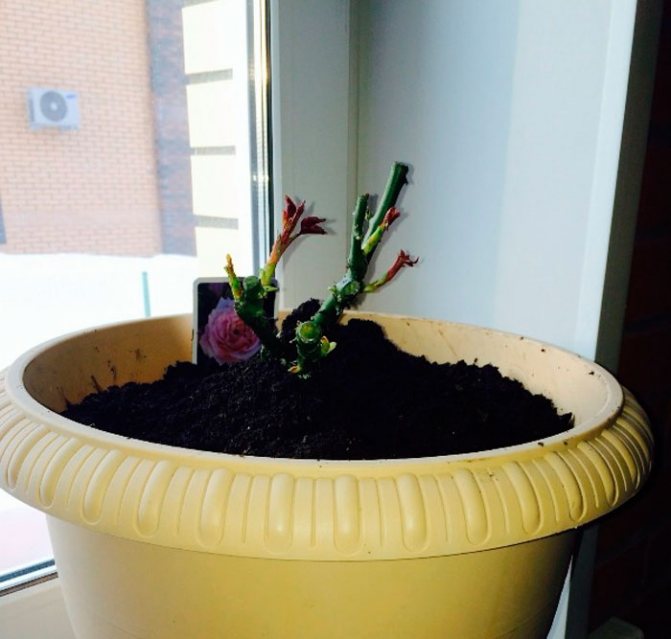
Rose is undoubtedly one of the most popular ornamental flowering plants that almost any grower would like to grow at home. Today there are a huge number of different varieties, each of which is charming in its own way. Each type of rose has its own characteristic features. Many growers from buying a rose seedling are stopped by its rather high cost, as well as uncertainty about the quality of the planting material. However, there is still a way out of such a difficult situation. At home, it is quite possible to grow a rose from a cuttings taken from a garden plant in the fall. But in order for the rose to take root, as well as to grow and develop normally, you should know several important nuances.
What varieties of roses can be cuttings
Most of the existing varieties are suitable for such propagation. Some of the features that can influence the choice are listed below:
- Groundcover, climbing, polyanthus and miniature varieties ideal for cuttings, the survival rate of seedlings in the open field is high.
- Hybrid varieties belonging to a group called Floribundatake root in half of the cases.
- Large-flowered varieties of climbing varieties, as well as hybrid tea and park roses are virtually unsuitable for grafting., since seedlings are poorly rooted and have an underdeveloped root system, which in most cases leads to their death.
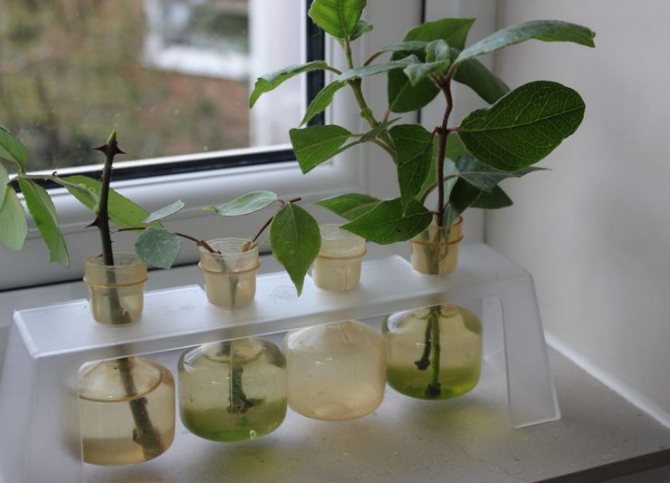
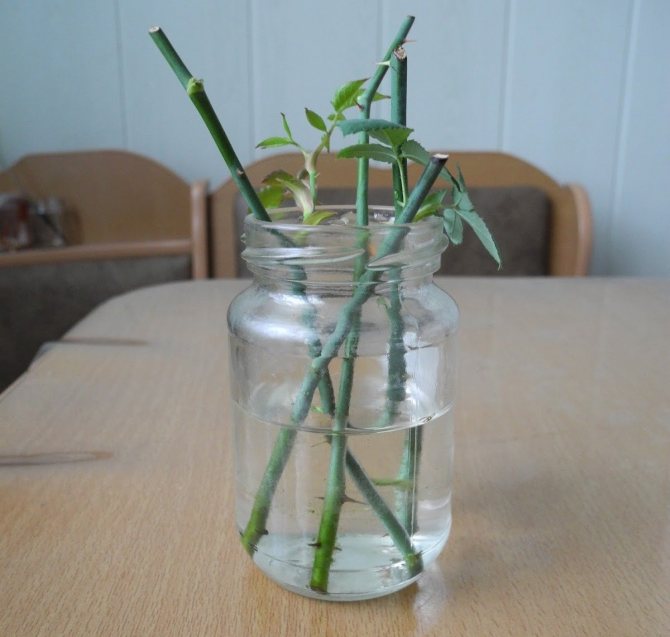
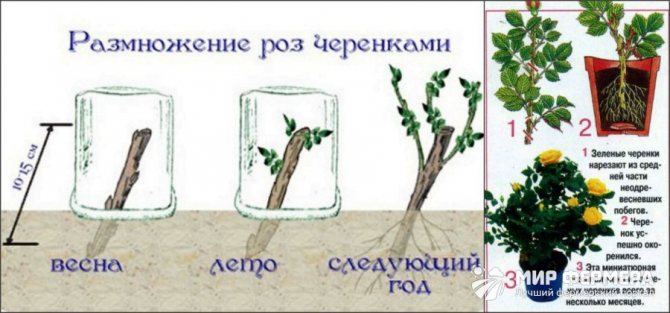
Rooting in water

This method is most suitable for the propagation of miniature and dwarf varieties of roses. One-year-old shoots are selected that have either faded or are just preparing for this.
How to propagate a homemade rose at home? Water rooting is more productive in the presence of long daylight hours - this is summer or spring. Cut the cuttings, process as described above, place in water. To prevent the liquid from blooming (which adversely affects the plant), take an opaque container. It can be a dark glass flask, a mug, a plastic glass.
Do not put the stalk in the freshly collected tap water, it needs to be kept for a day. The liquid should be at room temperature. Further, the water will evaporate day after day, and this must be taken into account. Add settled water steadily, but never change it.
Cutting roses in autumn: methods and benefits
There are various techniques for such propagation of rose bushes: the most popular of them are discussed below with all the characteristic features and advantages:
- Planting cuttings before winter. The main advantage of this method is that the seedlings do not have time to significantly develop their root shoots, so by the spring they will remain in a good and completely ready state for vegetation. At the same time, you do not need to store the planting material at home, following the conditions of its maintenance. To implement this technique, it is necessary to plant in open ground at the end of autumn, but it is imperative to organize a dry shelter, otherwise the seedling will die from a strong decrease in temperature.
- The Trannois method has the advantage of providing the stem with as much starch as possible even before it becomes a cutting. Such measures make it possible to obtain a fairly strong planting material with increased viability. It is necessary to prepare roses for reproduction in this way from the summer, choosing the most healthy and suitable shoots. In the fall, when they are finally ripe, cuttings are cut, which are immediately planted in open ground at an angle of 45 °, and on top are covered with caps made of plastic water containers with a cut off neck and a tapering part. It is necessary to regularly water the seedlings and loosen the soil in the immediate vicinity of the planting site so that the root system does not experience oxygen starvation.
- Burrito's way is to repeat the following sequence of actions: cutting of planting material; processing of the lower part of the cuttings with root or any other stimulants of root growth; wrapping with well-dampened newspaper or soft paper; keeping for several weeks in a dark place while observing the temperature regime within + 15-18 ° C. The technique is not practiced very often, since it does not have visible advantages over the other methods given. In most cases, only half of the cuttings survive.
- Reproduction in a bag, which is filled with a suitable soil, previously sterilized and moistened with a solution of ordinary water and aloe juice. Cuttings are placed in the bag, after which it must be inflated, securely tied and suspended near the window opening. Thanks to the created conditions, a special microclimate with a high level of humidity is formed inside, which leads to stimulation of the growth of root shoots. Among the main advantages of this technique are the possibility of its implementation at home and the simplicity of the technology.
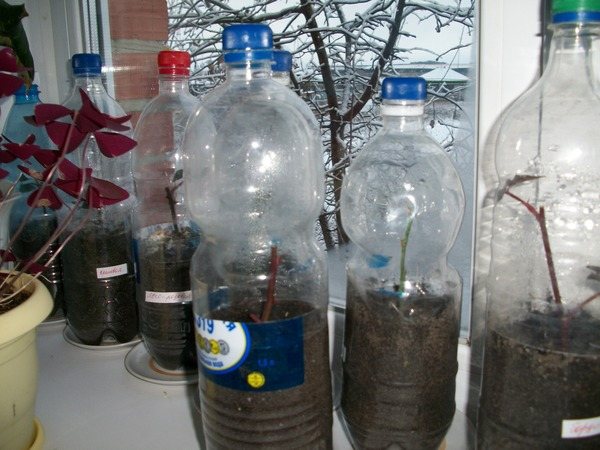


How to propagate roses correctly and what you need to know for this
The period from June 15 to the end of July is the best to carry out propagation of roses by cuttings at home in open ground beds. You can do this in spring, autumn and winter, but this requires either greenhouses specially prepared for rooting plant shoots, or a place well-lit by the sun on the windowsill and planting pots.


Queen of the garden
Autumn cuttings take place after pruning and preparing rose bushes for hibernation. By this time, plants accumulate many nutrients in their tissues, contributing to the rapid growth of callus (tissue that protects plant wounds) and the formation of roots.
Varieties of ground cover, climbing and polyanthus roses reproduce well and take root. It is very difficult to achieve rooting of remontant and park varieties. Tea and hybrid tea varieties, although with difficulty, still lend themselves to propagation by cuttings.
Note! The branches of a bouquet of imported roses do not need to be propagated. In order to preserve their presentation for a long time, they are treated with chemical reagents that prevent root formation.
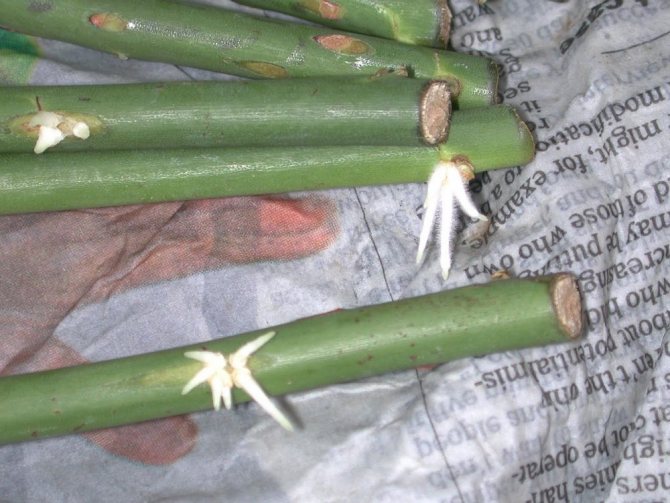
The suitability of the branches of the rose for rooting is determined by the condition of the thorns: on suitable shoots, the thorn is easily separated from the peel. The juicy greenish color of the bark of an incompletely stiff shoot is also an indicator that it contains a lot of plastic substances and can be rooted.
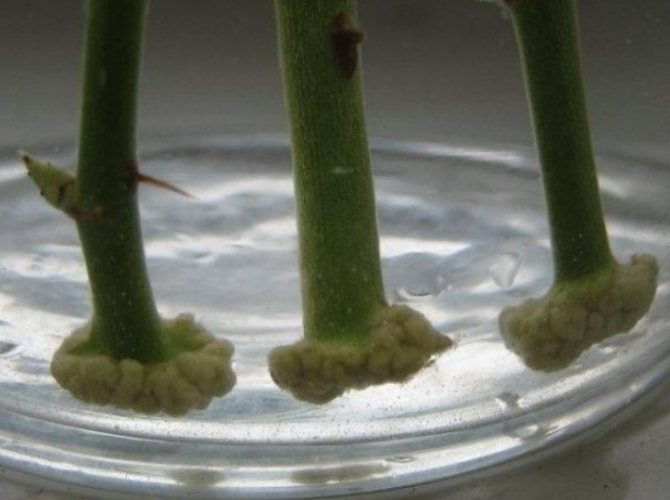


Callus
Cutting containers and substrate selection
Cuttings of roses require narrow and deep containers for planting, this is due to the peculiarities of their root system: the shoots grow quite long and at the same time rarely go in breadth.
For this reason, the best choice is plastic water bottles, which are prepared as follows:
- The neck is cut off and the entire upper tapering part.
- Several small holes are made in the bottom surface, which are necessary for air exchange, natural ventilation, enrichment of roots with oxygen and timely elimination of excess moisture.
Soil is poured into the prepared container to a mark of 2-3 cm from the upper edge, this is necessary for the convenience of watering: water will not pour out.
As a soil for young seedlings, you can use:
- River sand and peat masses, which are mixed with each other in equal proportions. The sand must first be calcined in the oven, since heat treatment allows you to get rid of viruses and microorganisms that like to settle in it and can pose a serious threat to grown roses. It is better to start the process of preparing such a substrate in advance, since after such a treatment, it is recommended to let the sand settle for a month.
- River sand and turf are also mixed in equal proportions. Then a small amount of leafy soil is added, the volume of which is several times less. The sand must undergo preliminary heat treatment and settling, when and in the previous version.
- Any substrate, regardless of the variety chosen, is recommended to be processed a weak solution of potassium permanganate to carry out high-quality disinfection.
After planting in the fall, only one top dressing is carried out, all the components that must enter the mixture, as well as their volume, are given below:
- Humus of vegetable origin, about 8 kg.
- Ground wood ash, no more than 200 gr.
- Salts of chloride or sulfate varieties of potassium, about 30 gr.
- Superphosphate, the volume is fixed and must be strictly 20 grams.
Mr. Summer resident advises: how to keep cuttings of roses in winter before spring planting in the basement, in the garden
You can save cuttings without planting in the ground. If there is a basement or cellar, in which a constant temperature of + 2 ... + 3 ° C is maintained in winter and humidity is no more than 70%, then the prepared shoots will perfectly overwinter there until spring. They are wrapped from below with 3-4 layers of burlap or other natural fabric, moistened with water and wrapped in cellophane. Once a week, the condition of the burlap is checked, and when it dries, it is sprayed. As soon as the warm days come, the material is unwound and checked to see if the plant has sprouted. With proper care, this will definitely happen. In this case, the shanks are planted at the summer cottage using conventional technology.
Experienced gardeners know how to protect young roses without a cellar, and without greenhouse conditions, right in the garden.
To do this, they choose a place on a hill so that it will not be flooded in the spring. Dig a trench up to 30 cm deep. Its length depends on how many shanks there are, the distance between them inside the trench should be at least 8 cm, and the width is 5-10 cm longer than the length of the seedlings. That is, if there are 10 cuttings of 25 cm each, then the length will be 80 cm, and the width will be 35 cm.
Planting cuttings in open ground
One of the important conditions for the living of seedlings is compliance with the technology of their planting. This process is detailed below:
- Initially, a hole is dug for planting, the indicators of its depth and width are determined individually and depend on the size of the grown roots. When planting, it is recommended to maintain a distance of at least 50 cm between seedlings.
- The surface of the bottom of the pit should be well loosened, for this it is best to use a garden pitchfork.
- When planting in infertile soil, you will need to fill compost into the pit, and sprinkle it on top with ordinary garden soil to avoid direct contact with the roots.
- Unlike spring planting, significant shoot shortening is not required in autumn., it is enough just to cut off the tips of the processes.
- The handle is placed in the center of the pit, the root processes need to be spread with your hands so that they are in a natural position.
- The pit is covered with earth until the root collar of the plant is buried by about 5 cm, and for staff varieties by 10 cm.
- Planting location of the cuttings must be properly moisturized.
- The soil is compacted and compacted, it is best to do it with your hands so as not to cause accidental damage.
- The place directly next to the seedling must be additionally spud with loosened earth, and a small roller must be erected, its height should be about 15 cm. It is required to retain moisture, but with the beginning of the active growth of the rose, it can be eliminated as unnecessary.
- Soil mulching with vegetable humus or cut grass is the last mandatory measure when planting in the fall.
- From above, the cutting is covered with a plastic container with holes made. If rather cold winters are expected, then for this period such a cap can be sprinkled with soil or covered with a special layer of insulating materials.
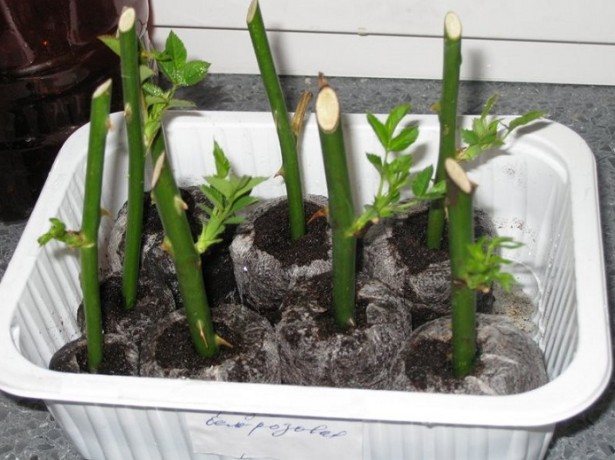


Problems and ways to solve them


When cutting a rose in autumn, flower growers have the following difficulties:
- Irregular watering... Rose prefers systematic watering throughout the growing season. The maximum amount of moisture is needed during the period of intensive growth and budding.
- Thickening of plantings... Because of this, the plants do not receive the proper amount of air, as a result of which they are affected by pests and diseases.
- Lack of lighting... Often, flower growers install a container with cuttings in a corner of the room where there is not enough light for the plant. Because of this, it may not give roots or bloom.
Cutting of a home rose is most often carried out in the fall. At this time, the cuttings root better and adapt to winter. If all the activities were carried out correctly, then in spring the rose will bloom and delight with its magical aroma.
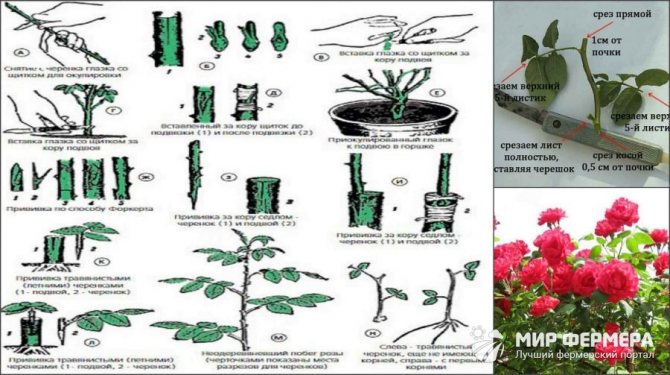
Requirements for cuttings
Not every planting material is suitable for the propagation of roses, so the cuttings must first be evaluated according to a number of criteria so that they meet the following requirements:
- The bush from which the cuttings are cut must be completely healthy, strong and free of traces of parasite activity.
- The length of the cuttings should be at least 10-15 cm, however, it is also not recommended to exceed this figure.
- The bottom cut should be under the kidney, and the upper one at a distance of at least 0.5 cm above it.
- Lower leaves, if present, should be completely removed, and the upper ones should be shortened by at least half.
- Planting material should not be taken from thick enough shoots or shoots are green.


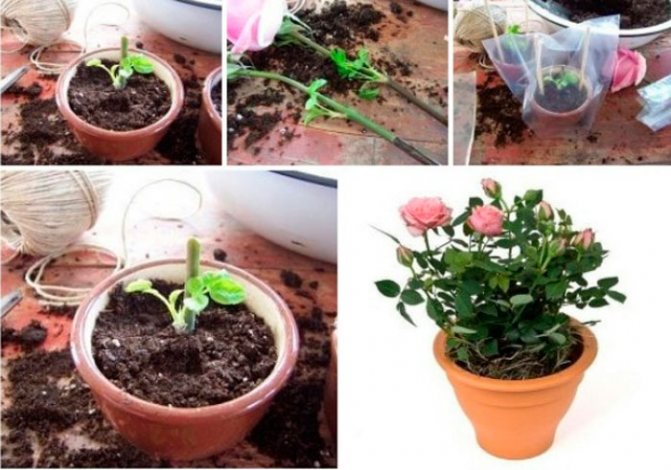
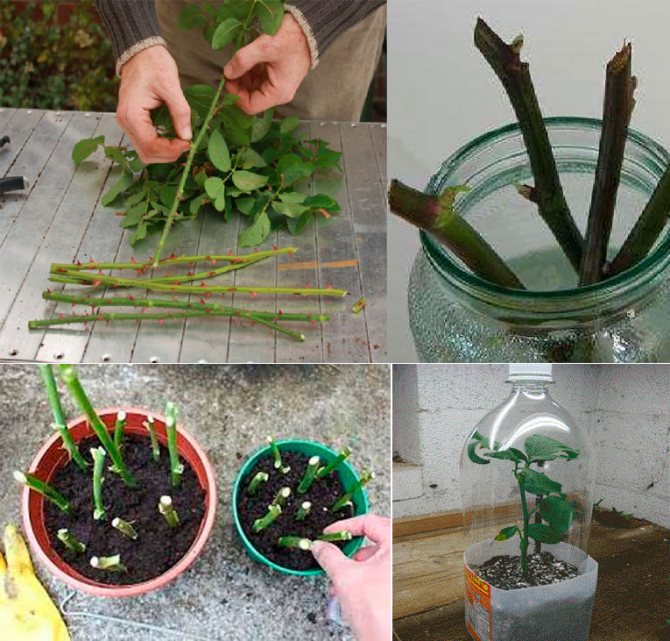
Propagation of roses by cuttings


Let's start with the most common way of propagating roses, namely cuttings. For propagation of roses by cuttings from a bouquet, cut off shoots of roses are often used. This is the easiest way of vegetative propagation, as a result of which self-rooted plants are obtained.
But not for all species this breeding method can be used, it depends on the characteristics of the variety.
Propagation by cuttings is best suited for polyanthus, miniature, hybrid tea, tea, English, ground cover and climbing roses, scrubs, floribunda, patios, which come from warm, humid areas that have a high transpiration (evaporation) function and loose mechanical tissue saturated with water ...
Root cuttings from a bouquet it can be outdoors, in boxes, on racks or in greenhouses, it all depends on the planting season.
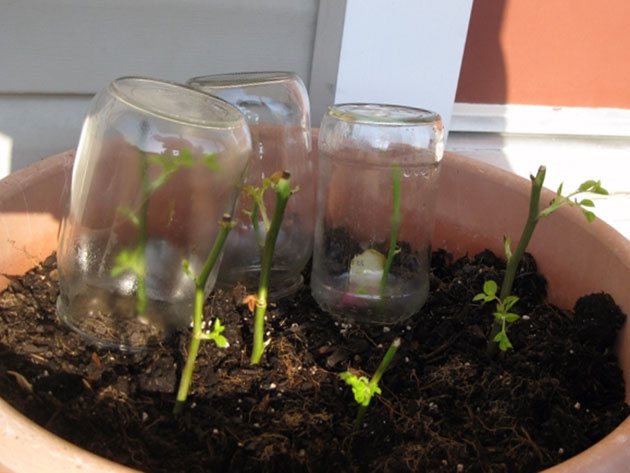
Of course, some growers root cuttings under glass in greenhouses, hotbeds. For beginners, it is enough to use cuttings planted in a pot, a box on the windowsill or in the ground, covered with a jar or film.
Recently, however, glass coverings in greenhouses and greenhouses are replacing synthetic light-transmitting films. It is both cheaper and gives better results, so each of us can try it.Of all the synthetic films, polyethylene is used, it is lighter than glass, transmits ultraviolet rays and high humidity is formed under it.
For professional florists, greenhouse designs are greatly simplified when using polyethylene film, it can be a hangar, a frame for which a dart is used. Such structures can be moved from place to place.
Favorable conditions for propagation and rooting of roses by cuttings
The most optimal conditions for reproduction (and better rooting) are air temperature + 22-30 (soil temperature should be several degrees higher). The relative humidity should be 70-90%.
This regime should be maintained for a month until the cuttings take root. Sharp temperature fluctuations should not be allowed, because this will lead to the death of the live bait.
When you are engaged in such propagation of roses as cuttings, in cold weather the air temperature can be created by steam, water electric heating. Sometimes roses are rooted not in the soil of the greenhouse, but in boxes installed in the greenhouse or in the room. If a harsh winter comes, such boxes can be easily transferred to the greenhouse, or to your windowsill. However, in indoor conditions, boxes with cuttings should be installed on a southern, well-lit window, covered with a jar or film. For areas with a warm climate, cuttings of some polyanthus and climbing roses can be rooted in the open field, without heating.
The best period for the propagation of roses by cuttings from a bouquet is the period of the first flowering.
This means that immature, healthy flower stems are selected that have not yet bloomed (thorns break off easily in them), then their base is not completely lignified. Cuttings are harvested from semi-lignified shoots with a bud. Short lateral shoots cut from the "fifth" also root well, then they have a thickening at the base.
Cuttings cut from too green and lignified (faded, with a hard substance) shoots of roses germinate worse or do not give any effect at all, since they are less likely to sprout roots. Remember that healthy rose stems should be selected, otherwise, in addition to poor survival, there is a danger of infection of plant neighbors.


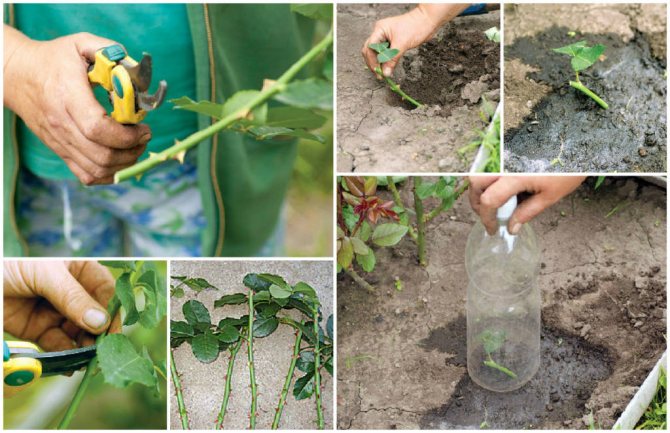
The central semi-lignified part of the shoot is cut into cuttings. For rooting, thin stems are chosen that should have bloomed. The harvested long stems are cut into cuttings - segments with three to four leaves with 3 buds, about 8-10 cm.
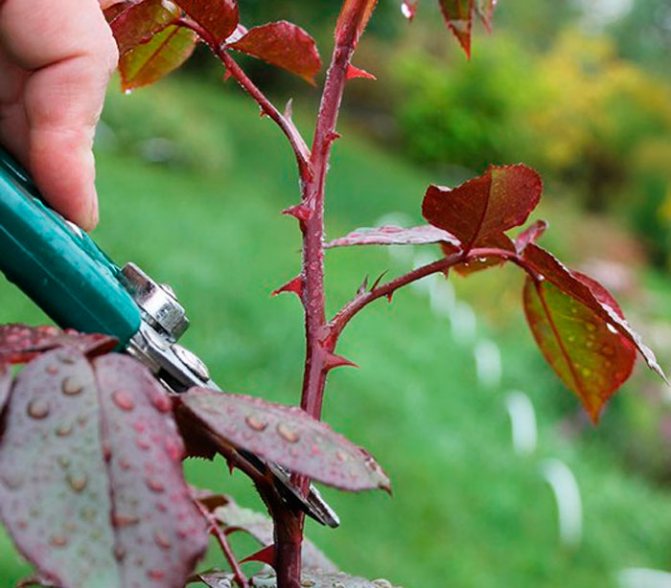
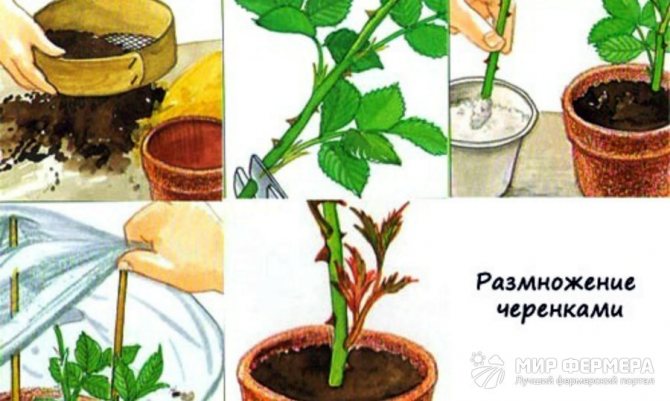
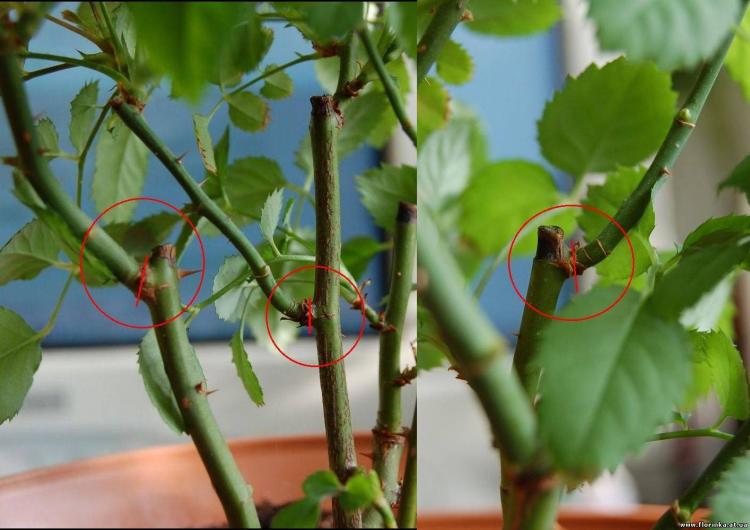
You ask how and where to cut such cuttings? Usually for an inexperienced beginner, this is not an easy task. If you take a stem on a rose bush from above, the first 2-3 leaves after the bud are not floral, but dormant. Therefore, when you start cutting cuttings from them, you will not succeed in anything expedient. It is worth starting the segment after them. It is important to make the cuts at the top and bottom correctly, as you will find out now. The lower cut is made immediately under the kidney at an angle of 45 °, and the other upper cut is made at a distance of 0.5 - 1 cm above the kidney horizontally, but carefully so as not to damage the kidney of the live bait.
Some growers lubricate the upper cut with paraffin wax or garden varnish, however, you can do without this, since the result is the same. The tools (scissors, pruning shears) that you use when pruning must be sterile (washed with alcohol or potassium permanganate).
To reduce evaporation, remove the bottom leaf and part of the top, or cut the leaves in half. From other sources, you may have read that the leaves should be removed, but this should not be done. This conclusion is based on experience. Part of the leaves is left so that nutrients can be more easily supplied to the cuttings. The use of growth substances stimulates rooting and accelerates root formation.
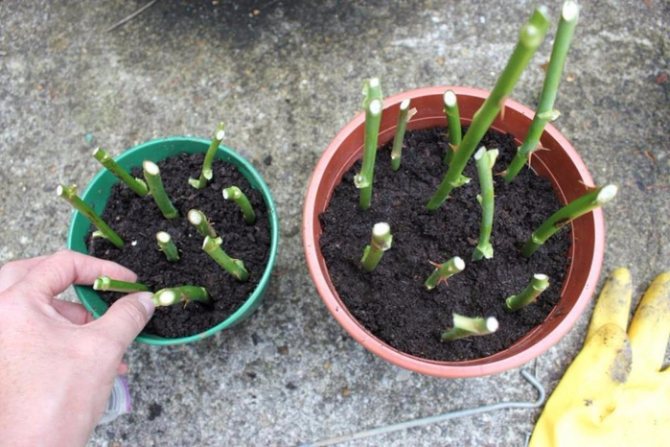


Substrate for rooting cuttings - sand, a mixture of sand with peat, flight, etc. It is poured with a layer of 4-5 cm thick layer of sod-deciduous soil. Before planting, the soil in boxes or greenhouses is watered with a pink solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection. Cuttings prepared for propagation are buried with a lower cut into the substrate, placing them obliquely. The seeding depth of cuttings is 2-3 cm, the distance between cuttings in a row is 4-5 cm, and between rows is 5-6 cm.
Before planting, the tips of the cuttings are immersed for 1-2 days in growth substances (Kornevin, heteroauxin), which stimulate the formation of roots. Rooting stimulants can be purchased at a flower shop. You can root the cuttings in water, and then plant them in the ground. The planting is covered, if you have a couple of seedlings, you can use jars (glass or others, let the light through), and if more, then make a frame, arcs over which a plastic film is spread.
By propagation of roses by cuttings, a self-rooted rose emerges from the bouquet. They are weaker at first than grafted ones, so they need loose (to make the roots easier to break through), permeable, humus-rich soil.
When you have a heavy soil, it is necessary to drain from a gravel layer and sod-deciduous soil, sand with peat (1: 1), otherwise the roots of the roses will begin to rot from stagnant water.
The leaves of the cuttings should always be moist. To do this, in hot weather, they are sprayed several times a day, but not too much, this can lead to decay of the plants.
After 15 - 20 days, callus is formed at the lower ends of the cuttings, and after 35-40 days - roots. After that, the spraying is reduced and the plants are aired more. During propagation by cuttings, as mentioned above, you can use a sealed cover of the plants with plastic wrap or a can. After planting the cuttings, the substrate is watered, and the frames are laid with gauze, and on top of the film, pressing the edges so that moisture remains.


Roses rooted in the greenhouse in March-April are transferred to open ground for growing in May-July. Propagated by cuttings in June, roses develop a strong root system. Such flowers can be left in greenhouses or insulated beds. When you propagate the rose later, it may die because the weak roots easily rot or freeze. In areas with harsh winters, it is better to transplant roses into boxes or pots and bring them to a warm place. When transplanting, you need to remember that young roots break off easily and the plant will die. Therefore, you should not rush with a transplant.
Rose bushes from a bouquet - it is possible
Roses can be propagated not only with the help of planting material taken from cultivated bushes, but also with cuttings obtained from bouquets.
This technique often gives very good results, and the seedlings are distinguished by their vitality, but it is important to consider the following features:
- The bouquet must be fresh: the longer it stays indoors, the less chances that the cuttings will take root and not die.
- It is necessary to choose the flower with the most stiff stem in the bouquet., it can be distinguished by its characteristic darkish, and in ideal situations, brownish, shade.
- Stem thickness should be medium, too thick or thin shoots are unsuitable for reproduction.
- Inflorescences, unblown buds, thorns and leaves must be immediately removed from the stems. All of them will take away from the plant a large amount of strength and nutrients that it will need for subsequent rooting.
- It is possible to achieve the appearance of the first root shoots by any existing means., but it is recommended to place cuttings 20-30 cm long in a container filled with distilled or filtered water.When the first roots appear, it will be possible to transplant into soil or nutrient mixture and wait for the right moment to plant in the garden.


Features of the procedure in the autumn


In autumn, cuttings of roses have the following features:
- shoots taken from a plant will take root better and get sick less often;
- if you root several dozen cuttings, then you can get a mini-rose garden at home without much material costs;
- the plant is preparing for winter dormancy and maximum accumulation of nutrients;
- when pruning in the fall and preparing ornamental crops for wintering, there is an opportunity to choose the most suitable and high-quality planting material.
Major mistakes
- The use of imported bouquets or other sources grown in other countries for the extraction of planting material. Usually they are processed with various preservatives and chemical preparations, allowing to extend their life and safety during transportation, but this negatively affects the possibility of reproduction. In addition, imported plants are not adapted to Russian climatic conditions and take root in them worse, therefore it is recommended to use only domestic roses for such purposes.
- Landing in open ground perpendicular to the ground surface. This is one of the most common mistakes, as maintaining a 45 ° angle between the seedling and the soil is imperative.
- Using too thick cuttings as planting material. Many novice growers mistakenly believe that only thin shoots do not take root well, but in fact, thick cuttings are also known for their poor survival. The optimal indicator is usually equal to the thickness of a regular pencil.
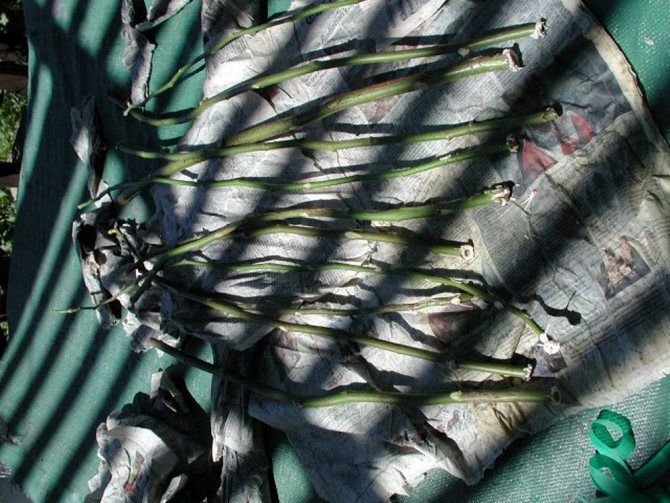
How to keep cuttings until spring
Having cut the cuttings in early November, it is not necessary to immediately root them in the standard way. They can safely wait for a more favorable time, having overwintered in your barn or on the balcony. To do this, they only need to be dug into sand or other substrate.


For residents of apartments, the most successful option would be the following: on the bottom of the prepared plastic bucket, you need to pour a six-meter layer of expanded clay (pours out to the bottom), and then add to it the main layer of soil mixed with perlite and vermiculite. Alternatively, you can mix the soil with sand or purchase a special "rose" substrate.
Perlite is able to hold a liquid, the volume of which is five times its own weight, which means that only 20% of the substance is enough for you. Having made small depressions in the prepared substrate, place bundles with cuttings in them with the lower side and lightly sprinkle. The top can be sealed with warm paraffin, but this is not necessary.
Another good option that will not take a lot of energy from you to prepare is use for storing refrigerator cuttings. In this case, the harvested planting material is placed in a leaky bag and sent to storage in the refrigerator door. They need to be removed and sprayed from the spray bottle about once a week. You can store rose cut pieces in this way for about three months at a temperature of no more than + 1 ... + 3 ° C.
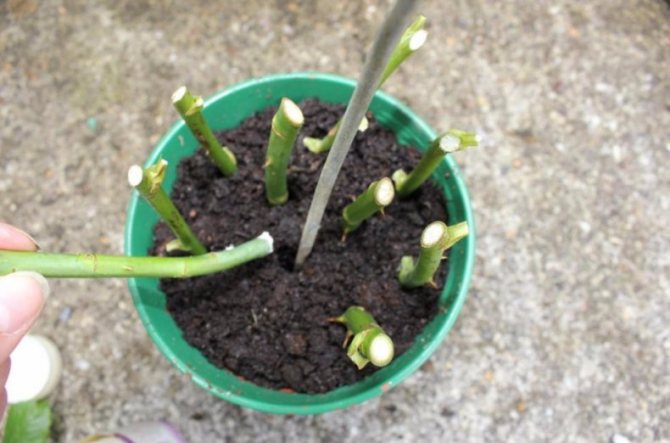


Alternatively, you can
put all the cuttings in a cardboard box and just sprinkle it with peat, then choose the darkest corner at the summer cottage (in such a place the snow will lie the longest, without forming puddles) and place the box there, covering it with snow on top.
As a result, you will get a small snowdrift, and so that it does not melt quickly, you can cover it with pine or spruce branches. Seal the bag again (you can use clothespins), waiting until the liquid has completely evaporated.
Gardening Tips
- It is recommended to plant cuttings immediately in their permanent place., since a transplant for the next year may delay the flowering period, because the seedling will again have to go through the process of adaptation to new conditions.
- Cuttings should only be cut with a sharp instrument that does not leave lacerated and soaked wounds with a long regeneration period. All knives used must be clean, for this they are pre-treated and disinfected.
- If you plan to plant the resulting cuttings without long-term storage, it is recommended to leave 2-3 leaves on it, which will facilitate the feeding process.
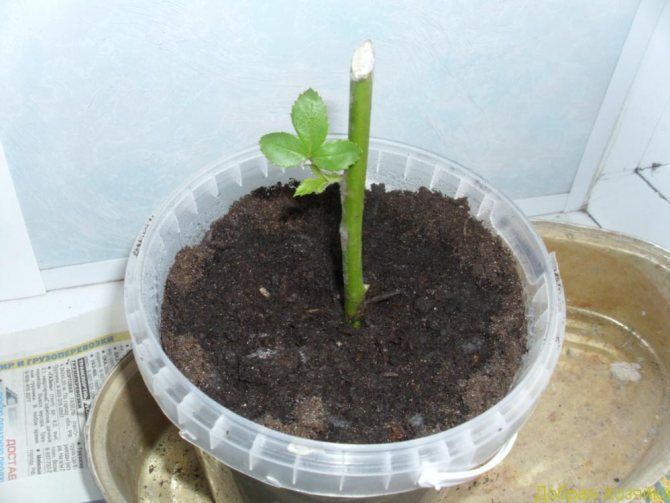
Care after rooting
As soon as a small new leaf appears on the rooted cuttings, it means that the process of root formation has begun. This can happen in 6-8 weeks. After that, it is recommended to gradually ventilate the greenhouse, increasing the ventilation time every day. It is necessary to ensure that the soil is always moist.
In the spring, when new leaves appear on the plant and the earth warms up, the rooted cuttings of roses are planted in the ground in a permanent place. This should be done not earlier than the end of April, preferably in May, when there will be no night frosts. Subsequently, over the course of several years, the roots will have to be insulated for the winter.
Dates of the
It is impossible to indicate specific dates for grafting, since all regions are accompanied by climatic features.
Some growers strongly recommend that the procedure be carried out before mid-October, ensuring that it is completed before the arrival of the first frost.
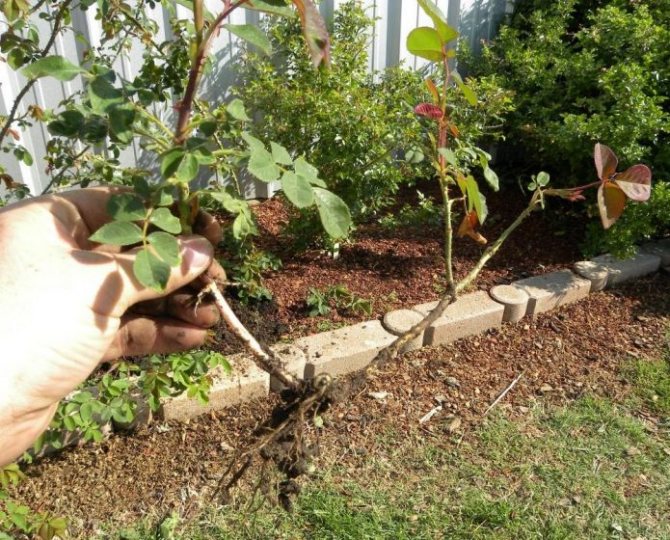


However, other growers recommend, on the contrary, to choose a period when the daytime temperature will be above zero, and the nighttime only slightly drop below zero (it will be about 1-3 degrees of frost).
The only thing in which the opinion of these two groups of gardeners coincides is that the timing of autumn pruning and autumn cuttings should be the same.
Some subtleties
In order for the cultivation of roses from cuttings in the fall to be successful, you need to know and observe some subtleties. This will help speed up their growth in the autumn and winter and avoid the development of diseases. The rules for preparing the material are as follows:


- Shoots for making cuttings are best obtained from a rose flower when pruning old bushes.
- Rose is a plant that does not thrive on all types of soil. Acidic soil and soil with a high clay content are not suitable for it. For planting in pots and open ground, it is necessary to prepare a mixture of humus with turf soil and river sand.
- Before planting, the soil must be disinfected.
- As the top layer dries out, the soil needs to be moistened.
- The film or plastic jar is periodically removed from the cutting to ventilate the plant.
Practical tips for growing
Rose is a rather capricious plant. In order to achieve a positive result with cuttings and increase the survival rate, it is worth listening to a number of tips from experienced florists.
- The best workpiece for breeding will be a stalk with a so-called heel - a piece of wood. These sprouts are not cut, but broken off. On the heels at the site of injury, a protective growth is more actively formed - callus. Growing a rose from such cuttings is better and faster.
- For autumn cultivation, flower growers recommend leaving 2 to 4 leaves on the processes in the upper part. They will become an additional source of power for the branch.
- To increase the safety of branches during wintering, dipping the ends into melted wax and then into cold water for solidification helps.
- In the fall, cuttings are planted with a double margin: with the intention to get 5 adult established plants, 7-10 blanks are rooted.
- When the cuttings are blackened during rooting, the earth is watered with Fitosporin (1 tsp / 1 l of water).
Where to put the rose?


Indoor roses are still finicky! When it's hot, they feel bad, they begin to shed their buds, leaves, grow slowly.The best place to grow this plant is the windowsill on the east or west side. The south window is too hot and will need to be watered and ventilated frequently. The northern one is the thing, but there is little light here, you will have to purchase additional lighting.
The rose feels good at temperatures from +10 to +25. Further, it is too hot, and therefore the plant may start to hurt! The rose tolerates temperature extremes and even small frosts well, so do not worry about the beauty if you forgot to close the window in the winter, leaving the house.
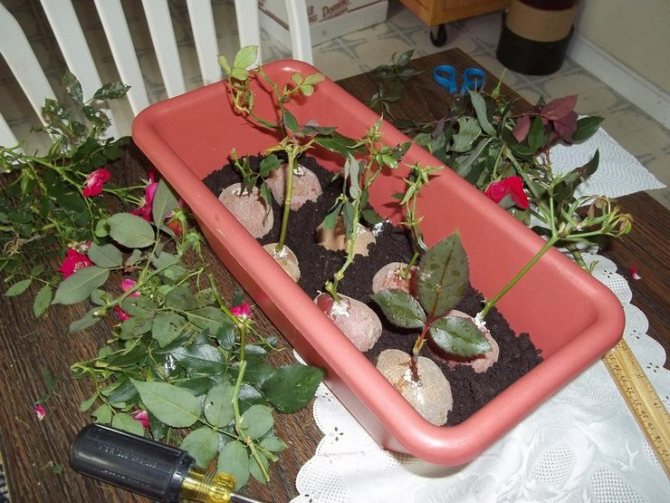
Vegetative propagation in potatoes
This unusual method shows excellent results. In addition, it does not require extra time and special attention. Required:
- Prepare a medium-sized container, some young, beautiful medium-sized potatoes, fertile soil, transparent film or glass jars, and planting material.
- Process the pink twigs in the usual way. After the trimmings are soaked in water with root solution, insert them one at a time into individual potatoes. Clean the eyes of the tubers in advance and pierce the hole.
- Place the potatoes in a container, sprinkle with earth so that the tubers half peep out.
- Pour with settled water (you can add manganese), cover with cellophane or jars.
- In the future, moisturize as it dries. The potato will provide the shoots with nutrients that will aid rooting.
We use bouquet flowers


Looking at a beautiful presented bouquet of roses, I want the flowers to remain the same fresh and bright for a long time. Of course, it will not be possible to prolong the "blooming" of cut roses. But you can try to grow a "new bouquet" of them. To do this, the stems of flowers must be cut into cuttings. They can be rooted at any time of the year in flower pots or other containers.
For these purposes, you can also use cellophane bags, filling them with chopped moss or fibrous peat. Then moisten the filler with a special solution - 1 tsp. aloe juice for 9 tsp water. Inflate the bags slightly, tie them up and hang them from the window frame. In an environment with high humidity, a greenhouse effect will arise, and roots will begin to form in the cuttings.
Qualified florists collect stunning bouquets, the life of which you want to extend, because the roses are so beautiful in them. This is, of course, impossible. But you can grow roses yourself and collect your own bouquet. To do this, you need to cut the cuttings from the shoots. You can plant them at any time of the year in flower pots or other convenient containers, even in a plastic bag.
The container is filled with fibrous peat or crushed moss. Now you need to pour the contents with a special composition, which is prepared in the ratio of 1 teaspoon of aloe juice to 9 teaspoons of water. Inflate the bag a little, tie it tightly and hang it, preferably to the window. This will create a greenhouse effect and the stems will quickly take root.
Pluses of autumn cuttings
To grow new rose bushes from cuttings, it is better to wait until autumn. The optimal time for this procedure is from late October to early November. For regions with a cold climate, preparation for breeding is postponed to September - early October. Cutting has some advantages compared to vaccinations:
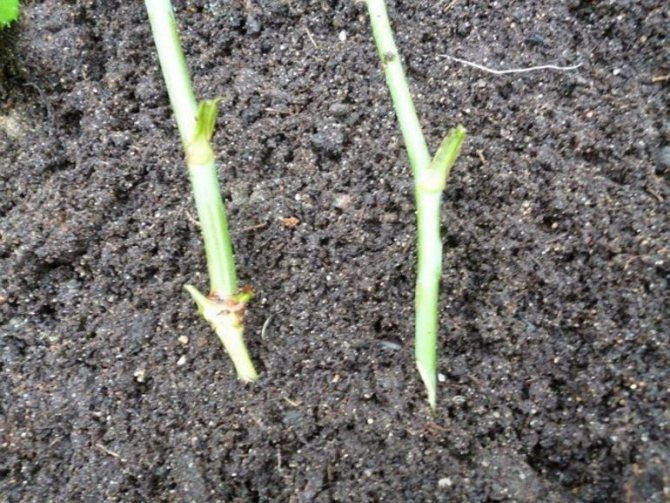


- it is easier to care for such bushes, since they do not form excess root growth;
- rose bushes obtained by cuttings withstand the harsh winter better and can recover from a dormant bud even with significant freezing;
- planting material can be obtained from any rose.
Helpful! Thus, the propagation of roses by cuttings in the fall in the ground allows you to avoid many difficulties when breeding new plants.
Getting started planting blanks
The procedure for preparing cuttings is usually completed by placing them in the ground where they will grow.Thus, the plant will be less stressed, take root and, with the arrival of spring, will actively start growing. Now let's consider the general requirements for this process:
- after cutting the required number of segments, the cut must be treated with Heteroauxin;
- now you need to dig holes, about 30 cm deep, 2/3 of the total volume needs to be filled with grass and compost;
- the cuttings must be placed at an angle of 45ᵒ, only 1/3 of the entire length and up to 2 buds remain above the ground level;
- then you need to spill well with water.
Information! In order for future roses to survive the winter, they must be covered. This can be done using a glass jar or a cut-off plastic bottle. Punch a few holes in the container to allow air to enter, or place it at a certain height above the ground. The plastic shelter should be covered with fallen leaves and non-woven material. Mark the landing site with stakes or in another way you understand. You can wrap it up with straw.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
The division of the bush for propagation of roses is performed with mature bushes, which have formed many shoots. In early spring, they are dug up, shoots, and roots are shortened by 2/3 of the length. For this purpose, a pruner is used, disinfected with cologne or alcohol.
Each part of the bush should have a shoot with two buds and a root. Then they prepare a chatterbox by mixing clay and mullein, where the prepared plants are immersed. Having made deepening in the soil, up to 5 cm, they are planted. After one to two years, a bush with strong shoots is formed from the divided plant.
Alternative way
Some growers prefer other methods to propagate roses by cuttings in the fall. The shoots are placed in boiled cold water, which changes every 2 days. In this state, the cuttings are kept for 15 days. During this time, a whitish ball should form at the tip of the shoot - this is the embryo of the future root. You can transplant the cutting into the ground already at this stage, or you can hold it in water for another week to form full-fledged roots. However, this method of rooting also has some disadvantages - the roots lack oxygen in the water and they can begin to rot.
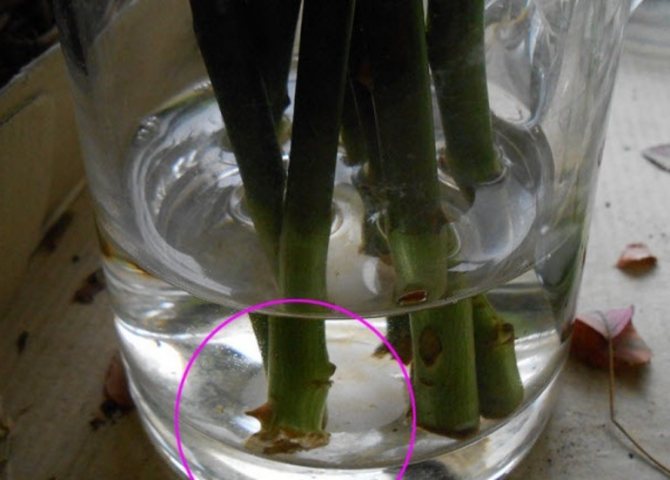


Important!
For the shoot to form healthy, viable roots, it needs a sufficient amount of oxygen. In addition, it is important to maintain an optimal level of air and soil temperature, as well as a sufficient amount of sunlight.
During the first 2 years, it is necessary to remove all formed leaves and buds from a young cutting. If this is not done, the rose bush will spend all its energy on them and will not be able to form a good root system. The resulting seedlings must be regularly watered and ventilated. After the formation of strong roots, you can move the rose to a permanent pot.
Disease and pest control
Roses can suffer from diseases such as:
- Powdery mildew - progresses in the second half of July, quickly spreads to all plants. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of a white coating on the leaves and shoots. If the first symptoms are found, treat with the "Skor" preparation (2 ml / 10 l of water), cutting off the previously affected parts of the plant. For prophylaxis in the spring, treat with a solution of copper sulfate (100 g / 10 l of water).
- Rust - caused by fungal spores. Signs of the disease are the appearance of orange cushion-like seals on the leaves and shoots. Spraying with Hom (40 g / 10 l of water) will help to cope with the disease.


Among the pests for roses are dangerous:
- Aphid - to get rid of the pest will help three times spraying with an interval of 10 days with the drug "Agrovertin" (2 ml / 1 l of water).
- Spider mite - carry out 3 treatments every 7 days with colloidal sulfur (40 g / 10 l of water).
- Leaf roll - a one-time treatment with Iskra (1 tablet / 10 l of water) will help.
- Clicker beetle - you can get rid of the pest by introducing the preparation "Bazudin" (20 g / 1 m²) into the soil.
Important! After pollination, roses form fruits in place of flowers. The wilted bud must be removed from the bush, otherwise the formation of ovaries will jeopardize further flowering this season, since the plant will direct all its forces to planting seeds.
Rules and optimal growing conditions
Roses should be placed in southern, well-lit areas, closed from drafts. Plants thrive better when planted in higher elevations, where the distance to groundwater is more than 1.5 m.


The optimum temperature for the full development of roses in the warm season is + 15 ... + 35 ° С. For the winter, the plants are cut and covered with burlap to ensure the air temperature is within 0 ... + 7 ° С.
During the period of growing the root system by cuttings, the humidity should be maintained within 70-80%. For adult plants, this indicator is insignificant. They develop normally even when the air humidity is in the range of 40-60%.
Brief description of the plant
General characteristics of roses:
- the height of the bush is 25–90 cm, depending on the variety;
- the bush consists of a main shoot, skeletal branches of several orders and bisexual flowers;
- on each shoot, from 5 to 15 leaf plates are formed, predominantly of a dark green color, in some varieties a copper or purple hue may appear;
- the surface of the sheet is matte or glossy;
- all shoots are covered with large or small thorns;
- flowers are formed at the tops of the shoots or over their entire area;
- the color palette of the buds can vary from snow-white to almost black.
Did you know? The smallest rosebuds are produced by a variety called C. Their size does not exceed 1 cm.