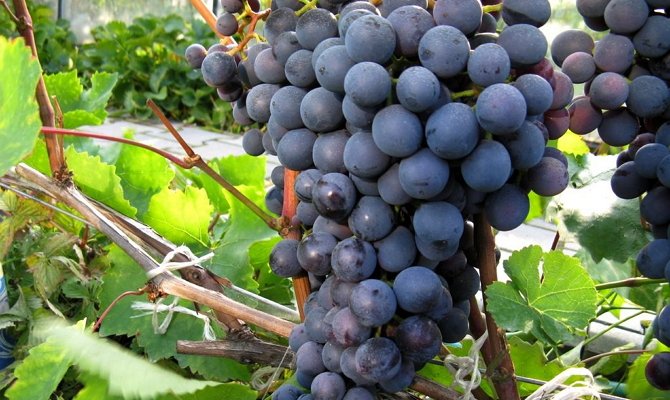
In August, the berries on the grapes ripen, and the vines themselves, as well as the buds of the next year. The harvest of not only the current year, but also the future depends on the quality of care this month. There are activities that are required during this period, but something is not worth doing.
- Removing stepchildren
- Emergency rationing of the harvest
Video: rationing grapes, thinning bunches
- Video: caring for grapes in August
- Video: a very simple way to root cuttings in the summer
Proper care of grapes in autumn

Grapes as a culture have been known for over a thousand years, the name comes from the Latin word "vitilis" and means "climbing". This plant is long-lived: even without special care in natural conditions, healthy bushes could live up to 150 years! But since 1963, grape phylloxera, an insect pest that feeds on the roots of the plant, was brought to Europe from America. Later in the article, we will learn how to care for a vineyard in the fall. What to do in October and how to water and prune in winter.
Signs of maturity


The most important indicators for determining when to pick berries are:
- Its sugar content.
- Acidity.
The industrial ripeness of grapes differs from the technical condition of the fruit. This means that the fruits contain as much sugar, acids and other substances as needed to obtain the desired type of wine (table or dessert). Technical maturity is determined based on the results of chemical analysis.
In addition to this indicator, it is important to distinguish between the full and physiological maturity of the fruit. When the fruit is fully ripe, the level of sugar and acids stabilizes for a certain period, mainly for several days.
Main care activities in September and October
Modern varieties, most of which are obtained by the selection method, resistant to many diseases and adapted to various climatic conditions and regions. But in order to get stable, high yields every year, to increase the immunity of grapes, to maintain the size of the berries and all their qualities, you need to work on preparing trees for winter:
- phased pruning of the vine;
- abundant watering;
- top dressing;
- treatment against pests and diseases;
- grape roots catarovka;
- shelter of plants in the winter.
Let's consider in more detail what each of these actions is, their benefits for the plant.


Autumn pruning of grapes
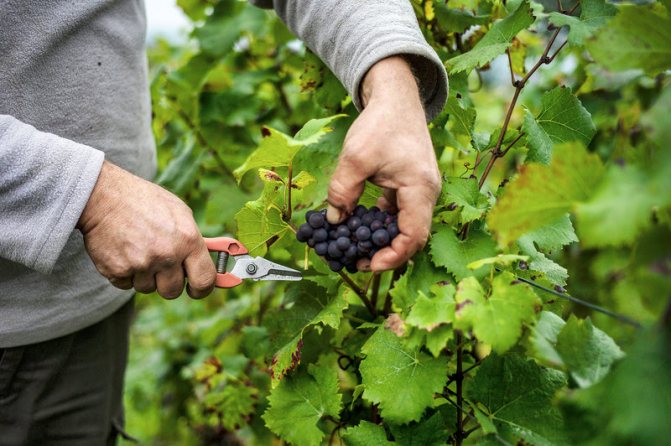
Harvesting rules


To get a high-quality harvest, you should know how to cut the fruits correctly:
- An unsuitable time for harvesting is considered too early in the morning and rainy weather.
- The work is carried out in several stages, as the brushes mature. To obtain accurate results, a hydrometer is used to measure the amount of sugar. This process is troublesome, but it pays off with the high quality of the harvested crop.
- Farmers advise harvesting berries precisely in the pre-lunch hours, when there is no dew on the brushes.
- If a lot of rotten berries appear in the bunches, the harvest time is slightly accelerated. Rotten berries can not only affect the quality of products, but also cause all kinds of diseases in a wine drink.
- When the collection is completed, it is imperative that the grape bushes be examined with the discard of rotten and still green fruits.
Rules for pruning grapes in winter in the fall
This is a necessary event that has a very beneficial effect on the development of the plant:
- the bushes are rejuvenated every year, the yield is significantly increased and the berries are much larger than those of uncut grapes;
- the ripening of the crop is faster by about 10 days;
- facilitates the care of the bushes and their processing.
It is recommended to prune bushes in two stages: in mid-September and in October after the last harvest. Of course, these terms are approximate, because it is necessary to take into account the region and climatic conditions.
The first preliminary pruning takes place in September. The bushes are freed from dry, diseased branches, which must be burned in order to avoid the spread of diseases. Remove 10-15% of the growth of shoots grown on the main trunks (sleeves) above the upper wire (60 cm).
Closer to the root, in the place of branching, replacement knots are formed annually: the growth part is left, the fruit bearing this year is harvested. Cut the strongest young vines closer to the root as follows:
- the shoot from the outside of the sleeve is cut off, leaving 3 buds on it;
- 1-2 shoots from the inside are left under the fruit arrow and cut off, leaving the number of eyes equal to the diameter of the vine + 1-2 buds (for example, if the diameter is 6 mm, 7 eyes are left).
If the variety gives not very large weighty bunches (up to 500g), then you can leave another 2-3 more buds.
Removing leaves in the area of bunches
The bunches are poured due to the leaves growing above the vine, and the lower ones by August turn into useless parasites. As a result of their removal, the strength and juices will not be wasted. In addition, the bottom of the bush and berries will be better ventilated, illuminated and warmed by the sun. But if it's hot, the vineyard is under the scorching sun from morning to evening, then the berries can bake and get burned. In this case, it is necessary to leave the leaves shading the bunches.
It is recommended to arrange the rows of grapes from north to south. Then the sun will illuminate one side of the bushes in the morning, and the other in the afternoon.


The lower leaves must be torn off: they take away nutrients, but do not bring benefits
Last autumn watering
After harvesting, the grapes are watered as needed so that the plant does not dry out. If the weather is humid, rainy, then the bushes do not need to be watered, with the exception of one plentiful moisture-charging irrigation before winter.
The most convenient way is to dig in pipes while planting grapes in order to supply the plant with the necessary moisture and liquid fertilizers. But if you have not done this in advance, you need to make small holes or grooves around the bush so that the water does not spread, and the root is saturated with moisture as much as possible. After that, the soil must be loosened, saturated with oxygen. These activities will help the plant overwinter.
Autumn vineyard pruning
Autumn pruning of grapes is carried out after the entire harvest has been collected and the foliage has completely fallen off. Usually damaged, old, excess shoots are removed. In addition, all vines are also subject to pruning, 5-7 eyes are left on them, and all excess is carefully cut off with a pruner.
In the middle of the bush, all excess shoots are removed, leaving only two. They are also cut off, leaving no more than 8 eyes on them.
The vineyard should be pruned every year after the end of fruiting in order to form the bushes correctly, avoiding excessive overgrowth.In addition, every 4-5 years, fruiting whips should be renewed, cutting out old and leaving new young shoots.


Autumn pruning of the vineyard is designed to properly form the bush
Timing of top dressing for the vineyard
Fruiting, of course, takes a lot of vitality from plants., therefore, autumn feeding is recommended during the preparation of the grapes for winter. This will guarantee a good harvest next year. It will be enough to add a little aqueous solution of potassium and phosphorus fertilizers under each bush: potassium nourishes the grape root, and phosphorus strengthens the immune system.
The soil must be loosened after watering and fertilizing. Organic liquid fertilizers should not be applied; it is best to mulch the soil around the grape trunk with rotted manure mixed with wood ash in winter.
Weeding the vineyard
The berry does not ripen on time if the plant is uncomfortable. Weeds rob the vine of the essentials. Perennial grasses have amazing vitality, displacing other crops from their territory. They create a dense turf layer. The roots of the grapes are uncomfortable, the plant is inhibited. Top dressing will only aggravate the situation.
With regular weeding, the roots of the weeds become thinner, the soil is enriched with oxygen. When the grass is harvested, the sunlight warms the ground more, the vines are warmer at night. The movement of juice in cells is accelerated.
After good weeding, removing all the green cover, the grapes begin to ripen before our eyes. If you still feed him at this time ... But read on about that.
How to properly spray crops
Immediately after the last harvest, you need to start treating the grapes with chemical solutions. There is no need to delay with this, since pests and diseases can cause serious damage to the vines in a very short time. Processing of early varieties should be carried out without waiting for the end of the grape harvest from later varieties. Correct spraying is carried out in calm dry weather, when rain is not even expected.
Treatment with copper and iron vitriol is recognized as the most effective. If there are no traces of a fungal infection on the grapes, the spraying can be divided: in the fall, treat it with copper sulfate (dissolve 100 g of powder in half a liter of warm water, and then add the solution to 10 liters with cold water and spray from a spray bottle), and in early spring, before budding, process with iron sulfate.
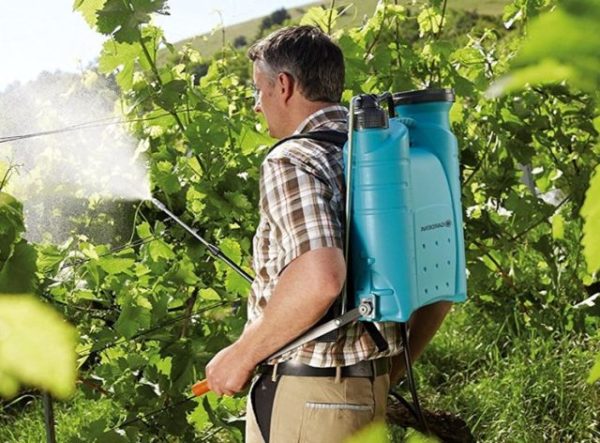


Processing grapes from hit in the fall
ZhK is very effective in combating all types of fungal diseases and saturates the plant with all the necessary trace elements. Thus, the vine receives protection and foliar feeding at the same time. For the solution, it is necessary to dissolve 300 g of ferrous sulfate in 10 liters of water and abundantly spray the vine and soil around the trunk.
If traces of fungal infections in the bushes are found in the fall, the treatment with copper and iron sulfate is carried out simultaneously.
There is another option that experts recommend: the autumn processing on the leaves is carried out with a soda-salt solution - for 10 liters of water 5 tablespoons of salt + 5 tablespoons of soda. It is necessary to spray 3-4 times in the beginning - mid-October, very carefully processing each leaf, vine and soil around the plant. In this case, the treatment with copper and / or iron sulfate can be carried out immediately before the vine is sheltered for the winter.
How to choose a grape variety for growing in Belarus
The weather conditions in Belarus are not very suitable for classic grape varieties. Here they often suffer from frost in winter and high humidity in the warm season. In addition, many of them do not have time to mature in a rather short summer by southern standards with a few hot days. Grapes and swampy soils with a high level of groundwater and a high content of peat, which occupy most of the country, are not beneficial.
There are advantages in northern viticulture. In Belarus, phylloxera (grape aphid), which has become a real scourge of southern vineyards, phomopsis (black spot) and viral infections are almost completely absent. For a long time, Belarusian winegrowers rarely encountered fungal diseases. But in recent years, due to the active import of southern seedlings into the country and global climate change, cases of infection of grapes with mildew, oidium and anthracnose have become much more common. But all the same, the level of spread of these infections is much lower than in the south.
In order to succeed in growing grapes, experienced gardeners are advised to choose varieties that meet the following criteria:
- winter hardiness;
- early and super early ripening;
- the ability to ripen when the sum of active temperatures is below 2600 ° for the southern regions and less than 2400 ° for the northern ones;
- quick recovery of the vine after damage caused by low temperatures;
- the presence of immunity to fungal infections.
Video: Belarusian winegrower talks about the intricacies of the selection of varieties
What is and why do you need katarovka
Catarovka of grape roots is the removal of small roots located at a depth of 20-25 cm from the surface, such roots are also called dew roots... Since they are located close to the surface of the earth, they take moisture and food from the surface layer. With a prolonged absence of watering and precipitation, dew roots can dry out.
In winter, even with light frosts, when the soil freezes at least up to t -5 °, there is a danger of freezing. In addition, it is the dew roots that are most susceptible to infection with phylloxera (very small grape aphids that live and feed on the roots).
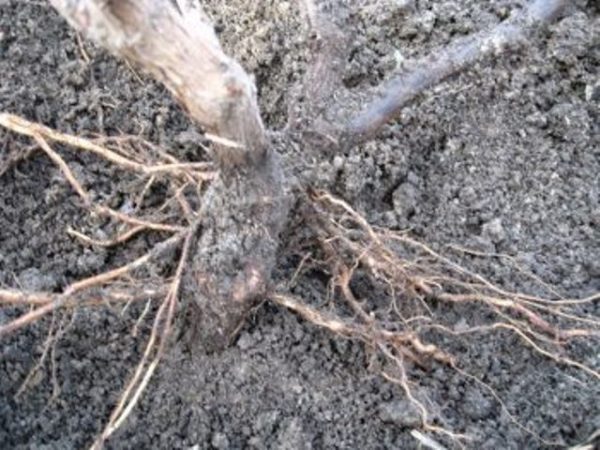


Catarovka grapes in autumn
To avoid all these troubles, catarovka is carried out: small roots are removed and this contributes to the development and deepening of the calcaneal roots (deep). But this process is quite laborious and dangerous for grapes, so you need to cut the roots with great care. Catarovka of the roots of young plants is carried out 2 times a year - in June and August. If the bush is not young, in addition to small dew roots, it can also have rather thickened ones. Their cutting should be done with extreme care and gradually - over 2-3 years.
Technology: the soil around the trunk is dug to the desired depth. The roots are cut with a sharp pruner without leaving knots. Sections can be disinfected with 3% copper sulphate or 1% boric acid solution, dried and covered with soil again.
In order not to repeat this procedure every year, the cut part is wrapped with a film in 2-3 layers (weakly, with a margin of 3-5 cm), or a plastic corrugated hose cut along the length, tied with natural twine and only then covered with earth.
For such plantings, it is very important that the grapes have a developed, deeply rooted root. On personal plots, it is not necessary to carry out this event, since timely feeding, watering and sheltering the bushes for the winter is possible.
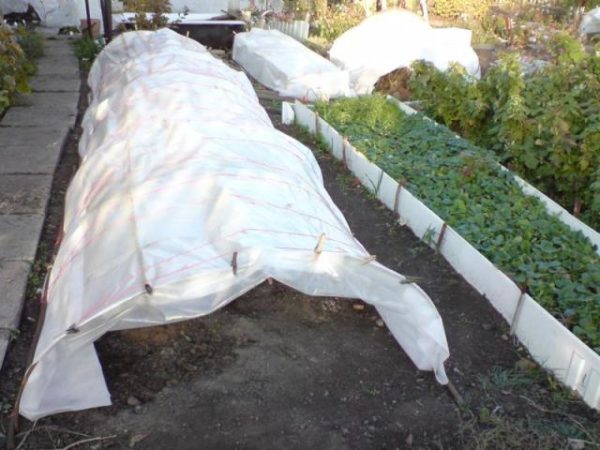


Shelter of the vine for the winter with ducking
We remove part of the harvest
Experienced gardeners usually know why the grapes have not ripened. For beginners, experts recommend starting with a yield estimate. There are certain norms of fruiting, they are established empirically:
- in large-fruited varieties with bunches of up to 0.8 kg, one brush is left on the shoot;
- a vine 1.5 m long is capable of feeding clusters weighing up to 0.5 kg;
- on table grapes, it is recommended to leave two brushes per shoot;
- bunches of technical varieties are best reduced to 0.2 kg per shoot.
Part of the crop is harvested in two ways:
- on each shoot, the vines are left with one bunch, the rest are removed, the released flow of nutrients is directed to the only pagon, it ripens faster;
- the brush will mature faster if it is thinned: remove the small, greenest and densest berries, uneven, crushed by the neighboring ones, pluck out carefully so as not to damage the bunch.
Practice shows that the ripening process is noticeably accelerated when the grapes are freed from 1/5 of the expected harvest. If you want to keep all the bunches intact, choose another method of stimulating photosynthesis.
Shelter and preparation of young vines for winter
After harvesting, grape bushes are sheltered for the winter, especially if there is little snow in the area. To do this, the vine is removed from the supports, the branches are loosely tied and laid on the ground. It is best to cover the vines with spruce branches - branches of pines and firs. Such a shelter provides good air circulation, traps snow cover - creates ideal conditions for wintering.
You can cover the top with a film, leaving gaps for circulation.
All these measures are necessary to protect the grape culture, for long and abundant fruiting. Whether you are in Crimea, Krasnodar or any other region suitable for growing grapes. Although the vines are not very whimsical, good care helps to obtain stable yields for many years - after all, grapes can grow and bear fruit for more than 100 years!
Propagation of grapes in August by cuttings and layering
At the same time, you can multiply your own or your favorite neighbor's grapes. Popular methods in August:
- Green cuttings. The very stepsons who shortened to two sheets are suitable. By August, their stems are already hard, and the leaves are fully grown. Break out stepchildren and root in moist and loose soil mixture. But you can cut cuttings from unnecessary shoots (barren vines, overgrowths).
- Layers. Mature bushes of grapes in summer give growth from the base of the bush. If you need to propagate a variety, then leave such a shoot, and root it in August. To do this, the shoot is cleaned of leaves, leaving them only at the top, placed in a groove and covered with moist and loose soil. It is better to leave separation from the mother bush until next year.
Features of care in the fall
Taking care of the grapes in the fall should take into account the characteristics of its ripening. If the fruits ripen before the end of August, the autumn maintenance of the vineyard will not be difficult.
Watering grapes in autumn
After harvesting, the grapes are watered if it is hot outside. At a moderate temperature, watering is carried out at the end of October, so the plant receives the required amount of moisture.
Top dressing
Fertilizer is applied in early September. At the same time, they mix:
- potassium magnesium - up to 70 g;
- superphosphate - up to 100 g.
The resulting mixture is poured under 1 grape bush. Half the dose is enough for a young plant. The bushes are fertilized for the second time after 2-3 weeks.
Ringing grapes
They make a ringing of 3-year-old bushes, earlier it is dangerous to touch the vine. Shoots ring at the very beginning of flowering. With a grafting knife, carefully remove a narrow strip of bark (no more than 5 mm) from the shoot, put on a ring 3 mm wide. There should not be large gaps, the place of the cut will float with a drop, the plant will weaken.
The procedure is carried out to limit the supply of nutrients to the upper part of the shoot. Water from the roots will continue to flow. Ringing is aimed at stimulating the ripening of berries, the place for the incision is chosen above the brush. Vineyards ring no more than once every three years. He gratefully responds to the procedure of small sweet varieties of grapes grown in the zone of risky farming: "Kishmish", "Korinka". The ripening period is reduced to two weeks.
Ringing is carried out not on all shoots, but only on one with a darkening bark. For the ring, use thick paper or film. Annealed steel wire oxidizes over time, it is better not to use it. The ringing tool is pre-disinfected.
Pruning
In vineyards, pruning work is carried out in the fall, this allows the bushes to form better and give larger yields in the future. Timely pruning affects the number of berries set in the next year and their taste.
Late October-early November is a good time for the formation of a bush that needs shelter in winter. On the fallen leaves in the fall, set a period for pruning the grapes. After the colored foliage falls, they wait 14-21 days and start pruning. During this time, the branches are saturated with useful substances.
Late pruning will damage the twigs of the plants. At low temperatures, shoots become brittle and break easily.
Pruning rules
Pruning grapes begins with the removal of diseased parts and branches with damage. A burning pit is being prepared for them. This helps prevent disease and pests from spreading to healthy bushes.
All shoots are not pruned: they can be useful for replacement. If all or part of the crown dies, the replacement shoots will be able to replace the entire bush.
Pruning methods
Grapes are pruned in autumn in different ways:
- Short pruning involves the elimination of a large part of the shoots; only 2-4 eyes are left on the twig. Pruning is suitable for sprouts needed to replace a dead bush.
- Medium pruning involves leaving up to 8 healthy eyes on each shoot. The arrowhead consists of 50 kidneys. The type of pruning allows you to get a frost-resistant variety with healthy vines.
- Long pruning assumes that up to 15 eyes will be located on the shoot, the total number of buds - up to 60. The stem consists of 4 side shoots.
- Mixed trim is a combination of short and long. Shoots are pruned for replacement, branches are left to ripen the future harvest. Using the method, a loop is formed, the vine is removed after fruiting, and a replacement sprout appears instead.
A mixed method for growing a plant at home is considered the best. With it, the bush is renewed, the fruits increase in size, their taste improves.
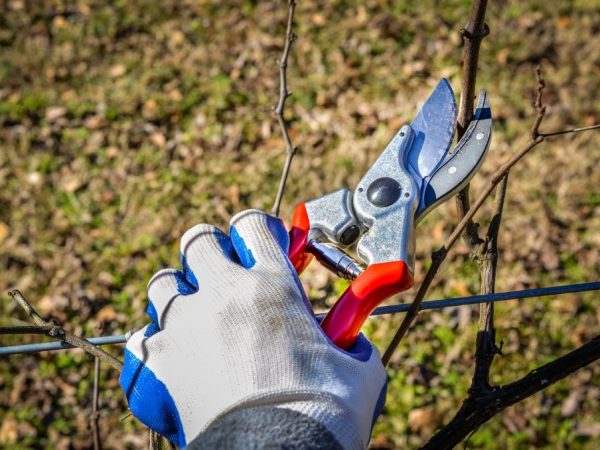


Pruning the vine for a better harvest
Grape pruning 1st year
In the first year, the bushes are not pruned in the fall. If the bush has curvatures or damage, the haircut is carried out in the first year, leaving 2 healthy eyes.
Pruning a 2nd year plant
In the second year, a vine of 2 buds is formed on the bush, in the spring it is reduced by 4 eyes. In the fall, each peephole on the branches adds a branch, the result is a bush of 8 sprouts. There are 4 branches on each side of the trunk. At the end of autumn, 2 large shoots are selected each, others are cut, and the stumps are left, since when the trunk dries, it can burst.
By the age of 2, 4 strong sprouts grow. In the fall, pruning is carried out in a long way, in the spring they are shortened by 4 eyes.
Pruning grapes of the 3rd and following years
In the fall of the 3rd year, the grape bush has 4 large stems, 4 branches on each of them. For pruning a bush of the 3rd year in the fall, the largest shoots on each side are chosen, 2 weak branches are subject to pruning.
After pruning, they try to graft the branches. Of the large remaining sprouts, 1 must be shortened by 3 eyes (it will become a replacement sprout), the other remains with 12-15 buds.
In the third year, the bush is rejuvenated, which bears fruit in the future. In the fourth year, pruning is carried out, as a result of which the yield will increase, the vineyard grows stronger.
In the autumn, in the 4th year of the growth of the bush and in all subsequent periods, when pruning, the vine is removed after fruiting, new growth buds are formed on the replacement shoots.
Top dressing after pruning
After the end of pruning for the winter, grape shrubs are fed with fertilizers. The following fertilizers help accelerate the maturation of young shoots:
- wood ash - 500-650 g;
- potassium sulfate - 20-25 g per bucket of water.
Use additional feeding:
- superphosphate - up to 80 g;
- phosphorus-potassium fertilizers - 60-75 g;
- potassium chloride - up to 30 g;
- manure - 10 parts are mixed with 1 part of superphosphate.
Top dressing is applied on 1 m² around the base of the bush.
Non-covering varieties
Grapes are a thermophilic culture. In the conditions of Belarus, he needs shelter for the winter. Only some varieties, the winter hardiness of which exceeds -28 ° C, can endure the cold season without it. For example:
- Minsk pink;
- Lepsna;
- Alpha;
- Somerset Siddles;
- Sharov's riddle;
- Marshal Foch.
Lepsna
A universal grape variety of Lithuanian selection. Easily tolerates air temperatures below - 28-30 ° C. In addition, this variety is highly resistant to mildew and gray rot, and medium - to powdery mildew.
Lepsna bushes are vigorous, ripening well along their entire length. Berries are dark red, weighing 3-4 grams, form small cylindrical clusters of medium density. The pulp is fleshy-juicy, harmonious taste with a light labrusca aroma. It contains up to 19% sugars with an acidity of about 5 g / l.
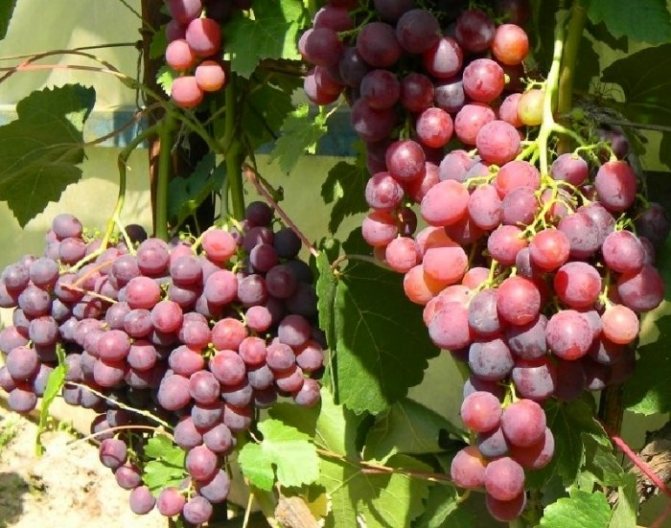


Lepsna berries tolerate transportation and storage well.
In the conditions of Belarus, Lepsna ripens 100–110 days after the leaves bloom. Its berries are eaten fresh and used for making juices, wines and compotes.
Somerset Siddles
Seedless grape variety originated in the United States of America. Possesses unique winter hardiness. According to various sources, it ranges from -30 to -34 ° C.
Somerset Sidlis vine has medium vigor. The berries are light pink in color with a very juicy and sweet pulp with a delicate strawberry flavor. They ripen within 110-115 days after the beginning of the growing season. Rudiments of seeds in berries are quite rare.


Somerset Seedlis is a very hardy, seedless grape variety
Somerset Seedlis is immune to most fungal diseases, but often suffers from attacks by wasps attracted by its sweet and aromatic berries. The yield of the variety is average.
Recent Entries
Rose Petal Jam and Its 7 Health Benefits You Likely Didn't Know About What Fruit Are You According to the Zodiac Sign 11 Best Grape Varieties That Will Help You Create Unique Homemade Wine
In my conditions, one of the few who survived the rehearsal of nature without tangible losses, loaded with fruitful shoots, pleases. Last season, no rudiments were found when eating. A good replacement for the ubiquitous growing in our places Alpha.
serge47
Marshal Foch
A technical grape variety belonging to the group of Franco-American hybrids. Easily withstands frosts down to -29 ° C, and according to some reports, even up to -32 ° C. Marshal Foch is included in the State Register of Varieties of the Republic of Belarus.
The vines of this variety are characterized by medium vigor. The berries are round, small, dark blue. They produce high-quality rosé and red table wines with good coloration.
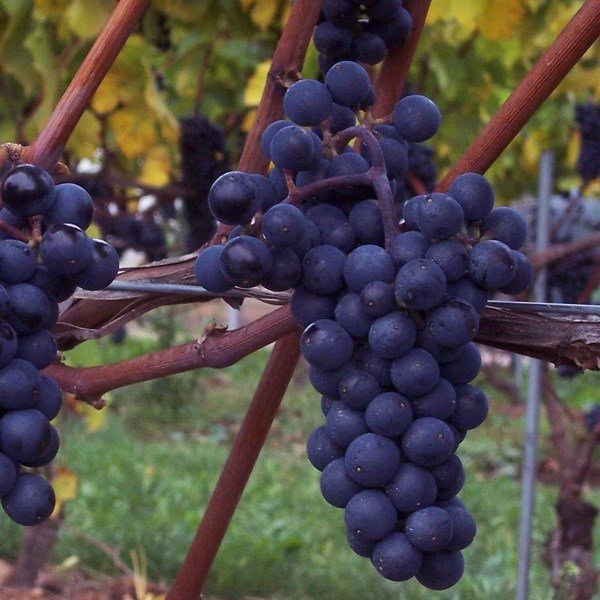


The Marshal Foch grape variety was named after the head of the French Armed Forces during World War I, Ferdinand Foch.
Marshal Foch is resistant to mildew and oidium. The yield of the variety is average. To increase it, experienced growers practice overloading the bush with eyes, followed by a fragment of infertile shoots.
The wine was made. It turned out almost 5 liters. Yesterday we made a test tasting with family. So dark, thick, rich! For me, a beginner and loved ones, just awesome. Urgently, the remaining 4 liters, I corked and put in the cellar for storage. At least until spring. This year the wine from MF is the best! This is a preliminary estimate.
Dima Minsk
Preparing for winter
Pruning is the initial stage of preparation for winter, after it is carried out, shoots are removed from the trellises, the shoots are tied. When the temperature changes to -3 ° C-5 ° C, the plant is covered for the winter.
There are the following methods of sheltering vineyards in late autumn:
- The ground. A pit-trench 25 cm deep is prepared near the base of the vineyard.The previously removed vines are sprayed with insecticides against pests and placed in a pit, top them with a 20-30 cm soil layer. Pegs are placed for spring detection. The method is not suitable for cities in the northern regions due to heavy rainfall: this leads to wetting of the earth and wetting of the vine. The bush rots and freezes.
- Dry. Grape sprouts are placed on the ground, hay, sawdust or mulch, and they are covered on top with a material that does not allow moisture and precipitation to pass through. Suitable plastic bags, tarpaulin, roofing felt, nylon films. From above they are fixed with clamps or staples. During the wintering period, a microenvironment is formed under the shelter. Untimely removal of the shelter provokes the development of fungal diseases.
The constructions protect against rodent penetration. Poison is placed in the center. The penetration of dangerous inhabitants harms the grape bushes, they destroy the buds and vines.
We save yeast
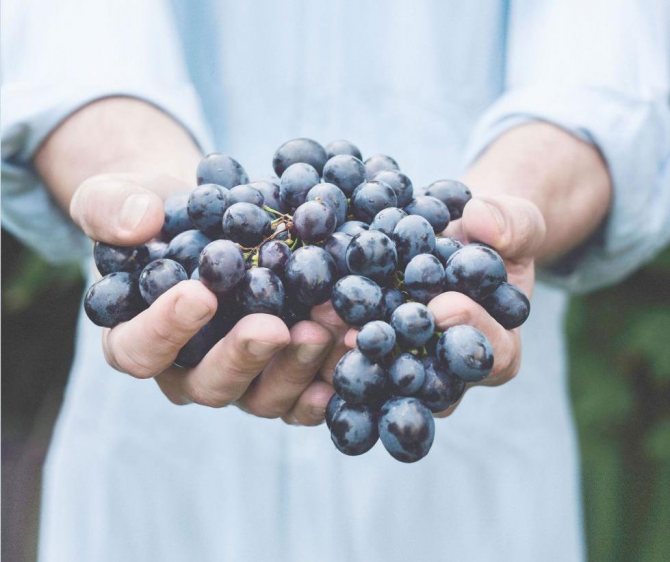


Wine newcomers, using traditional recipes, prepare wine using wild yeast. Colonies of microorganisms "live" in abundance on the surface of grapes. To start the natural fermentation process, it is necessary that such "savages" get into the wort. Otherwise, the sugar contained in the berries will not ferment in its entirety or will not ferment at all. For this reason, the grapes are not washed before processing. If the berries are heavily soiled, wipe them with a dry cloth.
To preserve the greatest amount of wild yeast, winemakers advise following simple guidelines during the harvest:
- There is no need to pluck bunches of berries immediately after the rain, as well as for three days after it. This is due to the fact that most of the yeast is washed off by streams of water, and it takes time to breed those that remain alive. If it rains a lot in the summer and it is not possible to find the best time to harvest the grapes, it is necessary to prepare in advance a homemade sourdough that can support fermentation in the future.
- Winemakers advise against cutting off the fruits early in the morning, while the dew is still lying, as well as at night, when it has already fallen, and in fog. In addition to the fact that excess moisture adversely affects the state of the yeast, it also spoils the taste of future wine or champagne, making them watery. When the grapes are cut at the wrong time, putrefactive processes are activated already in the warmth. If there are rotten grapes in the bunch, they can infect all their neighbors in a short period of time.
- The grapes, which were grown for the preparation of wine drinks, are harvested by cutting off the bunches with scissors or pruning shears. At this stage, it is important not to damage the plaque on the fruit. To avoid this, the bunches are held by the petiole.
- To minimize damage to the grapes after cutting the bunch, they are stacked in flat containers for safe transportation. The use of buckets and similar containers is not recommended.
Autumn watering
Regardless of whether it is old or young grapes, care in the fall, preparation for winter, first of all, requires water-charging irrigation. While berries are still hanging on the vine, it is impossible to flood the culture with water strongly. The berries will begin to crack from excess moisture. Wasps, bees, small flies will flock to the sweet juice and the crop will be spoiled.
Watering the grapes begins in the fall after harvesting the berries. Often it is not necessary to fill the bushes, but the soil should be kept moist. After the return of the crop, the roots require recharge. The amount and intensity of watering are determined by growers intuitively, guided by the weather, the state of the soil, the depth of the underground water layers. Despite all the nuances, in October the vineyard is necessarily poured abundantly with water once. In order for moisture to penetrate precisely to the roots, grooves are dug in the ground around the bush or holes are drilled with a drill.
You need to take care of the grapes wisely, that is, do not pour water under the bush just like that. First, the composition of the soil is taken into account. Loose soil, sandstones absorb a lot of moisture and do not retain it.On such soil, a bush of grapes is poured into 60 liters of water. Heavy soil with admixtures of clay or black soil poorly permeates moisture, retains it. Vineyard care in such a plot is reduced to minimal watering. It is enough to pour 25 liters of water under the bush.
In the video, grapes, care in the fall, methods of water-charging irrigation:
Termination of watering
In August, fruiting grapes are not watered, on the contrary, they are protected from rain by installing visors or organizing the outflow of water from the roots. You can cover the ground with a film or lay sheets of slate with a slope from the bush. Excess moisture in August leads to cracking of the berries, and the plant itself begins to actively throw out green shoots to the detriment of the ripening of the vine.
By maturing vine growers understand lignification of shoots, covering their surface and buds with brown bark. A green, immature vine will not survive the winter. Lignification occurs from the bottom up. The more buds the vine ripens, the richer the harvest will be and the easier the formation will be, there will be a choice: which buds and shoots from them to leave, which ones to remove.
Pruning for the winter
One of the important stages of caring for grapes in the fall is pruning the vines for the winter. The procedure has the following positive aspects:
- After pruning in the fall, the bush is rejuvenated in the spring. The yield increases. The berries grow larger than uncut grapes.
- After pruning in the fall in the grown young stems, metabolism and the movement of sap occur more intensively. The berries ripen faster.
- Pruned vines withstand severe frosts better.
- A neatly shaped crown of grapes is easier to care for.
- Pruning diseased and diseased branches reduces the likelihood of spreading the disease throughout the bush.
Leaving associated with pruning grapes begins after leaf fall. The vine goes into dormancy in the fall, and the removal of branches is painless. Before the leaves fall off, the branches cannot be cut off. Such withdrawal will only harm the culture. Until the bush has thrown off the foliage, the process of photosynthesis continues in grapes. Early removal of leafy branches in the fall will weaken the vine. The grapes will not have time to accumulate nutrients that help to endure the winter easier.
It is also impossible to delay with leaving. Pruning too late with the first frost in the fall will cause unexpected damage to the vineyard. The vine becomes fragile in the cold. During pruning, the branch may crack in an unnecessary place.
Vine care begins with the removal of diseased, dry and damaged shoots. The branches are burned immediately after pruning, as they are infected with pest larvae and fungal spores. The next stage of care is the formation of the bush in the fall. In the vineyard, cut off the extra branches. The scheme for pruning a vineyard in the fall may differ for each variety, but in general terms, caring for a bush takes place according to the following principle:
- The load of the bush is regulated by shortening the annual branches. Two buds at the base of the shoot are not counted. They are not considered mature. For example, if a feature of a variety requires shortening the shoot by 4 buds, then taking into account two unripe buds, six of them are obtained.
- They start leaving in early autumn at the beginning of September. All young growth on the old vine is removed, the tops of which rise from the ground level by 60 cm. The branches, the tops of which rise 30 cm from the ground level, are shortened by 15%.
- Further maintenance of the grapes, related to pruning, continues in October. The process is aimed at the formation of a bush in the fall. Fruit branches and replacement knots are left on the vine. First, the lower strong, but short shoots are cut into three eyes. The knots of replacement are obtained from them. The upper long branches on the bush are shortened by six eyes, forming fruit arrows. The eyes may be less or more, depending on the varietal characteristics of the grapes.
The cut sites are treated with garden varnish, which protects the wood from infection.
The video shows the care of the vine in the fall:
Timely harvest, protection from wasps and birds
In August, the harvest is already ripe for early and medium varieties. Collect it on time. Do not overdo the ready-made bunches on the bushes, this slows down the formation of bark on the vines. In addition, overripe berries can crumble, crack, rot in damp weather, and turn into raisins in hot weather. The ripening berries attract wasps and birds. The most effective and inexpensive way to protect crops from winged fish is a fine mesh netting. You can cover the bushes completely or make bags for each bunch.
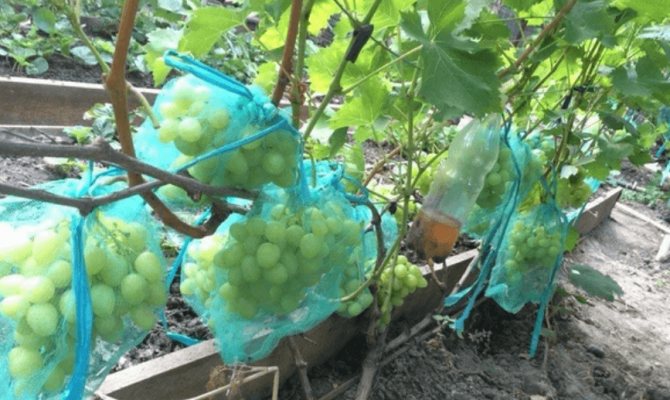


These bags can be bought or sewn by yourself.
Top dressing and tillage
Taking care of the vineyard is not complete without top dressing. In the fall, after harvesting, the crop is in a depleted state. In order for the vine to overwinter and give a good growth in spring, it needs to restore the lost strength.
Leaving in the fall means feeding the crop only with phosphorus and potassium. From mineral fertilizers, 40 g of superphosphate are applied under an adult bush. The substance enriches the grapes with phosphorus. From potash fertilizers, 30 g of potassium sulfate or potassium magnesium are applied. Many gardeners give preference to potassium monophosphate, contributing 40 g of the substance under the bush. Dry mineral fertilizers are diluted in a bucket of water, poured under the root, combining top dressing with watering.
Instead of mineral fertilizers, fertilizing in the fall can be done with organic matter. Under an adult vineyard, 300 g of ash or 15 kg of compost are introduced. The organic matter is dug up with the soil to a depth of 30 cm, departing from the trunk 50 cm.
Feeding the vineyard
In rainy, cool weather, it is useful to replenish the supply of potassium and phosphorus. The following is introduced into the soil:
- ash of deciduous trees;
- potassium nitrate (potassium chloride impairs the taste of berries, adds bitterness);
- superphosphate;
- complex mineral fertilizers for berries with a low nitrogen content.
Fertilizing with organic matter during the ripening period of the crop is ineffective, nitrogen causes rapid growth of shoots. The vine ripens more slowly.
During the growing season, the vineyards are fed several times:
- in the phase of crown formation, the plant is given nitrogen;
- during the budding period, foliar feeding is carried out with boric acid or flowering stimulants;
- at the stage of "peas", when the active formation of brushes begins, the main macronutrients are needed: potassium, phosphorus, calcium - they prevent the berries from cracking, make the skin dense;
- during the ripening period for sugar content, potassium, magnesium, zinc are introduced.
The last feeding is done 4–5 weeks before the onset of frost, the bush needs time to rest before hibernation.
If there are enough nutrients in the soil, to stimulate ripening, instead of root complex feeding, sprinkling with preparations containing boron is carried out. It is permissible to use the drug "Ovary" with amino acids that accelerate intercellular metabolism.
Protection against diseases and pests
An important process of caring for grapes in the fall and preparing for winter is the preventive protection of the vine. The choice of a spray product depends on the condition of the vineyard:
- If, during the inspection, traces of mildew are revealed, the affected shoots with leaves are cut off and burned. The vineyard is sprayed with "Folpan", "Ridomil" or another similar preparation.
- If signs of oidium are detected, the vine is sprayed with any preparation containing sulfur even before dropping the foliage in early autumn.
- Against anthracnose, drugs used to treat oidium and mildew are used.
- When, when examining the grapes in the fall, traces of a leaf roll are found, the bush is treated with a decoction of tobacco or medicinal chamomile.
- The raining of berries and bunches in early autumn may be associated with cercospora. The disease still manifests itself in brown spots on the leaf plates. For the care of a sick vineyard, use "Fundazol". "Polychoma" helps a lot.
- In the fall, ticks like to get along on the vine. Most often, they sit on the tops of young branches. A measure of getting rid of the pest is pruning the tops of the shoots.
- In the case of the development of gray rot in autumn, the processing of the culture is carried out with "Euparen" or the preparation "Skala".
Healthy bushes also need preventive care. The vineyard is sprayed in late autumn after leaf fall with a 3% solution of copper sulfate.
Chasing
Removal by pruning the tops of vines with young and still small leaves is called chasing. The bush spends strength on the development of these leaves, to the detriment of the filling and coloring of berries, the ripening of the bark and buds. By minting, we correct this situation, exclude the consumption of vital juices for unnecessary greens. It is necessary to cut off the upper part of the vine, 30–40 cm long, to the first well-developed, already hardened leaf.
But it will be a mistake to carry out the chasing if the crown (hook) at the top of the shoot has not yet straightened out. This means that the vegetation of the shoot continues. The bush will respond to its shortening by the violent growth of the stepsons, or even worse - the buds of the next year will wake up. Therefore, it is often necessary to cut vines not all in a row, but selectively only those that have stopped growing. This is evidenced by a straightened crown.


The crocheted top of the shoot speaks of its growth, it is too early to be minted
Shelter for the winter
Caring for grapes in cold regions is not complete without another important activity - the shelter of the vine. Most cultivated varieties can withstand frosts from 17 to 24 o C. It is impossible to rush with early shelter. On a sunny day, fruit buds can push against. The procedure is started in late autumn, when frosts of about -5 o C. were established on the street. However, before that time the vine should be tied with a tourniquet and laid on the ground. If you try to bend branches during frost, they can break.
For shelter, a warm, lightweight and breathable material is used. Straw, reeds will do, sometimes gardeners use old clothes. Burying the vine in the ground is practiced. First, a ditch is dug, a vineyard tied with a rope is laid, a layer of straw or foliage 30 cm thick is poured on top, and this whole cake is covered with loose earth.
From above, the shelter can be reinforced with foil. The waterproof material will prevent organic matter from rotting and saturating it with water. The film itself cannot be used without insulation. A greenhouse effect is formed under the shelter during the thaw. The buds will begin to awaken, and with the return of frost they will freeze.
The last feeding of the vines
Caring for grapes after harvest includes the last dressing before sheltering it for the winter.
Before winter, the grape vines should be lignified and fully ripe. In order for the vineyard to endure the frosty winter well, it must be fed after the autumn pruning of the shoots. At least 10-14 days should pass between pruning and top dressing for the grapes to fully recover after this procedure and be able to take nutrients from the soil.
After the entire crop has been removed, only potash fertilizers are applied to the grapes. Potassium increases the resistance of the vineyard to cold and disease, and the fruits that will ripen next season will become sweeter.
For autumn feeding, you can use potassium sulfate, potassium sulfate, potassium chloride or ordinary salt. These fertilizers should be applied in strict accordance with the instructions for the use of these fertilizers, so as not to harm the vines.
If there are no such mineral fertilizers at hand, then ordinary wood ash can also be added. It is best to use ashes from grape twigs or sunflower husks.
At a distance of about 0.5 m from the main trunk, a deep circular groove is dug into which dry potash fertilizer or its solution is applied. Liquid fertilizer is applied if there is little moisture in the fall. If autumn is rainy, then it is better to apply dry fertilizers.
Once every few years after the harvest is harvested, organic fertilizers (rotted manure or compost) are applied under the bushes of the vineyard.Usually, this type of fertilizer is applied simultaneously with the digging of the vineyard before winter.
The best varieties for the Kuban
The main focus of viticulture in the Kuban is the cultivation of table varieties from the earliest ripening to late ones. This allows for the possibility of long-term consumption of fresh grapes. Let's list the best table grape varieties for the Kuban.
In order to enjoy the taste of delicate nutmeg berries all season, it is enough to have a plot of grapes for 35-40 bushes. Of these, about 40% should be superearly varieties, 25% - medium, 30-35% - grape varieties of late and ultra-late ripening periods.
- The growing season for early ripening grapes is only 80-90 days. These are the varieties: "White Rose", "Super Early Seedless", "Early Magaracha", "Russian Early", "Kara Dzhijigi", "Kuban", "Nadezhda AZOS".
- Mid-season varieties: "Radiant Kishmish", "Kesha", "Lydia", "Original", "Senator", "Talisman".
- Late varieties: "December", "In Memory of Negrul", "Odessa Souvenir", "Autumn Black".
- Ultra-late varieties that do not ripen in other regions: "Moldova", "Kutuzovsky".
Inspection of grapes and elimination of possible problems
Visually examining the grape bushes, they reveal the damage acquired by the grapes during the winter. Some problems can be solved on the spot, others require radical action - you have to replace the dead bushes.
If the vine is withered or snuffed
Frequent temperature changes accompanying winter thaws lead to damage to the shoots. The annual vine is particularly affected. Damage options:
- The vine has dried up. The bark of the shoots is cracked. If you raise the shoot - to tie it up, a well-audible crunch is heard.
- The vine has melted. The sprouted shoots are wet to the touch, they are darker than others - they look like damp wood. The bark may have a whitish coating and mildew.
Such damage is not a reason for uprooting the bush. Try to fix the situation:
- in a black roofing film (50 x 50 cm), cut a hole with a diameter of 10 cm in the middle;
- open the shoots so that the heel roots appear - dormant buds may well wake up on them, which will grow;
- cover the seedling with a film, crushing its edges with something heavy, pour the bush through the hole with water (temperature 45-55 ° C);
- add a growth stimulator and biofertilizer to the water.
After 1-3 weeks, a result should appear - shoots will begin to grow from the awakened buds.
Sudden spring frosts
For many crops, recurrent spring frosts pose a huge danger. When the frost catches the plant "by surprise" - after the start of sap flow, the consequences can be catastrophic. The owner of the vineyard risks losing part of the harvest, or even without it. Freezing kills all buds that have blossomed.
The task of the grower is to prevent kidney death. When the cover is removed, it is necessary to slow down their opening. For this, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of ferrous sulfate. This drug will not only delay the growing season by half a month, but also prevent the development of many grape diseases.
Condensation problems under cover
Condensation can accumulate under cover due to moisture in the soil and air. This leads to mold and mildew growth. If the weather is cold and it is too early to clean up the shelter, it is useful to arrange daytime ventilation.
If the airing option is not suitable, and the grapes run the risk of stifling under cover, do this:
- Remove the film. Do it on a warm and sunny day.
- Cover the trunk circle with soil. Do not tamp it. For one bush, 2 buckets of earth are enough. This procedure is carried out if the vine was not dropped in for the winter.
- A hill around the bush will protect the roots of the grapes from spring frosts.
- Pin the vine to the ground and cover with fiberglass.This lightweight and breathable material will prevent moisture build-up, which can cause the shoots to grow out and cause fungus.
Some interesting points to consider when pruning grapes
Young bushes of grapes in the first couple of years of their life are pruned in almost the same way. However, before you start pruning, you need to plan in advance not only your actions, but also the shape of the future bush. This will be the key moment from which further actions will be planned.


If pruning grapes in August is done using garden tools, then you need to make sure that it is clean and sharp. Cuts should be made as smooth and even as possible, and try to position them on the inside of the vine. This will contribute to the speedy tightening of the wounds and will not injure the bush very much.
It should be borne in mind that the August pruning will also be followed by the final, pre-wintering, so you should not cut the bush very much. In the first year of life, bushes in the summer can not be cut, it all depends on the intensity of their growth. After summer pruning, the bush may weaken a little, and it may well be affected by a fungus. For this purpose, a preventive fungicide treatment can be carried out. If, in the process of carrying out these works, you also noticed the first signs of the appearance of gray rot, then do not be too lazy to spray the bushes with a solution of potassium permanganate, and the bunches themselves need to be treated with a solution of baking soda. If these diseases are started and not given importance at the initial stages, then the fight against them can be very difficult, and part of the harvest will be lost.


If in the process of pruning you notice that it is difficult for the branches to hold the weight of the brushes, then they should be immediately tied up and secured. It is undesirable for the fruits to touch the ground, as this increases the chance of their spoilage. Also, from the very heavy weight of the brushes, the vine can break and part of the crop will be lost, never reaching maturity. In order to avoid such troubles during the August pruning, you need to carefully examine your bushes and attach importance to the little things, as well as react to threats in time.
Shaping value
Do I need to prune the grapes? If you give free rein to the grapes, it will cover everything around in a season. However, this will negatively affect the yield of the plant due to its peculiarity - polarity. The culture will begin to distribute nutrients unevenly, and most of them will go to young shoots, which is why the eyes located in the middle or bottom will greatly slow down in development.
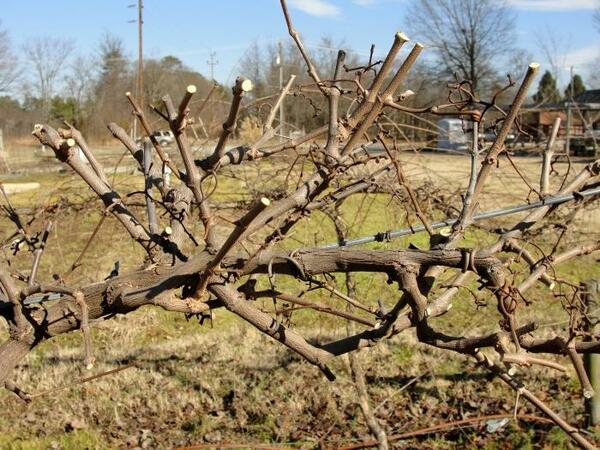


Pruning a grape bush
But pruning serves other purposes as well:
- Stimulation of growth - renewal of branches leads to their better saturation with juices.
- Bush formation - natural ventilation is improved, the amount of light required by the plant is provided, care and harvesting is simplified.
- Plant rejuvenation - the procedure prolongs the life of the vine.
- Increased frost resistance - leads to thickening and strengthening of the main stems.
So, the need for a procedure is based on the biological characteristics of the culture.
Agrotechnical techniques
Of the many types of forming grape bushes in the northern part of Belarus, it is worth highlighting the capitate forming. Its essence lies in the fact that the fruit shoot is laid in an arc on the upper trellis, and the green shoots with bunches are not tied up, but hang freely. Due to the fact that they are directed not up, but down, their growth is naturally limited, and this minimizes the number of green transactions.

The capitate shape of the bush allows the green shoots to hang down, which is why the bush does not grow much
Prune the vine in late October - early November. The grapes are propagated by rooting lignified cuttings with growing in plastic sleeves.
How to send grapes to winter
For the winter, grapes are covered when the cold snap becomes stable.The vines are bent to the ground, tied up and covered with heat-insulating material (spruce branches, dry non-caking grass). Rye straw is a good covering material; mice do not favor it. Under any shelter, you can spread the poison for rodents, and remove its remnants in the spring.
If we are talking about winter shelter with straw, then the danger, apparently, exists. True, the mice under the straw damaged my eyes only once, when I brought the straw straight from the farmyard and immediately spread it out. Apparently "scattered" the mouse's nest on the site. Usually, by the time the grapes are hiding, the mice have already found their winter shelter.
Alexander Mchedlidze
From above, they arrange an impromptu hut made of the same spruce branches, wooden shields for the entire width of the garden, cover them with polyethylene and fix them with something heavy. The ends of the "tunnel" are left open until severe frosts - freely circulating air will not allow condensate to accumulate... If there is no dampness in the shelter, and if it is covered with snow from above, the grapes will survive any frost.
Photo gallery: types of winter shelters of grapes for the winter


Light cellophane shelters are used for relatively resistant grape varieties


Straw - keeps warm well, and mice will not start under the rye straw


Grapes winters well in huts made of boards covered with roofing material from precipitation


In an unheated greenhouse, the synthetic winterizer shelter does not get wet and perfectly conserves heat Lapnik is a good heat-insulating plant material, the vine under it remains dry
How to open grapes in spring
In the spring, the insulation is checked for dampness and is not removed until the return frosts have passed. At the same time, the ends are left open, in such conditions, buds may even wake up on the grapes and shoots appear. In this case, the insulation is removed gradually, because the grape shoots are extremely fragile, and the broken shoot will expire with juice.
When it gets warmer up to + 15… + 20 ° C during the day, and at night + 3… + 5 ° C, the upper shelter is turned to one side in order to exclude the appearance of the greenhouse effect. For two days the vine "breathes" fresh air and dries up, after which a prophylactic spraying of 3% Azophos is carried out to disinfect its surface. Then, water-charging irrigation is carried out, spending 20-30 liters of water under one bush.
It is not yet possible to fully open the grapes, because return frosts are not excluded. For example, in 2019 there was a sharp drop in temperature to -7 ° C. It is scary to imagine how many bushes opened before the deadline froze! But it is also impossible not to open the shelter, because the temperature under it rises and grape tops - the buds can start to grow. Since the earth has not yet warmed up, the roots of the grapes are still sleeping, and the buds will live on the internal reserves of the cuttings. When nutrients are depleted, the kidneys tend to dry out.
Landing features
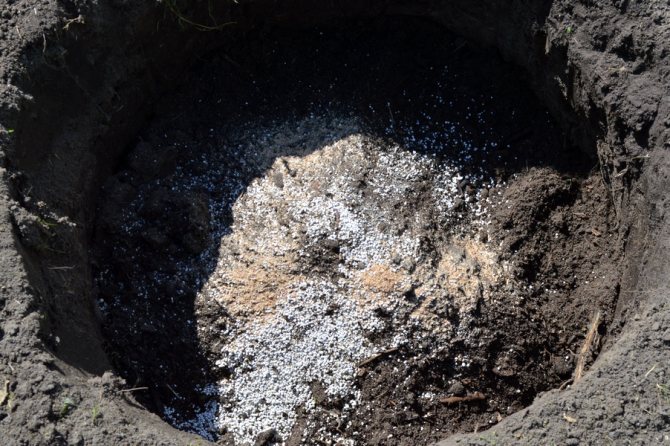
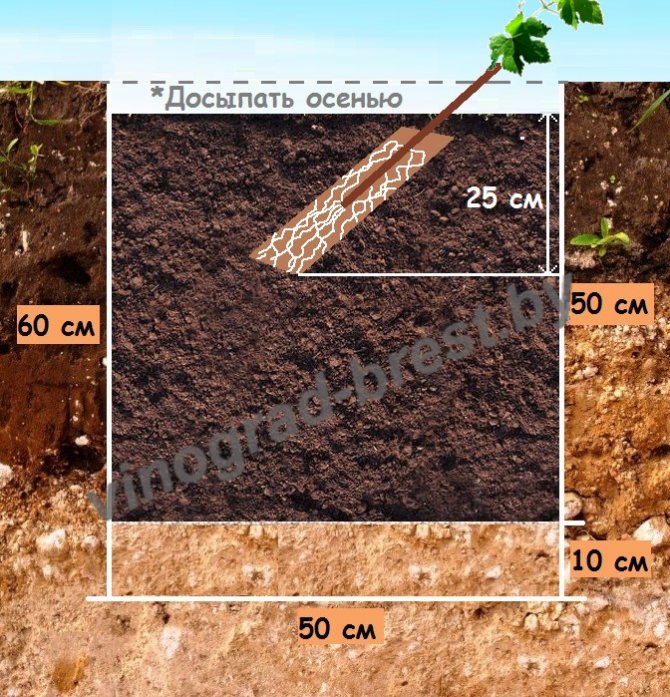
The main difference between Belarus in planting grapes is the poverty of soils and low temperatures. The first is solved by filling the pit with a fertile mixture for a couple of years in advance, the second - with a shelter for the winter.
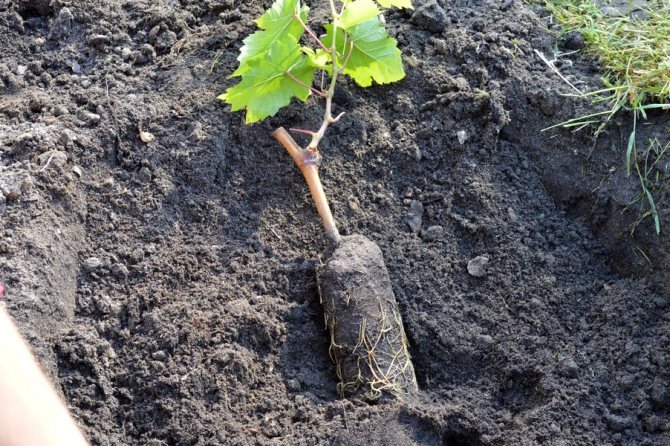
You need to plant grapes in warm ground - these are the same numbers as for planting vegetables (May-June). It can be planted in early autumn, but then it is necessary to pour a small hill over the seedling for protection in winter. Tall varieties should be planted 1.5–2 m apart. It is better to grow different varieties at a greater distance. The deepest planting in Belarus is recommended in the southern region - to a depth of 30 cm.The minimum planting depth should be in the north - 20 cm.
As noted above, it is better to create a supply of nutrients: for this, drainage is poured onto the bottom, and then enriched soil is poured - usually this is soil mixed with manure, compost and ash. On a third of the filled hole, a slide is poured, where the seedling is placed, its roots are straightened and the soil is poured. Trim the seedlings so that there are two buds on the surface. It is necessary to plant at an angle of 45 °.Then the soil is well watered with warm water and filled up to the previous level. With such a planting in the first year of life, the vineyard does not need to be fed.
Stopping the "crying vine"
"Weeping vine" refers to the flow of juice from the cuts left after pruning. If the juicing is moderate, nothing should be done - this is a normal process for grapes, indicating a good metabolism and plant health.
The volume of liquid released during "crying" depends on the size of the bush and is 0.3-2 liters. With prolonged and abundant sap flow, the soil becomes depleted and dehydrated, therefore, if necessary, it is stopped.
How to stop juicing:
- Add 5-10 g of complex non-mineral fertilizers to the trunk circle of all grape bushes.
- Loosen the soil thoroughly and water the plants.


How to refine an overgrown plant?
It should be borne in mind that the more time has passed since the last trimming, the more difficult it will be to carry out it. The same rules apply here as in the usual - the procedure must be carried out in the spring during the rest period with sterile and sharp instruments.
- Determine which of the shoots are healthy and which are sick. You can check this with the help of cuts, if the cut is green, but dry - the vine has dried up or suffered from frost and must be removed.
- Shape the bush using a scheme suitable for the variety being grown. In this case, the fruit link must be formed from annual shoots. If any parts are missing, then the work continues for several years.


Reference! Young shoots should not be spared - they need to be removed almost completely, but perennial vines are best preserved, if possible.
Read more about the technique of pruning old grapes in a separate article.
Care rules
Of course, by planting a plant, you will not get the desired harvest without effort. Some grape care will be required. In order for the bush to form like a fan, it is necessary to break off some of them when the shoots grow back. From the cutting itself there should be 2-3 shoots, from each of which there may be 3-4 more. Then the time will come and put a support for fastening the vine as it grows. A well-known and not laborious method of support is stakes with a wire stretched between them.
Also, for the formation of grapes, pruning and pinching are critical. Weak shoots should be removed in the spring. And before flowering, the tops are pinched - for better growth to the sides. In the fall, you also need to remember to look after - cut off the grapes (the youngest shoots, and those that are stiff are shortened).
Mulching works well to keep the soil near the trunk loose and free of weeds. Despite the fact that the grapes need regular watering, in the second half of the summer they should no longer be irrigated. If the autumn is without rain, then for the winter the bushes need to be well watered. Adult grapes need feeding three times a year: in spring, before flowering, and when the berries are the size of a pea.
Climatic features of the region
When growing grapes in Belarus, one must take into account the moment that significant changes occur in nature every year - a shift in agro-climatic zones. The increase in the duration of the frost-free period greatly influenced the climate in all regions of Belarus:
- in Brest, Gomel, in the southern parts of Minsk and Grodno, it is 235-240 days;
- in Vitebsk - over 210 days.
Daylight hours in summer in the northern regions of the republic in relation to the southern ones are 1 hour and 10 minutes longer. This indicates the receipt of solar radiation throughout Belarus in the same amount.
Removing the winter shelter
The timing and technique of removing the shelter depends on the characteristics of the regional climate. If the spring weather is unstable, the opening of the bushes is done gradually. As soon as a positive temperature is established, holes are made in the covering material - for ventilation. When a green cone appears, the shelter is removed.
Swollen kidneys are not a reason to remove the cover. The emergence of shoots on the vine serves as an unambiguous signal.
If the bushes grow in lowlands or trenches, they make narrow grooves - to drain the water. If you do not dig them, you will have to scoop out water from under the bushes, otherwise the roots will rot.
When and how to open a grape bush in early spring, you can see in the video below:
How to determine maturity
In order not to be mistaken with the timing of collection, you need to learn how to correctly determine the degree of maturity of the product according to the main features:
- the color of the fruit should be rich. When dark varieties ripen, their skin becomes evenly colored, without brown spots, light ones acquire a golden yellow hue;
- the stalks of the bunch are covered with a thin bark;
- the taste of berries becomes soft and sweet, without a pronounced sour taste;
- the skin of the fruit becomes thinner;
- the seeds turn brown;
- the berries are effortlessly detached from the bunch.
Did you know? In order to prepare 1 bottle of wine with a volume of 750 ml, you need an average of 600 berries.
In addition to general external signs, the ripeness of grapes is determined by the level of sugar in it. For this, about 3 kg of berries are collected from different bushes, juice is obtained from them and a test is carried out for the percentage of sugar in it. The ratio of acid and sugar fluctuates depending on what product is planned to be made from raw materials: for dessert wine, the sugar content should be at least 22%, and for juice, 17% is enough.
Pest control
Fight against insects usually begins after their appearance. Use insecticides. But also prophylactic spraying is carried out. So, with the help of Nitrofen, you can destroy almost any parasite. For prevention, the bushes are sprayed with Nitrofen, diluting 200 g of the drug in 10 liters of water.
The most dangerous pests for grapes are phylloxera, mealybugs and spider mites. For prevention, grapes are sprayed with Karbofos. 100 sq. m use 15 liters of solution. For its preparation, 60 g of the drug is dissolved in 8 liters of water. It is possible to destroy the phylloxera when it appears with the help of the preparations Zolon, Aktelik or Confidor.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures in spring:
- To prevent mildew infection, after removing the cover, immediately tie the vine to the trellis. Do not allow leaves and shoots to touch the ground and absorb moisture - this contributes to the spread of infections.
- After the garter, the soil is disinfected. The soil in the near-trunk circles is treated with Bordeaux liquid, iron vitriol, Cineb or Ridomil Gold preparations. The last drug is preferred - it is the least toxic. The lower branches of the grapes are especially carefully sprayed - the root zone is more affected by diseases than others. Bushes can also be sprayed with biological products - Fitosporin, Trichodermin, Aktofit.
Preventive spraying is carried out at intervals of 10-15 days or as recommended by the manufacturer of the drug.
Find out more information about how, when and how to spray grapes in the spring on the pages of our site.
Planting northern grapes
When planting grapes, there are two purposes - to accumulate heat and prevent root rot.
Autumn arrangement of the landing pit:
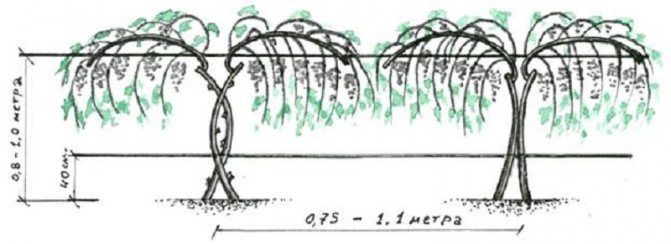
- They dig a trench 0.8-1.0 m deep and 1 m wide. If a row of grape bushes is planted, the length of the ditch is calculated based on the distance between the bushes - 0.75-1.1 m. The fertile soil is folded separately.
- On sandy soil with a groundwater height of more than 2.5 m, the bottom is compacted with soft clay.
- A layer of construction debris, plant residues, semi-rotted manure is poured.
- The previously deposited soil is mixed with clay, drainage (pebbles, broken brick) and humus, taken in equal parts. For each running meter of the trench, double superphosphate is added to the resulting substrate - 200 g, meat and bone meal - 1 liter, wood ash - 2 liters.Spread the prepared soil over the plant residues so that about 0.5-0.6 m remains to the edge of the trench.
- Large stones are stacked mixed with rubble in a layer 15–20 cm thick.
- A plastic tube 3-5 cm in diameter is inserted into the stones at an angle; this is a probe through which the grapes will be fed and watered. The end of the tube is placed under the roots.
- Coarse sand is poured with a layer of 15–20 cm.
- The rest of the soil with fertilizers is poured on top. You should get a ridge with a height of about 20-30 cm.
- The prepared trench is left until spring to settle.
- In the spring, they fill up the soil to make a ridge 20 cm high.
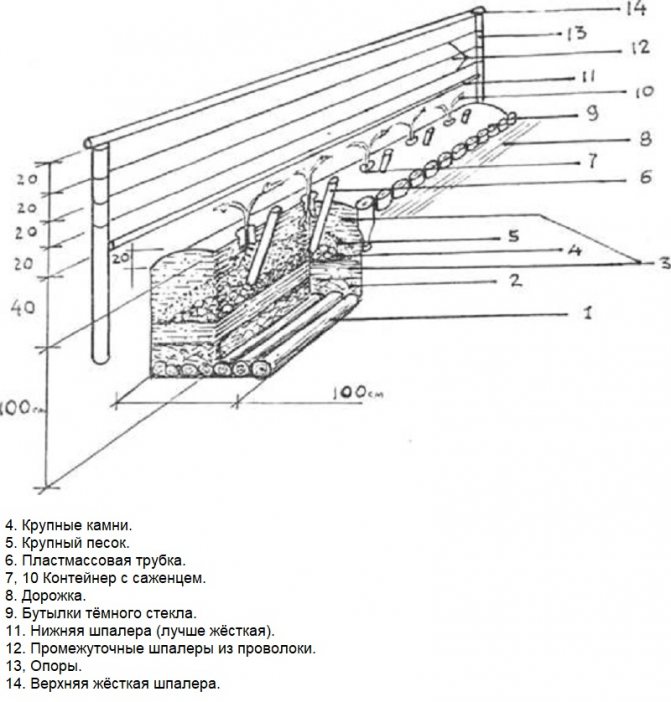

The planting trench for Belarusian grapes has a thoroughly insulated bottom
Plants are planted to a depth of 25-30 cm, this is how the soil warms up in the northern regions of Belarus. The upper trellis is made rigid, it will serve as the basis for a temporary greenhouse during recurrent frosts.
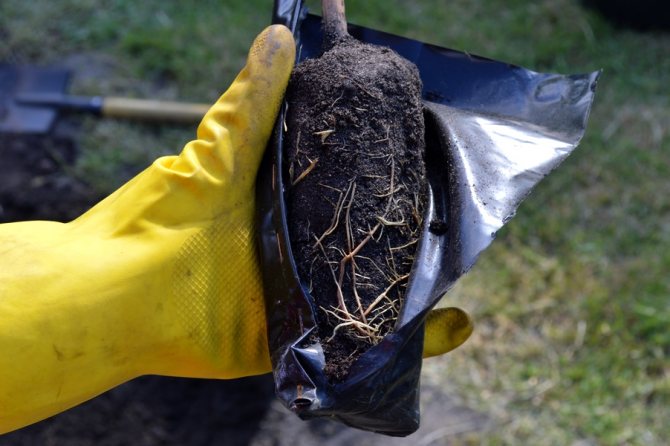
If the garden for grapes is not prepared, and the seedling is purchased, it is left to grow in a plastic bag with a volume of 10 liters. Why not in a bucket? It is easier to transplant from the package to a permanent place, it is enough to cut it from the bottom and lower it into the pit. The package is removed through the "head". So the earthy ball is not destroyed, the roots are preserved intact and the seedling does not experience stress.
When and how to mulch the soil?
Mulching involves covering the soil with different materials. This is done to improve the properties of the soil. Benefits of mulching:
- the formation of an earthen crust is prevented;
- moisture is well retained in the soil;
- the roots are protected from overheating and drying out;
- the soil remains loose for a long time;
- during rain and watering, soil particles do not fall on the leaves, on which there may be pathogens;
- the lower clusters remain clean after rain, are less covered with dust;
- the carryover of fertile soil particles by the wind is prevented;
- organic mulch is at the same time a fertilizer that forms humus over time;
- the growth of weeds is prevented;
- the vineyard looks more attractive.
Mulching is a simple and inexpensive process. It is carried out in the spring, after water-charging irrigation. Different materials are used as mulch. Sprinkle the soil with straw, wood chips, sawdust, bark, needles, cones and other suitable materials.
Correct chasing of grapes
Pruning grapes in August, otherwise called minting, is designed to accelerate the ripening of the fruit. In this case, the tip of the shoot can be removed by about forty centimeters. Pruning shoots too much is not worth it, and pruning too early. In this case, the plant can begin to create stepchildren more intensively and spend much more energy on it. With a strong pruning of the vines, photosynthesis slows down and the fruits ripen longer, therefore, instead of the desired acceleration, the opposite effect may be obtained.


When chasing, you should leave about 14 leaves on each shoot. This amount is optimal for the normal life of the plant.
Twisting the bunch
Another contested method. He helped some, hurt others. The brush is turned over on the vine with its other side to the sun. At the same time, the flow of food and water to the berries is difficult, they stop growing and begin to ripen. In addition, the rotation around the axis contributes to the uniform coloring of the berries on both sides of the bunch. Cons of the method:
- Not all varieties tolerate such an operation; the brush may come off entirely.
- You can only twist brushes with completely filled berries that have begun to stain, otherwise they will wither and will be tasteless.
- Do not twist immediately after the rain, the stalk is juicy and fragile at this moment, the brush will come off, you have to wait 1-2 days.
Only hand-picked
In order for the grapes to have integrity and an attractive appearance during harvest, special technical means are used. Cutting the bunches by hand is carried out using a garden pruner, scissors or a sharp knife.Harvested by hand is rarely damaged. This method allows the simultaneous sorting of clusters according to their appearance. The use of technical mechanisms for harvesting grapes damages part of the harvest.


Load distribution on bushes
If the bush is overloaded, it is recommended to remove excess clusters from the lower part of the plant - this will not only accelerate the maturation of the upper crop, but also stimulate the ripening of the vine (this is necessary for the formation of future fruiting). It is necessary to form the bunches themselves correctly: with the help of scissors, remove the unripe tops for full-fledged pouring of the berries.
In September, you should regularly inspect bushes and trellises:
- damaged berries must be removed;
- fallen branches must be lifted and tied up;
- drying leaves should be removed;
- peeled berries and leaves must be removed from the soil.
Common beginner mistakes
Due to their lack of experience, novice growers often make the following mistakes:
- They feel sorry for the plant and do not cut off most of the growth, which is why the vines get confused, block light from each other and receive less nutrients.
- Cut off the wrong shoots. Do not remove only young or perennial vines. You should be guided by functionality: you need to remove the sprouted shoots and those that thicken the bush.
- Cut length is incorrectly determined. The parameter depends on the thickness: the thicker, the longer the vine should remain.
- They do not know in what cases a stump should remain after pruning. Young shoots are cut off completely, otherwise there is a risk of rot, a stump of about 1 cm is left from perennial vines.
- They choose the wrong time for the procedure. In order not to face the problem of "crying" grapes, pruning is important in early spring. Spring pruning terms: March-April at temperatures from +5 degrees Celsius.
- Leave the stepsons. They only thicken the bush and inhibit the development of other shoots.
So, we learned whether it is possible to prune in early spring, according to what schemes the beam should be done, when it is necessary to prune in the suburbs, in the Kuban and in the middle lane. Spring pruning of grapes is a complex, troublesome procedure that requires knowledge and accuracy.... But if you strictly adhere to the technology, the result will not be long in coming - the fertility of the bushes will increase, the number of diseases will decrease, and the appearance of the vineyard will delight the eye.
Features of agricultural technology
To obtain a bountiful harvest in summer, grapes need to be regularly watered, nutrient-rich, loosened and mulched.
Watering
The first moistening of the soil after planting is carried out after 15 days, then the procedure is performed every 2 weeks. The frequency of watering directly depends on the weather conditions; in the heat, irrigation is performed more often. For one planting, 5-10 liters of settled water are consumed.
Top dressing
The initially laid down nutrients support the plants for two to three years, therefore, during this period, additional fertilization is not worth it.
At the end of summer, you can feed the plantings with a mixture of potassium sulfate (10 g) and superphosphate (20 g). Calculation for 1 sq.m.
Methods and schemes for pruning bushes of different ages
It is very important for novice gardeners to know when to cut grapes in Belarus. Since the quantity and quality of the future harvest depends on this.
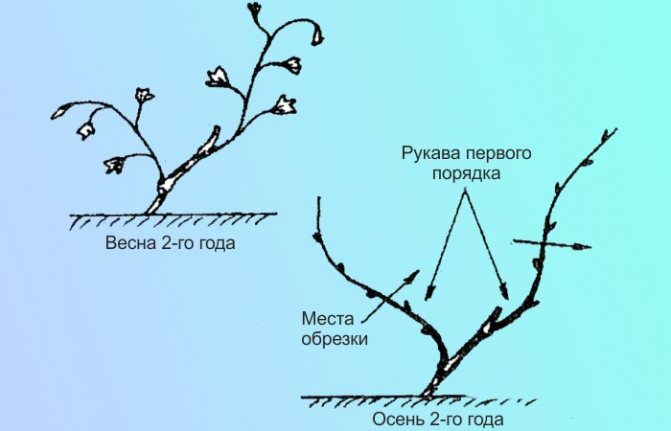
Seedlings of the first year of life
The vineyard is pruned in the spring so that only the 2 lowest buds remain. In the future, when forming a bush, two shoots will need to be made of them. In late autumn, one shoot is shortened to 2 buds, and the other to 4 buds.
Features of pruning at the age of 2 years
In the spring, when the weather is warm, the shelter is removed to prevent the shoots from drying out. In the fall, a long branch is shortened without touching 2 shoots. As a result, the sleeves will become equal.After that, the vertical stems that grow closer to the center and lower along the main one are cut off, leaving 2 buds. This will be the knot of replacement. The vertical stems that are further down are shortened, where 4 buds are left - these are fruit arrows.

How to prune three-year-old and mature bushes
In the spring, the grapes are opened, the trellis are tied horizontally to the lower wire, and the tops are bred on opposite sides. The replacement knots are left to develop in an upright position. During the summer, stems will form from the buds, which are shortened by 10-20 cm in early August. In autumn, the last 4 vertical shoots that have borne fruit with a part of the sleeve should be cut off. As a result, one link with two shoots (vertical) should remain on each shoulder. They are treated as biennial plants.
Subtleties of care during the formation of ovaries, formation and ripening of fruits
So that the grapes do not waste their energy on growth, they do a pinch. As a result, the berries are better formed and ripen faster, the stems become strong, unnecessary shoots are discarded. The timing of the procedure is before the beginning of the flowering phase.
Caring for grapes involves watering, rationing in bunches, leaving only promising inflorescences. If necessary, manual pollination is carried out.
Diseases and pests of grapes
Among the dangerous ailments, mildew, gray rot, and oidium are distinguished. It is effective to use 3-5% copper or iron vitriol (before bud break), Bordeaux mixture (before and after the flowering phase), Ridomil Gold, Shavit (before flowering) against diseases. To combat pests (aphids and spider mites), a solution of colloidal sulfur 75%, Aktellik, Fozalon, Fastak is used.
What to do with the vine after the procedure?
Pruned vines should not be left in the vineyard after the procedure, so gardeners either take them out and burn them, or use parts of the shoots for propagation and feeding.
Cuttings
Is it possible to make cuttings from a vine cut during formation? Propagation of grapes by cuttings is the simplest and most effective method. For this, it is better to use an annual, well-ripened vine - it has good resistance to adverse conditions and takes root easily.
The main parameter for choosing a vine for cuttings is the absence of lesions and curvatures. Billets for planting should have a length of 50 cm to 1 m and more than 5-10 knots. The value depends on the planting depth: the cutting should exceed it by no more than 1.5 times the length of the upper internode. More details about the stub can be found here.
Top dressing
Pruned vines can be used as fertilizer: in the form of compost or freshly ground mass, which is immediately applied to the soil. To prepare compost, you need to grind the shoots, add activated sludge, grape pomace, yeast, sulfites and sulfates.
Then a place for storage should be prepared, taking into account that it will be necessary to moisten and shovel the mixture 1-2 times a month. It will take 6-12 months to "ripen".
It is easier and faster to make a crushed mass: you need to collect shoots and grind them using a grinder. Such fertilizer should be placed at a depth of 10-15 cm.
You can learn more about feeding grapes from our separate article.
Destroy
Most growers get rid of the pruned vine by burning it. However, at the same time, from each hectare is lost:
- 10-15 kg of nitrogen.
- 6-8 kg of phosphorus.
- 12-16 kg of potassium.
In addition, in the place where the fire is set up, the amount of organic matter decreases and heavy metals accumulate. And sulfur dioxide, soot, dioxins, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, benzopyrene and other harmful substances get into the atmosphere. Therefore, it is worth burning only diseased plants, and recycle the rest.
Reference! The vine has recently become popular for making wicker items.
Graft
The grafting is done in order to improve yields, increase frost resistance and immunity. For grafting, cuttings 10-15 cm long are used. They should have 2-3 eyes. They are cut in the fall and stored until spring, after dipping them in a solution of potassium permanganate, drying them and wrapping them in foil. Store them in the cellar or in the refrigerator.
In order for the spring grafting to be successful, varieties that have the same growth force are grafted. Use only disinfected instruments. Inoculate grapes end-to-end, copulating, splitting or semi-splitting.





































