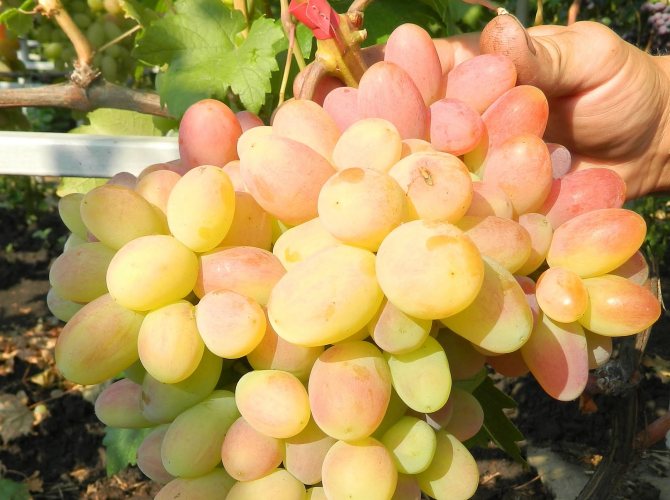
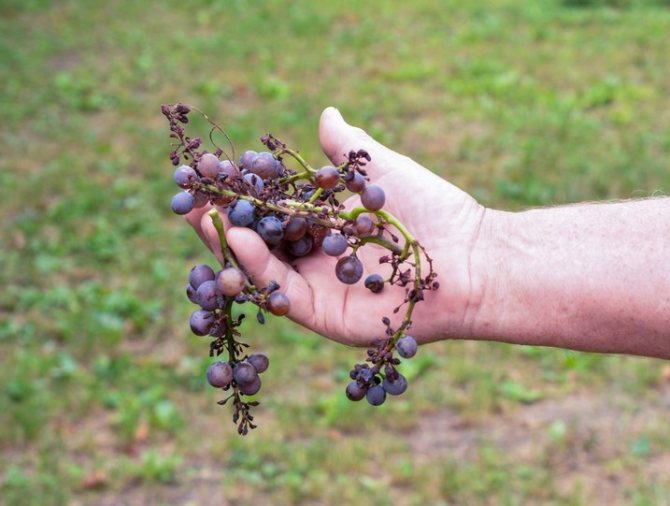
With the onset of the autumn period near the vineyard, the phase of active vegetation is coming to an end. Top dressing of grapes in autumn allows fruit-bearing bushes to recover, replenish mineral reserves and prepare for a long winter. A sufficient amount of nutrients ensures high yields of grapes in the next season.
- 2 Features of fertilization of young and old grapes
- 3 Terms by region and frequency of feeding
3.1 Fertilizer compatibility table
- 4.1 Organic food
4.1.1 Rules and frequency of top dressing
- 4.2.1 Rules and frequency of fertilization
The final stage is mulching
Autumn is the time for rains. This point must be taken into account when applying fertilizers and mulching must not be ignored. Well-rotted compost, mowed grass (for example, from a lawn) or spruce legs will help. Mulch is excellent frost protection, don't ignore it.
A vineyard growing on loose fertile soils is fed no more than once every three years. If the soil is of inferior quality, apply additional fertilizing after two years. Annual feed is needed only for plants located on sandy soils.
Pre-winter watering

Autumn care of grapes in September in the middle lane assumes continuation of watering as usual, with the exception of periods of rainy weather. Moisture deficiency hinders the preparation of wood for the winter season.
It is especially important to maintain moisture if the grapes grow on sandy or sandy loam soil. In this case, it is necessary to water the vineyard often, in small portions, but plants on clay soil or black soil need more rare but abundant irrigation.
After shedding the leaves and carrying out the main pruning, but before the soil has time to freeze, you need to do water charging. Water should be poured into trenches 10 cm deep around the bush. On average, each plant needs to be given 5 full buckets of water. Old and tall vines will need up to 10 buckets, young plants will need 10-30 liters. Sandy soil requires an increase in the irrigation dose to 6 buckets (relative to the average figure), and clay soil reduces it to 2.5-3 buckets.
Typical mistakes gardeners
Novice growers often make mistakes when applying fall fertilizer for grapes. The most typical:
- feed young seedlings, not adult plants;
- make only complex preparations;
- bring in an increased amount of nutrients.
Grape bushes 1-2 years old do not need additional feeding in the fall: the vines do not bear fruit or give them in a minimal amount. Plants have enough soil minerals, they do not have time to deplete it. Active mature bushes quickly take nutrients from the soil.
Complex preparations contain a standard set of minerals: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium. The grape culture needs these elements, but besides them magnesium, zinc, boron, sulfur, calcium are required, which are absent in conventional complexes.
An excess of fertilizing and its random introduction into the soil leads to root burns, a decrease in plant immunity. Fertilizing the grape crop is recommended according to a strict scheme.
The better to feed the bush so that there is a good harvest
During the fruiting period, the reserves of nutrients in grapes are excised. They will recover thanks to the autumn feeding. How can you feed grapes after harvest? The composition of fertilizers requires the presence of trace elements: zinc, phosphorus, magnesium and potassium. These elements strengthen the immune system and give the plant a chance to survive the winter frosts.
In the autumn, organic matter and mineral compositions are introduced. The procedure is carried out in two passes. First, organic matter is added, then complex mineral compositions are used.
Required autumn feeding:
- organic matter includes: droppings, compost, ash, rotted plant residues;
- mineral compositions: phosphorus, potash, nitrogen;
- complex fertilizers: ammophos, nitroammofosk, azofosk, nitroammophos.
For your information! Top dressing is selected based on soil analysis and crop deterioration. Only by trial and error are substances that affect the development of culture and its fruiting determined.
Features of fertilization of young and old grapes
If fertilizers were used when planting young grapes, then in the next 2-3 years no additional fertilizing is required. From the third year, organic matter is used first, and then mineral supplements. Proper fertilization increases the frost resistance of grapes, is a preventive measure against diseases and pests, and enriches the soil.
Before wintering, old grapes are saturated with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. The formed bark on the stems and a sufficient amount of minerals help the plant to endure frost without shelter. And in spring, a healthy bush will actively enter the growing season.
Common mistakes
Inexperienced growers can ruin a young vine before it even begins to bear fruit.
Typical beginner mistakes:
- Insufficient pruning. Cutting off the tops of the lashes will not give an effect, in addition, it is dangerous for the plant, since the unripe shoots will rot under cover, and the plant will not rest.
- Neglect of katarovka. This procedure is especially important for a young plant. Since the upper roots will take over the main function and the deep ones will weaken as unnecessary. When the soil freezes, the dew roots will die.
- Wrong choice of lashes for the next fruiting. You should not leave the thickest or the youngest, it is better to choose branches of medium thickness, with a rusty trunk.
How the culture is fed
Various minerals have an impact on the vital functions of grape bushes. Nitrogen stimulates the growth of green parts of the plant. Phosphorus provides a healthy and abundant flowering and fruit setting. Without magnesium, photosynthesis and protein formation do not occur. Zinc increases the abundance of fruiting, and boron accelerates the ripening of fruits, affects their weight and taste. Potassium increases resistance to frost and temperature extremes.
Grapes require less nitrogen than other horticultural crops. Other elements are much more important for the plant.
Root and foliar feeding is carried out with minerals throughout the year. Organic matter is applied less often when there is a need to improve the structure and fertility of the soil.
Mineral dressing
Before wintering, grape bushes must be treated with phosphoric and potash dressings. You can use a complex preparation, which also includes magnesium, zinc and sulfur. The top dressing should not contain chloride ions: the plant does not tolerate chlorine ions.
Helpful hints
If you want to grow a healthy, richly fruitful vineyard with a tasty harvest, you need to follow these simple rules:
- Feed the bushes in a timely manner and in the right amount, both root and foliar.
- Remember that such fertilizers need to be applied not only in autumn, but also in spring - at the beginning of the growing season, during flowering and ripening of the crop.
- For better absorption of nutrients, it is advisable to apply root dressing during watering.
- When fertilizing grapes with this or that preparation, strictly follow the instructions on the package. An overdose does not have the best effect on the health of plants and their further development and fruiting.
As you can see, feeding grapes in the fall is not particularly difficult. By observing the above rules and recommendations, you can grow healthy plants and enjoy a juicy, tasty and healthy harvest every year.
Minerals for the growth of grapes
Fertilizers are essential for plant life. But before using the formulations, instructions are studied so as not to harm the already weakened grapes. A list with their description and characteristics is below.
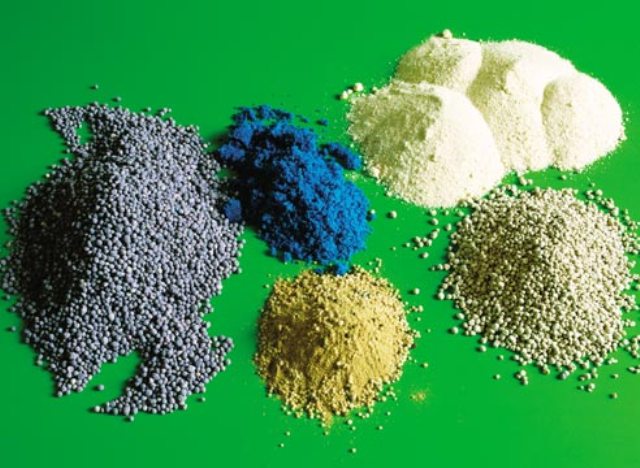


Mineral fertilizers must be chosen carefully so as not to harm the bush
- Nitrogen fertilizers. Such fertilizers are not used in autumn feeding. The chemical element activates the growth of the vine. The grapes give it all their strength, so they will not have time to prepare for winter. Even mild frosts lead to death of the bushes. Therefore, nitrogen is used only in spring. Among the nitrogenous compounds, urea is considered the best, containing 46% of the substance. The product is well absorbed in liquid and granular form. There is also a lot of nitrogen in sodium nitrate (16%), ammonium sulfate (21%), ammonium nitrate (35%).
- Potash fertilizers. Their presence in the autumn feeding depends on how the grapes will overwinter, and what the harvest will be next year. The element helps the formation and ripening of brushes, supports in drought conditions, protects from cracks in the berries. Lack of potassium causes the foliage to dry out. Effective potassium-containing preparations: potassium sulfate containing 50% of the substance, potassium salt (40%), potassium magnesium (30%). These dressings do not contain chlorine. They are often used in conjunction with phosphate fertilizers.
- Phosphate fertilizing. Influence primroses, the appearance of the ovary and berries. Simple superphosphate, in which 21% phosphorus, is suitable for any soil. If the soil is acidified, chalk and lime are added to the superphosphate to lime the earth. Double superphosphate contains 50% phosphoric acid. Compared to the first composition, there is no gypsum in this fertilizer. A good remedy for acidic soil is phosphate rock, which has 23% phosphorus oxide.
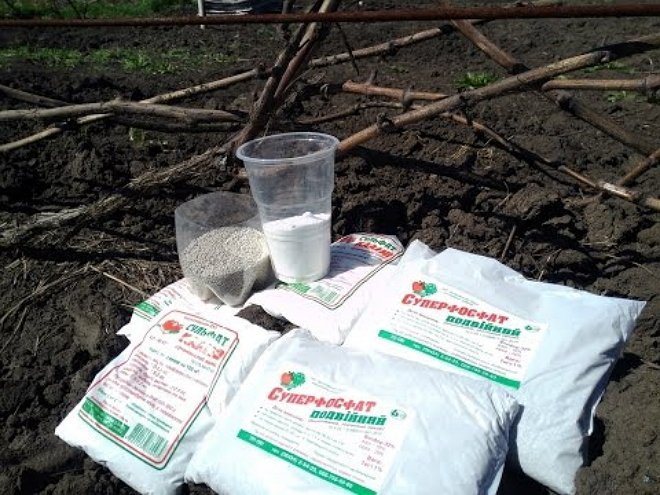


Phosphate fertilizers
Important! To make mineral fertilizers easier to assimilate, in the fall they switch to foliar dressing of grapes.
How to feed grapes in spring?
The most important element in the spring for any plant is nitrogen. Therefore, in the spring fertilizer for grapes, there should be an abundance of nitrogen, the rest of the components are secondary, but no less necessary. If you give the culture only nitrogen, it will not be of any use. So, how to feed grapes in spring?
- In early spring, after the snow has melted and the young vineyard has begun to grow, chicken droppings should be added under the bushes. Half a bucket of fertilizer (not diluted) is taken on the bush. It is better to pour it into a trench dug in a circle around each bush. Then the trench is poured abundantly with water (5 buckets / bush) and, after absorbing the water, it is covered with earth.
- If the vineyard is already "aged" (over 4 years old), it needs more nutrients. Therefore, at the beginning of spring, 0.5 buckets of bird droppings, a bucket of mullein, 1 kg of ash are taken on it. All this is mixed, filled with 4 liters of water and infused for 1 week. After the solution is ready, you need to dilute a liter of infusion in 10-12 liters of water, and water the culture. For each bush, 2 buckets of solution are taken.
- You can also use wood ash. It is mixed with water in a 1: 2 ratio and infused for 2-3 days. After that, the infusion is mixed with water in a ratio of 1: 3 and the grapes are watered. You need 0.5-1 liter of infusion per bush.It not only nourishes the plant, but also protects it from fungal diseases.
- If there is no organic fertilizer, you need to know how to feed the grapes in spring from minerals. On the bush, 30 g of dry potash mixtures, 40 g of superphosphate and 40 g of nitrogen are taken. The dry mixture is poured into the trenches near the bush, and poured with water (1-2 buckets). But if there was a lot of snow and the ground was already wet, then watering is not necessary, you just need to sprinkle fertilizer on top of the ground.
- Foliar top dressing is recommended before the first flowers appear. For this, 20 g of superphosphate and 30 g of nitrogen are used per 10 liters of water. Before using the drug, up to 50 g of sugar is added to it so that the substance slowly evaporates from the leaves. Instead of this funds, you can also use the preparations "Florovit", "Biopon", "Master" according to the instructions.
- In May, the bushes can be fed with a mixture of 30 g of potassium nitrate, 40 g of nitrogen-containing substances and 50 g of superphosphate. By this time, there should already be quite a lot of leaves, so you should make sure that the plant has enough strength to form flowers, and then berries.
- If at the end of spring the first berries (peas) have already appeared, you can feed the grapes with 30 grams of complex mineral fertilizers. This amount is diluted in a bucket of water.
The vineyard is fed in the spring no more than 3 times. The first time is in April, when the shelter is removed, the first swollen buds are shown (the beginning of sap flow). The second time falls in May - 2 weeks before flowering. The third time fertilization is applied, a week before the appearance of the ovaries (grape peas). But, most often this period falls on the summer, and not in the spring.
Autumn feeding of grapes with ash
If you regularly apply fertilizer, did it in the spring, the soil is most likely not yet depleted, so the time for heavy artillery has not come. It will be enough to feed the grapes with ordinary ash. Bring in the product when digging (sprinkle the earth on top and work with a shovel). You can choose the option with watering. Dissolve 0.3 kg of ash in 10 liters of water - this volume is enough for one bush.


Top dressing of grapes with ash
What is the plus of ash? The fertilizer contains all the necessary elements, just in less significant quantities. A big plus of ash is a significant decrease in soil acidity. Fertilized plants ignore harmful insects.
The benefits of catarovka


Before winters, you need to remove small roots, which are located at a depth of 25 cm. You should not ignore the recommendation. These roots are too close to the surface. During winter standing, when watering and fertilizing are rare, they will die off, drawing strength from the grapes. The scheme for removing surface roots looks like this:
- carefully dig up the soil around the trunk to a depth of 25 cm;
- roots are removed with pruning shears;
- the sections are treated with a solution (3%) of copper sulfate;
- wrap the cut-off site with 3 layers of foil and tie it with twine;
- the hole is covered with earth.
It is necessary to carry out katarovka for those who grow grapes on a farm or in industrial volumes.
How to fertilize grapes in the fall
When applying dressings near the trunks, only superficial roots receive nutrients. As a result, green shoots, long vines and few ovaries are formed in spring.
Important! Roots that are close to the surface are less important to the bush than those that go deeper. If damaged, they quickly recover.
In order for nutrients to reach deep roots, fertilizers are scattered or poured at a distance of 50–80 cm from the trunk, depending on the age of the bush. The funds are placed in grooves or pits so that they do not dry out, dissolve and go deeper.


Step-by-step instruction
Autumn processing combines soil loosening, crop feeding and removal of all weeds:
- Dug up the ground around the bushes (radius - 50-60 cm).
- Grooves are made along the edges with a depth of 20 cm.
- Water-charging irrigation is carried out using the existing wells.
- Mineral fertilizer is added to the grooves and everything is sprinkled with earth.
In this way, a "long-playing" fertilizer is laid, which is slowly absorbed, for example: potassium magnesium, phosphate rock, potassium sulfate. The roots of the grapes penetrate into the soil to a depth of 6 m, the granules gradually dissolve during rain and watering, and minerals go down.
Having retreated 30 cm from the trunks, the surface of the holes is sprinkled with wood ash or cow dung. Horse, sheep manure, bird droppings are also suitable.
Important! Fresh manure is not applied - they use humus that has lain for more than a year in a place protected from sunlight.
Chicken droppings are dissolved in water, kept until fermentation, then diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 4 and 3 buckets of solution are poured under the bush closer to the edge of the hole.
By analogy with organic fertilizers, agents that quickly dissolve in water are applied. When the moisture is completely absorbed, the holes are covered with leaves, chopped grass. From above, to the very trunk, mulch with straw. This method of autumn processing will provide the grapes with adequate nutrition and protect the roots from frost. Moisture remains under the straw for a long time.
Fertilizers


During the season, grapes consume nutrients that need to be replenished. Top dressing must necessarily include:
- Potassium.
- Phosphorus.
- Magnesium.
- Zinc.
- Copper.
Potassium provides frost resistance, allows the berries to ripen quickly. It affects the growth of the bush itself. If potassium is low, the edges of the leaves begin to die off. Phosphorus is essential for the formation of the ovary. Zinc, copper and magnesium increase plant immunity, increase resistance to drought. Thanks to zinc, yields will be higher next year.
Nitrogen is not needed in the autumn, as it accelerates the growth of the green part of the grapes... It delays the ripening of the vine, preparation for wintering.
With natural ingredients
Organic products are applied first in early fall. They are used simultaneously with digging, scattering them under the bushes. They improve the properties of the soil - looseness, composition, air permeability.
Compost
Rotten plant residues contain a full range of trace elements. They are mixed with peat, manure, phosphate rock. This combination is superior in nutritional value to other organic products. It loosens the soil, protects against weeds and helps to retain moisture. The product is suitable for perennial grapes and young plants.
The compost is spread in grooves or directly around the grape bushes. Layer thickness - at least 5 cm. Compost is also used for irrigation. To do this, it is diluted in 10 liters of water. The tool is made independently from food and garden waste (sawdust, plant residues, peat, straw). Usually it is put in a pit or barrel, where it is reheated. Before that, it is mixed and tamped. The place is chosen where water is quickly absorbed into the ground. The compost pit is made small - 1.5 m by 1 m.
- How to make healthy nutritious compost at home.
- Leaf compost is good for plants and is available to every summer resident.
- How to use chicken manure with sawdust for the garden ?.
Manure
Manure or mullein is one of the best organic fertilizers. He gives the vine potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen. Manure enriches the soil with beneficial bacteria, facilitates the access of air and water. Waste is never used fresh. They are allowed to peel or bred with water. To do this, take 1 part of manure and 4 parts of water, mix and let it brew for 3 days. For 1 sq. it takes up to 10 liters of such a liquid.
Another way to apply manure is to put it in grooves. They are dug between the rows of grapes. The grooves are filled to the top with humus mixed with compost and sprinkled with earth. In order not to damage the roots, grooves are not dug in every row, but after one. Subsequently, any watering of the plant is carried out through these grooves.
During the winter, the layer of manure overheats and nourishes the roots of the grapes. The substances contained in it remain in the soil for several more years. If a thick layer of manure is spread, it protects the area from weeds. Also, it does not need to be mulched.
Mulching - we preserve moisture, eliminate weeds, improve soil structure and increase yields.
Experienced gardeners never lay out fresh manure as methane and ammonia are released from it.
It is important to apply fertilizers correctly. With superficial application of organic matter, the roots grow close to the surface. In winter, they freeze out, and the deep elements of the root system remain without nutrition.
- What is the best horse or cow manure to use?
- Cow dung as a valuable fertilizer for the garden, how to use organic fertilizing on the site.
Chicken droppings
Poultry droppings are affordable and effective feeding. Trace elements in it are in a form that is easily absorbed. After it, the level of potassium rises in the soil, it is enriched with bacteria. The acidity of the soil is also normalized.
Chicken manure is applied dry or a solution is prepared. The dry mix is suitable in those regions where it gets cold early. It is absorbed into the root system for a long time and nourishes the plant for a long time. Dry droppings are purchased ready-made, packaged in plastic bags.
The solution is prepared in a glass container. The process has several stages:
- dilute fresh droppings in water in a ratio of 1: 4;
- put in heat for 10 days;
- once again diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10;
- 500 ml of liquid is poured between the bushes.
The infusion should not be poured directly under the bush or onto the rosette of leaves. So that the fertilizer is well absorbed, the soil is watered abundantly before application. It is also used after rain. At the end of the feeding, the area is again moistened with water.
Fertilization with droppings is carried out no more than 2 times a year. It has a high concentration of acids and urea, which can damage the roots of grapes.
How to Recycle or Turn Chicken Dung into Black Gold for Plants.
Dry vermicompost
Vermicompost is a widespread fertilizer. It can be purchased at any gardening store. The mixture includes humus itself, B vitamins, vitamin PP, magnesium, zinc, iron, copper. Potassium humate also contains potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen. The solution is used for root dressing of grapes. First, the site is well watered, then the drug is applied along with watering every 3 days. It is suitable for black soil and peat soil.
A solution is prepared from the preparation: 3 caps of vermicompost are taken for 1 liter of water. It is advisable to prepare the water - to defend or take distilled water. Another option is to chill the boiled water. Wear rubber gloves before spraying. Upon completion, hands and face are washed with soap.
The drug is not used on dry soil or diseased plants.
Dry vermicompost is purchased for grapes growing on sandy or depleted soil. The drug is poured out when loosening with a hoe or during deep digging. In dry form, the product is used once every 2 years.
Secrets of homemade vermicompost.
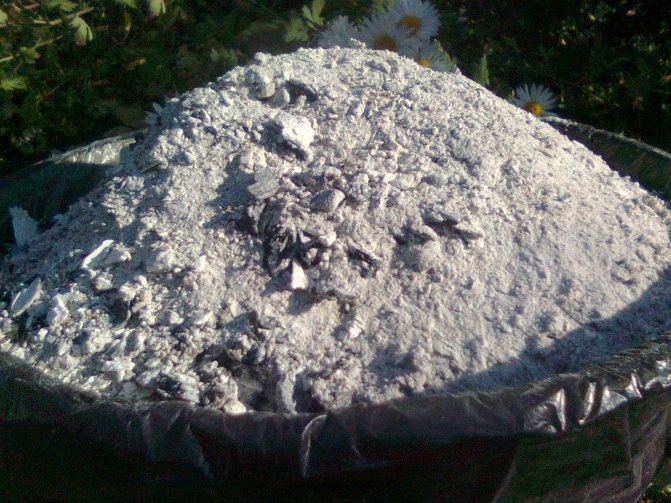
Ash
Ash is a natural source of potassium. It contains magnesium, calcium, sodium and phosphorus. Most of them remain after burning sunflower seeds. If you need to feed the grapes with phosphorus, choose coniferous ash. With a lack of potassium, take the ash of deciduous trees. The product is used during flowering and at the end of fruiting.
Wood ash is scattered when digging a site or introduced in the form of a solution. For dry application, it is important to moisten the soil well. About 4 buckets of water are poured under each bush. Then the dry matter is sieved and spread between the rows. For 1 sq. requires 150-300 g of ash.
Ash infusion is prepared in this way:
- A glass of ash (300 g) is poured into a bucket of water.
- Insist 3 days.
- 500 ml of infusion is poured onto 1 bush.
Ash is useful for grapes, as it enriches it with Ca, Mg, Na, K, P.It repels insects and reduces soil acidity. The product prevents gray rot.
Autumn rains wash away fertilizers, so the grapes are mulched with grass, needles, compost. They also prevent the plant from freezing.
Furnace ash is not inferior in properties to superphosphate and potassium salt. Potato, wheat, birch and rye ash are also useful.
Peat
Peat is used for soil mulching. It serves not only as protection, but also as a fertilizer. The product is never taken in its pure form, as it contains acidified substances. They are not suitable for grapes.
Where to get peat and how to properly use it for the garden.
With minerals
Mineral dressing is used in the middle of autumn. Dry products are scattered under digging. Immediately after this, the soil is deeply shed. Liquid preparations are simply poured into the trunk circles. For industrial cultivation, grapes cannot be done without mineral fertilizers.
Superphosphate
The product consists of P (21%), sulfur, magnesium and gypsum. It has good solubility and is suitable for various soil types. They also use double superphosphate containing 2 times more phosphorus.
Phosphorus and potassium enhance each other's action, so they are added as part of one product. They buy it ready-made or do it yourself. A homemade solution is prepared from 20 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium salt. Instead of the latter, you can take potassium sulfate 25 g. The components are diluted in 10 liters of water.
The main varieties of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers for feeding vegetables and fruit crops.
To increase the nutritional value of the mixture, zinc sulfate 2 g or boric acid 1 g are added to it.
Potash remedies
Potassium salt is a red substance. It consists of 40% potassium, chlorine and crushed sylvintes. Digging for 1 sq. m add 40 g of potassium salt. The tool is used in the autumn and is practically not used at other times. It is used in pure form or mixed with other drugs.
Potassium salt.
Another representative of the group is potassium sulfate. These are gray crystals, readily soluble in liquid. It contains over 45% potassium, as well as magnesium and calcium. It is free of chlorine, which ensures a pleasant berry flavor. It is not recommended to use it on acidic soils and mix with lime preparations.
The next popular remedy is potassium magnesium. It contains 30% potassium, sulfur and magnesium. Kalimagnesia is suitable for both feeding and basic nutrition.
Nitrofosk
Phosphorus preparations have a greater effect on the roots of grapes. They increase resistance to frost and pests. Nitrofosk mainly consists of phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen in the same amount. For 1 sq. m takes up to 50 g of funds. With good soil fertility, it is enough to add 20 g of the preparation. The same amount is taken if nitrophosphate is combined with other means.
In case of an overdose of nitrophoska, leaves fall off.
Calcium nitrate
The product contains water-soluble calcium. It affects the absorption of other trace elements, improves the growth of the root system, and normalizes metabolic processes. For fertilization, take a weak solution (less than 2%). It is brought in at the beginning of September. With the onset of cold weather, it is not recommended to use calcium nitrate.
Calcium nitrate for tomatoes.
Solution
Solution is a liquid fall fertilizer. It includes potassium (up to 30%), phosphorus and nitrogen, 18% each. It is rich in trace elements (Cu, B, Mo, Zn, Mn). The solution is sprayed onto bushes or poured into the soil as an irrigation element. The solution requires 10 g of the product and a 10-liter bucket of water. After fertilization, it is important to thoroughly wash exposed areas of the body.
Kemira Autumn
Kemira's preparation prepares grapes for wintering, enriches the soil with beneficial microorganisms. Besides phosphorus and potassium, it contains important trace elements. It is introduced into the soil in dry form (50 g per 1 square meter) or diluted with water (20 g of powder per 35 l of water).Dry top dressing is applied once, and liquid dressing - several times a week.
Florovit
Florovit is classified as a mineral fertilizer consisting of many elements. It is used to fertilize large bushes and as a stimulant when planting seedlings.
Florovit contains no nitrates, which makes it safe for the environment.
For one plant, 10 g of the substance is enough. If necessary, the dosage is increased to 50 g. The fertilizer is applied 2 times in the fall. If the drug is used for planting, 10 sq. M. add 1.5 kg of Florovit.
And a little about the secrets of the Author
Have you ever experienced unbearable joint pain? And you know firsthand what it is:
- inability to move easily and comfortably;
- discomfort when going up and down stairs;
- unpleasant crunching, clicking not on their own;
- pain during or after exercise;
- joint inflammation and swelling;
- unreasonable and sometimes unbearable aching pain in the joints ...
Now answer the question: does this suit you? How can you endure such pain? And how much money have you already "poured" on ineffective treatment? That's right - it's time to end it! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish an exclusive interview with Oleg Gazmanov, in which he revealed the secrets of getting rid of joint pain, arthritis and arthrosis.
Attention, only TODAY!
Organic means for feeding grapes in the winter
Organic fertilizers for autumn application under grapes, it is necessary to prepare in advance. Experienced growers have become convinced of the efficacy of some of the available nutrients for naturally occurring crops.
Rotted manure. A lot can be said about this tool, because the value of this fertilizer can hardly be overestimated. Manure loosens the soil, improving the access of air and water to the roots, enriches it with nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, necessary for many crops, stimulates the reproduction of microorganisms in the soil, helping the grapes to assimilate various elements.
Compost. Replacement for manure that is not inferior in efficiency. To create compost, a special pit is usually made, where organic waste is thrown off. Compost does an excellent job of being an autumn fertilizer for grapes.
Output
Many people often ask themselves how to feed their grapes in autumn and spring. Indeed, for normal development, the plant needs nitrogen, copper, potassium and phosphorus, and in the soil these elements are often lacking. Fertilizers will help the gardener solve this problem. It is advisable for a beginner winemaker to purchase multi-component mixtures that contain all the necessary substances. How to properly handle this culture:
- When the temperature becomes positive, you need to fertilize the soil in a dry form.
- When the first leaves begin to appear on the plant, add nutrients to the soil in the form of an aqueous solution.
- Water the ground again after flowering.
- The last time you need to add nutrients is after harvesting.
Remember that nitrogen should not be added in the fall - this element prevents the wood from ripening.
Processing foliar components of grapes (leaves, vines) also makes sense. Prepare an aqueous solution of beneficial trace elements, and then spray them on the plant. This should be done at night or in cloudy weather.
Autumn preparation of grapes for winter
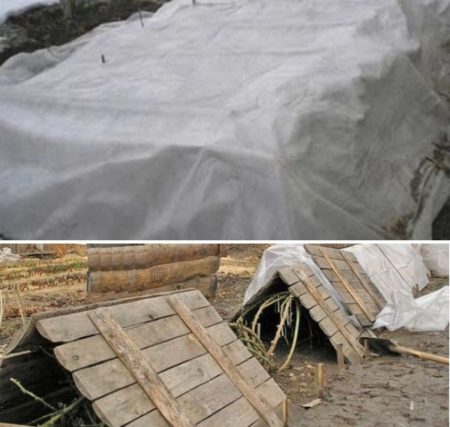


The first step is to gently bend the vine to the ground before the onset of cold weather. The next step is the introduction of nutrients. The gardener should remember the need to feed the grapes before sheltering for the winter after the completion of fruiting. It is not worth saving, otherwise there will be no active vegetation in the spring. Phosphorus and potassium are often used. In cases where mineral fertilizers are used in the garden, superphosphate is added to the soil in a volume of up to 30 g for each 1 m2.If the stake is made on potash fertilizers, then potassium sulfate is added to the soil in a volume of up to 20 g per 1 m2.
Read also: Grapes Memory of the Surgeon: a description of the variety, cultivation features and reviews
Regardless of the type of fertilizer, the focus is on wet root dressing. With its help, nutrients will reach their goal faster. For each plant, 10 liters of water are spent, in which fertilizers are dissolved. In summer cottages, the owners of which prefer organic fertilizers, use wood ash as top dressing. For each plant spend up to 200 g. It is brought in dry during digging or in dissolved form. In regions with a harsh climate, slightly rotted humus or compost is additionally used. Each plant needs to be processed with 15 kg of substances.
Mandatory application of fungicides


Among the tips on how to prepare grape bushes for winter in the middle lane, not the least is the recommendation to use one of the fungicides. The first place among the popular substances is held by ferrous sulfate. It contains substances that prevent the development of bacterial flora. Even with jumps in temperature, the berries are not threatened. When processing seedlings, the following recommendations are followed:
- spraying can be carried out before pruning, but for such a procedure you will need 50% more solution;
- processing is carried out with a 3% solution (if the berries are not sick) and 5% solution if the grapes are ill;
- for every 10 liters of water, take 500 g of the substance;
- young plantings are allowed to be treated with a 1% solution of ferrous sulfate - for every 10 liters of water, 100 g of the substance is taken;
- after processing, the vine will darken a little and this is not scary;
- urea (100 g for every 5 l) added to the solution will help to improve the quality of spraying.
Despite the fact that urea contains nitrogen, in small quantities it destroys the larvae of pests. Spraying is carried out only after all the leaves have fallen. The second condition is that all the buds are closed on the bush.
Carrying out pruning of bushes


Proper preparation for winter begins with the removal of individual elements. Every action must be verified, so don't rush. Direct care of grapes in the fall and its subsequent pruning for the winter includes harvesting cuttings. They will be used for berry propagation. You can start working immediately after all the leaves have fallen off. It doesn't matter if the bushes grow only for the first year or for several years, the recommended procedure is as follows:
- the first pruning is carried out in mid-September;
- the second pruning is carried out 3 weeks after the harvest in October;
- during the 1st pruning, diseased and dry bushes are removed (no more than 15% of the total number of bushes);
- it is allowed to cut only those shoots that are localized on the main trunk 60 cm above the upper wire.
Gardeners who want to know how to prune grapes for the winter should always keep in mind the variety of berries and the climatic characteristics of the region. Both factors shift the trimming time up or down. In order for the grapes to feel good in winter, the summer resident pays more attention to the II pruning in October:
- the shoot is to be trimmed from the outside of the sleeve;
- up to 3 kidneys are left on it;
- up to 2 shoots are left on the inside to form a fruit arrow;
- you need to leave such a number of eyes, which coincides with the diameter of the vine + about 2 buds.
Compliance with watering rules


As soon as the pruning is completed, the plants need to be watered. The first rule is that watering is carried out before the soil freezes, otherwise it does not make sense. The optimal time is the end of autumn. The more moisture is applied, the less likely it is to get a small crop. Gardeners' reviews indicate that a vine soaked in water quickly enters the growing season in spring. Late fall preparation includes the following recommendations:
- the recommended amount of watering for sandy soil is 60 liters for each bush;
- for loams, the indicator is 30 liters for each bush;
- before the start of watering, a small depression is made around the main trunk - up to 10 cm.
Watering is necessary so that the water gets into the groove. This way, you can save moisture and make sure that every shrub gets enough moisture.
Autumn pruning in front of shelter
Why is it better to prune grapes in the fall? If this is done in the spring, a liquid - "juice" will flow out of the slices. It will take time for the bush to recover, the vegetation slows down by about two weeks. Accordingly, the harvest will ripen later.
Pruning can only be started after complete flying around the foliage. Even damaged, semi-dry leaves continue to nourish the bush with useful substances. It is advisable to carry out the procedure in dry weather. The correct time for autumn pruning of grapes before shelter for the winter depends on the region and the actual weather, in the Urals and Siberia it can be September, in the Moscow region - October, in the Krasnodar Territory - November.
Not only beginners, but also experienced growers often neglect the processing of the pruner during pruning. When you need to process a lot of bushes, it is a pity to waste time wiping. But this is really dangerous. Different grape varieties have different resistance to infections. An infected vine with high disease resistance will not show anything outwardly, but it will be the source of the disease. During pruning, the infection will spread to the rest of the bushes, some of them will not be able to fight, it will not be easy to cure the disease.
In order not to waste time wiping the secateurs, we prepare a disinfectant in advance, based on alcohol, pour it into a jar. Having finished trimming one bush, we dip the tool into the solution and continue working.
Pruning vines before winter
First you need to prune the vineyard. You need to start work after yellowing and falling leaves. If there are dried yellow leaves on the vine, but they do not fly around, you can cut them off yourself. At this time, the flow of sap in the vine stops.
The question often arises, is it possible to do without cropping? No, without pruning, the grapes will weaken, lose a lot of nutrients, and this will affect the future harvest, and can ruin it during the long winter.
Read also Allergy to carrots in a child photo
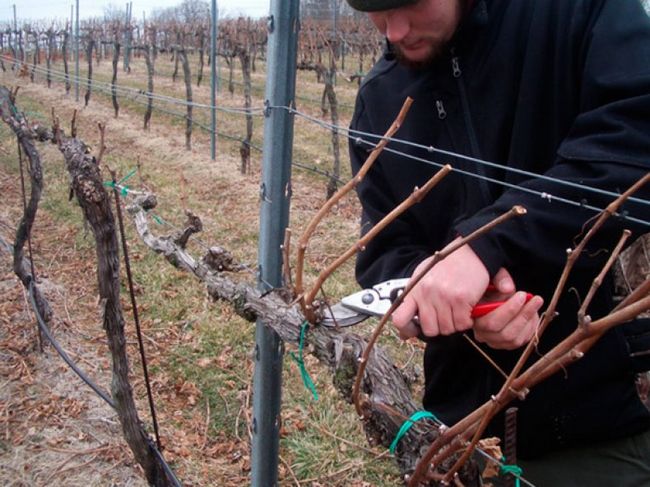


Pruning is carried out according to the following rules:
- Only healthy vines should be left on the bush, the thickness of which is no more than 1.2 cm.
- Large and thick branches must be removed, since they practically do not produce a crop, consuming a large amount of nutrients.
- Pruning is carried out closer to the trunk, leaving 6-10 buds on the fruiting branch, 4 buds are left on the shoots of old vines.
- All damaged and diseased branches must be removed.
- All cuts are made in such a way that they are facing the inside of the plant. It is necessary to remove all arrows that will not bear fruit.
- After cutting off unnecessary branches, the cuts must be treated with antifungal drugs.
When is it better to feed grapes
The first feeding of the grapes must be done before winter is over. In early spring, when all the snow has melted, the procedure should be carried out immediately so that the plant has good nutrition at the beginning of flowering. The next time feeding is recommended in May to help the grapes grow greenery.
For the third time, the procedure should take place around mid-July. Top dressing is needed so that the appearance and taste of the fruits come out good.
And last but not least, the feeding stage falls in the fall, when the harvest is over. Fertilizing grapes in the fall is necessary so that it does not lose its resistance to the approaching frost, as well as for additional nutrition before a long wintering.
Terms of feeding
In autumn, grapes are fertilized after harvest, when the leaves begin to become covered with brownish specks and are easily separated from the shoots. Depending on the variety and region of cultivation, feeding is carried out from the end of August to the end of October. The plant must receive nutrients before the cold snap in order to grow the root system, complete metabolic processes, and stock up on the necessary nutrients for successful wintering.
Also, once every 3-4 years, organic fertilizers are required to improve the structure of the soil (rotted manure). It is recommended to perform it 2 weeks after the annual procedure. Phosphate fertilizers are needed from mid-August to early September, when the berries ripen. Potash - after harvest, starting in late September.
If the ripening of bunches or vines is delayed due to the absence of any element, foliar feeding with the necessary nutrient in a chelated form is carried out in the fall at least 2 weeks before or after the expected harvest.
Shelter of the vine for the winter
There are grape varieties that do not require shelter for the winter, they easily tolerate frosts up to -30. But it must be borne in mind that only absolutely healthy plants grown with a high level of agricultural technology have such resistance. Lack of trace elements, fungal diseases and other factors reduce winter hardiness. When sheltering in the fall, special attention is paid to young grapes - annual seedlings, in Siberia and the Urals they are grown in buckets and brought into the basement for the winter, in the middle lane, the Chernozem region, in the Moscow region and the Leningrad region, they can be grown in open ground or greenhouses.
Answering the question, at what temperature should the grapes be sheltered, we note: you should not do shelter immediately after the first cold snap. Lowering the air temperature to 5 degrees below zero will not harm the vine. On the contrary, a hardened plant tolerates wintering much easier. The vine is left open for as long as the air temperature permits. If the thermometer dropped below -5, it's time to cover the grapes. It is impossible to name the calendar dates for the shelter of grapes for the winter, they are different for each region. In addition, even in one locality there is no year after year. For example, in Crimea, grapes are harbored closer to January, but from time to time it is necessary to wrap up the bushes in November. You need to focus on the actual weather and forecasts for the next week. In winter, grapes are threatened by two dangers: freezing and damping of the buds. The first occurs when exposed to low temperatures, and the second provokes high humidity at temperatures near zero and above. Damping off threatens a covered vine during thaws and in early spring, when it is impossible to open the grapes, since subsequent frosts will destroy the buds. When choosing a way to protect grapes for the winter, keep in mind that a good shelter is dry, humidity makes wintering difficult.
The choice of frost protection for grapes depends on the financial and physical capabilities of the owner. The cheapest, but energy-consuming method - the vine is laid in a trench and sprinkled with dug earth. During the winter, they cover and trample the snow. This method is not suitable for the southern regions, the snow is blown away by the wind, during thaws, the waterlogged vine is subject to damping. Also, with great care, they use the shelter of grapes for the winter with land in areas with heavy, clayey soil. There is a fierce debate about the creation of the most correct shelter from frost. There are about the same number of options as there are winegrowers. But all the methods can be reduced to one formula: to prevent frosty air and excess moisture from getting to the vine, as well as to avoid compaction and damage to the covering material. As a rule, several layers are created:
• Air bag; • Moisture-proof; • Protects against mechanical damage.
Most growers believe that in winter direct contact with the soil harms the vine, so the trunk and branches are wrapped in plastic wrap, spandbond, and polypropylene bags. An air cushion is a layer located directly above and below the vine and is made from the following materials:
• Sawdust; • Hay; • Husk of sunflower seeds; • Lapnik; • Leaves; • Cardboard; • Rags; • Non-woven materials.
Sawdust is taken fresh, not rotted. The larger they are, the better, the layer will be more airy. It is undesirable to use waste from wood chopping. Dry trees are most often taken for firewood, the likelihood that they died due to infection with a fungal or bacterial infection is very high. If there are no other options at all, carefully treat both the vine and sawdust with fungicides.
Hay is a popular wintering material not only among grape lovers, but also among mice. In addition to the fact that rodents damage the kidneys, predators, while hunting for them, often break up shelters. If not noticed in time, the grapes will freeze. The same story is with the husk from sunflower seeds. If you cannot refuse these materials, be sure to lay out the poisoned grain along the vine. It is not for nothing that many people consider the Lapnik the ideal material for shelter. Mice rarely build nests in it, coniferous branches do not thicken, retaining a lot of air. Has a slight antimicrobial effect. Unfortunately, it is not available to everyone.
Dry leaves are as accessible as possible, it is not difficult to collect a sufficient amount. But it should be borne in mind that during the growing season they have accumulated a huge number of pathogens that can infect the soil and vine. By the way, there is a legend among summer residents that mice do not settle in walnut leaves, due to the iodine content. It's a shame, but this is just a fairy tale, mice don't care which leaves to use for the nest. Be sure to use rodent poison. Modern non-woven materials for sheltering grapes for the winter, such as geotextiles, spunbond and others, do not contain pathogens and do an excellent job of protecting them. But the high cost often makes this material unsuitable for use. Sometimes, before putting the next layer, a frame is built on top of the first. It does not allow the lower layer to be compacted. Use:
• Arcs; • Wire; • Boxes.
Arcs are installed at a distance of 60-70 cm from each other. The disadvantage of the arches is that in winter snow blows off them, the grapes are deprived of additional protection. Wire is a simple and budget option. It is stretched over the vine in several rows, special attention is paid to the middle of the structure, where snow and water will accumulate in case of sagging. They create pressure by compressing the lower layers. Often, a large number of low plastic or wooden boxes accumulate on the farm. They can be used too. To protect against moisture, plastic wrap, roofing felt, rubberized fabrics are most often used. They are pulled over arcs, wire, or simply covered with the first layer.
To protect against damage to the structure, boards, shields, slate and other available materials are used. We should also mention the shelter in the boxes. Boxes are a way of planting. The grapes are planted in a trench with reinforced walls. It is very simple to cover it in the fall, it is enough to lower the vine, cover it with insulating materials and shields. Sheltering the grapes in boxes for the winter is considered the best way to grow grapes in the northern regions. Growing grapes is a creative process, but without knowledge, the result can be sad. We try our best to provide the most up-to-date information to help you.
Popular drugs
To facilitate the work of gardeners, special preparations are produced for processing plants. They can have a complex effect - to protect against pests, fungi, diseases and serve as root and foliar feeding. Or perform a specific task.
Preparations, their composition and purpose:
- Urea (urea).This is an artificial nitrogenous compound. The product looks like white granules. It dissolves well in water. Used for root and foliar processing. It is mainly used in the spring, but to protect against pests and saturate the soil with nitrogen, it is also applied in the fall, after all the leaves have fallen off.
- Copper sulfate. Effective fungicide. Represents blue crystals. Suitable for the prevention and protection of fruit crops from fungal diseases. The most effective treatment is in late autumn, before sheltering for the winter. The drug should not be combined with other similar agents.
- Bordeaux mixture. The preparation consists of quicklime and copper sulfate. Many growers do not use this remedy in the fall, leaving it in the spring. But after the vine has thrown off the foliage, its use is permissible. The mixture protects the plant from black rot and other fungal diseases.
- Colloidal sulfur. Inorganic fungicide. Fights grape diseases such as oidium, powdery mildew, anthracnose, tick infestation. In the fall, it is used for prophylaxis. After spraying, it forms a protective film on the vine.
- Iron vitriol (ferrous sulfate). Green crystals, soluble in water. Heals the plant from mildew, oidium, spotted necrosis, grape cushion. Prevents the development of winter mold. The processing of the vine is carried out before frost.
- Lime. This tool protects the plant from mold during winter and spring thaws, saturates with calcium. The powder is simply quenched in water and stained with the mixture from the base of the vine to the root or introduced into the soil.
- Inta-Vir. Chemical insecticide. Destroys most pests: aphids, caterpillars, beetles. The duration of its action is no more than 1 month, therefore, prophylactic use in the fall is impractical, but if the plant is affected, then it is necessary to process the vine before wintering.
Read also: Arched grapes: description of the variety, cultivation and care
Recommended reading: Harvest Star Vario
Do not use all drugs at the same time. It is better to choose 2-3 products with different types of effects and apply them with a break of 1-2 weeks.
Useful Tips
To carry out high-quality and effective autumn feeding of grapes, you should heed the following tips:
- In order for the fertilizers to be absorbed by the main root system, dig circles around each bush with a radius of 0.5 m and a depth of 35-40 cm. Do not be afraid of damage to the roots - they will quickly recover. If fertilizing is applied directly to the surface of the soil, without making depressions, they will be absorbed by the upper roots, and not by the main ones. This will lead to their branching on the surface, rather than strengthening at a depth and during the winter, the roots will freeze.
- Abundant watering in October, after harvest, will help the accumulation of nutrients in the grapes and protect it from low temperatures. In addition, the accumulation of potassium will prevent the fruit from cracking in the next season. It makes no sense to fill the plants. It is enough to maintain the moisture content of the soil, focusing on the weather conditions. The amount of water required for irrigation is also determined by the type of soil - in sandy soils, grapes need up to 70 liters for each bush, and in clay soils, 20-25 liters are enough.
- After the autumn pruning and feeding, it is necessary to spray the grapes to prevent diseases and pests.
The use of autumn feeding of grapes will help not only to saturate the plant with useful elements, but also to prepare it for the coming winter. The bush will bear the cold much easier, and in the spring it will spend less energy on recovery.
0
Gardening Secrets
A young gardener needs to know not only how to feed the grapes, but also how to do it correctly. The advice of experienced gardeners will help to achieve a bountiful harvest and rapid crop growth.
- In order not to burn the vine or roots, you need to apply root dressing not at the base of the bush, but in the furrows dug out in the form of a ring around the plant with a diameter of 1 meter and a depth of 40 cm.
- Ash is a universal fertilizer for grapes. It contains 40% calcium, 20% potassium, 10% magnesium, phosphorus and some other trace elements. But ash is brought in not at a certain period, but several times per season (spring, summer, autumn). The main thing is that for the whole season no more than a bucket of ash was introduced under each bush.
- If the gardener uses both organics and minerals for fertilizing, then it is better to alternate them, rather than mix them.
- Nitrogen evaporates very quickly, so it cannot be simply scattered dry on the surface of the earth. It is always embedded in the soil or used during watering. Spraying with nitrogen does not give the best result.
- Of the minerals for grapes are used: "potassium salt", "nitrophoska", "superphosphate", "ammonium nitrate", "ammophos". Complex substances are also suitable: "Aquarin", "Solution", "Kemira", "Novofert". If there are none, you can use others with a similar composition.
- Closer to autumn, the amount of nitrogen in top dressing should be reduced, otherwise the grapes, even in autumn, instead of resting or fruiting, will start up new pagons and grow actively.
- Any foliar dressing of grapes is carried out in dry, calm weather.
- Many gardeners argue about when to make the third top dressing for grapes. Some insist that this is done a week before the ovaries appear, others - during the appearance of the peas (berries). But, in fact, the difference is small if fertilizers are applied regularly and in the correct proportions.
Summing up
Simultaneously with root feeding, foliar should also be carried out. This is guaranteed to increase the overall yield of the grapes, as well as the resistance of the bushes to various diseases. Competently carried out foliar feeding should be carried out using special solutions of macro- and micronutrient fertilizers. You can buy them inexpensively in a specialized store.
All types of fertilizers should be applied on calm days, in the morning or evening. In this way, leaf burns can be avoided. In order for the leaves to better absorb all the useful components, it is enough to add three tablespoons of sugar to the solution. If you adhere to all the rules for fertilizing, this is the only way to grow healthy vines and get a bountiful harvest with tasty fruits.
Spraying against diseases and pests
Spraying grapes before shelter for the winter is carried out so that the vines get rid of pests, diseases that "cling" to the shrub in the fall, when it is most exposed to external influences. Experienced growers recommend that such spraying of the vineyard be carried out for preventive purposes in order to prevent harmful effects on the plant.
You can treat the vineyard with any chemical that will not harm it, but each bush should be thoroughly sprayed. For example, you can use to process:
- copper or iron sulfate;
- slaked lime;
- Bordeaux liquid.
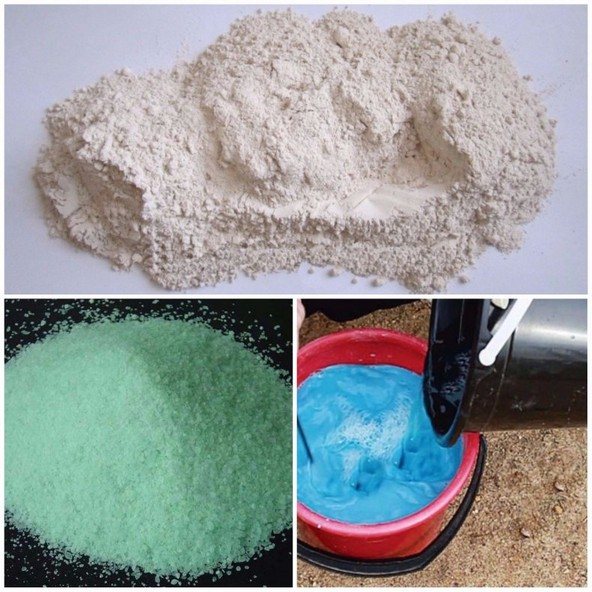


Also, summer residents who trust chemical fertilizers carry out the processing of the vineyard with folk remedies.
Fungicides
Fungicides are chemical agents for fungal diseases of plants. They are widely used in viticulture as a reliable, proven and inexpensive means that can preserve the future harvest.
Experienced growers who have been growing this plant for more than one year do not recommend processing the grapes in the fall before sheltering for the winter with iron sulfate. This is due to the fact that, despite its effect against insects, ferrous sulfate significantly weakens the plant's protection against the cold, your vineyard simply may not survive the winter.Since the autumn processing of grapes with iron sulfate should not be carried out unless absolutely necessary, it is better to carry it out in the spring. In the spring, the dosage of ferrous sulfate for spraying a plant is 500-700 g per 10 liters of warm water.
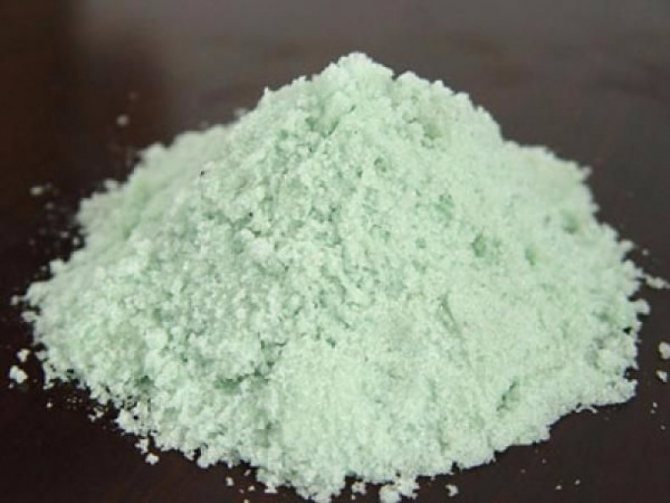


Processing grapes in the fall before sheltering for the winter with copper sulfate should be carried out as follows. Immediately before processing, dilute half a glass of the product (or 100 g) in a bucket of water with a capacity of about 10 liters. Stir the copper sulfate granules well until they are completely dissolved in water. Use 2 liters of product per bush.
The next remedy is Bordeaux liquid, which is a fungicide that you can buy at any plant protection store. Still, it's better to cook it at home. Experienced agronomists and winegrowers recommend sprinkling the vine with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, since a high concentration can easily burn the vine. To prepare the necessary mixture, take half a glass of copper sulfate and a little more than half a glass of slaked lime, stir everything in a bucket of water. After that, you can start processing.
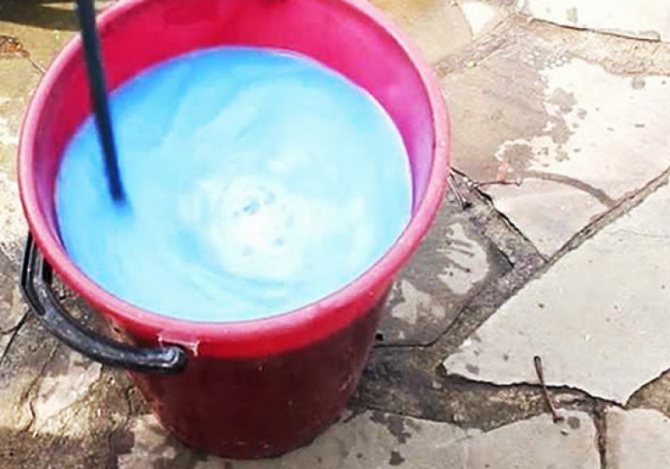


A very old and effective way to protect grapes from infection is slaked lime. First, prepare a solution of quicklime, extinguish the lime in water (in a consistency of 2 liters of water to 1 kg of lime), then pour 10 liters of water and mix the solution. Using a paintbrush or broom, apply the solution to each bush and branch of grapes. Such a simple solution will reliably protect the plant from mold and mildew until spring, even if the temperature rises.


Folk remedies
There are some folk remedies that will help protect grapes from pests and fungi in the fall, they were developed over a thousand-year history of viticulture.
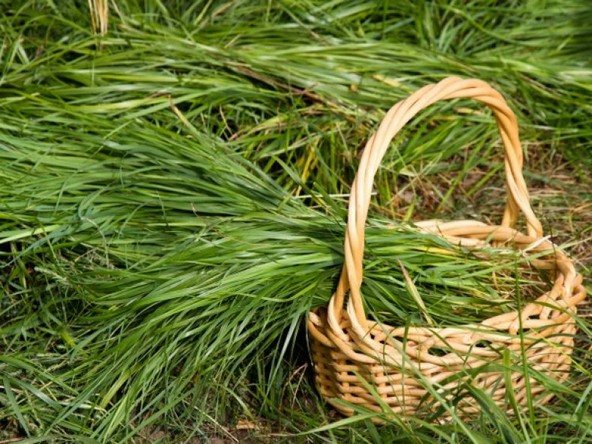
If you want to protect the plant from powdery mildew - take freshly cut grass, put it in a pile and wait until gray mold appears in the middle of the pile of grass. Then put the grass in a bucket of water, stir and drain. Then spray the resulting liquid on the vine.


You can protect yourself from spider mites with this solution: pour 2 kg of green potato tops with 10 liters of hot water, then let the solution brew. After settling the product, treat the bush with it.
The most affordable folk remedy is a solution of infused onion peel. To prepare this miraculous remedy, pour half a bucket of onion peel with water, boil it for 20 minutes and let it brew for a day. Then add water to a solution of 10 liters, add 20 g of honey, strain the solution and treat the vine with it.
Features of autumn nutrition
During the growing season, the grapes build up a large part of the aboveground. The plant takes the necessary elements from the ground, so feeding should be carried out 3-4 times per season. In the fall, the nutrient composition of the soil is enriched, the bush is provided with everything necessary for recovery after fruiting and spring awakening.
During this period, the culture needs an increased amount of potassium and phosphorus. The first nutrient contributes to the timely ripening of the vine, increased immunity, resistance to drought and frost. Potash fertilizers improve the taste and aroma of berries. Phosphorus strengthens the root system, participates in metabolic processes, is necessary for the growth, development of the plant and the formation of seeds.
When preparing grapes for winter, microelements should be present in autumn dressing, especially if the soil in a given region does not contain them in the required amount.
Sandy soil protects bushes from moisture retention, provides air exchange, but does not retain useful elements. For this reason, on sandy loam and sandstone, the introduction of additional components in the fall is mandatory.
Boron promotes the rapid ripening of berries, increases their sweetness, is necessary for the full development of the bush.Copper protects against fungal infections, is required for the growth of the vine, increases frost resistance. Zinc increases productivity; it is important to add this element to the soil with low acidity. Calcium contributes to the growth of the root system, participates together with magnesium in the formation of chlorophyll. Manganese is necessary for the growth of the rootstock with the scion, increases sugar accumulation, accelerates growth and fruiting.
Thus, in the fall, grapes are required to provide:
- potassium;
- phosphorus;
- microelements.
The only nutrient that cannot be actively fed to grapes in the fall is nitrogen. The mineral causes the growth of green shoots and is required only in the spring, in the first half of summer. If you add it after that, the plant will grow leaves, and not pour berries, the vine will not have time to ripen. A small amount of the element should still come in in the fall, since nitrogen promotes the assimilation of phosphorus, participates in metabolism. But it is enough in organic supplements, therefore, in mineral supplements, it is completely excluded.


Organic fertilizers
Organic types of feeding contain many mineral trace elements. They significantly improve the quality of the soil cover in autumn, improving its heat transfer, oxygen saturation and moisture content. In addition, organic components fill the earth with beneficial bacteria.
At the very beginning of September, the soil under the grapes must be dug up and fertilized with chicken droppings, compost or manure in order to improve its air permeability, and also make it looser.
Ash
Wood ash also contains a large amount of minerals, especially potassium. This makes it an excellent means for fertilizing grapes in the fall, since the plants really need them during the cold weather. In addition, ash contains calcium, phosphorus, a little sodium and magnesium.
One of the many advantages of this fall dressing is the absence of chlorine, which often negatively affects the grapes.
Ash should be applied on soils with high acidity or low levels of potassium and phosphorus. It works as follows:
- reduces subacidity;
- makes the composition of the soil better;
- creates useful microflora, which is necessary for a good harvest.
Ash can have a positive effect on grapes for 3-4 years after feeding.
Important! This substance works best in tandem with humus or peat.
This mixture is rich in various minerals that grapes need. It is not recommended to use ash with manure, poultry droppings, ammonium sulfate or superphosphate as top dressing in the fall.
Compost
One of the effective substances that belong to organic fertilizers is vegetable humus. This feeding is easy to prepare yourself. To do this, you just need to dig a hole in the area of the site, where moisture is well absorbed during the rainy season. The compost pit should be 2 m wide and 1 m deep.
After creating a pit, you need to place in it:
- plant residues;
- animal droppings;
- sawdust;
- household kitchen waste;
- and straw.
All this needs to be mixed and tamped. To improve the quality of humus, you can add any other fertilizer to it.
Manure
The best organic top dressing for grape shrubs in the fall will be manure. It is very important that he be stubborn. Fresh manure will overwhelm the soil with excess nitrogen, which will adversely affect the grapes.


Bird droppings
Before feeding bird droppings in the fall, its mass must ferment. When this happens, it must be diluted 1: 2 with water. After two weeks, the resulting procedure must be repeated, but the proportions will already be 1: 5. One bush of grapes should account for half a bucket of ready-made dressing.
Main seasons for top dressing
Basically, fertilizers are introduced into the ground in the spring with the onset of the growing season, when sap flow begins, and the buds have not yet blossomed. In the summer, the plant also needs additional nutrition. But at this time, foliar fertilizers are mainly used, sprayed, if necessary, along the crown of the bush. Autumn is an important season in horticulture. It is at this time of the year that the grapes receive their main food. Good feeding helps the plant not only survive the cold season, but also promotes high-quality maturation of the wood.


It would seem that all the trees and shrubs are sleeping in winter, and there is no reason to fertilize the grapes the day before. This is mainly the thinking of novice gardeners. But such a mistake will affect in the spring, and when the time comes to harvest. Indeed, in order for the shrubs to winter well, they need additional warmth, and with the onset of heat, nutrients will begin their work.
Grape care in September and October


Autumn grape care has two goals: to lay the foundation for high-quality fruiting in the next season and to prepare the plant for the winter period. The bush is considered completely ready for winter if it is healthy, not affected by pests or diseases, has well-ripened wood, recovered the strength spent on fruiting, and went into a dormant state in time.
These objectives and growing conditions determine how to care for grapes in the fall. List of main works:
- the last top dressing of the season;
- pruning grapes;
- catarovka roots;
- protection against fungi and insects;
- pre-winter watering;
- shelter for the winter.
The quality of autumn care is especially important for late grape varieties, limited in time for wood ripening and slowing down of life processes. When grown in temperate climates, even medium-ripening varieties may not have time to prepare for winter. In view of this, it is recommended to follow two rules:
- It is necessary to start autumn work as early as possible - as soon as the harvest is taken from the vines. The preparation of early grape varieties must be started without waiting for the end of the fruiting of the entire plantation.
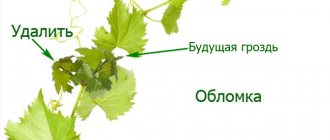
- Care should be taken in advance to ensure that the vines are not overloaded. If the plant spends too much energy on the ripening of the crop, it will be difficult to restore it in a short time. It is worth sacrificing the volume of the crop in favor of the bush and performing normalization by thinning the bunches.
We advise you to read
- Oidium grapes and control measures
- We study the nuances of care and planting grapes in Siberia. ...
- How to spray grapes after flowering and during the ovary period
- Wine from grapes at home
- Features of growing grapes in the middle lane ...
- Growing grapes from cuttings
- How to plant grapes correctly: tips and practical ...
- When and how to feed grapes?
- How to care for grapes for a good harvest
Wine glasses
How to prepare grapes for winter: what to do, pruning, shelter for the winter
Proper preparation of grapes for winter will protect them from cold and pests. Despite the fact that most of the varieties are obtained as a result of selection, you should not rely 100% on the ability of sweet berries to resist the influence of external negative factors. Proper preparation of grapes for wintering includes several stages. The first one begins in the fall. The specific period is determined by the gardener, taking into account the climatic zone and characteristics of the variety. The optimal time is mid-September - early November. In the middle lane, preparations begin in October.
We recommend to read: Lawn mower al-ko (alco): gasoline, self-propelled, electric, price, reviews - Special equipment Info