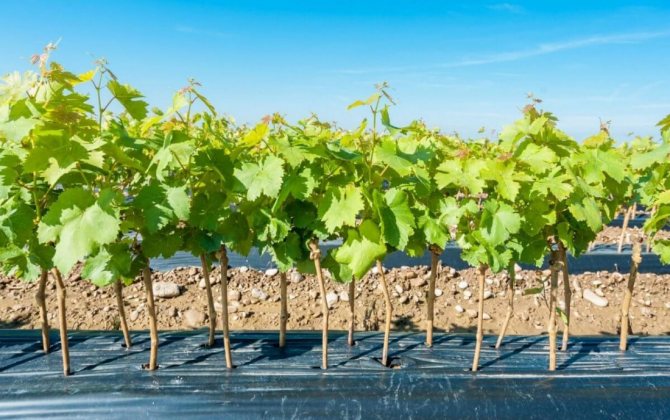
When it comes to which region is best to grow grapes, Crimea or Kuban immediately comes to mind. The latter is the globally recognized granary of Russia, which has all the climatic conditions necessary for the cultivation of not only grapes, but also many fruits and vegetables.
Special attention is paid to the cultivation of sweet berries. Planting grapes in autumn with seedlings in the Kuban gives an excellent result and contributes to the maximum harvest even in those years when the harvest of other crops leaves much to be desired. The question of how to grow this culture in the above-mentioned region will be answered below.

When is it better to plant grapes - in autumn or spring
Planting in spring has one distinct advantage. The root system of the seedling is guaranteed to take root in the ground over the summer, and it will not be damaged by sharp frosts.
At the same time, the autumn planting has many advantages. Namely:
- autumn soil is ideal for rooting a seedling - it is quite moist, it contains many useful substances accumulated over the summer;
- in the fall, it is easier to find high-quality seedlings on the horticultural market - it is during this period that the healthiest, strongest and freshest young plants are sold;
- with a successful planting in the fall, grapes for the next year are immediately taken to actively develop, and adaptation does not take too much time.
Despite the fact that the autumn planting is associated with additional risks and requires a careful approach, it is still worth taking advantage of its benefits.
Care and its features
In order for the grapes to develop well and in the future to please with a rich harvest, one should not only plant it correctly, but also carefully look after this crop. The classic list of such actions includes the following:
- timely watering;
- rationing of bunches and pruning;
- garter and shelter for the winter;
- pest control and disease protection.
Watering should be carried out at least 5 times per season, each plant should receive about 15 liters of liquid. If it rains in the region, the number of irrigations is reduced so that the soil does not crack. Together with watering, fertilizing is immediately carried out with fertilizers by root or non-root methods.
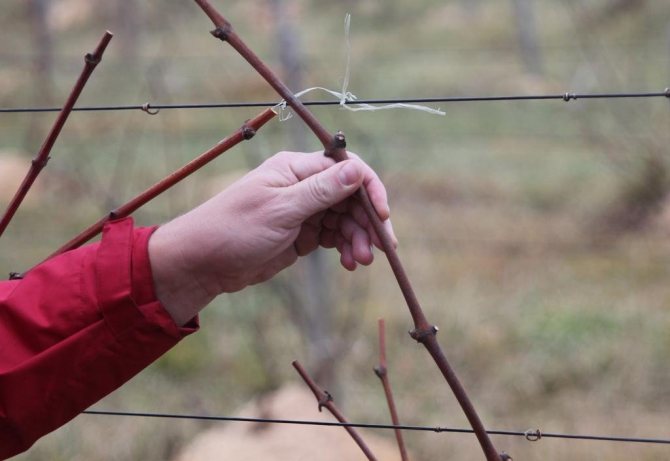
As the vine grows, it is tied to a support. For the first year of life, these can be pegs (for those plants that were planted in spring with seedlings), then a trellis will be required.


For her, grape bushes form or tie them up in the form of a fan. Plucking out extra bunches is carried out both on early frost-resistant varieties and on grapes of medium ripening. Another important stage of care is pruning.
Dates of planting grapes in autumn with seedlings in the middle lane
The timing of planting grapes in the fall is quite late - seedlings are rooted from October to mid-November, until the onset of the first frost. Do not be afraid that the autumn soil will be too cold for the plant. The heat accumulated over the summer remains in the ground for a long time, and in the planting pit the roots of the grapes fall into fairly comfortable conditions. In the middle lane, planting can be carried out at temperatures from + 15 to + 5 degrees, and it is desirable that the same conditions persist for another 2 weeks after rooting of the seedling.
Attention! In the southern regions, planting is carried out even in November - under favorable weather conditions. But the planting of grapes in autumn in Siberia is not carried out in principle - the first autumn frosts here come too early, in September.
Which seedling to pick?
Today, seedlings for planting can be easily purchased. However, among the wide variety of varieties and prices, it can be easy to get confused.
Advice! It is recommended to purchase planting material from trusted suppliers and reliable sources. Otherwise, you run the risk of being deceived.
Before buying seedlings, familiarize yourself with their main types and characteristics. They are classified into substandard, elite, first and second grade.
Elite ones have evenly spaced four roots, 2 mm in diameter and about 15 cm long.At the same time, the minimum height of the mature growth is about 25 cm, and preferably 50-80 cm, and its thickness is 5-8 cm.
Saplings of the first grade are characterized by the presence of a 20-centimeter growth, in which at least two roots have a thickness of about 2 mm. Seedlings of the second grade have three nodes of mature growth and 2 roots.
All the rest are substandard. They are not suitable for planting, but they can be left to ripen and used later.
How to plant grapes in autumn with seedlings
Before starting work, it is best to watch a video of planting grapes in the fall. In addition, you need to carefully study the basic rules for rooting seedlings - and strictly adhere to them during planting.
Selecting and preparing a landing site
Grapes are light-loving and heat-loving plants. Therefore, it must be planted in an area where there will be enough sunlight - best on the south side. It is good if the plant is located next to the wall of a house or garage - then the vine will be protected from strong winds and drafts.
The soil of the grapes loves fertile and loose, but without waterlogging. Black soil, sandy loam and loam are ideal, but it is better not to plant the plant on clay and waterlogged soils. It is also not recommended to plant grapes where groundwater flows too close to the surface - closer than 1.5 m from the roots.
Even with good soil, the area for grapes must be carefully prepared.
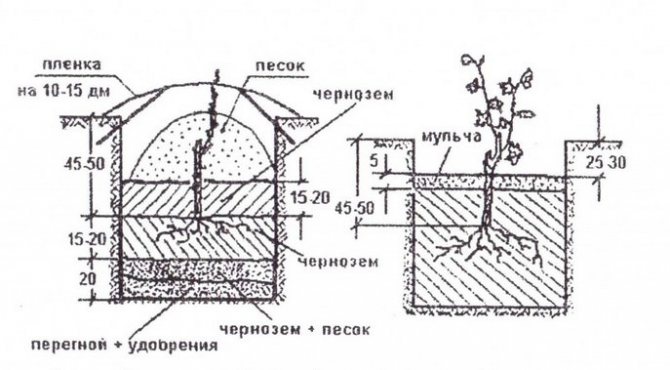
- For a young seedling, a rather voluminous hole is dug - 80 cm in depth and width.
- At its bottom, fertile soil is laid, mixed with fertilizers - 3 buckets of humus and 300 g of nitrogenous, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers.
- About 2 kg of ash are added to the fertilizers, the soil is mixed, and abundantly watered with 2 buckets of water.
- After that, a layer of ordinary soil is poured over the moistened fertilized soil to the level of the seedling planting.


In the soil prepared for planting a grape seedling, it is worth adding sand or expanded clay in the amount of a couple of buckets in advance. This will allow good drainage and air exchange over the root system.
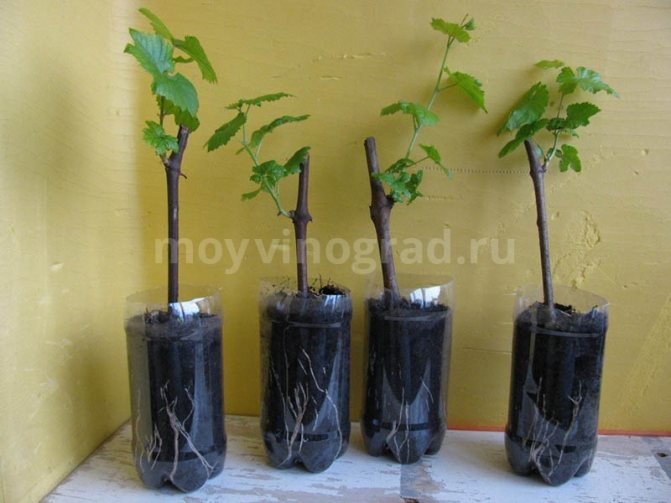
Grape seedling preparation
A quality vine seedling must have:
- well-developed roots in the amount of at least 3 pieces, and it is better if there are 5 or 6 of them;
- green shoots about 20 cm in length, extending from the trunk;
- calcaneal roots - rather long, from 15 cm;
- strong healthy trunk;
- growth buds.
The ideal height for a seedling is considered to be 40 - 55 cm, the thickness should be 8 - 10 mm. For planting in the fall in the ground, annual grape seedlings are well suited.
Prepare the plant as follows:
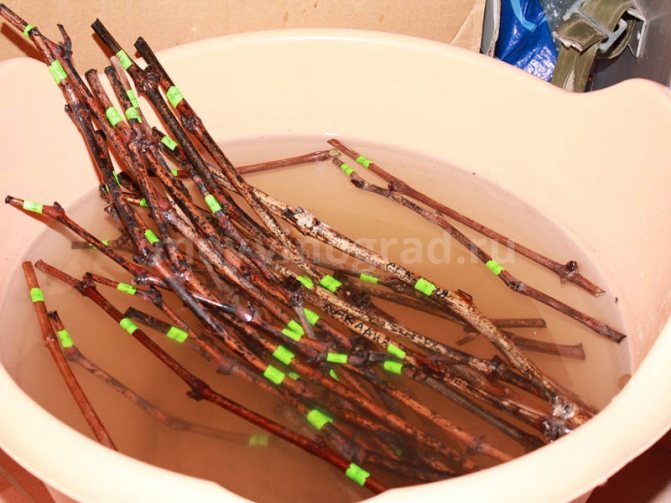
- the day before planting, the seedling is immersed in water with its roots for at least 12 hours;
- the top of the seedling is slightly pruned, the heel roots are also shortened - by 2 cm;
- for a better result, the roots are additionally kept in a growth stimulant solution;
- immediately before planting, the roots are briefly dipped in a liquid mixture of water, humus and clay.
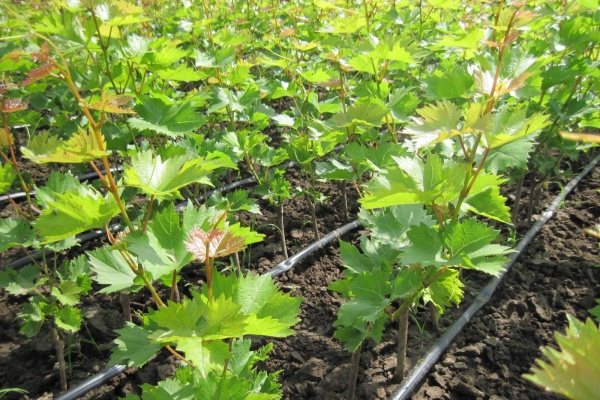


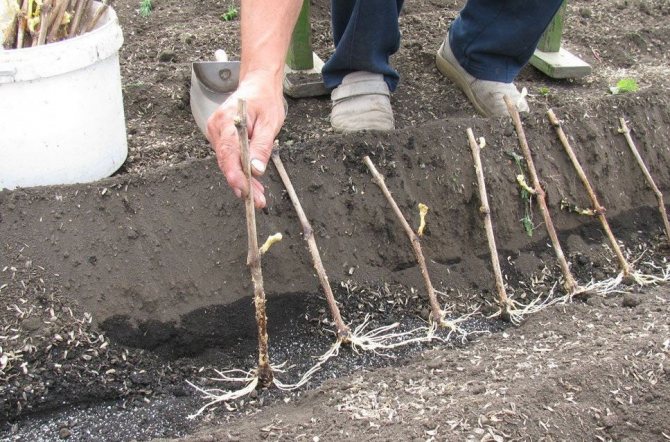
Planting a seedling
The algorithm for planting grapes in the fall in the ground is quite simple, but requires care.
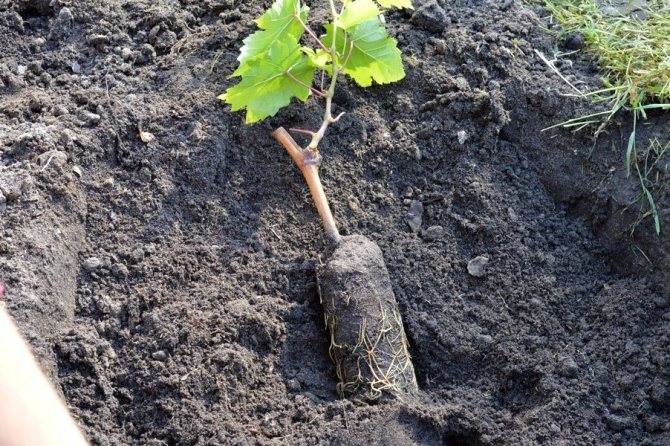
- A young seedling is placed on the ground in a prepared hole with a "heel". It is necessary to deepen the plant to about the level of 4 eyes.
- The roots are gently spread over the surface of the soil, directing them at an angle downward, and covered to ground level with soil mixed with sand or expanded clay.
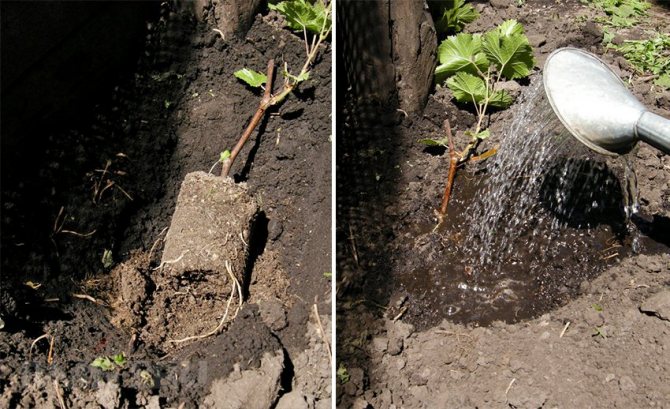
- The seedling is watered with water in the amount of 2 buckets, then loose soil is poured into the small hole formed around the trunk. There is no need to compact this soil.
Important! Under no circumstances should the roots of a grape seedling turn upwards - this will slow down the growth of the plant and lead to the death of some of the roots.
Preparing the seedling pit
A pit for grape seedlings must be prepared in advance. Most growers advise doing this 2 weeks before planting. Some say that the preparation of the pits should begin at the end of August. Grape roots develop best in the top fertile soil layer. Therefore, they cannot be deepened by more than half a meter. The pit is made as follows:
- The diameter should be 80 × 80 cm or meter by meter.
- A drainage layer is poured onto the bottom - crushed stone, pebbles, crushed brick or expanded clay. The layer thickness should be 5-7 cm. If the groundwater is high, drainage can be done up to 10 cm thick.
- A mixture of manure, humus and fertile soil is poured on top. The thickness of this layer is 10-15 cm.
- Grapes need mineral fertilizers, it is best to use wood ash (1 liter per pit) and phosphorus complex fertilizer (100-200 g per pit).
- Pour 20-25 cm of fertile soil on top, which will become a kind of buffer between the root system and fertilizers.
The finished pit with all the fertilizers should stand for a while for the earth to settle. Only after that we plant a grape seedling there in the fall. It is important to select the right material. The thickness of the vine should not exceed 8-9 mm, in extreme cases a centimeter, length - 60-70 cm. Too thick or long stems take root and develop worse. The short and very thin ones are less likely to survive the winter.
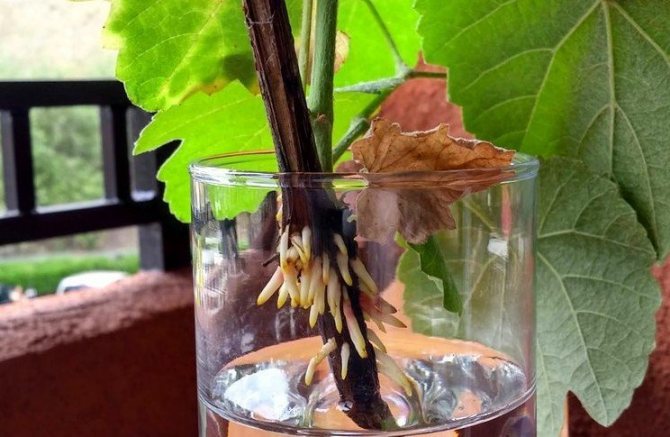
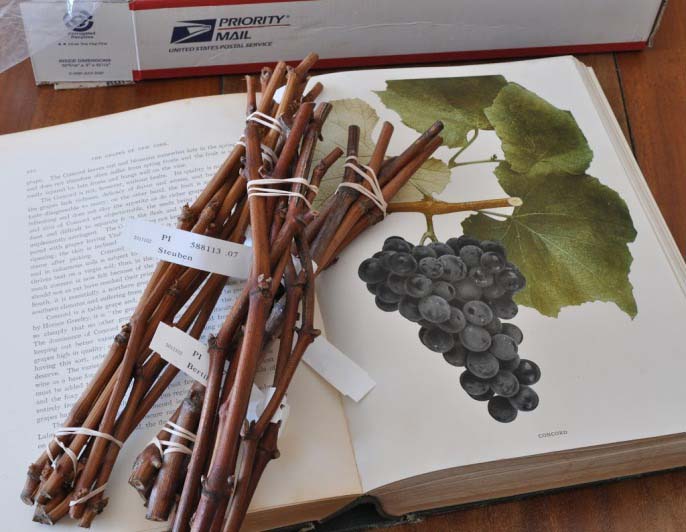
How to plant grapes in autumn with cuttings
Planting grapes with cuttings in the fall in the ground is one of the options for rooting a plant in your garden. Cuttings can be purchased at horticultural markets, or you can prepare yourself if you have an adult grape tree at hand.
For grafting, it is best to use a strong and long, about 1 m, ripe vine. From one such vine, 2 - 3 cuttings of 30 - 40 cm each are obtained, at least 3 buds should be located on the cuttings. The cut cuttings are placed in water for a day, then they are immersed in a growth stimulator for another day, and the top is treated with melted paraffin.
Planting grapes in autumn by cuttings is carried out as follows.
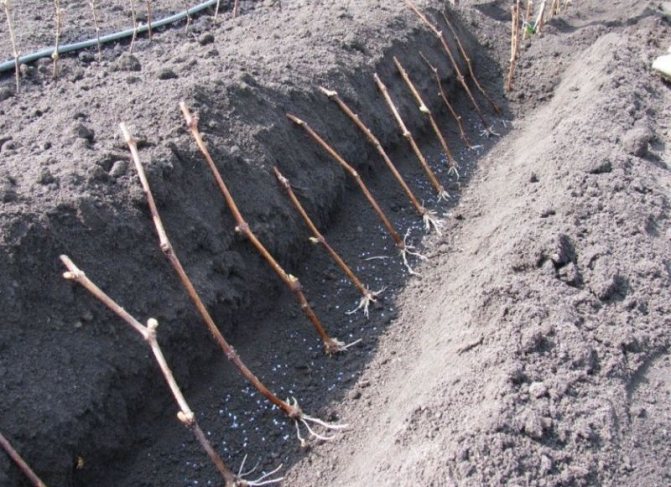
- Small trenches are prepared for planting material - 1 m wide and 15 to 40 cm deep.
- At the bottom of the trench, drainage is arranged, a small layer of soil is poured on top and the trench is watered with warm water.
- After that, cuttings are placed in a long hole with an inclination at an angle of 45 degrees. The spaces between them must be at least 10 cm.
- Cuttings set on the ground are covered with fertile soil and watered again.
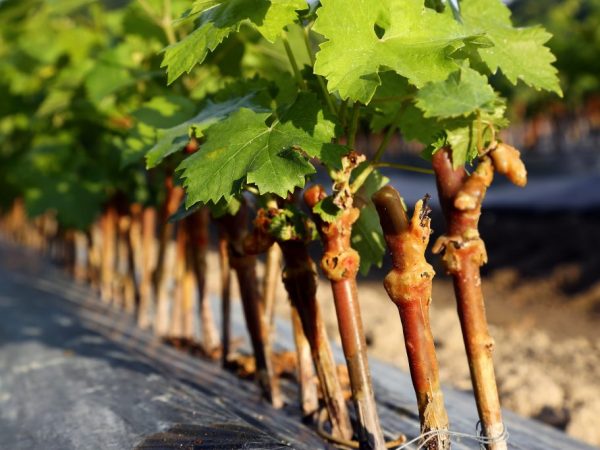


Since grape cuttings are always weaker than sprouted seedlings, at first they must be covered with a film to create a greenhouse effect and faster rooting.
Advice! Despite the fact that planting grape shanks in the fall in the ground is quite acceptable, it is recommended to do this only as a last resort - there is always a high risk that the shoots will not have time to take root.
When to buy planting material
Seedlings are purchased all year round, if possible. However, it is important to follow the planting and care conditions in order to get the desired result from the plant. When buying planting material, you need to pay attention to some features:
- developed root system with 3-6 young roots. The heel roots should be no shorter than 15 cm. In grapes, the root system develops for a rather long time, so it is better to take a seedling with a more powerful rhizome;
- the plant must have green shoots up to 20 cm long;
- the normal length of a seedling is 0.5 m, with a diameter of at least 8 mm;
- the plant must be healthy, free from damage and signs of disease.
Care after landing
After planting in the ground, seedlings and cuttings of grapes still require attention - before the onset of winter, several mandatory measures must be taken.
- Grapes after planting in the fall need abundant watering - several times before the first frost in the amount of 2 - 3 buckets. This is especially important if the autumn was warm enough, and there was little rain in September and October. If autumn is damp, then watering can be reduced to 1 - 2 times.
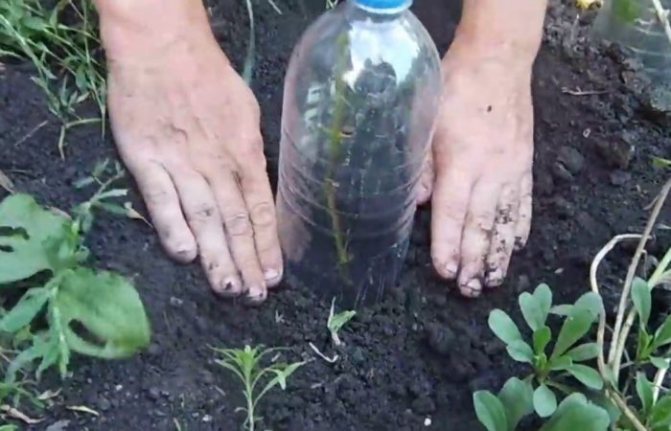
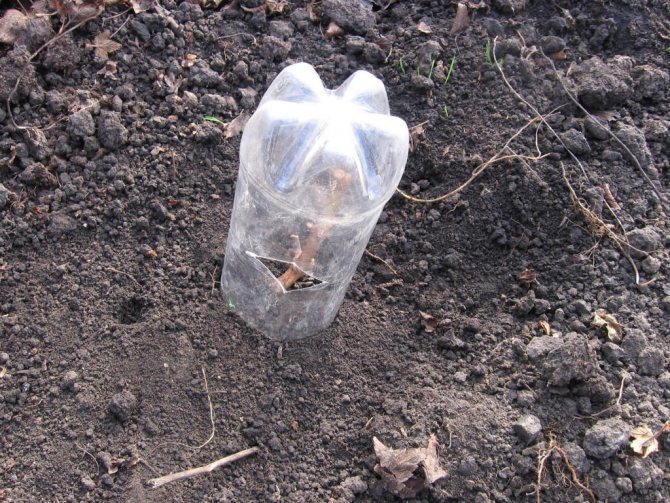
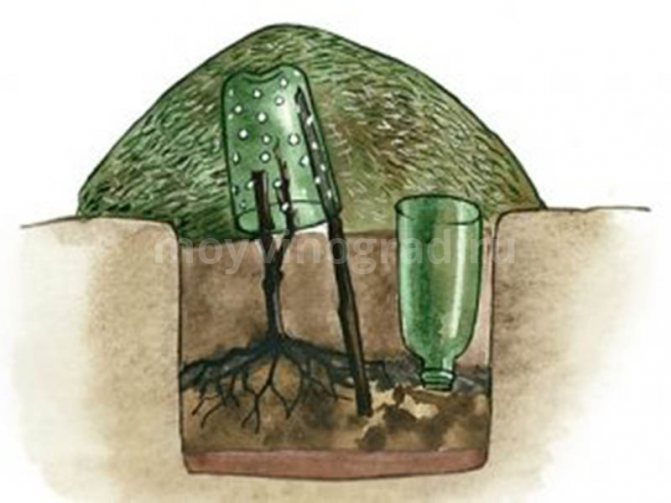
- With the onset of cold weather, young seedlings and cuttings must be covered. The shoot is cut from above, leaving only 4 - 5 strong buds, and a cut plastic bottle is put on it, and then covered with earth in a dense layer. There should be at least 5 cm of soil above the bottle. Such a protective layer will help the seedling survive frost and protect it from damage in the very first winter. In the spring, after the snow melts, the shelter is taken apart and the bottle is removed.
Important! Before the onset of winter, the grapes should not go into active growth. If, after planting and watering, young leaves began to appear on the seedling, watering should be stopped immediately and the seedling should be sprayed with a potassium solution.
When to trim?
Typically, pruning grapes in the fall is the most important step in crop maintenance. They practice it in the fourth year of cultivation, during this process, diseased and weak shoots, as well as those affected by diseases, are removed. After wintering, they also remove frozen shoots and those that have broken.
You should not get carried away with frequent pruning, this will lead to the degeneration of culture. Caring for grapes in the fall involves removing unnecessary shoots immediately after all the foliage has fallen and the first frost occurs.
Lunar calendar for planting grapes in autumn
Many gardeners take into account the lunar calendar when planting grapes. At first glance, this seems like a simple superstition. But in fact, the phases of the moon affect the growth of grapes, as well as all other processes occurring on the planet.


In particular, it is considered that:
- when landing on a waning moon, the roots of grape seedlings will develop most actively;
- planting with a growing moon will promote the growth of aerial parts of the plant.
Thus, for the successful rooting of seedlings and cuttings, it is the waning moon, and specifically its third quarter, that is best suited. The same applies to planting an adult grape or transplanting it to a new place - for rooting, the waning moon in the 3rd and 4th quarters is considered the best time.
At the same time, the lunar agricultural calendar does not recommend planting directly on the full moon or new moon.
Attention! When planting grapes in the fall, it is recommended to pay primary attention to the weather conditions. And only then it is worth taking into account the lunar calendar, using it as an auxiliary tool for determining the dates.
What varieties to choose for planting
Each grower chooses his favorite variety for planting, while, of course, taking into account such components as winter hardiness and frost resistance, taste, appearance and many others.It is important to listen to the recommendations of those who are engaged in the cultivation of this crop professionally, on a huge scale.
To date, there is an official list of those varieties that are recommended to be bred in this region. Let's get acquainted with some of them:
- Shasla - medium-sized, early, with bisexual flowering.
- Hamburg muscat - vigorous, medium ripening, ripens well, resistant to late frost.
- Narma - medium ripening, medium-sized, with a stable yield. The downside is poor resistance to disease.
- Rkatsiteli - medium early, average frost resistance. Suitable for long-term storage.
- Traminer pink - medium ripening, small clusters, high sugar content in berries.
- Chardonnay - medium ripening period, featuring recoverability after freezing, unstable to diseases.
The list goes on for quite some time. After all, it is supplemented by those varieties that are imported by local grape lovers. All slope varieties and varieties brought to the Kuban are successfully cultivated in this area, adapting to local conditions. Cultivation is carried out by cuttings.
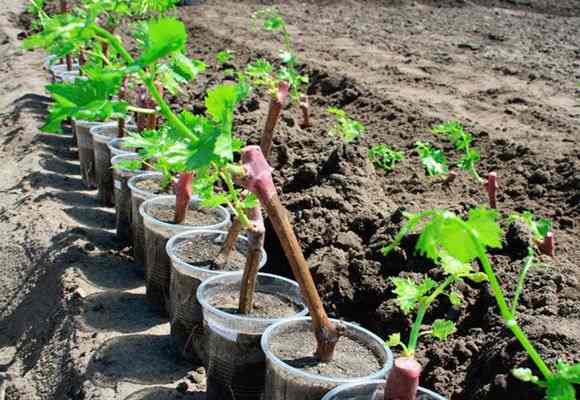


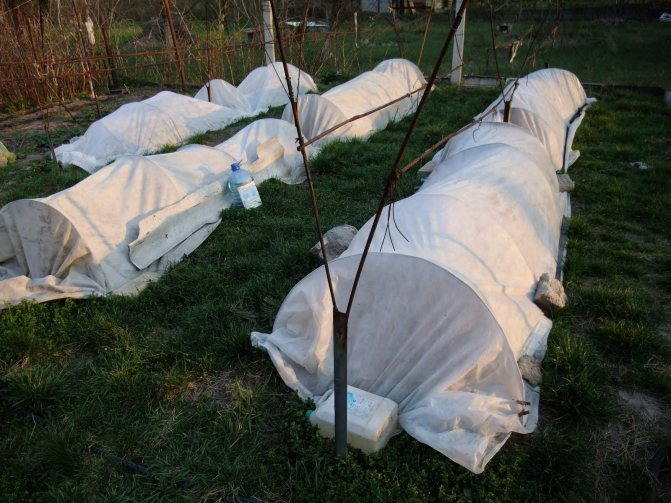
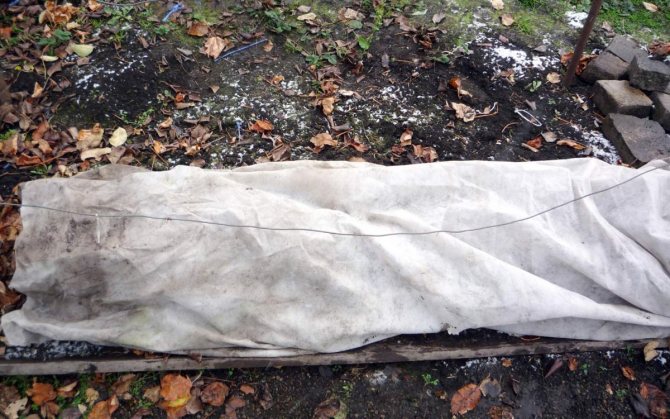
Shelter for the winter
Caring for grapes in cold regions is not complete without another important activity - the shelter of the vine. Most cultivated varieties can withstand frosts from 17 to 24 o C. It is impossible to rush with early shelter. On a sunny day, fruit buds can push against. The procedure begins in late autumn, when frosts of about -5 o C. were established on the street. However, before that time the vine should be tied with a tourniquet and laid on the ground. If you try to bend branches during frost, they can break.
For shelter, a warm, lightweight and breathable material is used. Straw, reeds will do, sometimes gardeners use old clothes. Burying the vine in the ground is practiced. First, a ditch is dug, a vineyard tied with a rope is laid, a layer of straw or foliage 30 cm thick is poured on top, and this whole cake is covered with loose earth.
From above, the shelter can be reinforced with foil. The waterproof material will prevent organic matter from rotting and saturating it with water. The film itself cannot be used without insulation. A greenhouse effect is formed under the shelter during the thaw. The buds will begin to awaken, and with the return of frost they will freeze.
Choosing a landing site
The correct orientation and a well-chosen plot will guarantee a healthy and rich vineyard. For full development, the bushes need an abundance of heat and light. The best solution would be to choose a southern or southeastern site on a hill. To ensure uniform lighting throughout the day, it is recommended to orient the bushes from north to south.
The grapes are sensitive to winds, so prefer the most protected area. A good solution would be to break a vineyard near the walls of buildings or outbuildings. A solid fence or other natural barrier will also work. So you will not only protect the planting from drafts, but also improve the microclimate around the bushes.
Interesting! During daylight hours, the walls of buildings heat up naturally and retain heat. Gradually, they emit it, which leads to an increase in temperature near objects by about 2 degrees Celsius. This can provide additional warmth to the vineyard.
The plant grows well on fertile loams and does not like acidic and waterlogged soils. If the acidity is high, it must be lowered by adding lime. With a high level of groundwater, above 1.5 - 2.0 m, it is necessary to arrange a drainage system to remove excess moisture.
To provide the necessary space for the development of bushes, when planting seedlings, maintain a distance between bushes of 2-3 meters, and between rows 2.5-3.0 m.This scheme will not only provide the plant with the necessary nutritional area, but will also facilitate vineyard maintenance and harvesting.
Frequent mistakes
- One of the most common mistakes budding winegrowers make is planting seedlings in holes with insufficient depth... The root system of such a bush is simply not able to cope with negative temperatures. The problem can be solved by transplanting the cuttings into a new hole, at least 60 cm deep, and preferably 80 cm.
- Choosing an unfavorable landing site able to cause a lot of problems for winegrowers The cold, shady side of the site will cause a weak bush to form or the entire vineyard to die. Lack of solar heat inhibits development, contributing to the formation of low quality crops. At the same time, the bunches become small, the berries become sour, prone to peas.
- Another misfortune of gardeners is selection of unsuitable planting material. Buying seedlings in questionable places will leave you not only without bushes, but also without money. It is important to trust specialized stores or your friends.
- Planting weak and unhealthy seedlings can lead to the death of the vineyard. It is best to prefer elite quality or first class seedlings, which have a very high probability of survival and compliance with the parent plant.
Now you know how to properly carry out the autumn planting of grapes. Compliance with the necessary requirements and recommendations will provide you with a rich and beautiful vineyard.
Step-by-step instructions for autumn planting
After choosing a place and preparing the planting material, you can proceed directly to the disembarkation procedure.
To begin with, you should prepare pits, measuring about 80 x 80 cm and a depth of about 80 cm. You should dig in such a way that in one side you collect the upper soil, which is about a third of the entire depth of the hole. The lower layers of the soil are placed separately, on the opposite side.
After that, the top layer must be mixed with 1 kg of ash, rich in potassium and phosphorus, and 0.5 kg of organic fertilizer, such as humus. The resulting nutrient mass should be poured down each hole to a depth of about 30 cm. Water abundantly and top up with earth again to the desired level. In this form, it is necessary to leave the pits for two weeks in order for the soil to settle.
Saplings or cuttings suitable for planting must be soaked in water or humate solution for a day. This will accelerate the development of the root system, and increase the survival rate of the bushes. Next, lower the planting material into the hole. Drive in a peg nearby and tie the top of the shoot to it. Fill the hole with the remaining soil from the first pile.
The bottom soil from the second pile must be mixed with coarse sand or crushed stone and also filled into the hole. A small 30-centimeter mound should be formed above the ground. After that, each bush needs to be watered with 3 buckets of water.
Important! Hilling and placing the cuttings should be so that the fruiting buds remain above the ground.
The final step is mulching the soil around the bushes. This is done with onion husks or grass cuttings. A three-centimeter layer of mulch is placed evenly at the base of the bush to retain moisture. It is recommended to repeat the procedure after each watering. In order to avoid the death of young plants, they should be covered for the winter.

Gardeners reviews
Oleg, Lyubertsy
In our conditions, it is better to plant from the east-southeast side - with spring frosts it thaws earlier.
Love, Eagle
Planting annual grape seedlings can be done in the fall before the onset of frost, or in the spring, but before the buds bloom. One of the easiest ways is to land in the pits. In a special hole 70-80 cm wide and the same depth.
A bit of history
As early as the 6th century BC, grapes were cultivated on the territory of the present-day Krasnodar Territory.He came there from Greece, while the Greeks shared the secrets of its cultivation.
Only in the 15th century, the culture began to be supported at the state level, centrally importing the best varieties from France and Georgia.
Prolonged Turkish wars adversely affected viticulture, many plantations disappeared. It was only at the end of the 18th century that it began to revive. New plantations were established, many of which bear fruit to this day.
In the 70s, the USSR was in the top 3 largest wine producers. The cardinal struggle for a sober lifestyle in the 80s hurt the industry, but did not destroy it at all. Good Kuban wine continues to be produced today.
Private gardeners are also very fond of this culture.
Grape care in the Kuban. Pruning grapes in the Kuban
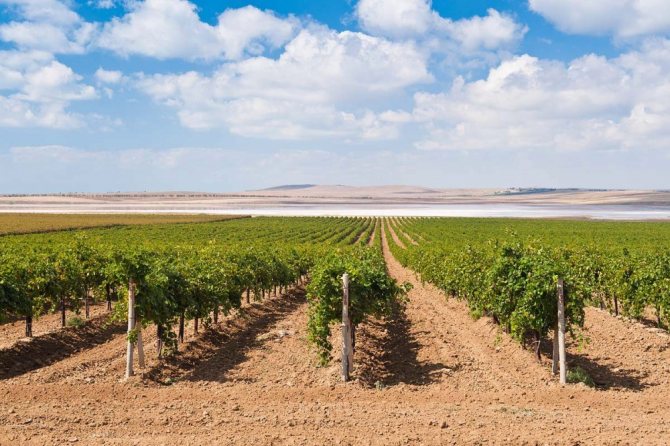
Kuban is rightfully considered the breadbasket of Russia. It is from this region that a part of fresh vegetables and fruits comes to the counters of the country. The vineyards of the Kuban deserve special attention and respect.


Vineyards of the Kuban
Fertile soil with a high level of mineralization provides the population with a rich harvest every year. There is a humorous belief among local residents that even a dry stick will bloom in the Kuban land.
Nevertheless, grapes are a very capricious culture and, even under favorable climatic conditions, require special care. The plant needs good lighting and constant moisture of the land. Only with professional agrotechnical measures can a high yield be expected.
Regardless of the grape variety and type, it is necessary to carry out planned pruning. These actions ensure the correct growth of shoots. In addition, pruning allows you to maintain the bush in the desired shape, while forming new fruiting links.
Effect of pruning on grapes
Pruning vines becomes key in solving such problems:
- resistance of the vine to frost, this is especially important for those grape varieties that love warmth;
- by removing old and disturbing vines, the productivity of the plant increases; the required amount of perennial wood is formed,
- the taste of berries improves,
- well-formed vines are much easier to insulate and harvest for the winter, an earlier harvest,
- it becomes easy to care for the bush, since there are no dense thickets,
- beautiful appearance - it is more pleasant to contemplate a well-groomed plant than dense thickets.
Pruning of grapes in the Kuban is carried out in 2 stages - preliminary autumn and final spring pruning. Sometimes circumcision is allowed in the winter. Summer is an extremely unfavorable period for these purposes.
Autumn pruning of a grape bush
Pruning in the fall, in turn, is also divided into several stages. It depends on the age of the bush, its variety and vigor. It is believed that you can start pruning after the foliage has fallen, it is at this time that the bush is at rest.
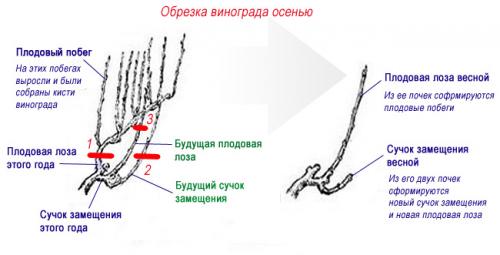

Pre-pruning is done in early October before frost. In its process, green, unripe shoots are removed. The ripe shoot is characterized by a bright dark brown color, while the vines are bent, a slight crackle of wood is heard.
Formative pruning is basic and should be done in mid or late October (immediately after the first frost). Before starting the process, you should inspect the bush and the condition of the vine. First of all, it is necessary to check the branches for the presence of pests, painful injuries, frostbite.
After a thorough examination, you need to lighten the grape bush. In the process of clarification, the following parts are removed:
- poorly ripened, thin, broken vines,
- uncomfortable growing branches,
- the head of the bush is cleared, stumps from last year's circumcision are removed,
- the most developed fertile branches are cut into arrows,
- old dry sleeves are cut off, on which annual vines are very thin or completely absent,
- tops and shoots are cut out (only if they are not needed to form the sleeve),
- the underdeveloped tops are also reduced.
When pruning grapes in the Kuban, the probability of freezing of shoots is taken into account. Therefore, to achieve good results, you should always leave 40-60 percent more than the annual growth.
Pruning grape bushes in spring
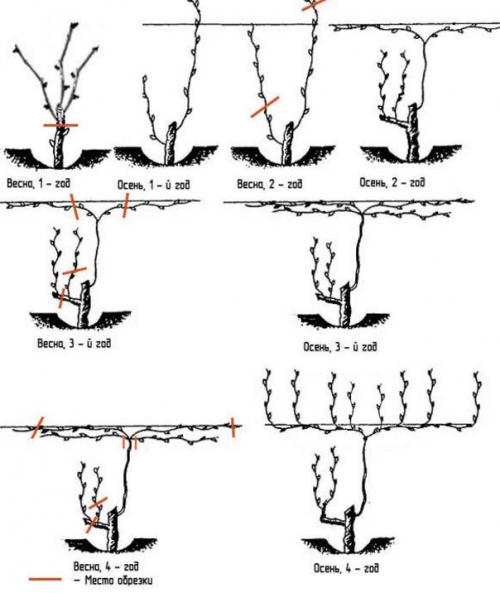

Spring circumcision should begin before bud break. Pruning processes depend solely on the age of the grapes; young bushes must be properly formed. With high-quality and competent pruning both in autumn and winter, abundant fruiting is guaranteed for the 5th year of the grape's life.
Experienced gardeners harvest earlier without losing the flavor of the berries.
1 year . The growing season should start with 4 eyes. If a young bole already has 2 shoots, they are both cut into 2 eyes. If only 1 has grown, it means 4 eyes, these are the future sleeves. When pruning grapes in the Kuban, the four-armed formation is the most popular type.
2 years. Future sleeves are trimmed for a few more eyes.
3-4 years. Fruitful links begin to form on the bushes. This year it is necessary to remove the entire vine except for the two shoots closest to the root. The lower branch decreases by 2 eyes (replacement knot), the upper one - by 7-8 eyes (this is the fruit arrow).
Further actions are to maintain branches and timely eliminate problem areas.
Summer grape care
At the end of the spring pruning, the care of the grape bush should continue. To ensure full development, you need to monitor the plant throughout the growing season. Generative and vegetative loads are evenly distributed through breaking, pinching, pinching and embossing.
Do not forget about the fight against pests and fungal infections. Several times a season, the bushes need processing and spraying. Fertilizing, moisturizing and feeding the plant will have a positive effect.
Top dressing and tillage
Taking care of the vineyard is not complete without top dressing. In the fall, after harvesting, the crop is in a depleted state. In order for the vine to overwinter and give a good growth in the spring, it needs to restore its lost strength.
Leaving in the fall means feeding the crop only with phosphorus and potassium. From mineral fertilizers, 40 g of superphosphate are applied under an adult bush. The substance enriches the grapes with phosphorus. From potash fertilizers, 30 g of potassium sulfate or potassium magnesium are applied. Many gardeners give preference to potassium monophosphate, contributing 40 g of the substance under the bush. Dry mineral fertilizers are diluted in a bucket of water, poured under the root, combining top dressing with watering.
Instead of mineral fertilizers, fertilizing in the fall can be done with organic matter. Under an adult vineyard, 300 g of ash or 15 kg of compost are introduced. The organic matter is dug up with the soil to a depth of 30 cm, departing from the trunk 50 cm.
Protection against diseases and pests
An important process of caring for grapes in the fall and preparing for winter is the preventive protection of the vine. The choice of a spray product depends on the condition of the vineyard:
- If, during the inspection, traces of mildew are detected, the affected shoots with leaves are cut off and burned. The vineyard is sprayed with "Folpan", "Ridomil" or another similar preparation.
- If signs of oidium are detected, the vine is sprayed with any preparation containing sulfur even before dropping the foliage in early autumn.
- Against anthracnose, drugs used to treat oidium and mildew are used.
- When, when examining the grapes in the fall, traces of a leaf roll are found, the bush is treated with a decoction of tobacco or medicinal chamomile.
- The raining of berries and bunches in early autumn may be associated with cercospora.The disease still manifests itself in brown spots on the leaf plates. For the care of a sick vineyard, use "Fundazol". "Polychoma" helps a lot.
- In the fall, ticks like to get along on the vine. Most often, they sit on the tops of young branches. A measure of getting rid of the pest is pruning the tops of the shoots.
- In the case of the development of gray rot in autumn, the processing of the culture is carried out with "Euparen" or the preparation "Skala".
Healthy bushes also need preventive care. The vineyard is sprayed in late autumn after leaf fall with a 3% solution of copper sulfate.