Planting cucumbers in greenhouses allows you to get harvests faster, as well as have fresh vegetables at any time of the year. The plant adapts well to the greenhouse microclimate, bears fruit stably and gives early harvests. Self-pollinating varieties are considered the best for greenhouses, however, it must be remembered that it will not be possible to collect seeds from them on your own. In this article, we will look at how cucumber seeds are classified and which are the best varieties of hybrids for greenhouses.
A simple test: what are your expectations?
Plan the cultivation of this vegetable based on what kind of crop you want to get, how soon to harvest it and how beautiful it should be. When choosing a variety, industrial greenhouse farms, for example, are guided by how well the fruits are then stored during transportation, how much they keep their presentation. All this is rarely interesting for an ordinary summer resident, and therefore it is not worth focusing on the "most bought" ones.
When choosing seeds for planting in your personal greenhouse, proceed from what is important for you in the first place: taste, yield, salad and pickling qualities, disease resistance, ease of growing? The fact is that there are seeds specifically for greenhouse farms, which are only interested in yield and presentation, there are seeds for home cultivation, which are most suitable for salting conservation, and the market offers simply breeding novelties that can give the most unexpected result. It's simple: when buying hybrids for industrial cultivation, do not expect either taste or quality.
Bush
Cucumbers of this category look attractive on the site - they are compact neat bushes, the height of which does not exceed half a meter. Such plants are easy to care for when harvesting.
Elegant
Cladosporium resistant bush variety. Not afraid of temperature extremes, cold-resistant. Belongs to the category of early ripening - the technical maturity of zelents occurs after 40-50 days. The weight of the vegetables is 140 grams, the length does not exceed 13 centimeters.
Nezhinsky
If you are looking for the best bush cucumbers for pickling, we recommend planting the Nezhinsky variety on the site. It is unpretentious, resistant to a number of diseases characteristic of the culture - cladosporiosis, bacteriosis. The pulp of the fruit is crispy, juicy, aromatic. The weight of one green leaf is 110 grams, the length is 11-12 centimeters.

Competitor US SB
From the moment of sowing to the fruiting phase, 46-52 days pass. The competitor feels equally well in the open field, greenhouse, greenhouse conditions. The plants are highly branched. Zelentsy are large - up to 15 centimeters, weight about 95 grams. Cucumbers are great for pickling, making fresh salads, sandwiches.
Which is better: conventional or hybrids?
To make you understand the notation a little, we will reveal this mysterious F1. This is how hybrids are denoted, "F" in Italian is the first letter of the word "children", and "1" is the first generation. Hybrids are always more expensive because such plants are obtained by crossing two species already.
What is good, the seeds of modern hybrids from well-known companies do not need to be disinfected or hardened - usually all this has already been done.And there is even a difference in how to form hybrids and varieties.


So, if you planted cucumbers, then when 4-5 leaves appear in plants, pinch the top. Thanks to this method, side shoots will begin to grow much more actively, which will have a good effect on the future harvest. What's the secret? There are more female flowers on the lateral processes, and it is from them that the fruits are formed. But if you are planting hybrids, then we do not touch the central stem, and we pinch only the lateral stepsons. We leave two leaves on the first, four on the second, up to 6 on the third, and up to 8 on the fourth.
But know that there is no point in collecting seeds from hybrids for subsequent planting - you will have several plants that are unlike each other at once, which will either give a poor harvest, or even leave without it.


Benefits of parthenocarpic cucumbers
Self-pollinated cucumber varieties consist only of female flowers and can independently produce fruits. They do not require insect pollination.
They have the following advantages:
- Ideal for indoor use. You can grow self-pollinated cucumbers on the loggia, on the windowsill, and on the balcony. It's hard here
- infiltrate bees and other pollinators. Despite this, they feel great in the garden.
- Friendly shoots.
- Fruits of the same size and shape, color.
- There is no bitterness.
- No yellowing because no seeds.
Parthenocarpic cucumbers, HYBRIDS & GMOs! - video
Attention!
It would be more correct to call these species not requiring pollination, because there are no male flowers (pistils).
Moreover, Parthenocarpic cucumbers have excellent taste and are widely used in cooking.
Can be eaten both fresh and prepared.
What kind of greenhouse cucumbers are there?
The varieties are divided into greenhouse and open field varieties. Many of them are suitable for both those and those conditions, but some types have a strict purpose. So, for open beds, hybrids are usually bred that are well adapted to the wind and low air humidity. And for greenhouses, seeds are well processed to protect against diseases and pests, which are especially fond of a humid and hot microclimate.
In addition, those that must grow in direct sunlight in the seven winds are completely unadapted to the difficulties of closed wet ground and quickly begin to hurt.
For salad, pickling or sale?
According to economically useful characteristics, varieties are divided into pickling, salad and universal. Salad is not salted, because they lose their properties, and fresh pickling is a little rough.
The sweetest and most delicate, ideal for salad, are Armenian long vegetables of an unusual yellow-green color. The Dutch also have a wonderful taste, with a thin skin and no coarse seeds. Lemon cucumbers, yellow, round, sweet and seedless, are also gaining popularity. But the Persian ones are like cybri, delicate in taste and generally without crunch.


Early, super early or late?
So, early and super early are those that are intended for a quick harvest.
According to the ripening period, there are the following:
- The early ones, which begin to bear fruit as early as 40-45 days.
- Medium early - 46-50 days.
- Mid-season - 51-56 days.
- Late ripening - bear fruit after 56 days.
And usually varieties with different ripening rates are planted in the greenhouse - in order to harvest as long as possible.
What will we pollinate with?
According to the method of pollination, the varieties, like hybrids, are bee-pollinated and parthenocarpic, i.e. self-pollinated. For the former, pollinating insects (bees, bumblebees) are needed, or you will have to wield a brush yourself, and in the latter, both the pistil and the stamen are in the same flower:
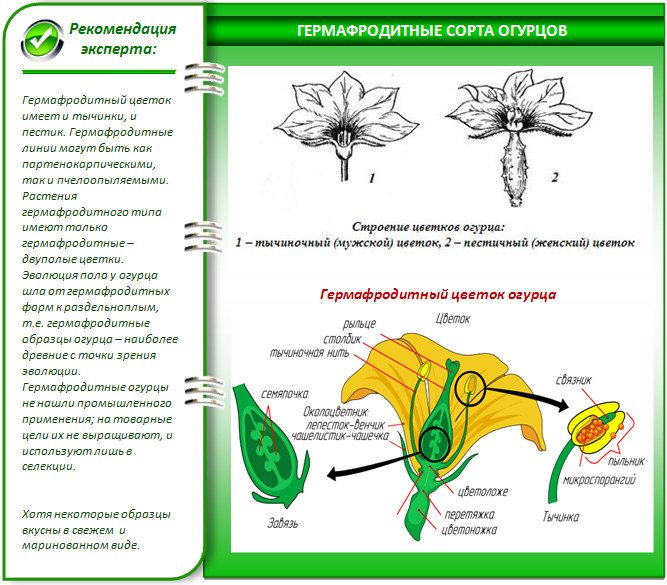

Parthenocarp is the ability of a plant to set its fruit without pollination.The term "self-pollinating" is not entirely correct for them: such cucumbers are not pollinated at all, they develop ovaries on their own. This is a valuable property for greenhouse vegetables, especially winter ones. Even by the fruit, you can easily recognize these varieties - they do not contain the seeds at all, which you usually see when cutting. Although some parthenocarpic species have few seeds, in some part of the fruit, which is why it turns out to be pot-bellied or pear-shaped.
Of the parthenocarpic species, which all flowers produce with an ovary, the Dutch "Hector" is considered the best. The fruits do not turn yellow, do not outgrow, grow small and the bush itself does not require a garter.
For a greenhouse, of course, self-pollinated varieties are more suitable, because there is less trouble with them. But many adherents of "everything natural and natural" are sometimes ready to walk day and night with brushes, just to grow a "natural" variety. And, I must say, with a competent approach, the harvest will turn out to be much larger and better than any scientist agronomist could have planned for his androgynous brainchild.
Experienced gardeners can even distinguish between male and female seeds. So, the seed of a boy-cucumber is flat on one side, and there is a slight break in only one plane, while the woman has a break in the edges on both sides, and the seed itself looks a little pot-bellied.
You can plant different varieties for greenhouses, but they must all be either parthenocarpic or bee-pollinated. Note: some authors of books on gardening even recommend mixing these two species, some are categorically against, because if parthenocarpic ones receive stronger pollen from pollinated ones, then the fruits will be crumbled (blown away from uneven filling with seeds).
Shade tolerance for winter growing
Distinguish between fruits and shade tolerance. So, if you purchase hybrids for the spring-summer period, such cucumbers are photophilous and will bear fruit well only in good sunlight. But, if some outbuildings or trees give shade, there will be little fruit.
But winter ones tolerate shade well and feel quite comfortable in a greenhouse even in January, but there is no point in sowing them in the middle of summer: firstly, the fruits will be late, and secondly, such varieties are in no way protected from typical summer diseases.
Cold resistance and hardening
There are differences in cold resistance between cucumbers. And this is already one of the most important indicators for different regions, because there is a difference, do you grow vegetables at the equator or in Siberia? Even with good thermal insulation in the greenhouse, plants can catch cold - in the morning, for example, when cold dew and condensation accumulate on the plastic wrap. Therefore, at the end of summer, only cold-resistant species should be planted, which are more protected from viral diseases (with hypothermia, a physiological weakening occurs in plants).
Productivity and number of ovaries
Recently, more and more varieties with the so-called bunch fruiting have begun to be produced, when several ovaries develop in the leaf axil at once. These are short-fruited species with particularly intense fruiting, which is important to properly care for. What is their advantage? In a huge number of small cucumbers, which are great for pickling.
Plants also differ in such a feature as branching - the intensity of the growth of lateral shoots. There are three groups of them: with good branching, with moderate and weak. When good, lateral shoots appear from almost every node from the main stem, they are long and need to be pinched. With moderate branching, there are many side shoots, but they are short. And cucumbers with weak branching form very few lateral shoots, all of them with short internodes, "bouquet". But remember that the intensity of branching depends not only on genetics, but also on external conditions.So, at low temperatures and shading, side shoots grow weaker, and in sunny weather and with generous watering, they are already bolder.
If you decide which vegetables are best to plant in your own greenhouse so as to get the maximum yield in a short time, literally in 3-4 weeks, then take weakly branching hybrids. Only they need to be planted densely, 5-6 plants per square meter, instead of the standard 2-3. If the crop is needed within one month, then plants with moderate branching are suitable for you. But for salting, when the sugars in the fruits are the most, hybrids with rich branching are suitable for you.
Another difference is the duration of fruiting. If you grow for sale and it is important for you to get a good harvest in a short period, then buy seeds of early ripening sprinter hybrids, which will give most of the fruits in the first month. But in order to regularly collect small cucumbers for pickling and not rush anywhere, use hybrids with the so-called extended fruiting period.
Care rules
Self-pollinating garden varieties, despite the enviable resistance to external factors, require care and the use of agrotechnical techniques. To begin with, in the fall, prepare the soil, carefully digging it up and applying fertilizers. Use organic matter (mullein, ripe manure, humus), add nitrophosphate. In the spring, after thawing, the earth is once again dug up with the addition of mineral components, then harrowed.
The preparation of seed material begins with the selection of full-bodied, intact seeds, for this they are placed in a saline solution and the floating ones are removed. Those settled at the bottom are dried, and before planting, they are soaked in a mineral solution (2 g of the substance are put on a bucket of water). After drying one more time, the seeds can be planted in the ground.
Planting and preparing seedlings
Seeds are planted for seedlings, this can be done in separate pots made from a combined mixture of humus and peat. If you use this method of germination, then the finished seedlings can be buried in the ground without removing the sprout, and the improvised container will subsequently dissolve. One or two seeds are planted in each pot, deepening them by 2 cm, the containers are placed in warm conditions with good ambient lighting, and covered with polyethylene.
The sprouts will appear on the 5th day, the pots are placed in a brighter place for the day, and at night they are removed to a place with a temperature lowered to 15˚C. They monitor the soil moisture in the pot, pouring it with settled water at room temperature. Two weeks later, the first feeding is done with mineral components, and after 4–5 leaves grow on the sprout, the seedlings are moved to the garden bed. The holes are made according to the depth of the planting container, adding 3 cm to this size, at a distance of 20 cm from one another, the row spacing is formed by 60 cm.
Secrets of growing cucumbers in the open field
The wells are watered before placing the pots in them, then sprinkled with earth 3 cm above the edge of the pot. A trellis is prepared so that the cucumber curls over it.
Weeding and watering
Care consists in weeding, constant maintenance of soil moisture, feeding with mineral components. Weeding involves thoroughly loosening the soil. to saturate the soil with air around the roots and to remove weeds. When watering, the amount of moisture is regulated so as not to flood the ground, watering not the ground under the bush, but the surface in the aisle.
Growing cucumbers is profitable, useful and exciting activity... After learning all the intricacies, farmers are happy to harvest from greenhouses, greenhouses and garden beds.
What are the manufacturers talking about?
When buying seeds, pay special attention to the information from the manufacturer, which is usually indicated on the package.
When choosing seed bags for a greenhouse, pay attention to the image of the fruit itself. Namely - on the thorns. Thorns can be dense or almost absent, thorns can be small or large enough.And even different in color - white, black and brown.
- Cucumbers with white thorns are salad-type fruits, they are not used for pickling. And they can be most often seen on the shelves, and at any time of the year.
- Brown or black thorns are pickled vegetables, sometimes universal. They are good both fresh and salted and preserved. But, unlike white thorns, they overripe faster, also quickly turn yellow and become tasteless.
By the way, it is not recommended to soak the seeds processed at the plant so as not to wash off the color protection from them. But many summer residents still break the rule by using simple wet gauze that does not wash anything. After two days, a tail just appears on the seeds, and the color remains the same.
Video
This video will tell you about the most popular varieties of self-pollinated cucumbers.
Cucumbers, regardless of the selected variety, must be tied up and placed on special trellises, then they will not creep along the ground and occupy large areas. Their self-pollinating varieties do not need special care, they are distinguished by good yields and high protection against various diseases inherent in cucumbers. A description of the variety Herman F1 can be found in this article.
A real "Russian" cucumber: in pimples and without bitterness!
Interestingly, in Russia they really love cucumbers with thorns, considering them "real". But in Europe, fruits with a smooth skin are preferred, while "pimples" are called cucumbers "in a Russian shirt."
Where does the bitterness come from in the fruit? This is the merit of a special substance - the alkaloid cucurbitacin, which is most actively produced in dry hot weather, especially if you did not water the plants much. Sometimes the soil is also to blame, or rather its composition. In simple terms, bitterness accumulates under the green skin if the active vegetation process slows down and the fruits stop growing within a few days.
Most cucurbitacin accumulates in dark green fruits. Although sometimes bitter cucumbers are grown on purpose - according to some reports, such cucumbers kill cancer cells in the body. If you need just such a crop, take not the newest species and just water less. After all, modern varieties, thanks to breeders, have practically lost the ability to accumulate cucurbitacin, and therefore are not bitter.
Growing features
The best varieties of self-pollinated cucumbers for open ground do not require special conditions for cultivation. You just have to focus your interest on important factors.
- The soil is prepared in autumn, digging it up together with organic fertilizers. In early spring, you can add minerals, burrow and level for planting.
- Sowing cucumbers begins at an average daytime temperature of + 15 ° C, not earlier. Seeds do not need to be buried deeply, a maximum of 2 cm. Early varieties are best grown by seedling.
- Cucumbers should be fed often - 2 times a month. In this case, fertilizers must be alternated. Top dressing is carried out in the evenings.
- This vegetable loves watering, after each it is necessary to loosen the soil.
- The bottom dry leaves must be removed.
Self-pollinated cucumbers have the main quality that distinguishes them from other varieties - to give significant yields. This is fundamentally important for places where bees fly little. By adhering to the correct cultivation technique and choosing the right variety, you can get a high yield.
Popular varieties in Russia
There are a lot of them, but we will note those that are most popular today:
- If you grow vegetables for sale, then "Courage" is 100% suitable for you, thanks to its marketable appearance and good harvest.
- Also one of the most popular in Russia - "Emelya". Yielding, strong, good in preservation and salting.
- One of the most beloved among modern summer residents is "Courage".The harvest is good, it almost does not get sick.
- The fruits of "Connie" are not prickly, without bitterness, have a good presentation and give an excellent harvest.
- Summer residents also speak well of the Claudia variety, which is ideal for growing in a small greenhouse.
- The famous "Athlete" is famous for its rich harvest and wonderful taste, but only bees (or you by hand) can pollinate it.
- Amur has a delicate sweet taste, grows well in a greenhouse, and Malyshka has a wonderful aroma.
Exotic, or how to surprise your neighbors
But if you dream of experimenting, you can grow white cucumbers in your own greenhouse. These are unusual hybrids that are gradually gaining in popularity. One of them is the Bride F1 variety, whose fruits are tender, fragrant, and behave well in conservation.
Many beginners in this business are also interested in the "Chinese" fruits. Note that in a greenhouse they do not always grow even, the presentation is almost completely absent, but the taste will definitely please. The best variety is Peking, which produces tender juicy fruits with small seeds. This variety bears fruit until frost, even in an unheated structure.
In any case, when choosing, give preference to varieties that are designed specifically for your region. These are more designed for specific weather conditions, are resistant to local diseases and bear fruit on time.


The best varieties of cucumbers according to reviews for 2020


Variety General
According to the reviews of vegetable growers in 2020, the following are recognized as the best varieties and hybrids of cucumbers:
- Berendey;
- Siberian garland;
- Emerald City;
- Courage;
- Little finger;
- Goosebump;
- Spino;
- General's;
- Horses;
- Mele.
Thanks to the efforts of breeders, a large number of varieties and hybrids of cucumbers have now been bred, which can be grown in greenhouses and hotbeds not only in the warm season, but also in the autumn-winter period. And it should be noted that cucumbers grown in winter do not lose their excellent marketable taste, are high-yielding, are not susceptible to most diseases, and are also quite unpretentious.
Therefore, many vegetable growers, especially those living in regions with rather harsh climatic conditions, prefer to grow cucumbers in greenhouses in order to get large yields of this vegetable crop and not depend on the vagaries of nature.

































