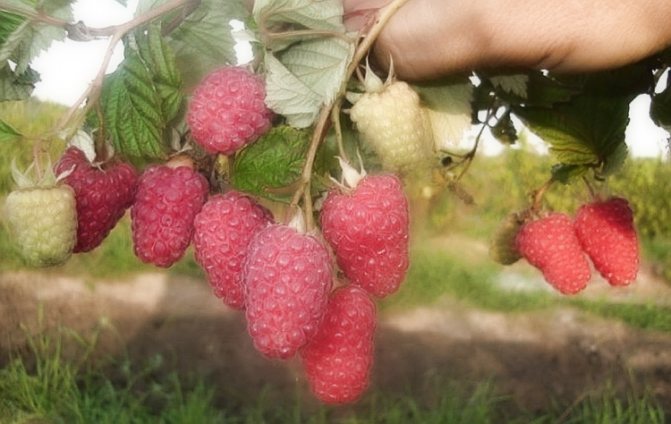
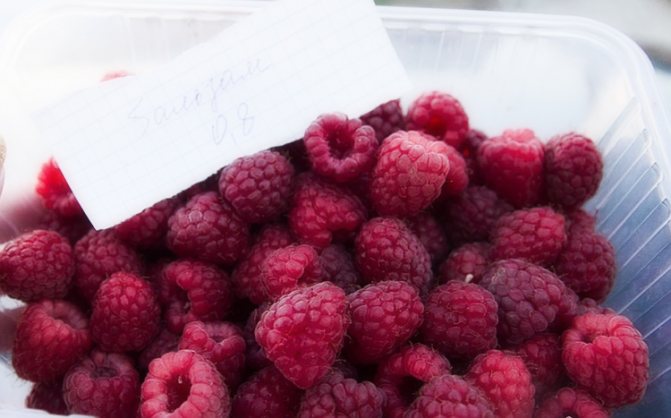
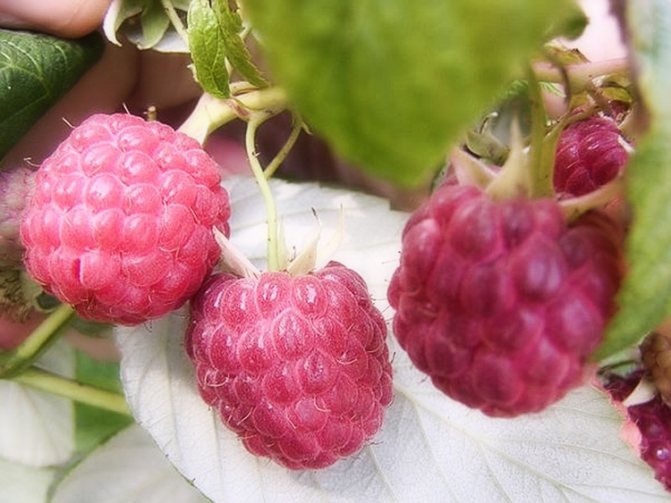
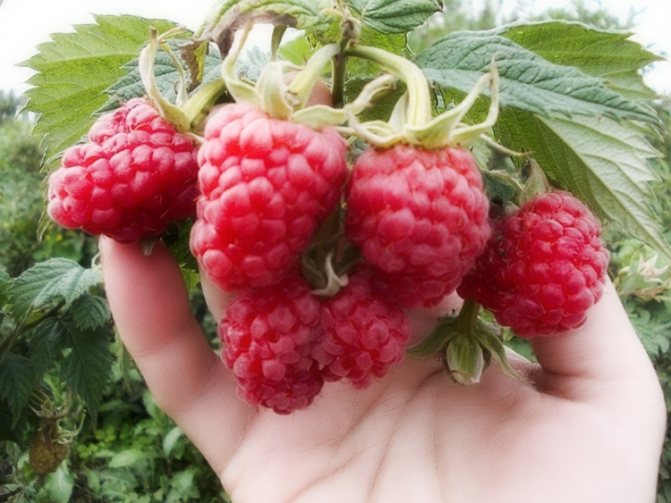
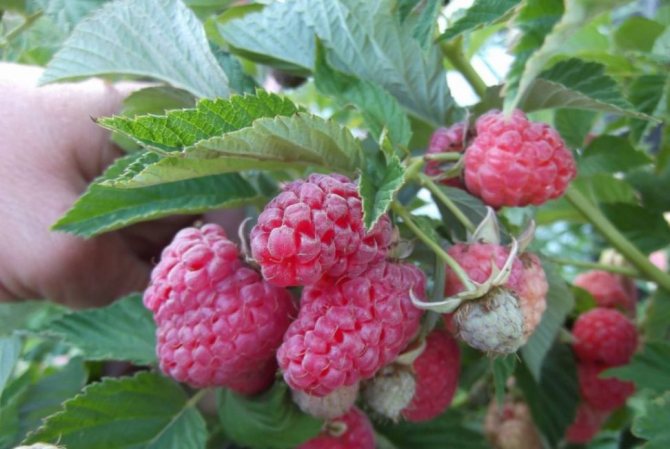
Photo and description of the variety of bush raspberries
Raspberry belongs to perennial shrubs of the Rose family. Young stems are soft, green, with small thorns, up to 2-2.5 m high. In the second year after planting, the stems become lignified, acquire a dark brown color and dry out at the end of the season. The next year, new young shoots grow in their place.
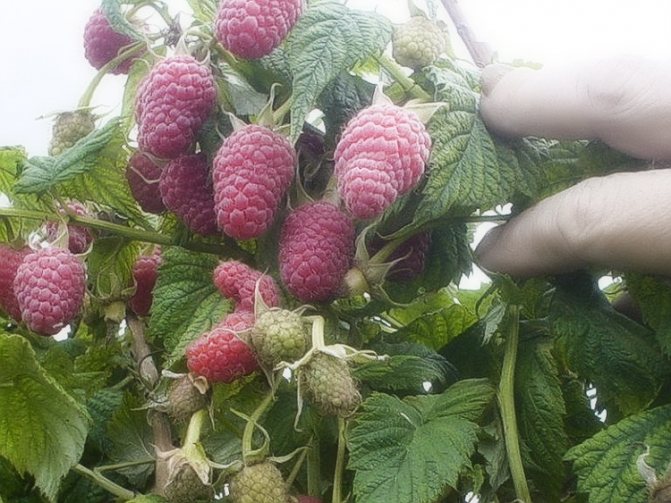
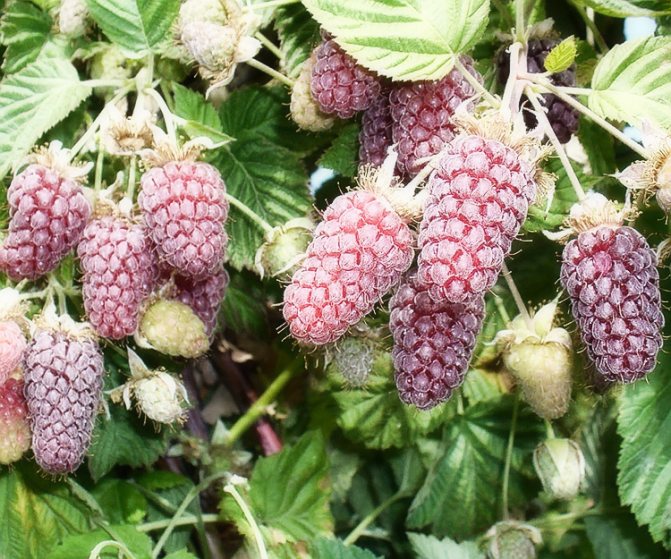
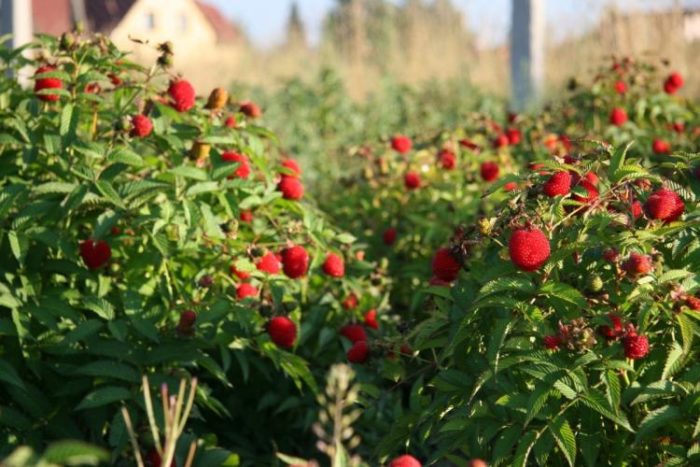
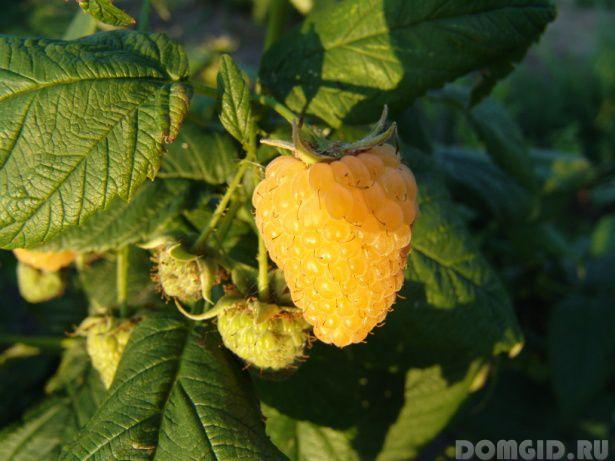
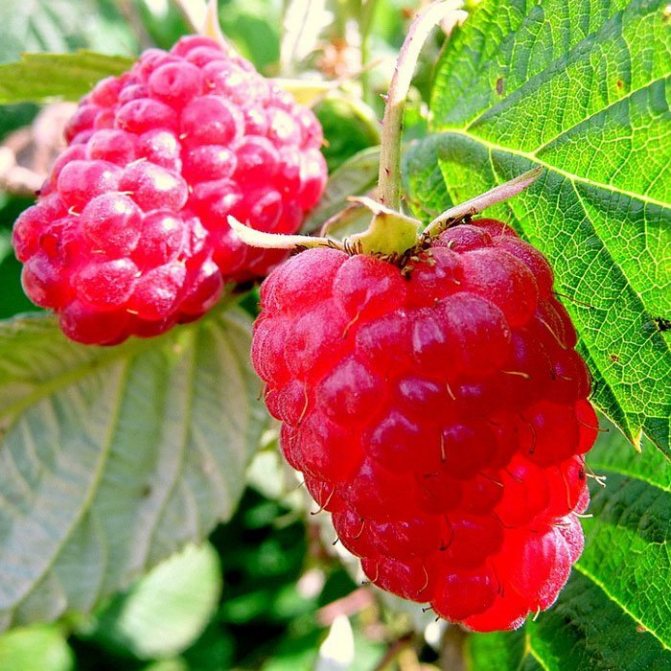
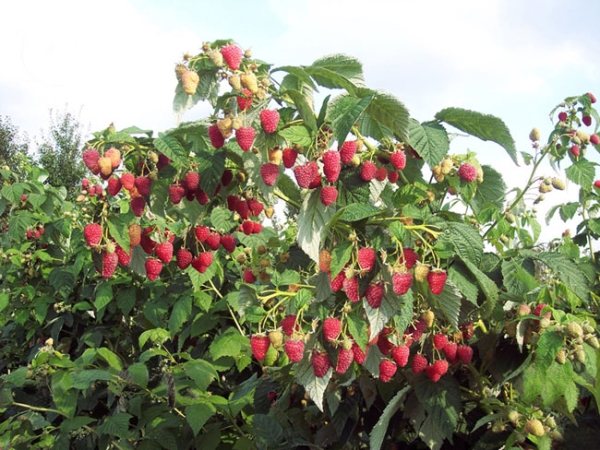
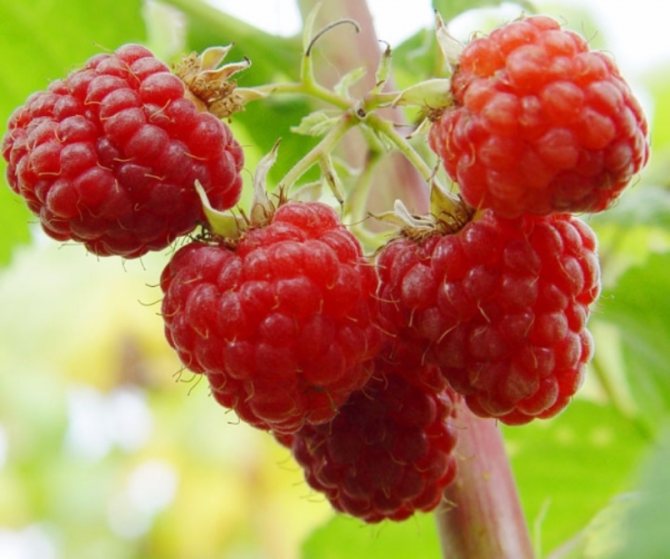
The most common varieties of bush raspberries have dark red large berries. A little less often, ripe raspberries can be yellow or purple in color.
Important! The main feature of the culture is early flowering and rapid formation of berries. Thanks to this, the crop can be harvested as early as mid-June.

The shrub has powerful roots located at a depth of 30-40 cm, and covering an area of up to several square meters. Leaves grow in 3-6 pieces on a short petiole. From above they are bright green, and from below they are covered with a whitish bloom.
Bush raspberry varieties:
- ordinary;
- repairing;
- large-fruited;
- standard.
The most prolific is the remontant raspberry, which gives two harvests in one season. But the most delicious and sweet berries are in large-fruited raspberries. The shrub blooms with small white flowers, and the fruits contain a huge amount of vitamins, glucose, tannins.
In all varieties, except for remontant, fruiting occurs in the second year after planting. The culture does not require additional pollination and bears fruit annually. With good care, high yields can be achieved.
Early varieties:
- Meteor;
- Scarlet Sails;
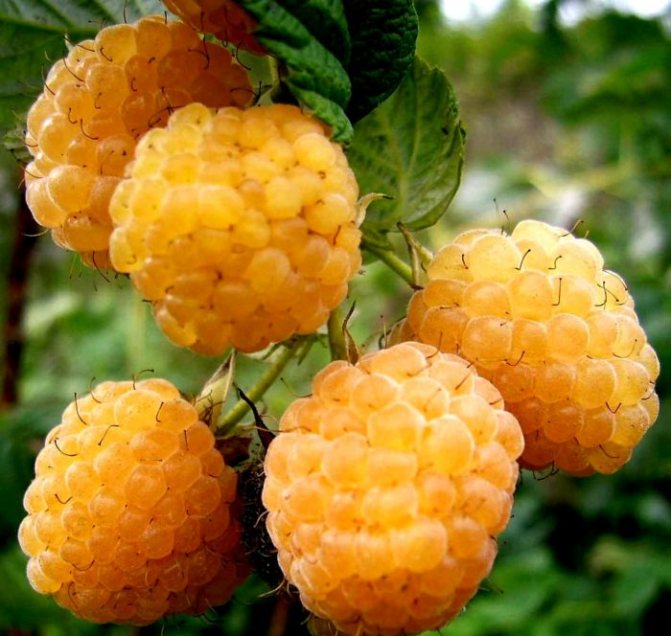
- Runaway (yellow).
In addition, there are mid-ripening varieties in which ripening occurs later, but the yield is higher.
These include:
- Hussar;
- Glen Ample;
- Purple Haze.
The most popular late types of bush raspberries are Terenty, Mirage and Biryusinka.
Mankind has known about this plant for a long time. Raspberry seeds were found by archaeologists, excavating settlements of the Bronze and Stone Ages. Although in those days, consumers were most likely not particularly interested in the cultivation of raspberries. The Roman writer Pliny (1st century AD) also has information about wild raspberries, talking about its cultivation in Central Asia.
Despite the fact that raspberry was originally a wild plant, the Greeks and Romans knew about the beneficial properties of berries and used it for various purposes. For example, with the help of these berries, they cured many diseases, scorpion and snake bites. In the sixteenth century, the domestication of raspberries began in Western Europe. They began to transplant it from the forests into the gardens of the monasteries. From the seventeenth century, different varieties of raspberries began to appear. Gardeners began to be seriously interested in this plant.
Content
- Types and varieties of raspberries video
- Raspberry planting and care
- Secrets of Getting a Good Harvest Video Video Video
- Watering raspberries
- Pests
- Raspberry diseases
- About the beneficial properties of raspberries and preparations for the winter
Types and varieties of raspberries


The raspberry bush is a plant with a perennial root system, reaching a height of about two meters. The main shrub varieties are divided according to the following essential indicators:
- according to the ratio of the size of berries - into varieties with large fruits and with traditional ones;
- according to the ratio in fruiting - remontant varieties and traditional ones.
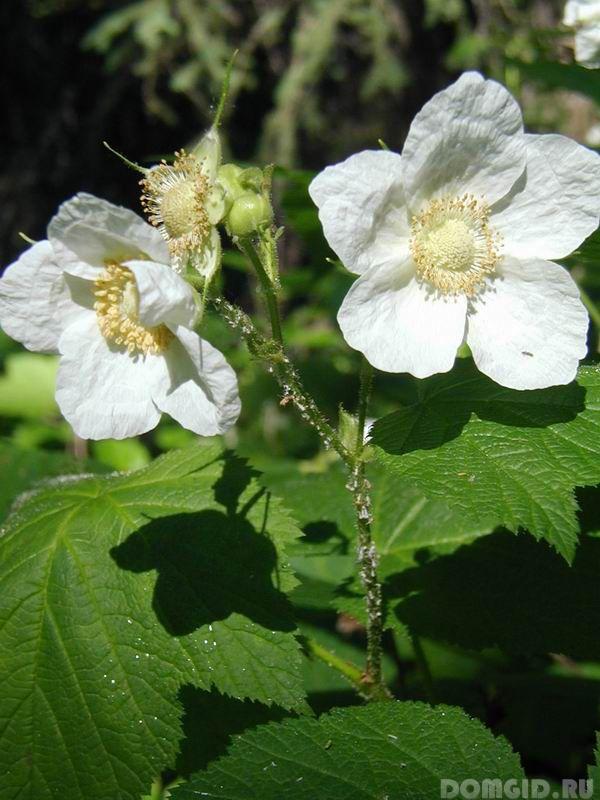


Naturally, all varieties and species have their own disadvantages and advantages.The types of raspberries that are traditional are considered to be not particularly whimsical. They survive severe frosts remarkably, reproduce well, releasing several young shoots from the root system every year. However, the berries are not very large. Their weight is only 3-4 grams.
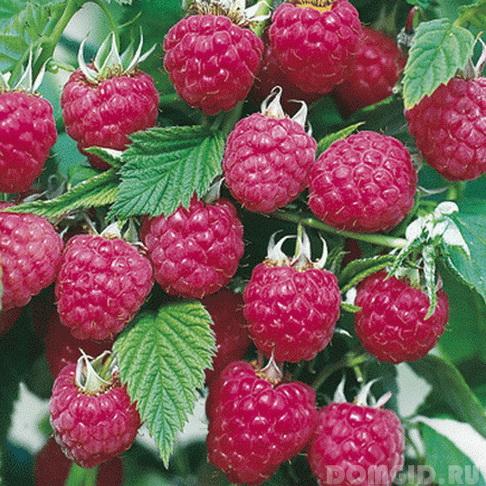


Varieties bearing large berries give a good harvest. Fruit weight from 4-12 grams. It happens that on the shoots alone, the weight of the fruit reaches 20 grams. Often, the branches of the large-fruited raspberry branch. As a result, five shoots can grow from one branch, which will also bear fruit well. The most recognized and popular large-fruited variety is Izobilny. Large-fruited varieties are famous for their good taste, pleasant and sweet aroma.


Repaired raspberries yield twice a year. Moreover, the berries from the second harvest will be larger than from the first harvest. Surprisingly, you can harvest the fruits of the second harvest until severe frosts.
Depending on the variety, any type of raspberry can be both sweet and sour-sweet, according to the duration of ripening - late, medium early and early, with berries painted in yellow, red and black colors. If you want to plant an early raspberry variety, buy, you will not regret, the Cumberland or Izobilny varieties.
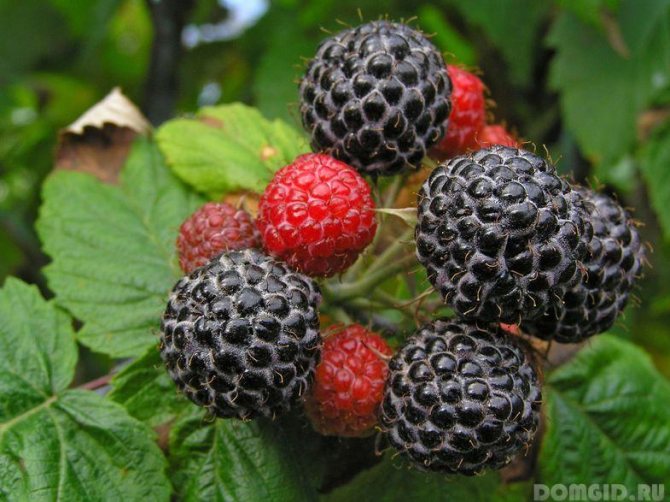


These two varieties have large enough fruits and survive frost well. Abundant raspberries will delight you with bright red fruits, and Cumberland will surprise you with black berries. Both varieties will perfectly, if necessary, tolerate transportation and will not lose their presentation.
Let's take a closer look at mid-early raspberry varieties. In the CIS markets, this species is represented by the following varieties:
- Arbat - gives not a small amount of large berries, weighing about 18 grams, but very badly survives strong frosts;
- Yellow giant - bears fruit with light yellow berries, belongs to the remontant species, fruits are about 8 grams;
- Lilac fog - not subject to viral diseases, a variety with large berries, weighing up to 10 grams.


Now there is not much about late ripening varieties. In this form, it should be noted such varieties as:
- Arabesque - a bush up to two meters high, burgundy-red berries, fruits weigh up to 8 grams, undemanding in care and planting;
- Tarusa - the height of this tree-like variety reaches 2.5 meters, the berries are bright red, the bush does not need props, the berries are unpretentious during transportation.


Raspberry planting and care
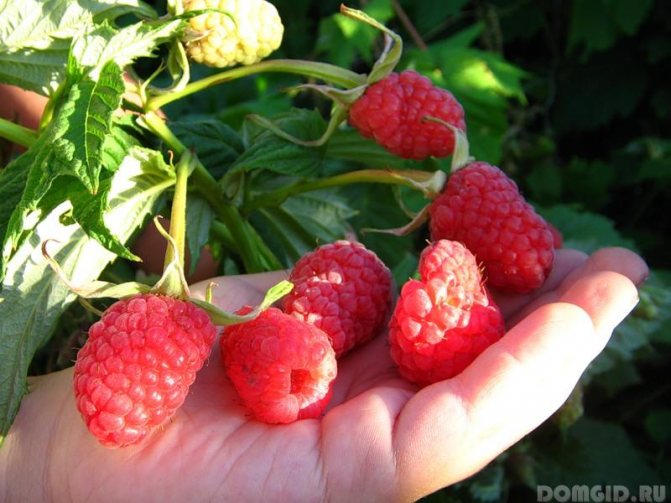


Raspberry seedlings should be planted in a place that is not very shaded, in a couple of rows, after which the shrubs should be strapped. The gap between them should be about 70 cm, and the row spacing should be at least 2 m.The depth of the hole should be 70 cm.
In each such hole, you can plant two seedlings - this will contribute to an earlier and better harvest. Sandy soil is well suited for planting, with a minimum content of clay impurities. Unfortunately, on soil with stagnant water, raspberry bushes will not take root.


Humus must be placed in the dug hole and filled with water. While water is absorbed into the soil, the seedling is cut, leaving 15 cm high from the root. Of course, with such a low stem, in the first year of life, the plant will not bear fruit, but this procedure will make it possible to strengthen the rhizome and overwinter painlessly. After the end of planting work, the raspberry bush is watered and mulched without fail. Do not neglect the mulching process - it will make it possible to keep all the nutrients and useful substances in the layers of black soil.


Secrets of Getting a Good Harvest
Any varieties, of different types and crosses, will reduce fruiting or even stop yielding if they are dismissive of caring for raspberries in spring and summer.In summer, high temperatures can become the enemy of plants - plants of this species cannot tolerate insufficient moisture in the soil. From this it follows that you need to water raspberries constantly - before flowering, before ripening and during the ripening period of the berries. On average, the amount of water poured out should be 30-40 l / m2 at a time.
Chernozem, in the place where raspberries are planted, must be constantly fertilized and loosened. It is necessary to feed the soil in the raspberry berry with fertilizers both in spring and autumn. Do not forget about the regular tying and shaping of the formed bush.


An important, significant point in the care is the preparation of the shrub for winter. When preparing remontant varieties, you need to remove the entire part that is above the ground. And the shoots of varieties that are resistant to cold are simply bent over and hidden under the snow layer.
There are several ways to increase the number of fruits of remontant varieties. In order to have time to grow and harvest them, you need:
- buy raspberries (seedlings) of high-yielding varieties,
- planting repair bushes, preferably in the ground, well fertilized with organic matter;
- in the spring you need to remove the snow around the shrubs, and when sprouts appear, cover them with a film.
Adhering to not very complicated care rules, you can grow raspberries without much physical exertion.
In order that the berries are not dry and small, the shrubs need to be watered according to the rules. The problem is that the part of the plant that is above the soil has enough area for evaporation. It is clear that because of this, the root system, which is not at all deep, will not be able to provide the plant with a sufficient amount of moisture to ripen the crop.


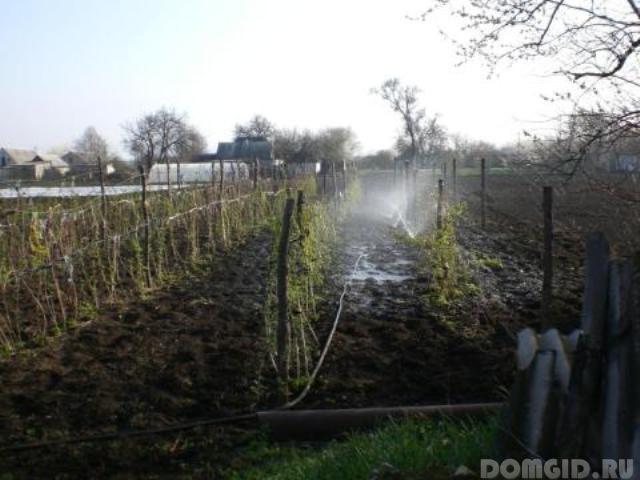
The amount and frequency of watering directly depends on the air temperature and the amount of precipitation. The largest amount of water is needed for raspberries during flowering, fruit formation and, of course, during their ripening period - for most varieties this time starts from the end of May and lasts until the beginning of June. Subject to the rules of watering and fertilizing the soil, the fruits will be larger than those of raspberry bushes with improper watering.
When the weather is hot for a long time, the bushes begin to fade - this is the first omen that they do not have enough moisture. The land under the bush must be watered constantly. With prolonged drought, it is necessary to water so that the water penetrates to a depth of at least 30 cm (it is at this depth that the root system is located). After such watering, after waiting until the water enters, you need to loosen the top 5 cm of soil under the bush. This procedure will allow the root system to feed on oxygen.
Watering raspberries
The best option for watering raspberry bushes is considered to be watering along previously dug grooves, the location of which is determined by the age of the plant and the structure of chernozem. Fruit-bearing raspberry, in the third year after planting, already has a well-developed rhizome up to 2 m in diameter. From this it follows that the grooves must be made between the rows. If the soil under the raspberry tree is heavy, then one groove is made in the center in the aisle, and if it is light, then several can be made by placing them 70 cm from the row. The depth of the groove is 9-12 cm, the amount of water for each meter will be 3-4 buckets. For irrigation, you should take water that has stood in the sun, it is better absorbed by the roots.


Starting from the end of August, watering of raspberries should be stopped, during this period there will be enough precipitation. Excess moisture will interfere with the formation of shoots and may reduce their resistance to frost. Also, excess moisture can contribute to the development of diseases. At the end of the summer period, it is recommended to water raspberries only if the weather is still hot and rain is not expected.
Pests
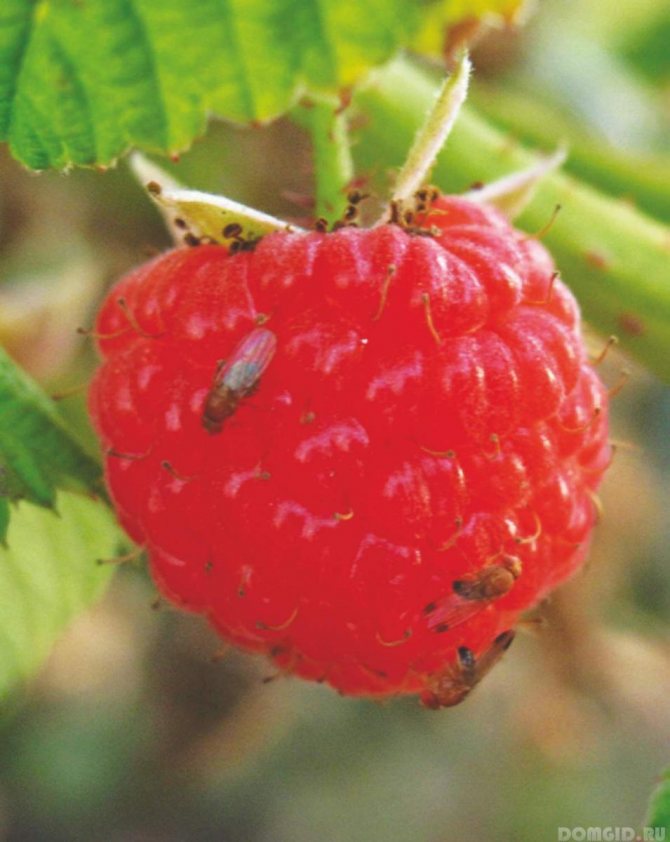


In those places where shrubs grow and bear fruit, pests will appear in any case. Unfortunately, this fact did not pass over Malin either. Here are some of the most aggressive pests:
- Raspberry stem fly is one of the most dangerous pests for raspberries. This insect is about 0.6 cm long, devouring young stems. in May, flies lay eggs on the leaves. The larvae that appeared later gnaw the stem, descend in it to the base of the shoot. After which the shoots rot and die.
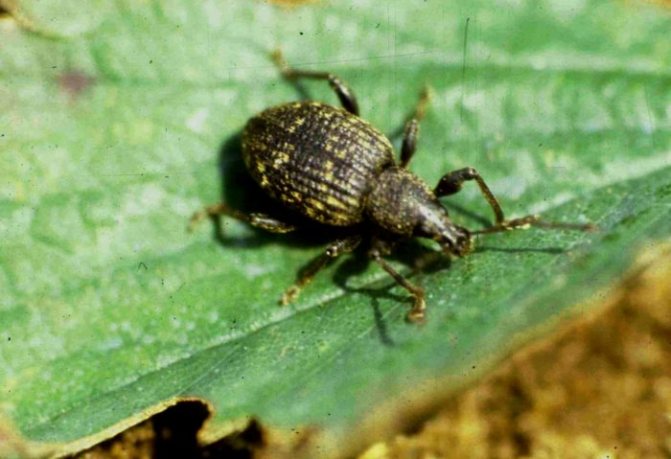
- The raspberry beetle lives in the upper layer of black soil in winter. In late spring, beetles gather on bushes, eating leaves, buds and flowers.
- Raspberry-strawberry weevil, with the arrival of spring, begins to devour leaves and buds. Females in buds lay eggs, destroying the pedicel.
- Raspberry shoot aphid - satisfying their appetites, deforms shoots, causes curling of leaves.
- Raspberry leaf aphid - lives in small groups on shoots or leaves and, worst of all, carries viral diseases.
- Raspberry shoot gall midge is one of the most famous pests. The eggs laid by them in various parts of the shoot form an infection, manifested by brown spots and drying of the shoots.
- Spider mite - feeds on the juice of stems and leaves, wraps them in cobwebs.
To combat raspberry pests, special treatment is needed. The best prevention would be constant grooming, removal of contaminated parts, digging in the ground and clearing away debris during the process.
Raspberry diseases


The most common viral diseases:
- Bushiness. Cicadas are infected with this disease. Stems are low and thin, lateral branches are poorly developed, leaves are affected. Infected shrubs do not bear fruit.
- Curliness. Infection occurs from aphids. The shoots have a normal appearance, the leaves are very deformed, the berries are altered and sour in taste.
- Mosaic. Infection occurs from the same aphid. Shoots and leaves are also affected. The foliage turns yellow. Plants with mosaics inhibit growth, the leaves change, the shoots are thin and weak, the fruits are dry and tasteless.
- Ring spot. The nematode is the carrier. The virus infects the plant and soil. Initially it appears on the leaves, changing their color and shape. The yield is very low. A healthy plant may well get it through contaminated soil.
- Infectious chlorosis. The carrier is aphid. Leaves are the first to turn yellow with chlorosis. By the middle of summer, the bush is almost completely yellow. The berries are very poorly developed.
In densely planted raspberries, infection with pathogenic fungi occurs quite often, which adore poorly ventilated places.
A wide range of raspberry disease control products are offered by shops specializing in the sale of plant protection products. Caring for raspberries in the spring must necessarily include preventive treatment.
Common fungal diseases:
- Anthracnose. Shoots and leaves turn brown and dry out soon. In autumn, the fungus forms black dots on plants and hibernates on the remains of affected stems.
- Septoria (raspberry white spot). The disease affects both leaves and stems, covering them with brown round spots, eventually changing color from almost white to a black, already familiar, dot. After septoria, the plant cannot survive the winter, but the fungus does not die, but goes to infect other shrubs.
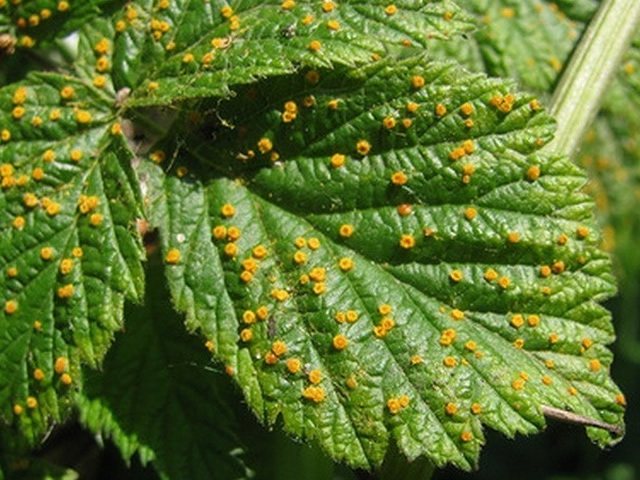
- Rust. This disease of leaves and shoots. It appears as yellow bumps on the outside of the leaves. In the summer, whiter, warm period, forms similar tubercles on the inner side of the leaf, but already of a rusty-brown color. On the stem, near the root, lesions appear similar to ulcers.
The fight against these diseases is basically the same - following the planting rules, thinning, removing and burning infected plants, cleaning the site, digging up the soil with the introduction of phosphorus fertilizers, and spraying.
About the beneficial properties of raspberries and preparations for the winter


Raspberries are very useful, they are rich in vitamins, glucose and organic acids, pectins, fiber, tannins, minerals and trace elements. Berries, flowers and young stems have long been used in folk medicine for the prevention and treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and colds, manifestations of sciatica and neuralgia. The systematic use of berries saturates the body with folic acid. In addition, raspberries have antidepressant properties.
A wonderful, very tasty raspberry jam is prepared from the berries. Berries can also be frozen or dried. Frozen raspberries can be used in winter for making pies or dumplings, you can cook compote from them. Tea with frozen or dried raspberries will help cure colds or SARS faster. It is very useful to consume raspberries throughout the year for diabetics - they can lower the level of sugar in the human blood.
10
Advantages and disadvantages
Each variety of bush raspberries has both advantages and disadvantages. Common early varieties are Scarlet Sails, Beglyanka and Meteor.
Meteor has a tall, not very sprawling bush, and fruiting occurs in the second year after planting.


Pros:
- yield;
- frost resistance;
- excellent taste and aroma;
- immunity to fungal diseases.
There were no minuses for this species, and the gardeners' reviews are only positive.
Scarlet sails are distinguished by a powerful, branched bush with large bright berries.
Advantages:
- yield about 1.7-2kg per bush;
- winter hardiness;
- resistance to fungal infections.
The disadvantages include frequent lesions with spider mites and mycoplasma.
The Runaway is one of the most popular varieties of yellow raspberry with straight, smooth stems and a medium-sized bush.


Pros:
- high productivity;
- frost resistance;
- wonderful taste;
- insensitivity to fungal diseases.
Of the minuses, it can be noted that it is not transportable, it is damaged by pests.
Among the mid-season varieties, Glen Ample is distinguished separately. It has no drawbacks, has a high yield, is not affected by diseases and pests. The berries are very large, sweet, store well and tolerate long-term transportation. The same characteristics are possessed by the varieties Gusar and Lilac fog.
Biryusinka is the newest late raspberry variety, with very large fruits and high yields.
Attention! The yield of Biryusinka is about 10 kg per bush, and the weight of one berry is more than 10-15 g.
The plant is unpretentious in care, it is not exposed to diseases and pests.
Terenty differs in the same characteristics, but the Mirage's yield and winter hardiness are slightly lower.
Seasonal outdoor pruning of raspberries
A good raspberry harvest cannot be achieved without regular and correct pruning of the bushes. This is due to the life cycle of the shoots. It takes two years, after which the shoots die off, interfere with young branches, become carriers of diseases and pests.
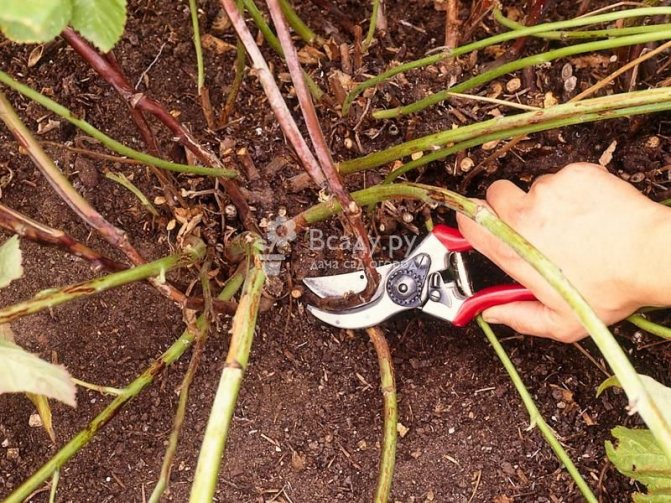


Pruning raspberries in spring
Spring pruning is needed to normalize shoots and stimulate their growth. They spend it as early as possible, when the snow melts. Frozen, broken and weak shoots are cut as close to the ground as possible, trying not to leave hemp. 12-16 strong shoots are left per running meter of raspberry, the tops of which are also shortened to the first strong bud.
Important!
All plant waste after pruning must be removed from the site and destroyed.
The next pruning is carried out in the summer, removing all fruiting branches to the base. It is not worth delaying with this procedure, since the fruit branches of this year have already completed their life cycle and only inhibit the growth of new shoots.
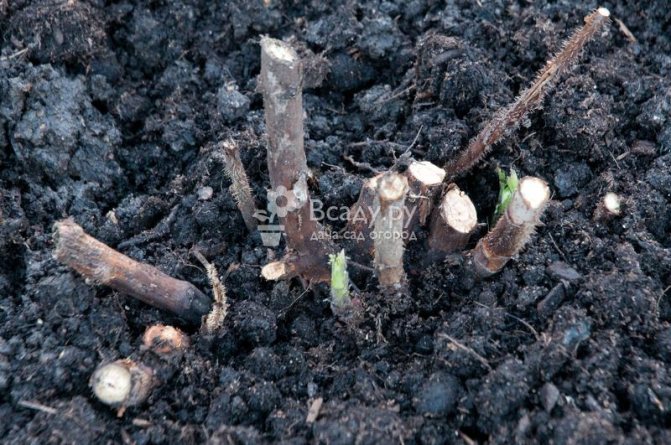


Pruning raspberries in summer to the ground
In autumn, shoots with signs of disease, broken by the wind or technology, are removed in the raspberry tree. You also need to cut out young shoots that did not have time to gain strength over the summer (stem diameter up to 10 mm). You cannot leave the leaves on the branches, they must be removed.When the raspberry is removed, the shoots are tied and bent to the ground. This will help them survive the winter without loss.
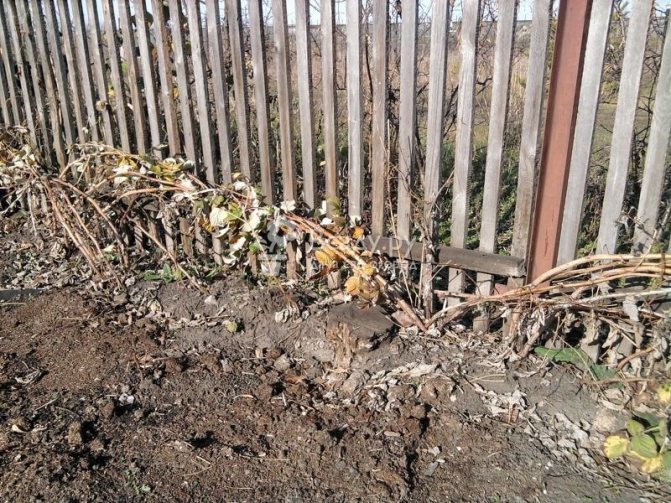


Bending raspberries to the ground for the winter
Advice
With autumn pruning, 30-35 shoots are left in the raspberry plant per running meter. This amount allows you to make a stock that will replenish frozen and broken shoots in the spring.
Raspberry overgrowth problem
The growth pattern of raspberries is aggressive. Growing up, it can occupy large areas, forming a distant growth. You need to get rid of it as quickly as possible for several reasons:
- Distant seedlings take a lot of strength and energy from the mother bush;
- Shoots of root suckers are capable of clogging up a large area of nearby areas in a short time.
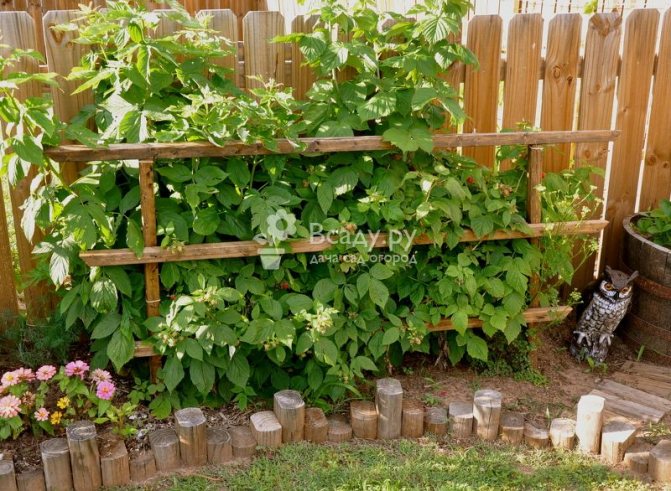


Support fence to limit the growth of raspberries
Unplanned raspberry growth can be avoided by using underground barriers at the raspberry border. To do this, pieces of slate or boards are driven into the ground to a depth of 40-50 cm. They should rise 10-15 cm above the soil surface. If the growth still breaks through the barrier, it is cut out at the root immediately.
Advice
All shoots that are more than 20 cm away from the mother bush must be cut out. You cannot pull the roots out of the ground, you can injure neighboring bushes.
Pruning remontant raspberries
Particular attention should be paid to pruning remontant raspberries. When growing it for harvesting one harvest, in the fall all shoots are cut out, while the hemp does not need to be left. In the spring, young shoots will grow, which will yield a harvest at the end of the season.
For two harvests - pruning remontant is carried out in the same way as for regular raspberries. In this case, two-year shoots will give a summer harvest, and annual ones - in the fall.
Landing
Raspberry is photophilous, but does not like extreme heat. The soil on the site should be clay-sandy, moderately moist, but not heavy, with neutral acidity. For landing, it is better to choose a place protected from the wind, on flat areas or gentle southern slopes.


Best predecessors:
- beet;
- dill;
- carrot;
- radish.
It is necessary to plant bush raspberries in the fall, from late September to mid-October.
There are three main planting methods:
- With the bush method, it is necessary to dig small pits, 40 cm wide and 30-35 cm deep.They are placed at a distance of a meter from each other, and a distance of about 1.5 m is left between the rows.The pits are filled with a pre-prepared nutrient mixture of humus, superphosphate and ash ... 2 seedlings are placed in each hole, added dropwise and tied to a peg.
- The tape provides for a denser planting, when a distance of no more than 0.5 m is left between the seedlings.The row spacing should be wide, about 2 m.
- Trench planting requires digging long trenches, 55 cm wide and up to 35 cm deep. The bottom is covered with humus and bushes are planted. After planting, the plants must be well watered, at the rate of a bucket of water per bush and mulched with sawdust.
Reproduction methods
Raspberries can be propagated both in spring and in autumn, but autumn transplantation is undesirable for bush varieties.
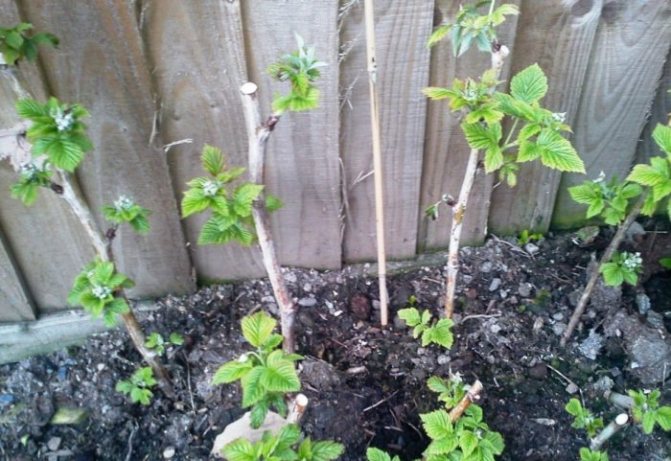


Breeding methods:
- dividing the bush;
- young cuttings;
- lignified cuttings.
If the bush raspberries are quite old, then they need to be transplanted. To do this, the bush is completely dug up, the old lignified shoots are cut off, leaving about 20 cm.The roots of the bush are carefully divided and planted in pre-prepared pits, 40 cm wide and 30 cm deep. Young seedlings are watered, the soil is mulched.
Cuttings about 15 cm long are cut from young shoots of basal shoots, the lower leaves are cut off and the upper part is removed. The cuttings are soaked in Kornevin's solution and wrapped in moist moss for rooting. As soon as the roots appear, the seedlings are planted in the garden. It is better to carry out the procedure in early June.
Lignified shoots are pruned in the fall, at the end of October, divided into several cuttings 10 cm long and stored in a cool place until spring. In early spring, the cuttings are placed in cups with a mixture of peat and sand, and when they take root, they are planted in open ground.
Site selection and soil preparation for raspberries
The site for planting raspberries should be well-lit and protected from the wind. The most successful planting of seedlings along the fence or wall of the house on the south side. In this case, the bushes will receive enough light in the summer, the fences will protect the bushes from the wind, and in the winter, trap the snow.


Choosing the perfect place to grow raspberries
If the site is located on a slope, it is worth taking away its middle part under the raspberries, since in the lowland the bushes can freeze out in winter, or you will have to deal with waterlogging of the soil in spring, during melt water.
Crop rotation rules for raspberries
- Precursors such as tomatoes, potatoes, and strawberries are undesirable for raspberries. The proximity of these crops with raspberries is also best avoided.
- The root secretions of raspberries help protect apple trees and pears from a fungal disease - scab, and an apple tree can save raspberries - from gray rot.
- You can avoid the growth of raspberries by limiting the planting to sorrel. Two to three rows of casing along the contour will increase the acidity of the soil, and the roots will not grow in that direction.
- Berry bushes with proper soil preparation can grow for 10-15 years in one place.
Soil preparation
Raspberries love fertile, light and well-drained soils. To grow it on sandy and peaty soils, it is necessary to annually apply humus and compost to stimulate the activity of microorganisms.
Heavy clay soils are not suitable for growing raspberries as the roots will rot. The acidity of the soil under the raspberry tree should be neutral or slightly acidic.


Preparing the soil for the raspberry tree
The soil for the raspberry tree is prepared in advance, digging deeply and applying organic and mineral fertilizers. For autumn planting - not less than a month, for spring planting - from autumn. From fertilizers, manure or humus is introduced, urea or ammonium nitrate, superphosphate and potassium salt are added.
Growing and care rules
Caring for bush raspberries is not difficult and does not require much effort.


Care requirements:
- watering;
- top dressing;
- garter;
- weeding;
- mulching.
Following these simple rules will help you get rich yields every year.
When and how to water?
- It is necessary to water the plant rarely, no more than 2 times a month, but abundantly.
- The first watering is carried out at the beginning of the growing season, and the second - during the setting and ripening of berries.
- One bush will require about 15-20 liters of warm, settled water.
- The last pre-winter watering is required in the fall, in October.
- After each watering, the soil is slightly loosened and must be mulched.


Application of useful fertilizers
In early spring, after the snow melts, the first top dressing is carried out with a urea solution, at the rate of 40 g / 1 sq. M. As for organics, in the spring you can water the soil under the bushes with slurry diluted in water.


Interesting! The first three years, young plants are fertilized only with mineral nitrogen fertilizers.
In the fall, raspberries are fed with rotted cow dung or chicken droppings with the addition of compost. From mineral fertilizers, you can use calcium nitrate. The next year, the autumn dressing is changed to a complex fertilizer for fruit crops.
Shrub pruning
It is necessary to cut the plant so that it does not grow, but is gradually renewed. In the first year after planting, the fruiting stems are cut, leaving 40 cm. In the second year, pruning is carried out in the fall, cutting off all dried, damaged and diseased shoots. In addition, the bush must be formed annually, leaving the 10 strongest stems, about 1.5 m high. After the final harvest, all the shoots of the second year must be removed.


Diseases and pests
Like any berry bushes and fruit crops, raspberries are attacked by pests and fungal diseases.
Diseases and pests:
- anthracnose;
- brown and white spotting;
- powdery mildew;
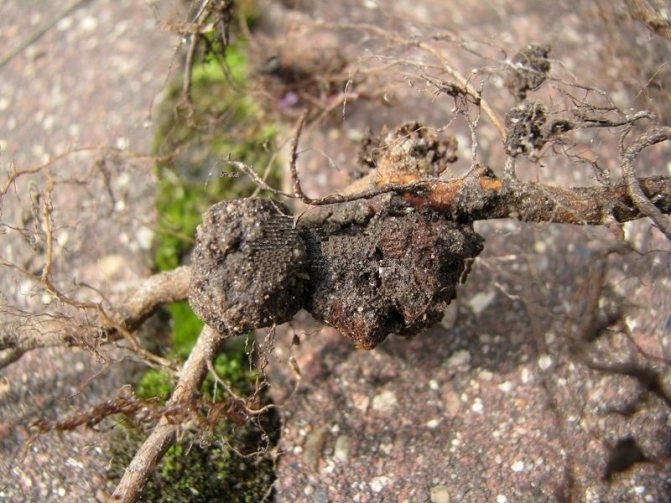
- root cancer;
- mosaic;
- raspberry beetle;
- spider mite;
- shoot aphid;
- stem gall midge.


Annual spring treatment with nitrophene solution will help protect the bush from anthracnose or spotting. It is impossible to cure cancer and mosaic, so diseased plants are dug up and burned.
Digging and loosening of the soil, mulching and weeding can be used as a prevention of pest attacks. If this could not be avoided, then insecticide treatment will help, but after the end of fruiting. Tall, overgrown plants require a tie to the trellis, which will increase yields and reduce the risk of developing fungal diseases.
Planting raspberries in open ground
Possible spring planting in late March - early April for the Moscow region. It is carried out as early as possible, before the start of sap flow.
Advice
The best time to plant a raspberry tree in central Russia is autumn (late September - mid-October). Raspberries planted during this period will have time to take root by frost, which will help it to winter well in the future.
If it was possible to acquire the desired raspberry seedlings only in late autumn, they are buried in a temporary trench, and transplanted to a permanent place in early spring.


Planting raspberry seedlings in spring
Annual, well-ripened shoots are used as planting material. Reproduction is also possible by root layers, which are laid out in parts in trenches or holes.
Ways to book a raspberry tree
There are several ways to book a raspberry tree:
- Belt planting - planting of seedlings is carried out in trenches, observing the distance between the rows of 1.5-2 m, the distance in a row is 30-50 cm.Two-line planting in trenches with a distance between the lines of 30 cm is possible.A wire or twine is pulled along the entire length of the row, to with which future bushes will be tied. This method is considered more successful for planting.
- Shrub - when seedlings are planted in separate holes, 40x50x50 cm in size.


Bush method of growing raspberries
- Stamp - you can read about this method in our other article.
Raspberry planting technology
When planting raspberries, it is worth following some rules so that the seedlings begin to bear fruit as early as possible:
- If fertilizers were not applied during the digging of the site, they are applied directly into the trenches or holes, mixing with the ground in order to exclude direct contact of the roots with them.
- Trenches and holes are poured abundantly before planting with water, at least 2.5 liters in each.
- Before planting, the roots of seedlings are dipped in a clay mash.
- Deepen the seedlings 2-3 cm below the root collar. After complete post-planting shrinkage of the earth, the neck will come out, and the bush will develop normally.
- The planted seedlings are covered with loose soil, which is lightly tamped, after which the seedlings are watered again.
- The planted raspberry tree is mulched with peat or humus. With the arrival of spring, mulch is embedded in the ground.
Gardeners reviews
Ivan: “I have been growing raspberries on the site for a long time, and I specially planted varieties of different ripening periods. It turns out that my raspberries bear fruit all summer, and I collect several crops per season. "
Alina: “I planted bush varieties recently and was very pleased. The culture is unpretentious, requiring little effort. I do 2 dressings: spring and autumn, pruning, watering and shelter for the winter. The harvest is excellent. "
Kira: “Growing raspberries is not difficult at all, but you need to follow simple rules of care. I feed and water the bushes in a timely manner, tie them to tall trellises, and keep the distance between the plants at least 1.5 m. Pruning and the right choice of varieties are important. "
5 / 5 ( 1 vote)
Diseases and pests
| Root cancer Ways to fight:
|
| Rust Way of struggle:
|
| Chlorosis Ways to fight:
|
We carry out a pick
The transplant is practically no different from the initial landing. The disadvantage of raspberries is that they are actively growing. In the spring-summer period, the culture forms a large number of shoots, which are offspring.
I recommend pruning them and replanting the shrub to a new location. The pick is carried out together with an earthen lump. Before replanting raspberries, I also recommend adjusting the stems by a few centimeters.
A pick is best done in the spring. Experienced gardeners do not allow raspberries to creep throughout the garden. Small iron sheets are installed near it.
Useful properties of raspberries. What diseases does raspberry treat?
Raspberries are a tasty, aromatic and healthy berry that can help treat a wide variety of diseases. That is why raspberry bushes can be found in many garden plots today. According to statistics, this berry is considered the third most common in our country, passing ahead only strawberries and currants. The fruits of common raspberries are eaten fresh, fragrant jam, jams and compotes are cooked from them, marmalade and marshmallows are prepared, frozen, dried, used in the production of wine and liqueurs. Raspberry flowers are used in cosmetology for the manufacture of lotions and creams.
The benefits of raspberries are really significant. Raspberries, as they ripen, become the owners of a unique composition. The fruits of this shrub contain a lot of vitamins, acids and useful microelements. For example, any variety of raspberries is endowed with:
- useful sugars (glucose, sucrose and fructose);
- malic, citric and salicylic acids;
- vitamins A, C and B;
- minerals and salts;
- trace elements (iron, zinc, copper, calcium);
- provitamin A.


It is worth noting that there is much more iron and vitamin C in raspberries than in other fruits and berries. That is why it is actively used to treat a large number of diseases. Raspberries are widely used in medicine as a diaphoretic and antipyretic agent for various colds. Raspberry is a unique berry, as it can be safely taken in case of diseases along with medications. In this case, the fruits will only contribute to a speedy recovery, and will also endow the body with vitamins and useful microelements. Such a "tasty" medicine is gladly taken not only by adults, but also by children, who are very well aware of the benefits of raspberries.
Raspberry jam, tea with dried raspberries or fresh berries can speed up the treatment of diseases such as:
- colds, flu;
- gastritis;
- severe cough with angina;
- atherosclerosis;
- scurvy;
- anemia.
How can raspberries be processed?
Raspberry beetle remedies These insects appear en masse during flowering and destroy buds, flowers and leaves; their larvae feed on berries and are capable of destroying a significant part of the crop. Raspberries are treated from the beetle immediately after the snow melts and the shoots are tied up, abundantly sprinkling the bushes and the ground with Nitrafen solution (200 g per 10 liters of water).
Before flowering, they are treated with a mixture of infusions of marigold and wormwood. To prepare the infusion of marigolds, take 200 g of dry crushed raw materials per 10 liters of water and leave for 48 hours.Wormwood infusion is made in the same proportion, but kept for no more than 2 hours. Then both infusions are mixed and filtered. Good results are also shown by two-time treatment of raspberries with biological products Fitoverm and Agravertin. Spraying is carried out in early May - early June.
Remedies for raspberry gall midge
The larvae of this insect are dangerous. They damage young shoots, cause them to die off or freeze in winter, can contribute to the penetration of the fungus, as a result, the next year's harvest is threatened. Signs of damage by gall midge larvae are characteristic and easily distinguishable growths ("galls") on the stems, destruction of shoots.
To combat gall midge, it is necessary to examine the raspberries as carefully as possible after wintering, if growths are found, cut and burn the affected shoots. In early spring, it is recommended to loosen the soil to a depth of 5-10 cm and spray it with Fufanon (15-20 ml per 10 liters of water). At the stage of bud appearance, raspberries are sprayed with Fufanon (10 ml per 10 L of water, consumption - 0.2 L per bush) or Aktellik (15 ml per 10 L, similar consumption).
Stem fly remedies
This is one of the specific raspberry pests that affects this particular crop. Fly larvae gnaw the tops of the shoots, which leads to decay and infection. Prevention consists in spring mulching of the trunks. This makes it difficult for insects to leave their wintering places. In early May, before flowering, you can process raspberries with Aktellik, Fitoverm or Agravertin.
Protecting raspberries from disease
Of the raspberry diseases, anthracnose and gray rot are considered the most dangerous. To prevent anthracnose, you can treat raspberries in early spring with Nitrafen solution (200 g per 10 liters of water). At the beginning of bud break, it is recommended to apply Bordeaux liquid (200 g of copper sulfate and 200 g of lime per 10 liters of water).
Gray rot is a fungal disease that thrives in warm and damp weather. It affects leaves and berries. Prevent the appearance of gray rot by spraying raspberries with Bordeaux liquid: in early spring, use a 3% solution, before flowering - 1%. Spraying Fitosporino also helps, ”which can be carried out at any time if the plants show signs of disease. From folk remedies, dusting of the soil with crushed charcoal or ash is used.
Description
The raspberry bush can grow up to 2 m and has several erect stems with thorny growths. The raspberry root is twisted and twisted, with numerous branches. The leaves are white-bristly below, green above, oblong-ovoid.
Raspberry
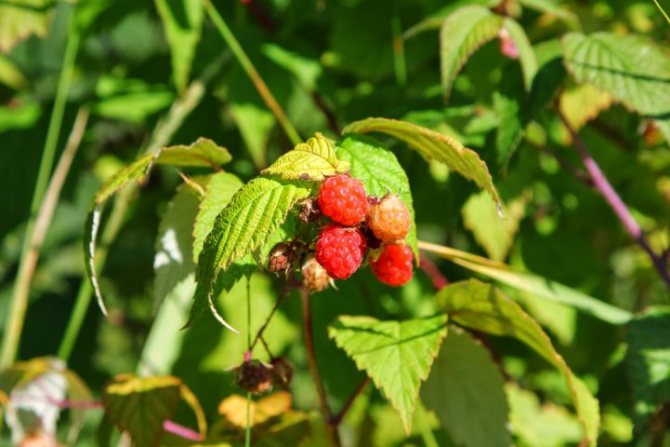
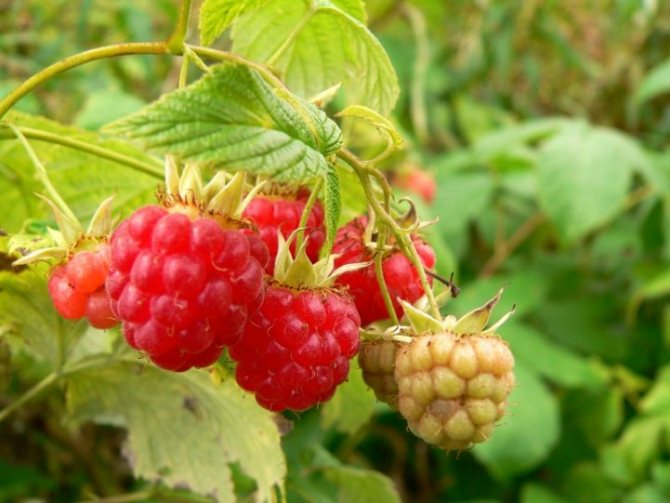
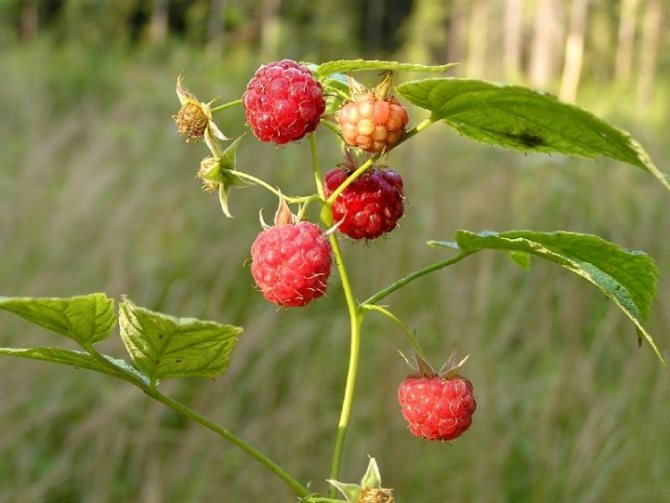
The raspberry fruit is a complex drupe, formed by many accrete fruitlets. The color of the berry ranges from orange, yellow and pink to almost black. Raspberry has a pronounced aroma and contains a whole range of unique nutrients, which made it possible to use it in folk medicine.
The berries are formed on the shoots of raspberries in the second year of life, after which they are removed to make room for young shoots. The exception is remontant raspberry varieties, whose shoots are cut annually. Garden raspberries begin to bear fruit by the end of June, and the fruiting period lasts no more than 2-3 weeks. Repaired varieties of raspberries enter the ripening season later (by the end of July, in August), but this period lasts up to 3 months. And often such raspberries, even under the snow, leave with fruits.


Mid-season varieties
The ripening dates of these varieties are somewhat later, however, their yield is also slightly higher than that of early maturing ones. Actually, mid-season varieties are what is called "raspberries" in the general sense. Speaking of raspberries, in 90% of cases they mean exactly them. There are about a hundred of these varieties in total. Most of them are highly resistant to disease and are relatively easy to care for.
back to menu ↑
See also: Raspberry: a description of the 22 best varieties, characteristics and reviews of gardeners
Tarusa


Tarusa She is a "raspberry tree" - a standard variety of raspberries. A sturdy tree-like shrub reaching 1.8 m in height. During the season, about 6 kg of the crop can be harvested from the bush. The mass of the berries is 5 g. Ripening dates are mid-July. Separately, it should be said that the thorns of the plant are atrophied, thanks to the chash, the collection of berries is greatly simplified.
back to menu ↑
See also: Homemade medlar: how to grow the favorite fruit of the Japanese from a bone on a windowsill (45 Photos & Video) + Reviews
Hussar


Hussar A relatively tall bush (1.5-2 m) with berries weighing 3-4 g. Within two weeks, you can harvest about 4 kg per bush. The color of the berries is intense, bright ruby. The berries are sweet and sour in taste. Without shelter, it tolerates winter to -10 ° С, under foliage and snow it can withstand temperatures up to -30 ° С. The plant tolerates drought well and practically does not need watering.
back to menu ↑
See also: Astilba: 12 groups of varieties, description of the most common, care, reproduction (50 Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Zeus


Zeus The plant is liked by gardeners not only for its high yield, but also for the appearance of the berries. Large berries weighing up to 5 g have an oblong shape and are collected in groups of 12-15 pieces. The productivity of the bush is high - up to 12 kg per bush, but it can be obtained with abundant watering and the presence of additional fertilizing.
back to menu ↑
See also: Barberry: description, types and varieties, planting in open ground, care, features for different climatic conditions including Siberia (65 Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Glen Ample


Glen Ample The variety was developed in England. It is the result of crossing the varieties Meekera and Prosen. Productivity is about 6 kg per bush, red berries have an average size of about 4 g. They have a conical shape and a moderately sweet taste. Ripening occurs at the beginning of July. Increased resistance to disease. Able to tolerate frosts down to -30 ° C without shelter.
back to menu ↑
See also: Gazebos with barbecue and barbecue - (80+ PHOTOS) Drawings of projects that you can implement yourself
For health


For health The growth of this variety can reach up to 2.2 m. On average, about 5 kg of the crop is removed from the bush per season. The size of the berries is about 6 g. The berries are able to maintain their shape during transportation, and are well suited for jam. The plant has a high resistance to fungi and spider mites.
back to menu ↑
See also: Campsis: description, types, planting in the open field, reproduction and care of a beautiful liana (85+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Preparing for winter
With the onset of cold weather, you have to remove the fallen leaves from the garden. Most of the larvae overwinter in the near-trunk zone. Therefore, her dug to a depth of 20 cm... Winter thaws can be dangerous for all shrubs. Soil freezing and thawing cycles push roots to the surface and contribute to root damage.
To eliminate this situation, after the soil is frozen, it is covered with mulch. It will serve as an insulating layer that “smooths out” temperature drops in the soil and maintains a stable temperature level.
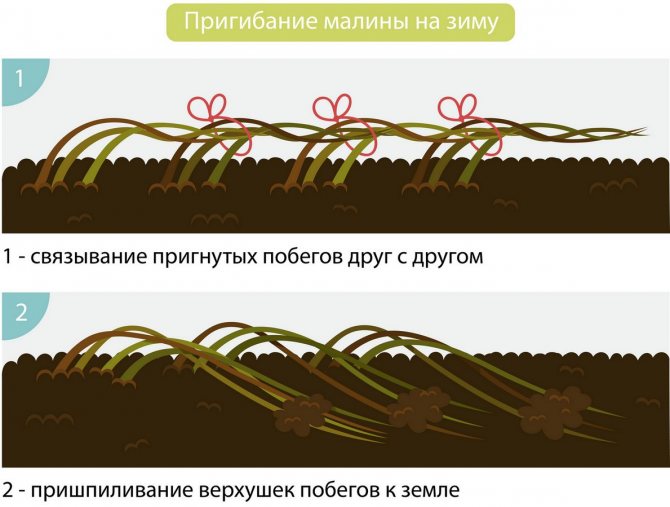

In regions with cold winters, it is recommended to remove the shoots from the trellis. Then they are bent to the ground and covered with a layer of mulch. They successfully overwinter under the snow, and in the spring they will be lifted onto the trellis again.
Growing in a greenhouse all year round
Raspberries are a highly valued crop ideal for year-round cultivation in greenhouses. She is always in demand and loyal to the conditions. Bushes do not require auxiliary lighting and thrive in cool conditions... Greenhouse temperature + 21 ° С is optimal for good development and fruiting of berry bushes. If in doubt, remember that raspberries belong to the same family as roses, and they have long been grown in greenhouses.
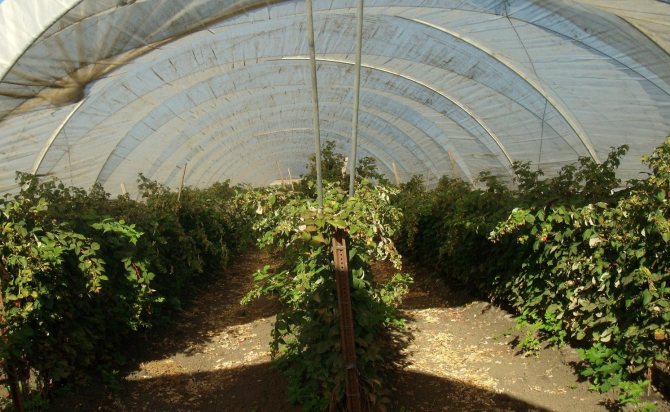


Raspberry seedlings can be purchased at the nursery or grown from their own varieties, if there are any on your site in the open field.Remove weeds from the soil before planting. Plan to plant raspberries in early spring... Place the rows moving from north to south so that they do not obscure each other. If you want to use a trellis, then you need to install it before planting so as not to damage the plants later. In small greenhouses, planting and growing can take place in bulky pots.
Use a drip irrigation system... Inspect the soil weekly to determine moisture and water as needed. After three months, start adding additional fertilizer to the soil.
Find out more about the features of growing raspberries in a greenhouse all year round.
The plant needs full daylight hours. therefore the greenhouse should not be shaded by trees... Raspberries do not need high light levels, but maintenance lighting is needed throughout the winter season. This will enhance growth, flowering and finally yield. Extend winter daylight hours to 16 hours.
Raspberries need 200 hours of winter dormancy to transition to the next vegetative cycle.... At this time, the temperature should not exceed + 4 ° С. Consider this when planning your greenhouse work. Flowering begins about 6 weeks after the bushes wake up and the leaves appear. The fruits will begin to ripen in 10 weeks. Harvesting will take about 8 weeks... At this time, the berries will ripen gradually, they need to be harvested once every few days.


Selection of seedlings
We want to say right away that this is a very responsible event. It is not easy to choose raspberry seedlings from the variety presented, so this issue should be approached very responsibly. It is more expedient to choose small specimens with two or three shoots and well-developed roots.
It is necessary to plant raspberry seedlings very quickly after purchase, after holding them for some time in a root growth stimulator. If the bushes were bought in late autumn, then it is better to postpone the planting of raspberries until spring. For this time, the seedlings are placed in slightly damp sawdust and left in an unheated room. It is important that the temperature in it does not rise above +4 ° C. Otherwise, young bushes may die.


How to prune bushes in spring and autumn?
Pruning can be done twice a year. The first time in the spring, before flowering, and the second in late autumn. This is done according to the following scheme. It is recommended to cut the bushes at a distance of 3 cm from the ground in late autumn... The resulting tops should be burned. This approach eliminates pests that are preparing to winter on the branches, and will give an impetus for the rapid development of young shoots in the spring.
In the fall, you can cut remontant raspberries as usual varieties, when only the tops of the bushes are removed. This will allow you to get young shoots and two-year-old shoots for the next season, which will stretch the ripening of the fruits.
Spring pruning consists of removing dry parts of the bushes that have not survived the winters.at. This sanitary pruning is done before the first healthy kidney. It is easiest to carry out it in April, when the plant begins to actively resume its vital activity. Then you can immediately see which kidneys are healthy and which ones have dried up. Sanitary pruning at this time does not take much time, but you need not delay with the beginning, because if you start work when the first leaves appear, you can damage them.


Autumn raspberry pruning
Planting density is controlled in spring... It is necessary to remove excess shoots in such a way that 1 sq. m there were 10-15 of them left. If this is not done, then the plants will compete with each other, and their fruits will become smaller and less sweet. If in the fall all the bushes were cut to the root, then in the spring there will only be a little thinning of the young shoots if there are too many of them.
Further care
After analyzing how raspberries reproduce, it remains to take care of the thematic plant. The branchy berry itself is unpretentious.


But in a state of neglect, raspberries turn into "wild", and its fruits become smaller. To prevent this, it is necessary:
- In May, until the flowers have blossomed, pickle the bushes with 1% copper oxychloride solution or 3% Bordeaux mixture;
- Prune old and dry branches with trunks throughout the summer;
- Tie up promising bushes as they grow;
- Separate young shoots from the main bush;
- Water the bush as the soil dries up;
- Feed the plant with 5% mullein solution or 1% nitroammophoska solution (matchbox in a bucket of water).


Raspberry care can also include laying straw to contain weeds and moisture within the soil. When decomposed, the corresponding mulch only enriches the soil.


Caring for remontant raspberries
The productivity of this raspberry largely depends on regular watering. It should be watered thoroughly so that the soil is saturated with moisture to the very roots. In the heat, you need to water the bushes more often, and less often in rainy or damp weather. During flowering and berry formation, watering should be intensive again.
The most effective irrigation method is drip. It doses the water supply, moisture rises well to the roots and the earth is more evenly moistened. In addition, water is consumed more economically with such irrigation.
Harvesting cuttings
Cuttings for reproduction of remontant raspberries are harvested in the spring. To do this, it is better to take shoots with a low aerial part (5 cm) after the rosette of leaves has fully formed. Larger shoots take root much worse, because their growth has already begun.
Cut carefully and remove the cutting along with the clod of earth. Sprinkle the cut with charcoal. You cannot put cuttings in water or rinse them. Loosen well, slightly moisten and fertilize the soil. After 3 weeks, the cuttings will begin to take root.
Raspberry Care - Fertilizer
So, raspberries have appeared in your garden. Caring for her should be regular throughout the year. This plant needs soil fertilization. Every year in the fall or spring, 20 grams of potassium sulfate, 5 kilograms of humus and 25 grams of superphosphate should be added to the soil. This is the norm for one square meter. If you notice that your raspberries are growing too slowly, plant maintenance can be supplemented with bird droppings or manure in early summer. Repaired raspberries require a twofold increase in all these norms for active fruiting.


Formation of bushes
Tall varieties must be pruned, leaving branches 1.8 to 2 meters high. Low-growing bushes should be cut at the level of 1.5-1.8 meters.
Collecting method of formation
It provides for the preservation of bush cultivation with the removal of shoots that have grown between the bushes. Shoots are removed when they grow up to 10 cm. Those shoots that remain are tied to a stake at 55 and 170 cm.The upper part is either cut off, leaving a bush 2 meters high, or bent into an arc and tied to a stake at a height of 170 cm.


Narrow band formation method
The bush is divided into two parts. Stakes are driven in from the right and left sides at a distance of 25 cm from the bush. The divided bush is tied up, taking one side to the right, the other to the left. In this case, the height of tying does not change. Shoots grow in the center of the bush. Side shoots must be cut out.
Arched-stake method
The stakes are located in the center of the bushes. The stems, divided into two sides, are tied up as follows: in the second bush, the left stems are taken, bend over and tied to the stake of the first bush. The right stems should be tilted and tied to the stake of the third bush along with the left shoots of the fourth. And so on until the end of the row. With this method of tying, the lateral shoots should be removed, and a new bush should be formed from the shoots growing in the center.
How to grow raspberries
If forest raspberries can grow even on unfavorable soils, then cultivated varieties of raspberries need care and proper planting. When choosing a place for a plant, give preference to an open sunny area, or plant it in light partial shade. The soil must be enriched with humus and have good air and moisture permeability. It is advisable to plant in the middle of autumn, deepening raspberry seedlings 4-5 cm strictly vertically. For the correct development of the bushes and an excellent harvest, common raspberries are fed with minerals, and the aisles are mulched with organic fertilizer. Before wintering, two-year-old bushes are removed at the root, freeing the site from them.


Debunking the main myth
Now about the main thing - when it is necessary to cut out the fruiting shoot.
It makes no sense to “feed” this branch to get the harvest. The most logical conclusion is that immediately after fruiting, the shoot is removed “at the root”.
What does it give
- The root system only feeds young shoots that will bear fruit next year.
- The old branch is infected with all possible viruses and larvae, which over the summer have settled in the cracks in the bark.
- Young shoots are well lit by sunlight and gain strength much faster.
Looking for more reasons for summer pruning?
Harvesting and storage
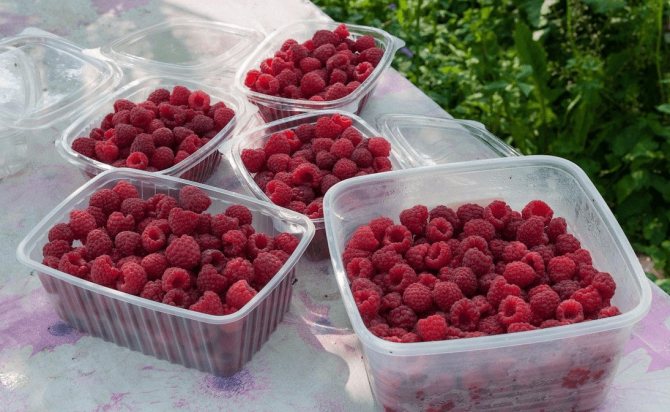
Harvesting begins in June for early varieties, July for medium varieties, and late July or early August for late varieties. Collection time is about 3 weeks. Pick berries every other day. It is preferable to do this in the early morning, as they will last longer when chilled.
Raspberries are very fragile, therefore collection is carried out in plastic containers with a volume of 200-400 g in order to keep the shape of the berries and not crush those that will be below. Store them in a cool place until processed or consumed.


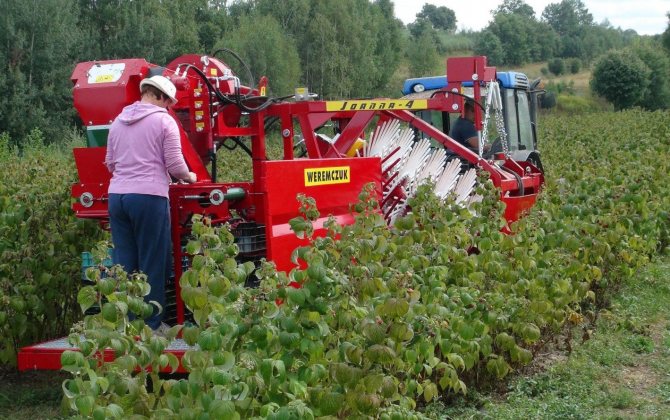
On an industrial scale, mechanized means of collecting berries are used. Such a collection is planned at night so that the fruits are as chilled as possible. When planning the mechanization of processes, do not forget that you will need to immediately plant plants with a row spacingdesigned for the passage of the harvester. Also keep in mind that not all varieties are suitable for mechanized harvesting, but only with lateral fruiting.


You cannot store berries for a long time. Their shelf life in the refrigerator does not exceed 1 week. You can eat them fresh, freeze them, or process them into jams or juices for winter consumption.
Growing raspberries can be beneficial both outdoors and indoors. Purchase varieties that are resistant to diseases, observe the basic agrotechnical requirements, and then the yield will be high and stable.






















