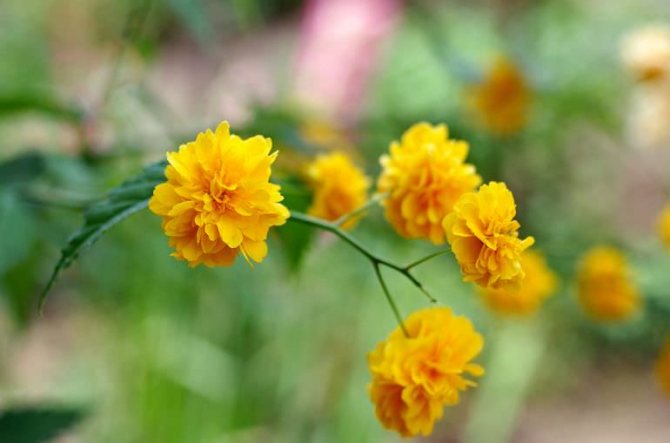
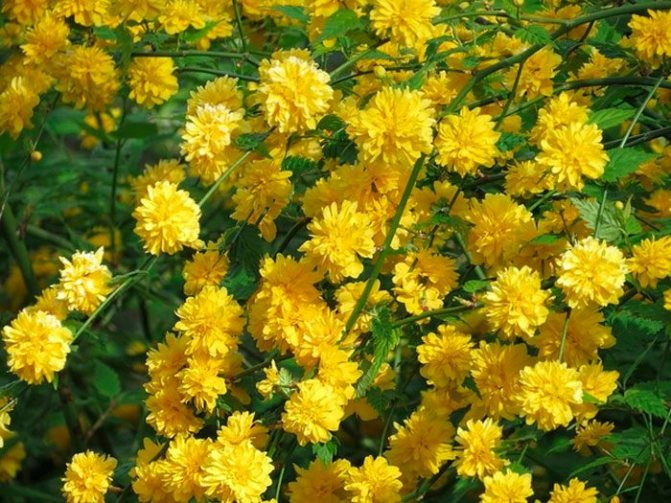
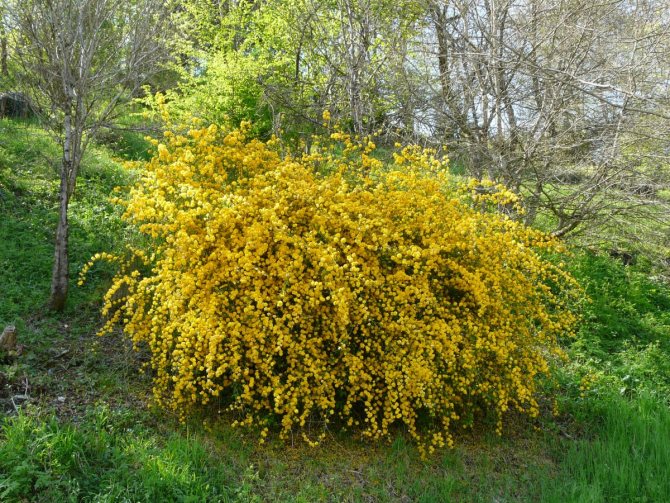
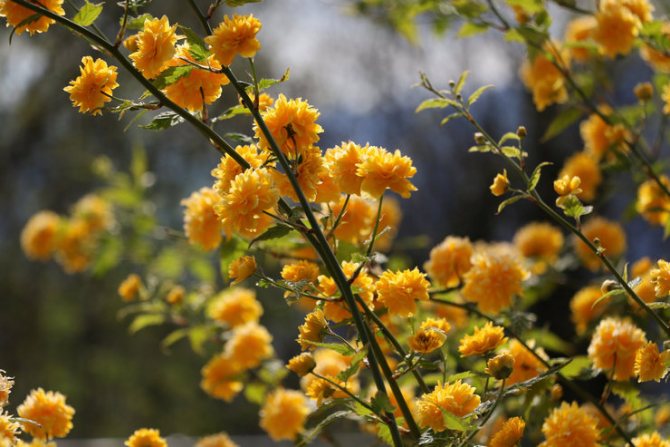
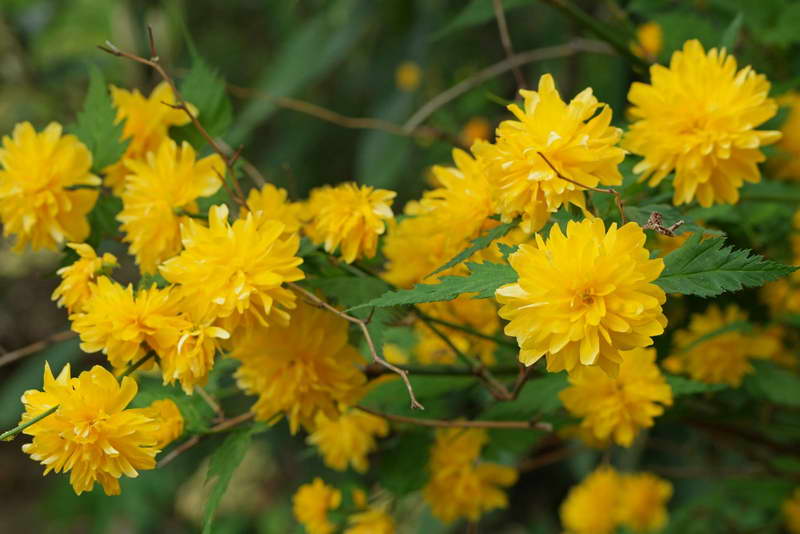
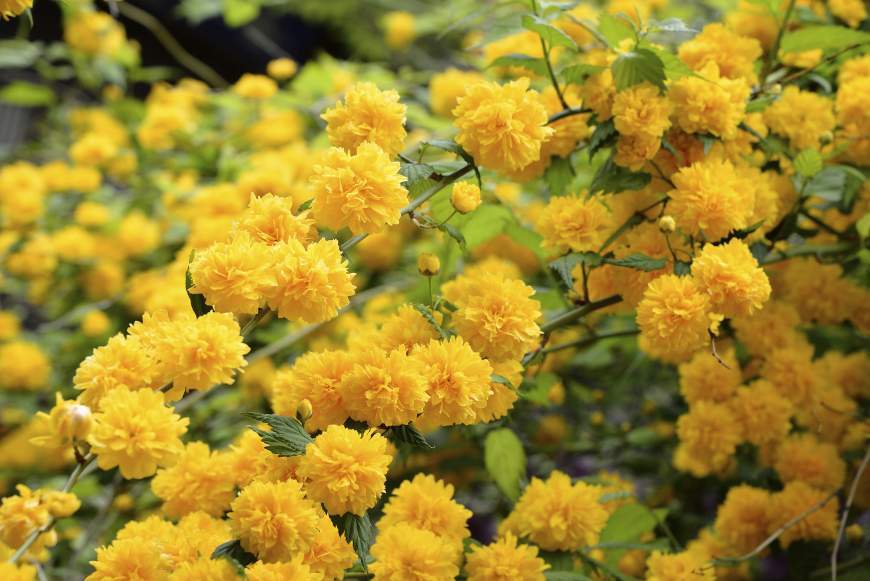
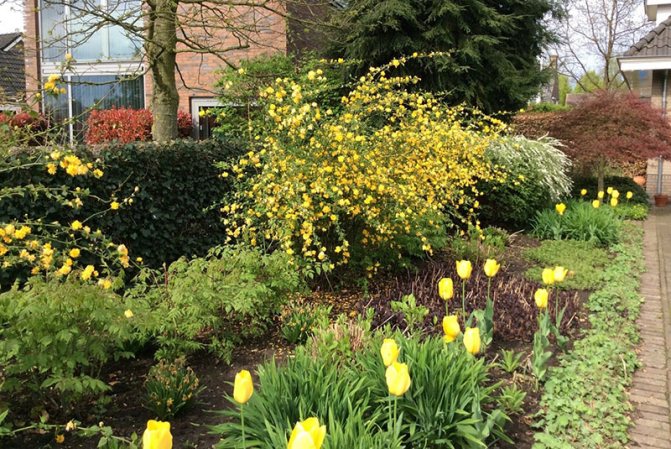
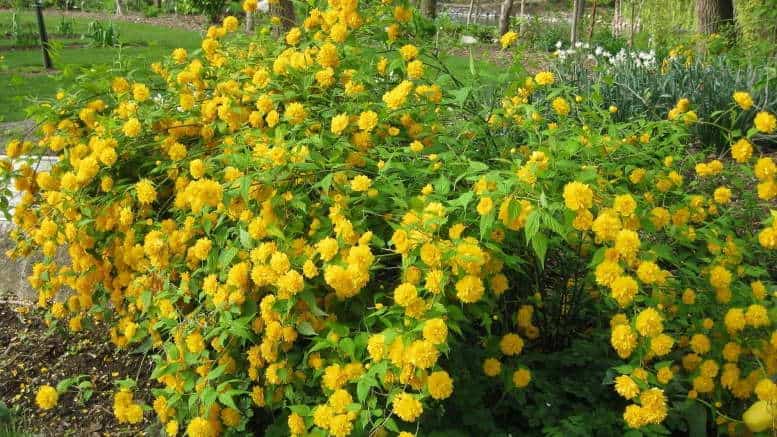
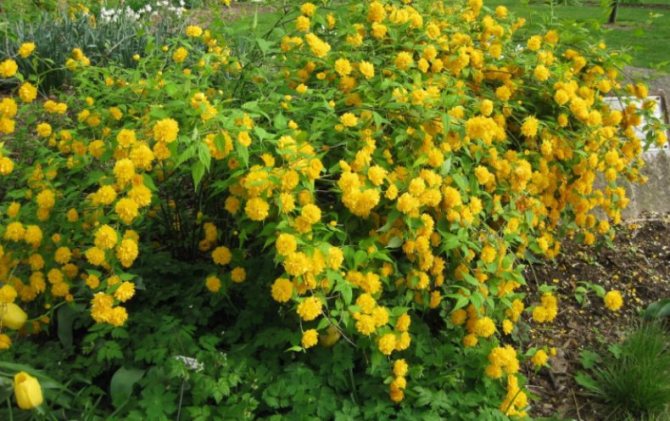
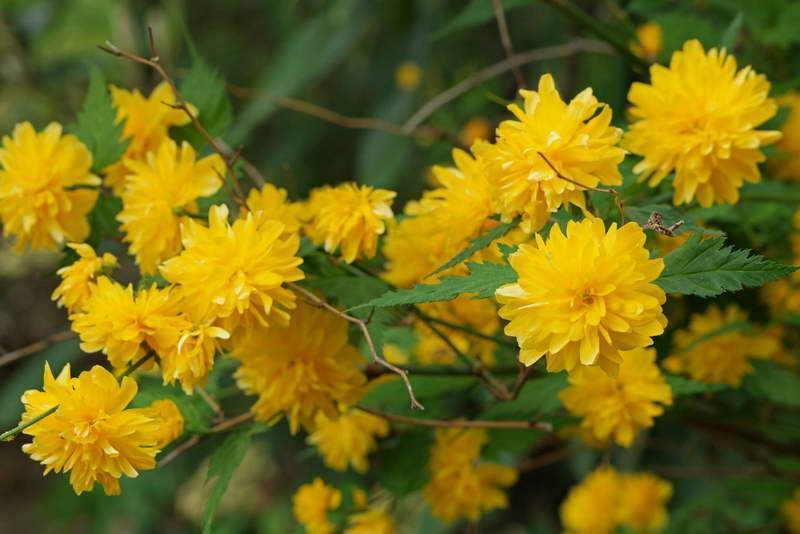
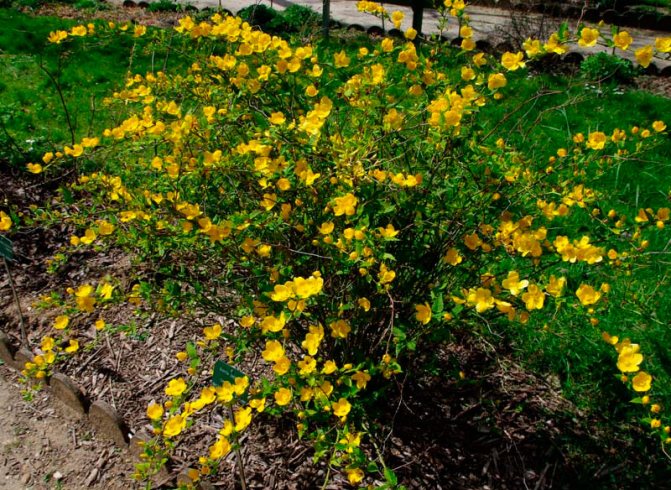
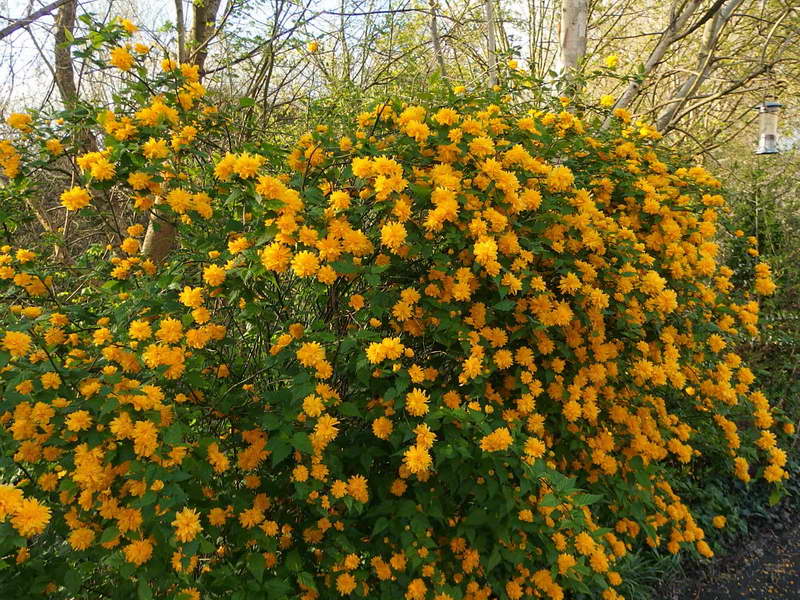
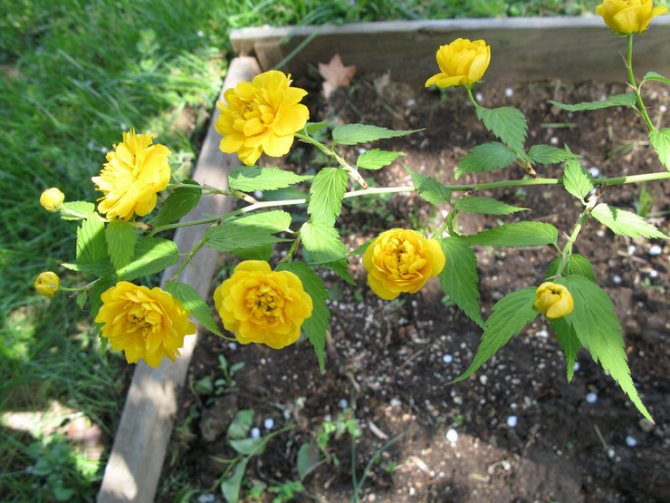
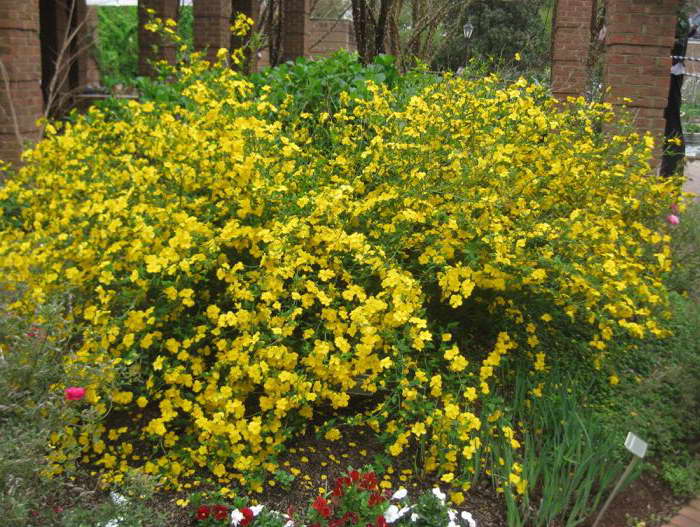
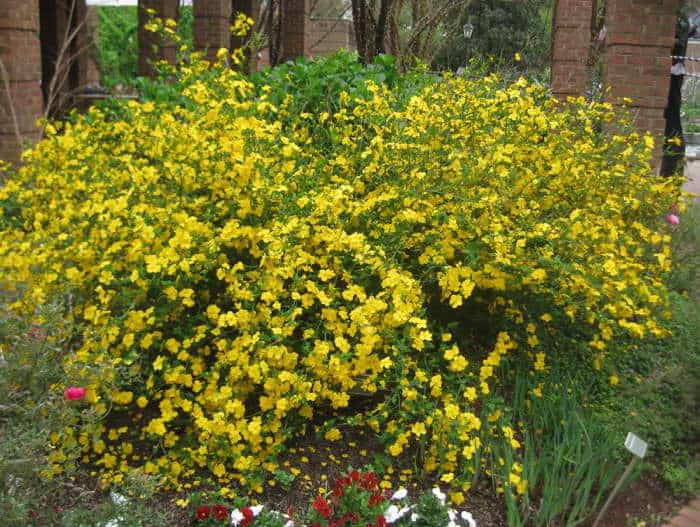
A deciduous shrub, Kerria, or keria, is a member of the pink family. In nature, this plant can be found in southwestern China, as well as in the mountainous and forest regions of Japan. This shrub is named after the first gardener of the Royal Botanic Gardens in Ceylon, William Kerr, who was also a renowned collector of plants. In this genus, there is only one species - Japanese kerria. Such a plant has a spectacular flower shape, for which it is also called the "Easter rose".
Briefly about kerry
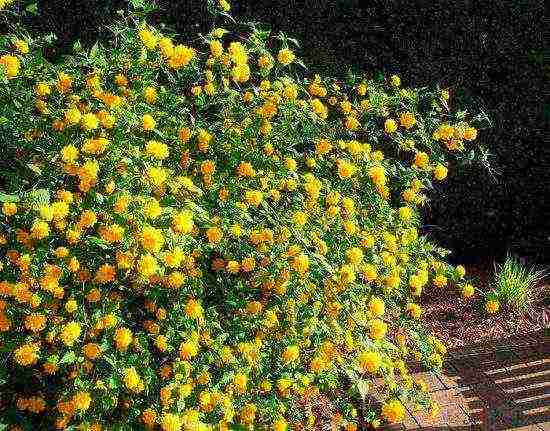
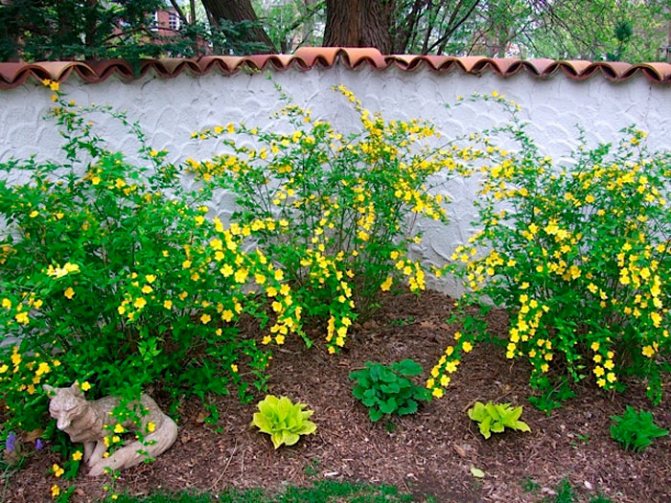
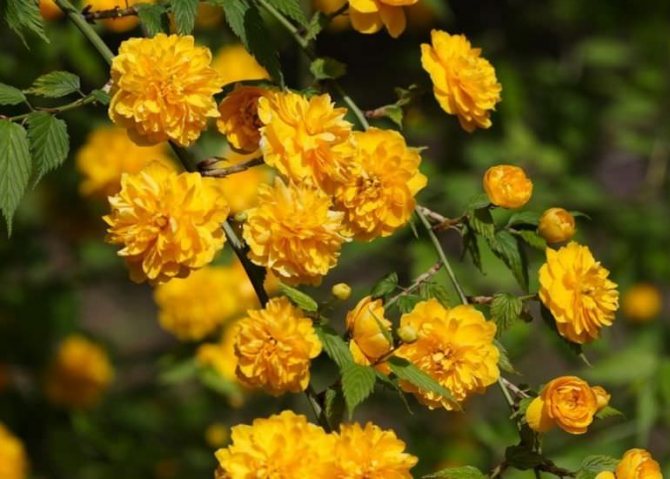
Kerria japonica (Kerria japonica) is an openwork deciduous shrub about 2 meters high. In the Moscow region, kerria blooms in May, even before the foliage appears, and blooms for a very long time: up to 25 days. Moreover: in the fall, kerria pleases with repeated flowering, and individual flowers appear throughout the summer. Even non-flowering shrubs are very decorative in summer due to the graceful shape and rich greenery of the leaves, and in autumn due to their bright color. Yellow-green shoots of kerria will also decorate the winter garden, vividly contrasting with the whiteness of the snow. However, the winter hardiness of kerry is not particularly high, so it is still advisable to cover it for the winter. Although the frozen shoots recover quickly, the frost-affected plant does not bloom well.
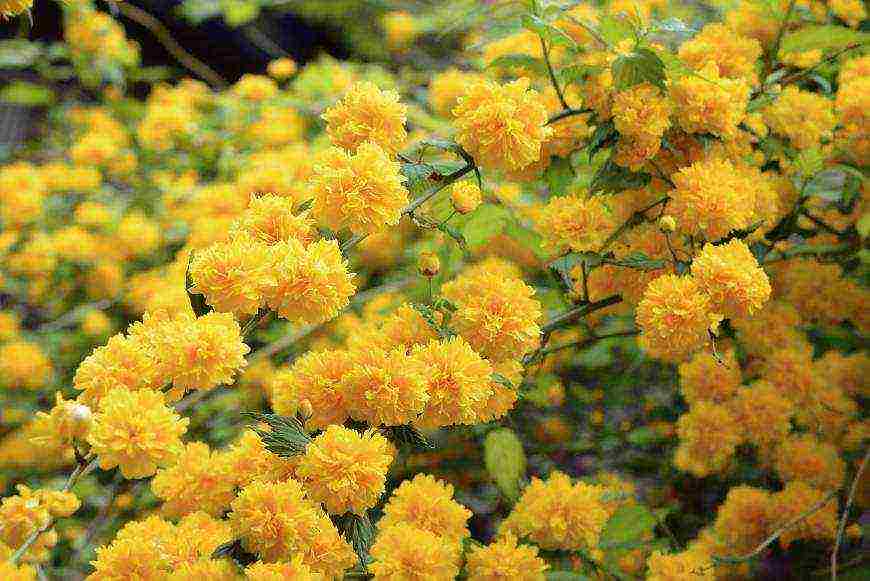

Kerria shrub - description
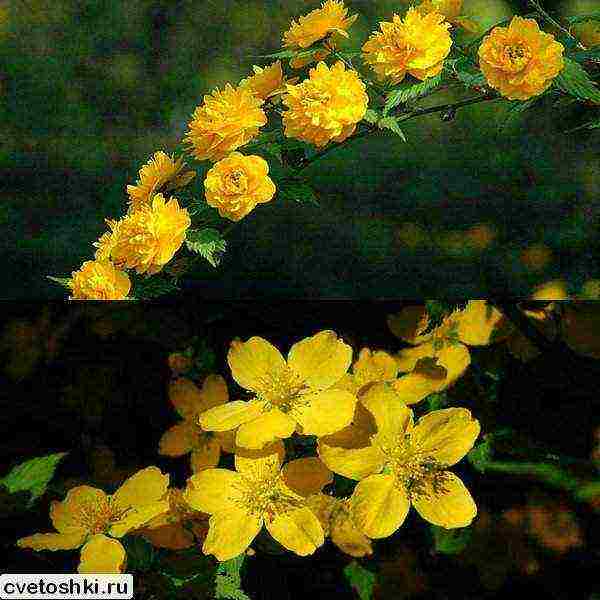
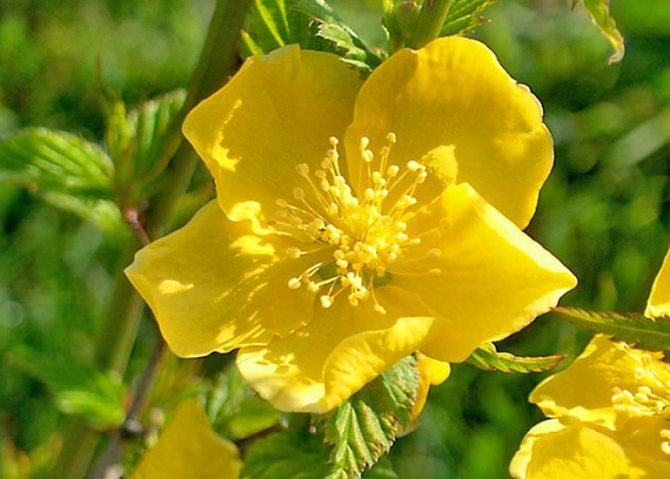
Kerria japonica is a deciduous, fast-growing shrub up to 3 m high with straight green twig-like shoots that form a crown in the form of a cone. Kerria leaves resemble raspberry leaves: up to 10 cm long, lanceolate, double toothed, pointed to the tops, glabrous above and pubescent on the lower side. They are light green in summer and bright yellow in autumn. Single, fragrant, simple or double kerria flowers up to 4.5 cm in diameter bloom for 25 days from May to August, in autumn the plant often blooms again. The fruit of kerria is a juicy black-brown drupe, but in the conditions of the middle lane the plant does not form fruit.


Thin shoots of kerrias can break from strong winds, so it is advisable to plant them surrounded by such flowering shrubs as spiraea, bubblegum or Chinese tea. In the midst of spring, it can serve as a spectacular backdrop for blue aquilegia, blue phlox spread out, dwarf purple irises, and nearby you can grow a buzulnik, which will be in harmony with kerria during its autumn flowering.
Planting kerriya japonica
The best place for kerrias is well-lit, sheltered from the cold winds. The plant feels good in partial shade, but with strong shading, the flowering will be more than modest. However, with constant exposure to direct sun, the flowers "fade", acquiring pale, whitish tips of the petals.
Kerria requires fertile, moist soil, preferably loamy.
The plant is planted in early spring, before the buds appear. An autumn planting is also possible - a month and a half before the cold weather. A bucket of compost mixed with garden soil, a glass of ash and 60-80 g of complete mineral fertilizer are introduced into a planting pit 60x60 cm in size. It is advisable not to deepen the root collar. After planting, the plant is watered abundantly, the trunk circle is mulched.
Kerria's shoots are thin and can break in strong winds, so it makes sense to plant it in the background, surrounded by other flowering shrubs, for example, yellow-leaved spirits, Kuril tea, bladders, which will take over from it and bloom later. In May, blue aquilegia, late double tulips and dwarf irises of purple tones, styloid phlox rugs and curtains of blue phlox spread out will look good against its background. Nearby, you can plant a buzulnik, which will overlap with the autumn flowering of kerrias. It goes well with conifers.
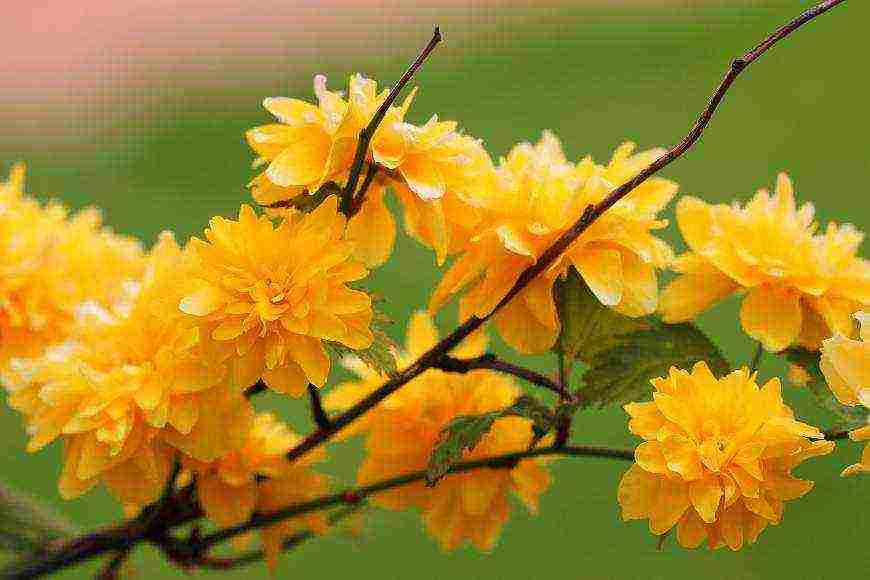


Kerria features


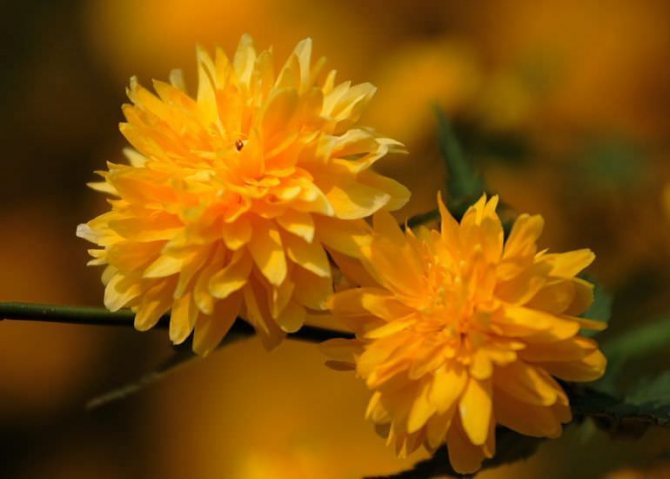
Kerria is a deciduous shrub, reaching a height of about 3 meters, it is distinguished by its rapid growth. The crown has a conical shape. Rod-shaped straight stems are colored green. The leaf plates of this shrub are similar to raspberry foliage. In length, they reach 10 centimeters, have a lanceolate shape, double toothed, pointed to the tops. The front surface of the foliage is bare, and the seamy side is pubescent. In the summer, it is painted in a pale green color, which changes to a rich yellow in autumn. Fragrant single flowers can be simple or double, they reach about 45 mm in diameter. The plant blooms from May to August, while the flowering duration is 3.5 weeks. Repeated flowering is often observed in autumn. The fruit is a juicy drupe of brown-black color, however, when grown in middle latitudes, no fruits are formed.
Strong gusts of wind can easily injure the fragile stems of kerria, so it is recommended to plant it surrounded by the following flowering shrubs: bubblegum, spiraea, or Chinese tea. In spring, such a shrub will serve as a chic background for the blue phlox spread out, blue aquilegia, purple dwarf irises. Buzulnik is often grown in the neighborhood of kerry, in harmony with this shrub during re-flowering in the fall.
Kerria: care
Watering... The plant is moisture-loving, but it does not tolerate excessive moisture, so watering should be abundant, especially during the flowering period and in the heat, but without stagnation of moisture in the soil.
Top dressing... Kerria Japanese is responsive to fertilization. In July, after flowering, it is fed with mullein infusion, if necessary, feeding is repeated after two weeks. The mullein can be replaced with matured compost with the addition of ash (100-200 g per sq. M.).
Pruning kerries are a prerequisite for preserving decorativeness. Frozen, damaged, broken branches are cut out in early spring. The remaining shoots can be shortened by a third - this stimulates branching. After flowering, faded shoots are cut out to branches on which there were no flowers - it is on them that buds will form for re-flowering in the fall. At the same time, rejuvenating pruning is carried out, removing all branches older than 4-5 years. With a strong thickening, the shrub is thinned out. Kerria Japanese grows quickly, so pruning is extremely useful for her.
Preparing for winter... With the onset of stable cold weather (in October-November), kerrias are sheltered for the winter. This should be done in dry weather. The bushes are carefully bent to the ground, laid on a dry bedding (for example, foam) and fixed with a frame made of stakes, which not only holds flexible branches, but also prevents the snow from breaking them. Top covered with dry leaves or shavings and covered with a double layer of lutrasil. The shelter must be dry and ventilated, otherwise the bushes are threatened with damping. In the spring, the shelter is removed in stages, preferably in cloudy weather, after waiting for the end of return frosts. It is impossible to open kerria immediately: the delicate skin of young shoots quickly gets sunburn.
Kerria, affected by frost, is recovering quite quickly, but you should not expect abundant flowering this year.
Variegated forms of kerria (Picta, Albomarginate) are more demanding in terms of care and growing conditions.
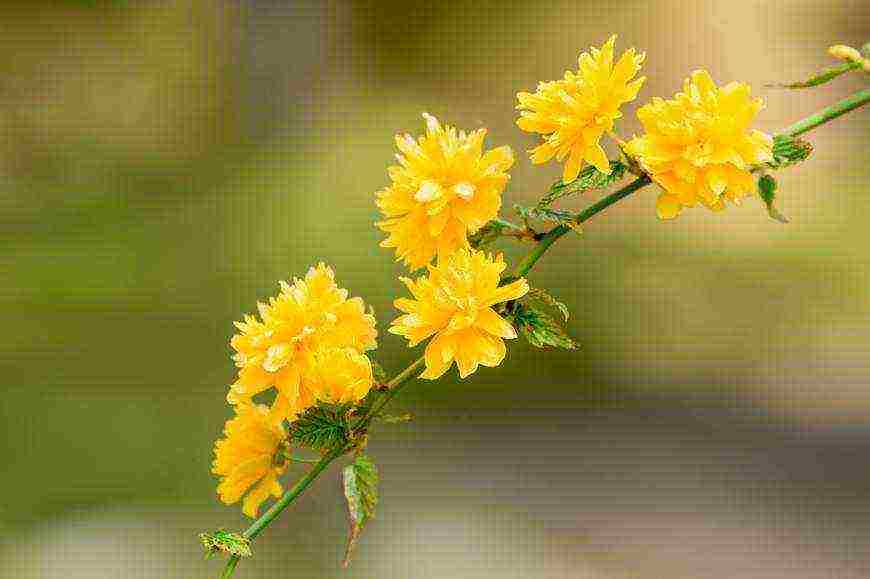


Correct pruning of the keria shrub, the key to lush flowering
But for these rods to be truly green, kerrias need to be pruned and rejuvenated. As a rule, all branches older than 3 years are cut out, and the young are left to replace them. Usually, pruning is done after winter, when it is already clear what has survived and what is frozen.
But in early spring, do not cut the kerria mercilessly, it blooms on last year's shoots. Prune tightly in the spring and deprive it of flowering. Do only sanitary pruning. But in May-June, after the end of the first wave of flowering, it can be cut off seriously, then it will bloom at the end of summer, and next spring.
By the way, with skillful pruning, you can keep the plant at the height you need, but you should understand that by shortening the shoots up, you cause intensive growth of shoots inside the shrub. And these shoots also need to be partially removed by thinning the plant.
Despite the unpretentiousness declared by me, the Japanese kerria bush will look good, which does not experience a shortage of water and food, it is cut off in time and planted in the right place.
Japanese kerria is a large and eye-catching bush, which means it is an excellent specimen.
Forms and varieties of kerrias
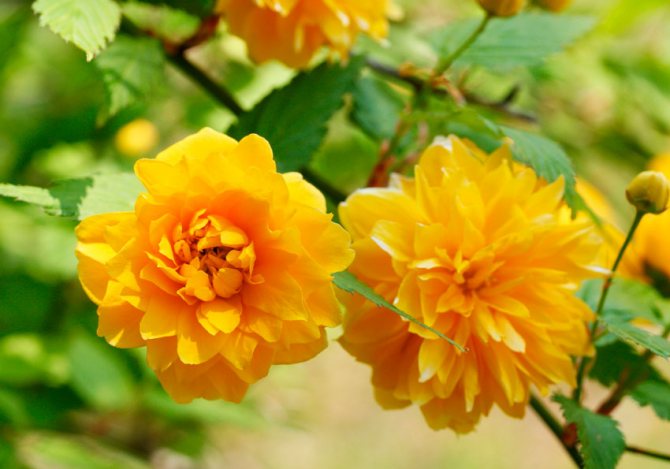
The natural form of kerrias has simple flowers, cultivars have been bred with spectacular double flowers, similar to small roses or cut rudbeckia flowers ("Golden balls").
The most common garden varieties:
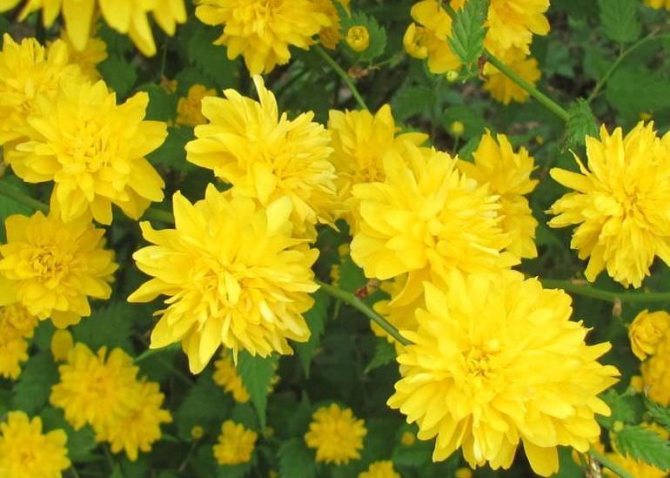
Pleniflora (Kerria Pleniflora, Plena) is a dense, upright shrub with abundant medium-sized (up to 3 cm) double flowers, similar to pompons.
Golden Guinea (Kerria Golden Guinea) is a shrub with graceful leaves and simple five-petal flowers of large size - up to 6 cm in diameter.
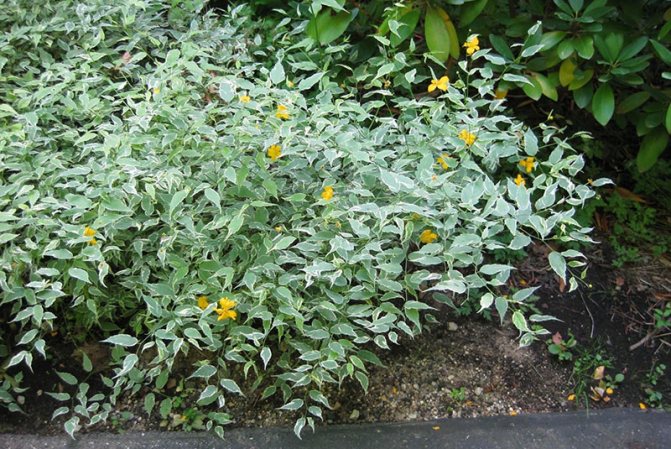
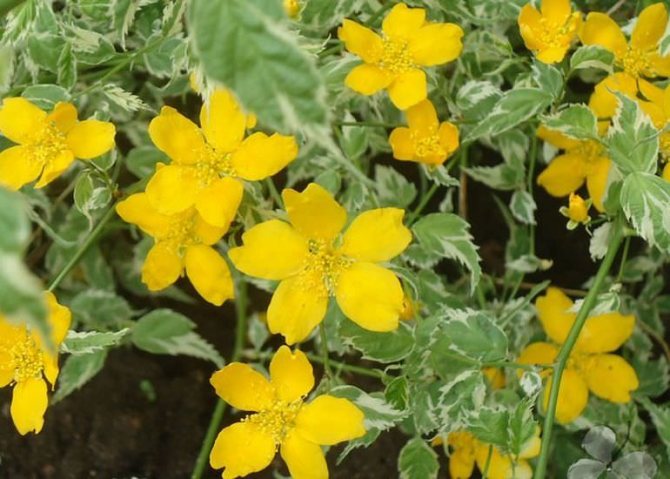
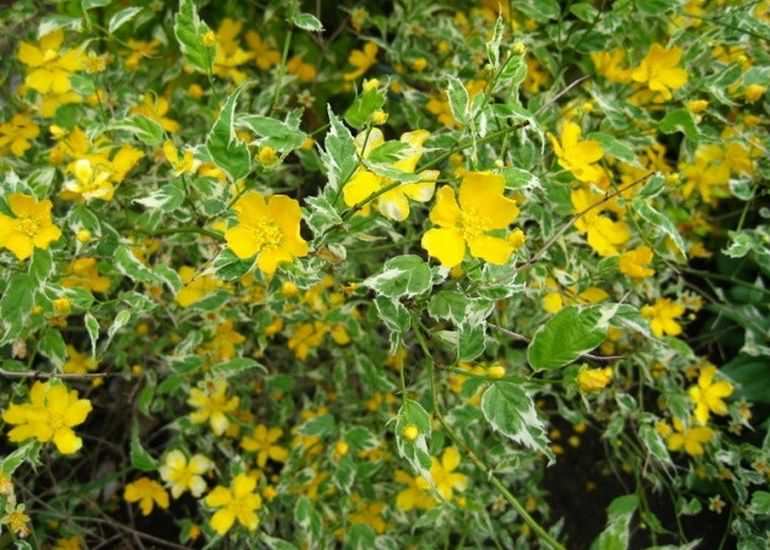
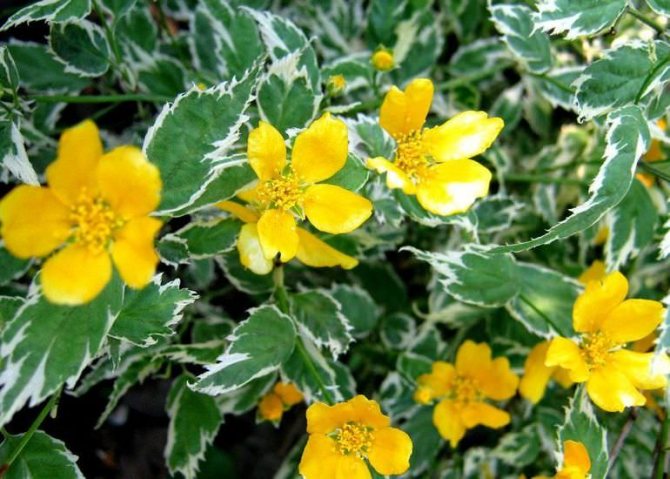
Variegata or Picta (Kerria Variegata, also known as Kerria Picta) - with simple five-petal flowers and very decorative gray-green leaves with a cream border.
Albomarginata (Kerria Albomarginata) - with simple flowers and graceful leaves with a white border.
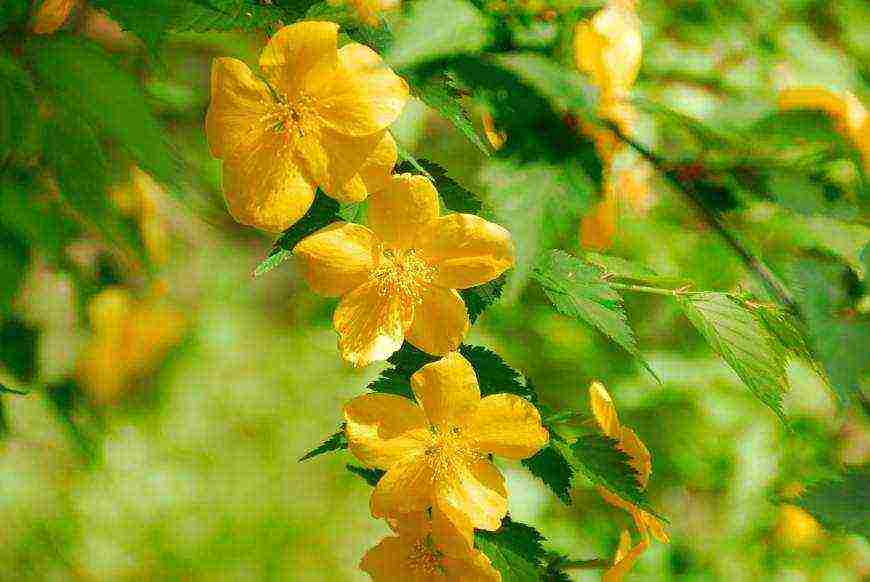


CARE RECOMMENDATIONS
Requires shelter for the winter.
Grows well in fertile, moist loamy soil.
Shade tolerant, but needs bright light for abundant flowering.
Watering is plentiful, but not excessive.
Cropping is required.
Kerria yellow is a plant that is rarely found in the vastness of our Motherland, despite its extraordinary decorativeness and bright lush flowering, and not only in the spring, but also in autumn. It is not difficult to grow kerria, the main thing is to remember some of the features of the plant and take them into account when taking care of the crop. Next, we will talk about the main varieties of the plant, planting and proper care for it in open ground (detailed photos of growing the plant are attached).
Description, main varieties and varieties
Kerria yellow (another name - Japanese) in natural conditions is found mainly in the mountainous regions of Japan and China. Europeans know the flower under the name "Easter rose" because of its external similarity and the beginning of flowering right before Easter. The plant is a fast-growing large shrub, reaching a height of 2-3 m, has straight rod-shaped stems that form a conical crown.
The leaves of the plant are very similar to crimson, strongly pubescent on the underside. The flowers grow singly, are distinguished by a delicate bright yellow color, reach 4-5 cm in diameter. The flowering of the plant is abundant, rather long - it is about a month (from May to August). With the onset of autumn, re-flowering occurs.
Although kerria is presented in only one form, there are a large number of different garden forms and varieties of this plant (you can familiarize yourself with them in the attached photo):
- Variegata. A fast-growing variegated kerria, reaching a height of about 0.6 m. The leaves are gray-green in color, covered with small cream-colored spots on top. The flowers are yellow and grow very quickly.


Variegata
- Albomarginata. Slow growing variety of kerria. The leaves of the plant are slightly asymmetric, and around the edges are as if surrounded by a white border. Due to such a specific external feature, the plant is often considered unviable, but in fact this is not the case.
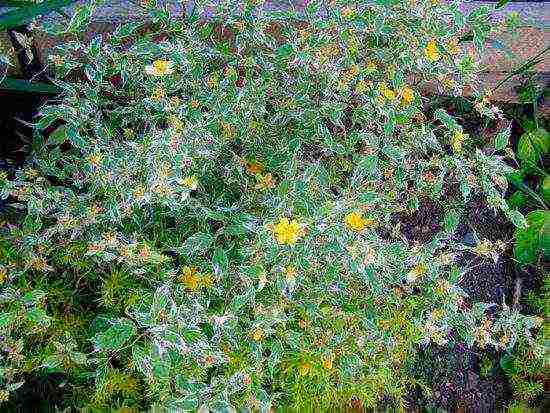


Albomarginata
- Kerria Japanese Aureovariyegata. Terry variety with flowers that have a rather complex structure. The shrub is medium in size and has a long flowering period: with proper care, flowers form within a few months.
- Kerria Golden Guinea. The plant is distinguished by graceful thin leaves and impressive flowers, reaching a diameter of 6 cm.
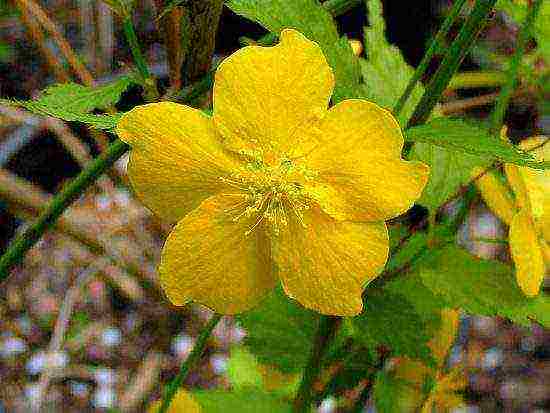


Kerria Golden Guinea
- Kerria pleniflora. The original variety, during the flowering period, pleases with luxurious double pom-pom flowers.
Correct planting of culture
Most often, this process is carried out either in early spring or in autumn 30-40 days before the onset of the first frost.
Advice. If you plan to plant seedlings with a closed root system, it can be done almost at any time of the year, except for winter.
When choosing a place for culture, an experienced gardener will prefer a dry, calm, sunny area. The plant will be able to survive, of course, in partial shade, but in this case it will be more difficult to achieve lush flowering. By the way, it is better to avoid places completely open to the sun: the plant can burn out.
The best option is considered to be areas with a light mesh shadow from tall trees with a lush crown. Kerria is quite picky about the soil: it is better to choose fertile, sufficiently moist and nutritious soil for planting the plant (loam is ideal).


Kerria loves the shadow
The well for planting should have the following dimensions: 60x60 cm and a depth of about 0.5 m.A soil mixture is poured into the bottom of the pit, consisting of the soil itself, as well as turf and humus in a ratio of 2: 3: 3 (you can add a little complex fertilizer there - about 70 g).
A seedling is set on top of a hill of earth. The roots should be carefully straightened, after which the plant should be covered with the remaining soil mixture, lightly tamped on top and watered abundantly with water. The root collar should be practically on the soil surface.
Subtleties of care: feeding, watering, protection from pests
Kerria is an unpretentious plant that requires care solely for the purpose of maintaining a decorative appearance, and in order for it to be such, it is necessary to take care of a high level of health and grooming of the shrub. This can be achieved by following simple rules that will lead to the desired result.
In order for a plant to really grow healthy and beautiful, it is enough to follow a certain set of care measures:
- Watering. Kerria does not need abundant watering, it is enough to monitor the state of the upper soil layer: it should not dry out. Particular emphasis should be placed on soil moisture during dry periods and during the flowering of the plant. Water for irrigation must be warm and well-separated. During the period of frequent rains, it is advisable to reduce watering to a minimum.
- Loosening and weeding of the soil. After each watering, it is imperative to weed the area with growing kerry and thoroughly fluff the soil.


Kerrias need frequent feeding
- Top dressing. Kerria does not require a significant amount of fertilizer: it is enough to add mullein infusion (in a ratio of 1:10) or compost only after flowering.
- Pruning the plant.With the onset of the first days of spring, all dead, old broken branches are necessarily removed, and the young are cut off by 1/4. As a result of such a preventive procedure, kerria will grow into a compact and at the same time very dense bush, and the flowering will be luxurious.
- Diseases and pests. Kerria is completely immune to both infections (of any type) and insect pests. At the moment, no recorded cases of the disease have yet been observed.
Plant propagation
Kerria propagation is carried out exclusively by vegetative methods:
- Cuttings. When a plant is propagated by cuttings, it is necessary to cut off only those branches on which 2 full-fledged buds have formed. The cut is done obliquely (usually in the middle of spring). The cuttings are initially planted in a closed, cold greenhouse. Rooting is rather slow, so the cuttings should be left in a greenhouse for the winter. And only by spring can they be planted in separate containers. In open ground, planting is carried out after a year.
- Layers. In early spring, young shoots of kerria fit into rather deep (about 7 cm) grooves and are fixed in this position. After a couple of weeks, new shoots begin to branch off from the buds of the cuttings. When they reach 15 cm in height, sprinkle the shoots up to half with earth and wait for the plants to take root (this usually happens in autumn). During this period, you can separate the layers and replant them.
- By dividing the bush. When propagating a plant by division, it is important to keep the bush intact at the time of digging out of the ground and thoroughly clean its roots from the ground. The bush should be divided in such a way that each of its parts has a fully developed root and strong shoots. Parts of the bush are planted in holes, carefully covered with earth and watered abundantly.
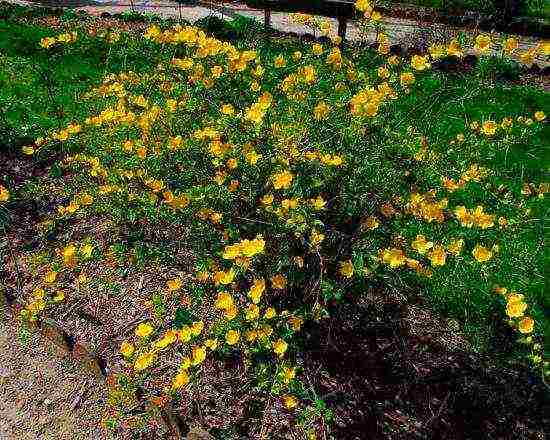


Kerria looks great in the garden
The combination of yellow kerrias with other plants
Most often, kerria is used either as a hedge or in close proximity with other plants when creating mixborders. The plant looks great in combination with spring primroses (rhododendron, mahonia, etc.).
Kerria branches often break from gusts of wind, so as protection against possible unpleasant consequences, plant it next to powerful flowering shrubs such as bladderwort or spiraea.
Also, next to the kerria, you can plant luxurious irises, a wonderful buzulnik, which will perfectly harmonize with kerria in the fall during its re-flowering period.
This concludes the consideration of the features of growing yellow kerrias in the open field. Now you know about all the intricacies of caring for this beautiful flower. Good luck!
Kerria: video
Care for kerrias in the garden
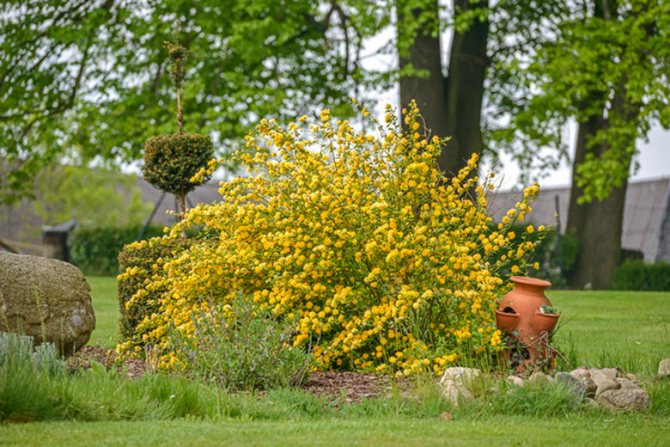


If the shrub is properly cared for, it will delight you with its most spectacular appearance. Kerria should be systematically watered, weeded, pruned and fed, and do not forget to regularly loosen the surface of the trunk circle.
Watering is carried out only if necessary, when the topsoil is completely dry. When the plant is blooming, as well as during the dry period, this shrub especially needs moisture. It should be watered with well-settled lukewarm water. In the event that a large amount of rain is observed in the summer, then kerria can do without irrigation, since it reacts negatively to stagnant water in the ground. After that, the bush will be watered or it will rain, it is necessary to loosen the top layer of the soil and pull out all the weeds.
For normal growth and development, the plant will require timely feeding. After the shrub has faded, it will need to be fed with mullein infusion (1:10) or with matured compost, into which wood ash is poured (from 100 to 200 grams of ash is taken per 1 square meter).
Transfer
This shrub easily tolerates a transplant, so you can transfer it to a new place almost at any time of the year, but not in winter or late autumn.However, it is best to replant kerria when there is no foliage on the bush, namely, in spring or in October. Dig in carefully around the perimeter of the crown, and then pull it out of the soil. Do not forget to prepare the planting hole in advance, it will be necessary to place the dug plant in it along with a lump of earth. Then do everything exactly the same as for the initial planting. For half a month from the moment of transplantation, the shrub will need systematic abundant watering, the root zone should be well saturated with water.
Reproduction of kerria
Such a plant can be propagated only by vegetative methods, namely: by layering, cuttings, dividing the bush, and also by shoots.
Cuttings
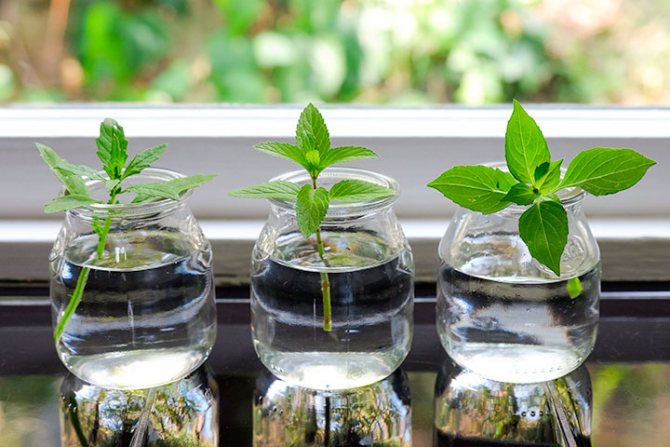


Green cuttings should be harvested in mid-summer, and woody cuttings in April. Each cutting should have a pair of buds, and do not forget to make the bottom cut oblique. The cuttings should be planted in a cold greenhouse, placed in a small partial shade. Rooting of cuttings is almost always successful, but this process is quite lengthy. In winter, the cuttings will stay in the same greenhouse. Next spring, in May, they will need to be planted in individual containers and grown in room conditions. After another 1 year, the cuttings can be planted in open soil in a permanent place.
Root offspring
To propagate the shrub by root suckers, it is necessary at the beginning of the autumn period to separate them from the parent plant and plant in a new place. The offspring have a developed fibrous root system, in this regard, if they are systematically watered and cared for properly, then the transplanted young kerrias will take root relatively quickly.
Layers
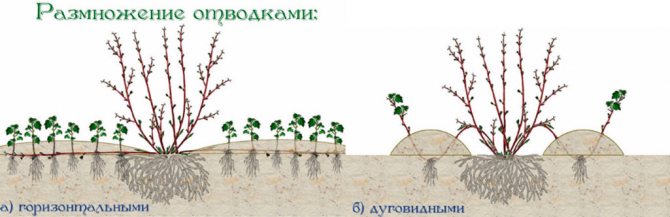

This shrub is fairly easy to propagate by layering. In spring, before sap flow begins, select a developed stem and lay it in a prepared groove, the depth of which should be 7 centimeters. Lock the stem in this position. After 10-15 days, young shoots will grow from the buds. After their height is equal to 10-15 centimeters, it is necessary to fill up the groove, as well as the shoots themselves up to half the height, using nutritious soil for this. In autumn, these plants will grow their own roots, and they can be cut off and planted in a permanent place.
Dividing the bush
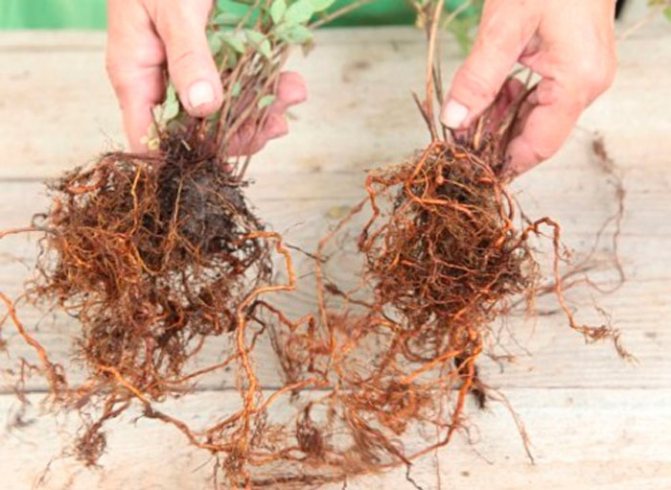


Often, when transplanting a shrub, it is divided. A dug out bush will need to clear the root system of soil, and then it is cut into several parts. It should be borne in mind that each of the parts must have developed roots and powerful stems. The planting of the cuttings is carried out in the same way as the initial planting of seedlings. Planted plants need abundant watering.
Pruning


At the very beginning of the spring, before the buds swell, sanitary pruning should be done. To do this, cut off all frost-damaged, injured and dried stems. The remaining young and healthy shoots should be shortened by ¼ part. As a result of such pruning, the bush will become more lush and compact, while the shrub will bloom even more abundantly.
When the plant fades, it will be necessary to cut the stems to the base, which are 4–5 years old. At the same time, young shoots are only slightly shortened, which will help the bush not lose its splendor.
Diseases and pests
Such a plant is highly resistant to diseases and pests. For many years of cultivation of kerria, there has never been a case of its defeat by a disease or pests.
After flowering
If the shrub is grown in a region with a warm climate, then it can survive the winter without shelter. When cultivating kerrias in middle latitudes, where frosty and little snowy winters are often observed, it is better to cover it.
Kerria for penumbra: planting and care
The ornamental shrub of kerria looks unusual on the personal plot.Outwardly, before the flowering period, it resembles an ordinary garden raspberry, but during the flowering period, bright yellow flowers against the background of still leafless branches look very impressive. The people call kerria an Easter or Japanese rose. It fits very harmoniously into a Japanese-style garden.
Kerria is an unusual deciduous shrub, it has green-yellow shoots, and the leaves are serrated, elongated. Flowering begins in early spring and lasts until summer, i.e. at a time when everything still looks dull and dull, such beauty will already bloom on your personal plot. The aroma of kerria is unobtrusive, very subtle.
In landscape design, kerrias are planted near the lawn, it looks organically against the background of the Moorish lawn, behind the mixborders. Perfectly relates to a number of growing primroses, mahonia, rhododendrons, weigels, forsythia and other plants. With the natural style of the personal plot, kerria is combined with geyhera, badan, hazel grouse.
It is not difficult to grow kerria in the garden, the main thing is to have the necessary information on the peculiarities of planting and care.
Place and soil
The ornamental kerria shrub feels great in partial shade! If it is planted in a place open to the sun, then it will be necessary to constantly monitor the moisture of the soil, while the color of the flowers will be pale. It is advisable to protect the landing site from the winds. The soil prefers moist, organic-rich, permeable.
Landing
Kerrias are planted in early spring, before bud break or in early autumn, 30-50 days before the onset of frost.
Prepare a planting pit 40-50 cm deep, 60 cm in diameter.The distance from the kerry to any other plant should be at least 60-80 cm.Fill the hole with fertile soil (turf soil, humus, a fertile layer of garden soil and 60 g of complex mineral fertilizer) , form a slide and place a plant with an earthy clod. Water and mulch well.


Care
During the first 2 weeks after planting, water kerrias abundantly.
Kerria is a very winter-hardy plant, practically not damaged by diseases and pests, but it is better to cover young plants in October-November with any dry shelter. First, the bush is loosely tied, set around the stakes, covered with dry leaves or sawdust, a film is put on the frame. In the spring, first, the leaves or sawdust are gradually removed, and then the film.
An obligatory procedure in the care of kerrias is pruning. In early spring, before the start of sap flow, cut off the broken branches. Every year after flowering, you need to cut the old branches at the age of 4-5 years to a stump for the growth of young ones, and simply shorten the young branches by a third. After pruning, top dressing is carried out with compost and wood ash (100-20 g per 1 square meter). Manure is not used as a top dressing for kerrias.
Reproduction
Kerria is propagated by green cuttings or root suckers. It is very convenient to propagate kerria with shoots, since it forms a large number of shrubs. Reproduction is carried out in September or May. If the reproduction of kerria is not included in your plans, then the root shoots must be removed in a timely manner.
Hybrid tea roses can harbor other varieties
Summer watering of plants. Watering the garden
Mountain pine (gnome, pug, pumilio). Photo
Common evergreen vines in the garden
Characteristics of shrubs: pyracantha, kerria, cinquefoil, mountain ash, fieldfare, plum, spirea, stephanander ...
Weigela planting, care and shelter for the winter
Rosehip breeding methods
The natural habitat of this shrub is in the mountainous terrain of Japan, and the culture is widespread in China. Kerria japonica belongs to the botinic rosaceous numerous family and occupies far from the last place there. The shrub has excellent aesthetic properties and is used in landscape design.Proper planting and caring for shrubs in the Moscow region allows you to maintain their external attractiveness for many years. All the intricacies of growing can be found in this article. Look at the photo of the varieties of Japanese kerriya ("Pleniflora", "Aureovarigata" and "Terry"):
Growing in the suburbs


Planting Japanese kerrias in open soil, as well as caring for them when cultivated in mid-latitudes, should be the same as in warmer regions. But do not forget that when growing a shrub in the Moscow region or the Leningrad region, he needs to provide a good shelter for the winter. The plant should be covered from the middle to the end of the autumn period, choosing a dry day for this. The stems must be bent to the surface of the soil, and lay them on a pre-laid foam. They should be fixed in this position, then they are covered with dried leaves or covered with spruce branches. A fixing frame should be made above the bush, which will prevent the branches from straightening. The shelter must be chosen so that it is well ventilated, otherwise the stems and branches under it will begin to rot.
With the onset of spring, you should choose a dry but cloudy day and gradually remove the shelter. First you need to remove the frame, and then remove the foliage. Experienced gardeners advise, on a sunny day, to protect the bush from the scorching direct rays of the sun with a covering material. The fact is that the stems can get severe burns, which can lead to the death of the shrub. Of course, the burnt stems can always be removed, however, after the appearance of young shoots, the splendor of the flowering is significantly reduced, and in some cases the kerria does not bloom at all.
Description of Japanese kerria and a photo of a bush
It's worth starting with the fact that this is a plant with a shoot height of up to 2 meters. This circumstance should be taken into account when planning a landing site. The description of Japanese kerria has been proposed by several botanists, but basically it agrees on all points. At the initial stage of development, the shoots are long branches of green color without the formation of an integumentary bark. The root system is evenly distributed in the depth of the soil. It has the ability to quickly increase the number of shoots already in the first year after spring planting. Look at a photo of the Japanese kerria shrub in various ways of using it on a personal plot:
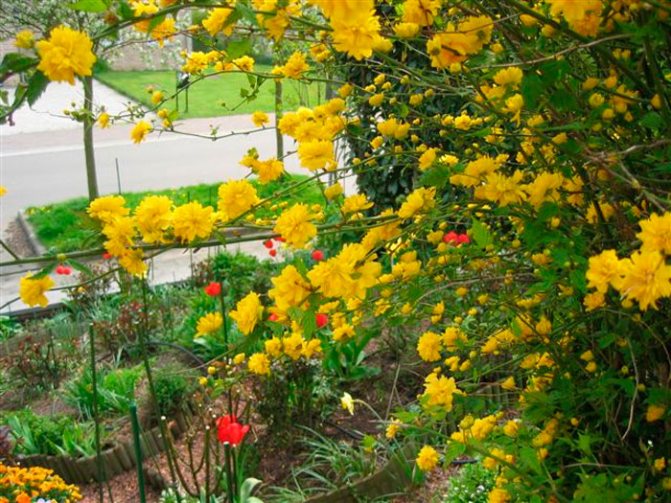
The lack of the ability to actively branch out forms a rather dense monotonous crown, which, with a high-quality haircut, remains throughout the season. The decorative value of a culture is its leaves and buds. Each leaf is slightly elongated and has a scalloped edge. The light green hue is replaced by rich orange and crimson tones closer to autumn. Duration of flowering is up to 2 months due to the continuous formation of new buds in the axillary buds of the shoots. Flowering begins in mid-June. The flower has a shape similar to a rose. The predominant color of the petals is yellow. The diameter of the blossoming bud is 60 mm.


Wintering plants
If the kerria is planted in a good place, then it is practically not afraid of low temperatures. In other cases, in the first frosts, the bush must be bent to the ground, having previously laid something there, for example, foam plastic. In this case, the branches will not be exposed to moisture. Then, fixing them, cover with spruce branches or lutrasil.
In doing so, pay attention to the density of the coating material. After all, the higher it is, the better it will keep the heat and the plant itself. After wintering, the shelter is removed, but in several stages, so as not to damage new shoots. If the shelter is made in dry weather, then it should be removed after the last severe frosts.
Thus, Japanese kerria can easily decorate your garden. After all, it begins to bloom earlier than other bushes and trees and pleases the eye even in autumn.Thanks to its easy propagation by cuttings, it will not cause much trouble, and diseases that practically do not concern it will not make you worry.
The main condition for good growth is watering and pruning, because without it, it will lose its so bright appearance.
Varieties of Japanese kerriya for the Moscow region (with photo)
Growing any crop requires a careful approach to the selection of suitable species. Varieties of Japanese kerriya for the Moscow region are resistant to adverse environmental factors. They have the ability to endure rather harsh snowless winters. Even in the case of freezing of the ground part, it is enough to carry out spring pruning and by mid-July the shrub will fully restore its decorative value. Next, we will consider some varieties - descriptions and photos can be found on the page. Keria Japanese "Pleniflora" (Pleniflora) is distinguished by the greatest decorativeness in the process of its flowering. The height of the shrub is up to 2 meters with a crown girth diameter of up to 1.5 meters. The green, springy branches are decorated with curly leaves that turn into a rich yellow in autumn. Refers to deciduous forms. Requires a small shelter for the winter, for this, the branches, after the foliage is dropped, are bent to the ground and fixed in this position. From above, a shelter is carried out with coniferous spruce branches, straw or plastic bags. In spring, the shelter is removed immediately after the snow cover disappears. With the preservation of the entire mass of shoots after wintering in the conditions of the Moscow region, flowering begins in the 20th of May. The buds have a compact, rose-like shape, with a diameter of up to 5 cm. They are painted in bright yellow tones. Often, under favorable conditions, a repeated flowering wave is observed at the end of August.
Kerria Japanese "Aureovarigata" is a terry variety with a complex bud structure. Differs in average bush growth and long flowering, reaching 3 months with proper care.
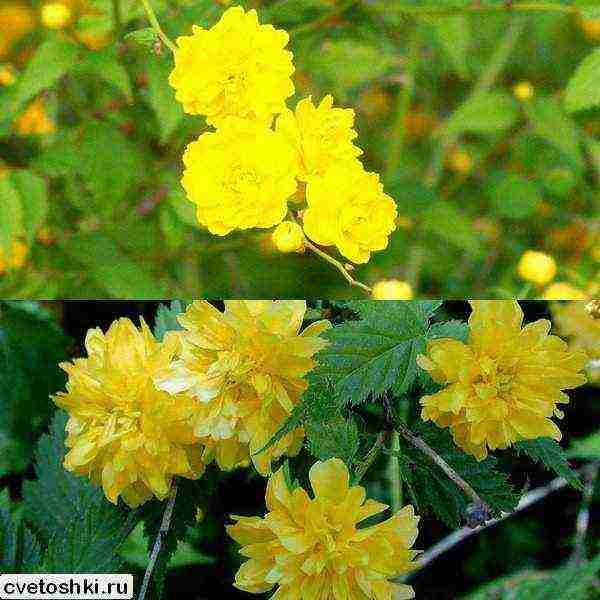


Among other varieties that deserve close attention, the dwarf form Variegata stands out, with a bush height of only 60 cm. It is suitable for decorating flower beds, rockeries and alpine slides. Looks great as a curb culture along garden paths. Simple buds with 5 bright yellow petals.
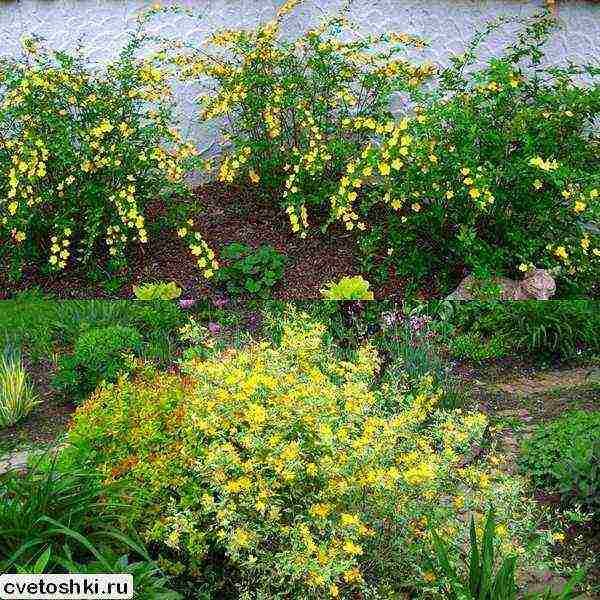


Crops with atypical colors of leaves and flowers are of particular value in landscape design. Japanese kerria "Albomarginata" belongs to such varieties. Its curly leaves with a rich green color are framed with a white stripe. By itself, this plant looks just great. And at the time of active flowering, it turns into a real yellow cloud due to the abundance of blossoming buds.
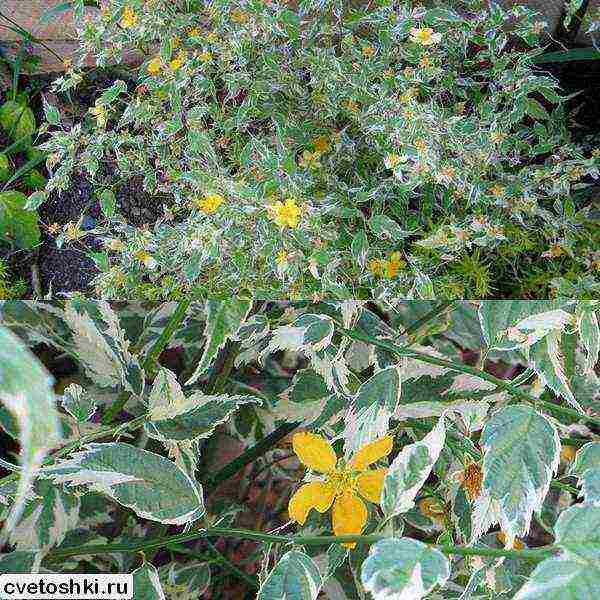


For lovers of exoticism, there will also be a valuable Japanese kerria "Albiflora", pleasing to the eye with a pleasant boiling whiteness of large double buds. Tall bushes up to 2 meters are decorated with densely planted curly foliage of dark green color. White flowers of a complex and simple shape bloom on the shoots in large numbers. Looks attractive in group planting with other varieties of kerrias.
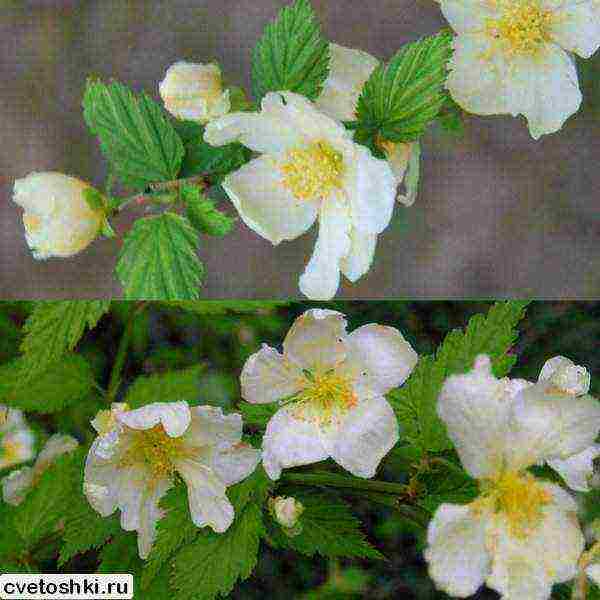


Botanical description
Kerria Japanese Is one of a kind, and its description is pretty simple. Belongs to the class of dicotyledonous plants and to the order of Rosaceae. Kerria is considered deciduous. Shoots can be 2 to 4 meters high. They are distinguished by their green color.


The flowers have a bright yellow color and reach a diameter of up to 5 cm. The leaves of the kerria resemble mint in shape. Bright green in summer, at the end of the season they acquire a golden hue.
After the shrub has faded, single flowers may still appear.
Reproduction, planting and caring for shrubs in the Moscow region
The culture is quite unpretentious. Reproduction is carried out mainly by cuttings during spring pruning of bushes. Rooting cuttings is not difficult even for novice gardeners.Correct planting and caring for shrubs in the Moscow region are presented in detail later in the article.


The main rule is the choice of a place for planting Japanese kerrias - the shrub prefers bright sunny places, without the influence of strong winds. In partial shade, it is possible to change the color of the foliage, strong elongation of the shoots. Due to this, decorative properties are lost. The soil should be sufficiently fertilized with organic and mineral substances. It is very important to dig a deep trench up to 1.5 meters deep before preparing the landing site. Broken brick or coarse gravel is laid on the bottom with a layer of up to 70 cm. Then a layer of organic humus up to 30 cm is laid. The remaining space is covered with planting soil. After that, the holes are prepared and the Japanese kerrias are planted with grown and rooted cuttings. Proper care of Japanese kerrias includes regular watering (the soil should not dry out to a depth of 10 cm). Mineral fertilizing with special preparations for ornamental and flowering crops is carried out every week. They are added to the water for irrigation. For reproduction, you should take apical shoots up to 6 cm long. They are cut with a sharp pruner and placed in water with the addition of succinic acid tablets. This drug is diluted at the rate of 4 tablets per 1 liter of water, stimulates the formation of the root system. After the appearance of small roots, the cuttings go deeper into the ground on a separate school. From above, they can be covered with small makeshift greenhouses. In the fall, you will get ready-made seedlings. But they should be planted in a permanent place only in the spring.


Landing in open ground
It is possible to plant Kerria Japanese in open ground in early spring, until the process of sap flow has begun, or in the fall - 1-1.5 months before the start of frost. If you purchased seedlings with a closed root system, that is, in a pot, then in this case they can be planted at any time of the year, with the exception of winter, of course.
The site for Kerria should be bright, well-warmed by the sun's rays and always protected from drafts and wind. It is possible for Kerria to take a place in partial shade, from this it will not die, but the flowering will not be bright and abundant. However, direct sunlight is also not good for the plant. The best option is an openwork partial shade, which is formed from tall trees.
Since in the wild, Kerria grows in wooded areas, therefore it prefers moist, humus-rich loamy soil.
Having found the appropriate place for the Kerria seedling, you can start planting. A planting pit is being prepared, the size of which should be 60x60 cm and a depth of 40 cm.In order for the young plant to take root well, to grow quickly, it is recommended to lay out a layer of fertile soil at the bottom of the hole, consisting of garden soil, humus and sod land in a ratio of 2: 3 : 3. It is also desirable to add 60-80 g of complex mineral fertilizer to this composition. After that, the Kerria seedling is carefully installed, its root system is straightened, after which the space is filled with the same fertile mixture. When the hole is filled, the soil is slightly compacted and water is poured abundantly.
Attention! When planting a seedling, pay attention to the fact that the root collar is at ground level.


Under favorable weather conditions, re-flowering may occur in the fall.
Landscaping: pruning and crown shaping
Landscaping is an established area of application for Japanese kerrias as an ornamental culture. But only by organizing the proper care of the shrub, you can get a great appearance of the culture. Not the last place in this process is taken by pruning and forming the correct crown.


The rules for the spring skim of the Japanese kerria include the following aspects:
- the first revision should be carried out immediately after the snow melts;
- the shelter is removed, all damaged and dry shoots are removed, they can become a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms and parasites;
- the second are those branches that strongly thicken the bush and interfere with the proper development of the culture;
- the last stage is pruning all the remaining branches, without exception, by без of their length.
Young bushes in the second year of life are cut completely at a height of 15 - 2 cm from the ground. This is how a rich crown of the correct shape is formed due to the formation of lateral branches. In landscape design, kerriya japonica is used primarily as a background crop for the horizontal spectrum of landscaping. Both single and group landings look great. The shrub can be grown along fences and facades, on alpine slides, along garden and park paths. The formation of compositions with various coniferous crops is widely used.
Date of publication: Landing in open ground
Features of planting a shrub in the garden
Kerria Japanese is unpretentious, and caring for it will not be difficult. The landing site should be protected from strong winds. Soil is needed with enough clay and sand.
The plant looks great against the background of conifers. Sometimes it is planted surrounded by spirits. Its shoots, which resemble the rays of the sun thanks to the flowers, will decorate your garden.
Where is the best place to plant kerria, lighting
For kerrias, as for many plants, sunlight is important. Planting in the shade is possible, but there is a chance that the shrub will not be so lush and brightly blooming. An excellent option is partial shade.


Soil requirements for planting
Kerria japonica, like any other forest plant, loves moisture, requires soil with good water permeability, so planting in loam will be the best option.
The land mixture looks like this:
- 3 pieces of sand;
- 1 part of humus;
- 1 part compost;
- 1 part of turf land.
Reproduction
The shrub can be propagated in several vegetative ways.
Cuttings
Harvesting of green shoots is carried out in the middle of summer, lignified ones - in spring. Cut them at an oblique angle using sharp scissors or pruning shears. Each stalk should have several buds. Place them in a moist substrate, cover with foil. Leave to root in a cool place. Rooting is usually successful, but it is a rather lengthy process. Cuttings should overwinter in a greenhouse. In May next year, they are transplanted into separate pots and grown warm. Only after a year can the plant be planted outside.


Layers
In the spring, before the start of sap flow, attach a well-developed shoot to the ground, deepen it into the groove by 5-7 cm, and fix it. After 2 weeks, young shoots will begin to germinate from the layers. When they grow roots by autumn, separate from the mother bush and transplant.


By dividing the bush
The procedure is usually carried out during plant transplantation. Dig out the bush, remove the soil from the roots. Cut with a sharp tool into several parts, which must have developed roots and healthy shoots. Dig holes in advance, place drainage in them, add complex fertilizer. Plant delenki, tamp a little and water the soil, mulch it. After planting, the bushes need to be watered abundantly until they take root.


Winter hardiness of kerria
Winter hardiness in Japanese kerrias is average. In the south of the country, where the climate is mild, the bush can be left without shelter for the winter. In conditions of middle latitudes and in the north of Russia, the plant is insulated. It is very important to cover the kerry where there is little snow in the winters.
The peculiarities of the color of the shrub give it a decorative look even in the winter months - the green shoots that give off yellowness contrast perfectly with the white snow.
Important! The pluses of Japanese kerria include its ability to quickly recover. Even if the shoots of the plant freeze in winter, they will quickly recover. But the bloom will not be as abundant.
The combination of yellow kerrias with other plants
Most often, kerria is used either as a hedge, or in a friendly neighborhood with other plants when creating mixborders. The plant looks great in combination with spring primroses (rhododendron, mahonia, etc.).
Kerria branches often break from gusts of wind, so as protection against possible unpleasant consequences, plant it next to powerful flowering shrubs such as bladderwort or spiraea.
Also, next to the kerria, you can plant luxurious irises, a wonderful buzulnik, which will perfectly harmonize with kerria in the fall during its re-flowering period.
This concludes the consideration of the features of growing yellow kerrias in the open field. Now you know about all the intricacies of caring for this beautiful flower. Good luck!
How kerria blooms
The shrub blooms in late May-early June, there are also late-flowering varieties. The positive qualities of the plant include a lush flowering extended in time - it lasts for 3-4 weeks. Depending on the weather conditions in the region, the duration of the flowering time of the bush may decrease or, conversely, slightly increase.
Sometimes, in especially favorable years, the bushes can bloom again. Although the second bloom will no longer be as abundant, it will still add some decorative effect to the garden.
The fruits of Japanese kerrias are small juicy drupes of dark brown color, obovate or hemispherical in shape, wrinkled 4.8 mm long. If you grow a shrub in the middle zone of Russia, then the fruits of the plant are not formed.
Important! Due to the fact that the Japanese kerria blooms in May, and its flowers resemble roses in shape, the shrub is sometimes called the "Easter rose".
Subtleties of care: feeding, watering, protection from pests
Kerria is an unpretentious plant that requires care solely for the purpose of maintaining a decorative appearance, and in order for it to be such, it is necessary to take care of a high level of health and grooming of the shrub. This can be achieved by following simple rules that will lead to the desired result.
In order for a plant to really grow healthy and beautiful, it is enough to follow a certain set of care measures:
- Watering. Kerria does not need abundant watering, it is enough to monitor the state of the upper soil layer: it should not dry out. Particular emphasis should be placed on soil moisture during dry periods and during the flowering of the plant. Water for irrigation must be warm and well-separated. During the period of frequent rains, it is advisable to reduce watering to a minimum.
- Loosening and weeding of the soil. After each watering, it is imperative to weed the area with growing kerry and thoroughly fluff the soil.
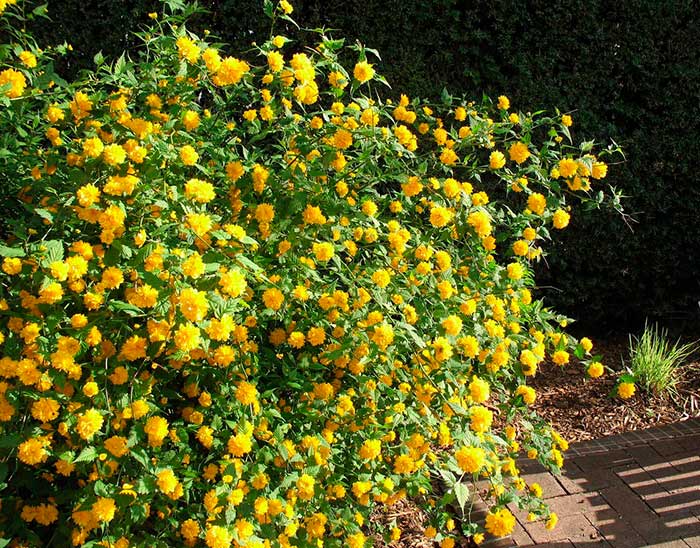


Kerrias need frequent feeding
- Top dressing. Kerria does not require a significant amount of fertilizer: it is enough to add mullein infusion (in a ratio of 1:10) or compost only after flowering.
- Pruning the plant. With the onset of the first days of spring, all dead, old broken branches are necessarily removed, and young ones are cut off by 1/4. As a result of such a preventive procedure, kerria will grow into a compact and at the same time very dense bush, and the flowering will be luxurious.
- Diseases and pests. Kerria is completely immune to both infections (of any type) and insect pests. At the moment, no recorded cases of the disease have yet been observed.
Conditions Needed by Carries
Kerria perfectly adapts to a wide variety of lighting conditions. This shrub will be an adornment of both sunny and light, and semi-shady, and even shady locations, where only white-flowering shrubs can compete with kerry in the effect of highlighting. The possibility of growing large trees even in the diffused shade without completely losing the ability to bloom luxuriantly can be explained simply: kerria begins a parade long before the bulk of the leaves bloom from the trees.But the intensity and abundance of flowering kerrias in strong shade is reduced compared to plants growing in open areas. In sunny southern places, the flowers are prone to fading. When choosing a place for planting kerrias, it is worth remembering that the plant does not like open and blown places, is not wind-resistant enough due to the fragility of the shoots, and will fully reveal its beauty only in protected areas.
The soil requirements for this shrub are also quite modest. Kerria is able to take root anywhere, but it achieves the greatest decorative effect on high-quality garden soils. Kerria japonica prefers moderately moist soils, it can grow even in dampness, provided that good drainage is laid. The main thing is that the soil is loose, loamy or sandy loam, not too fertile and not depleted. During planting, it is worth adding sand to heavy soil, organic and mineral fertilizers to infertile soil.
One of the main advantages of kerry is its resistance to contaminated environment. It can be used in urban landscaping, decorating areas near highways and other places with increased gas pollution.
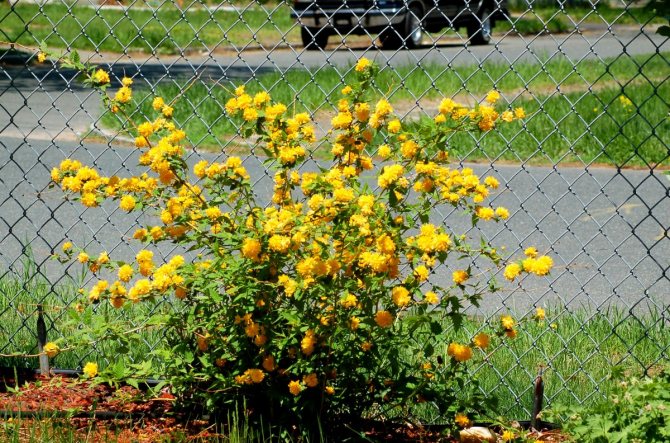


Japanese kerria (Kerria japonica).
Choosing a location for kerry and soil
The site for planting a plant is selected illuminated, but not blown through. It is advisable to create a light shade from the midday heat. In full shade, the bloom will be less abundant and colorful. Tall fruit trees and berry bushes will become a good neighborhood.
Kerria feels well in the company of other decorative representatives and low conifers. Grown as a natural hedge and for decorating mixborders.
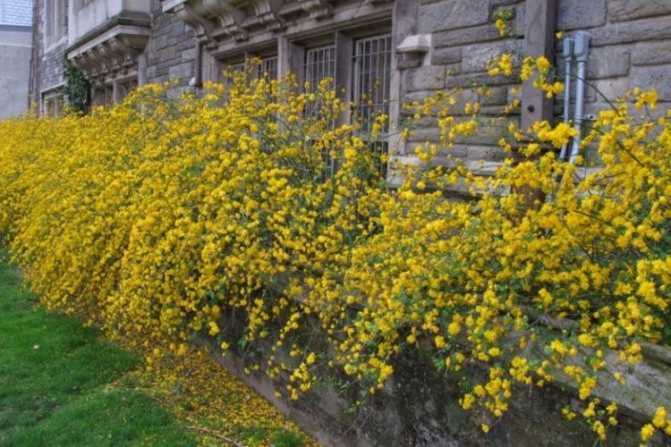


The close occurrence of groundwater is unacceptable, which leads to rotting of the roots and the death of plantings. Prefers loose loamy soil with good moisture and air permeability. The soil mixture is prepared by mixing: humus, sand, garden soil and leaf compost. The ratio is taken - 1: 3: 1: 1.
general description
Keria yellow was named after William Kerry, a famous collector of exotic plants. He was the first caretaker of the Ceylon Royal Botanic Gardens. Yellow keria is a representative of the rosaceous family, one of a kind. But the base species has hybrids and varieties, which makes it possible to choose a suitable hybrid for planting in your own garden.
Under natural conditions, the height of the shrub is 2.5 - 3 m, but there are also undersized specimens. Please note: when grown in a more severe climate, even tall bushes practically stop growing above 1 m.Even competent care does not help: the bush grows in width, not in height.
The Japanese rose blooms twice a year. First time in spring, abundantly, for a long time. On average, the flowering period lasts at least a month. The second time - at the beginning of autumn, there are fewer buds at this time. Over the years, the bush grows well in width - up to 3 m in diameter. Branches can be either erect or flowing. From spring to autumn, the stems are covered with large bright green leaves, similar to those of mint or raspberry. The leaves are smooth above, pubescent below. Thanks to them, the shrub looks beautiful even between flowering. In the fall, the foliage falls off.
Keriya has other names. Double-flowered varieties are called Japanese or Easter roses. They are really very similar to roses, and they bloom around the church holiday of Easter. Hybrids with simple flowers are more like buttercups, they are sometimes called buttercup bush. Most varieties have yellow flowers, but there are hybrids with white buds.
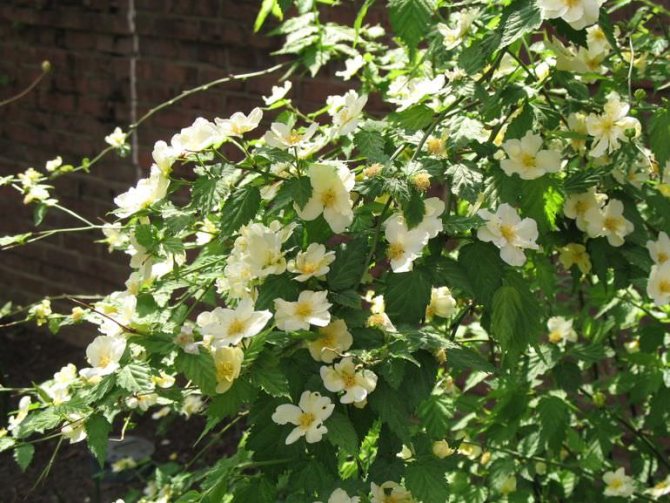


Varietal variety
Most often, the following varieties are grown in gardens:
- Pleniflora: grows up to 2 meters in height and 1.5 in width. Flowers are yellow with a diameter of 3.5 cm, double. The variety is not frost-resistant, therefore it needs shelter at low temperatures.
- Aureovarigata: can grow up to 1.5 - 2 m, a distinctive feature is long flowering, up to 3 months. Terry buds, yellow.
- Albiflora: the main difference between this hybrid is double white flowers, reaching a height of 2 m.
- Picta or Veriegata: compact cone-shaped bush, low (up to 1 m), with simple five-leafed flowers.
- Golden Guinea: reaches two meters in height, the color of simple buds is dark lemon. Externally, the five-leafed flowers resemble an old guinea coin, both in color and in size (6 cm).
- Captivity: yellow simple flowers with a bright shade adorn the shrub. Ideal for hedges due to its fast growth and abundance of young growth.
- Kin Kan: one and a half meter variety, grows compactly, on buds with 6 bright yellow petals.
- Albomarginata and Argenteomarginata: differ from others in edged with white foliage. Because of her, sometimes these subspecies can be perceived as sick. They grow rather slowly. The buds are simple.


Pleniflora


Aureovarigata


Picta or Veriegata


Golden Guinea


Captivity


Kin kan


Albomarginata


Argenteomarginata
Drop off location
When choosing a landing site for yellow keria, you should pay attention to the ground. Loam is considered ideal, although the plant can also be planted on sandy loam soils. Ordinary soil fertile garden soil with a good drainage system is also suitable.
You should also consider the following factors:
- illumination: it is best to plant bushes in partial shade, places near coniferous trees are perfect, they grow and bud in full shade, they burn out under direct sun;
- wind regime: they do not tolerate strong gusts, can be planted near a fence or a house, under a hill or in calm areas;
- space: when choosing a place, you need to take into account the volume of the shrub, for a single planting, a site with a diameter of up to 3 meters is allocated, with a compact (for example, to create a hedge), the seedlings are placed closer to each other.
These growing conditions are suitable for all varieties of keria.
Mr. Dachnik informs: how to grow kerria in the Moscow region
Special conditions must be observed when landing in the central region. They also apply to the Leningrad Region. Such requirements are associated with the peculiarity of the climate.
In late autumn, in dry weather, lay foam around the base. Cover with coniferous branches or dry leaves so that the shoots are slightly pressed to the ground. So that they do not straighten up, build a frame. It should be borne in mind that the shelter must be well ventilated. Therefore, holes must be left in it for air circulation.
In early spring, in cloudy but dry weather, remove the structure. First, remove the frame, then clean it of spruce branches and foliage. The bright sun can harm kerria, so at first it needs to be protected with a covering material. It can be purchased at the gardener's shop. Burnt shoots, of course, can be cut off, but then the flowering process will be disrupted.
Subject to the rules for planting and leaving, kerria begins to form buds earlier than other trees. Her flowering is colorful and abundant, the shrub will decorate any landscape design. It is not difficult to keep it in Russian gardens, it is enough to water, prune and fertilize in a timely manner. If you do everything right, no diseases and pests are terrible for the plant.
Diseases and pests
Kerria is one of the strongest decorative deciduous plants. When creating the necessary conditions for keeping it, insect pests and various infections are rarely affected.
In rare cases, a spider mite can begin to live on seedlings. This is due to mistakes in care: dry air, dust and dirt on the foliage, the presence of dry leaves in neighboring pots. You can destroy the pest with insecticides. For example, Fitoverm, Fufanon and others. To prevent damage in the room, it is recommended to install a humidifier, wipe the bushes with a damp cloth, and remove fallen greenery in a timely manner.
Shrub varieties
Kerria has several decorative varieties with simple or double flowers. The most popular among them:
- Kerria Japanese Pleniflora. Lush upright shrub. It blooms with small flowers up to 3 cm in diameter, externally resembling pompons. Flowers are located in the axils of the leaves one by one or in groups of 2-3.
- Kerria Japanese Picta, Variegata. A graceful low shrub, distinguished by unusual variegated leaves with white spots and a border. The flowers are simple, bright yellow.
- Keria Japanese Golden Guinea. The plant got its unusual name due to its large, simple flowers. With their size and color, they outwardly resemble a British gold coin.
- Kerria Japanese Albiflora. The peculiarity of this subspecies is small simple white flowers with five petals.
- Kerria Japanese varieties Simplex and Kin Kan are bushes with simple yellow flowers.
Reproduction methods
Keria is easy to plant with root shoots, layering and cuttings. Shrub seeds in the middle lane do not ripen.
The root shoots are separated from the mature bush in late summer or September. Young shoots take root well in a new place.
At the end of spring, you can bend the keriya branch to the ground, lower its middle into a pre-dug depression and sprinkle it with soil. For reliability, the twig is pinned to the ground with a wire staple. By the end of summer, the shoot will grow good roots underground, and it can be transplanted to a permanent place.
Lignified or green cuttings can be cut in April or June. The branch should have at least a pair of well-developed buds. The soil for cuttings is prepared from a mixture of peat, sand and humus. It is better to choose a bed in a shaded place. A film cover is installed over the cuttings to maintain high humidity. Planting is regularly watered, ventilated, loosened the ground. Young plants are transplanted to a permanent place next spring.
Keria in landscape design
This shrub can be used on the site as a tapeworm, as well as in compositions with other crops against the background of a green lawn or ground cover perennials and primroses:
- witch hazel;
- periwinkle;
- primroses;
- geycher;
- azaleas;
- rhododendron.
Other shrubs are suitable neighbors for keria:
- purple-leaved hazel;
- bloodroot.
The culture is planted as a hedge. Combine it with upward-facing conifers: thuja, juniper, host.


Keriya is an ornamental shrub that has rightfully taken a place of honor in the design of personal plots. It begins to bloom early enough, when many flowering crops are just opening their leaves. With good care, flowering is possible even in autumn. The plant is easy to propagate and does not depend on the growing conditions. And unlike many other horticultural crops, it practically does not turn white and is not damaged by pests.
Further video, after watching which you can find out more useful information about growing Keria on the site:






























