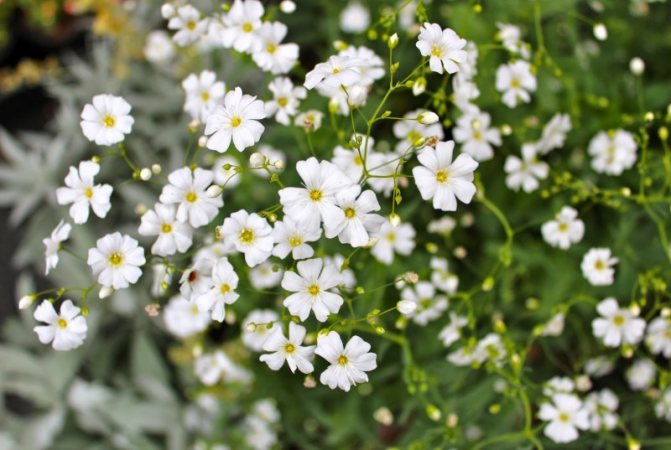
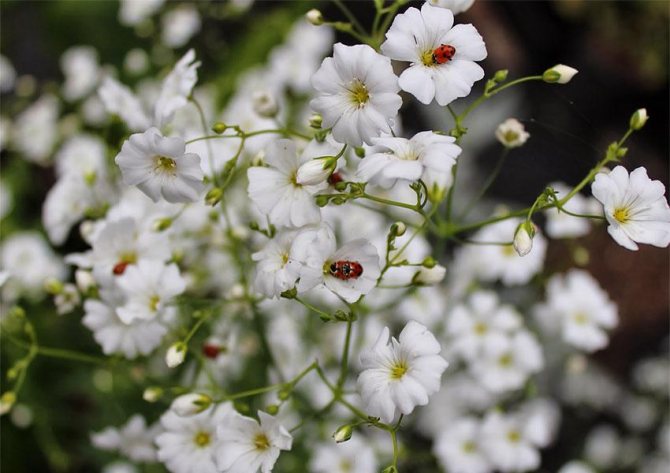
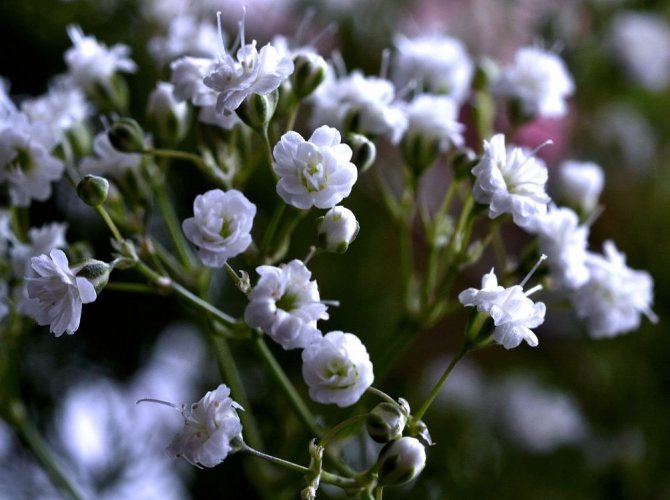
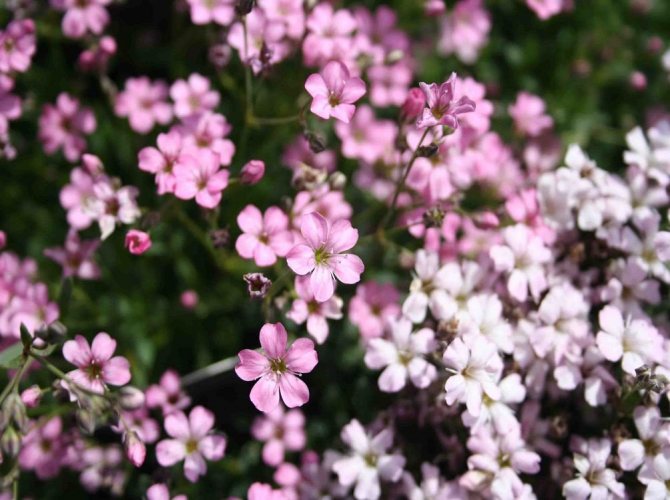
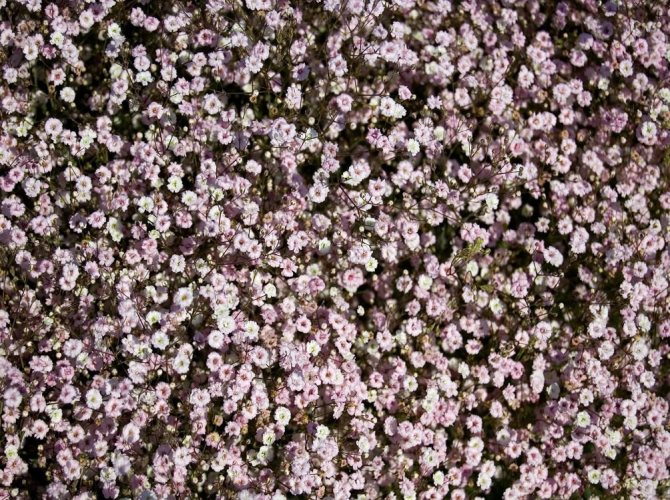
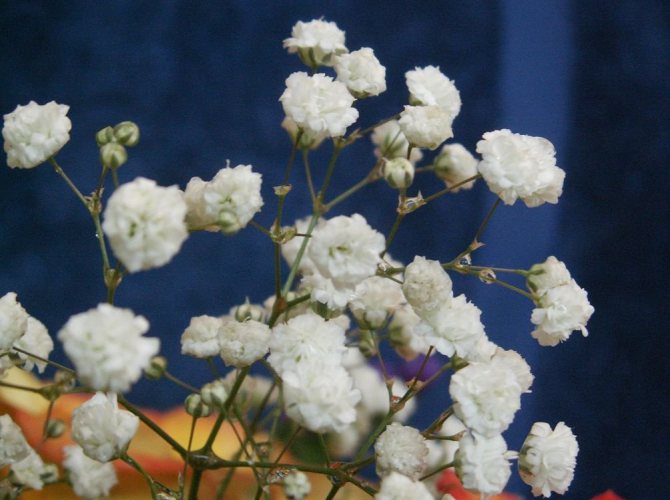
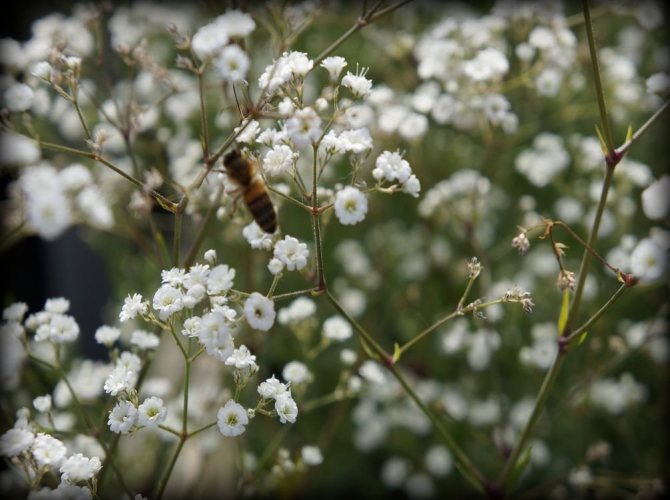
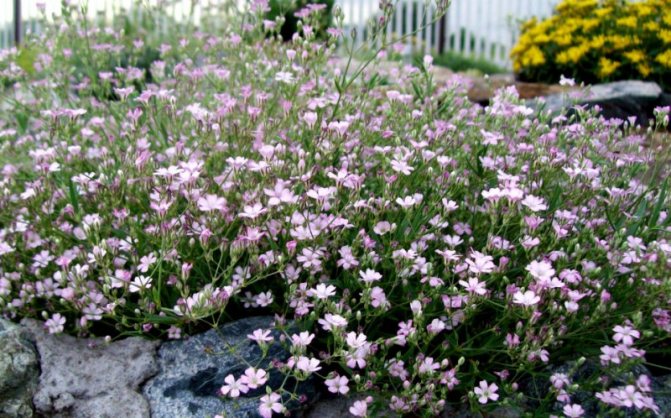
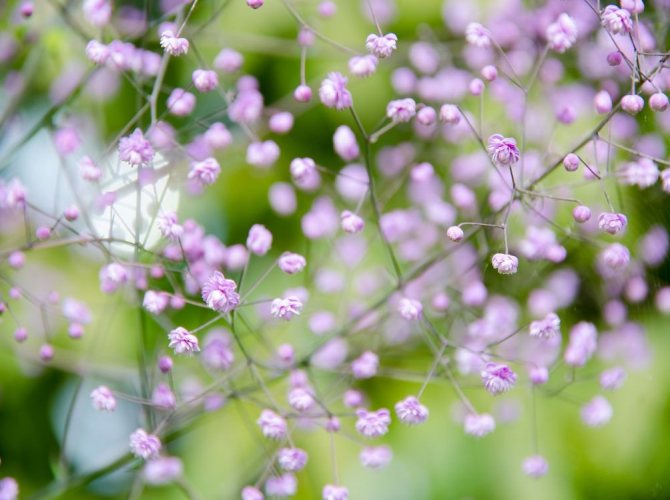
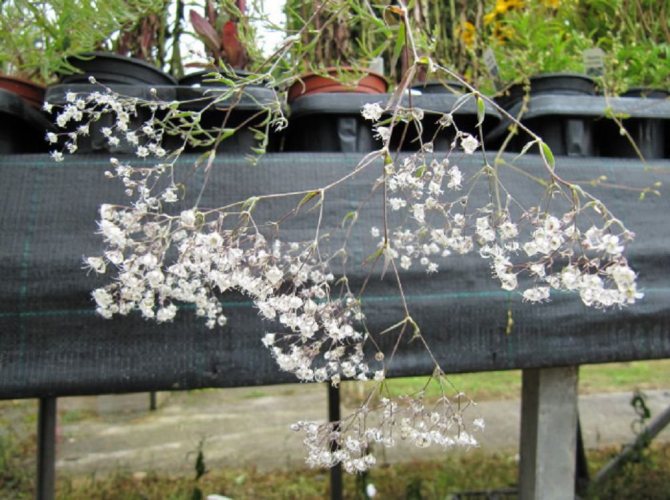
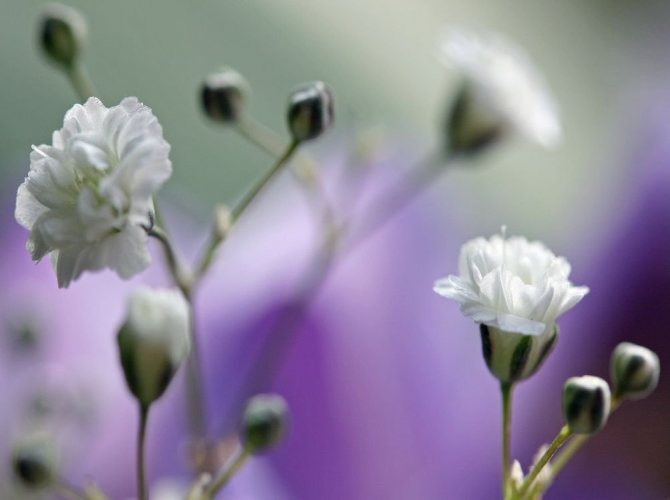
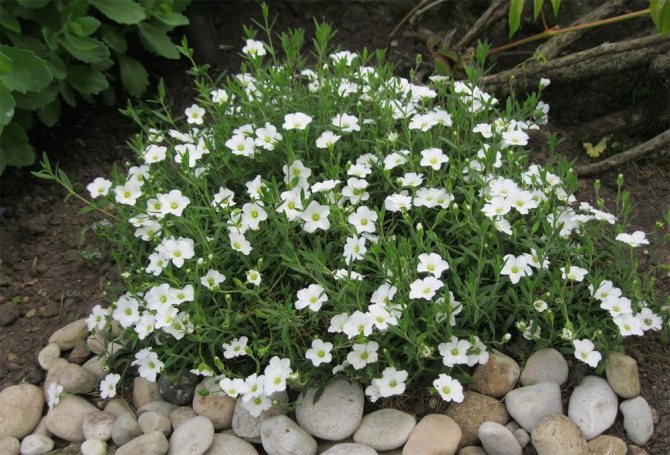
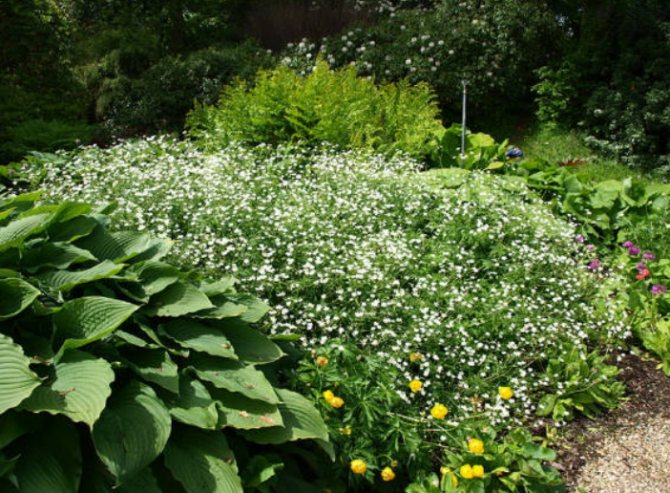
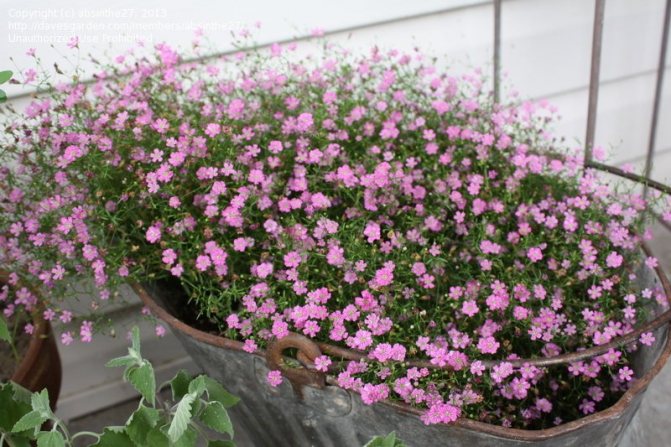
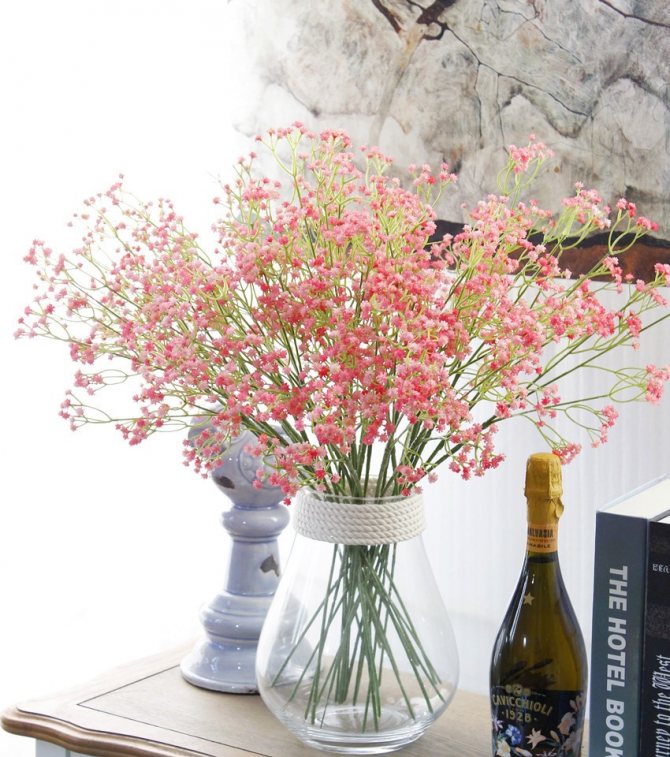
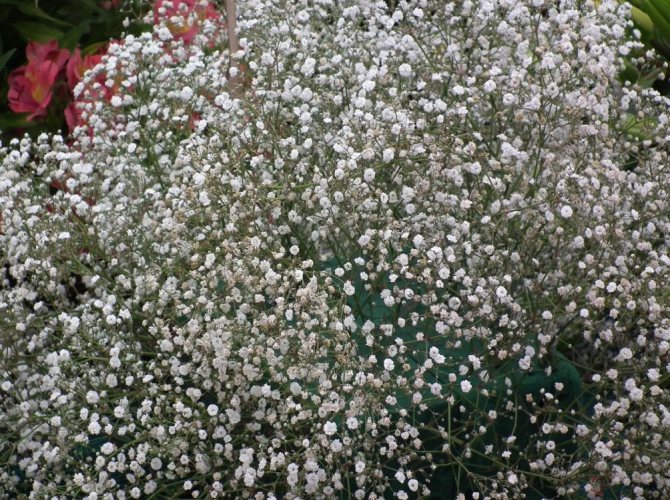Just as large gems look better surrounded by small sparkling pebbles, tall flowers with bright inflorescences look more impressive surrounded by grassy greens with small leaves or buds. One of these satellite flowers is gypsophila - a herb for open ground. This unpretentious garden culture has several varieties and is successfully grown on almost all continents of the Earth. Gypsophila is used for framing ridges and borders, in the complex design of flower beds and flower beds, bouquets and flower arrangements complement its graceful twigs.
Photos and descriptions of gypsophila paniculata, the rules for planting and leaving it are given in this article. Here we will talk about the popular varieties of the plant, list its strengths and methods of reproduction.
Perennial gypsophila: varieties and varieties
About one hundred and fifty species of an attractive, unpretentious garden plant are known. For breeding a fluffy bush, some species and varieties are distinguished.
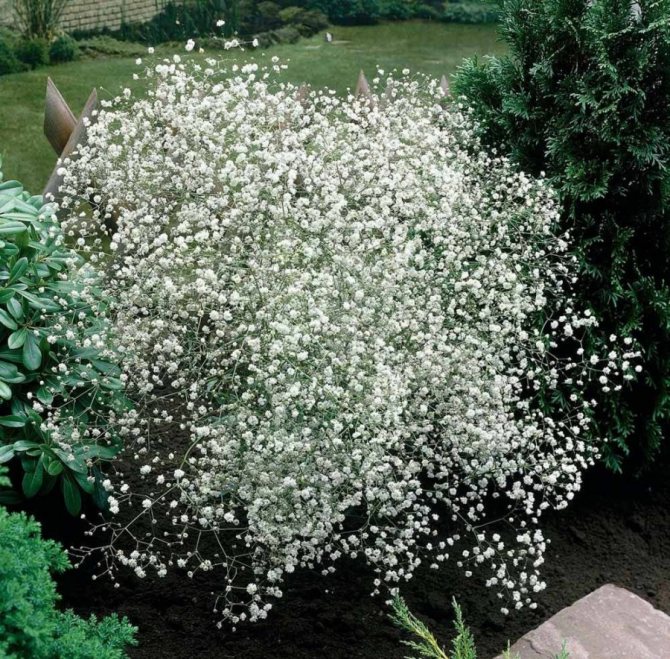
- Gypsophila paniculata (Gypsophila paniculata)
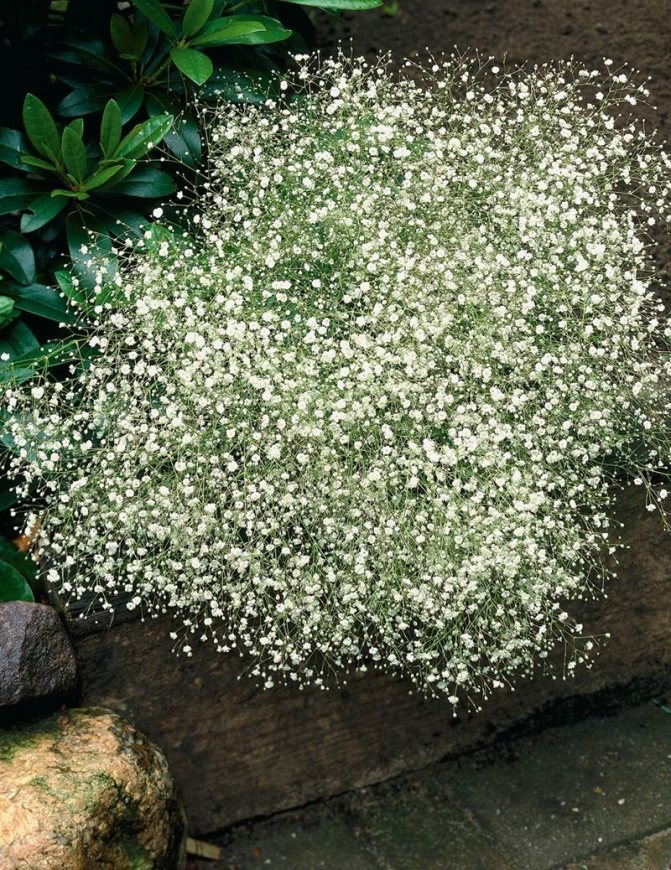
Perennial with a peculiar life form of tumbleweed. A characteristic feature is the strong branching of the stems from the base, forming a ball-like bush. The stem dries out after the seed has ripened and breaks. Rolling in the wind, scatters seeds.
Distributed in the steppe and black earth belts of the European part of Russia, in the Caucasus, in the southern part of Western Siberia. Grows well in dry meadow steppes, on forest edges, mountain slopes, rocky surfaces. Any non-acidic soil is suitable, but mainly sandy, stony, gravelly composition.

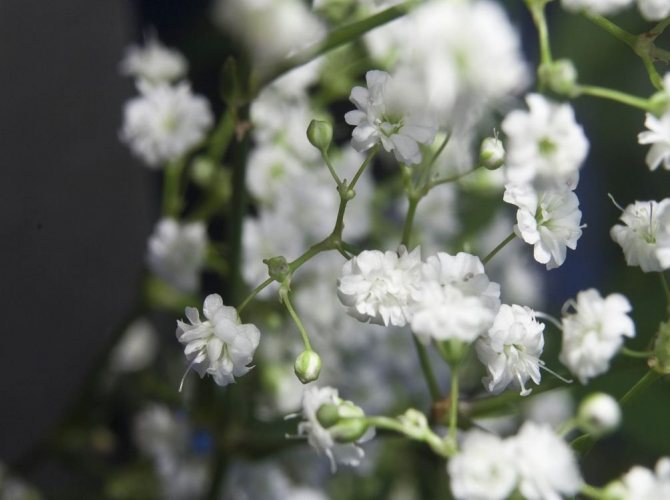
The height of the herbaceous blizzard is from fifty cm to one meter. The roots are powerful, thick, taproot. Branched, smooth or fibrous stems. The bush looks like a ball. The leaves are elongated, pointed at the top, from two to seven centimeters, two to ten wide. They have up to five arcuate veins.
Numerous white flowers are located on a spreading paniculate branch. The filiform pedicels are several times the length of the outer perianth. Wide, bell-shaped calyx. Length one and a half millimeters. White petals up to four cm.
Flowering begins in mid-June and ends in late summer. The fruits are similar to rounded bolls, up to three millimeters in diameter. Seed reproduction.
It is bred as an ornamental plant for composing compositions in bouquets. Due to its disinfecting effects, it is widely used in medicine. The roots contain saponins, which allows their use in the food industry.
Paniculata includes some varieties:
- Snowflake;
- White holiday;
- Flamingo;
- Terry.
- Gypsophila graceful (Gypsophila elegans)
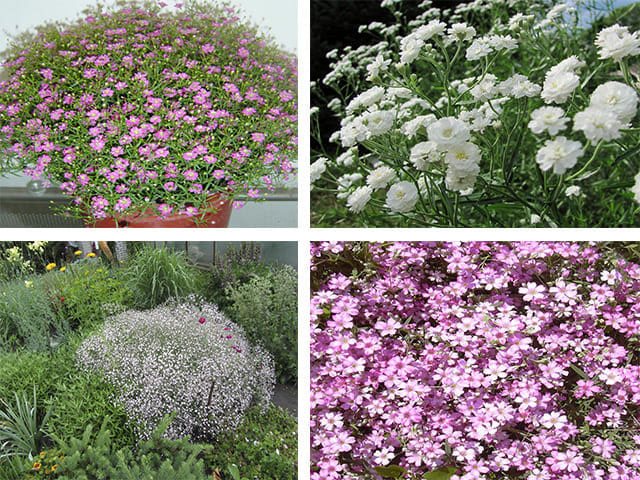


Up to fifty centimeters high. The branching structure is rounded. Oblong leaves with a white bloom. Small flowers form a corymbose inflorescence. Blooms in late May for four weeks. Artificial extension of the flowering period is known. Resistant to cold and drought. Prefers light, fertile, non-acidic, sandy, calcareous soil.
- Gypsophila creeping (Gypsophila muralis)
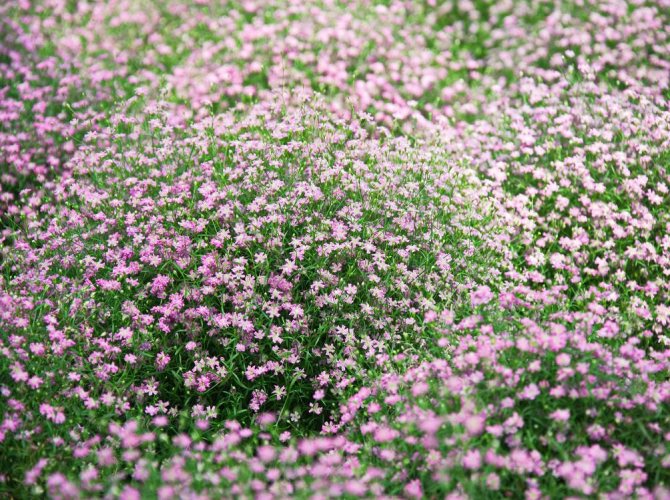
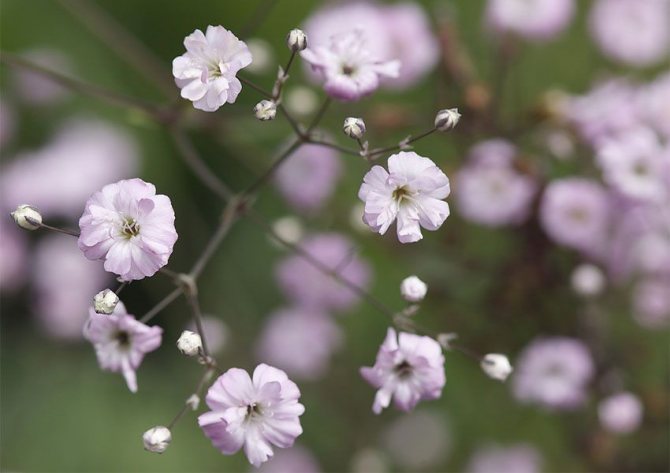
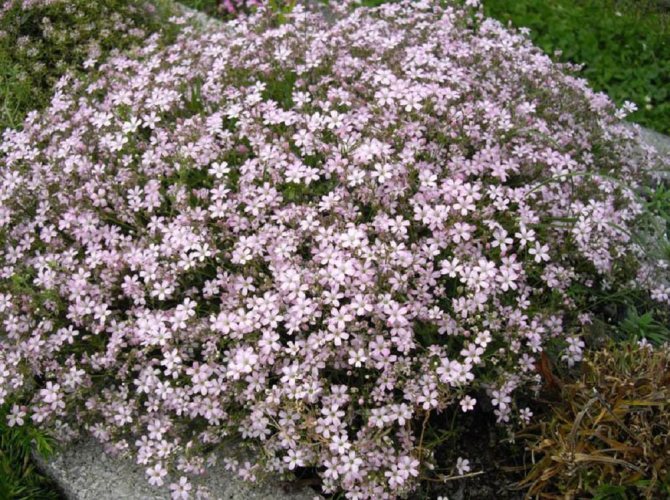
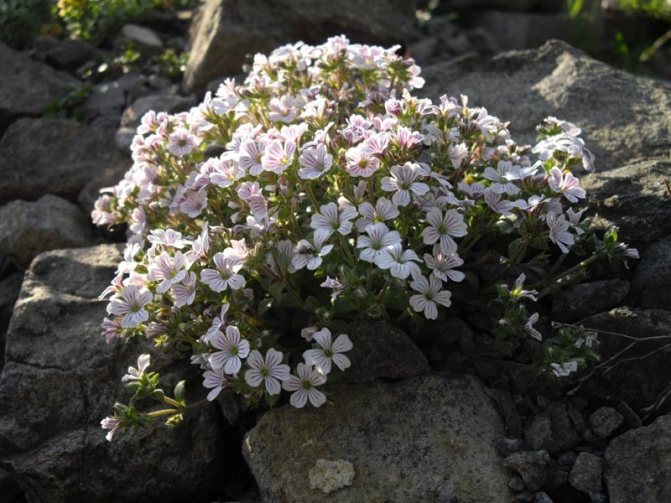
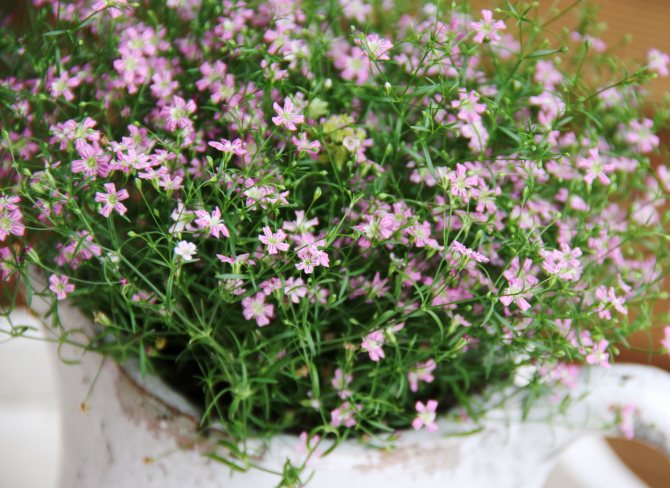
Creeping dwarf species. The mountain species prefers stony ground. Dense bushes in the form of hills up to forty-five centimeters.Graceful leaves of a dark shade. A powerful root system has been developed. Snow-white or pink flowers are only ten millimeters in diameter. Blooms twice. The first time in early summer, then in autumn, on the last warm days.
- Pacific (Gypsophila pacifica)
A large bush up to one meter high. Differs in large, peculiar stems with many shoots. The leaves are lanceolate, dark, green with a gray or blue bloom. Light, pinkish flowers bloom in August. Collected in lush, delicate inflorescences.
- Jaspolkovidny
Small, growing with a thick, lush carpet up to eight centimeters in height. The foliage appears to be ovoid, one and a half centimeters long. Lilac, purple, white, small flowers with red veins. The mountain species blooms once every two to three years. Grows on sunny slopes.
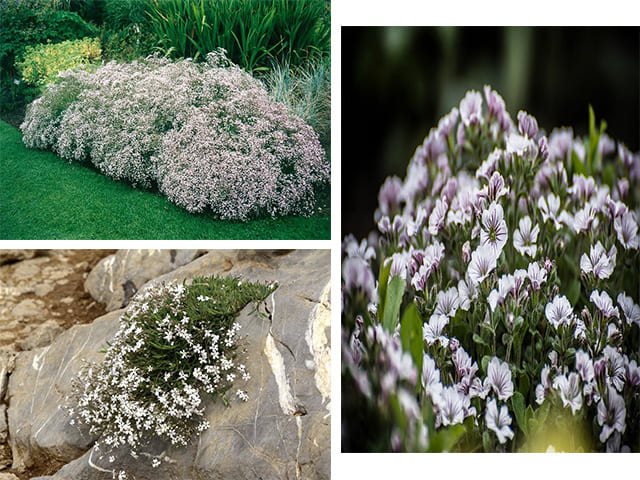


Description of the plant
Gypsophila is an ornamental flowering plant that takes the form of herbaceous growth or dwarf shrubs. It has a powerful taproot that extends far into the soil. Thin erect stems are covered with many lateral processes, so very quickly the gypsophila bush acquires a spherical shape. The height of the vegetation is 10-120 cm. There are creeping ground cover forms. Their stems are located close to the ground.
On the shoots covered with smooth green bark, there are practically no leaves. Most of the small leaves are concentrated in the basal rosettes. They are lanceolate with solid edges and a pointed end. The foliage is painted dark green or grayish. It has a smooth, shiny surface.
In June, loose paniculate inflorescences bloom at the ends of the shoots. They consist of snow-white or pink flowers with a diameter of 4-7 mm. The bell cup consists of five wide, serrated petals, on which there is a green vertical stripe. There are 10 thin stamens in the center.
After pollination, the seeds ripen - polyspermous capsules of spherical or ovoid shape. Drying, they open on their own into 4 valves, and the smallest rounded seeds are scattered on the ground.
Landing
Proper planting and caring for gypsophila will provide beautiful flowering for years to come.
Soil and place
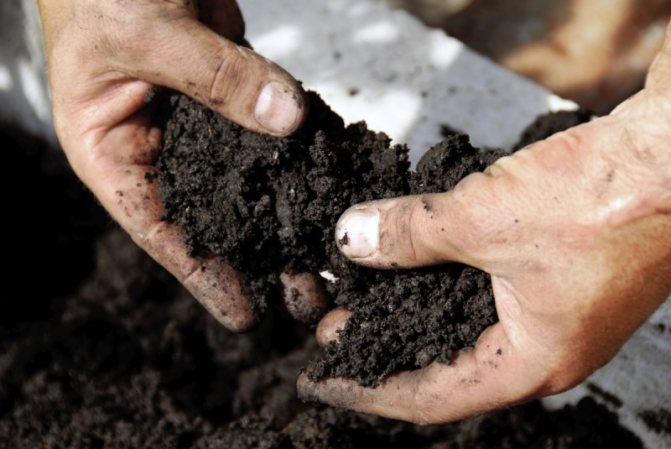
It is important to properly prepare the soil. It is preferable to choose a light soil, excluding clay composition. Well suited neutral soil, calcareous composition, loose, drained, sandy with a rocky surface. Recommended for growing on the sunny side of the garden.
Sowing, seedling, cuttings
Annuals are sown at the beginning of autumn in separate beds, after the harvest has been completed and the soil has been processed. With the onset of spring, the seedlings germinate. They are transplanted to a permanent place, where they will grow up until the fall.
Number of seeds per square meter:
- creeping - twenty pieces;
- medium tall - ten;
- large - five seeds.
An adult perennial bush is capable of self-seeding annually for five years.
Creeping hybrid varieties are reproduced by cuttings. Shoots are cut immediately after the flowering period. This further stimulates the roots. The seedling method promotes abundant flowering in the current year.
Sowing seedlings:
- in the middle of spring, the seed is sown in a greenhouse, the sowing is covered, protecting it from temperature extremes;
- in the greenhouse, planting is carried out in March, thanks to the use of modern materials, a strong bush is easily transferred into the ground.
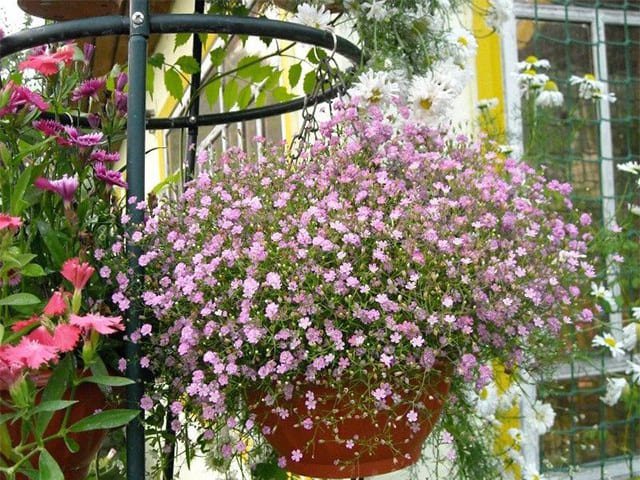


Breeding seedlings in boxes. The height of the walls must be at least ten centimeters. Filled with a suitable loose substrate. For even distribution of seeds, it can be mixed with sand. It is not worth deepening, it can be supplemented with a top layer of soil mixture. Moisten with a spray bottle and cover with foil. The first shoots appear in two weeks.
After germination of several leaves, it is necessary to transplant into cassettes, pots with a diameter of up to twelve centimeters.
Before picking, peat tablets are soaked to increase several times. Using a pencil or a straw, make a depression and plant a seedling. When the flower grows up, you can transplant it into open ground without removing the roots.
Landing in open ground
Plant in open beds after two to three leaves have germinated. A distance of sixty centimeters is observed between flowers, at least one hundred and forty centimeters between rows. The root collar does not sink into the ground. Water it immediately after transplanting. Thin out in a few years. The first flowering will delight after the germination of twelve pairs of leaf plates. The maximum effect is noticeable after three years.
Seed collection
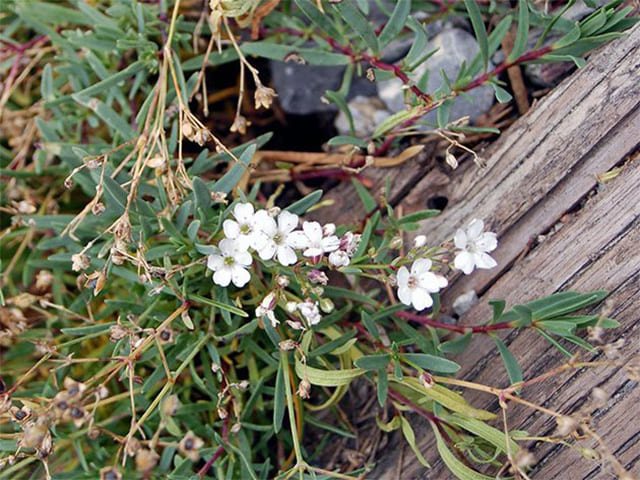


Collected after complete drying of the culture. The seed box is carefully cut and dried. The extracted seed is dried, evenly distributed over the surface of the table paper. This helps the moisture content to be absorbed better.
Stored in paper or natural fiber fabrics in a dry, unheated room. For safety, it is important to prevent an increase in air humidity.
Care
No special care required. The plant is not picky, even a beginner can handle it. Water in dry and hot seasons by the root method. Feed up to three times a season with organic and mineral fertilizers. After flowering, the bush is cut off and prepared for the winter regime.
Diseases and pests
Gypsophila is not susceptible to various diseases and pests. Only in the complete absence of minimal maintenance does gray rot, rust or nematodes start. For treatment, drugs are used to kill insects and their eggs. Rust fungi are removed with a solution of copper sulfate and an antifungal mixture. If the treatment does not give an effect, then the plant must be dug up and rinsed under running water at least forty degrees.
Wintering
Perennial varieties are quite resistant to low temperatures. To maintain healthy bushes during the cold season, it is necessary to provide proper preparation for wintering. Cutting the stems is carried out, leaving eight to ten sentiments above the soil. The land is mulched with a peat mixture. To trap the snow, you can sprinkle with foliage, cover with spruce and pine branches.
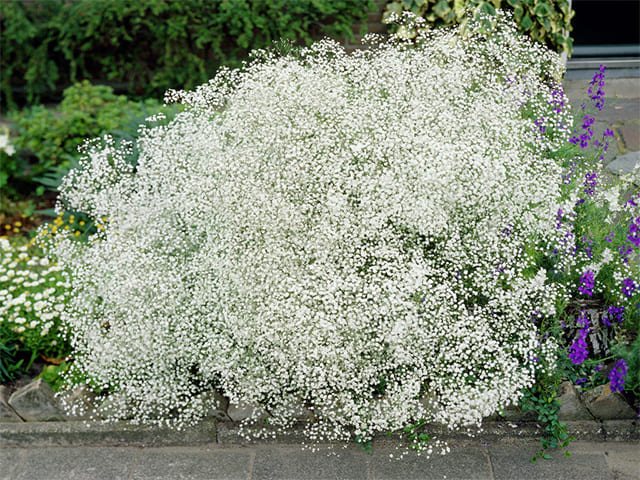


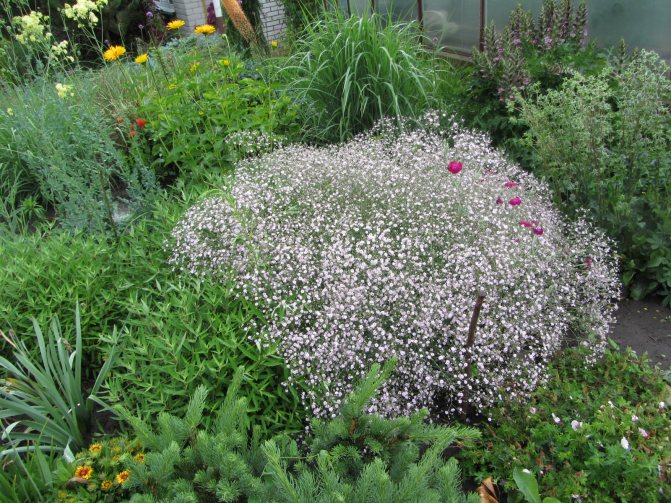
Tumbleweed care
Paniculata gypsophila is one of those plants that may not need to be cared for at all. However, if flowers are grown for cutting, play an important role in landscape design, the owner will be interested in the high decorative effect of the paniculate gypsophila and in the large size of its inflorescences.


You need to take care of gypsophila like this:
- water only during periods of severe drought, pouring water strictly at the root;
- two years after planting, thin out the bushes, leaving only every second of them (if this is not done, the inflorescences will be small and non-decorative);
- feed the bushes twice a season, using mineral fertilizers in the spring, and organic matter (humus, wood ash, etc.) before winter;
- for gypsophila, they pose a danger of rot and nematodes, therefore it is important to observe the irrigation regime, prevent waterlogging of the soil, treat the bushes with phosphamide and fungicidal preparations a couple of times a season;
- in the fall, after flowering, you can collect the seeds of the panicled tumbleweed, after drying them and placing them in paper boxes;
- at the end of autumn, the bushes are pruned, leaving 3-4 longer shoots at the root, and the flowers are covered with dry foliage, sawdust or spruce branches.


Paniculata gypsophila is a frost-resistant plant, it can freeze out only under the condition of a snowless but cold winter or in an unstable climate with temperature extremes and high humidity.
Advice! You cannot fertilize tumbleweeds with fresh manure - this will destroy the plant.In extreme cases, the use of mullein infusion is allowed in a limited amount.
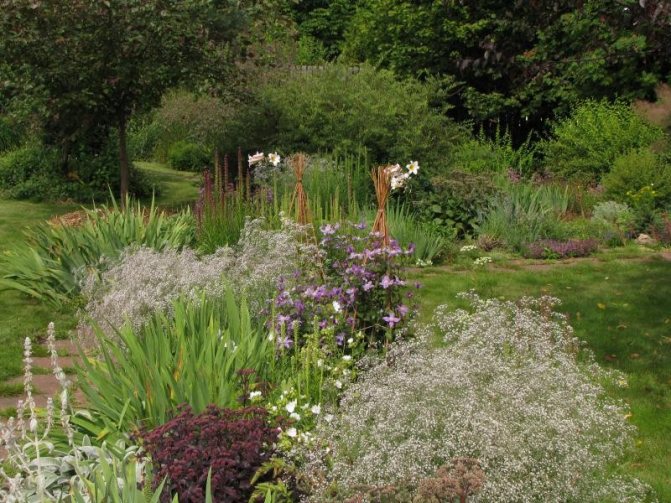
In landscape design
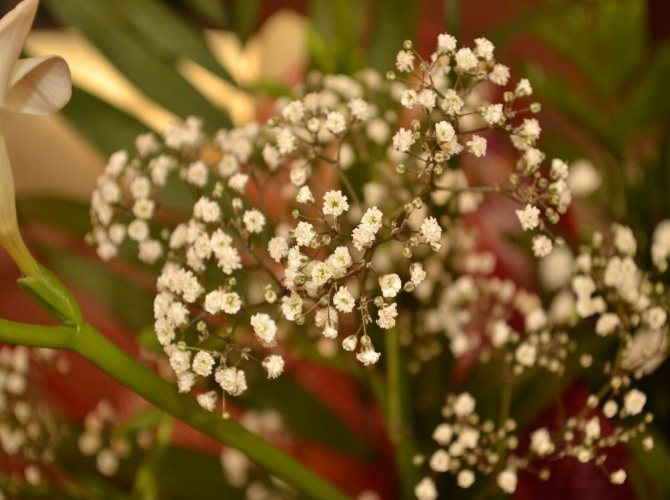
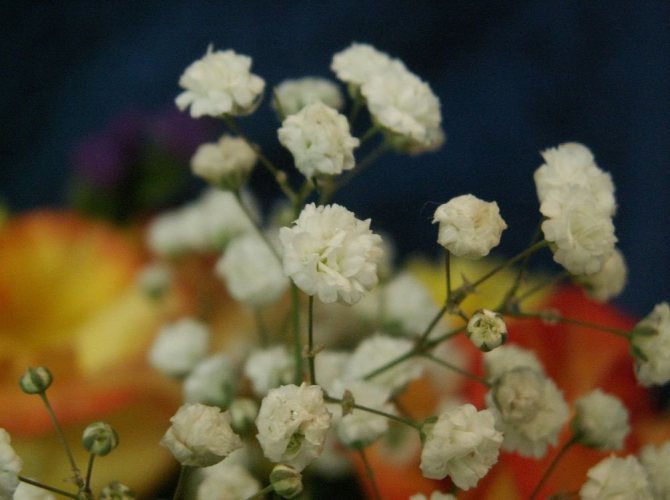
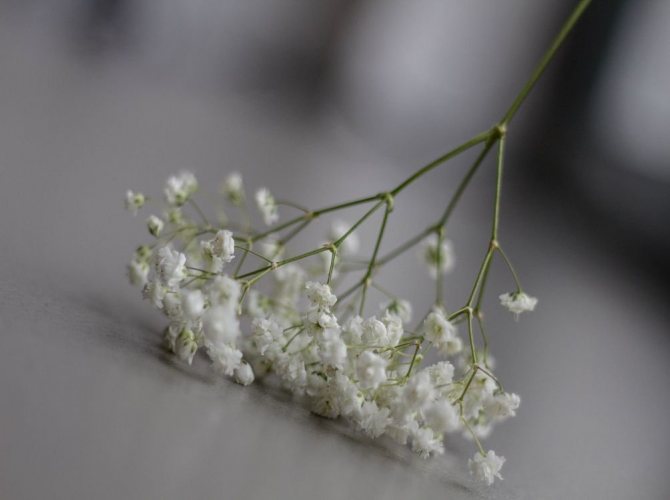
Multiple small flowers form a fluffy cloud. They are considered an elegant element of landscape design. Florists prefer to complement flower arrangements with delicate twigs. In the interior it is used as a dried flower. Gypsophila is able to decorate any personal plot, square, park.
Miniature views are complemented by alpine slides, rockeries, rocky slopes. Accentuate the boundaries of floral arrangements. Garden decoration with a gentle cloud visually enlarges the site, forming an amazing landscape.
Tips from experienced gardeners and summer residents
- in the process of growing plants from seed, such as perennial gypsophila, it is important to be patient, since often varietal qualities begin to appear after a few years, so the best way of propagation is cuttings;
- for the preservation of decorative qualities for the winter, the stems should be covered (with leaves, peat), especially when severe frosts have already hit, and the snow has not fallen;
- in the process of rooting, a young plant should be watered systematically, but not abundantly;
- some types of gypsophila, for example, paniculata, do not like transplants very much, so the planting site is chosen on an ongoing basis.
Perennial rudbeckia: planting and care
Perennial gypsophila will not leave indifferent even the most inexperienced gardener or summer resident. It will look attractive in mixboards, alpine slides or just in flower beds. And the combination in bouquets with bright and large flowers looks exquisite and stylish, being an adornment of any interior.
Composition rules
Airy gypsophila gracefully complements bright plants with large inflorescences, for example, from a rose or phlox. Favorable neighborhood will be with woody shrub groups growing next to stones, in limestone soil:
- barberry;
- derain;
- lavender;
- boxwood;
- elder.
Looks good in single and group planting. Gives special tenderness to neighboring plants, highlighting their bright inflorescences against a white or pink background.
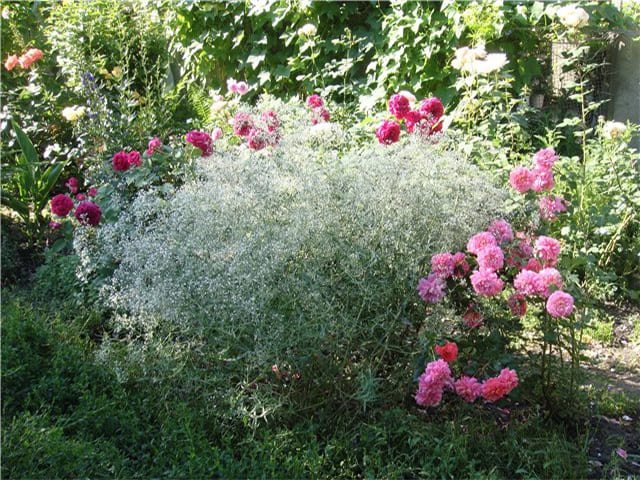


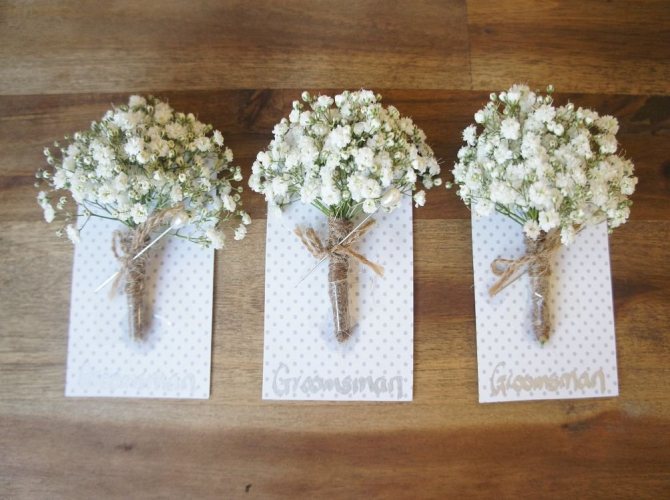
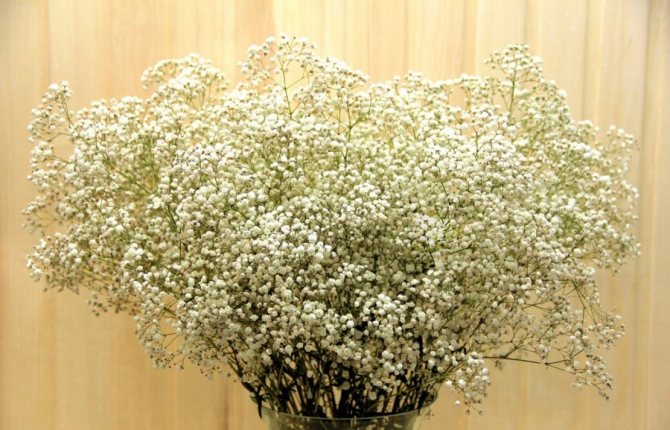
Airy inflorescences are often used in bouquets. One of the green decorative elements. The bouquet looks lush, voluminous, contrasting in combination with asparagus.
Views
There are 150 types of gypsophila. The following describes the most famous of them.
Graceful
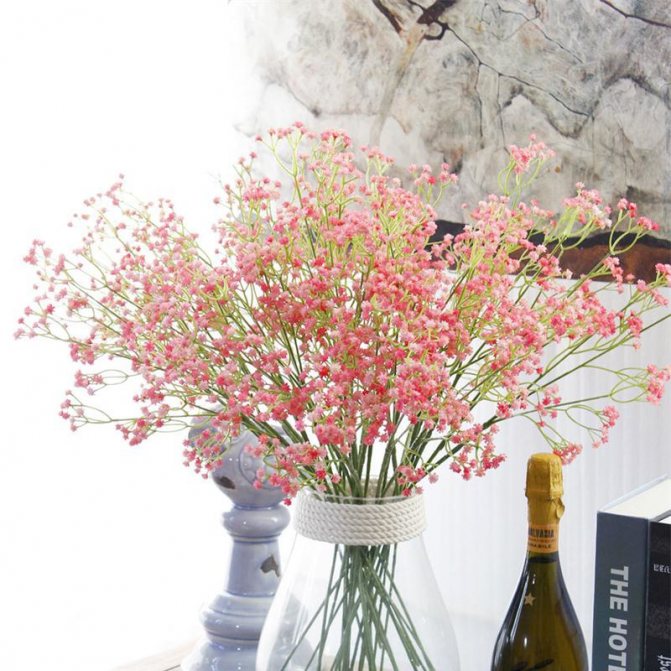
This species is an annual plant. The bushes are spherical and 50 centimeters high. The leaves have a gray-green color. They are lanceolate. Small flowers are collected in loose panicles of white, red, cream or pink color.


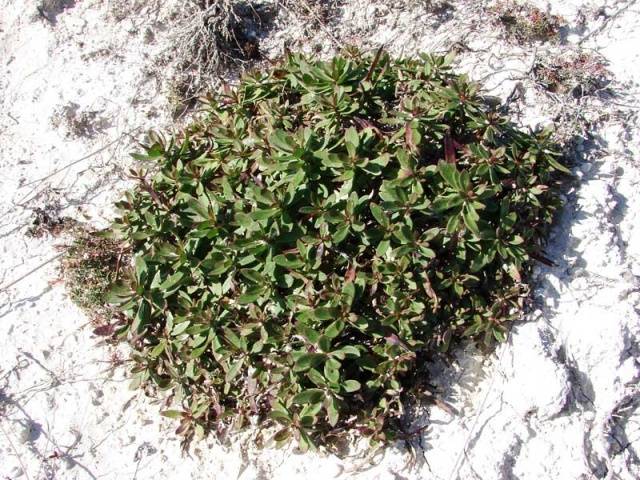
Creeping
It spreads above the ground. The height of the shrub does not exceed 30 centimeters. A large number of very small flowers growing densely. The leaves have an oblong shape. The stem is tighter than other species. The plant is common in the mountains of Central Europe.
Pacific
Gypsophila grows in China and Primorye. It is a perennial species. It is relatively tall - the bushes grow up to a meter in height. The leaves are blue-gray. They are wide, lanceolate. Flowers have a pink, faint, pale color shade.
Jaspolkovidny
This gypsophila has highly branching stems and practically lies on the ground. Its height does not exceed 10 centimeters. In June and May, during flowering, the shrub is densely covered with white or purple small flowers. The homeland of this species is in the Himalayas.
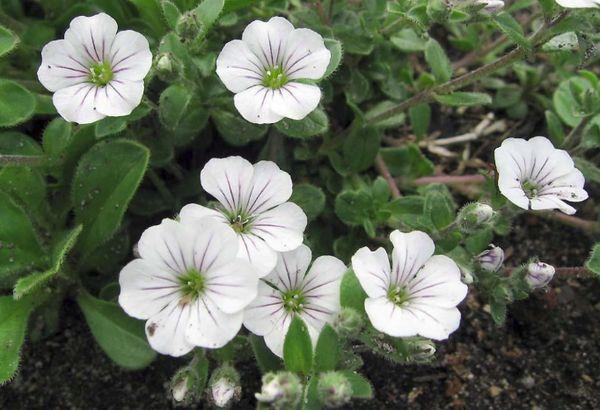


Areciiform
The homeland of this species is the mountainous part of Iran. It spreads along the ground, located within three centimeters from the ground. It grows slowly. The foliage has a gray-green color. Gypsophila flowers are sessile, white. It blooms in July. This species is rare.
This plant prefers to grow on a calcareous soil.It loves good lighting. If the low temperature is combined with excessive humidity, this can lead to the death of the plant.
Delicate
It grows in Altai and Siberia. The height of the shrub is 12 centimeters. Small flowers can be white or pinkish. The leaves are collected in rosettes. Flowering occurs in July. Grows well in sunlit areas. During the growing season, it needs constant watering.
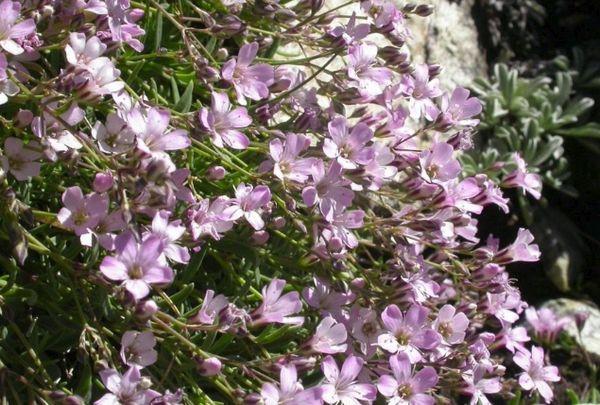


Patrena
Distributed in Central Asia, Europe and Mongolia. Usually found on river banks or in steppes on rocky soil. The shrub looks almost naked. Straight, branchy shoots are woody. The thick root has a curved shape. Leaves are narrow, lanceolate, bluish-green in color. The flowers are rare, white.
Wall
It differs from other species in that it has a single long stem with branches. This structure allows you to grow by clinging to the wall. The leaves are arranged in pairs on the branches, have a bluish-green color. Flowers in this species are white or pink.
See also
When and how to plant hyacinths in open ground, rules of care and cultivationRead
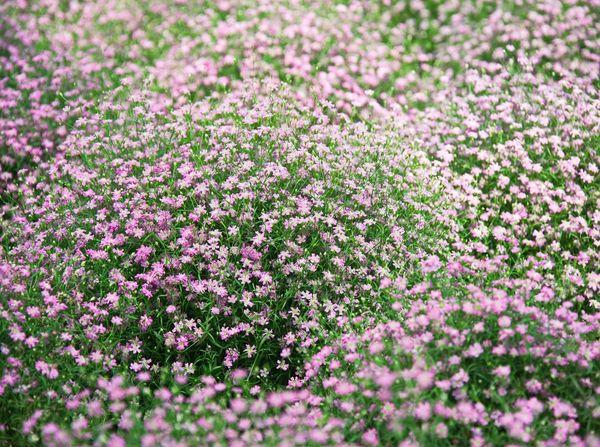
Spherical
The flowers are small, collected in spherical inflorescences.


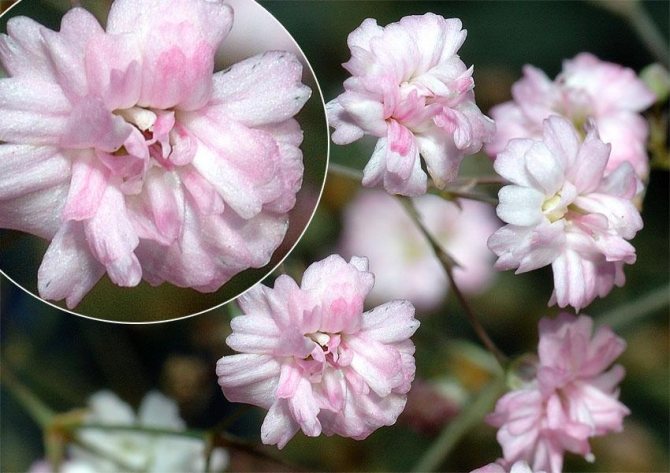
Terry
It is known for its white flowers. The height of the shrub is 90 centimeters.
Common cultivation and care shortcomings
Even an unpretentious plant has its own nuances of cultivation:
- The composition of the soil affects the decorativeness of flowering. If planted in the soil of medium acidity, then the tender bush will die.
- Tall varieties do not tolerate dense planting. An adult plant will have to be thinned out, without the possibility of transplanting.
- Large varieties are not suitable for home breeding. A strong root system is cramped in small pots or containers. It is best to grow creeping varieties at home.
Popular varieties
A wide variety of varieties will allow you to choose the type of gypsophila most suitable for the site.
rose flower
The inflorescences resemble rose flowers.
Carmine
The variety got its name from the carmine-red color of the flowers.
Double star
It blooms in bright pink. The height of the shrub is 20 centimeters.
Fratensis
This variety is known for its pink double flowers.
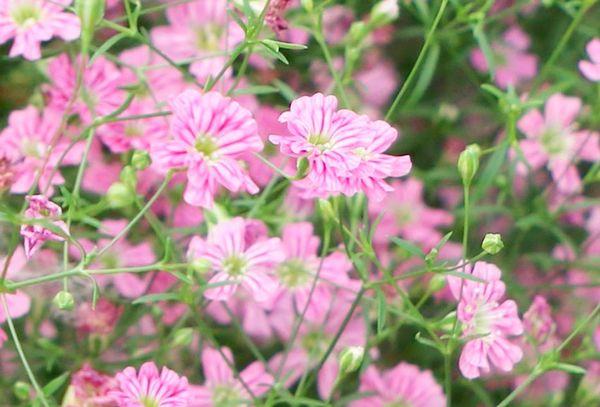


Monstroza
This variety grows snow-white flowers.
Blush
It is a shrub of short stature with bright pink flowers.
Snow blizzard
This variety of gypsophila grows up to 90 centimeters. The branches cascade down to the ground. Small and graceful flowers form a white-pink, lush cloud.
Fluffy snow
The shrub is winter-hardy. It grows to a height of 80 - 100 centimeters. Stems are knotty and highly branched. This is especially noticeable in the upper part of the bush. Flowers can be double or semi-double. Their diameter does not exceed 6 millimeters.
Cobweb
It is a spherical bush 1 meter high. When it blooms, a large number of double white flowers are formed on it. Flowering time: June to August. It can grow in one place for 25 years.
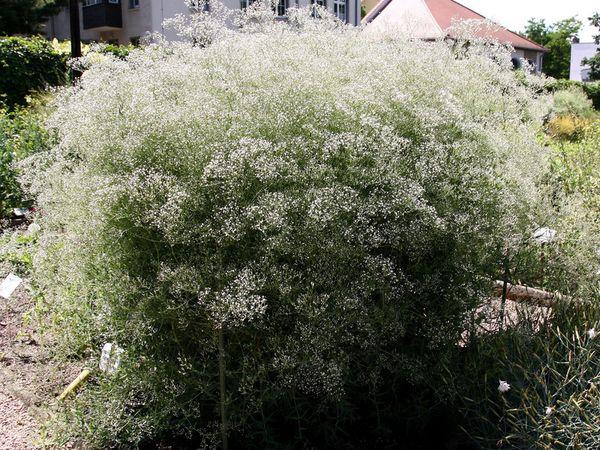


Pink haze
This variety has bright pink inflorescences that grow so densely that they almost completely cover the foliage.
Pacific
Pink flowers are collected in large inflorescences. For Pacific gypsophila, it is necessary to provide high humidity.
Rosenschleier
The stem of this variety spreads. Height no more than 40 centimeters. The flowers are white-pink in color. Flowering continues for two months.
Aurora
This variety has a highly branched stem. The leaves and flowers of these bushes are small.
Panic Rose
Small flowers look like a fluffy cloud. Bushes have different heights 0 from 30 to 120 centimeters. Grow well in intense sunlight in loose soil.


Mirabella
It is a picturesque bush with small white flowers.
Snowflake
This bush grows up to 50 centimeters. It has dark green foliage. Terry flowers of snow-white color.
After flowering
Gypsophila delights the audience with luxurious flowers. However, there comes a time when flowering ends and you need to take care of the bushes of this plant.
Seed collection
To collect, you need to wait for the seed pods to appear and remove them, then place them on a blank sheet of paper, allowing them to dry well. After that, the seeds are poured out of the box and stored in paper bags.
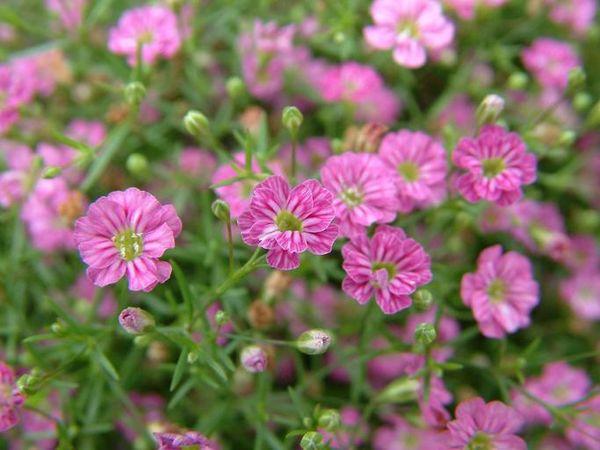


Preparing for winter
Most species and varieties of gypsophila have high frost resistance. Despite this, helping plants during cold weather will be useful. To do this, they will need to be covered. In areas where winters are mild, there is no need to take any additional measures for wintering the plant.
Transfer
The plant does not tolerate transplanting well for almost its entire life, with the exception of the first years. Only at this time can the gypsophila be transferred to a new place. In late autumn, the plant must be pruned so that in spring it blooms with renewed vigor.
Wintering
Gypsophila is prepared for wintering in advance. Before the onset of cold weather, watering is stopped, the plants are allowed to dry out.
The stems are cut off, only 4-5 stumps with a height of about 2 cm should remain above the ground in one bush. Fallen leaves, dry grass without peduncles and seeds, and coniferous spruce branches are applied to them. After the appearance of snow, a snowdrift is formed.
Note! In order for the roots of plants under the shelter not to rot, in the spring, immediately after the onset of warm weather, the snowball and vegetation cover from the roots of the gypsophila must be removed.
Picture 14 gypsophila
Mr. Dachnik advises: gypsophila in the landscape
Designers widely use gypsophila for rock gardens, lawns, alleys, curbs, squares, parks. It blooms magnificently, emits a pleasant aroma. In landscape design, it is combined with roses, peonies, liatrices, monads, phloxes, barberries, box trees, lavender, elderberry. The plant beautifully borders the borders of the garden unpretentious and lives in one place for many years.
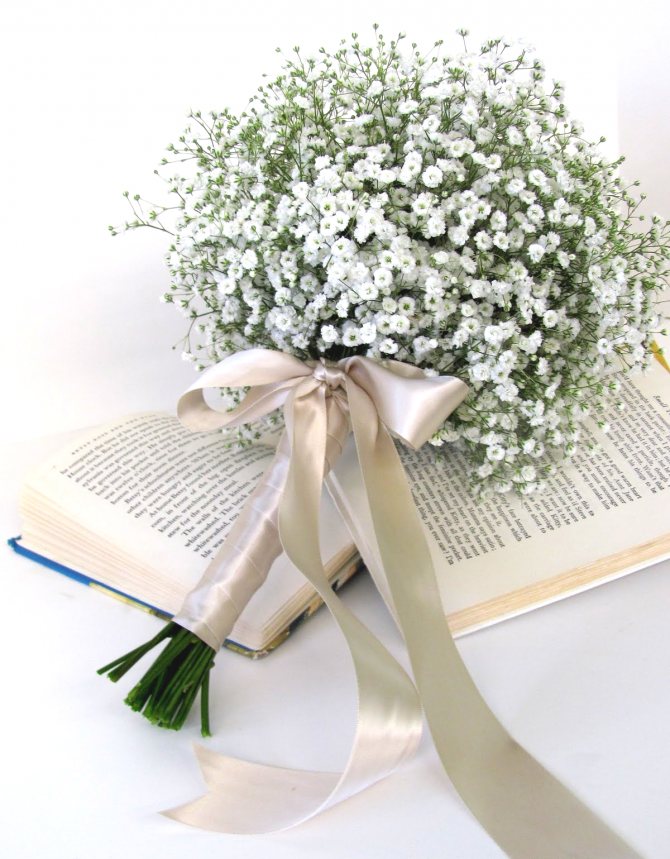
Florists decorate festive events with flowers, decorate tables, arches, hairstyles at weddings. Gypsophila does not fade for a long time and retains freshness.
How to care for
Flowers that are grown from seed begin to bloom when 12 pairs of leaves are formed. Within three years, the plant reaches its maximum potential. The plant is drought-resistant, therefore it will be necessary to water abundantly only in very hot and dry weather, bringing water under the root. In such dry periods, up to 5 liters are applied per 1 week.


Gypsophila care involves feeding. For this, mineral and organic fertilizers are alternately added in the spring and during the flowering process up to 2-3 times. Manure or compost is used as organic matter, which must be rotted.


Towards the end of autumn and the beginning of winter, the vegetation is carefully cut off. Stumps should remain on the surface. The soil must be covered with a covering material - spruce branches or foliage.
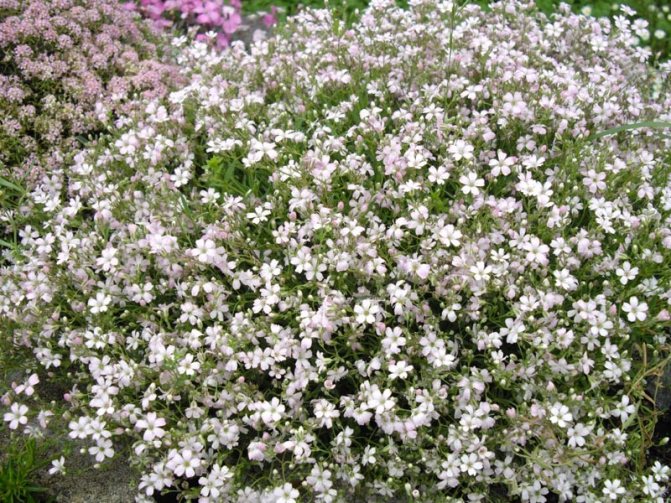


When snow falls, it is advisable to create a snowdrift on the flower garden. The plant will survive the winter safely. However, it is important on the eve of the melting of snow and the onset of warm spring days, it is necessary to remove the shelter in order to exclude the accumulation of moisture and subsequent decay.


Growing conditions
Requirements for soil, temperature conditions, air humidity, illumination depend on the type of kachima. Gypsophila can be grown at a temperature of about 20 ° C. The plant does not like excessive moisture, grows in open ground. Prefer light, alkaline soil.
Soil for gypsophila
On humus or excessively damp soil, swing grows poorly. For growing bushes, use sandy-loamy, clayey soils with a pH of at least 6.3. For planting gypsum loves, experienced gardeners prepare a sandy substrate. Add lime, small stones to the soil. The soil should be air permeable.
Temperature regime
Heat is an important factor for the growth and development of a plant culture. Gypsophila begins to bloom at 12 ° C. During the growing season, the temperature should be higher. Maintain 25 ° C during the day and 22 ° C at night. Protect the sprouts from the wind.
Illumination
The plant loves sun and warmth. The minimum day length for successful growth is 12 hours. In the spring, if there is a shortage, arrange additional artificial lighting with LED, fluorescent or gas-discharge lamps.
Ornamental value
The plant is used as a backdrop for other brighter plants. The compositions are built on mixboards and alpine slides. Will look great in a stone garden.


For combination, it is recommended to plant with tulips, as well as marigolds and even decorative cereals. Blooming gypsophila is often cut to decorate bouquets.


The unpretentious and strong gypsophila reproduces easily, and therefore is often grown in personal plots. It can be perfectly combined with other ornamental plants, used to decorate flower beds.


Sowing seeds of gypsophila paniculata
Reproduction is carried out vegetatively and by means of seeds. A perennial plant is grown mainly using the seedling method. That is, in early spring, they take seeds, sow them so that there is room between them, put them in seedling boxes to a depth of 0.5 cm.It is important to cover the crops with glass and put them in a well-lit and warm enough place.
After the emergence of seedlings (and this usually happens after 1-2 weeks from the moment of sowing), they must be thinned out so that a distance of 15 cm is maintained.
Advice! You can plant them one at a time in special pots and then grow them using additional light.
Main application
Due to its versatility, white gypsophila paniculata is ideal for complementing festive bouquets. Any set of flowers, whether for a wedding or for a birthday, will look more original and graceful if you add a couple of plaster lovers to its design. The plant will go well with large flowers of bright colors. When planning landscape design, gypsophila will also come in handy. For this, a plant of dwarf forms or shrubs is used. As a result, you can get the following options:
- the flower serves as the central part of the composition of a flower bed or flower garden. It is ideal when decorating elements of an artificial landscape in the form of slides;
- decorative design of stone gardens;
- creation of an individual type of borders;
- decoration of a veranda or garden.
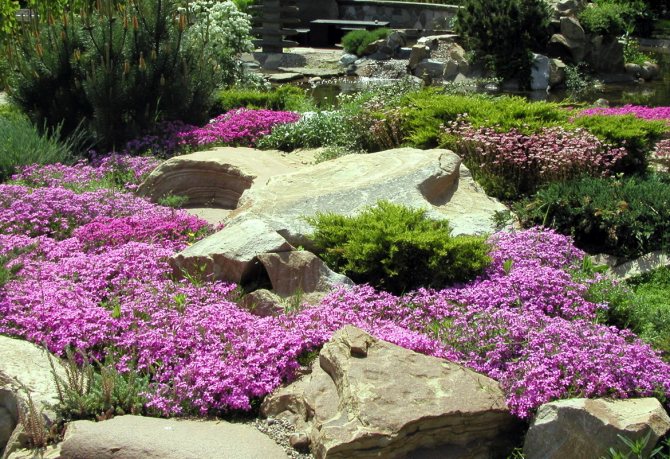


Rock garden with gypsophila
Choosing a soil for gypsophila
The area for planting gypsophila should be light, darkening is not desirable, but not large is allowed. The place for the constant growth of the plant is chosen carefully, since it cannot be transplanted because of the roots that penetrate deeply. The soil should be sandy with a lime content. If there is no lime or a small amount, then it is worth adding it in such proportions - 20-50 CaCO3 per m2. There should be no stagnation of water, therefore, it is better to drain the soil before planting. Soil acidity - 6.3 pH. Gypsophila loves dry soils; it will not take root near groundwater.
Seed collection
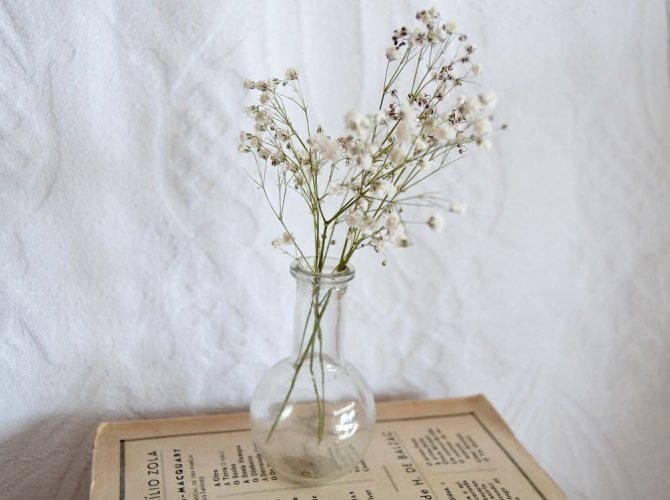
Gypsophila seeds photo How to collect seeds
If it is necessary to propagate gypsophila by seeds, they should be carefully collected. To do this, after the bush has dried, the resulting box is cut and dried.
After removing the seeds from the boxes, you need to dry them a little more, usually they are simply scattered over the paper, so all the moisture is absorbed, and the seed material will not disappear.
It is better to store the harvested seeds before sowing in the ground in a paper bag or a bag made of natural fabric. You do not need to leave them in a hot place, it will be better to have a dry room without heating, but so that there are positive temperatures in it.High humidity is unacceptable, otherwise the seeds will lose their germination and may simply overheat.
Snowflake: variety description, care
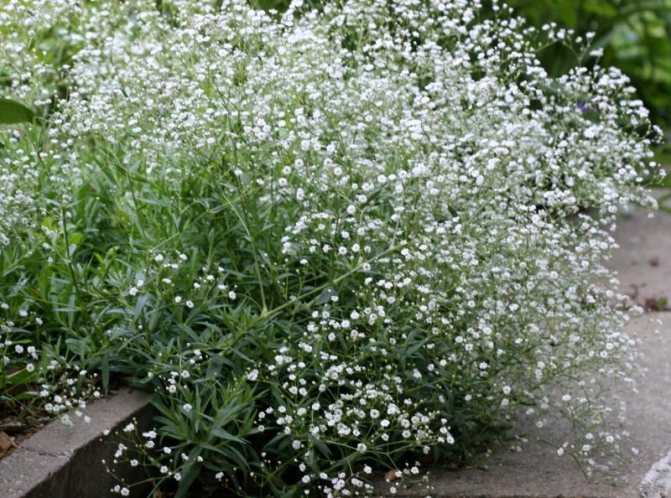


Planting the perennial gypsophila Snowflake, the photo of which is presented a little higher, caring for it is not much more difficult than the previous option, but you still have to familiarize yourself with the basic theoretical information so as not to ruin the culture with excessive watering or the scorching sun. This variety has quite spreading bushes that reach half a meter in height. The flowering period is characterized by the covering of the entire plant with small white double flowers, which are very similar in shape to snowflakes. This is a fairly light-loving and drought-resistant variety that grows calmly both in the light and in partial shade. Also, the plant looks great in combination with other brightly flowering crops and various decorative flowers.
Fertilization
Gypsophila is one of those crops that are not demanding for feeding. However, if you have a desire to start fertilizing the soil, then for this you can use cow dung diluted in ordinary rainwater in a ratio of 1:10. It is best to do this two weeks before the onset of abundant flowering, so that the flower will use all its strength to form buds.
If you do not have a desire to breed manure yourself, then you can purchase a complex fertilizer for horticultural crops in a specialized store. It is best to give preference to organic fertilizers with a natural composition. Mineral trace elements should be enough of those found in the soil.
Landing in open ground
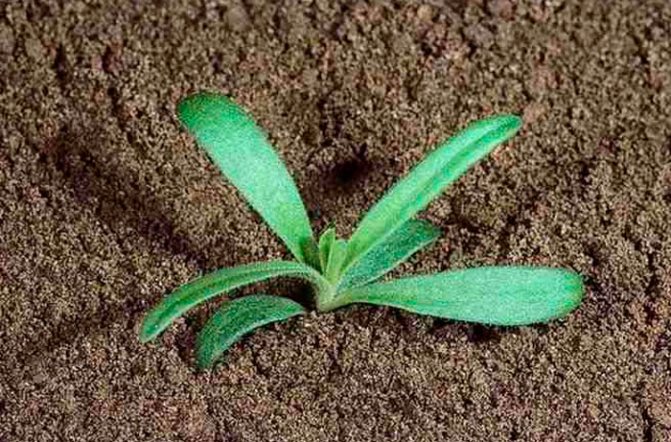


What time to plant
After the flower has 1-2 true leaf plates, they should be planted in a permanent place. When choosing a suitable site, it is worth considering that perennial gypsophila can grow without transplanting for many years in a row. It is preferable to choose a well-lit and dry place for such a flower, while the soil should contain lime, as well as a little humus. If there is no lime in the soil, then it must be added there. To do this, you need to take from 25 to 50 grams of CaCO3 per 1 m2, while the pH of the soil should ultimately be in the range of 6.3–6.7. When choosing a site, remember that groundwater should not lie close to the soil surface, since gypsophila reacts negatively to dampness in the root system.
How to plant
When planting between flowers, a distance of 70 centimeters must be observed, and the aisles must be 130 centimeters long. When planting seedlings, remember that in no case should the root collar be buried in the ground. Planted flowers need to be watered. After a couple of years of planting, it will be necessary to thin out, since at this time only 1 plant should grow per 1 m2. For those bushes that will be dug out, you need to cool the roots, and then they are planted in another place. This is to make the bushes look more spectacular during flowering. Cute flowers of such a plant are used for cutting, for example, they are often used to decorate composite bouquets.
The first flowering of such a plant can be seen after it grows at least 12 pairs of leaf plates. The most spectacular bush becomes 3 years after planting in a permanent place.
Diseases and pests
With poor care, gypsophila can be attacked by fungi or pests. In this case, it is necessary to take measures to treat it.
Rust
In this case, an appropriate fungicidal agent must be used.


Gray rot
To combat gray rot, oxyhom, Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate can help.
Nematodes
To destroy them, it is required to spray with phosphamide several times. If this does not help, you need to dig the plant and rinse the roots in water at a temperature of 50-55 degrees.
Unique culture
Gypsum is unique.It is short, has a branched stem and narrow leaves that grow abundantly in the lower part of the stems. A distinctive feature of the plant is the presence of thousands of small flowers, which together create a panicle effect. Outwardly simple, this plant goes well with other flowers. Even if it blooms separately, it pleases the eye with its attractive volume and airy lightness.
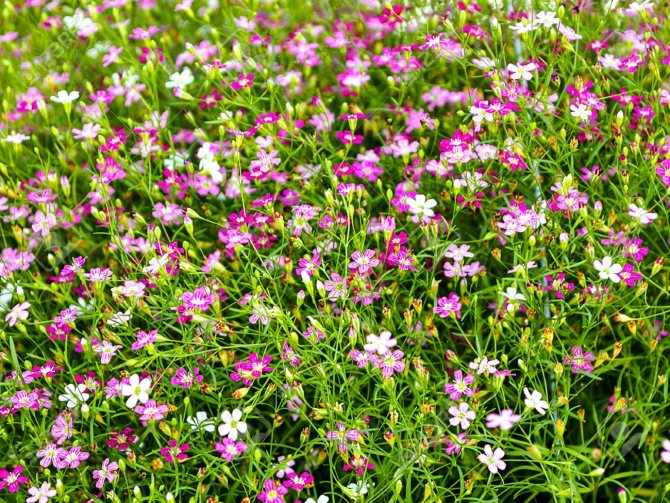


A bright variety of gypsum loves Paniculata L.
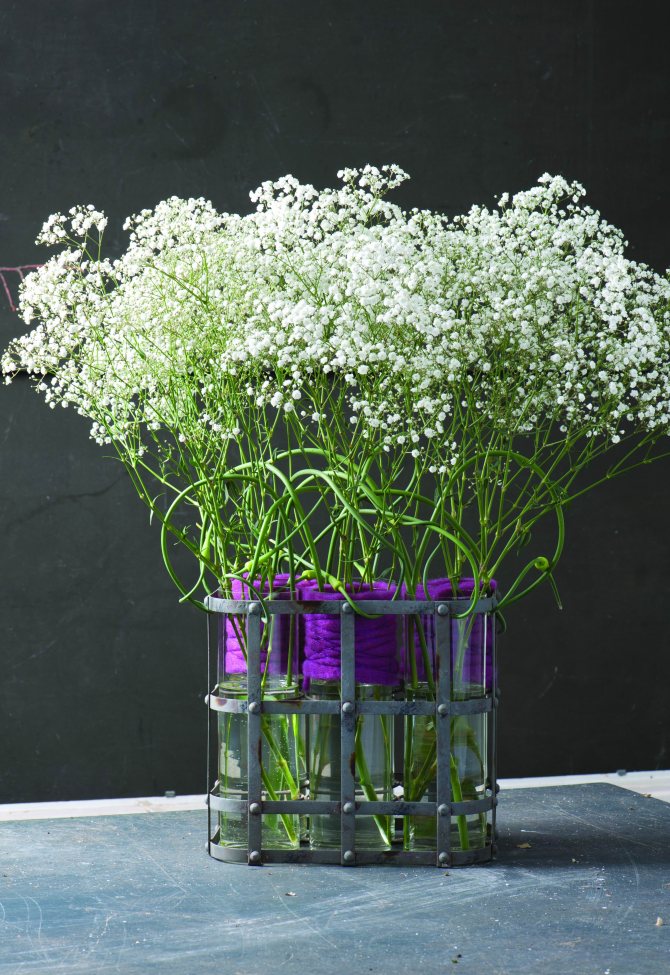


Magnificent do-it-yourself decor from fresh flowers
On a note! The ground part of the gypsophila is small, which is compensated by an impressive root that extends 70 cm deep. Despite the external simplicity, the plant can take root for life.
Thanks to the presence of such a powerful root, the plant acquires several key features at once:
- low threshold of sensitivity to drought;
- resistance to low temperature conditions, including frost;
- noble and original appearance.
1
4








All these features make this flower preferred by many growers.
Reproduction methods
The plant is grown in gardens or greenhouses. Even dried gypsophila retains its decorative properties and is used to decorate bouquets. When growing a plant indoors, remember that kachim needs a long day of light (12-14 hours). Gypsophila can be propagated by sowing seeds or cuttings.
Seeds
Sow annual plants in early spring. Grow under plastic to protect young flowers from possible frost. Sow perennial plants in an unheated greenhouse. In summer or early autumn, transplant shoots into open ground. Move the young plant to the beds no later than mid-April. The gap between the shoots is 60 cm. Cover the transplanted gypsophila with a film until May.
Cuttings
Use this breeding method for paniculate gypsum. In a heavily overgrown bush, cut off the young shoots to form inflorescences. Perform the procedure in late April or early May. Outdoors, cuttings should take root before fall.
Breeding rules:
- Loose soil with a slight addition of chalk.
- Planting depth - 2-2.5 cm.
- The air temperature is about 20 ° C.
- Provide 12-hour daylight hours with lamps.
- Treat the cuttings with a solution with heteroauxin.
Watering rules
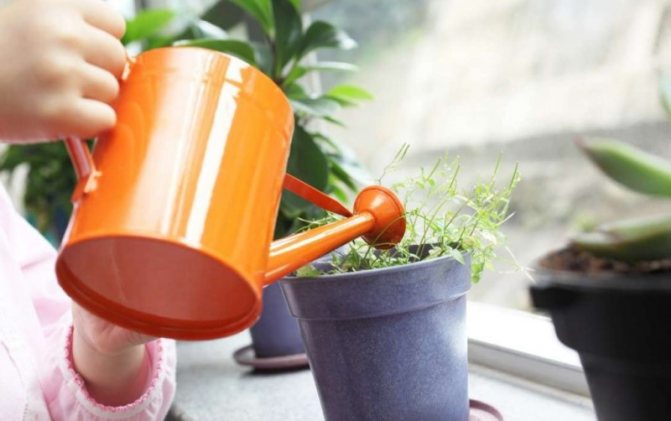
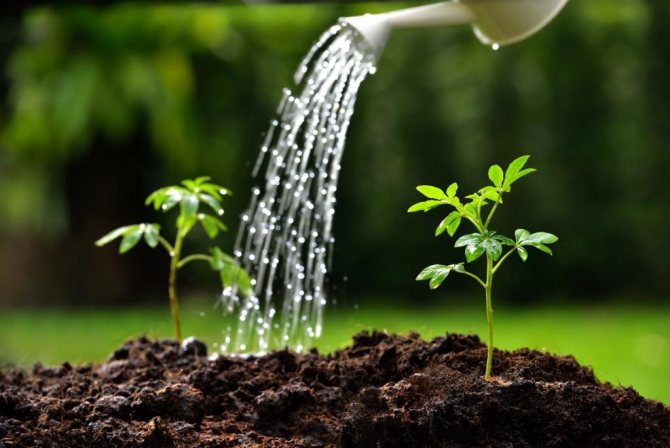
In order to more accurately understand when to water the gypsophila, you need to check the soil moisture with your finger or a wooden stick. If the top layer has dried deeper than 3 centimeters, then it is necessary to pour the gypsophila with not too cold water using a watering can, on which a rain sprayer must be installed.


Most often, the culture is watered in the summer season - about 3-4 times a week. In autumn and spring, everything depends on the amount of precipitation, so you need to constantly monitor the state of the substrate. It is also highly recommended to cover the garden area with a polycarbonate canopy, this will protect the culture from cold torrential rains and create additional shading in the summer.