blooms in early April. At a temperature of +1 and below, the branches should be covered so that the color does not fall. Among the disadvantages of the variety is the sour taste of berries.
Chrome
The Swiss variety Kroma has thick branches up to 2 cm in diameter, like a tree.
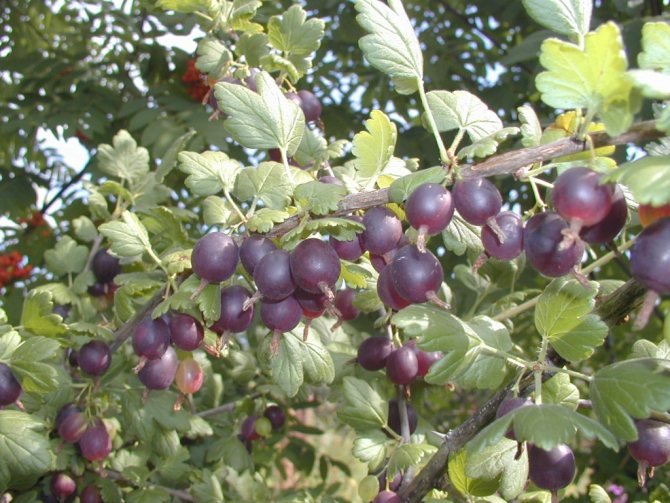


Features:
- The bush is small, has straight dense shoots.
- Berries can reach a weight of 6-7 g, outwardly they look more like currants.
- The yield is small - 3-5 kg per bush, provided there is a sufficient level of moisture.
- The plant is quite resistant to extreme conditions and pests.
Rext
Many gardeners use a variety called Rext as a decoration for the garden, as it has a beautiful appearance. But the shrub attracts not only with its decorative effect, but also with its high yield.
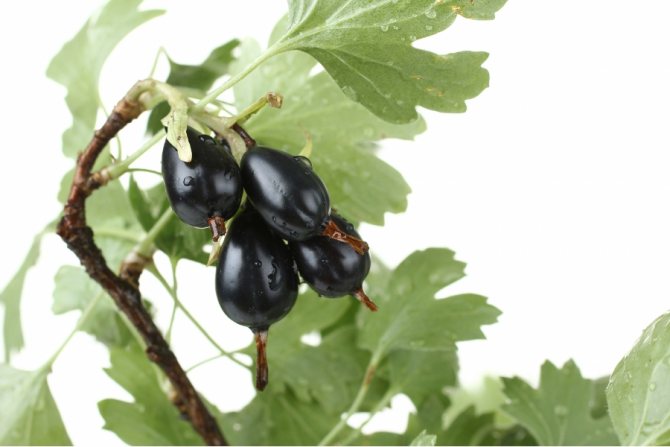


The hybrid features are as follows:
- It reaches a height of 1.2 m, a spreading bush.
- The berries are amber in color and covered with a gooseberry pattern. The fruits are very tasty, the average size is 5-9 g.
- Productivity - 5-10 kg per bush.
- The plant is recommended to be planted in shady corners of the garden, as the leaves burn in the sun.
Yochilina
It is a high-yielding variety that is gaining more and more popularity in our country.
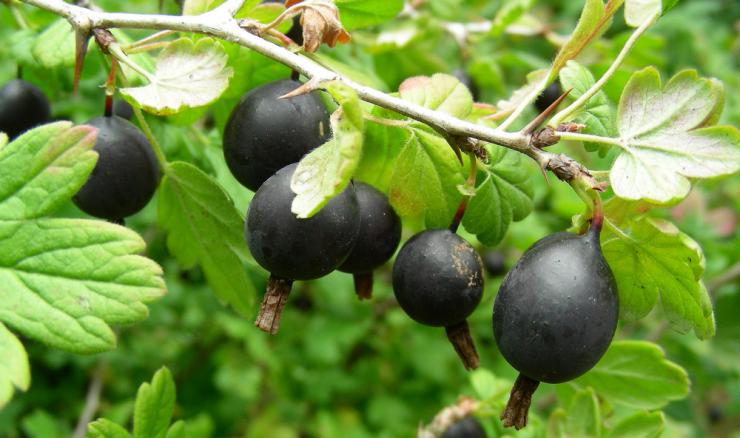
Photo of berries:
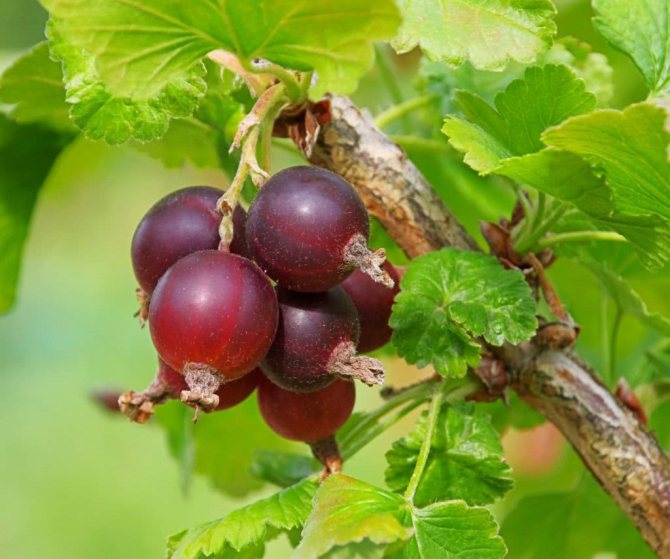


The characteristics include:
- The bush is of medium size, it can reach a height of up to 1.5 m. It grows in dense and spreading shoots, which must be thinned out so that the fruits are not small.
- The berries are large, weighing 5-12 g
- The yield is good, on average, you can collect 5-8 kg of berries from a bush.
On average, a crossed shrub lives up to 30 years. For good pollination, experts recommend planting it next to gooseberries and black currants. Unlike its "parents", Yoshta is immune to numerous diseases and pests.
Landing


Yoshta is planted in open ground with already grown cuttings or seedlings. The plant quickly takes root in a new place, takes root and adapts to the climate. To maintain the health of the shrub, as well as to achieve early fruiting, it is important to properly plant.
When to plant?
It is recommended to plant yoshta in early spring before the start of sap flow. It is recommended to wait until the end of frost, the air and soil should warm up to a stable temperature in the range of 8 to 12 ° C.
In the southern regions, the plant can be planted from the first decade of April, in the northern regions, you should wait until the beginning of May.
Planting is also permissible in the fall, which allows you to achieve early vegetation for the next season. The procedure is carried out before the onset of return frosts. The optimal time is the second half of September - early October. With this method, you should lay a thick layer of mulch and cover the shrub from the cold.
Seat selection
Yoshta prefers well-lit places, but can also bear fruit in darkened conditions. For planting, it is recommended to choose a site both on a hill and in a lowland, the shrub does not suffer from the effects of the wind.
The soil must be fertile and breathable with a neutral acid reaction. Yoshta grows best on sandy loam, chernozem and loamy types of soils. Good drainage is required during the first year of growth.
Some gardeners believe that abundant fruiting requires the presence of a number of currant or gooseberry bushes, but in practice this arrangement is not essential.
Soil preparation
The shrub is unpretentious to the quality composition of the soil. 2-3 weeks before planting, the site must be dug at least to a depth of 1 shovel bayonet. Remove all weeds, plant residues and large stones.
As a fertilizer, it is recommended to use organic matter, for example, humus or mullein at the rate of 7 kg / m2. On depleted soils, it is desirable to use mineral compositions. A mixture of superphosphate, ammonium nitrate and potassium sulfate at 30 g / m2 is best suited.
The right choice of seedlings
The material should be purchased only in a nursery or specialized stores; it is not recommended to purchase seedlings from private individuals. When choosing, you need to carefully examine the root system.
She must be developed, healthy and powerful. The color of the bark of a healthy seedling is dark green without any spots and pigments. Leaves and shoots should be checked, in a healthy plant they have a uniform color, there should be no mechanical damage, dryness and signs of disease.
For autumn planting, it is recommended to cut off all leaves, leaving only shoots and buds.
How to plant?
Before planting, the seedling should be soaked for 24 hours in water or growth stimulant solution to speed up rooting. Dig up the site again, level the surface and pour plenty of water.
Step by step algorithm:
- Dig a hole 50x50 cm in size. The interval between plants is 150-200 cm. When growing yoshta as a hedge, the distance is reduced to 40-50 cm.
- Lay a drainage layer up to 10 cm thick at the bottom, as well as 200-250 g of wood ash. Fill a third of the volume of the hole with fertile soil - a mixture of humus, peat, garden soil and sand. Loosen the soil.
- Place the seedling exactly in the center of the hole, spread the roots and distribute them evenly over the surface.
- Cover with a nutritious substrate, while shaking the seedling. Tamp the area of the trunk circle and water the shrub abundantly.
1-2 hours after planting, the soil should be mulched with a thick layer of peat, sawdust or grass. Cut off the seedling, leaving the healthiest shoots, each of which should have at least 3 growth buds.
What is included in Yoshta
- Fats (100 g of the product contains 0.2 g).
- Proteins (0.7 g).
- Carbohydrates (91 g).
- Sugar. Its amount is only 7%. This is very small.
- Pectins (i.e., polysaccharides). These substances significantly improve the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and heart muscle; help to reduce the level of bad cholesterol; accelerate the metabolic process; sorb and remove toxins, anabolic steroids and other unhealthy compounds from the body; and also normalize blood circulation.
- Phytoncides (or biologically active substances), which are sometimes called a natural antibiotic. They not only kill the simplest bacteria, fungi and viruses, but also inhibit their growth.


- Organic acids (that is, carboxylic compounds formed as a result of an exchange reaction and exhibiting their acidic properties). Alkalinizing the body, they stimulate the process of secretion of gastric juice, promote the active work of intestinal peristalsis and slow down the growth of harmful bacteria; and also prevents fermentation in the large intestine and normalizes stool. That is, the main task of organic compounds is to maintain the acid-base balance in the body.
- Anthocyanins (a group of water-soluble pigments).Because of their presence, vegetables and fruits have such vibrant colors. Anthocyanins increase the elasticity of blood vessels, activate metabolic processes at the cellular level; prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels; help to reduce capillary permeability and lower blood pressure; suppress the development of malignant tumors and strengthen the retina.
- Iron. It is with the help of this microelement that oxygen is transported to tissues and organs. Also, iron is directly involved in the formation of nerve impulses and in the process of conducting them along the nerve fibers; improves the functioning of the immune system, brain and thyroid gland.
- Copper. It participates in the process of collagen production, on which the elasticity of the skin depends to one degree or another; normalizes the activity of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract; and also enhances immunity. The presence of this element in the human body helps to strengthen bones.
- Vitamins C and P. Ascorbic acid increases immunity, improves the functioning of the central nervous system and endocrine glands, and also participates in processes such as metabolic and hematopoiesis. Without it, the growth and development of collagen fibers and connective tissue is impossible. In combination with ascorbic acid, vitamin P reduces the permeability of capillary vessels, prevents the formation of blood clots, and also reduces arterial and intraocular pressure.


- Potassium. Affects the activity of the heart muscle, regulates the water-salt balance in the body, is responsible for the transport of amino acids and sugar to the cells, has a beneficial effect on gastric motility, supplies oxygen to the brain and, as a result, improves mental activity and memory; and also supports the excretory function of the kidneys.
- Iodine. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, brain and central nervous system; increasing the level of immunity; destruction of damaged cells and foreign microorganisms; growth and development of children; the formation of bone and cartilage tissue, proper metabolism, increasing stress resistance, maintaining water-salt balance, accelerating the breakdown of fats, carbohydrates and proteins; as well as improving the condition of hair, skin and nails.
Important! Yoshta berries are best stored in a cool place (such as the refrigerator) or used right away. Otherwise, the fruits may lose most of all that useful that was listed above. By the way, there are ways that allow you to preserve the beneficial properties of yoshta - drying or quick freezing.
Care after landing
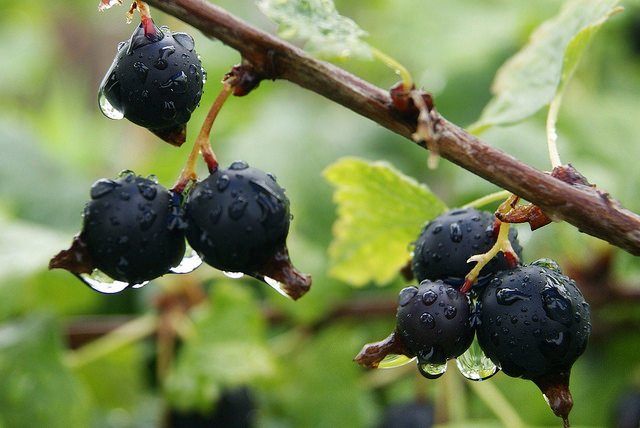


Yoshta is considered an unpretentious culture. Can bear fruit even with minimal maintenance. It is especially important to carry out all the necessary procedures in the first year, when the plant adapts, the active growth of the root system and the main stem takes place.
To maintain health and early flowering, you should monitor the moisture content of the soil, systematically carry out top dressing and work with the soil.
Mulching
After 2-3 months from the moment of planting, the soil next to the shrub must be loosened to a depth of 4 to 6 cm, then this procedure is repeated during the entire first year of growth every 20 days.
The layer of mulch should also be maintained, which will reduce the number of weeds, as well as retain moisture and heat on the surface layer of the soil. The optimum thickness of mulching is 5-10 cm. Sawdust, wood chips or peat are suitable as material.
Watering
Moderate watering is required throughout the summer. Prolonged drying and waterlogging of the soil should not be allowed, which can lead to the development of diseases, a decrease in yield.
Watering is carried out in the morning or evening, the optimal regime is 1 time in 10 days. 1 m2 requires 10-15 liters of water. It is recommended to deepen a small groove around the perimeter of the trunk circle to avoid stagnant water and soil erosion at the root of the shrub.
After the end of fruiting and until the beginning of the growing season for the next season, watering is reduced to a minimum.
Top dressing
If you added fertilizer during planting, then no additional fertilization is required in the first year.
Starting from the second year of growth, they are applied three times per season:
- before the beginning of budding in spring, the bush is watered with an aqueous solution of mullein or bird droppings at a concentration of 1:10;
- during the flowering period, it is recommended to add potassium sulfate and superphosphate, 30 g of each agent;
- during active fruiting, you can use a combination of organic matter or complex mineral fertilizing for fruit and berry bushes.
In autumn and spring, it is desirable to additionally treat the root area with wood ash at the rate of 200-300 g per plant. This not only provides the shrub with potassium and nitrogen, but also reduces the risk of contracting diseases.
Reproduction of yoshta shrubs by cuttings
The technology of reproduction of yoshta by cuttings has been worked out by many gardeners and is successfully applied. In June, a 10-15-centimeter green shoot is selected, broken off with a "heel" and dipped into boiled cooled water to restore turgor for about 1 hour. Then two or three lower sheets are removed, the next 3-4 sheets are removed by half. The lower part of the green cutting is treated with root powder and planted in a loose substrate under a film or in a plastic bottle. The planted cuttings are placed in diffused, but bright light, overheating is not allowed. Artificial fog conditions are created until the cutting begins to unfold new leaves. It follows from this that the root formation process was successful. Then the shelter is removed, gradually getting used to the environmental conditions and growing until the moment of digging for autumn planting is carried out.
Lignified cuttings are harvested in the fall. Planting is carried out in well-cultivated loose soil, free of weeds. Cuttings are cut from long shoots, cutting out of them two or three at least 20 cm long. Autumn-type fertilizers with a high content of phosphorus and potassium are applied for planting. The lower part of the planted cutting is dipped in a clay mash with root-formers. The stalk is planted obliquely at an angle of at least 45 °, the upper bud is left above the ground. The plantings are watered abundantly, with the onset of cold weather they spud and mulch with compost. Spring care is similar to that of blackcurrant cuttings. The main task of the gardener is to provide optimal moisture and nutrition for successful rooting.
How to reproduce?
Like other garden shrubs, Yoshta responds well to vegetative propagation. This allows you to increase the planting size and renew the plant without losing the varietal qualities of the crop.
The procedure can be carried out in the fall or spring, depending on the method used. The choice of propagation method depends on the gardening skills, the age of the plant and the characteristics of its growth.
Dividing the bush


Usually, the procedure is combined with a planned transplant of an old bush as needed. The work can be carried out both in autumn and in spring before the start of active vegetation.
To do this, cut off all the old and deformed parts of the plant, leaving no more than 2/3 of the shrub. Carefully dig out the yoshta, and then divide it into 2-3 parts with a sharp instrument. After that, the cut area should be treated with crushed coal or wood ash, and immediately planted in a new place.
Cuttings
Depending on the age of the yoshta and the duration of the procedure, two types of propagation by cuttings are used:
- Lignified... The procedure is recommended to be carried out in the second half of September. As a planting material, choose healthy and strong shoots from a bush for 2-3 years of dew. The minimum length of the cutting is 15 cm; it must have at least 5 growth buds.Rooting is carried out directly in the ground, after preparing the seedlings and processing the cut points, they are planted in a permanent place at an acute angle. After that, the soil is watered abundantly and a thick layer of mulch is laid;
- Green cuttings... This breeding method can be applied throughout the summer. Planting material - apical shoots with a length of 10 cm. The lower leaves should be removed from them, leaving only the buds of growth. On the lower part of the bark, you need to make 2-3 thin cuts and place the cutting for 12 hours in a growth stimulator (Epin, Kornevin). After that, they are planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse at an acute angle. Rooting takes up to 4 weeks, after which you can replant the seedlings to a permanent place.
The choice of grafting method directly depends on the duration of the procedure. The planting material quickly forms roots, after which it can be planted in the prepared area.
Layers
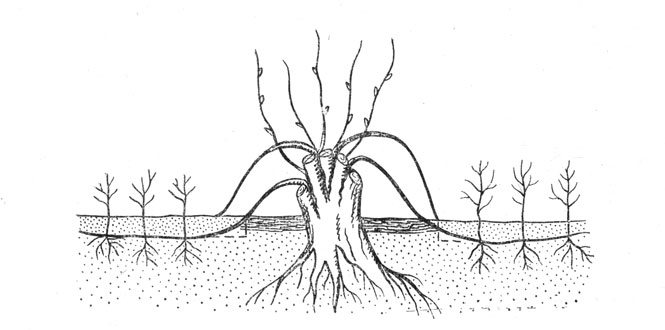

In practice, it is used less often, since the procedure is long and laborious. Reproduction by layering is carried out in early spring, when the soil and air warm up to a stable warm temperature.
Work technology:
- On an adult shrub, you need to choose a healthy and developed shoot of 2-3 years of growth.
- Tilt it to the ground and lay it in a loosened groove with a depth of 10 cm.
- Secure with wire or staple, sprinkle with fertile substrate.
- After the formation of young shoots on the layer, carry out hilling to a height of 10 cm, repeat the procedure 2-3 times during the summer.
Separation from the mother plant is desirable in the fall. Cut off the rooted and developed cut with a shovel or knife, transplant to a permanent place.
Pruning yoshta
Yoshta pruning is carried out in the spring, before the start of sap flow, and in the fall, after leaf fall.
Pruning yoshta in spring. In the spring, sanitary pruning of yoshta is carried out: broken, diseased shoots are removed and those that have frozen over the winter are shortened to healthy tissue. Yoshta does not need formative pruning, but over the years it is necessary to shorten the branches that are 7-8 years old, leaving only segments with 6 buds from them.
Pruning yoshta in the fall. Every autumn, when the leaves fall, and the shrubs and trees go into a dormant period, they carry out sanitary pruning, cutting out the shoots affected by the glass, broken and thickening the bush, and the healthy branches of the yoshta are shortened by a third.
Diseases and pests, their treatment
Yoshta is affected by diseases that are observed on currants and gooseberries. The greatest danger is represented by fungal infections, which develop quickly and are difficult to treat.
Typical diseases:
- anthracnose;
- rust;
- downy and powdery mildew;
- septoria.
In addition, the shrub can become infected with terry leaves or mosaics. These viral diseases are considered incurable; in case of severe damage, the bush must be removed. All other infections are treatable with chemical fungicides. The most effective are Fundazol, Topaz, Skor and Bayleton.
Among pests, spider mites, moths and aphids are dangerous. When the first signs of infection are found, the planting and soil should be treated with an insecticide. For treatment, Actellik, Intavir, Decis and others are used.
Yoshta as a standard culture
As a trunk, this product of crossing of two related crops can become an alternative to golden currants. The advantage of yoshta is its tall stature, strong root system, and the absence of root growth. In addition, it is resistant to anthracnose, powdery mildew, and is not damaged by the currant kidney mite. Varieties of black and red currants, as well as gooseberries, can develop normally on a yoshta stem, even without any additional support. The survival rate of many varieties of gooseberries and currants is high.
Advertisement 3




























