Indoor plants at home are more than just an interior design element. The green leaves and vibrant flowers are relaxing and enhancing the well-being of family members. Due to transpiration, air humidity increases.
Some species have the ability to absorb harmful chemicals. It is not surprising that flower lovers are interested in increasing the number of their wards. Houseplants can be propagated in a variety of ways, one is by rooting apical cuttings.
What indoor plants can be propagated by apical cuttings?
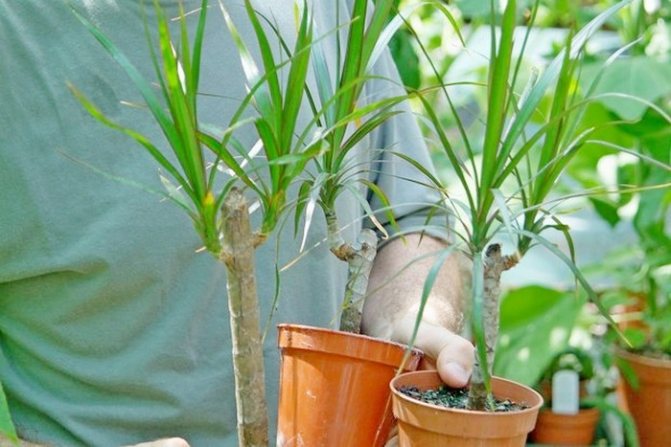

The method for propagating indoor flowers is simple, does not require special procedures, and in most cases ends successfully. Plants especially suitable for apical cuttings propagation:
- Small-leaved boxwood (Buxus microphylla);
- Dracaena (Dracaena draco);
- Fuchsia (Fuchsia);
- Chinese rose, or hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis);
- Large-leaved hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla);
- Laurel (Laurus nobilis);
- Oleander (Nerium oleander);
- Olive (Olea europeae);
- Podranea ricasoliana (Podranea ricasoliana);
- Kurasavsky cotton wool (Asclepias curassavica);
- Shrub chrysanthemum (Argyranthemum frutescens);
- Ficus benjamina (Ficus benjamina);
- Bougainvillea naked (Bougainvillea gabra);
- Common pomegranate 'Nana' (Punica granatum 'Nana');
- All citrus fruits.
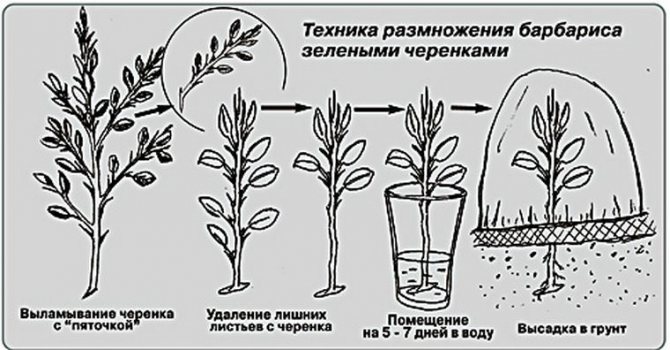
Propagation of indoor plants by cuttings
Propagation by cuttings (vegetative method) is the most popular among flower growers. A stalk is a part of a plant that is specially cut off. She has the ability to root and grow. In floriculture, several different types of cuttings are distinguished, namely: stem, leaf, apical, and middle.
Propagation by apical cuttings
This method is used for all ampelous plants, as well as for touch-me-not and balsam.
To obtain this kind of cutting, cut off the part of the non-lignified stem, which is located at the top. On such a cutting, there must be developed leaves in the amount of 2 to 4 pieces. You need to step back a centimeter below the knot and make a cut. It is on this node that the roots appear first. To make rooting faster, it is recommended to treat the cut with growth stimulating agents (phytohormones).
For rooting, the cuttings are planted in a soil mixture for young plants, and then watered. To keep the humidity high, cover the container with plastic wrap.
Propagation by stem cuttings
Ficus, geraniums, all succulent plants, as well as cacti can be propagated by stem cuttings.
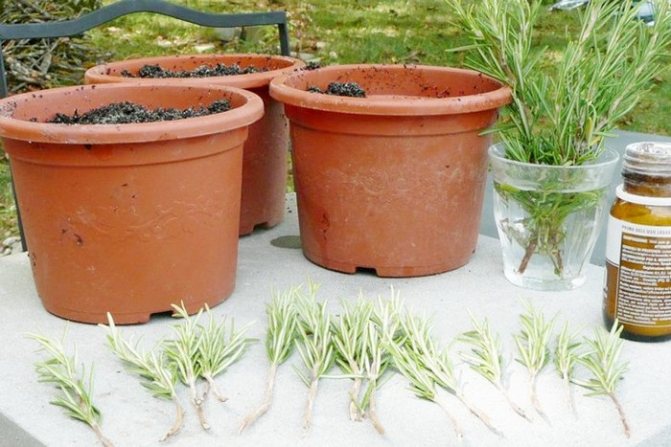
This type of stalk can only be cut from a healthy plant, and the cut must be made slightly below the node. Such a stalk should consist of 3 or 4 nodes and leaves should be present on it. Pay attention to the cut, it must be fresh and even. There should be no flowers or buds on the handle. If desired, the leaves from the bottom can be torn off. Rooting is carried out in moist soil, which contains a lot of sand, or a soil mixture for young plants is used for this. After the roots appear (after about 3-4 weeks), the plants are transplanted into an ordinary soil mixture. Most cuttings are rooted simply by dipping them in a glass of water.
If you propagate succulent plants or cacti in this way, then the cutting should be left for several days in the open air for drying before planting for rooting. At the same time, the place of the cut should become tightened, and the edges of it should be bent inward. This will avoid the appearance of stem rot. After planting, the soil is slightly moistened with a sprayer (do not watered).
Cuttings of geraniums, as well as succulent plants, are not covered with a film during rooting. All other plants need high humidity at this time, so they must be covered with foil.
As a rule, it is recommended to place the cuttings in a well-lit and warm enough place. It should be borne in mind that they must be protected from direct sunlight.
As a rule, such cuttings are propagated in spring and summer, when the plant is growing intensively. But there are plants that are best propagated in this way in the last summer days, for example, geranium, fuchsia.
The middle stalk is considered part of the stem. Cut it off from the middle or bottom of the shoot. As a rule, such cuttings are used for propagation of Tradescantia.
Substrate for rooting cuttings
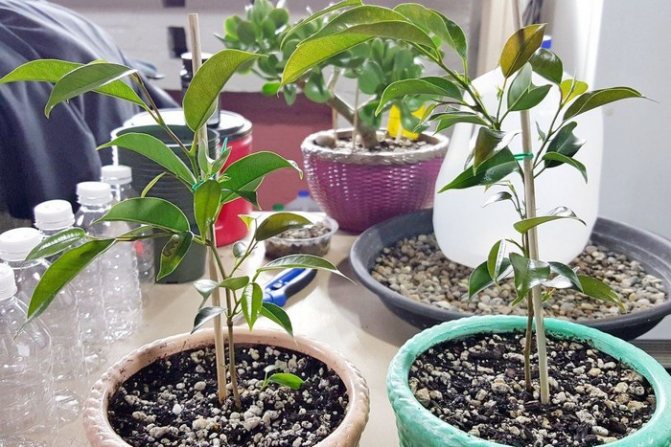


As a substrate for the rooting of apical cuttings, a substrate poor in nutrients, permeable, and retaining moisture is suitable. Ordinary flower soil is useless. A mixture of peat and washed sand with mineral additives can be made by yourself or purchased. The substrate cannot be too fertile, since the plant has no motivation for the development of the root system - after all, food is “at hand”. If the roots make an effort to obtain nutrients, the plant transfers energy to this area of activity. By increasing root surface, growth and depth, the chances of reaching food sources are increased.
The cutting surface of the cutting must be treated with a root former. The seedling begins to produce roots faster when planted on the edge of a ceramic pot. Clay pots have porous walls - more oxygen enters the roots, stimulating development.
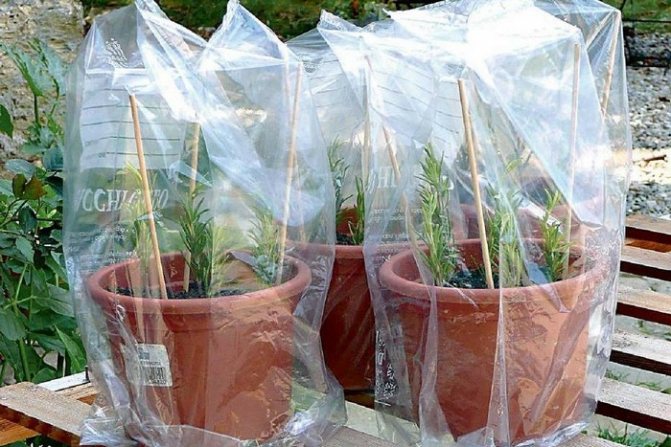


The above-ground part must be additionally protected from excessive evaporation of water with a glass or film covering. During rooting, the substrate is kept evenly moist, without stagnant water. Root development is faster when the surface temperature is 20-30 ° C.
Brugmansia, oleander and various types of ficus root easily in water. Seedlings are lowered 3-5 cm into a vessel with water. When roots are formed, the cuttings are transplanted into pots.
Before cutting off the tops of the shoots to prepare the seedlings, you need to know more information. It is imperative to know whether the species can be propagated by apical cuttings, in the ground or in water? In what conditions is the species easier to root? It may turn out that the flower reproduces by other methods - by dividing or layering. Anyone who sets a goal to grow plants with certain characteristics, for example, with an identical shade of inflorescences, must decide on generative reproduction.
Reproduction by layering
Climbing, as well as ampelous plants with long shoots, for example, ivy, chlorophytum and others, can be propagated by layering.
This type of reproduction differs in that a young plant is formed without being separated from the mother plant.
After sprouts appear on rather long shoots, they try to fix them with a wire or hairpin on the surface of a special soil mixture. Rooting is pretty fast. A young plant should be separated when its root system is formed, and it begins to grow by itself.
Artificial root formation at the branch
If it is not possible to bend the branch to the ground, make a hole in the plastic bag and place the bag on a straight branch, and then fill the bag with soil.Tie the bag loosely, providing air access to the branch, slightly moisten the soil. After the roots are formed, separate the seedling with pruning shears and transplant to a new location.
The question of how to propagate an apple tree arises at different stages of the hobby for gardening. Someone wants to have a large garden, someone wants to clone a tree of their favorite variety, renew old trees. Of course, it is easier to buy a seedling, but it is always a risk.
Reproduction by offspring
Bulbous and bromeliads, as well as cacti can be propagated by offspring.
The daughter plant that develops from the base of the mother is the offspring. After such plants develop well, they are separated from the mother with a sharp knife or with your hands, while trying to make a cut closer to the main flower. We must try to ensure that the separated offspring has many of its own roots. The separated offspring are planted in an individual pot, and they are provided with the same care as for cuttings.
Small bulbs appear on the mother bulb plant. They must be carefully separated and placed in a separate container. They usually bloom after 1 or 2 years.
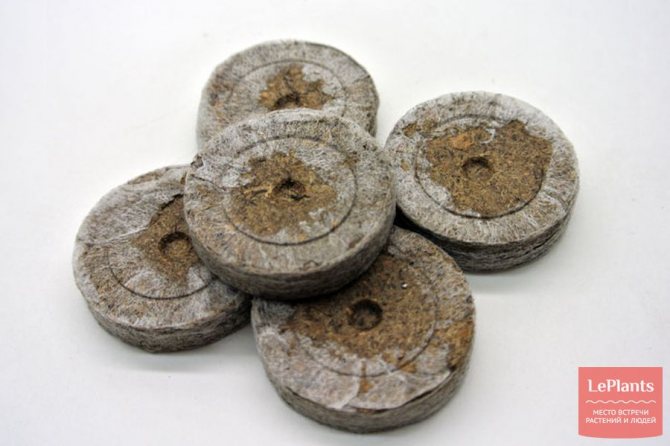
Rooting in a landless mixture
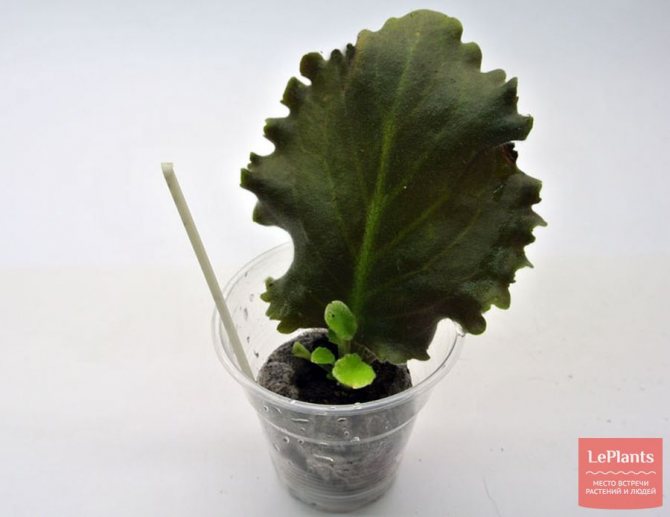
This method of rooting does not allow observing the formation of roots, but when using it, the germinated leaf is free of stress when changing environments, and the time for the appearance of "babies" is reduced. It is recommended to root varieties of miniature violets in this way.
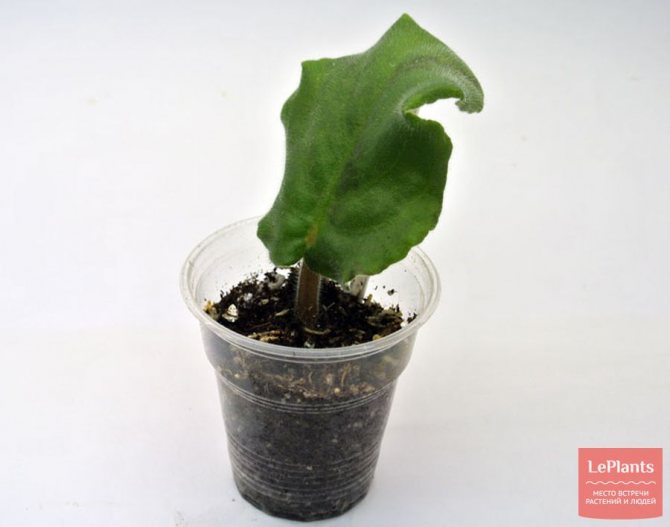


ON THE PICTURE: Rooting a leafy cutting of a violet in a landless mixture
High-moor peat, perlite and vermiculite are used to prepare a light water and air-permeable landless mixture. The mixture is poured into a small pot 5–7 cm in diameter or a plastic disposable cup, slightly moistened. A prepared leaf cutting is planted in it to a depth of no more than 1.5 cm and placed under a bag or in a greenhouse. The pot or cup must have drainage holes to remove excess moisture.
Reproduction by division
When growing, these plants are able to form rosettes (small daughter bushes). In this regard, such a plant can be divided.
It is recommended to propagate by division in spring or June. The mother plant is removed from the soil, the soil is removed and the daughter part of the plant is carefully cut off or broken off. In this case, you need to cut where the daughter and mother flower are connected. The cut should have a healthy growth point, as well as developed roots. They are planted in a moist soil mixture. Before a young shoot appears and full rooting occurs, the soil must be constantly moist. And the plant also needs to be protected from direct rays of the sun.
What is the danger of acquiring a "baby"?
It often happens that the mother plant, from which the "babies" are sold, did not have time to bloom before the exhibition. You can judge what will eventually grow out of such a purchase either by the photograph attached to it, or by a violet of the same variety exhibited by another collector. And it is not a fact that a violet grown from such a "baby" will bloom in exactly the same way as an exhibition plant that has struck your imagination. Different specimens of Saintpaulias of the same variety often differ from each other in color saturation, amount of "fantasy", border width, etc.
In addition, you need to know that the "kids" obtained from the leaves of fantasy varieties do not always repeat the original varietal color. A young plant can bloom without strokes and peas, or even change the color of the flower to the color of these same peas and strokes. And, the more complex the flowers were painted, the more sophisticated their shape was, the more likely it was to get "sports".
"Sport" is a plant that has lost varietal characteristics during reproduction, i.e. prosperous out of grade.
Therefore, experienced collectors advise buying leafy cuttings - in this case, there is a better chance of growing the same plant as the one you like. This is the most common breeding method for Saintpaulias.
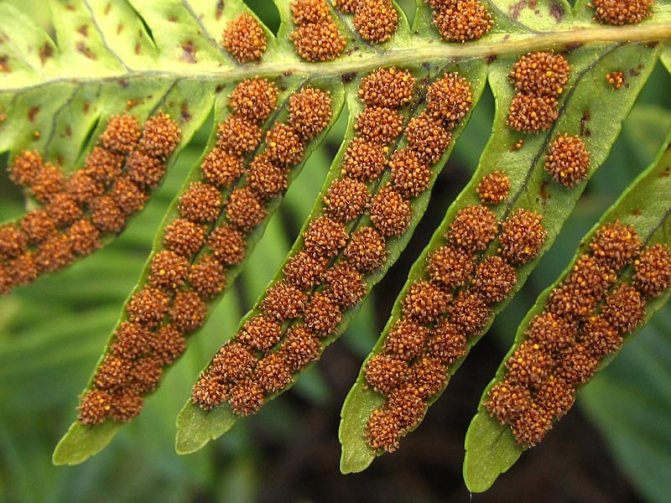
Reproduction by spores
Fern can be propagated by spores.
This method is quite difficult, but fern lovers can try it.
With proper care, spores appear on the seamy side of adult leaf plates. If desired, such disputes can be bought in the form of mixtures of different or one type. To plant spores, you will need special soil, which includes crushed brick chips and peat mixture.
The substrate is poured into a pot, which should be small, low and wide. Smooth its surface and compact slightly. After that, spores are evenly distributed on the surface of the soil. Cover the pot with glass on top, and then place it in the water poured into the container. To improve the result, instead of tap water, it is recommended to use thawed or rainwater (it is softer). Spores should be placed in a dark and warm place, while making sure that there is always liquid in the container. The first shoots can be seen after about 4–5 weeks. You should remove the cover from the pot after 4–8 weeks, after the seedlings get stronger. Grown plants need a pick, which is made in special trays for germinating seeds. The grown seedlings need to be planted in separate pots.
Content
- 1. What is the danger of acquiring a "baby"?
- 2. Choice of leaf cuttings
- 3. Rooting in water
- 4. Rooting in a landless mixture
- 5. Rooting in a peat (peat) tablet
- 6. Rooting in sphagnum moss
At exhibitions of violets, hundreds of varieties of uzambar violets are offered to the attention of buyers, but it is far from always possible to buy an adult flowering plant you like. Basically, the so-called "babies" (young plants grown by collectors from leaf cuttings) and leaf cuttings from exhibition plants are sold.


ON THE PICTURE: "Baby" or a leaf?
The undoubted plus of the purchase of varieties by "kids" is a reduction in the time of cultivation and, accordingly, the approach of the moment of flowering. But there are some nuances here.
Seed propagation
Seeds can propagate several types of cacti, primrose, fuchsia, cyclamen, coleus.
Houseplants are rarely propagated by seeds, because this is a rather complicated method. However, if you wish, you can still try to grow a spectacular plant from a tiny grain. Also, thanks to this reproduction method, it is quite possible to get a new plant shape (for example, with a different color). It is recommended for beginners to choose annual plants for the first sowing, as they are relatively easy to grow.
New tree from branch
The method of propagation using layering is simple if you follow the rules. There are 2 ways to grow an apple tree from a branch, both refer to propagation without grafting.
The first way is to plant a seedling of the desired variety at an angle in the fall so that the branches touch the ground. In early spring, examine the tree, select young shoots and pin them to the ground with staples. During the summer, you need to huddle the place several times in which the roots will grow from the bud, and maintain the moisture level necessary for rooting. Thus, by the fall, quite viable seedlings will be obtained. The advantage of this method is in obtaining a large number of new seedlings. The downside is the need to buy a young tree. That is, it will not work to grow an apple tree sapling from an old tree.
Dig in the branches of the apple tree
How can you root a branch of an apple tree without being able to dig it in? Here a more convenient method comes to the rescue: propagation of an apple tree by air layers. You need to carefully examine the tree and select developed branches with good annual growth (those that have shoots).You need to take it, step back from the top about 10 cm and use a sharp (this is important) knife to peel off the bark with a ring about 3 cm wide.This area is treated with a special solution that stimulates root growth. You can find one in a garden store. Dilution of the solution - according to the instructions.
Greenhouses and lighting
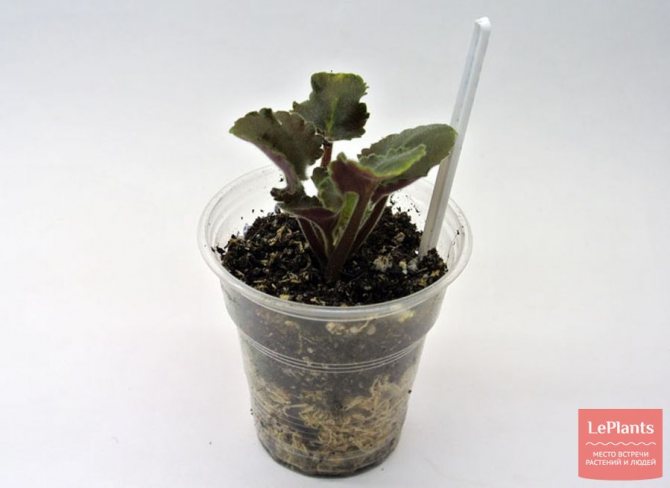
After planting, you need to spray the cuttings with water with Zircon and put them in a greenhouse. The greenhouse is a container covered with plastic wrap, which includes cuttings with a margin of height. A greenhouse can be made from an old glass, maybe not completely sealed, an aquarium, a deep plastic bowl or container. A mini greenhouse can be built from a 5-liter or 1.5-liter water bottle by cutting it across.


Rooting cuttings
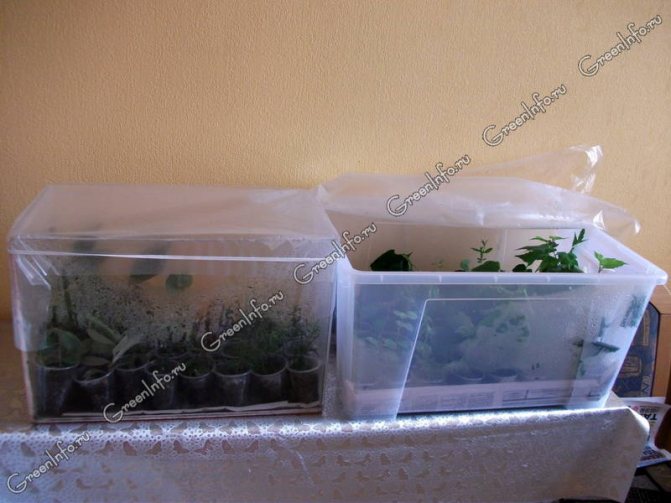
Cuttings should be kept in high humidity conditions until they form their roots, which will take over the process of supplying the plant with water. But in addition to 100% moisture, cuttings need light for rooting. It is not recommended to put cuttings in the sun, since overheating inside the greenhouse is possible, therefore additional lighting is organized. Special phytolamps, especially LED ones, are best suited for illumination, but it is quite enough to use cheaper, albeit less economical, fluorescent lamps. By the way, among them there are energy-saving phytolamps, which, however, give a pink light that is not very pleasant for the eyes.


Rooting cuttings
Daylight hours should be optimal for 12 hours. Observance of day and night is mandatory. The optimum temperature for rooting is +25 degrees; at lower temperatures, root formation is reluctant. For many plants (eg bougainvillea) bottom heating is desirable when the substrate temperature is higher than the air temperature. On my shelves, this is achieved by heating from a fluorescent lamp that illuminates the shelf below.
I expect the first rooting results in 2 weeks for myrtle, melaleuc, callistemons, rosemary, abutilones, figs, ficuses. A month later - for hibiscus, bougainvillea, metrosideros, eugene, psidium, citrus, olives. Gently take out the cups - the resulting roots are clearly visible through the transparent walls of the cups.
Graft


Grafting is the transplanting of a part of one plant (cuttings or eyes) onto another. As a rule, fruit and ornamental trees and shrubs are propagated by grafting. The transplanted part is called the scion, and the plant to which the transplant is carried out is called the stock. The graft is pressed with a cut to the incision in the rootstock. Scion and rootstock tissues grow together and a new plant is obtained. The graft is usually taken from a tree or bush that has a high quality fruit or other aerial parts. For rootstock, plants with a well-developed root system are used.
In the process of grafting, the internal tissues of the scion and rootstock are connected. This process is carried out in several ways. The most common are cleft and kidney (or eye) inoculations.


When cleft inoculation a gap is cut in the rootstock hemp and the wedge-shaped pointed ends of two scions are inserted into it. In this case, the diameter of the rootstock should significantly exceed the diameter of the scion. For the vaccination to be successful, certain conditions are met. The optimal time for grafting is spring, as the graft should only come out of dormancy. After the vaccination, the contact area of the scion with the stock is protected from drying out and pathogens by coating it with garden varnish.
When peephole the bark of the stock is cut in a T-shape. Then the scion is inserted into the slot, it is tightly wound and everything is coated on top with garden varnish. This vaccination method is recommended in late summer or early autumn. It must be done before the rootstock bark becomes very hard.In this way, plums and cherries are successfully propagated. From one branch, you can immediately get a large number of scions - buds.
There is also such a method of vaccination as ablation (rapprochement)... It is carried out if the sources of the rootstock and scion grow side by side. An incision is made on each shoot, then the incised places are connected and fixed (by tying, covering). After the two shoots grow together, the scion is cut off from the root, and part of the shoot is removed from the rootstock above the scion location. Sometimes branches of two trees grow together in a similar way in nature.
- <Back
- Forward>
Terms of plant cuttings
Most garden plants can be propagated all year round, but spring and autumn will be most favorable for indoor crops. The "kids" that have taken root during the fall enter a state of dormancy by winter, gradually taking root, and in the spring they begin to grow rapidly. In temperate latitudes, many lignified and shrubby crops, the same roses, for example, should be cut in spring so that the root system has enough time to gain a foothold.
Here is a table with the recommended terms for vegetative propagation of garden plants:
| Cultures | Procurement terms cuttings | Percent rooting | Duration (in days) |
| rose flower | Budding - the beginning of flowering | on average: 83.9%, individual varieties up to 100% | from 10-15 to 28 |
| Lilac | Fading stage | up to 90-100% | |
| Clematis | Budding - the beginning of flowering | 40-100% (depending on the variety) | 25-30 |
| Chubushnik | Fading shoot growth - the beginning of flowering | up to 90-100% | 15-25 |
| Spirea | Beginning - mid-June | from 30 to 100% in different species | 12-25 |
| Forsythia | First half of June | up to 70% | 20-30 |
| Viburnum | Flowering period | 100% | 14-21 |
| Cotoneaster | End of June - beginning of July | 100% | |
| Action | Early June - mid July | 100% | 17-25 |
| Privet | Mid June - early July | 80-90% | 14-21 |
| Derain | Mid June - early July | 100% | |
| Honeysuckle | End of shoot growth | 100% | 11-20 |
| Hydrangea | June July | 80-100% | 20-23 |
| Rhododendron | July-September | 72-76% | 50-70 |
| Actinidia | June July | 36% | |
| Scumpia | End of June - beginning of July | 100% | 20-30 |
| Barberry | June | 33-100% | |
| Colquitia | Early July | 46% | |
| Weigela | 100% | ||
| Euonymus | 45% | 45 | |
| Currant | 83% | ||
| Chaenomeles | 100% | ||
| Cotoneaster | up to 100% | up to 28 | |
| Keriya | up to 100% | ||
| Kuril tea | 100% | ||
| Juniper | 70-90% | ||
| Thuja | June | 30-60% | 30-60 |
| Spruce | June July | 50% |
If something went wrong
The main reason for the death of cuttings, despite the efforts of the grower, is the wrong choice of rooting time. They root them in early spring or late autumn, when the plant is in a dormant phase, and they need watering and cannot stand any manipulation with themselves.
Gloxinia rots due to the grower's unwillingness to root it in an intermediate container... In this case, the whole plant dies, and this can be avoided by planting each petiole in a separate cup. This avoids the spread of rot throughout the plant. Sometimes growers forget to make drainage holes in the pot, thereby pushing it to rot on its own.
Often the reason for the disappearance of gloxinia is the wrong choice of soil. It is planted in garden soil, not in soil for violets. Garden land is full of earthworms, centipedes, lacewings, which sooner or later crawl out of the pot, becoming a threat to other plants. If you ignite it, it will lose everything that is useful and necessary for the growth of the flower.
It is better to root the petioles in a ready-made violet soil purchased from a store... It will never be overloaded with fertilizers and will have a neutral soil response. Gloxinia often dies due to excessive and improper watering. It is watered only with boiled settled water after the top layer of the soil has dried.
Steps for preparing lignified cuttings:
- Immediately before rooting, we update the oblique cut at the bottom of the cutting and make two cuts in the bark to the cambium on the sides of the cutting, approximately 3-4 cm long.
- We remove the lowest bud, if there are many buds on the handle (up to ten), then we remove the three lower buds.
- If you work with a large number of cuttings, and even from different trees, then be sure to hang tags on your charges. It now seems that it is impossible to forget where which stalk is growing. But believe me, everything is forgotten very quickly.
- For insurance, the cuttings can be dipped into a solution of root growth stimulants (for how much? See the instructions for use of the drug you bought).
For example, you can prepare a root growth stimulator yourself by mixing water (5 parts), clay (3 parts) and bile (1 part) of any animal. You can store it in the refrigerator. But with strict observance of the cambium rule (up in the cold, down in the warm), all these tricks with all sorts of stimulants, chemical fertilizers will be an extra cost of effort and money.
What to do after?
A young plant is regularly watered, and for the first time they are fed with fertilizer Kemira Lux one month after planting in the ground. This pink powder is sold packaged in 20 and 100 gram packs. For 2 liters of water, take 1 coffee spoon of powder. They are fed a young flower 2-3 times a month. For active growth, the pot is placed on a windowsill, which is intensely illuminated by indirect sunlight.
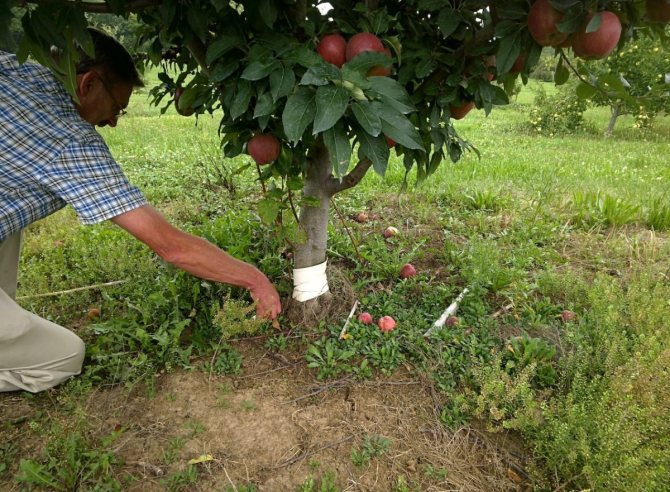
What varieties of apple and pear are well rooted
Not all varieties of apple and pear trees give roots equally well when propagated by green cuttings. Some take root better and faster, some take longer and worse. The smaller the fruit, the easier the cutting takes root.
The best pear varieties for growing from a cuttings: Lada, Muscovite, Elegant Efimova, Autumn Yakovleva, Memory of Zhegalov.
The best varieties of apple trees for growing from cuttings: Altai dove, Altai dessert, Altai ruddy, Aport Alexander, Aport blood-red, Vityaz, Gornoaltayskoe, Long, Zhebrovskoe, Zhigulevskoe, Kitayka Saninskaya, Kuznetsovskoe, Dream, Moscow red, Father's renti, Nakhodka Lebedyanskaya, Pepin Shafranskaya, Pepin Shafranskaya gardeners, Ranetka Ermolaeva, Ranetka purple, Severyanka, Ural bulk, Flashlight.
How to plant a dracaena
Flower transplantation is carried out in spring or summer. When replanting, you need to take care of the soil. The easiest way is to buy a suitable composition for palm trees in the store, but you can also make it yourself by preparing the following composition:
1/3 vermiculite.
This option is the most optimal, as it will not allow the roots to rot.
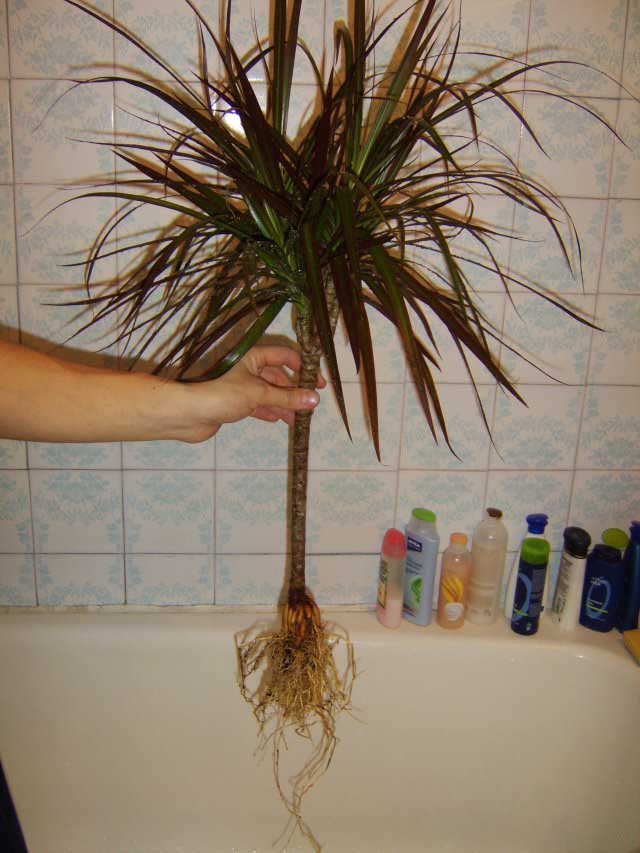


When planting, it is very important to free the dracaena from old soil. To do this, you can simply rinse the root system under running water.
The finished container requires drainage, which takes up about one-eighth of the pot, as well as holes for excess moisture to escape. After transplanting, it is necessary to feed the plant from May to September. Dracaena is transplanted once a year.
How to root cuttings before winter
Cuttings in the fall begin during or immediately after the pore of leaf fall. It is best to root the cuttings from the annual growth after a cardinal shearing of the bushes. When trying to root roses, it is not advisable to use top shoots
Also pay attention to the age of the shrub plant: it is best to take cuttings from specimens of two to five years
So, let's proceed to the procedure for cutting autumn blanks:
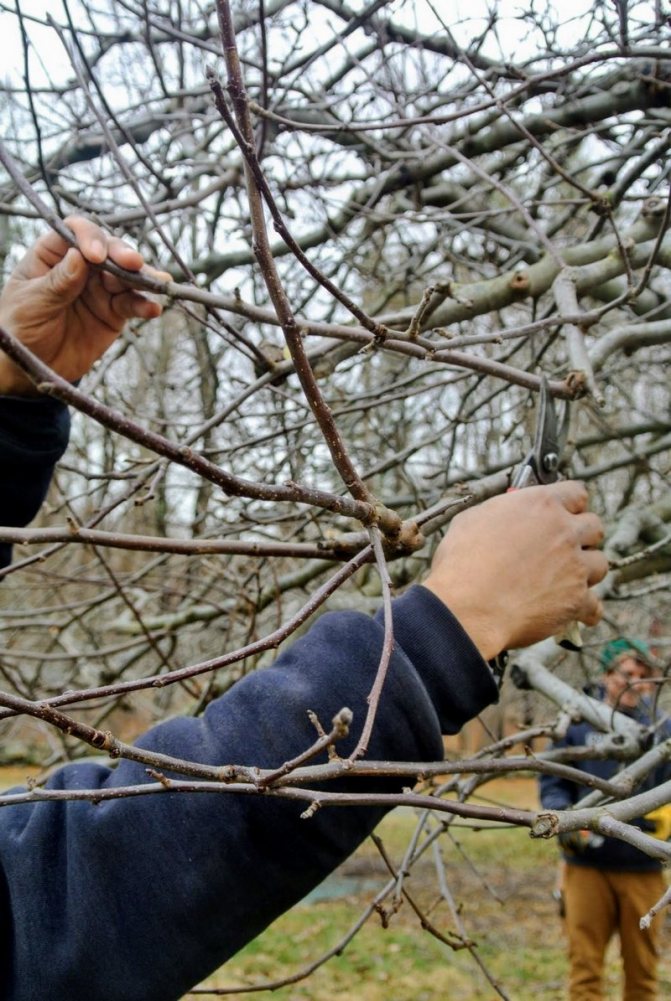
- Select cuttings for propagation that are even, neat and free of signs of disease. Depending on the plant, they are cut 8-13 mm thick and 15-30 cm long (so that there are from 3 to 5 buds).
- The upper cut should be straight and located just above the upper kidney, the lower oblique cut should be directly below the latter. At the upper level of the workpiece, you need to leave a couple of healthy kidneys, and the lower ones are cut off.
When harvesting slow-growing shrubs such as boxwood, euonymus and other evergreens, to speed up the process of beautiful formation and branching, do not remove the lower small branches from the cuttings, just trim them to one lower fork (as shown in the photo above). Everything that goes into the ground: leaves and twigs, should be carefully removed, soaked in phyto-stimulants and planted in the ground.
- Place the cut blanks in loose nutrient soil at an angle of 45 degrees (from north to south).The grooves for planting are prepared in advance, their optimal depth is 20 cm, the orientation relative to the cardinal points: from north to south - in this position in the spring, each sprout will receive maximum sunlight.
- Many stem cuttings will root faster in the fall if the bark is cut at the bottom and then immersed in rooting powder.
- After planting, we lightly tamp the ground around the cuttings so that the shoots have direct contact with the ground. If weeds appear next to the planted shrub, we remove them immediately so that the soil does not lose moisture. After that, the soil should be watered and covered with compost - mulch.
The optimal conditions that will help to safely root the cuttings of shrubs in the fall are in three important points:
- High level of air humidity around the seedling;
- Low soil moisture;
- Pretreatment of cuttings before acceleration with phytohormones.
It turns out that it is not enough just to carry out the autumn cuttings of shrubs, they also need to be properly looked after: to protect them from pests and diseases, to maintain the proper condition of the soil and air.
Gardeners recommend planting them before winter under greenhouse frames and covering them with a kind of caps made of cut plastic bottles. You can transplant rooted cuttings to a permanent place as early as next fall, that is, a year after planting.
If young shrubs look weak and undeveloped, give them another year to develop and leave them in the school again.
Grafted and rooted apple and pear trees


The vast majority of fruit trees in our gardens are grafted. In some nursery, a wonderful variety of apple or pear was planted to some stock, they sold us a ready-made seedling, and we planted it with the hope of a harvest. However, hopes are not always justified.
There are a lot of nurseries selling seedlings, and few people think about the compatibility of the rootstock and the scion. As a result, we often get sick apple trees with small fruits that are unstable to winter cold. And pears from the incompatibility of the rootstock and the scion may generally die.
An alternative to grafted seedlings are self-rooted pears, apples, cherries, plums, etc. They are grown from cuttings of varietal trees, they do not need grafting, which means that there are no compatibility problems for them. Own-rooted trees have two more advantages: they better tolerate a high occurrence of groundwater (very important for pears) and they are easy to propagate further, even by cuttings, at least by layering, at least through root shoots.
We do not in any way claim that grafted seedlings are evil, and seedlings on their own roots are ideal for everyone. It also happens vice versa. Growing seedlings of pears and apple trees from cuttings is not a panacea for all troubles and problems, but just another way of vegetative propagation of fruit trees.
How to grow your own rooted apple and pear from a cuttings
Horizontal planting of a seedling


One of the options for obtaining a rooted apple tree suggests doing without cuttings at all. But for this you need a ready-made two- or three-year-old seedling of the desired variety. Which seedling - grafted or self-rooted - does not matter.
In the spring we plant our seedling, placing it horizontally in the planting hole.
The lateral shoots of the seedling should be pulled out of the pit, set vertically and tied to pegs. At the junctions of the lateral shoots with the trunk, you can make notches, an annular incision with the removal of a strip of bark, or a constriction with copper wire to accelerate root formation.
Timing of harvesting cuttings
cuttings harvesting periodperennials are divided into two groups
TO first group
includes species with active regrowth of young shoots during most of the growing season. These include:
- all perennials with wintering aerial shoots,
- cushion and turf-forming plants;
- rhizomatous, root-sprouting, stolonic plants with herbaceous shoots, blooming in late autumn or fading early in spring, but characterized by prolonged vegetation, the ability to form summer rosettes of leaves and shoots.
from late April to mid-August
Second group
combines species with active shoots at the beginning of the growing season, sometimes continuing until flowering.


Shoots for cuttings are harvested from healthy, well-developed, fairly young (3-4-year-old) plants. In species first group
long shoots can be cut into cuttings of 3 cm or more (2-4 internodes). In this case, the lower cut is made at a distance of 3 mm from the leaf node, the upper one - 6-10 mm above the leaf node.
In species second group
not the entire shoot is cut into cuttings, but only the apical part of the young shoot with closely spaced internodes and poorly developed leaves, when the shoot has not yet become hollow. Such cuttings give a higher rooting percentage compared to more lignified cuttings from the lower part of the shoot.
The exception is peony
, from which they take the lower part of the shoot with the heel. In moisture-loving plants with large or medium-sized, but highly moisture-evaporating leaves, part of the leaf blade is shortened by 1/2 or 1/3.
How to grow an apple tree seedling in other ways
Experienced gardeners are looking for easier and more interesting methods of growing apple seedlings. One of them is to propagate the apple tree by cuttings grown in the potato tuber. You need to take a large tuber (ideally without eyes, or cut them yourself) and stick the prepared branch into it. The tuber is placed in the ground, moistened, covered with a jar and placed in a warm, bright place. The only action that needs to be taken is to moisten the earth. As practice shows, cuttings root quite quickly with this method. The cutting will take all the nutrients it needs from the tuber.
Important! All the methods described are also suitable for pear propagation.
Propagating an apple tree by cuttings, layering or a branch is not the most difficult thing. Yes, perhaps not the easiest, but definitely worth a try. You may have to master several ways before you find the perfect one. As a rule, a positive outcome is guaranteed in most cases. Usually only those who are not looked after at all die. If all the necessary conditions are met, you can grow your own apple orchard from your favorite varieties.
The main —- Fruit trees and bushes —- Own-rooted fruit: how to grow an apple tree and a pear from a cutting
In one of the previous articles, we already talked about the method of preserving a variety of your favorite apple tree (or other fruit tree) without grafting - using air layers. The method is certainly good, but there are others.
Tell me, would you like apples and pears to reproduce as easily as currants? Cut the cuttings, rooted, planted and order! Dreams, dreams ... Not such a pipe dream, as it turned out. Gardeners tried to grow a pear or apple tree from a cuttings and many succeeded. It's worth it for us to master this method, isn't it?
Plants from test tubes


Many people know about the existence of plants from test tubes, but it is difficult to call this method simple and affordable. Microcloning can be classified as vegetative propagation, but using microscopic pieces of tissue. Microclonal plant propagation at home is possible, but practically unavailable. Vegetative propagation of indoor plants in this way requires not only knowledge and skills, but also special nutrient media and equipment. However, nothing is impossible, and there are a huge number of successful examples of home experiments.
Growing under sterile conditions on nutrient media allows you to solve the problem of germination of orchid seeds. In such conditions, there is no need for symbiotic fungi, which supply the microscopic seed with everything necessary, and the seedlings are clearly visible after a few months.
Any of the selected breeding methods allows you to get a new copy of your favorite indoor plant, but good results can only be expected if you choose the optimal method and proper care. Before starting reproduction, it is worth studying the specific features of the plant.
Principles and advantages of the method
Gardeners refer to a specific part of a plant as cuttings, for example, a piece of root, a stem, or a single leaf. The vegetative method involves the reproduction of a culture with the help of a separate fragment of it, since the representatives of the flora world are able to recreate themselves even from a small particle. In modern terms, cuttings allow propagation of the original plant, preserving all its innate or acquired properties. As a result, it is possible to expand the collection of garden vegetation in a short time and without special costs.
The plant grown by cuttings has weaker immunity than the parent. You should not take slices from plants that themselves grew from a cuttings.
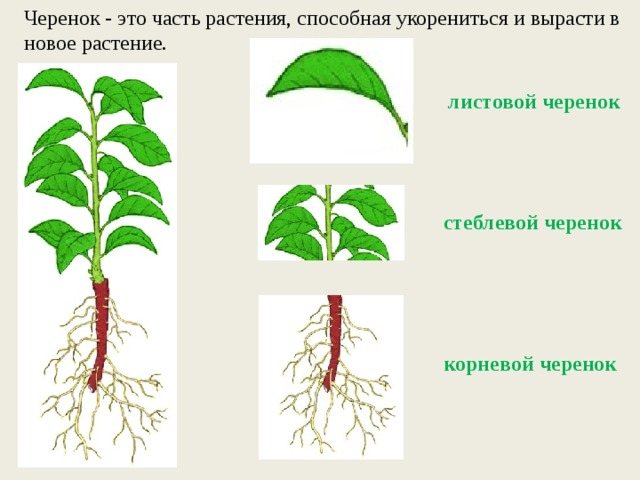

Cutting is the most popular method of plant propagation
Methods to improve rooting efficiency
Reproduction of gloxinia by cuttings, seeds. Tuber division
It is known that the process of root regeneration is regulated by growth substances - auxins, carbohydrates and nitrogenous substances. In many species and varieties, under the influence of growth regulators, the percentage of rooting cuttings, the number of roots, the quality of plants increase, and the rooting time is reduced. Some hard-to-root crops become easily rooted, but sometimes, depending on the biological characteristics of a particular species or variety, there may be no response to stimulants.
Good root stimulants are:
- Heteroauxin (indoleacetic acid (IAA)) - from 50 to 200 mg / l,
- Kornevin (indolylbutyric acid (IMA)) - 1 g / l of water,
- Zircon (a mixture of hydroxycinnamic acids) - 1 ml / l of water.
Treatment with stimulants should be done in the dark, at a temperature of + 18 ... + 22 degrees. The cuttings are immersed in the solution so that the leaves are not processed. The concentration of the solution and the exposure time must be kept exactly, exceeding them may lead not to an increase in the effect, but to a toxic effect. Therefore, it is better to use Kornevin in solution and maintain a strict exposure for 16-20 hours, and not dust the cuttings with it.