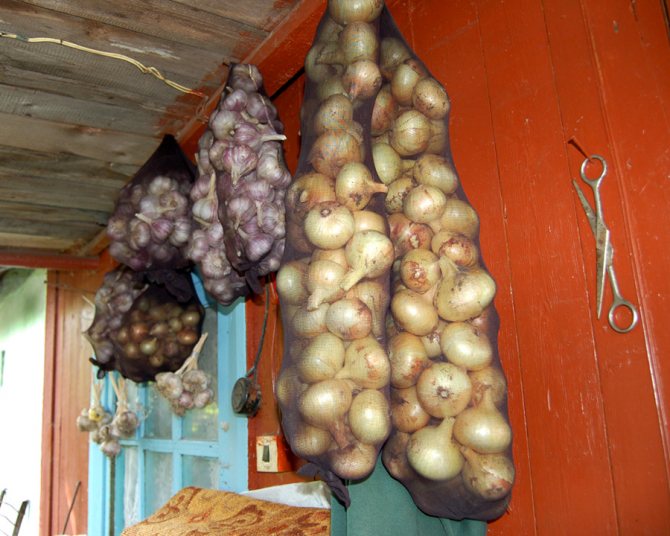
Vegetables in the cellar
After harvesting garden crops, the problem arises of how to preserve it during the winter months.
Considerable sums were spent on seed material and fertilizers, not counting the physical labor invested in growing.
Following simple rules will help preserve the results of the harvest, enjoy the taste of vegetables. First, it is recommended to prepare the cellar, and then transfer the fruits, prepared properly.
The preservation of vegetables and root crops depends on the ability of gardeners to provide optimal storage conditions, to eliminate rotten fruits in time.
Preparing the cellar for storing crops
Before storing the crop for storage, the cellar must be prepared for work. Even a clean and dry room must be properly processed in order to destroy fungi and bacteria left over from the last season. These microorganisms cause spoilage of vegetables: mold or decay.
To destroy the microflora, the cellar is dried and then whitened or treated with sulfur dioxide. This can be done according to the following scheme:
- For complete drying at the end of summer, remove all remnants of last year's vegetable products from the premises. In the cellar, you can install a powerful electric heater or do as they do in the villages: make a fire. The latter option is hazardous to health, since when firewood is burned, poisonous gas and smoke quickly accumulate in the pit, so you can burn out already at the time of kindling a fire. Villagers sometimes build a fire in a bucket outside and then lower it into the cellar. The generated heat and smoke heat up the walls. There is no need to close the lid or door of the vault.
- After drying, ventilate the cellar for 1-2 days, and then start whitewashing. Only storage facilities lined with brick or wood are whitewashed. For whitewashing, a solution of freshly slaked lime is prepared with the addition of a solution of copper sulfate (until a blue tint is obtained). Walls and other surfaces (shelves, drawer walls, etc.) are covered with lime in 2 layers. After processing, the cellar must not be closed so that moisture does not accumulate in it.
- The earthen cellar is treated with sulfur dioxide. To do this, you need to light a special sulfur stick (buy in a gardening store). The number of checkers is specified in the instructions and depends on the area of the room. The processing time must be at least 48 hours: the doors or the cellar lid will remain closed. After processing, the storage should be ventilated for 1-2 days so that no traces of gas remain, from which a person can also suffer. Only then is it allowed to enter the premises for further work.
If the storage has wooden racks, chests and other equipment, then it cannot be dried using fire or electricity. A cooler and more efficient way of fumigating with a smoke bomb should be preferred. After processing, the cellar can be considered ready for storing vegetable products.
Useful Tips
After all, it is quite expensive to buy tubers in the store all year round, it is more profitable to make supplies in advance. And if you grow vegetables on your own plot, storing potatoes becomes especially important. Where to define the bags with dug tubers so that you can prepare a variety of dishes before the next harvest?
Of course, the best option is to store potatoes in a cellar, but if you live in a city apartment, and there is no underground or basement in your house, you can put bags of potatoes in the pantry, in the corridor, adapt boxes for harvest in living rooms, or take out them to the balcony. In warm rooms, tubers can be stored for three months, and on the balcony, potatoes in insulated boxes can withstand frosts down to -15 degrees.
Video on how to save potatoes until spring
Keep in mind that successful storage largely depends on the preparation of the tubers. They need to be dried well (if possible in the fresh air) for several hours or days to prevent rotting and the occurrence of potato diseases. In addition, sorting of potatoes is of great importance: well-dried medium-sized tubers without flaws are placed for long-term storage, and for an average period, select the largest potatoes, since voids form in them over time, due to which the taste will deteriorate.
Features of storing vegetables
The grower should know how to keep vegetables from freezing, sprouting and rotting in winter. In winter, the storage temperature should be 0 ° C without strong fluctuations. If it is negative (below -5 ° C), then the vegetables will freeze and become unusable. At a positive temperature, potatoes and root crops will begin to germinate.
In underground cellars, it is easier to protect products from the cold: for this, the entrance to the pit is laid with boards and straw mats. In the absence of a hood, during thaws, the mats are removed, and the cellar is ventilated.
Aboveground structures can freeze through in cold winters. If this has already happened, then the walls of the cellar must be insulated with EPS or other types of thermal insulation.
In order to provide the vegetables with the most favorable storage conditions, supply and exhaust ventilation is installed. When the temperature rises, it is enough to open the inlet and ventilate the room. In cold weather, the ventilation holes are closed.
The presence of the hood also solves the problem of excess moisture that occurs when vegetables are stored for a long time in cellars and basements. Normal air humidity is 85%. But juicy roots release moisture, in a closed room it accumulates and leads to rotting and the development of mold. In a storage without ventilation, it is very useful to install containers with lumps of quicklime (3-5 kg for every 2m²).
Absorbing water vapor from the air, lime turns into a fluff state - it crumbles into powder. It must be replaced as necessary. Fluff can be used for liming acidic soil in the garden during spring digging.
What can be stored in the cellar?
Most often, the following types of vegetables are left for winter storage:
- potatoes;
- cabbage;
- onions and garlic;
- roots.
In addition, pumpkins and zucchini, horseradish rhizomes, Jerusalem artichoke and other vegetable products are well stored in cellars. A well-equipped basement can store apples, tomatoes, bell peppers and eggplants, as well as leeks.
Only late varieties of vegetables are suitable for long-term winter storage. They must be fully matured, without mechanical damage and signs of rot. When harvesting in damp weather, it is recommended to dry vegetables before storing them so that no wet soil and traces of moisture remain on the skin.
Among what is stored in the cellar, there may be not only edible fruits. At low temperatures until spring, you can keep warm-loving flower crops that do not winter outdoors (for example, dahlias). Cuttings of grapes, currants, planting material for garden strawberries and seed specimens of garden and flowering plants with bulbs or tubers are also well preserved in underground storage facilities.
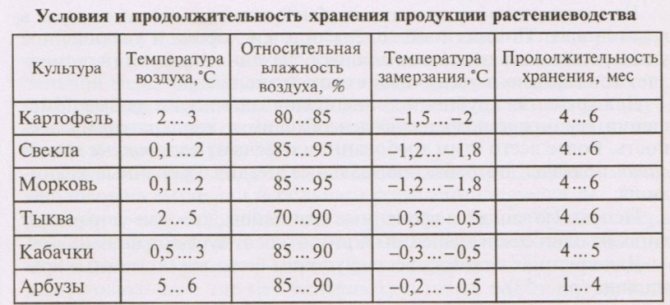
What temperature and humidity should be?


At temperatures close to zero, metabolism slows down rapidly, which contributes to greater safety of root crops. They have no rest period. The storage temperature of carrots and beets should not be more than 10 degrees, because already at +5 degrees, buds that could not be completely removed can begin to grow.
If the humidity is low, it threatens the wilting of the root crops, if it is high, it is fraught with rotting. Therefore, the humidity should be maintained at around 85 - 90%.
Read more about the required storage temperature in this article.
How to store vegetables in the cellar?
The laying of vegetable products for the winter is carried out depending on the strength of the skin and the density of the pulp of the vegetables. Potatoes and beets are among the undemanding storage conditions of vegetables. Carrots, various types of radishes, rutabagas and other thin-skinned root vegetables must be stored differently. They should not be placed in a thick layer, and should not be stored in bulk, like potatoes. The owner must choose the appropriate way of storing the root vegetables for each of their varieties.
Potatoes and carrots
It is best to place potatoes in a large chest or to fence off part of the cellar by laying the boards and on the floor. So that the top layer of the poured vegetables does not sweat, a straw chop, sawdust or other moisture-absorbing material is placed on top. It is advisable to place the chest of potatoes further from the entrance so that it does not freeze.
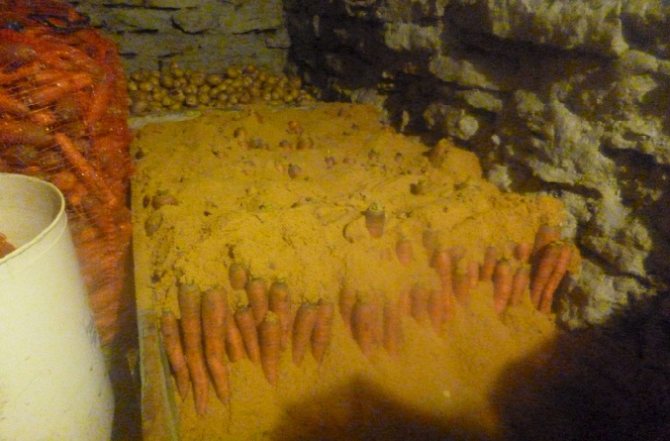
Carrots in the cellar are stored in nets or special boxes with a volume of 2-3 buckets. When laying in boxes, it is advisable to sprinkle the layers of root crops with sawdust or fine sand.


Storing onions and garlic
These vegetables require a dry, ventilated and cool cellar. Bulbs dry quickly or begin to sprout under room conditions or in a pantry, so it is best to store them at a lower temperature. It is advisable that it does not fall below + 2 ° C, otherwise the vegetables will begin to rot.
It is not recommended to store onions and garlic in a damp cellar without ventilation. Condensation that accumulates can get into the vegetable drawer and wet them. This will also lead to product decay.


Beets and cabbage
Storing beets in a cellar is as easy as storing potatoes. It can be placed in a separate closed chest or placed on top of potatoes. Beets tolerate high humidity well and absorb water vapor from the air, so they can protect the potatoes from sweating, and the owners will not have a question about why the roots wither.
Prepare cabbage for storage: leave 7-10 cm of stumps under the head during cutting. Green leaves are not completely removed from the head, leaving 2-3 pcs. Heads of cabbage can be hung or stored on a rack.


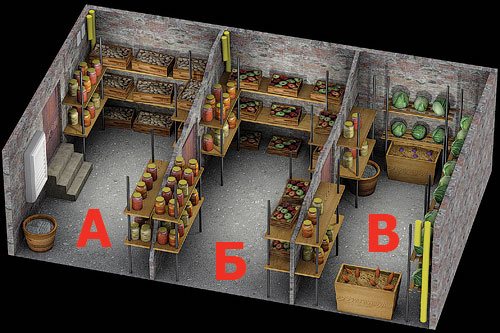
Shared storage features
At home, vegetables are stored indoors under the same conditions. But each type of product has its own temperature and humidity ranges. In order to keep different types of vegetables well in one cellar, they must be sorted, and the cellar must be conditionally divided into cool and warmer zones.
The coldest place is near the entrance and under the ventilation inlet (window). Under these conditions (about 0 ° C), carrots, beets, radishes or cabbage can be stored. Potatoes become sweetish already at + 2 ° C, so they need to take a place in the cellar away from cold air currents. Heat-loving crops - zucchini and pumpkins, tomatoes or eggplants, turnips, etc. - are stored only under freezing temperatures.
Leek intended for human consumption can be stored for a long time in conditions of average humidity for the cellar (85%) and at a temperature of about + 2 ° C.
The stems must be placed vertically in boxes of wet sand, filling up the entire white part. You can put them in the same area where the potatoes are.
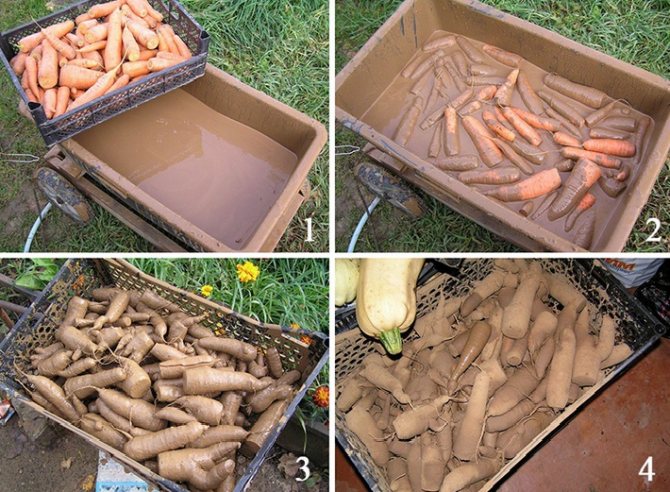
To prevent delicate roots from withering due to moisture loss in a storage that is too dry, they can be covered with a clay crust before laying.To do this, make a creamy solution in which daikon or green radish, root celery, goat, parsley, horseradish, etc. are dipped. Vegetables are laid out in 1 layer and dried until a strong crust is formed. After that, they are carefully placed in boxes and stored on the upper or middle shelves of the shelving.
For storage of vegetables that require high humidity, polyethylene packaging is also used. You can cover the boxes with the stored vegetables with foil or place the root vegetables in perforated bags. When using polyethylene for storage in the cellar, you should not tightly close the container with vegetable products: all types need air circulation.
Winter apples should be placed on a rack where the temperature does not drop below + 3 ° C. It is advisable that the fruits lie in a box, sprinkled with shavings that isolate them from each other. If spoiled, rot will not be able to infect a large number of apples.
For storing seed onions, boxes or boxes with a capacity of no more than 10 liters are required. Sevok should be laid in layers, sprinkled with wood ash or sand. Temperature changes should not be allowed, since the bulbs will begin to germinate. Boxes with sets are placed away from air currents, in a place with a temperature of about + 2 ° C.
Suitable varieties
For storage, you should choose late-ripening varieties of root crops... The following carrot varieties and hybrids are best stored:


Gribovchanin F1.- Nantes 4.
- Incomparable.
- Nevis F1.
- Samson.
- Chance.
- Moscow winter.
- Incomparable.
Beet varieties suitable for long-term storage:
- Bravo.
- Incomparable.
- Bordeaux 237.
- Red ball.
- Wintering.
- Mulatto.
- Detroit.
- Nosovskaya flat.
There are no definite recommendations on how best to preserve at home and where, in the basement or underground (underground), everyone decides for himself empirically. The determining factors for further preservation are:
- choice of variety of root crops;
- preparation technology;
- temperature regime in the room;
- humidity mode;
- lack of excess oxygen supply;
- protection from pests.
Among the methods intended for storage, each gardener will find his own, the most convenient and profitable. First, you need to decide when and how to remove the root crop for storage.
You can read more about suitable varieties of carrots and shelf life here, and here we talked about which varieties are suitable for long-term storage.