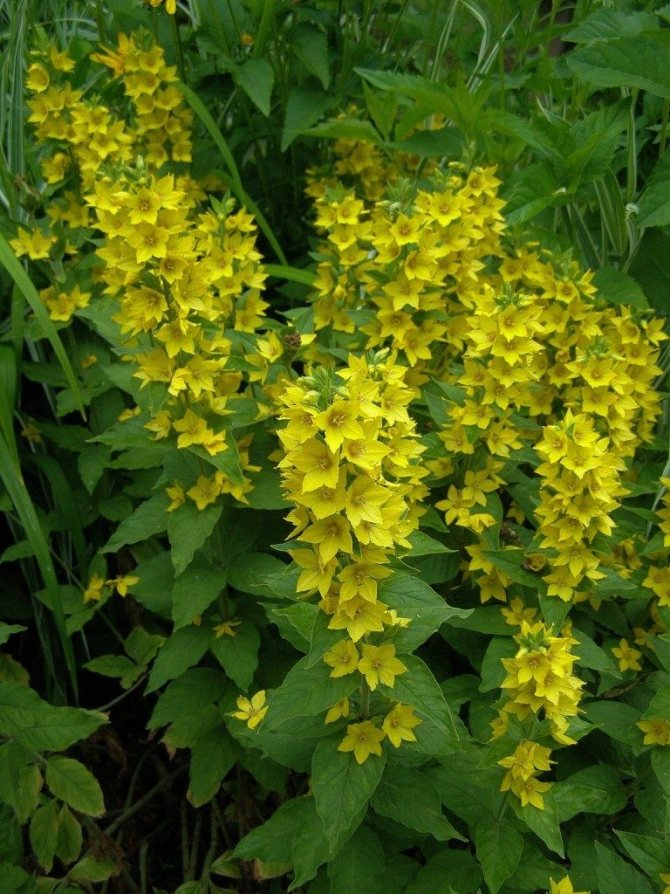
Basically it is loved for its pronounced healing properties, and it is also famous for its special decorativeness.
Loose worm grows for a very long time, and it also needs simple care, because it grows very quickly.
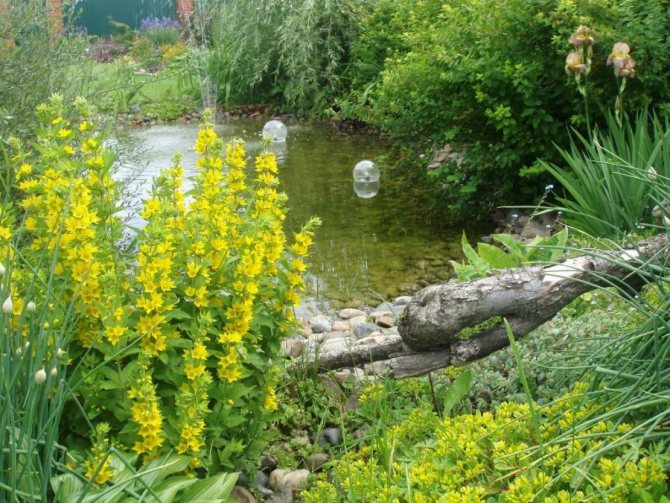
Such significant features made it an incredibly special plant for creating the future magnificent so-called rock garden, as well as other landscape compositions.
So, let's talk about how to create truly excellent conditions for a plant to grow.
- 1 Description of the Monet Werbeynik
- 2 Appearance and origin
- 3 Plant properties
- 4 Beautiful views of the Verbeynik monetchaty
- 5 Variety Aurea
- 6 Goldilocks grade
- 7 Growing and care
- 8 Planting Coinfoam Wormwood on a flower bed
- 9 Choosing a site for planting Moneta verbeinik
- 10 What soil will be the best choice for Monet Werbeinik
- 11 Reproduction of Monet Loafers
- 12 Growing from seeds
- 13 Vegetative propagation methods of a plant
- 14 Caring for the Verbeinik coin in the garden
- 15 Watering Verbeynik in the garden
- 16 Fertilization schedule
- 17 Transplant, pruning and winter
- 18 Plant in Landscaping
- 19 Why this plant is useful
Growing loosestrife from seeds
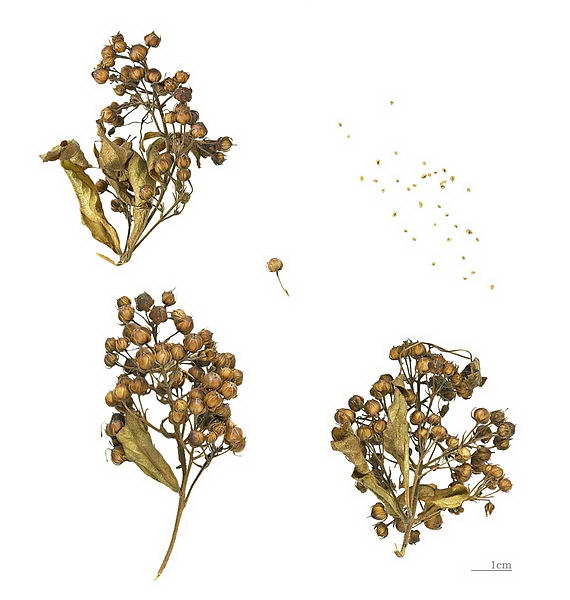

Loosestrife seeds photo
How to sow in the ground
- Sowing loosestrife seeds in open ground is carried out at the end of April.
- The seeds must first be stratified (keep them in the vegetable section of the refrigerator for 6-8 weeks).
- It is more convenient to sow before winter (approximately at the end of September): the seeds will undergo natural stratification, and friendly shoots will appear in the spring.
Dig up the area, remove the weeds, sow the seeds, covering them with a rake.
Growing from seed to seedlings
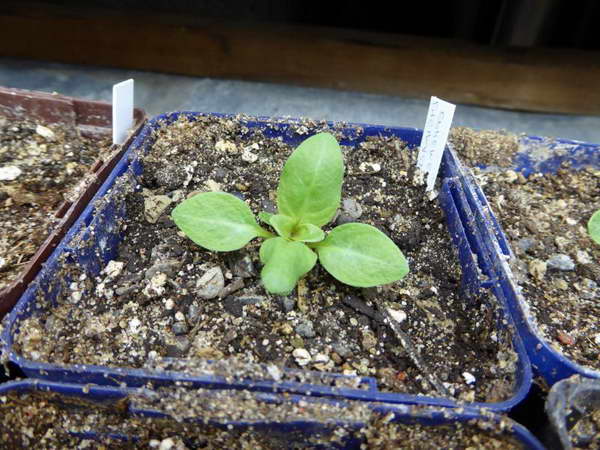


Loose leaf seed photo of seedlings
You can grow seedlings. Start sowing in March. You will need wide containers and a sand and peat mixture taken in equal proportions. Moisten the soil, spread the seeds evenly over the surface of the soil, only slightly pressing into the soil. Cover crops with foil or glass. Keep it cool (air temperature within 15 ° C) and bright ambient lighting.
Air the crops - it is necessary to get rid of condensation. Seedlings will appear in 1.5-2 weeks. Remove cover, water sparingly, and provide bright, diffused lighting. Dense shoots thin out or dive the plants into separate containers in the phase of 1-2 true leaves.
A couple of weeks before planting in open ground, start hardening the seedlings: take them out into the garden for several hours, each time increasing the period of time the seedlings stay outside. Transplanting into open ground is carried out with the establishment of real heat - from about mid-May.
Diseases and pests
The verbeynik is hardy and stable, it does not have a predisposition to any diseases that often affect green spaces. The main trouble that can befall such a culture is the attacks of aphids. This is evidenced by the stunted and unhealthy appearance of the plant. To cope with the problem will help drugs Biotlin or Antitlin, which are easy to purchase in a specialized store.


Verbeynik point is not predisposed to any diseases.
Another problem, which will have to be faced only in rare cases, is the attacks of weevils.They feed not only on leaves, but also on loosestrife roots and are activated at night, so it will be somewhat more difficult to deal with them. Insects will need to be collected regularly, and this should be done after sunset.
Vegetative propagation of loosestrife
The verbain grown from seed gives flowering after 2-3 years of growth. Basically, gardeners prefer vegetative propagation methods (root division, rooting of cuttings, transplanting root shoots), since flowering can be expected in the 2nd year after planting.
Dividing the bush
The procedure for dividing the bush is carried out in early spring or in the fall during transplantation. Dig up the bush, separate the roots, and then cut the mother plant apart. Please note that each section should have a well-developed rhizome and stems. Plant immediately so that the roots do not dry out.


The root process of the loosestrife photo
If the time for transplanting has not yet come, you can carefully dig out the basal processes separately without disturbing the main bush.
Cuttings
After pruning, a large amount of planting material is obtained - cuttings. Their length should be 10-20 cm. Rooting is carried out in spring or autumn. The cuttings are placed in water (it is good if you add a few drops of a growth stimulant) until the roots appear. Then plant in soil.
Loosestrife properties: harm and benefit
The healing properties of loosestrife
The common verbeynik has a fixing, analgesic, wound healing and hemostatic effect. However, traditional medicine pays no attention to this plant. At the same time, in alternative medicine, such a flower is used for internal bleeding and diarrhea, as well as in the treatment of non-healing and festering wounds, stomatitis, eczema and thrush for a long time.
This plant contains saponins, tannins, rutin, carbohydrates, silicic and ascorbic acid, so it is widely used in homeopathy. For the treatment of abscesses, the foliage and flowers of the plant are used; it is recommended to apply fresh leaf plates to the wounds. From the dried roots, a powder is prepared that has analgesic properties, as well as the ability to heal burns and cuts.
Looseweed infusion can stop internal bleeding. To prepare it, you need to combine 1 tbsp. freshly boiled water and 1 large spoonful of dried foliage. The infused and strained mixture should be drunk three times a day before meals, 1-2 large spoons.
Looseweed tincture is used to restore strength after suffering a serious illness. For its preparation, it is necessary to combine 1 tbsp. vodka and a couple of large spoons of fresh herbs. A well-sealed vessel is removed in a dark place for 3-4 days for infusion. The filtered tincture is taken 20 drops 3 or 4 times a day.
Tea is also made from this plant, which is used for headaches and colds. To prepare it, you need to mix 1 large spoonful of rosemary foliage, chamomile flowers and loosestrife herb. Pour the mixture with a couple of glasses of freshly boiled water. After a few minutes, the tea will be ready.
Contraindications
Means prepared on the basis of loosestrife can not be used for thrombosis, varicose veins, as well as people with increased blood clotting, high blood pressure, or suffering from sclerosis of the vessels of the extremities. If a child has a dry cough, then giving him a loosestrife is also prohibited.
Site selection and preparation
It is preferable to grow the loosestrife in a shaded area or even in full shade. The loosestrife species can be grown in an enclosed area and in a well-lit place. The purple loaf should be grown in an area flooded with sunlight.
The soil requires moisture-consuming, nutritious, loose, well-drained soil. Favorably close occurrence of groundwater.Types of loosestrife brush-colored, common loosestrife, monetarist loosestrife can be planted in reservoirs to a depth of 10 cm.
Clay soils are contraindicated.
Using
Used for group landings. Monet loam is used as a ground cover plant in sunny, semi-shady and shady places, where it successfully replaces the lawn. It can cover walls and stones, which is why it is planted in large rock gardens. The Aurea variety is also used as an ampelous plant for planting in containers.


Purple loosestrife (Lysimachia atropurpurea).
To decorate the shore of a reservoir, spotted, ordinary, cage-like loosestrife is suitable. Tall loosestrife can be used in shady flower gardens, near reservoirs of various sizes and types. They are especially appropriate near reservoirs decorated in a natural or landscape style.
Planting and caring for loosestrife in the garden
Soil preparation
Preliminarily (a couple of weeks before planting), add compost or rotted manure for digging. During planting, prepare planting holes according to the size of the root system, place seedlings, cover with soil, lightly compact the soil with your hands, water well. Maintain a distance of about half a meter between individual plants.
Growth restraints
Looseweed rhizome (especially speckled (brush-colored) and ciliated loosestrife species) can grow aggressively, oppressing other plants. It is necessary to limit the growth of this culture. This is not difficult to do. During planting, set the restraints: dig in pieces of metal or unnecessary sheets of slate to a depth of about half a meter.
Watering
The culture is easy to care for and won't give you much of a hassle. If the loosestrife grows in a wet area, it is practically not required to water it. Moistening the soil should be taken care of only during a prolonged drought.
Top dressing
During the growing season, the plant does not need feeding. It is enough to dig up the soil around the bush in late autumn and add humus or compost.
Pruning
At the end of flowering, cut off the wilted inflorescences. For species with erect shoots, root pruning (keep a height of about 5 cm).
Care
Plants do not need shelter for the winter. During the summer, they maintain a constant high soil moisture. In vertically growing loosestrife, at the end of flowering, the faded parts of the stems are cut off. In the fall, the stems are cut to the bottom and compost is poured onto the plants. They do not touch the stalks of the loosestrife, but the compost is also added. In one place they grow up to 10 years. Speckled, ciliated and especially brush-colored, which are dangerous to release outside the container, are crawling out, it requires an eye and an eye. The coin crawls along the soil surface, it is weak and easy to control.


Lily of the valley, or cage (Lysimachia clethroides).
Types and varieties of loosestrife with photos and names
The genus has more than a hundred species. Consider the most popular in landscape design.
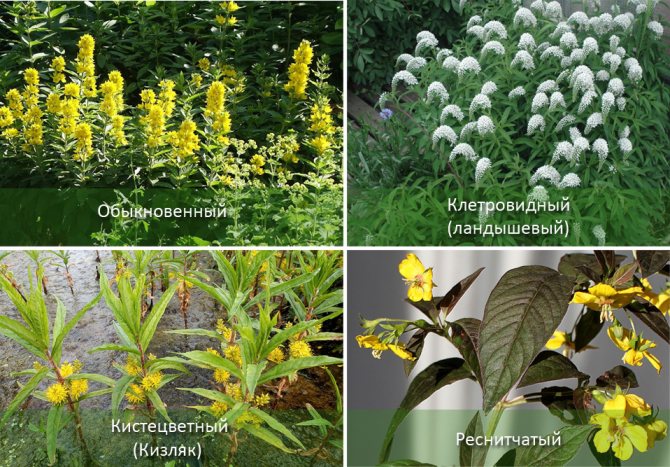
Common loosestrife Lysimachia vulgaris


Common loosestrife Lysimachia vulgaris photo
A herbaceous plant with erect stems 0.5-1 m high. In the natural environment, it is found on the continent of Eurasia and in North Africa, where it grows near swamps, along the banks of reservoirs, in forests. Leaf plates are oblong lanceolate, with solid edges, some are located opposite, some are collected in whorls. The surface of the leaf plates is smooth, the lower one is pubescent. Bell-shaped corollas are collected in a paniculate inflorescence located at the top of the stem. The color is orange, with a red-brown speck at the base of the corolla. The bloom lasts relentlessly all summer long. It is a honey plant. Can be grown in water, deepening by 10 cm.
Lysimachia nemorum


Lysimachia nemorum photo
It can be found on the territory of Europe along the banks of reservoirs, extending from the foothills to the subalpine belt. The height of the bush is only 30 cm.The leaf plates are large and wide. The inflorescences are solitary, sunny yellow, attached on long pedicels. Blooms in May, delighting for about 2 months.
Lysimachia thyrsiflora Lysimachia thyrsiflora
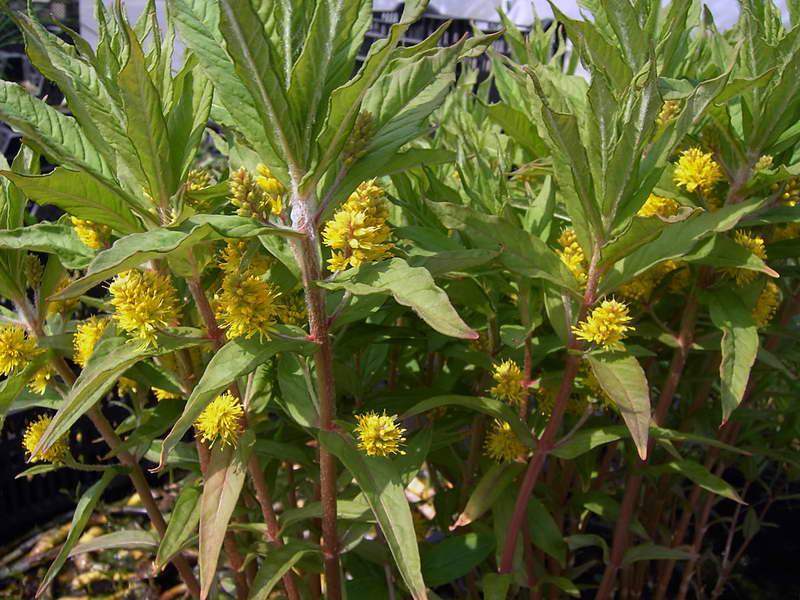


Lysimachia thyrsiflora photo
Stems are erect, powerful, reaching a height of 0.6 m. In the natural environment, it occurs along river banks and shallow waters. The leaf plates are narrow, sessile. In the axils of the leaves, racemose inflorescences are located, long stamens give them fluffiness. Corollas are yellow. Flowering begins at the end of May.
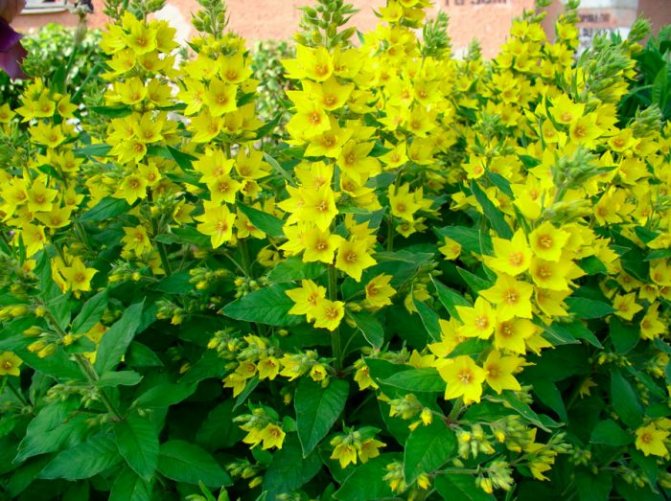
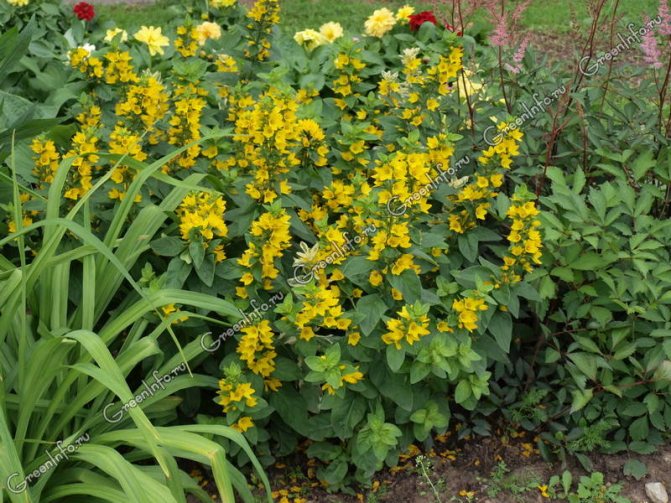
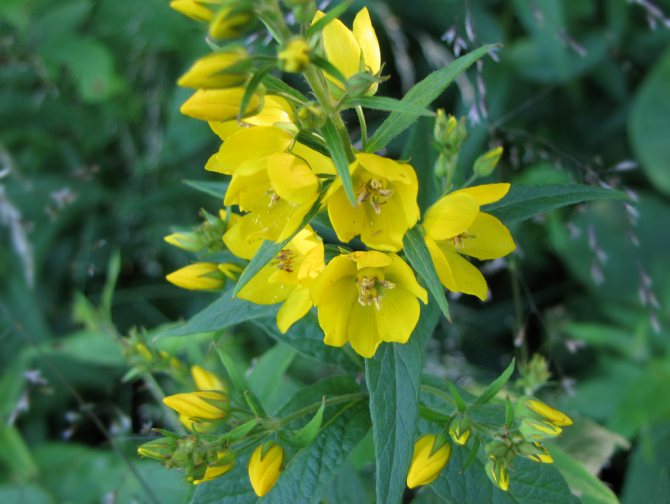
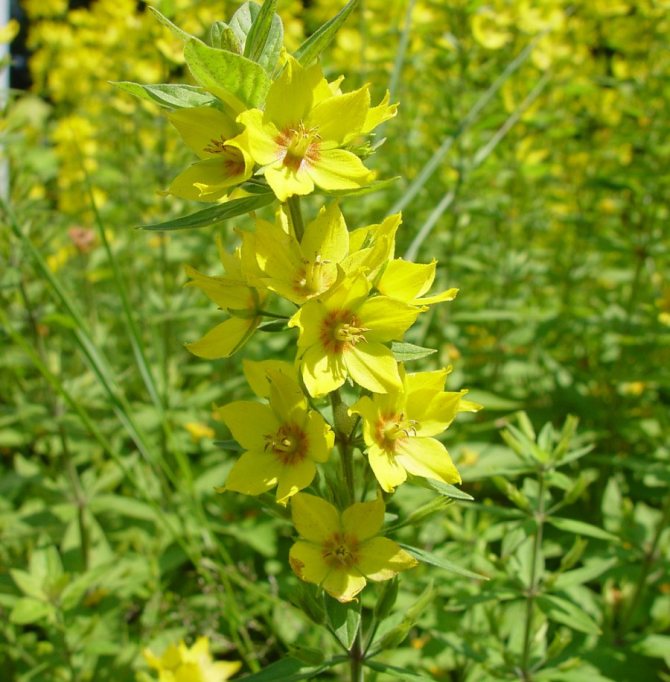
Loose leaf Lysimachia punctata
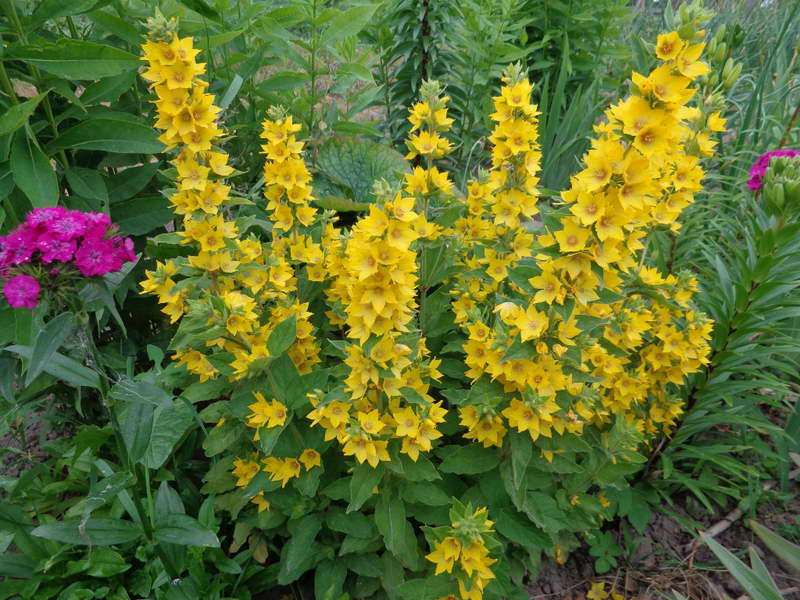


Loose leaf Lysimachia punctata photo
In the natural environment, it is distributed in the forests of Western and Central Europe. Erect shoots, the surface is covered with fluff. The shape of the leaf plates is broadly lanceolate. Leaves are sessile. At the tops of the shoots are flowers of a lemon-yellow hue. Flowering begins in late June and lasts about 4 weeks. Well-lit areas are preferred for cultivation.
The best varieties:
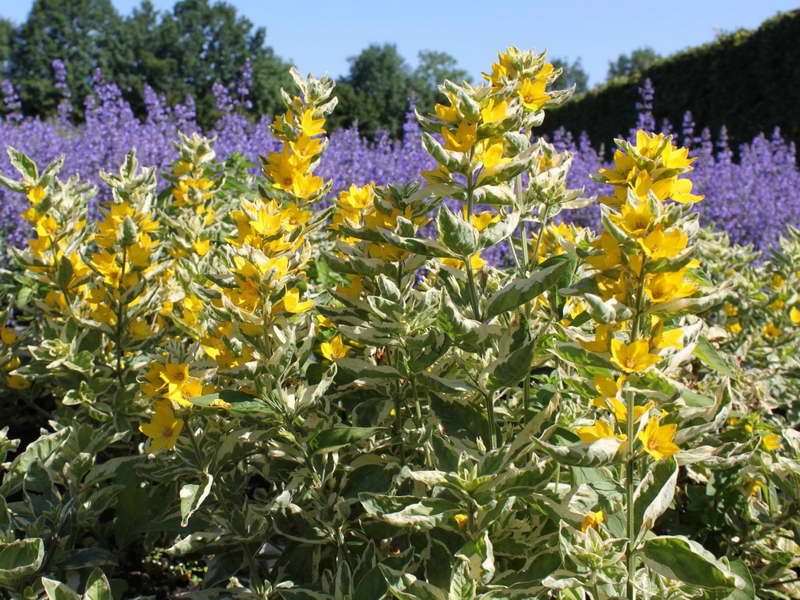


Verbeinik Alexander lysimachia punctata alexander photo
Alexander - leaf plates are bordered by a white stripe.
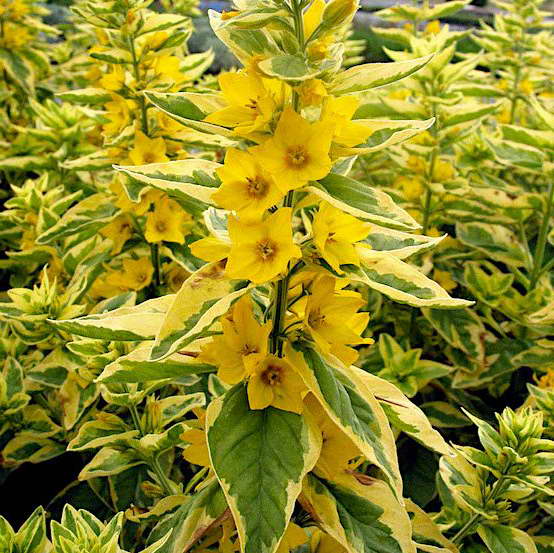


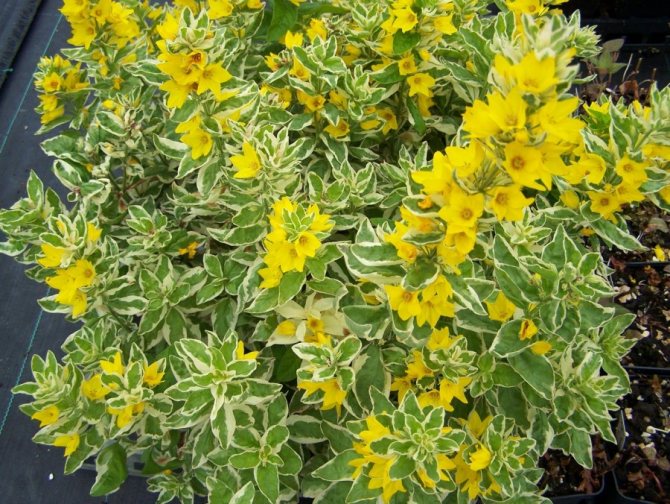
Verbeinik golden alexander lysimachia punctata golden alexander photo
Golden Alexander - green leaves are decorated with a golden border.
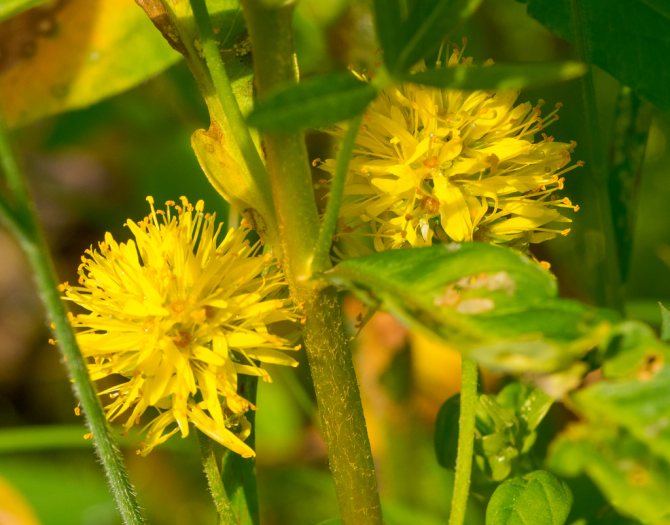
Lysimachia congestiflora
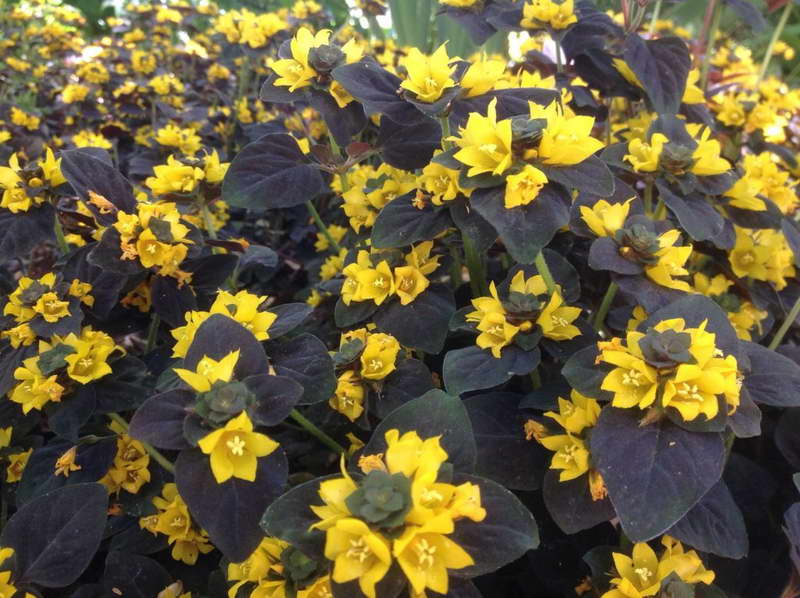


Lysimachia congestiflora Persian Chocolate 'photo
Originally from China, opened in 1992. A low bush with erect shoots. Leaves are oval in shape with a pointed tip. The top of the stem is crowned with several large corollas of a golden yellow hue.
Popular varieties:


Lissy loafer Lysimachia congestiflora Lissy photo
Lissy - leaves are bright green, inflorescences: spherical whorls of a yellow hue.
Outback Sunset - dark green leaf plates are decorated with a yellow stripe. The flowers are yellow.
Persian carpet - leaf plates are large, dark green in color, veins are highlighted with a reddish tint. Flowers are yellow.
Persian chocolate - golden yellow inflorescences. The leaves have a purple hue.
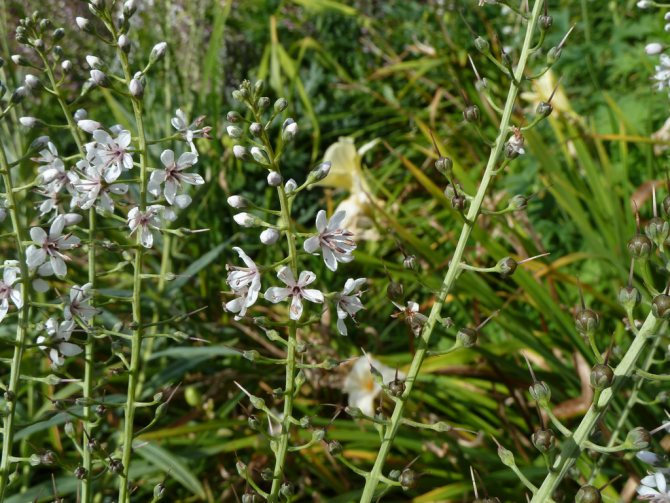
Lily of the valley or cage loosestrife Lysimachia clethroides
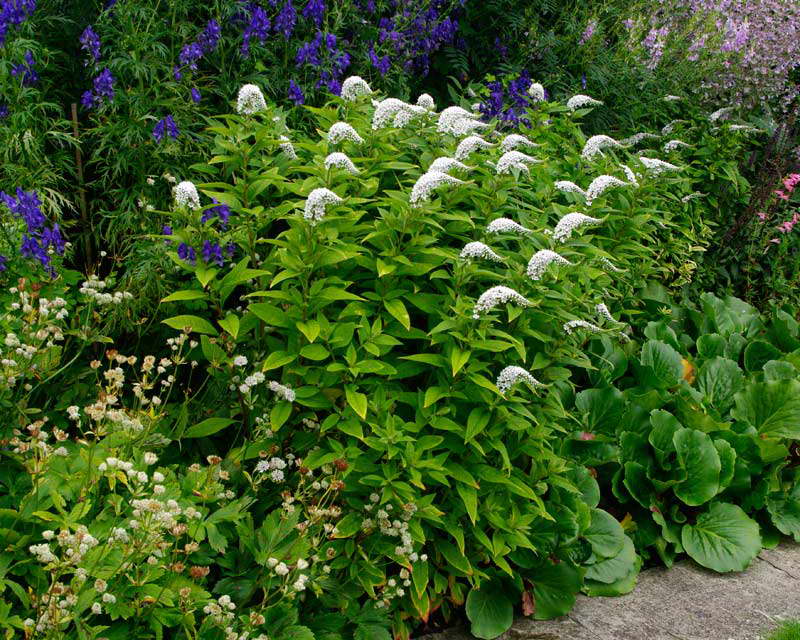


Lily of the valley or cage loosestrife Lysimachia clethroides photo
The similarity with lily of the valley is manifested in the structure of the root system, but the loosestrife has thicker roots. The stem height is 20 cm, the spike-shaped inflorescence adds about the same. Stems erect, pubescent. Small snow-white flowers gather in a dense spike inflorescence. The flowering period starts at the end of June and lasts about 20 days.
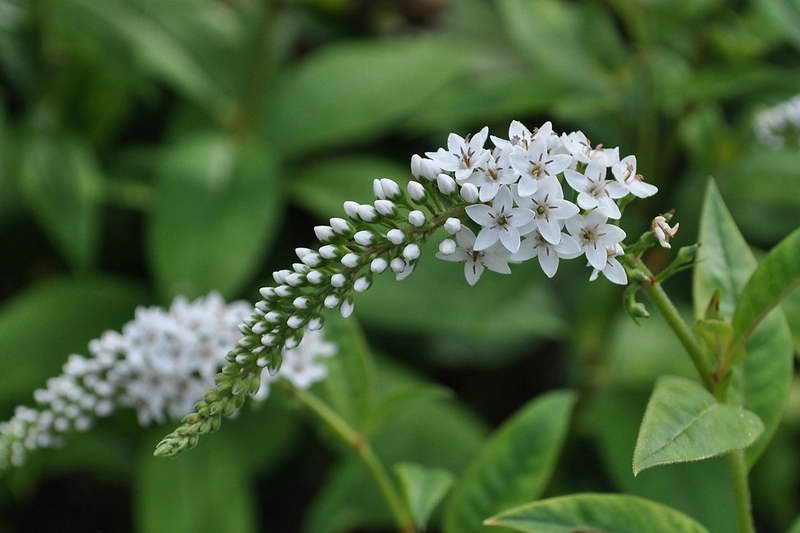


Verbain cage or lily of the valley Lady Jane Lysimachia clethroides 'Lady Jane'
Lady Jane - bushes 60-90 cm high, blooms in late summer.
Geisha is a variety with variegated leaves, their edges are decorated with a cream-colored border.
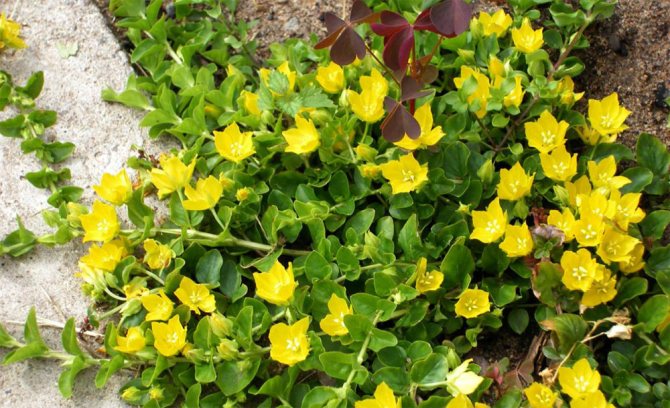
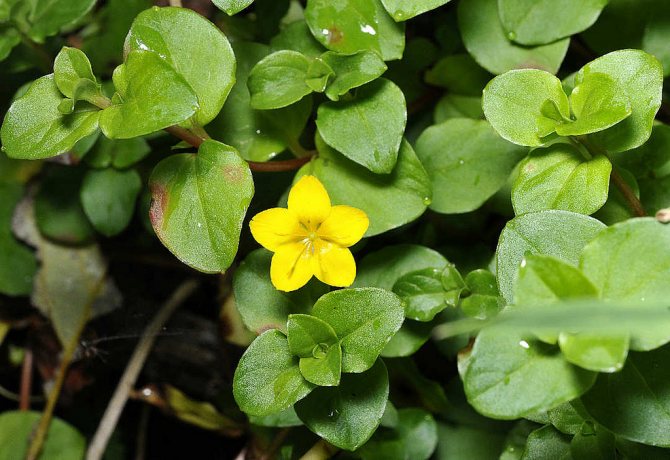
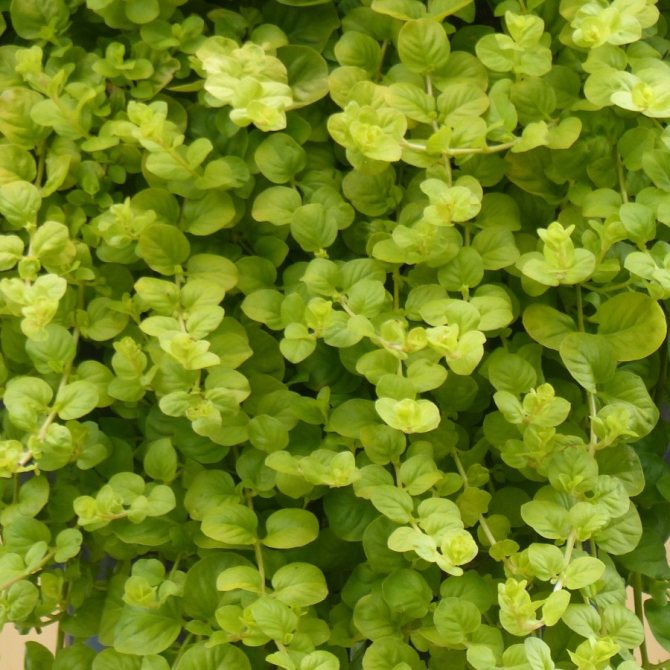
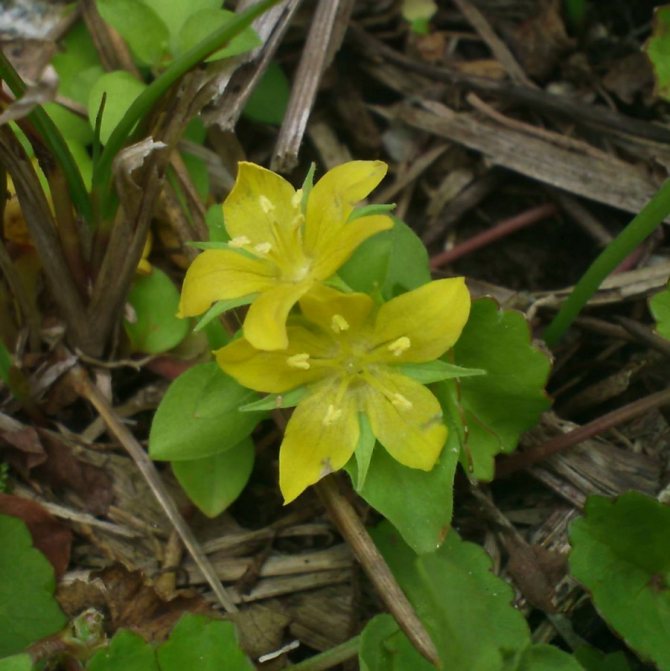
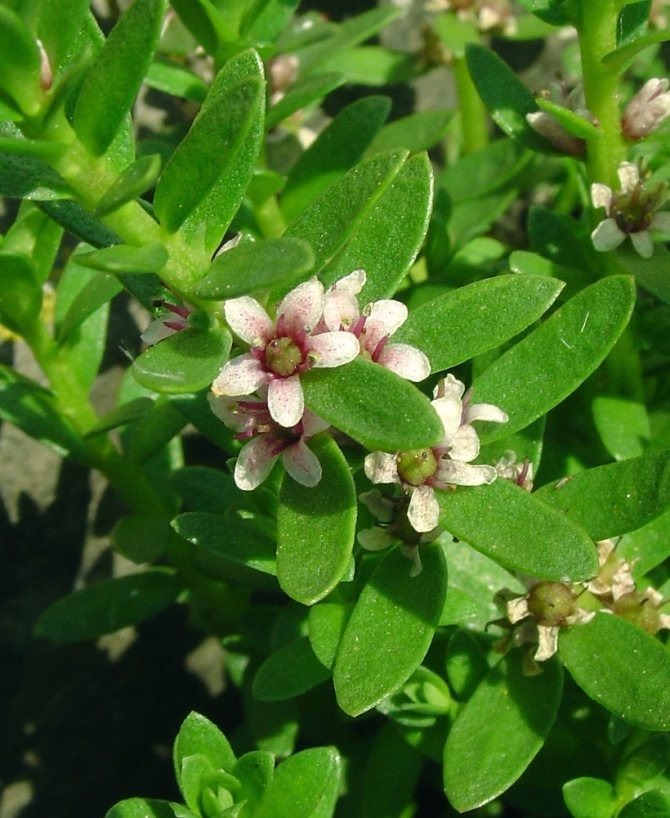
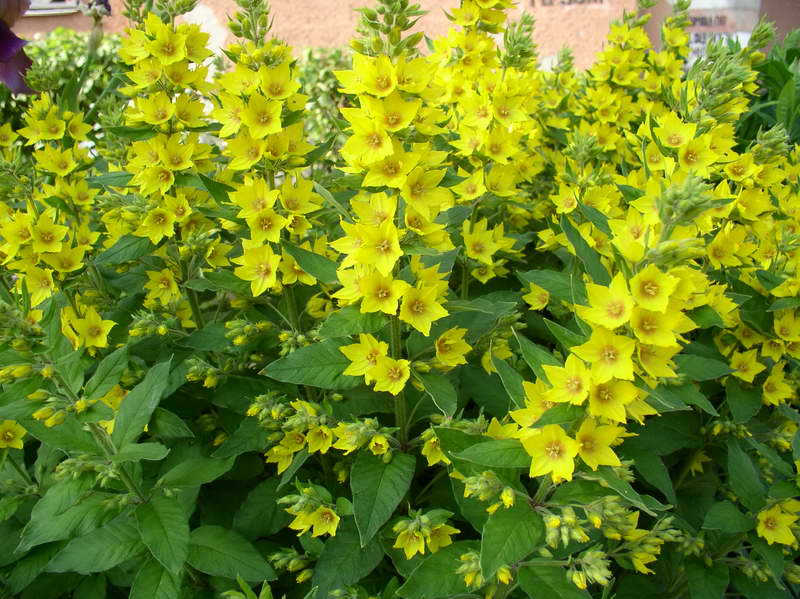
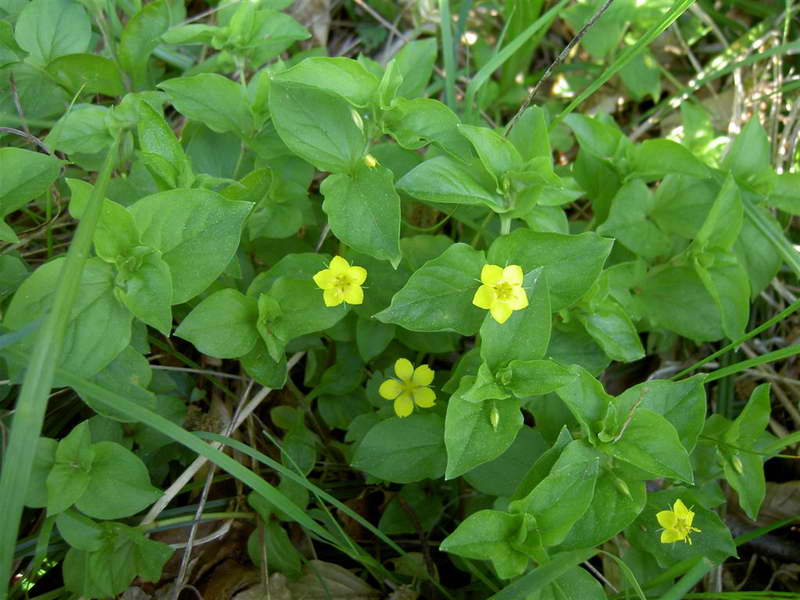
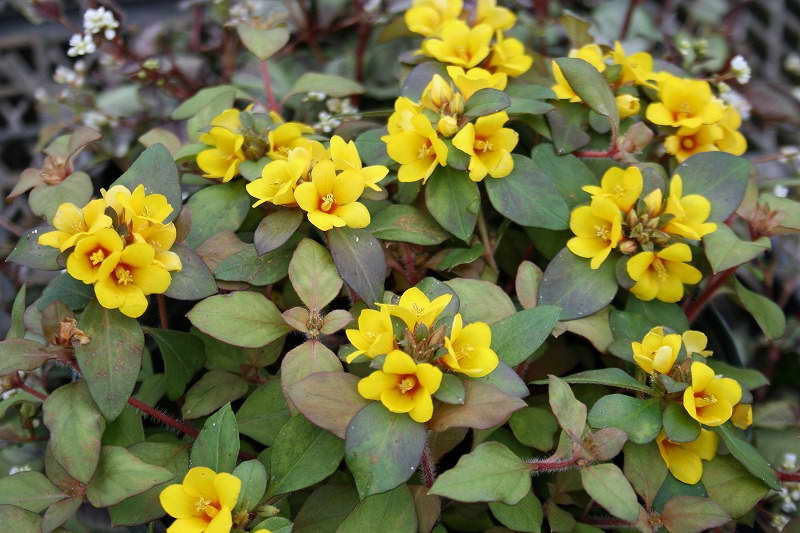
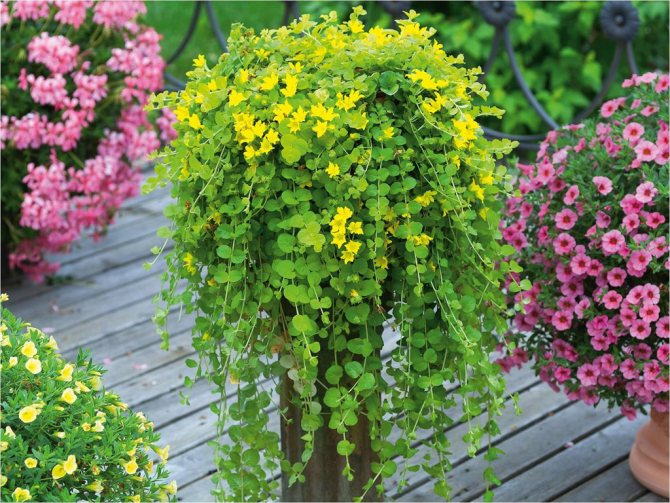
Loose loosestrife, also known as loosestrife, or meadow loosestrife, meadow tea Lysimachia nummularia
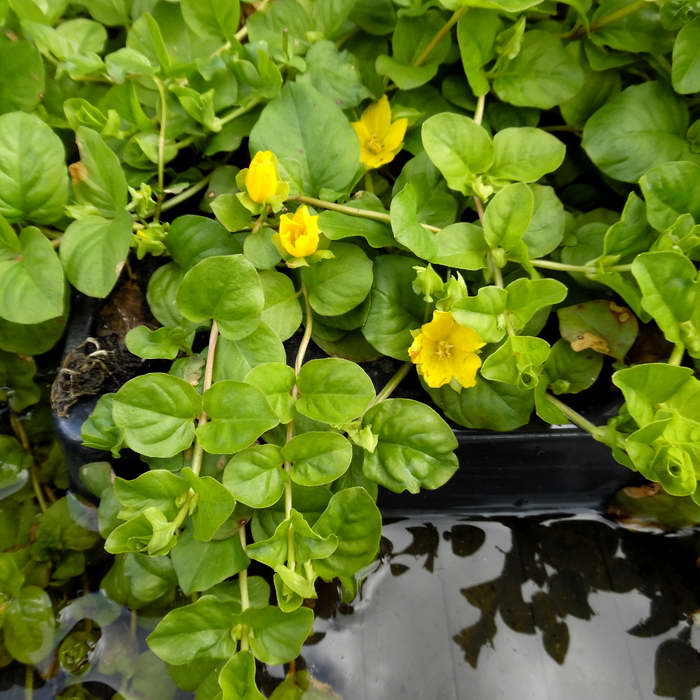


Loose-leaf monetar aka loose-leaf-coin or loose-leaf meadow Lysimachia nummularia photo
Under natural conditions, it is found in Europe, Japan and North America. Habitat: shady groves, bog edges, edges of reservoirs, floodplain meadows.
Grown as a ground cover: recumbent stems extend 30 cm. Creates a continuous coverage on level ground and on steep slopes. Small oval-shaped leaves cover the stems abundantly. Single flowers appear in the leaf axils. When grown in a sunny area, the flowering period begins at the end of May, in shade - a little later.
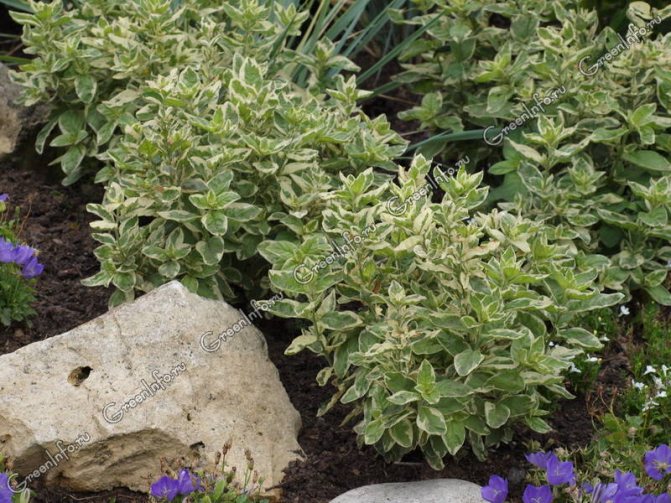
The most popular is the Aurea variety - green-yellow leaf plates. Frost resistance is lower than that of the original species; it is advisable to sprinkle with dry leaves for the winter.
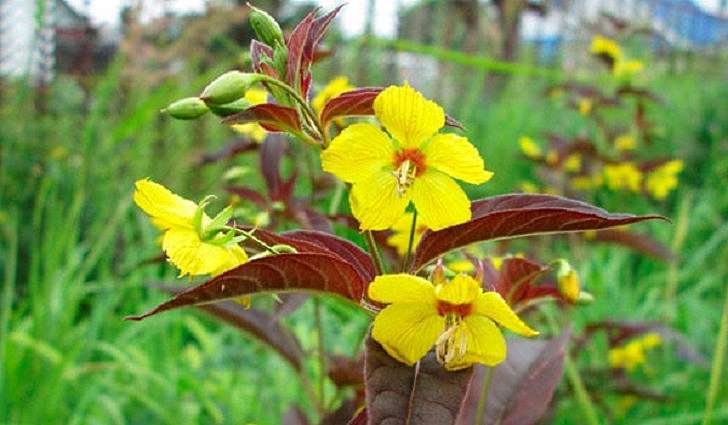
Purple loosestrife Lysimachia purpurea aka ciliated loosestrife Lysimachia ciliata
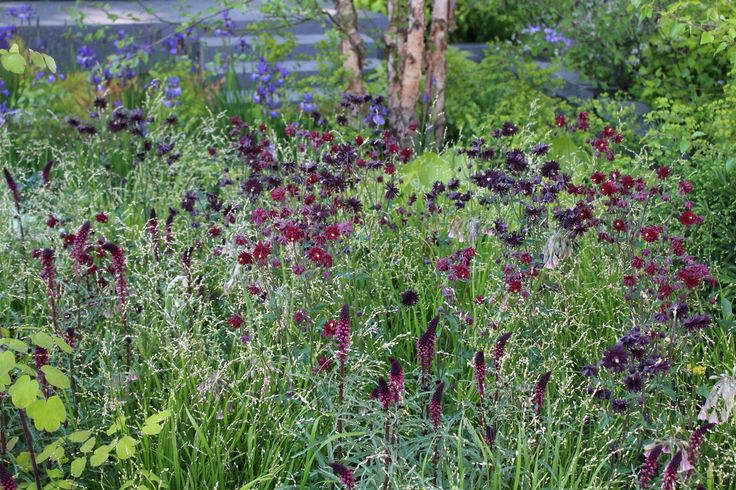


Purple loosestrife in landscape design in combination with aquilegia Lysimachia atropurpurea 'Beaujolais' and Aquilegia vulgairs var. stellata ‘Black Barlow’ photo
A bush with erect stems about 45 cm high. The species is common in North America. The leaf plates are wide-lanceolate, arranged in pairs, have a wine-red tint. Inflorescences are loose, they are located in the leaf axils. Corollas are sunny yellow.It is preferable to grow in areas with bright sunlight. Flowering occurs at the end of summer.
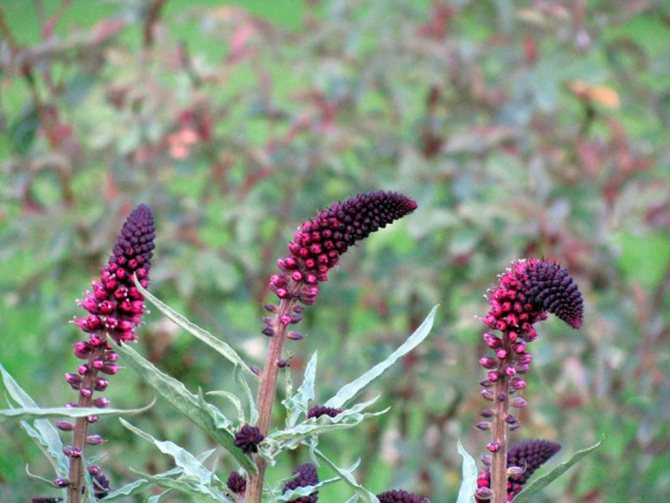
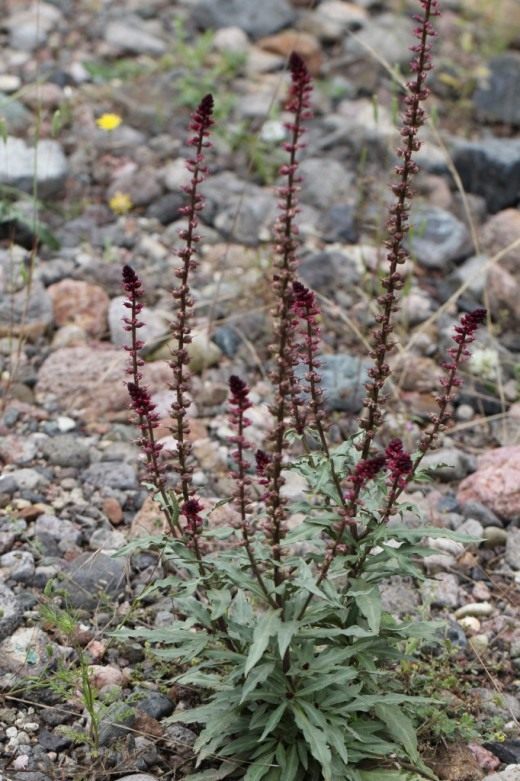
Lostweed black-purple Lysimachia atropurpurea
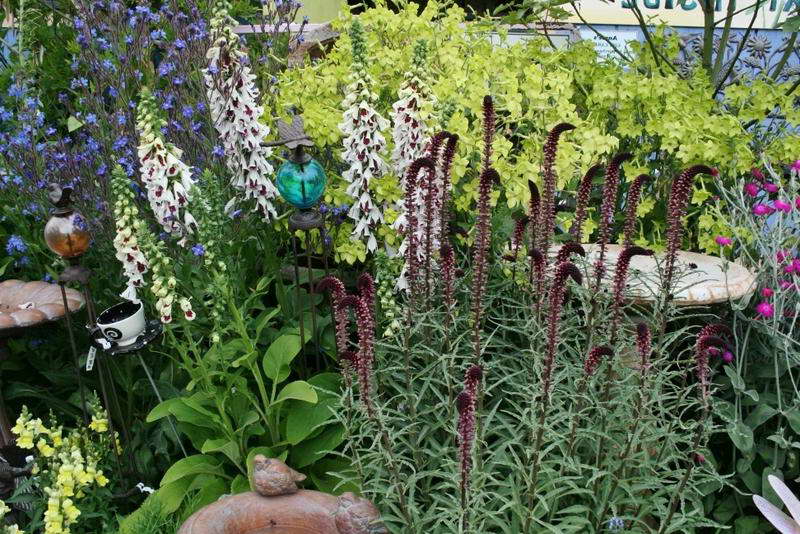


Lostweed black and purple Lysimachia atropurpurea in landscape design photo
Originally from Greece. The stems are erect, the height varies from 45 cm to 1 m. The leaf plates are oblong, the edges are slightly corrugated (this is better seen in young leaves). Graceful spike-shaped inflorescences consist of a large number of small eggplant flowers, almost black. Flowering begins at the end of July.
Beaujolais is the most popular variety with dark purple corollas.
Lost weasel ephemeral Lysimachia ephemerum
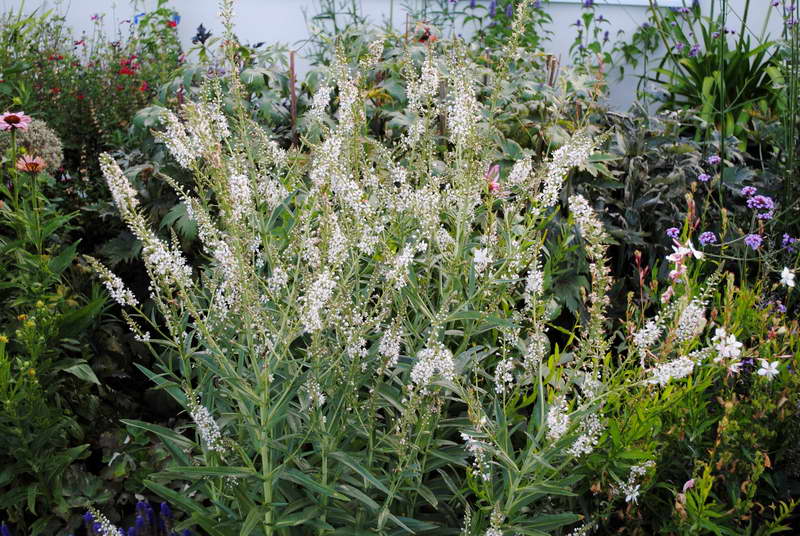


Ephemeral loosestrife Lysimachia ephemerum in landscape design photo
Found in southwestern Europe. The height of erect stems is 0.9 m, the bush grows rapidly in width. Small flowers in spike-shaped inflorescences begin to bloom at the end of summer. Combines very nicely with veronicastrum.
About coin loosestrife more
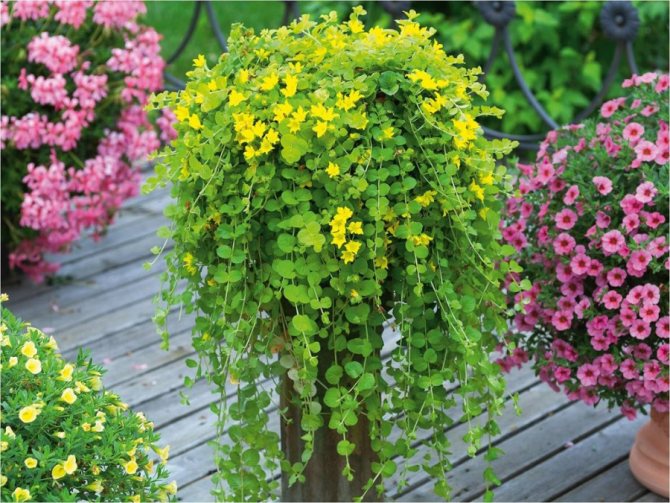
Why did we decide to dwell in more detail on this particular variety? It is this plant that attracts the most attention thanks to new varieties such as Aurea (cover photo). The plant has a unique ability to float onto the slopes, that is, the plant forms a carpet not only on flat or hilly surfaces, but is also able to create a beautiful framing on fences, retaining walls, and any vertical surfaces.
It is a perennial, the stems are recumbent, adjacent to the surface, the leaves are also very attractive, opposite ovals on short petioles. The plant blooms in June or later (it depends on the degree of illumination of the area) with flowers the same size as the leaves. Flowers appear one at a time in the axils of coin leaves. Its natural habitat is areas with variable lighting, with difficult water conditions (river banks, woodlands, meadows).
Given this history, the plant is extremely unpretentious and adapts to a variety of conditions: it can grow both in the shade and in partial shade, it is resistant to drought and at the same time tolerates prolonged flooding. It is extremely easy to recover from physical damage - for example, when trampled (which means that the plant reproduces quickly and easily).
Gold varieties
Varietal varieties ("Aurea", "Goldilocks") require more delicate handling, but not much. It also tolerates light trampling well and can grow in difficult soils. However, it is best to plant the plant in moist, well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. In summer, care must be taken to ensure that the ground does not dry out. The plant can be planted in partial shade, but the golden hue of the leaves will be brightest in the sun. Reproduction, like all lysimachia, is very simple. Seeds are sown in containers in the spring; you can transplant them into open ground both in early summer and in autumn.
The plant can suppress other crops. The leaves can be affected by rust, but, as a rule, serious problems with diseases and pests do not arise.


Lysimachia mint Aurea in landscape.
Verbeinik in landscape design
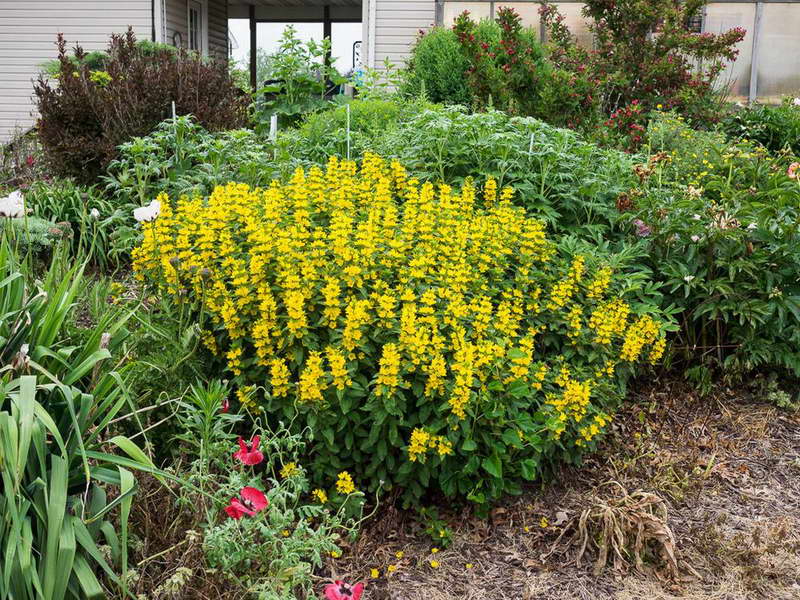


Verbeinik dot in landscape design photo
This unpretentious perennial is widely used in landscape design. Most species will be a wonderful decoration for shady corners of the garden, where sunny yellow inflorescences will give liveliness and warmth. The company can be astilbe, ferns, bells.
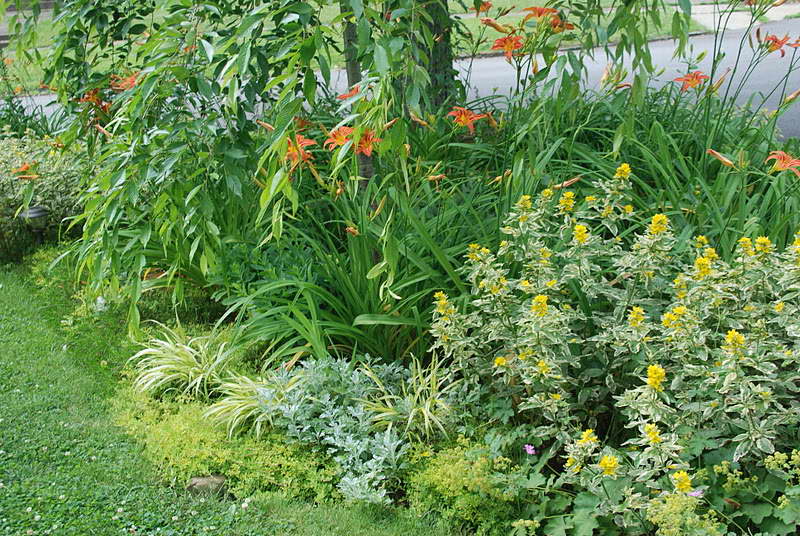


Verbeynik with daylilies on a flower bed photo
Also, loosestrife is used for framing borders, decorating ponds, planted on alpine hills, in rockeries.
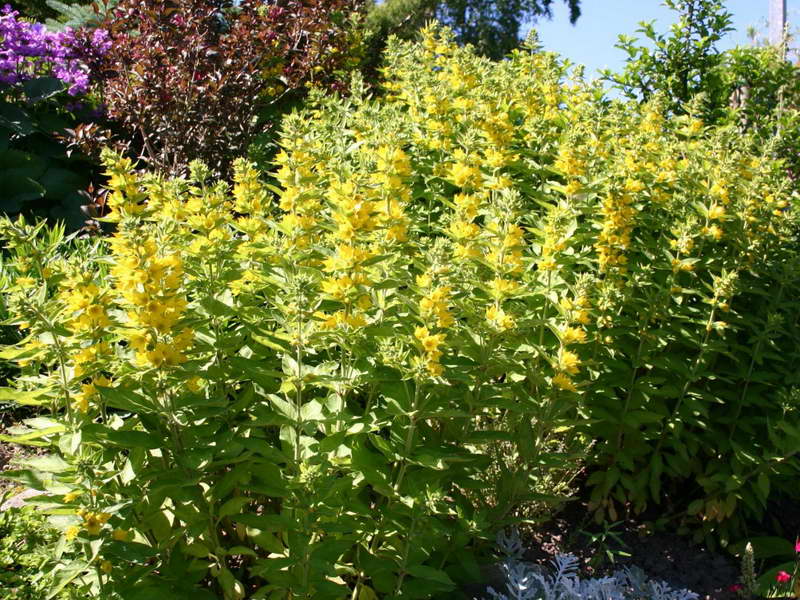


Verbeynik in the garden photo
Species and varieties with tall, erect stems form bright lush bushes that look self-sufficient in a solo planting. They are used as bright "marks" of the borders of flower beds, demarcation of the territory.
You can make beautiful compositions by combining loosestrife with conifers.
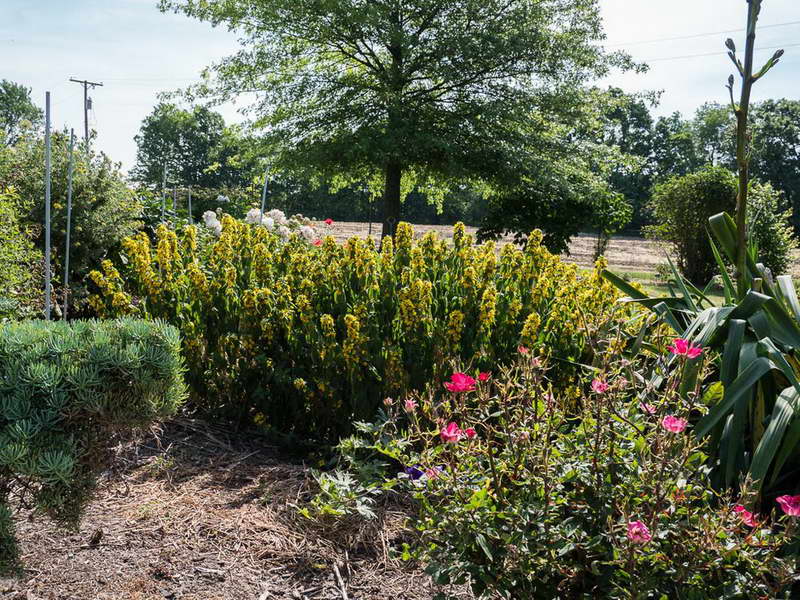


Verbeinik in landscape design photo
Creeping forms are planted in high flower beds, alpine hills; in hanging pots for decorating verandas, balconies, gazebos.
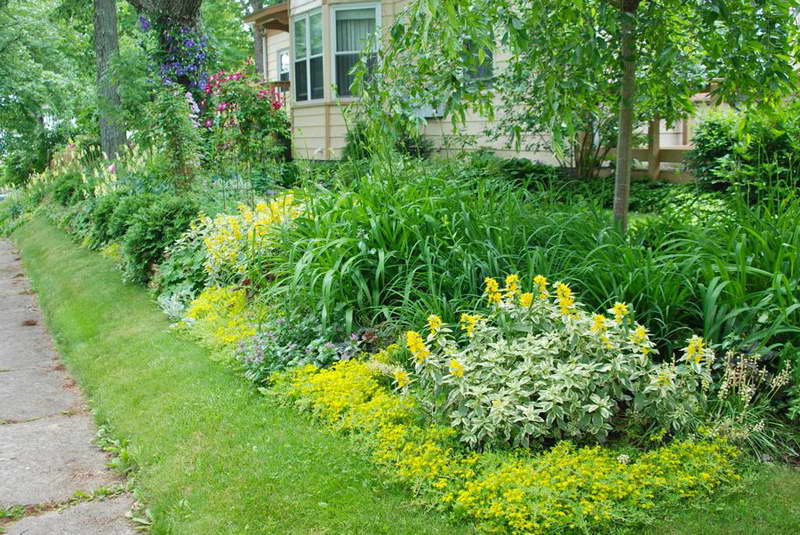


Verbeinik in garden design photo
Monet loam goes well with such ornamental deciduous plants as sedge, badan, rogersia, groundwort, hosta, red-leaved heycherella; combine with phlox, dwarf irises.
Why this plant is useful
Officially, Monet Verbeynik simply does not belong to any number of different medicinal cultures. However, this does not prevent the active use of Monet Verbeinik in folk medicine.
Flowers and foliage itself are used to brew a simple herbal tea with very pronounced antiemetic and antidiarrheal properties.
Decoction for the stomach
There is also a huge experience in the use of a decoction from the aboveground region of Verbeinik monetchaty in the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the stomach.
Tincture for wounds
The herbal tincture of loosestrife is also used externally.
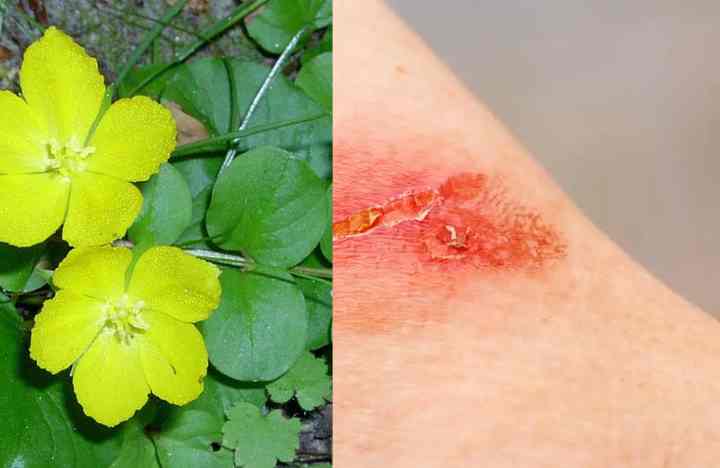

With the help of which various purulent wounds are treated, as well as relieve inflammation in acute rheumatism, alleviate the symptoms of hemorrhoids, reduce swelling in various bruises.
Cold tea
The so-called vitamin tea is prepared from Monet Verbeynik, it is used for prolonged coughs and colds. And also due to the presence of ascorbic acid in the plant, the flower is considered an immunomodulator.
By planting this plant in your garden, you will thereby acquire an unpretentious flower. It will delight you and bloom very nobly. In addition, you can brew yourself an excellent tea to raise your well-being and mood.
Where the loosestrife grows
Meadow tea is a typical European inhabitant. In Russia, it is distributed from the North Caucasus to the Kola Peninsula and from the Kaliningrad region to the Altai Territory. To the east of the Yenisei it is found in single specimens as an invasive plant.
The wild-growing loosestrife grows everywhere, but it forms more lush clumps in the depressions of the relief, where there is a little less sun and a little more water. Prefers floodplain meadows, small ravines, banks of ponds and swamps. Cultivated forms require a little shading.
Loose leaf - description of the plant
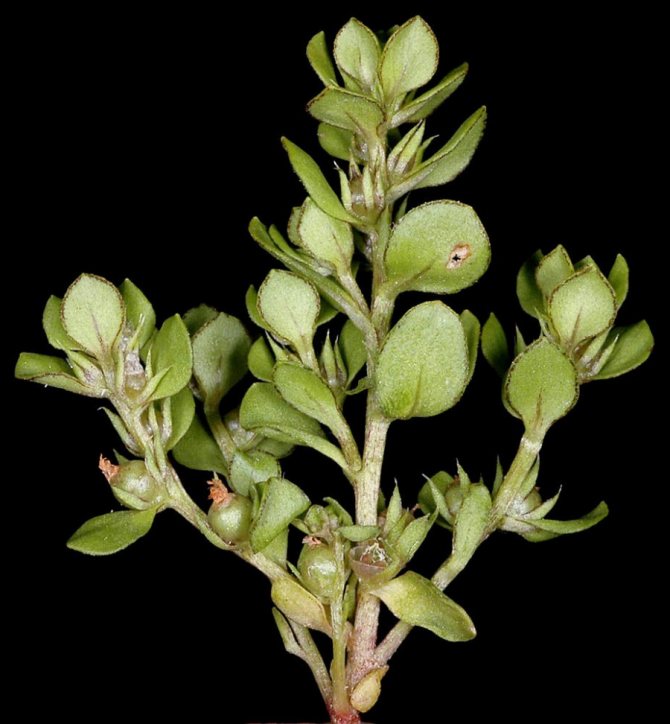
The most noticeable morphological feature of this perennial herb is its long creeping shoots, dotted with "ears" - paired opposite leaves. These leaves are almost round, for which the plant received the name "coin loosestrife" (it is allowed to write "monetary loosestrife").
Its Latin name is Lysimachia nummularia. The family name Lysimachia was given to loosestrife in honor of Lysimachus, one of the commanders of Alexander the Great, who, according to legend, first found him. The specific name is derived from the word "coin" - "nummulus". And among the people, the plant is known under the names of meadow tea, penny grass, nutlet, lawn. For its ability to quickly seize territory, the loosestrife was nicknamed "snake root".
The stems of meadow tea reach a length of 50-60 cm. They are light green, almost yellow, and are clearly visible in the foliage. From a distance it looks like canapé skewers, studded with kiwi fruit pieces. They lie on the ground, spreading in all directions from the center, and if a plant is rooted on a cliff, then picturesquely hang from it.
For a more complete botanical characterization, it is important to note that:
- stems, leaves and even petals are dotted with small dark glands;
- axillary flowers, on long pedicels, cover the middle part of the shoot;
- the plant is well adapted to wintering together with leaves.
Verbeynik is self-fertile and generally does not reproduce well by seed. This must be taken into account when growing it in garden plots and when harvesting medicinal raw materials.
Outdoor cultivation
It will not be difficult even for a beginner to grow a culture, since the plant takes root easily and quickly.
Seat selection
To breed loosestrife, you need to stop the choice in a shady place with moist, nutrient-rich soil.
Ground requirements
In the presence of infertile soil, equip it with a complex of mineral fertilizers before planting. The main condition is a very moist, moist soil with good drainage. Do not plant a crop on clay soils.
Seed preparation
To grow healthy loosestrife bushes, you must first prepare the planting material by stratification - hardening the seeds in the cold at temperatures of 8-10 degrees for 1-2 months.


Landing scheme
The loosestrife planting is carried out in the spring according to generally accepted rules and involves the following actions:
- Take small boxes, fill them halfway with a mixture of peat and sand.
- Sow the seeds, leaving a gap between the units of 2-3 cm.
- Sprinkle on top with soil mixture 0.5-1 cm.
- Close the containers with glass and send them to a place where it is warm and light.
- After 2 weeks, seedlings are formed, the shelter must be removed immediately.
- Dive when 2-3 true leaves are formed.
- A week after picking, start hardening the seedlings by taking them to fresh air for 2-3 hours.
- Hardened seedlings can be planted in a flower bed. To do this, make holes, observing the distance between them 40-60 cm, then place them in the holes and, sprinkle with soil substrate, lightly tamp.
- Moisten and loosen the soil.
In the fall, you can plant a culture with cuttings or shoots. The ideal time for disembarkation is September.
Growth restraints
Verbeinik forms a powerful root system that seeks to capture most of the territory. Therefore, to preserve the beauty of the flower garden, its growth will have to be regularly limited by removing excess shoots. You can also dig in restraints, which can be slate, brick, stone, buried 20 cm.


When cultivating a crop, it is imperative to prevent the spread of roots over the sites.
Characteristics of a perennial flower - loosestrife
The Latin name is Lysimachia. Russian transcription - lysimachia.
Under natural conditions, it grows in almost all temperate regions of the globe. The genus has more than 100 species, some of which grow on the territory of Russia.
According to one of the versions, the generic scientific name comes from the name of Lysimachus, the commander of Alexander the Great - earlier it was mistakenly believed that it was he who discovered this plant. Another version says that Dioscorides described one of the types of loosestrife and called it "lisi-macheyos".
According to botanical characteristics, loosestrife is a herbaceous perennial from the primrose family, which has an erect, pubescent, leafy stem, reaching a height of 130 cm. Some species reach 150 cm in height. They are not suitable for creating rocky slides, on which it is better to grow undersized species with creeping shoots. Moisture-hungry loosestrife is best planted near water, in a ravine and swamp. Snow-white small flowers are collected in a spectacular dense spike-shaped inflorescence up to 25 cm long, pointed and slightly curving at the end. Lysimachia blooms from late spring to mid-summer.
Choosing a landing site
The plant thrives on shady damp areas, near water and under trees, but does not like clay soils. However, it grows well in the sun, first of all it is spotted loosestrife (ordinary). Without a transplant, the perennial feels great for more than 10 years. Moreover, absolutely does not need any additional feeding or special pest control, does not get sick
... The only enemy of the bushes is different types of aphids, but she is also unable to harm him too much. Although sometimes the plant suffers from weevil larvae, which gnaw at the roots. Also, the bushes are not afraid of scythe and trampling.


Pharmacological properties


Due to the content of numerous biologically active compounds, especially the presence of flavonoids, the coin loosestrife exhibits antacid, antibacterial, antiseptic, hemostatic, astringent, expectorant and antipyretic effects.
The raw material is grass (aboveground part), harvested in the flowering phase (in June - August), which is simply harvested by hand, since it is easily torn out of the ground along with the roots. Large roots are cut off with the ground, and leafy stems are cut into pieces of 20-30 cm in size. Raw materials are dried in the shade on paper or cloth, preferably on grates or in dryers at a temperature of + 40 ° C. At the end of drying, the stems should crunch, not bend. The finished raw materials are stored in cloth bags or paper bags for 2-3 years. Grinding into powder is carried out only before the manufacture of medicinal forms (infusions, decoctions).
Tea "sausages"


The leaves and flowers can be used to make a medicinal tea that does not contain caffeine. This drink made from dried unfermented meadow tea has a specific taste and a slight greenish tint. Therefore, for the preparation of daily tea, it is better to use the fermented aerial part of the coin loosestrife.
To brew fermented meadow tea, take freshly harvested leafy stems, cut into 5-8 cm pieces. 10-15 such pieces are twisted into "sausages", rolling between the palms until the juice is released. Ready "sausages" are placed on a baking sheet, covered with a damp cloth and placed for 12-18 hours in a dark place (possibly in a cold oven) for fermentation. Then the cloth is removed and dried in the oven at a temperature of about + 40 ° C until they begin to crumble into powder. By adjusting the thickness of the "sausages", fermentation time, drying temperature, you can get tea with different tastes and aromas.
Botanical description
Monet loaf is a herbaceous perennial of the Sparrow-bean genus, Primroses family. As a wild plant, it is found everywhere in Eurasia, from where it was introduced to North America. The name "coin" or "coin" is associated with the rounded shape of the leaves of the flower. The flower received the second name "Meadow tea", since it has long been used to make herbal tea.

Belongs to the group of ground cover and anti-erosion crops. For this purpose, it is cultivated in wet areas of gardens and parks, the banks of decorative reservoirs. Monet loam forms a dense dense carpet, both on a horizontal and on an inclined surface. The plant is undemanding, frost-resistant.
The stem has no edge, creeping, creeping, knotty, leafy. Roots can form in the nodes, thanks to which the shoots are additionally rooted. Stem length can reach 20-60 cm. Leaves on short petioles (no more than 5 mm) are opposite. Their length ranges from 9 to 25, width - from 5 to 20 mm.
The edges of the leaf plates are solid, with small sparsely placed glands, light green (lime) in color, with a silky surface. The leaf is ovoid or round. Some beautiful species of loosestrife have monotonous leaves of a cordate or pointed shape.
The flowers are yellow, placed in the leaf axils singly on long (up to 2.5 cm) pedicels. The calyx is divided into 5 pointed heart-shaped or triangular petals, up to 1 cm long, covered with black dots and strokes.
The corolla has a diameter of 18-30 mm, it is also divided into 5 petals on a short tube. The petals are ovoid, narrowed towards the ends, covered with black dots and strokes and transparent glands on short legs. The plant is pollinated by insects, in particular - wasps. The loosestrife blooms from May to August. The seeds are formed in bolls. They can be harvested already in August-September.
The verbeinik of the monetary variety prefers moist soil: lake and river banks, damp ravines, forest glades. It grows well in swamps.
Due to the content of vitamin C and tannins, loosestrife is used in folk medicine as a remedy for scurvy and diarrhea.Outwardly, preparations from it are used to heal open wounds.
Landscape decoration
The verbeinik is used as a ground cover plant, perfectly decorates gazebos, rock gardens, and is simply irreplaceable for decorating pools and artificial reservoirs. Looks great with ferns, hosta. Tall varieties are in harmony with astilba, bellflower and other shade-tolerant plants. Excellent neighbors are phloxes and dwarf irises, red-leaved heuchera and wild rose, berry and sedge, Rogersia and others. In shady areas, the coin loosestrife can completely replace the lawn grass.
Answers on questions
Often gardeners ask such questions:
- How to trim the loosestrife correctly? The plant needs to be pruned. The operation should be carried out after flowering, removing dry branches, and for the winter, completely cutting the bush at the root.
- Need to transplant a crop? When growing, the degree of growth of the plant should be taken into account, young branches are recommended to be transplanted from the mother bush. If this is not done, the loosestrife will take over all the flower beds in the neighborhood and drown out other crops.
- How to deal with caterpillars? Threats to loosestrife and caterpillars. To combat them, you can resort to mechanical methods: remove damaged parts of the plant, dig up the soil near the bushes, destroy the nests with eggs and larvae found. A folk remedy is also effective: treating the plant with an aqueous solution of liquid soap.
Growing loosestrife will be a pleasure, since its advantages in undemanding care, beautiful appearance and quick adaptation to various weather conditions have won over many gardeners. And the mass of useful properties is of great interest to the healers of traditional medicine.
The chemical composition of loosestrife
The biochemical side of loosestrife has been well studied. Our ancestors intuitively felt in the meadow tea from loosestrife a rich list of biologically active substances:
- the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and its precursor choline;
- rutin and other glycosides with P-vitamin activity;
- fatty oils abundantly secreted by glands;
- caffeic and other organic acids;
- vitamin C.
The verbeynik is not poisonous at all, it is allowed to enter green fodder and hay for farm animals.
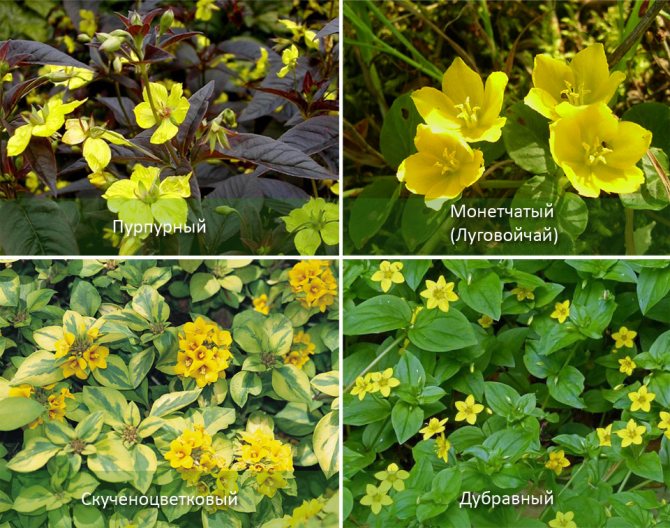
Varieties of loosestrife for florists
The unpretentiousness of the loosestrife, beautiful and long-lasting flowering attract gardeners in their use for landscape design. The natural and inconspicuous beauty of the plant allows it to be used in garden design to create natural natural corners. Alpine slides are decorated with this plant, flower beds are decorated, ponds and ponds are decorated.


The most famous species in Russia:
- monotonous,
- ordinary,
- point,
- whorled
- oak.


Such adapted varieties differ in the structure of the stem and its length, color, shape, arrangement of leaves and flowers. Some plants creep, transforming a large area into a green carpet with bright flowers. Others, like thin candles, burn with burgundy and yellow fire of inflorescences. And the third, when the fruits ripen, like chameleons, change the green color to burgundy.
Photos of loosestrife confirms their diversity and originality can be viewed in our gallery.
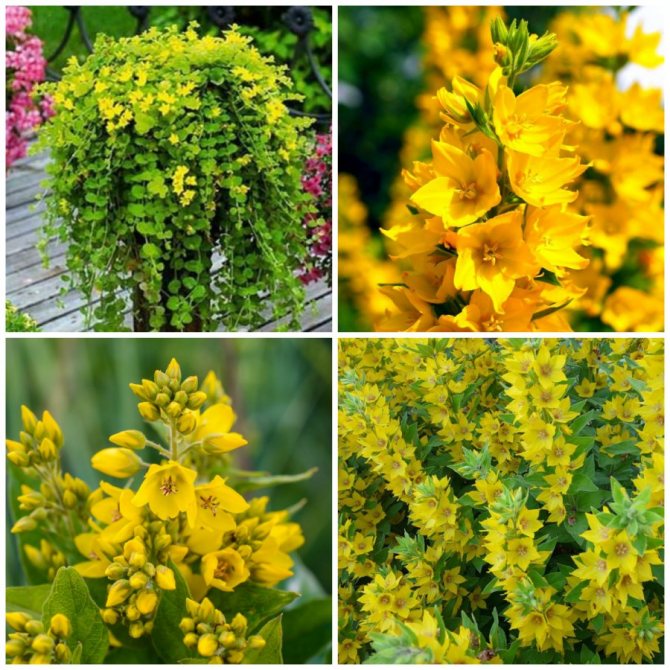


But despite such external differences, all varieties of loosestrife have properties that unite them - unpretentiousness, ease of planting and care.









































