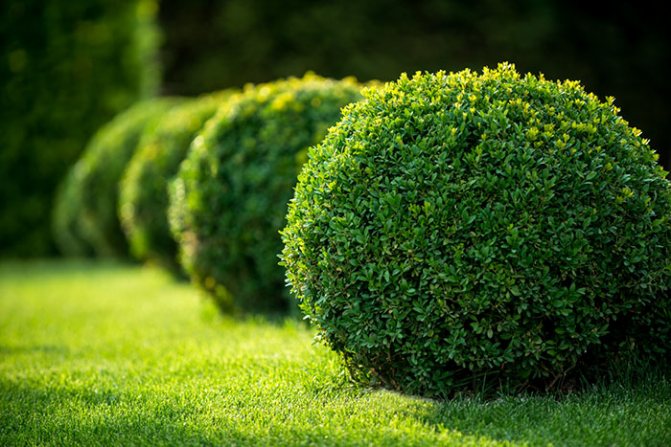
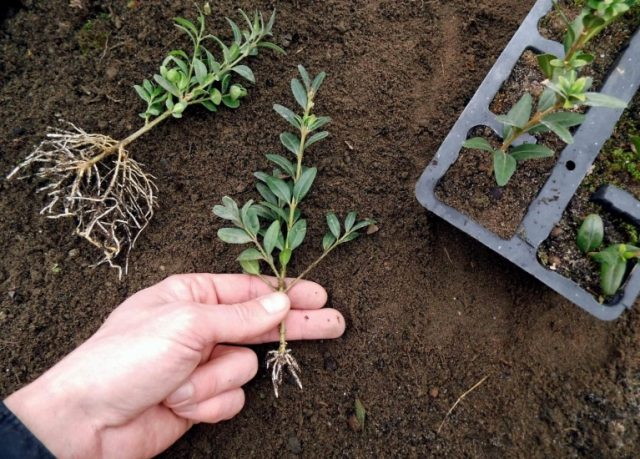
Boxwood is a beloved evergreen plant with small leathery leaves, which has long been used in landscape design and to decorate interiors.
Now you will not surprise anyone with a flower bed with dahlias or petunias. Today it is customary to decorate city streets and houses adjoining with special care and subtle artistic taste, using perennial plants for this purpose. Living green hedges, arches, gazebos, tunnels under overhanging foliage help residents of large cities to feel the beauty of nature again and again and not to lose touch with it. The art of topiary, known in ancient Rome - the creation of living green sculptures from plants, has gained wide popularity today.


From those ancient times to the present day, boxwood was considered one of the best plants for creating such garden forms. It grows so slowly that 2-3 haircuts per season are enough to keep topiary and hedges in good shape. In addition, boxwood is very malleable. This means its ability to respond to a haircut by growing new branches, which makes its crown only thicker and denser.
Large green sculptures are formed from several plants planted close to each other. Hedges and mazes are obtained by planting a huge number of boxwood seedlings according to a specific pattern. And then a logical question immediately arises: where to get such a number of seedlings? How to propagate boxwood?
Learning to propagate boxwood on your own


Boxwood is a beloved evergreen plant with small leathery leaves, which has long been used in landscape design and to decorate interiors.
Now you will not surprise anyone with a flower bed with dahlias or petunias. Today it is customary to decorate city streets and local areas with special care and subtle artistic taste, using perennial plants for this purpose. Living green hedges, arches, gazebos, tunnels under overhanging foliage help residents of large cities to feel the beauty of nature again and again and not to lose touch with it. The art of topiary, known in ancient Rome - the creation of living green sculptures from plants, has gained wide popularity today.


From those ancient times to the present day, boxwood was considered one of the best plants for creating such garden forms. It grows so slowly that 2-3 haircuts per season are enough to keep topiary and hedges in good shape. In addition, boxwood is very malleable. This means its ability to respond to a haircut by growing new branches, which makes its crown only thicker and denser.
Large green sculptures are formed from several plants planted close to each other. Hedges and mazes are obtained by planting a huge number of boxwood seedlings according to a specific pattern. And then a logical question immediately arises: where to get such a number of seedlings? How to propagate boxwood?
About the features of the plant
Boxwood has often been used as a basis for hedges and sculptures since ancient times. Such great popularity is due to some of the characteristics of the plant.Firstly, boxwood grows very slowly, so even 2-3 haircuts over the entire season will be more than enough to keep the garden looking good. Secondly, the leaves of the plant are very plastic, therefore, after each haircut, they begin to grow even more actively, which makes the crown thicker and more lush.
Boxwood is an evergreen slow-growing shrub native to East Asia and the Mediterranean.
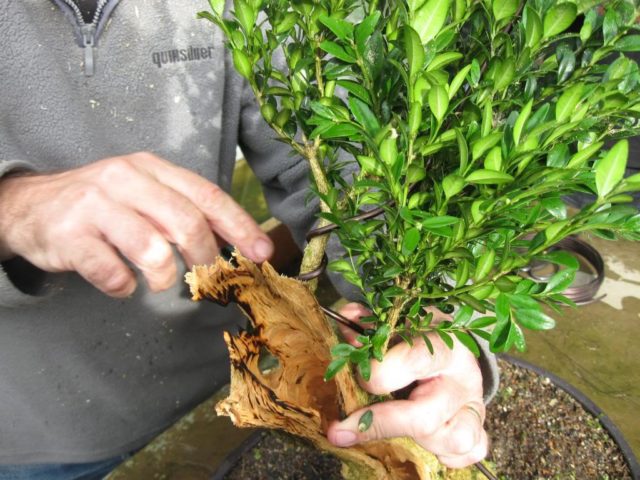
The plant is often actively grown not only as a garden decoration, but also for creating a home bonsai (the plant feels great and grows densely even in a small container).
Advice. Boxwood is a plant that perfectly tolerates the absence of the sun, therefore, when choosing a place for planting it in the open field, it is better to give preference to a shady area than a sunny area.
How boxwood reproduces


Reproduction of boxwood is usually done in two ways: seed and vegetative.
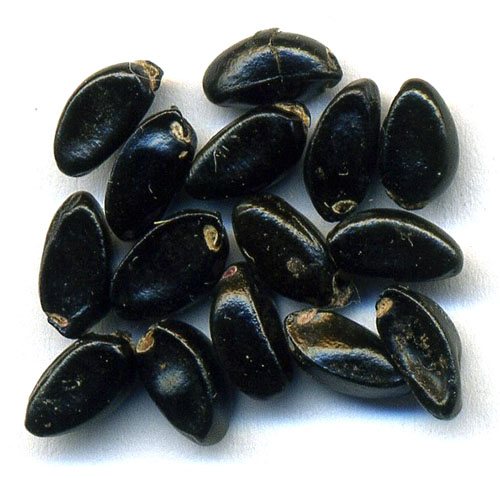


The seed method gives good results. The sprouts that hatch from the seeds grow back rather quickly and manage to turn into small (10-15 cm) bushes during the season. But the reproduction of boxwood by seeds has a number of disadvantages:
- Seeds lose their germination very quickly. Therefore, you can only sow very fresh seeds - from the harvest of the previous year.
- Boxwood seeds have a low germination rate. Even their pre-sowing treatment with growth stimulants does not give a noticeable improvement in germination. Usually only a third of the seeds emerge.
- Since boxwood plants are regularly trimmed and flowers removed for better crown formation, ripening on such plants becomes difficult. To get seeds for sowing, you need to get rid of one or more plants from clipping for the whole season, which, undoubtedly, will not have the best effect on its decorative qualities.


Cutting boxwood from this point of view looks more attractive, since it gives much more new self-rooted seedlings. Small twigs of boxwood are placed in a nutritious substrate and soon new young plants are obtained from them on their own roots.


There is another way to propagate boxwood: by rooting green cuttings. To do this, several young twigs close to the ground are bent and covered with earth. By the end of the season, roots are formed at the points of contact with the soil. After that, the layers can be safely cut off from the mother bush and planted as independent plants.
Reproduction of boxwood by cuttings in autumn, spring
Consider the features of boxwood cuttings. So, in order to successfully propagate a plant at home, you need to know some subtleties. Planting of cuttings is carried out traditionally in the spring-autumn period, but the result may be slightly different. So, when planting cuttings in the fall, the sprouts are stronger, but at the same time they will have little time for growth. Cuttings planted in the spring will root a little worse, but at the same time grow strong and in a shorter period of time.
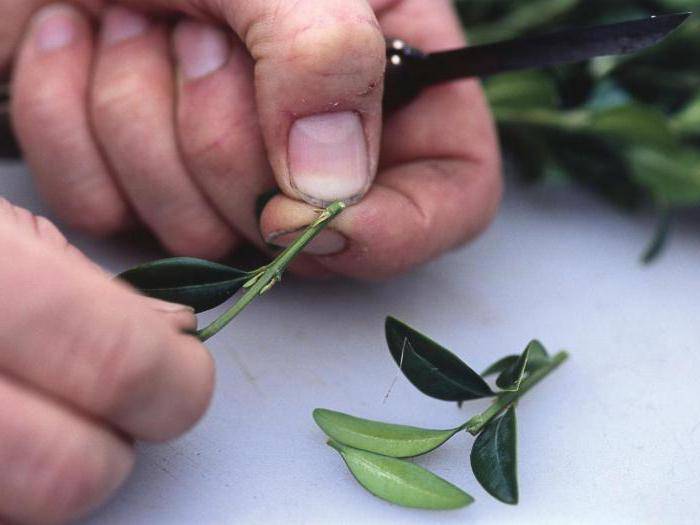
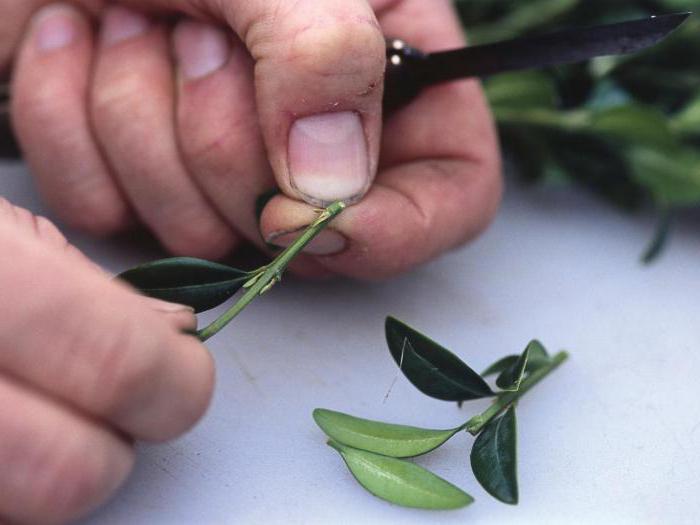
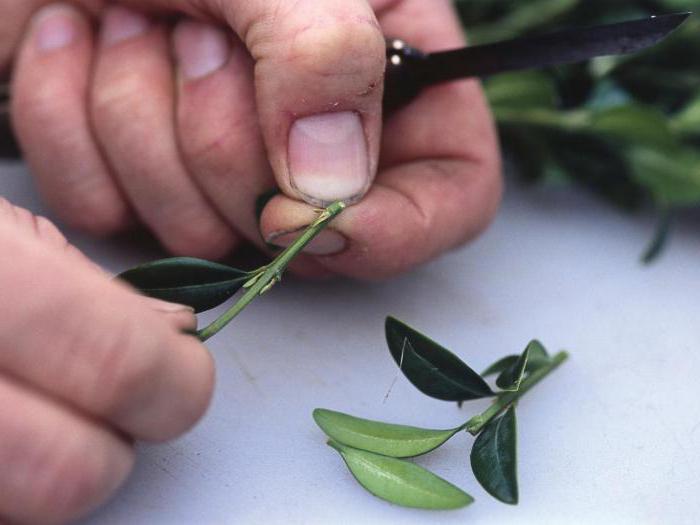
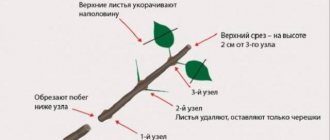
First of all, cut the cuttings from the lower branches of the bush: their length should be at least 10-15 cm. It is better to choose 1-2-year-old branches that are already well ripe (while the cuttings should not be woody). The lower part of the cuttings must be cleaned of leaves, and the bark must be slightly scratched with a needle or fingernail. In the future, callus is formed on such strips, from which young roots will grow.
Prepare deep, wide containers with good drainage holes. Cover them with nutritious potting soil. It should be light and well aerated. Place 1 to 4 cuttings in each pot. Cover them with plastic wrap. Open the foil periodically to water the young seedlings. After approximately 60 days, the first signs of rooting should appear - small leaves. In this case, you can transplant plants into the main containers.If the planting of cuttings was carried out in the autumn, it is better to leave the sprouts in pots until spring.
For growing by cuttings in the open field, the actions are almost identical to the previous ones, but, nevertheless, there are some differences. So, when propagating by cuttings in the open field, you should proceed as follows:
- We cut off young (1-2 year old) branches about 15 cm long from the lower branches of the tree. The cut should be beveled and the lower leaves peeled.
- We soak the cuttings for a day in a solution-stimulant of root formation, then we rinse.
- We prepare the soil mixture: we take the old compost, leafy soil and sand (equal proportions).
- We deepen the cuttings into the ground to the very leaves (we leave them on the surface). We close them either with cut-off bottle necks, or with polyethylene.
- We periodically water the plants, but at the same time it should not be excessive.
- Every day we ventilate young shoots, and after 60 days we remove the shelter.
The above breeding method is relevant when growing cuttings in the spring. If you decide to carry out this process in the fall, it is undesirable to plant young plants in open ground after rooting. This is due to the fact that the seedlings simply do not have time to root properly before the onset of cold weather, so they can die even under cover.
Cuttings are planted in deep pots and left in a cool room until spring, and with the onset of stable warm weather, they are transplanted into open ground.
That's all the subtleties that you need to know about the reproduction of boxwood by cuttings for its successful cultivation both at home and in the open field. Good luck!
Boxwood cuttings


To propagate boxwood by cuttings at home, you need to know a few simple rules.
Cuttings can be carried out from spring to autumn. In autumn, cuttings root better, but at the same time they do not have enough time even for growth. Such seedlings have to be planted in pots and kept at home in a cool place until spring. On the contrary, in the spring-summer period, the cuttings of boxwood, although the percentage of rooting is slightly lower than the autumn one, allows getting strong grown seedlings by the fall. At the same time, young plants become capable of wintering in the open field.
For grafting, it is necessary to cut branches 10-20 cm long with a sharp secateurs. It is better to cut them from the bottom of the bush. The twigs should be one or two years old, well ripened, but not woody. The twigs should be cleaned of several lower leaves, freeing at least two internodes. After that, you need to slightly damage the bark of the stem - lightly run along it along with a needle, a fingernail. Subsequently, callus is formed on such grooves, from which roots will grow. Before planting, boxwood cuttings can be treated with root stimulants, but this is not necessary. Boxwood already has a good rooting ability.
Boxwood cuttings should not be placed in water for rooting and should not be dried before rooting. This will lead to their death. Boxwood is one of those plants that need to be rooted only in the ground.


If you are going to breed boxwood at home, then for grafting you need to take wide pots with large holes in the bottom. This will prevent excess moisture from stagnating in the pot, as it damages the plants. The soil in which the cuttings will root should be light and breathable. You can use a mixture of turf, peat and sand.
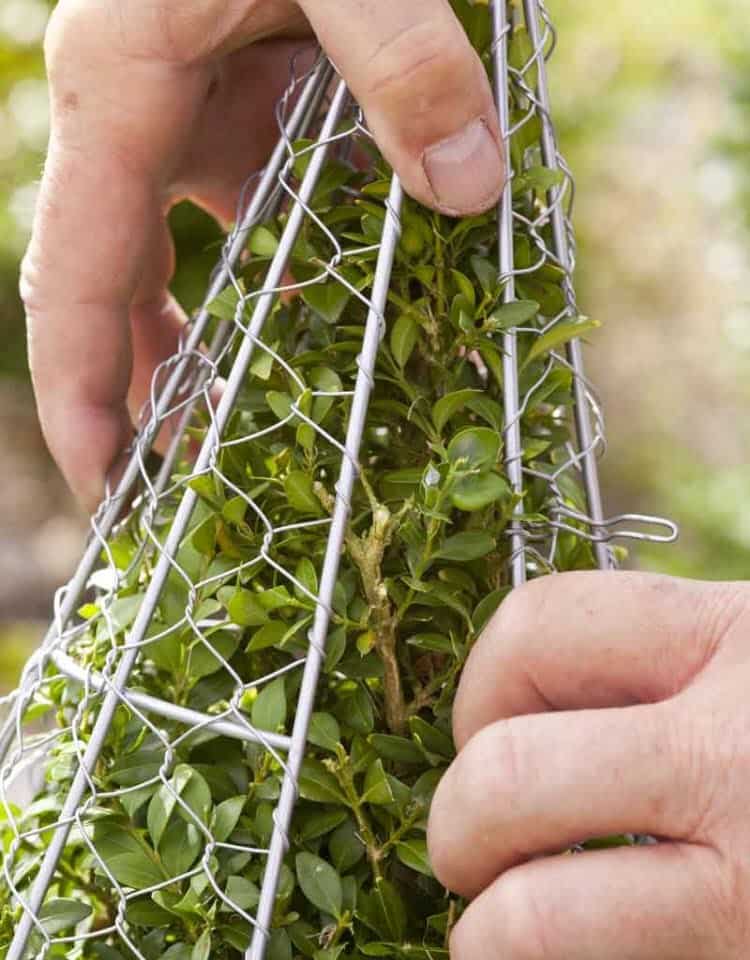
Cuttings are planted in a shaded area, 10 cm apart. You can plant them in several rows, leaving a distance between the rows of at least 20 cm. When planting in pots, 1-4 cuttings are placed in each.


When grafting boxwood, the planted twigs are best covered with foil or non-woven material.This will help create a microclimate for future seedlings that is independent of external conditions. Planting should be watered moderately but regularly. After about 2 months, the first sign of successful rooting of cuttings will appear - the plants will start to grow and form new leaves.
The most unpretentious when grafting is ordinary boxwood evergreen (Búxus sempervírens). Variegated varieties require more attention. When dry, waterlogged, or minor damage to the roots, they can shed their leaves.


Rooted boxwood seedlings can be planted in a permanent place or (in autumn cuttings) left in pots until spring. Young plants in the open field must be very carefully prepared for the first winter. The soil around them can be mulched with mature compost or needles. If the winters in the region are harsh, but it is necessary to provide shelter - from non-woven fabric or plywood boxes with holes. In winter, young plantings should be covered with snow.
Watch the breeding technology of boxwood cuttings in the video installed at the end of the article.
Propagation by cuttings
At home, boxwood is very easy to propagate vegetatively - by rooting cuttings. Spring cuttings are preferable, since you do not need to look for a room for seedlings for the winter. But there is one nuance - young, strong, but not lignified, shoots are suitable for reproduction. And in April such escapes may or may not appear, or there may be very few.
So, for the reproduction of boxwood in the spring, you should obliquely cut off the desired number of shoots 10-15 cm long and remove all the leaves in the lower third. The smoother and longer the oblique cut, the more chances for the cuttings to take root. To stimulate root growth, shoots already bare from the leaves can be soaked for a day in a root-forming solution.
After that, the cuttings are washed with water and planted immediately in open ground. To quickly form a bush, cuttings can be tied in bundles of several pieces and rooted all together. The soil for boxwood needs light and fertile. The ideal combination is to mix equal amounts of compost or humus, leaf soil and sand that have rotted for several years.
The cuttings are deepened to the height of the twigs bare from the leaves and the substrate is watered abundantly. It is very important to maintain a high humidity microclimate. For these purposes, the cuttings are covered with transparent materials - polyethylene, glass or plastic bottles until complete rooting. But you still need to air and water the bushes, so you should think about the upper hole in advance.
The easiest way is to cut off the bottom in a five-liter bottle and cover the planted stalk with it. And for frequent watering, simply unscrew the lid - this does not reduce humidity and greatly simplifies maintenance. Water so that all the leaves are moistened - for example, with a spray bottle. Filling the soil is not recommended, you just need to maintain constant moisture.
The first roots appear in a month, after two - the bush is completely rooted and it can be transplanted if necessary. At the same time, you can remove the shelter from the young bush. But in the first winter, young plants need to be covered with spruce branches or leaves. The main thing is to prevent fading under the covering material.
Reproduction in autumn
Breeding features in autumn are practically the same as in spring cuttings. The only condition is that the seedlings will not have time to root well and prepare for winter. Therefore, it is better to plant them immediately in pots or containers.
Covering cuttings planted in pots is also necessary, and with the first frost, the plants should be moved indoors. Until spring, it is advisable to keep seedlings at temperatures up to 10 ° C, and then plant them in a permanent place.This method of reproduction is convenient if the boxwood is grown for sale - in the spring, already well-rooted plants will easily transfer planting to a new place.
What to choose


We looked at several ways to propagate boxwood: by seeds, cuttings and green layering. Undoubtedly, the most productive is cuttings.
If there may be certain problems with the presence of seeds and lower layers in sheared boxwood bushes, then with cuttings everything is much simpler:
- Cuttings can be cut from your own previously purchased plant.
- You can buy inexpensively or even get free from other owners of boxwood plants after the next haircut.
- You can collect them completely free of charge in the park while cutting hedges and topiary.
The most important thing is not to dry out the cuttings and place them in the soil in time for rooting. And believe me, the results of your efforts will delight you with healthy and beautiful boxwood plants for many years.
Amazing decoration for your garden
Boxwood of tall varieties is usually used in garden design to create hedges. All species and varieties of this plant are characterized by very slow growth, but this has both pros and cons. The slow growth of the bushes allows you not to trim the hedges too often. Also, boxwood figures retain their shape for a very long time. Boxwood is ideal for a formative haircut and the plant tolerates it very well. A boxwood cut is needed in any case to make the bushes look neat.
Many gardeners do not know how to propagate boxwood on their site in a short time. In fact, it is easy to grow a lot of bushes. In the process of cutting bushes, a lot of scraps are obtained - this is free planting material. If you want to propagate a lot of boxwood in your area, then do not throw away the "waste" after cutting the bushes, but try to propagate boxwood using cuttings. Completely free and very quickly, you can make reproduction of boxwood by cuttings after pruning the bushes by typing them in a park or square.
Reproduction of boxwood by cuttings at home - step by step instructions with a photo
Adding an article to a new collection
Cutting boxwood is an easy way to propagate a spectacular evergreen on your own. This will allow you to get a beautiful hedge or border at no extra cost.
Boxwood can also be grown in containers. They form attractive balls from green bushes. However, the annual growth of shoots is only a few centimeters, so lovers of this evergreen plant acquire several seedlings at once. And those who want to save money, propagate one purchased bush by cuttings.
Boxwood: plant description
Boxwood belongs to the genus of slow-growing evergreen shrubs and trees of the Boxwood family. In nature, according to the latest updated data, there are about a hundred species of this plant. They grow naturally in East Asia, Mediterranean countries, West Indies. The Latin name Buxus was given to the plant by the Greeks.
There are three large areas of boxwood in the world - Central American, Euro-Asian and African. In culture, the boxwood tree is considered one of the oldest ornamental plants, which is grown as a garden and pot culture. In warm regions, the shrub is used not only as curbs and hedges. Picturesquely trimmed boxwood bushes adorn lawns and gardens.


At home, boxwood is very popular for bonsai, as the plant grows well in a small container, actively bushes, has small leaves and tolerates pruning well. Boxwood can be grown in containers. In this case, very cute balls are formed from the bushes.
However, as we said, this plant grows very slowly. The annual growth of shoots is only a few centimeters, so admirers of this beautiful plant acquire several seedlings at once.Or you can save a little by using boxwood propagation by cuttings. How to do it? Where to begin?
There are two ways to propagate boxwood: cuttings in water and in the ground. The first method is long and less effective, since shoots often rot in the water. The second method is very popular, so we will tell you more about it.
When to cut boxwood cuttings?
For propagation of the shrub, you can use the twigs that remained after the summer molding pruning. This will definitely not spoil the plant. If you've already missed this point, don't be discouraged. Boxwood cuttings can be cut at any time of the year (even in winter).
However, it is not recommended to do this from April to June. The fact is that at this time the boxwood grows intensively, and its young shoots are very tender and soft. Such cuttings must be handled delicately, carefully shaded from the sun. With insufficient care, they can die.
And cuttings, cut from July to March, root perfectly almost without the help of a gardener.
Features of growing boxwood
Boxwood is a very thermophilic plant, therefore it grows without any problems in regions with a mild climate. However, with proper care and shelter for the winter, it is quite possible to grow it in central Russia. The plant is unpretentious and grows quite well on any type of soil, is not afraid of direct sunlight and is shade-tolerant enough.
If the bush is not trimmed, then it grows quite powerful 3-5 m in height, but breeders have bred more compact varieties, the height of which does not exceed 2 meters.
How to propagate boxwood by cuttings at home?
To grow boxwood seedlings on your own, you will need:
- cassettes or other containers (for example, small pots);
- universal soil for ornamental plants, mixed with sand (in a 1: 1 ratio);
- boxwood cuttings;
- rooting agent for cuttings (for example, Kornevin);
- water for irrigation.
1. Select strong, healthy boxwood shoots with beautiful, regular leaves and cut off the small twigs that have grown this year. The cuttings should be about 10 cm long.
The branches can be cut with a sharp pruner or simply torn off with your fingers. In the second case, the cutting should be with a "heel" (a small section of last year's shoot).
2. Prepare containers and fill them with soil. Remove some of the lower leaves from the cuttings and dip the tips into a rooting agent that stimulates root formation. Use a stick to make one hole in the containers, plant the cuttings there and lightly press them around the circumference with soil. This will then allow, without disturbing the root system, together with the earthy clod, to transplant them into a more spacious container.
Be sure to dip the cuttings into the holes, and don't just stick them into the soil. Otherwise, the root will be erased from the tip of the branch.
3. Water the soil well and place the containers with cuttings in a shaded place. If you are cutting boxwood in the winter, leave the cuttings in an unheated greenhouse or lighted basement. In summer, it is recommended to put a plastic bag on each stalk. This will protect the plants from drying out.
Preparation of containers
First of all, prepare containers in which the shoots will root. For this, flower pots or small plastic buckets, compact but deep at the same time, are suitable. You will need a soil mixture for planting: light fertile soil and sand in equal shares. Rooting of cuttings is carried out without drainage.
Fill the selected containers with soil, compact it a little and make small indentations. In a medium-sized pot (about twenty centimeters), you can plant five cuttings at once, evenly distributing them around, closer to the sides.
When is it time to plant boxwood cuttings?
The cuttings take root within a few months. Some are faster and others slower.It depends on many factors. And the same cuttings under the same conditions may have a different root system.
Plants ready for transplanting, as a rule, form not only roots, but also new light green shoots.
There is no need to shake the roots off the ground, as shown in the picture. This is only done so that you can see the difference in the size of the root system between cuttings that are at first glance identical. Transplant the cuttings along with an earthen lump - then they will better take root in a new place.
If you still have questions about growing this attractive shrub, take a look at our article What to Know When Growing Boxwood.
Choosing the time for grafting
Boxwood bushes should be trimmed regularly. Typically, the plant is cut every four weeks throughout the season from April to October. The branches (usually the tops of the shoots) remaining after cutting can be rooted at almost any time, but still not every month is suitable for grafting. From August to September, you will not be able to plant the cuttings in the ground, as they will not have time to settle down and take root. Most likely boxwood planted in late summer - early autumn will die from the cold, never having time to get stronger. Although, gardeners do not throw out the clippings after the autumn haircut, but root the boxwood in boxes, which they put in a cool place with a positive temperature. In order for the cuttings planted in boxes to take root over the winter, they need a little warmth and a lot of light. If we talk about the spring planting of cuttings, then the April and May branches can also die. The fact is that young spring shoots do not yet have time to ripen by the time of the first haircut. The best time to root boxwood cuttings is from June to July. Rooted cuttings of boxwood in the middle of summer have time to take root and get stronger, and usually tolerate winter well.
Features of reproduction of boxwood cuttings at home
Boxwood is an unpretentious, evergreen plant that is widely used in landscape design. When purchasing one copy, flower growers often want to propagate it in order to grow a green hedge, create a beautiful border and make the suburban area more attractive. Breeding boxwood is possible by cuttings and seeds, but experienced gardeners recommend cuttings as it is a simple and effective method. To propagate boxwood by cuttings at home, you need to follow simple rules:
- cuttings are cut from a healthy, non-lignified shoot;
- light, drained soil is prepared for planting;
- for quick rooting, the cuttings create a favorable microclimate;
- care consists in watering and maintaining the temperature and humidity.


General breeding rules
Summing up, there are several important points to remember:
- boxwood reproduces by semi-lignified young shoots;
- for rapid root development, cuttings can be treated with root stimulants;
- any soil is suitable, the main thing is nutritious and light;
- spring cuttings are preferable if the plants are rooting in a permanent place;
- to maintain a humid microclimate, seedlings are covered for 2 months;
- watering boxwood seedlings, preferably every other day, well moistening the leaves.
It is quite easy to propagate boxwood, especially if there is an already grown three-year-old bush in the reach!
When to cut boxwood
You can cut boxwood in spring and autumn, it all depends on climatic conditions. To grow a beautiful, ornamental shrub, you need to know:
- when to cut the cuttings for propagation;
- what time to plant;
- how to root and care properly.
Cutting boxwood in spring
You can propagate boxwood by cuttings in the spring immediately on your personal plot.Planting material, cut and processed in a root formation stimulator, is placed in a well-lit, carefully dug place with fertile, well-drained soil. To create a favorable microclimate, the seedlings are covered with bottles or plastic bags. Also, spring reproduction can be carried out in containers at home. For fast rooting, the ground should not dry out, so the seedlings must be shaded from direct sunlight. In the evening, the microgreenhouse is ventilated, and the plant is sprayed with warm, settled water.
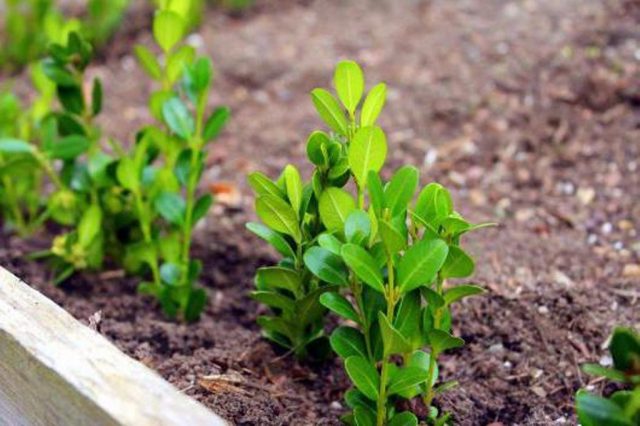
During the season, the boxwood will get stronger, form roots and will be ready to move to a permanent place by the fall. After transplanting, the trunk circle is mulched, and the young, immature plant is covered with burlap or agrofibre.
To have an idea of how to cut boxwood in the spring, you need to watch a video for novice florists:
Cutting boxwood in autumn
Since boxwood blooms in the spring, propagation by cuttings can be done in the fall. Cuttings are cut from healthy shoots in early September so that the wounds on the bush are healed before the onset of frost. The planting material should have a length of 10-15 cm and well-developed buds. For planting, a nutritious soil is prepared, the cuttings are buried to the upper foliage and covered with a jar or plastic bag to create a greenhouse effect.
Rooted boxwood seedlings are planted in separate containers, trying not to damage the earthen lump. The container with the planting is removed in a warmed greenhouse or a warm place with artificial lighting. Caring for seedlings at home includes regular watering, spraying and feeding every 10 days, using a mineral fertilizer complex.


With the onset of spring, the cuttings need to be hardened. To do this, they are taken out into the fresh air, daily increasing the time spent. After the end of the spring frosts and the soil warming up to + 10 ° C, boxwood can be planted in a prepared place.
Cutting boxwood in winter
After the end of the summer cottage season, gardeners often use the greenhouse as a place to store land and garden equipment. But the greenhouse can be used to advantage, for example, for winter propagation of boxwood by cuttings. In the fall, 2 weeks before frost, the earth is dug up, sod or leafy soil mixed with peat is poured on top, compacted and leveled with a rake. Then the river sand is poured in a layer of about 2 cm. The breeding ground should be light and well-drained.
For winter reproduction, planting material cut from 2-3-year-old shoots is suitable. After removing the lower foliage and processing the cut with a rooting stimulator, the cuttings are planted at a distance of 20 cm from each other. After planting, the plant is spilled and covered with polyethylene, which is pulled over a wire support.
Throughout the winter, it is necessary to ensure that the soil is always moist. By spring, the cuttings will take root, and after the onset of warm days, they can be planted in the selected area. In order for them to quickly take root and adapt to a new place, the first week they need to be covered from direct sunlight. Caring for the plant after reproduction consists in watering, feeding and removing weeds.


An alternative breeding method for boxwood
Sometimes gardeners are forced to resort to dividing boxwood bushes. Old bushes, even with careful pruning, end up filling the allotted space. With a lack of light and nutrition, the overgrown branches lose their decorative effect.
By dividing the bush, you can plant boxwood in the garden. You can transplant at any time from spring to autumn. To do this, you need to dig up the soil from the side where you plan to separate a part of the plant. Cut off a part of the root with several healthy shoots with a sharp shovel or knife.
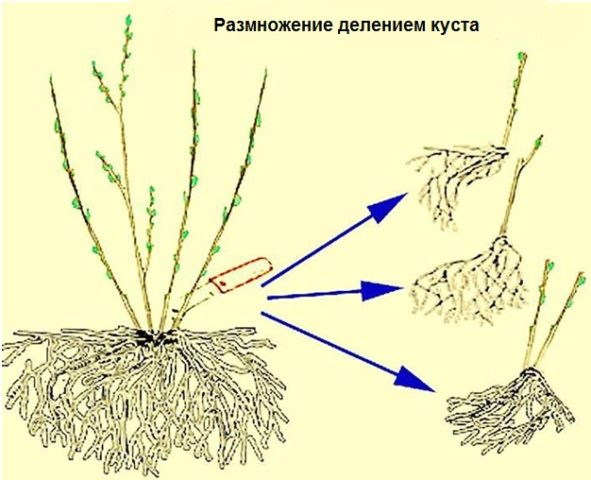

Place the seedling strictly vertically in the prepared planting hole with nutritious soil.Lay the soil, gradually compacting it. It is desirable that the soil is moist. This will avoid creating voids around the root system. New seedlings should be watered regularly and fed like mature plants. In the first days after planting, the culture must be protected from direct sunlight.
How to plant boxwood from a twig
Boxwood can be bred from branches. To do this, choose a healthy, non-lignified shoot and cut or separate cuttings no more than 15 cm long. When tearing off the planting material, it is necessary to leave a lignified "heel". Thanks to her, the area for the appearance of the root system will increase.
Preparation of planting tanks and soil
For rooting boxwood cuttings at home, any container, previously washed and disinfected, is suitable. To prevent water stagnation after watering, drainage holes are made at the bottom of the pot.
For high-quality reproduction, purchased soil or self-prepared one is suitable. To do this, mix sod or leafy soil with sand in a 1: 1 ratio and add complex mineral fertilizers. The mixture should be light, loose and nutritious.
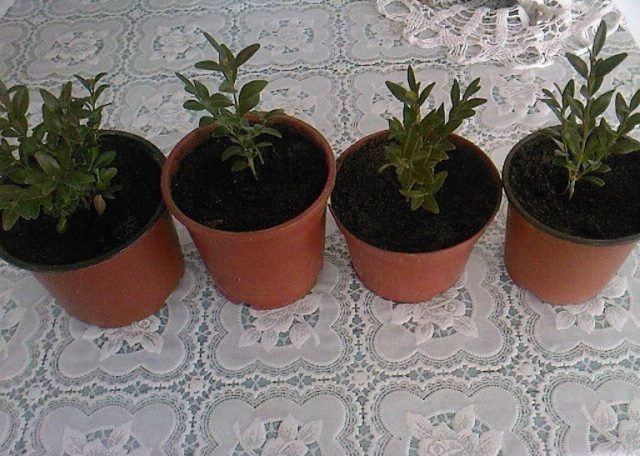


How to root boxwood from a cutting
The prepared soil is poured into containers, a deepening is made and the handle is set at an acute angle so that a small part with leaves remains on the surface. When reproducing boxwood at home, before the root system appears, the planted plant is not watered, but slightly moistened. This is due to the fact that the waterloggedness of the soil leads to decay of the cuttings cut.
To keep the soil always moist, you can put a wick under the soil mixture. To do this, a thick rope or twisted cotton cloth is laid at the bottom of the pot. Cover with soil so that the opposite end can be lowered into a jar of water. Thanks to this simple method, irrigation will take place automatically and in the right amount. In order for the process of root formation to occur much faster, it is necessary to create favorable, greenhouse conditions for the cuttings. To maintain the temperature and humidity conditions, the planted seedling is covered with a plastic bag or glass jar.
Care of cuttings
Caring for seedlings at home is simple, the main thing is to maintain the required soil and air moisture. For this:
- spraying with warm, settled water is carried out several times a day;
- regular airing of the mini-greenhouse;
- make sure that the cuttings do not come into contact with each other or with the covering material, since rot and black fungus often develop at the point of contact;
- after 14 days, the cuttings will begin to take root, and they can be fed with mineral fertilizers;
- if there is a lack of lighting, artificial light is installed;
- a month later, the cutting will grow a powerful root system, and then it will be possible to remove the shelter and carry out further care as for an adult plant (regular watering, feeding every 10 days, in hot weather, spray in the morning or evening hours).
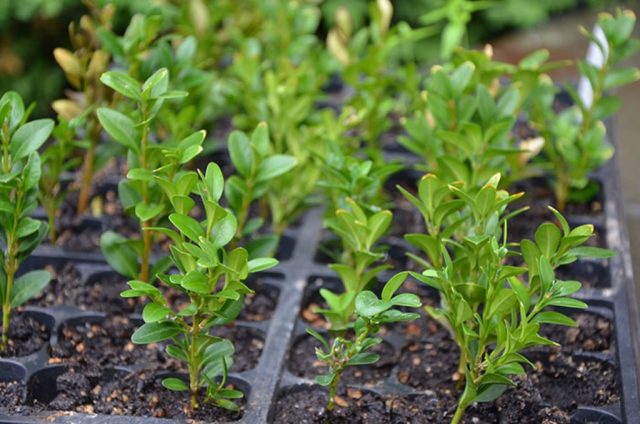


How to propagate a boxwood bush by layering
For novice gardeners, a method for propagating evergreen boxwood by layering is suitable. The procedure can be carried out at any time from spring to autumn.
For a strong, healthy boxwood shrub from two years old, you need to choose an outer branch located close to the soil surface. Then prepare a small trench up to 15 cm deep with loose fertile soil. The groove should be along the direction of the selected parent branch.
To propagate the boxwood shrub by layering, studs will be required to anchor the branch to the ground. You can use split-edged wooden pegs or bent metal wire. For the development of the root system, the branch should be cleaned of leaves and the bark should be slightly incised.
Tilt the branch, secure with pins and sprinkle with a loose soil mixture of peat, humus and sod land.
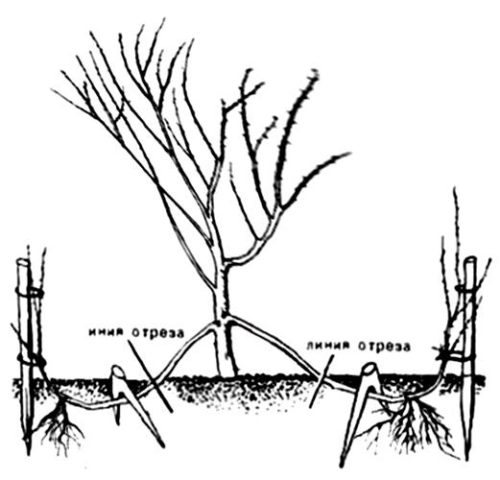

Caring for layering during reproduction consists in regular watering. The soil should not dry out. With the appearance of the first shoots, it is necessary to protect young shoots from direct sunlight.
Transplanting layers
If the sprouts from the dug-in branch have developed enough only by autumn, then it is better to leave the reproduction of the bush until spring. Before the onset of cold weather, they will have time to get stronger enough. For the winter, young shoots can be covered with the mother bush. And if the layers have grown at some distance from the adult plant, then the shelter is made of spruce or pine spruce branches.
To separate the planting material:
- Cut the mother branch from the bush with pruning shears.
- Gently dig in the soil to raise all the shoots at the same time without damaging the root system.
- Divide the seedlings with a pruner so that a small part of the mother branch remains on each. This will enable the development of additional roots.


A breeding site for boxwood must be prepared in advance. It will take a lot of skill and speed to prevent the roots from drying out. If possible, keep a lump of soil around the root system to avoid stressing the boxwood. Then the plant will quickly take root in a new place.
The soil under young plants should be moist and well fertilized. In this case, the feeding of the boxwood can be carried out one year after breeding.


To create comfortable conditions for reproduction, seedlings can be covered for a month with film caps or covering material. It is imperative to monitor soil moisture. Drying out or too much moisture will kill the plants. When breeding boxwood in autumn, it is imperative to cover the plants with layering before the onset of cold weather.
Open ground transplant
Planting boxwood cuttings is carried out on fertile, well-drained soil, in a sunny place or in partial shade. The place must be protected from drafts and gusty winds. The breeding site for boxwood is prepared 2 weeks before planting. For this, the earth is dug onto a shovel bayonet, rotted compost, peat, sand and mineral fertilizers are added. Reproduction technique:
- A planting hole is dug in the selected area, the size of the plant's root system.
- For better water permeability, a 15 cm layer of drainage is laid out on the bottom (broken brick, pebbles, expanded clay).
- The boxwood seedling is spilled abundantly and removed from the pot with a clod of earth.
- The plant is planted by transshipment, filling each layer, trying not to leave air voids.
- I tamp the soil, spill it with warm, settled water and mulch.
After transplanting, the boxwood seedling is not fed, but is constantly moistened, since the soil under the plant should not dry out. To retain moisture and stop the growth of weeds, the soil around the planted plant is mulched. Rotted humus or compost, dry foliage or hay are used as mulch. Also, mulch will be a good organic fertilizing.
2 weeks before the onset of frost, the multiplied boxwood is abundantly shed, fed with wood ash and covered with agrofibre or non-woven material. So that the plant does not suffer from the spring sun, the shelter is removed after the snow melts and the onset of warm days.
To obtain a rapid growth of lateral shoots, a young plant after reproduction can be cut off under a stump, and the cut site can be treated with garden varnish or any antiseptic.
Seeds
Boxwood seeds germinate well under a number of conditions. First, they need to be soaked in a growth stimulant solution for a day. After that, put them between layers of damp paper towels and keep at a temperature of about 21 ° C until white sprouts appear.
Seeds germinate within a month, during this period it is necessary to constantly maintain the moisture of paper towels, spraying them from a spray bottle.If there are no sprouts, the seeds are placed in the refrigerator for 3-4 weeks, and then again taken out into a warm room.
After the appearance of white shoots, the seeds are planted in a mixture of peat and sand with these shoots down and covered with a film. It is advisable to keep the container in a sunny place, or, at worst, in partial shade. Green shoots appear in 2-3 weeks - after that the film can be removed.
Sprouted seedlings need to be removed from the bright sun in partial shade or a shelter made of light material should be made for them. Strengthened seedlings can be planted in the ground in mid-spring. In the first few winters, they need to be covered - young bushes can freeze.
What diseases and pests are dangerous for boxwood
Boxwood leaves contain in their leaves a large amount of poisonous and dangerous components that can harm health and the human body, but these components are not able to protect the plant from the damaging effects of all kinds of pests.
Most often boxwood bushes are affected by boxwood gall midge and. These pests lay eggs on plant shoots. After some time, larvae hatch from the eggs, penetrating into the leaves and damaging them. In order to avoid infestation with these pests, it is necessary to constantly remove fallen leaves and regularly prune boxwood bushes. Chemical treatment of plants is also required from May to June.
Another known pest is a fungus called Volutella buxi. When a boxwood bush is attacked by a fungus, the shoots begin to die off. It is possible to effectively combat this pest by treating with fungicides and by cutting off shoots affected by the fungus.
Diseases of boxwood bushes and coloring of leaves along the edges in a yellow tint can occur due to irregular watering and poor-quality feeding. To avoid these problems, the shrub needs to create favorable conditions for growth and development. Thanks to the timely application of fertilizers, the trees are protected from damage.
A plant capable of ennobling any summer cottage or park area with its beautiful appearance.
This species is easily recognizable by its oval, leathery, dark green above and almost yellow below the leaves. Wild boxwood can reach a height of 15 m, cultivated - from 3 to 6 m yellowish-green small fragrant flowers. All parts of this
Boxwood tolerates a haircut well, therefore, decorative figures of various geometric shapes are often formed from it: cone-shaped, ovoid, pyramidal. There is nothing better than creating an original or framing a flower bed with a boxwood shrub. Planting, caring for this plant does not require serious effort. That is why it is so popular with gardeners.
Boxwood - planting, caring for cuttings during reproduction
It is advisable to plant this plant in an area with bright diffused light, but it does not like direct sunlight at noon. The planting of boxwood is carried out in the natural shade of more and more trees. The shrub should be planted in a fertile mixture of peat, turf and sand. It is necessary to plant young bushes from mid-August to the end of November. Two- or three-year-old seedlings can be planted between April and mid-May (you need to choose a cloudy day). Before planting, it is necessary to place the roots of the plant in water for a day. The area set aside for boxwood is dug up in advance and then pits are formed so that they are slightly larger and wider than the earthen coma on the rhizome of the plant.
This beautiful shrub is propagated by seeds and cuttings, but cuttings take root rather difficult and for a long time. They are cut in August, while choosing parts of plants with a semi-lignified base less than 7 cm long, with 2-3 internodes. For effective rooting, soil heating in the greenhouse and phytohormones ("Heteroauxin" or "Kornevin") are used. The container for planting should not be taken too large, otherwise the seedling will slow down in growth.
Boxwood: planting, leaving. Features of watering and feeding
Watering the plant in summer should be plentiful, in winter it should be more scarce. The soil should dry out, not dry out completely. Do not flood the plant, as it will suffer from this. Falling, yellowing, curling or drying of plant leaves may indicate a violation of watering or too dry, hot air. It is advisable to periodically spray the boxwood with water. He should also undergo a periodic haircut every six weeks between May and August. It is necessary to carry out feeding of the plant every two weeks, from March to August. You can purchase organic fertilizer for this. In the spring, the plant is fertilized with complex mixtures containing potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen. Mineral fertilization is applied only after the final rooting of the boxwood.
Boxwood: planting, leaving. Features of wintering in cold climates
Boxwood is a thermophilic plant, it is afraid of severe frosts and can easily die at a temperature of -20 ° C. In countries with severe winters, including the plant grows rather slowly, it is often stunted and requires mandatory shelter in the winter. Boxwood in the Moscow region requires shelter in late autumn with burlap, spunbond or wrapping paper.
Planting boxwood
—
a great way to decorate your garden with hedges and various green shapes.
For novice gardeners, it is best to start with this plant. Boxwood
(Búxus)
- an evergreen plant from the Boxwood family. This plant is found both in the form of a bush and in the form of small trees.
This plant is difficult to "kill", it easily tolerates a short period of drought or waterlogging. But boxwood grows best in warm, humid places, and this should be taken into account when choosing a planting site.
Optimal timing of planting seedlings
Many gardeners talk about planting boxwood in different ways: some say that it should be planted in the fall so that by spring it will please you with its new shoots, others say that this plant can be planted all season - with the first rays of March and until the first November frosts.
But still, most are inclined to believe that it is best to plant boxwood in the fall. If before that you grew your plant, and now decided to "settle" it in a permanent place in open soil, then it is best to carry out such a transplant of boxwood in the fall.
Important!
For the first shoots to emerge, at least one calendar year is required, so do not be alarmed if your plant did not emerge within the usual time frame.
If you do not need the boxwood to grow fully to give the desired shape in the first season, then the boxwood can be planted in the spring - then the plant will root better.
Choosing a landing site
It is best to plant boxwood in shady or semi-shady areas.
In principle, the plant is unpretentious, but it is very difficult to tolerate summer heat, open sunlight or cold winds and drafts. Therefore, it is best to plant the plant in the shade of trees.
How to prepare the ground for planting
Under natural conditions, boxwood grows on mountain slopes, the soil of which has a very high Ph level. But when planting this plant in your area, you don't have to think about the special composition of the soil. Although, of course, the soil for boxwood must be fertile. It is not so much the quality of growth that depends on this, but how quickly your boxwood grows.
Of course, in soil saturated with trace elements and natural minerals, the plant will grow faster. In loose soil, boxwood will grow faster and the shoots will be more abundant, while in poor soil, the shoots will lose their appearance faster.
Did you know?
Although boxwood is a fairly moisture-loving plant, it "does not like" stagnant water, therefore, if water accumulates in your flower beds after rain, then it is better not to plant a plant there.
Efficiency
Breeding methods for boxwood differ in the degree of labor intensity and the number of seedlings that can be obtained as a result:
- Cuttings are most popular with gardeners. During the season, from one bush, you can get several dozen cuttings suitable for reproduction. But not all of them survive, especially with early spring pruning.
- Reproduction by layering has a number of advantages. Feeding from the mother bush, the shoots develop quickly and survive when transplanting everything, if the conditions for watering and protection from the sun are met. This method requires minimal labor costs.
- The division of the bush is available, simple in execution and allows you to plant strong seedlings 2-5 years old. Their number is small, but there is no need for greenhouses, transplanting seedlings, and additional treatments. The bush can be propagated within an hour if fertile soil is prepared.
- The decision to propagate boxwood from seed is the most time consuming and labor intensive. Seedlings grow slowly, for 3 years, all this time they need to create optimal conditions for development, shade, but so that sunlight gets in, moisturize, cover for the winter or bring into a heated room. The only plus is the number of seedlings, because one adult bush can get up to hundreds of seeds.
Each gardener, wishing to propagate boxwood, chooses the most convenient option for him.


Planting boxwood delights the eye with rich greens, undemanding in care
Boxwood. Pest control
Boxwood leaves can be damaged by felt, from which small swells appear on the surface and the plant withers. To fight this disease, you need prune
and destroy the affected branches to healthy wood and treat the wounds. A mature boxwood bush can be affected by a spider mite. Treat the surface of the plant with special preparations and get rid of the pest without any problems.
The hedges that you so painstakingly cultivated on the site can amaze Psill's disease.
It is caused by beech gall midge larvae. The disease causes deformation of the leaves, slowing down the growth of the plant. To combat it, you need to remove the affected parts of the boxwood and treat the bush with appropriate insecticides. Be sure to follow all safety precautions during this procedure.
The use of chemicals, when treating boxwood from pests, helps to destroy not only pests, but also beneficial insects, which are boxwood orderlies
... These include ladybirds, predatory mites, lacewings and hoverflies. They are the real enemies of spider mites, aphids and scale insects. Boxwood orderlies help keep the plant healthy without the intervention of chemicals.
Boxwood is one of the few ancient ornamental shrubs that, to this day, are able to delight summer residents. Boxwood is widely used in landscape design - it greens territories and creates beautiful hedges from it. This shrub is an evergreen plant, therefore, even in the winter cold, it has a rather impeccable appearance. Consider the rules and recommendations for planting, caring for and growing boxwood at their summer cottage.
Seedling care
Boxwood cuttings planted in pots should be watered abundantly. They do not tolerate drying out of the soil and quickly die from this. It is necessary that the soil in pots with seedlings always remains moist. But you can't fill them. Excess water must drain out through the drain holes.
The lighting of the seedlings should be diffuse and very moderate. They cannot be kept in the sun even for several hours a day.
It is best to place the pots in shade or partial shade.... Under intense lighting, boxwood cuttings die quickly without forming roots. The temperature during rooting should be above 20 ° C.
If the cuttings are rooted under jars or in a container under a film, the seedlings must be opened daily for 1-2 hours for airing.This will avoid waterlogging and decay. They are then placed back under glass or foil to create a constant high humidity around the seedling. Under these conditions, cuttings take root much faster than outdoors.
Boxwood varieties - distinctive features
There are about 30 types of boxwood, native to the Mediterranean and some Asian regions. Each species has unique characteristics that make it different from other plant varieties. Boxwood shrubs differ in:
- Growth rate
- Distribution area
- Bark staining
- The shape and color of the leaves
Russian gardeners most often (95%) grow evergreen or ordinary boxwood. Many lovers of plants and, in particular, ornamental plants, like to grow them in tubs. In this case, it is optimal to use Chinese low-growing varieties.
Registration of a summer cottage with the help of boxwood.
Boxwood evergreen
- widespread distribution of this plant species in Mediterranean countries and in the Caucasus. Boxwood of this species grows well in partial shade and in sunny places. In cases where the bushes are not pruned, they reach a height of 3 meters.
Small-leaved boxwood
- this type of plant differs from the species described above in that this dwarf shrub is not afraid of winter cold. This plant is a descendant of the boxwood family, which grows in the territory of South Asia. It can withstand temperatures up to 30 degrees below zero - even in such frosts, it can not be covered. Gardeners appreciate this type of plant because of its compact shape and decorative crown.
Balearic boxwood
- is the largest species of the boxwood family. The size of its leaves reaches a length of 5 cm. In its natural environment, this plant grows in the Balearic Islands - this is Spain. This type of boxwood is also widespread in other territories: in the southern regions of Spain, on the territory of Portugal, on the coast of the Crimean peninsula.
Correct pruning of boxwood
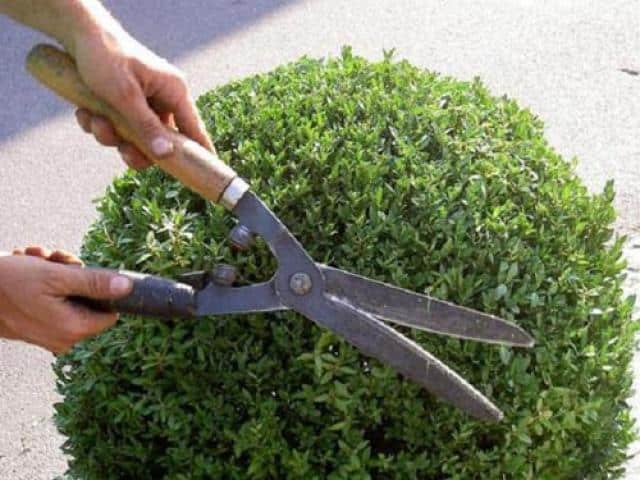
Similar to top dressing (the introduction of fertilizers into the soil), boxwood bushes are cut in the second year after planting, since it is necessary to finally make sure that the bushes have taken root. Pruning of bushes is carried out no more than once a month, during periods when the shrub grows most actively - in May-August.
Pruning boxwood will give your shrubs the right geometric shapes and create a well-tended look for your garden.
Using garden shears and other special tools, the plants are trimmed to the desired geometric shape. A month after the haircut, the shape must be corrected - remove the protruding branches.
Frequent pruning of boxwood shrubs requires more frequent watering and fertilization, which replenishes the loss of nutrients, and also protects the plant from loss of leaves.
Ornamental shrub boxwood: planting, care and reproduction
Boxwood: pruning in the fall, is it necessary? Pruning a plant is done to give a certain shape or just for decorative purposes.
Circumcision is performed on average once a month, but more often. This can be done from May to the end of September, during a period of active growth.
Pruning just before winter doesn't make sense. After cutting, more abundant watering should be done so that the plant recovers better.
Boxwood cells contain plant poison, the maximum concentration of which is in the leaves.
Only bushes that have reached 2 years of age, with sufficiently strong roots, are allowed to be refined. It is undesirable to prune in hot weather, this leads to burns to the tips of the leaves. Immediately after pruning, the bush must be watered abundantly, and so that the water also gets on the leaves. Fertilizers can be added to the water to stimulate growth.
Before wintering, the plant needs careful watering, but fertilization after September is highly undesirable.
Boxwood is relatively frost-resistant, but in regions with harsh winters, it is better to cover it with spruce branches or burlap. Small bushes can simply be covered with wooden boxes. This will allow the plant to successfully overwinter, and in the spring it will again please the eye with its unusual appearance.
selo.
Boxwood refers to evergreen trees and shrubs of the boxwood family, of which there are more than 100 species in nature. The homeland of the plant is India and Asia. In Latin, the name of the shrub is "buxus" (buxus). The plant is used to form hedges and grow in pots for interior decoration.
When can you transplant a plant into a garden
If the cuttings were harvested and put for rooting in spring or summer, then by autumn they will already be strong enough to survive the frosts. Such plants can be carefully transplanted into the ground in early autumn.
Experienced gardeners practice the rooting of spring and summer cuttings in open field bedsso that in the fall they do not require a transplant.
Spring and summer cuttings can also be kept in indoor grow pots. In this case, they are transplanted into the ground in the spring.
Cuttings cut in September will not be able to root well by winter, so they are always planted only in pots.
With the onset of cold weather, they are taken into the house and grown during the winter, like houseplants.
By the spring, such specimens will grow well and get stronger. With the onset of spring heat, they are planted in flower beds or in a garden.
Proper care
The basis for caring for planted branches is to keep the soil constantly moist. To maintain optimal moisture in the plantings, you need to spray them two to three times every day. Periodically, a homemade greenhouse must be ventilated so that the plants receive oxygen. A very important condition is that the branches should not touch either each other or with the shelter. There should be free space around each seedling.
If the leaves or shoots come into contact with the shelter or with neighboring seedlings, rot may appear due to high humidity in the greenhouse. If you find a rotting area on the buckle, but the affected area should be carefully cut off with scissors. Usually, parts of the leaves begin to rot.
Already two weeks after landing, the buxus will begin to sprout roots. After about a month and a half, the plants form a root system. After two months, you can remove the greenhouse. Watering the plantings is carried out as the soil dries up, trying to keep the soil moist all the time.
Planting cuttings
To plant boxwood cuttings, you need to choose a shaded place. Boxes with cuttings must be brought into the shade, and if you plan to plant boxwood directly into open ground, then the site must be shady. Cuttings are planted at a distance of 10 cm from each other. You can plant twigs in several rows, leaving about 20 cm between rows. If you plant boxwood in small pots, then you need to plant two or three cuttings in one pot. When grafting, all boxes and plantings in the open field must be tightened with transparent film. This will create a microclimate that will not be affected by weather conditions. When planting, the cuttings are simply stuck in the ground and then watered. It is necessary to deepen the cutting by 5-6 cm. It is advisable to soak the branches in a growth stimulator before planting in order to accelerate root formation. About two months after planting the buxus cuttings, roots will appear on them and young plants will grow.
When is it better to carry out cuttings and what is required for this
Cuttings of boxwood for reproduction can be cut:
- In the middle of spring;
- During the planned mowing of green spaces at the end of June;
- In September.
Most often, boxwood propagation by cuttings is carried out in the spring.
Cuttings root equally well, regardless of the timing of harvesting. But further care for rooted young plants depends on the timing of cuttings.
To cut boxwood cuttings and then prepare them for rooting, a garden pruner and a small sharp knife are needed.
The pruning shears are used to trim the bush, cut the stalk with a knife for further planting in the ground.
Before rooting cuttings, it is necessary to prepare containers and soil mixture for them. Cuttings can be planted in a container or in separate pots. It is important that the containers are deep enough - at least 10 cm. A mixture of garden soil with peat in equal parts is suitable as a soil for rooting cuttings. Sometimes, instead of peat, coarse washed sand is used.
How to properly water boxwood
If tub plants require daily watering, then box trees planted in open areas should only be watered on hot summer days. The rest of the year, watering is not required, since the plants have enough moisture, which they receive from rainfall. If the weather is dry for a long time, boxwood should be watered abundantly once every four weeks.
Periodically, the plants should receive a short shower - thanks to it, the dust that has settled on them is washed off the leaves. In addition, the shower has a beneficial effect on the seedlings - they take root faster. The main thing is to often loosen the soil near box trees so that their roots receive more air.
Planting boxwood in a permanent place
Already two months after planting, the branches of the buxus form a fully developed root system. During this time, they can be transplanted to a permanent place in the garden. If the cuttings were carried out in the middle of summer, then by the first cold weather in a new place the boxwood will take root and winter well.
This plant prefers fertile soil, although it can put up with depleted soil. If you have poor, sandy soil on your site, then before planting the axle in a permanent place, mature compost should be introduced into the ground. The soil in the selected area should be loose, well permeable to oxygen and water. In no case should boxwood be planted in areas in the lowlands where water stagnates. Buxus is not a demanding plant in terms of illumination, and it tolerates both bright sun and shade equally well.
Planting boxwood is carried out according to the same rules as planting other shrubs. Ripe compost is added to the planting pit, the plant is lowered, the roots are straightened and covered with earth, it is shed well. The seedlings are deepened to the depth at which they grew in the greenhouse. It is imperative to mulch young bushes, as mulch will retain moisture in the soil and prevent weeds from growing. Sawdust, foliage, grass cuttings, straw or peat will work as a mulching material.
Features of caring for boxwood in autumn: planting, transplanting and grafting


Boxwood is one of the most popular ornamental plants for decorating the territory. It is widely used as a spectacular element of landscape design.
It is a perennial shrub whose leaves remain green all year round.
Boxwood - present long-lived plant, with proper care of boxwood, it can live 500-600 years! In nature, there are about 30 species of this plant, however, in ornamental gardening, mainly only one species is successful.
A guest from southern latitudes takes root well in the climate of the middle zone, but requires care. Especially crucial periods are autumn and winter.
Boxwood: cuttings in the fall, planting and transplanting a plant.


Since boxwood blooms in spring, then
autumn is better suited for planting... For sufficient rooting, the plant needs about a month.
Therefore, the landing time should be chosen so that so that the roots have time to strengthen before the first frost... The nature of the soil does not really matter, the only difference is that the shrub will grow faster on fertile soil.
Do not plant boxwood on places where groundwater is too high and tends to stagnate.Swampy areas can kill the plant.
Cutting cuttings
Trimming boxwood into cuttings is done only with a sharp tool. It's great if you can cut twigs about 20 cm long. It is best to cut the cuttings from the bottom of the bush, as it is desirable that the twigs be at least a year old. It's great if you can cut young twigs into cuttings. It's important to know! Lignified boxwood twigs are not suitable for propagation by cuttings! Several lower leaves must be torn off from the cut cuttings, freeing at least two internodes. After that, the thin bark on the cuttings in their lower part must be slightly damaged - you can scratch it with a needle or a fingernail. During rooting, callus forms on the damaged part of the cuttings, from which the roots will grow.
Cuttings
The easiest way to propagate boxwood at home is by cuttings. There are two times of the year when the procedure is recommended. You can either carry out cuttings of boxwood in late spring - early summer, or in the fall. It is preferable to do cuttings all the same in the summer, because in this case, before frost, the seedling will already get strong enough and firmly rooted in the soil. This will give him the opportunity to survive the frosty winter safely and more likely.
Boxwood, which they try to root in the fall, survives less often. If in your area winters are long and cold, then it is better not to risk cuttings, planting them in the fall in open ground. In this case, you need to either wait for next summer, or carry out cuttings, but in pots and keep the immature seedlings in a covered room in winter. In the spring, you can plant them on the street, so it is more likely to grow a healthy adult plant. Just do not keep them in a warm room in winter, the plant should be hardened from "childhood". It only needs to be protected from frost and strong winds, so a cool indoor space is perfect for wintering.
Boxwood cannot be propagated in water, its roots do not grow in liquid. Also, it is impossible for reproduction to be carried out in the sun - the sections of the plant may dry out. Freshly cut boxwood cuttings are planted in the ground immediately. In this case, the foliage on the handle should not be removed. The shoot should be chosen from 18 to 20 centimeters long. Several such suitable cuttings are planted in the ground at a distance of 8-10 centimeters from each other. The earth around them should be compacted.
Boxwood seeds and cuttings need soil with a significant content of clay and lime, it is in such a land that they must be propagated. If your land is poor in these minerals, add them artificially before planting. If the soil is rich in sand, you will need to add old compost.
Reproduction of the boxwood plant by cuttings involves the use of young shoots of an adult plant, which are still flexible and not lignified. The smallest number of such shoots in the spring, and more - in the fall. For this reason, the reproduction of boxwood in the spring is not always possible. Watch a video on how to properly reproduce by cutting boxwood.
Procedure:
- Cut the shoot with green leaves obliquely and remove the leaves at the bottom of it. Keep in mind that the larger the cut area you have, the more likely the plant will successfully root and take root.
- In order to accelerate the formation of roots, soak the cut shoots for a day in a growth stimulator, for example, in "Kornevin".
- After a day, wash the shoots with water and plant in the ground in order to root. In order for boxwood to grow more densely and decoratively at home, combine several shoots into one bunch and plant them in one hole. Thus, you will immediately grow a bush, and not a separate plant.
- Water the cuttings well, and now you need to do this regularly. A plant, especially a young one, constantly needs water.
After the cuttings of boxwood are planted in the ground, the first roots will appear in about a month. In two months, the bush will take root completely, and if desired, it can be transplanted to a permanent place of residence. In general, propagation of boxwood by cuttings is a simple process.
Cutting care:
- Watering. After manipulating cuttings, it is necessary to water the young shoots of boxwood abundantly so that the soil is always well moistened. Also protect the young growth from sun damage.
- If you decide to propagate your boxwood by cuttings in the fall, then before the cold comes, do not forget to water the young seedlings well. This is necessary so that in winter the plant needs minimal moisture. Also, correct breeding requires peat warming of the soil between the rows of young cuttings.
If your winters are cold enough and you do not want to transfer the plant indoors for the winter, then cover the cuttings with burlap, properly securing it from the wind.
Top dressing of boxwood cuttings should be carried out for the first time a month after rooting. And in the future, regular feeding is needed once a month.
Experienced gardeners advise, before planting boxwood cuttings in the ground under the open sky, for the first 2-3 years to grow them in a cool indoor room at home. This protects young shoots and gives them time to grow strong enough. In this case, the likelihood that they will survive when transplanting and with the onset of winter will be much greater.
Reproduction and grafting
Reproduction of boxwood by cuttings at home in the fall. Cutting for autumn planting prepared in early September.
It should be about 7-10 cm long and have 2-3 internodes. The lower leaves are removed, only the upper ones should be left.
Cuttings are planted in a mixture of soil and peat, in a 1: 1 ratio. At first, it is helpful to cover the seedlings with glass jars or plastic wrap. As a rule, about 90% of cuttings take root successfully.
About after 3-4 weeks the cuttings will take root, and small leaves will appear on the trunk. It's time to transplant to the place prepared in the garden.
Care rules
It is quite possible to grow boxwood from a twig. But one competent landing is not enough. It is also necessary to follow the simple care recommendations.


Do I need to insulate boxwood for the winter
- If planting in open soil was carried out in the fall, then make a small frame over the cuttings that will protect the plant from breakage during the winter months.
- Considering the difficult winters in the middle lane, mulch the soil around the seedling to protect the root system. Put spruce branches on top.
- In the cold, cover the plants with agrofibre or foil. If the winter is snowy, then pour snow on top. If the plant is planted in an area with very harsh winters, then even an adult boxwood should take care of insulation.
Watering and soil composition
It consists in not flooding the plant, but moderately moisturizing the soil. It is better to plant boxwood in a permanent place in partial shade, but not in an area where there is constant sun. The soil should not be allowed to dry out, since on too hot days the bush may simply die.
Boxwood loves clay soils with a sufficient amount of lime. If the area has a high sand content, then add the required amount of mature compost.
Pruning


This procedure must be done only with sharp scissors or a blade so as not to damage the tissue of the branches. After pruning, be sure to fertilize the bush and water it. So the plant will recover much faster and will continue to actively develop and grow.
How to care for boxwood: crown formation with a photo
Throughout the season, the soil under the shrubs is mulched with peat or coniferous sawdust, needles. The main care of a plant is reduced to preparing it for a safe wintering. Winter is a real challenge for box trees. The shrub does not tolerate drying winds, temperature changes, thaw and spring sun rays.Therefore, with the onset of autumn, the plant must be well prepared for the cold.
1. Before the onset of frost, the plant is watered and the soil is well mulched.
Important! Dry leaves cannot be used as winter mulch, as they begin to rot and are a source of fungal diseases.
2. When the weather settles at -10 degrees, the boxwood is insulated. For this, boxes with ventilation holes are used.
3. Dwarf plants and boxwood borders are covered with non-woven material.
4. Tall plant varieties are covered with burlap. Shoots must be tied to a support so that they do not break off under the snow.
5. In early spring, the evergreen shrub must be freed from the shelter. It is not completely filmed. First, open half of the bush, and then remove the rest.
6. It is advisable to remove the covering material in cloudy weather.
Plant food
When caring for boxwood, one should not forget about dressing, with their help you can increase the plant's frost resistance and resistance to various diseases.
They begin to feed the plant from the moment of active growth. Throughout the season, fertilizers are applied every week. Good results were shown by the preparation "Baikal EM-1" and the infusion of bird droppings.
How to prune boxwood
This evergreen plant tolerates pruning well. Boxwood should be trimmed between April and September.
In return, the shrub will thank you with a beautiful lush crown and lush foliage.
Important!The more often a haircut is carried out, the more abundant watering and feeding should be.
The first time after planting, the plants carry out only formative and corrective pruning. Rejuvenating pruning is carried out in older specimens, the crown of which grows chaotically.
Boxwood looks beautiful on a trunk with a spherical crown. It takes years to form such a tree, but it's worth it. A template is used to shape the ball. The stem is formed as follows: cut off all lateral shoots to the desired height. Further, as the boxwood grows, a beautiful crown is formed using a template, all root shoots are removed.
Reproduction of boxwood by cuttings
After cutting the plant, a large number of cuttings remain, from which young seedlings can be obtained. With proper rooting, almost 100% of the cuttings take root.
For rooting, choose those cuttings, the base of which is slightly woody. The length of the cutting does not exceed 5-10 cm. All lower leaves are removed, only two upper leaves must be left.
Prepared cuttings are planted in loose soil, which is prepared from a mixture of garden soil and peat. Containers with plantings are covered with a bag and watered well. Throughout the entire rooting period, it is necessary to monitor the level of soil moisture. After 20-25 days, the plant forms a root system. Next, the boxwood is planted in a container for growing. A shrub can be planted in a permanent place in the garden next spring.
Caring for boxwood is a snap, even a novice gardener can handle it.
Compliance with temperature and humidity
Severe frost does not favorably affect boxwood bushes. If the air temperature drops to 20 degrees below zero, some weakened plants die if timely measures are not taken and they are not covered.
Therefore, before the first snow falls, preferably at the end of autumn, it is necessary to wrap up the plants, for which burlap or other materials are used that can protect the boxwood from icy winds and exposure to direct sunlight on frosty days.
To prevent the trees from being damaged by unfavorable weather conditions, plant them in semi-shaded areas. It is better to select frost-resistant species.
It is forbidden to use cellophane film to cover the boxwood. Excess moisture is created under the film, which has a detrimental effect on plants.
Transfer


How to transplant boxwood in the fall? An adult boxwood tolerates a transplant well at any age, and it is considered a favorable time for its transplant from July to November.
Immediately after transplanting boxwood in the fall, the plant needs increased watering.
To stimulate growth, boxwood is recommended to be replanted every 3-4 years, until the bush becomes large enough.
Transplanting an adult plant is carried out in the same way as the initial planting in open ground, that is, together with a lump of earth. After transplantation, in the area of the root circle, it is necessary to make mulching pine bark.
What cuttings are better to take
For successful reproduction of boxwood, semi-lignified cuttings are chosen. Green or, conversely, too old and dense parts of the shoots take root much worse or do not form roots at all.
Cuttings are cut into lengths from 10 to 15 cm using a garden pruner.
The apical parts of the shoots are most often used. They take root faster and then grow better.
The lower cut near the bud is made at an angle to increase the surface on which the roots will form. The cut should be smooth, so make it with a sharp garden knife. Additionally, several longitudinal cuts of the bark up to 1 cm long can be made in the lower part of the cutting.
As a rule, boxwood cuttings do not take root well. Not all of them take root and grow. Therefore, for successful rooting, they are soaked for a day in a solution of a root formation stimulator.
Or, before planting in the ground, you can dip their lower part in water, and then in stimulant powder. This will increase the number of rooted cuttings. If this drug is not used, then less than half of them take root.