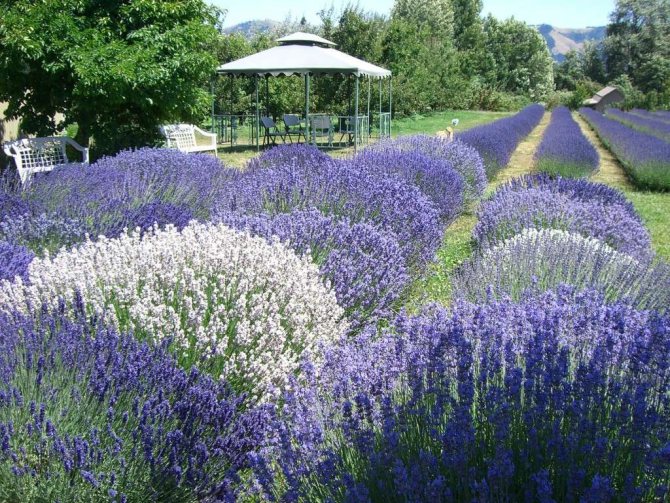
Lavender (Lavandula) is referred by botanists to the Lamiaceae family, which has two synonymous names in Latin - Lamiaceae or Labiatae. According to various sources, the genus includes about 25 to 50 different species that grow in nature in the southern regions of Europe, India and Arabia. Such plants are not uncommon in the northern and eastern regions of the African continent and in Australia. If we talk about the cultural forms of lavender, then gardeners are engaged in their cultivation almost all over the world, mainly in our country using only two types of them - broad-leaved lavender (French - Lavanluda latifolia) and narrow-leaved lavender (English - Lavandula angustifolia), which we will talk about in the following sections of the article. Today there are several bred hybrid forms.
| Family name | Lamiaceae |
| Natural growth cycle | Perennial |
| Growth form | Shrub or semi-shrub |
| Breeding method | Seed or vegetative (dividing a bush, rooting cuttings or cuttings) |
| Time to transplant to a flower bed | End of May or beginning of June |
| Landing rules | The distance between seedlings is at least 30 cm |
| Priming | Dry, well-drained, sandy or loamy |
| Indicators of soil acidity, pH | Neutral soil (6.5-7) |
| Lighting level | Open sunny location |
| Recommended humidity | Abundant and regular, during dry seasons frequent |
| Special Requirements | Drought tolerant |
| Plant height values | 0.6-1 m |
| Inflorescences or type of flowers | Spicate |
| Flower color | Blue or blue-lilac |
| Flowering period | Second half of summer |
| Decorative time | Spring-summer |
| Application in landscape design | Rockeries and alpine slides, border decoration |
| USDA zone | 4 and more |
There are versions that the scientific name in Latin "lavandula" the plant bears thanks to the word "lava", which translates as "wash". This is due to the fact that in ancient Rome it was customary to take baths with lavender, as it had wonderful aromas and gave a feeling of freshness. You can hear how lavender is called "butterfly" because of the characteristic outlines of flowers, and in Egypt, the nickname "Indian stripes" is found.
On our territory, only in the northern regions of Russia, lavender can be subjected to freezing, in this case the plant is grown as an annual by sowing seeds.
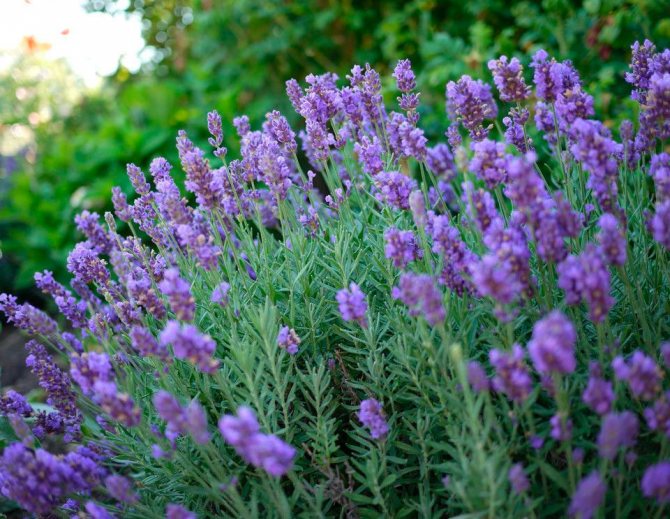
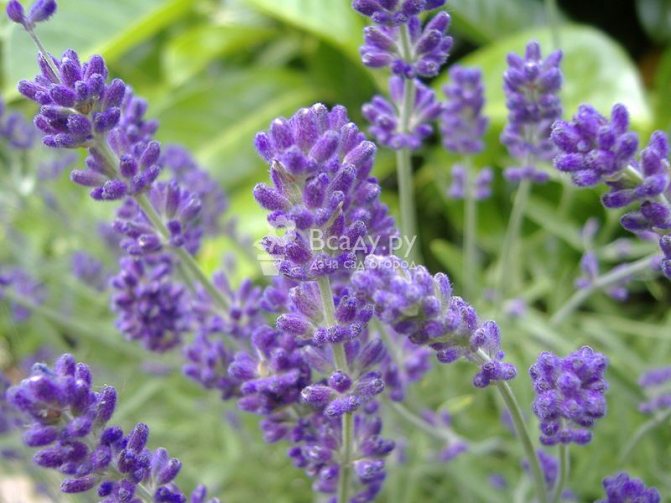
All types of lavender are perennials with a shrub form of growth. The root has a fibrous outline, woody and can go deep into the soil up to two meters. There are a large number of shoots in the bush, in the lower part of the bush they usually become lignified. The height to which they are able to stretch reaches 0.6–1 m. All stems are covered with oppositely grown leaf plates. Leaves are devoid of petioles (sessile), are characterized by a linear shape and a silvery-greenish color. At the same time, soft pubescence is present on the leaf surface.
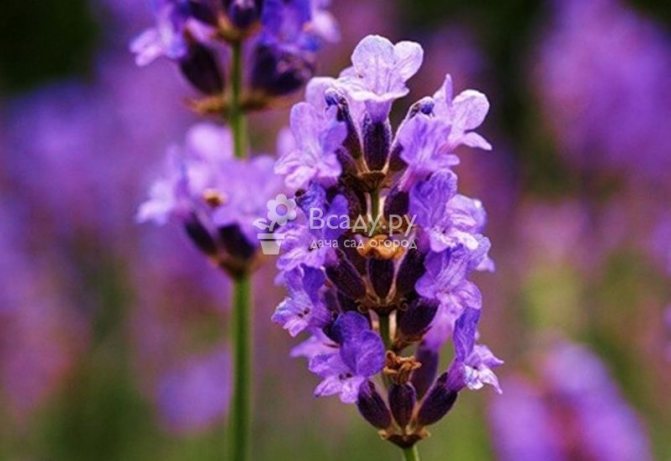
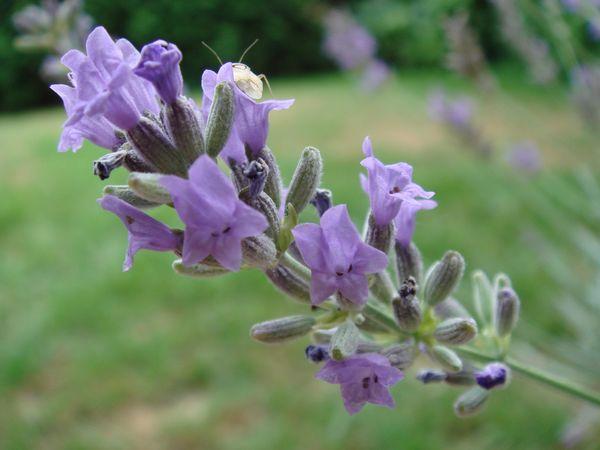
When flowering, which occurs in the first or second half of summer, lavender blooms flowers that have a blue or blue-lilac hue. Inflorescences are collected from them, taking the shape of spikelets, the buds of which are arranged whorled, 6-10 pieces in each. The inflorescences usually crown the tops of the leafless stems.
Lavender is considered to be an excellent honey plant. Seeds that ripen after pollination of flowers by insects (if storage conditions are not violated) can remain viable for many years. The color of the seeds is dark - from grayish to black, the surface is glossy, the size is small. The shape of the seeds of the "butterfly" is oval.
It is best to plant in a subtropical climate zone, but with a little effort, you can get fragrant summer plantings of "Indian stripes" in your garden, following the recommendations below.
Description: varieties and varieties of lavender
Lavender is an evergreen, rather unpretentious plant widely used in cosmetology and medicine. The scent of lavender has a calming effect and helps relieve headaches. But not only medicinal properties are appreciated in lavender. It is widely used in perfumery and cosmetology. Lavender and cooking did not pass by, because this plant has a specific spicy taste. And in everyday life, dried lavender sprigs are used as a reliable remedy for moths.

There are many varieties of lavender. Which one to plant in your garden - choose according to your taste
More than 25 types of lavender are known, but several varieties are most popular in the garden culture.
Narrow-leaved lavender (English). It is a bush no more than a meter in diameter. The leaves of this variety are medium-sized, narrow, gray-green. Blooms in June and July. The variety is unpretentious and tolerates low temperatures well.
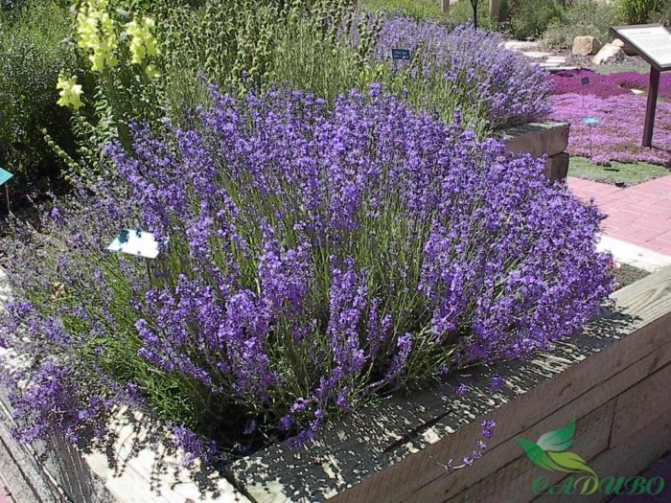
Broadleaf lavender (French). This lavender variety is considered the ancestor of the decorative varieties. It differs from other varieties in a wide color range of inflorescences, as well as a very strong and not always pleasant aroma.
Hybrid lavender (Dutch). This variety is considered to be the largest. Its bushes can grow up to two meters. It is a natural hybrid of narrow-leaved and broad-leaved varieties. Blooms in July. Its frost resistance is lower than that of the narrow-leaved one. Refers to industrial grades.


Dutch lavender has the most beautiful flowers
Lavender toothed. One of the most thermophilic varieties. Prefers to grow indoors rather than outdoors. It is the owner of soft silvery leaves and inflorescences of large flowers in all shades of purple.
Botanical portrait
The genus Lavandula of the family Lamiaceae or Lipocytes includes 47 species of annual or perennial herbaceous plants or shrubs.


Lavender has a powerful woody root, extending almost 2 m deep, and branched stems, slightly woody at the bottom.
The shape of the leaf plates in various plants of the genus is different - in some the leaves are simple, in others they are pinnate-toothed, in some they are slightly dissected.
Almost all representatives of the genus have pubescence of foliage, stems and petioles, giving them a silvery-green hue, many have glands containing essential oils.
Flowers in whorls of 6-10 pieces, blue-lilac, blue or blue-violet, collected in an inflorescence-spike on the tops of the leafless upper stems.
They bloom in the second half of summer, collecting swarms of bees. Seeds remain viable for a long period - up to several years.
Planting a plant
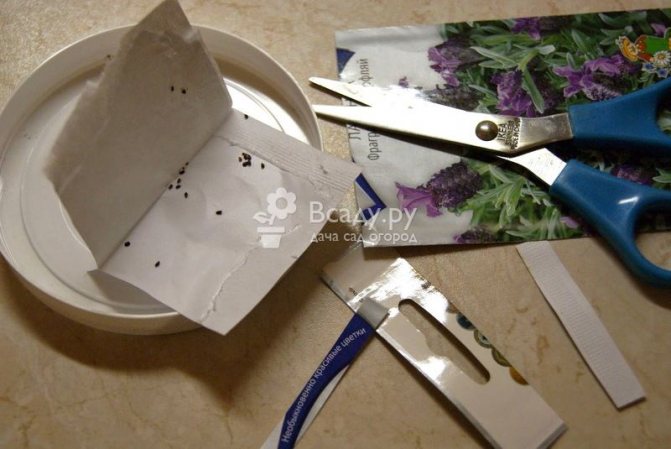
Lavender can be propagated in different ways: cuttings, dividing the bush, layering, seeds. Lavender seeds can keep germinating for many years, if you follow the rule: store them in sealed containers.
Attention! Lavender seeds need to undergo preliminary processing - stratification. For this, the seeds must be kept at a temperature of +5 ° C for at least two months. Most often, for this purpose, the seeds are mixed into wet sand and placed in a refrigerator.
Lavender seeds can be sown directly into open ground, but certain requirements must be met.
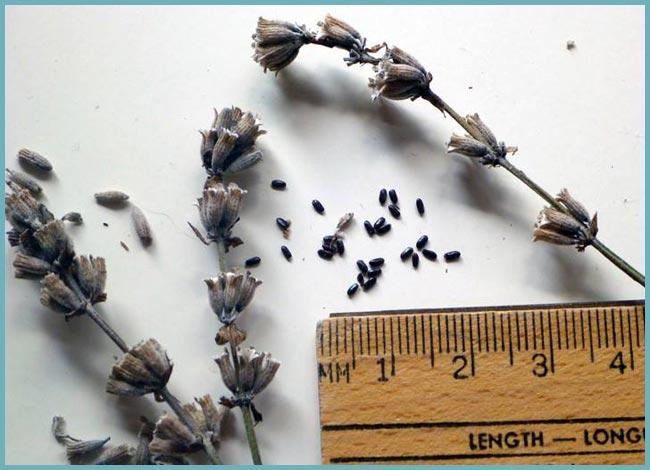


Lavender seeds
The best time to plant lavender outdoors is October. It is sown to a depth of no more than 4 mm, the soil must be slightly compacted. If the weather is dry, then the seeds can be watered. In winter, the area sown with lavender should be covered with snow as much as possible.
In open ground, you can sow seeds in the spring. To do this, first, in March, you need to remove the seeds in the refrigerator for stratification, and in May sow in open ground in a previously prepared place.
Advice. Choose a place for lavender in a dry and sunny area. This flower does not like waterlogging.
The subtleties of growing a flower
To get blooming healthy lavender in the garden or in the country, you need to choose the right place, know when to plant a crop, how to plant a plant in open ground. And then the beautiful flower can be admired from May until late autumn.
Seat selection
The guarantee of successful cultivation of lavender is the correct planting site. Therefore, it is important to know where to plant the culture. The plant loves open areas that are illuminated by the rays of the sun. Bushes can take root in the shade, but they will not please with abundant and long flowering. The root system of lavender reacts sensitively to increased soil moisture. Therefore, you need to abandon planting it in wetlands.
See also
Planting and caring for perennial garden primrose, growing from seedsRead


The plant is demanding on the level of acidity and soil structure. Before planting, add wood ash or lime to the soil, these substances will effectively reduce acidity. And to provide porous soil, compost is systematically applied to the flower bed. Fertilizer will loosen the soil and enrich it with all the necessary nutrients.
When to plant
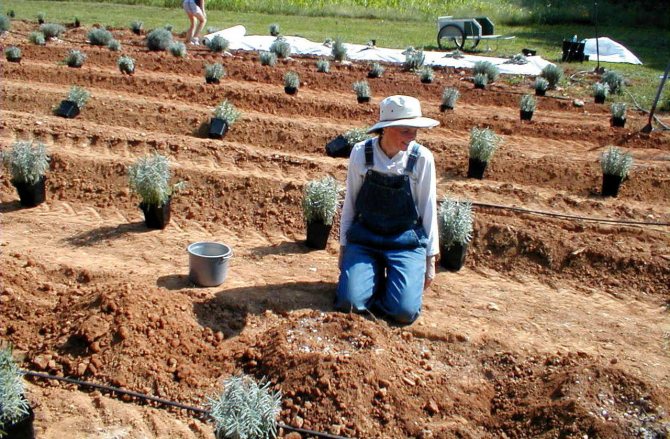
Sow seeds in the ground in October. Seedlings are planted for seedlings in February or March. Seedlings are planted in the soil in the last days of May or in the first decade of June.
Landing features
Flowers can be bred not only from seedlings, but also from seeds. The seed method is more labor intensive, which is why gardeners choose seedling cultivation. To do this, sow the seeds in the last days of February - early March, so that the young sprouts have time to grow stronger before moving them into open soil.


You need to plant lavender seedlings at the end of May. Prepare landing pits in advance. Effective perception of the flower bed is created while maintaining the optimal viewing distance. In the process of planting, adhere to a distance between planting units of 80-90 cm for compact varieties, and for tall hybrids - 120 cm. The depth of the grooves depends on the size of the roots of the seedlings.
Place the seedlings in a hole, spreading the roots, and cover the lavender so that its root collar is 5-6 cm deep, then water abundantly.
If the flower bed is located in areas with a warm climate, then lavender can be grown using seeds. For this, podzimny sowing is used, which includes planting seeds in the soil in October. Planting material must be sown to a depth of 3-4 cm, and the soil must be tamped from above. Watering is necessary in dry autumn weather. In winter, cover the flowerbed with snow.
Lavender care
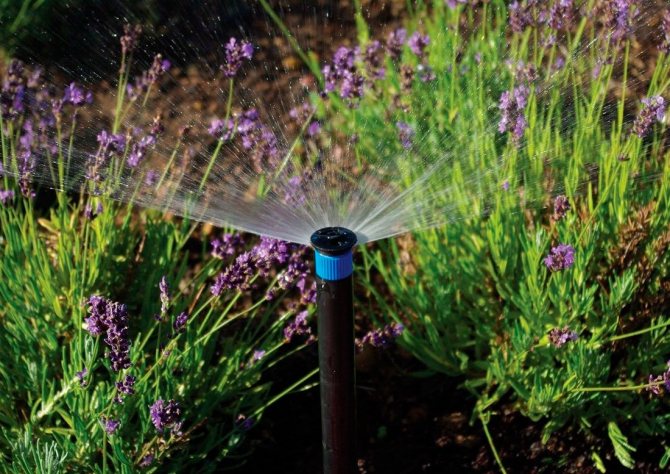
Water the lavender only when the soil is dry. Excessive moisture leads to root decay, but it is not recommended to dry out lavender either.
In autumn and spring, shrubs need to be hilled, and cutting lavender significantly extends the life of the plant. A small pruning can be done immediately after the lavender has faded, but a more significant shortening should be done only at the end of autumn, leaving up to 4-5 new green shoots.


Prune the bushes - this will not only give them a more decorative look, but also benefit the plant.
If your lavender will be hibernating outdoors where temperatures drop below -25 degrees, provide a warm shelter. To do this, it will be enough to cut the bushes before wintering and cover them with branches of coniferous trees.
Attention! Covering lavender with foliage, as is usually done to protect plants from freezing, should not be, this may result in plant decay.
Choosing a location for lavender
Lavender is a thermophilic shrub suitable for indoor growing. This plant does not differ in a particularly capricious character, but when choosing a suitable place for planting, one should be guided by its preferences.
What conditions are necessary for good growth:
- Adequate lighting is a must when choosing a landing site. In the shade, the shrub will wither, so it is necessary to place the plantings away from tall trees and the shadow of buildings.
- The soil for planting lavender should be moderately dry. With a low groundwater table, it is better to plant bushes on a hill (the alternative is good drainage). In addition, the root system of the plant is very sensitive to excessive moisture. That is why, when watering, it is better to focus on the principle "less is better, but more often."
- Lavender grows well only on neutral soils, so be sure to check this indicator before planting. Too acidic soil - lime, soils with an alkaline reaction - acidify.
- The plant responds well to compost fertilization. Such a substance, in addition to providing nutritional value, also helps to loosen the soil, which has a beneficial effect on the growth of shrubs.
- Almost all varieties, especially broadleaf lavender, cannot boast of frost resistance. In warm climates, bushes need winter shelter, and for regions with harsh conditions, it is advisable to plant a plant in pots. With the onset of frost, the container is simply brought into a cool room, providing peace until spring.
You may be interested in: Drummond's Phlox: growing from seed, when to plant
All varieties of lavender can be roughly classified into plants with wide and narrow leaves. Narrow-leaved species tolerate frost relatively well and are able to hibernate under cover even in cold winters. At the same time, humidity is destructive for them, therefore, when a thaw sets in, it is imperative to “ventilate” the shelter and watch out for possible rainfall getting inside.


Fertilizing and feeding lavender
In spring, it is recommended to feed lavender with nitrogen fertilizers. To do this, you need to dilute 1 tbsp. l. urea or 2 tbsp. l. "Sodium humate" for 10 liters of water. The consumption of such a solution for 1 bush should be no more than 5 - 6 liters.
At the beginning of flowering, lavender can be fed with a fertilizer solution "Agricola-Fantasy" (it is diluted in a proportion of 2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). The consumption of this solution is 3-4 liters per one bush.
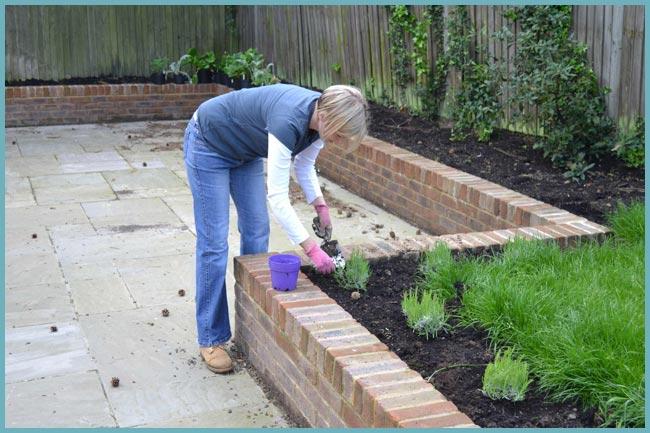


To make lavender bloom better - feed the plant with mineral fertilizers
Instead of Agricola, a solution of organic fertilizer Rossa Universal is also used, dissolving 2 tbsp. spoons in 10 liters of water. And the third option for feeding: 2 tbsp. l. dilute nitrophosphate and half a liter of liquid mullein in 10 liters of water. The consumption of the last two solutions is 10 liters per bush.
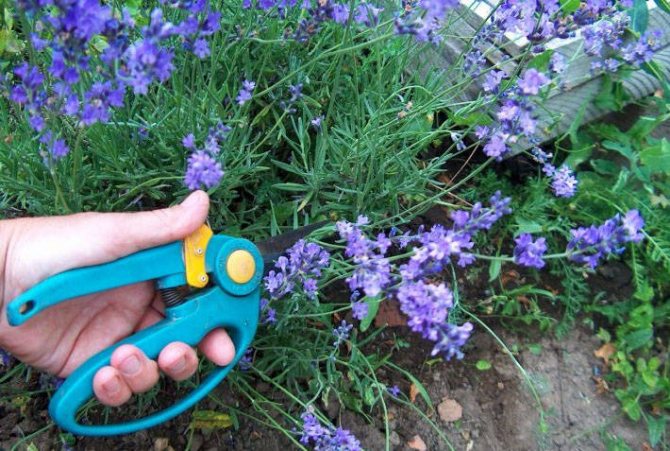
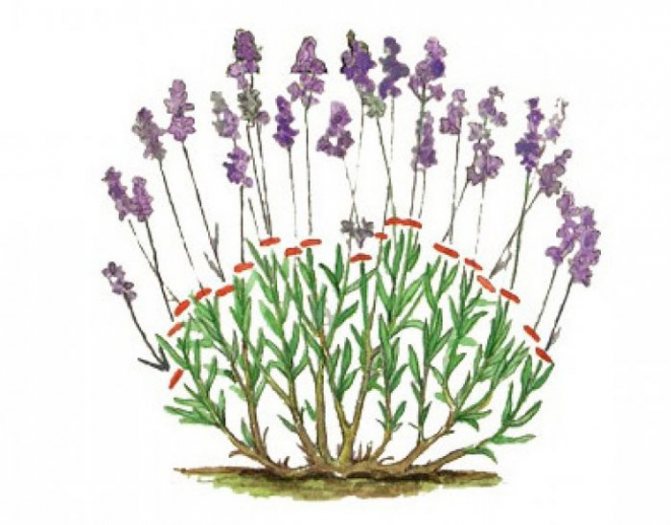
How and when to trim
Spirea - planting and care in the open field
One pruning per year will be enough for the plant, which will allow the bush to grow, and the shoots to woody. Long-term experience suggests that this procedure should be carried out immediately after the end of flowering - in the second half of July. The advantage of summer pruning is that lavender can grow a sufficient amount of fresh, compact and beautiful green mass in a short time.
Since the plant blooms only in the summer, it is allowed to cut the bushes in the spring, when the frost ends. The recommended cutting rate is 2 times a year.The first procedure will stimulate flowering, and the second will ennoble the bush.
For curly spring pruning, it will be enough to shorten the tips of the shoots by a third, to give the plant a semicircular shape. In the summer, it will be necessary to remove the peduncles and 2-3 upper pairs of leaves.
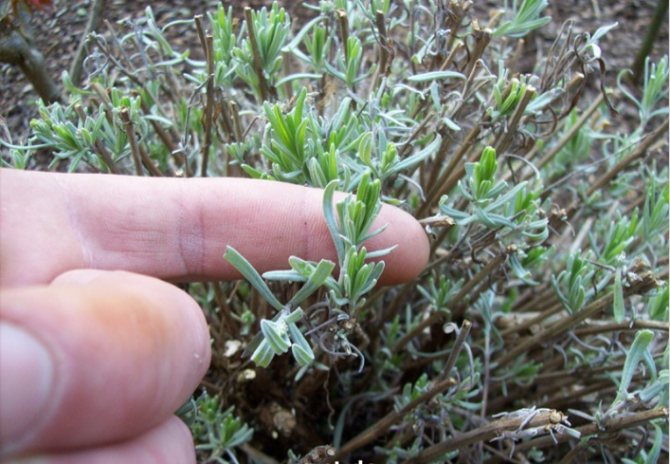


Pruning lavender
Plant propagation
Lavender is propagated by division, cuttings or layering.
Reproduction by division perhaps when there are already lavender bushes on the site. In summer, lavender produces a lot of young growth. It is something that can be rooted. To do this, you need to cut the plant and huddle in such a way that all the free space between the stems is densely filled with earth. And by the fall, the bush can be divided.


Dividing the lavender bush
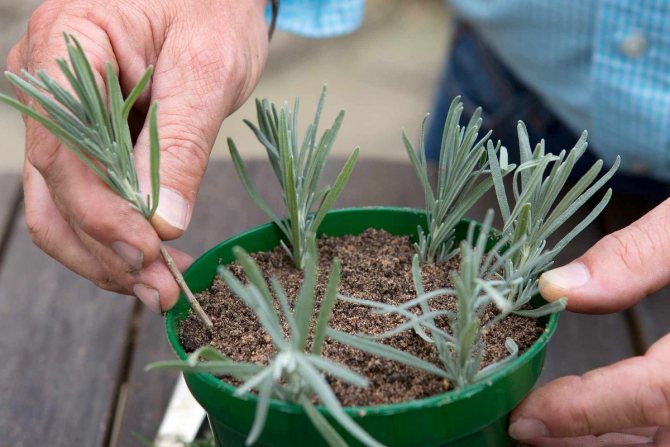
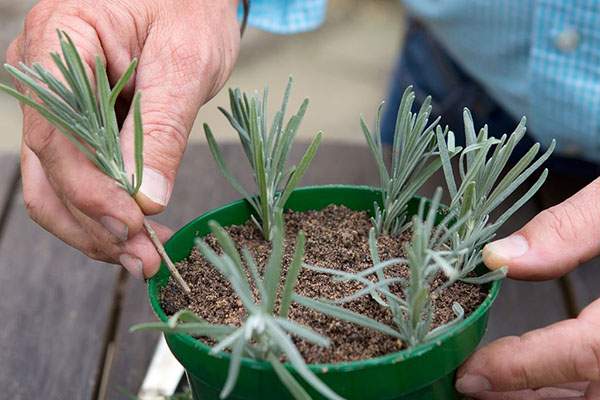
The most suitable way to propagate home-grown lavender is propagation by cuttings... To do this, lignified annual shoots should be divided into cuttings no more than 10 cm and root.
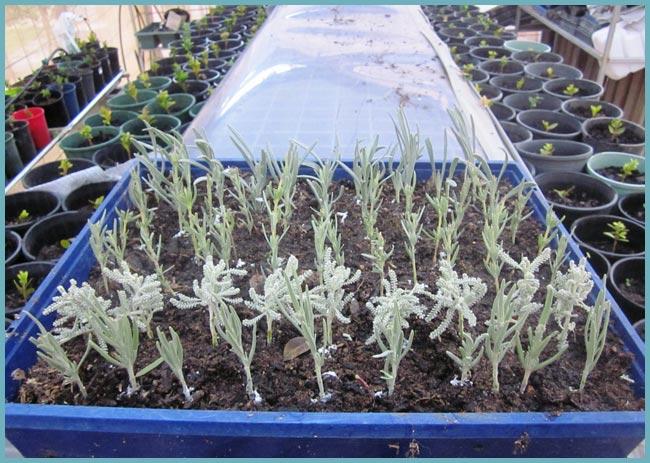


Propagation of lavender by layering
The easiest breeding method, which is suitable even for novice gardeners, is reproduction by layering... With this method, in the spring, 2-3 shoots are carefully folded back and placed in a groove 3-5 cm deep, fixed, sprinkled with earth and watered. These shoots need to be watered a little more abundantly in order for the formation of lateral roots to occur successfully. After a year, the shoots are already completely independent, and you can plant them from the mother bush.
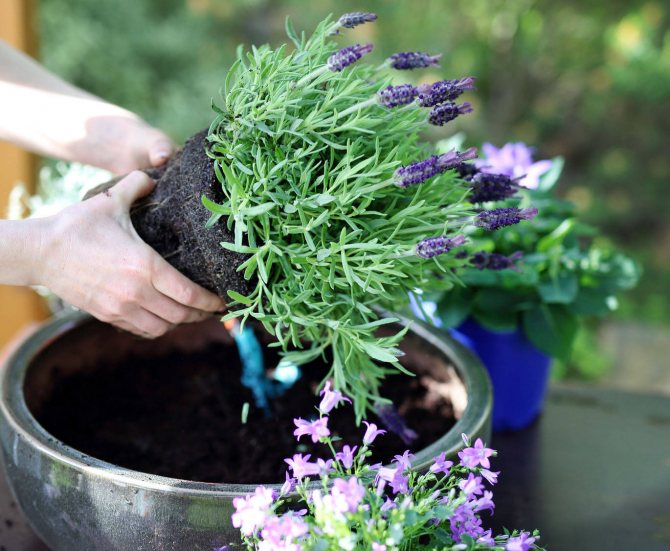
How to plant lavender
It is advisable to plant the acquired seedling on the same day in a permanent place. The older the plant, the more difficult it will withstand such an intervention, therefore it is preferable to grow lavender with seedlings or cuttings, rather than replanting an adult bush.
How to plant a lavender seedling:
- For better rooting, before planting, it is necessary to leave the plant for an hour and a half in warm water. For guaranteed successful rooting, it is advisable to use stimulating solutions.
- On a previously prepared (dug and fertilized) bed, make narrow trenches. The distance between the rows depends on the varietal characteristics and is usually 50-60 centimeters.
- Before planting, it is necessary to trim the roots and top of the plant a little, and remove the side shoots and leaves completely.
- Landing is carried out at 15-20 centimeters of depth. The roots must be carefully straightened, pressed lightly with your hand and covered with soil. Water and mulch the planting site.


Further care includes watering and loosening. Despite the fact that lavender is an excellent honey plant and attracts many pollinating insects, pests try to stay away from it. That is why in organic farming, lavender beds are planted between vegetable crops. This will scare away insects without any chemicals, besides, it is pleasing to the eye and improves mood.
You may be interested in: Planting and Growing Potatoes in Ridges
Highlights of growing lavender from cuttings:
- For propagation of lavender, cuttings of the plant can also be used. To do this, it is necessary to cut off the one-year lignified shoot.
- The stalk is soaked in warm water or growth stimulating solution.
- A day later, the shoot is buried in a nutrient substrate by 2-3 centimeters.
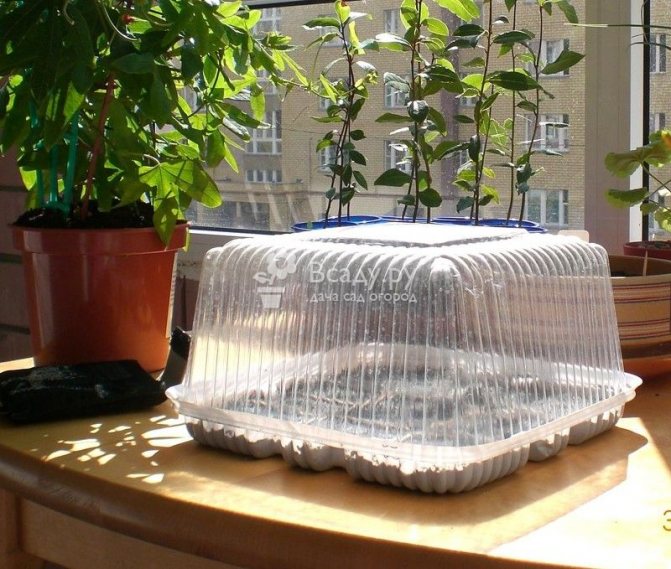
- For better survival, the plant is covered with a jar, creating a miniature "greenhouse".
Rooting and growth of shoots occurs quickly enough. After numerous basal processes are formed on the cuttings, the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place. It should be noted that any transplant for lavender is a lot of stress, so you need to act very carefully. You cannot expose the root system; it is better to transplant together with an earthen clod. After planting in a new place, the plant needs complete rest. For irrigation, warm, settled water is used, additional darkening is organized for young leaves in extreme heat.


Diseases and pests
Lavender is not very susceptible to diseases, and parasites attack it infrequently, but this does not mean that nothing like this can happen. Of the diseases, gray rot is most common. Caring for a diseased plant consists in cutting off the damaged parts. The cut off parts must be burned.
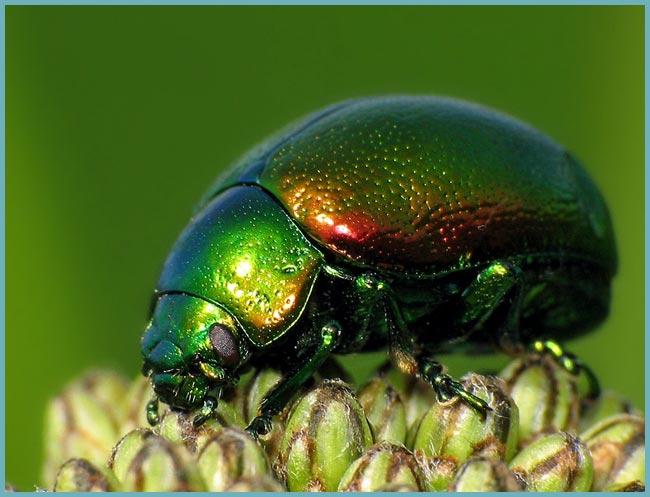


Monitor plant health and remove insects
Of the garden pests on lavender, you can find the rainbow beetle eating leaves. You need to collect it from plants by hand. But more often lavender is subject to the dominance of pennies, which do not cause any damage to the plant, but spoil the appearance pretty much, because they cover their larvae with a layer of white foam, which looks very much like saliva. Caring for lavender that has been attacked by pennies is very simple. It is enough to rinse off the foam with a stream of water.
Lavender: Combination with other plants
It is known that smells have a great influence on a person's subconsciousness. Therefore, when growing flowers, it is important that the flower bed is not only pleasing to the eye, but also enchants with its aroma. When planting plants, it is important to take care not only that the appearance of the flowers complements each other, but also that the floral aromas do not mix. This means that you will have to carefully consider the selection of flowers that you want to plant, otherwise you will hardly be able to rest or recharge in your garden.
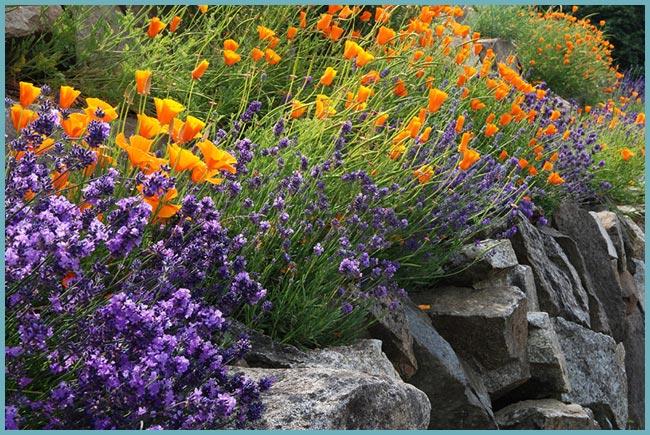


Lavender looks very good next to plants with contrasting colors.
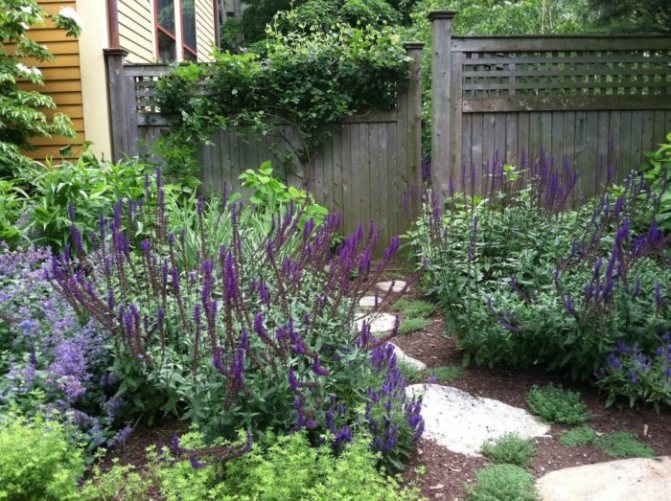
Lavender goes very well with sage and catnip. She also looks amazing next to yarrow and garden hydrangea, liatrix, or surrounded by grown herbs and perennials.
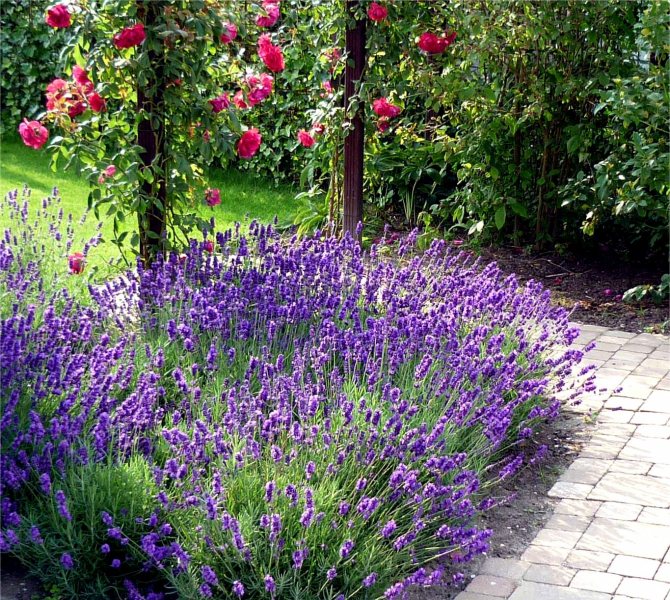
Lavender in landscape design
Lavender, planting and caring for which is so easy that any budding gardener can handle it, is ideal for decorating an area. A significant advantage of lavender among other landscaping plants gives a bright and intense color in various shades, from pale pink to bright lilac. This makes it possible to accentuate the grace of any corner of your garden.


Lavender in landscape design
Advice. Use decorative designs to highlight the originality of your flower garden.
There are several options for decorating your garden with these flowering shrubs.
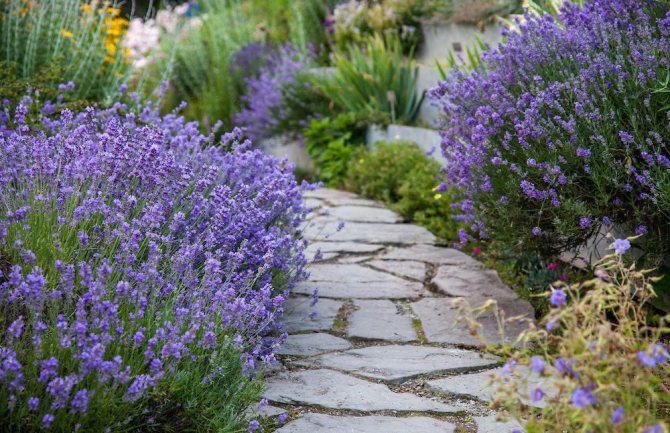
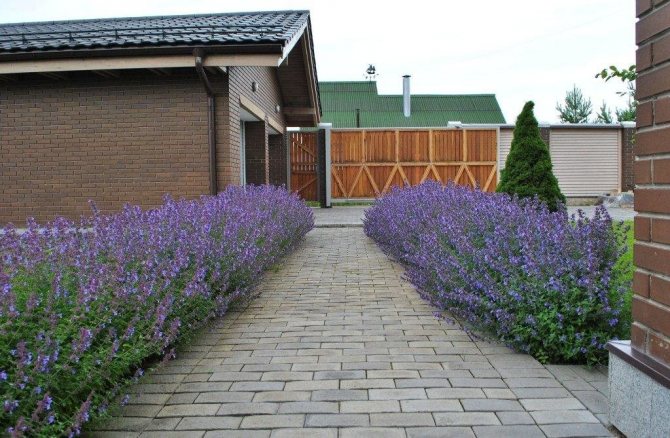
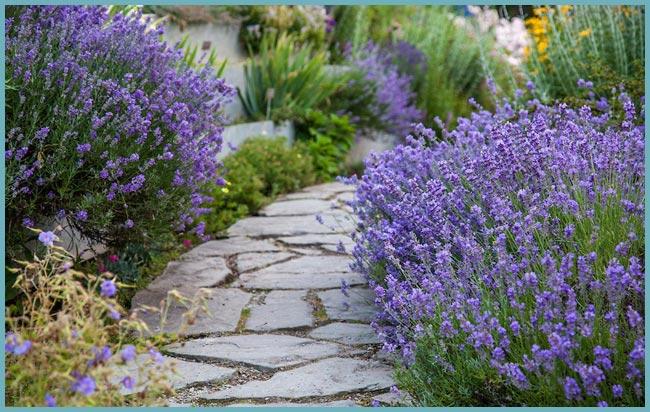
- Perhaps the most well-known and common way is to plant lavender along paths and sidewalks. This design of your site makes it possible to visually limit, as well as create a clear division of the garden into zones.
- The second option is to plant the bushes in such a way that the lavender will grow in accordance with the order of the cells on the chessboard. But this type of landing will only work on a completely horizontal surface.
- Another unusual way to emphasize the originality of a garden plot or flower garden is to form a "carpet" of these shrubs. If you decide to choose this option, you need to immediately determine the height of the lavender and regularly cut it at this level in the same plane. Such a carpet will not become a semblance of a soft grassy one on which you can comfortably sit, but planting shrubs in this way will allow lavender to brilliantly show its color.
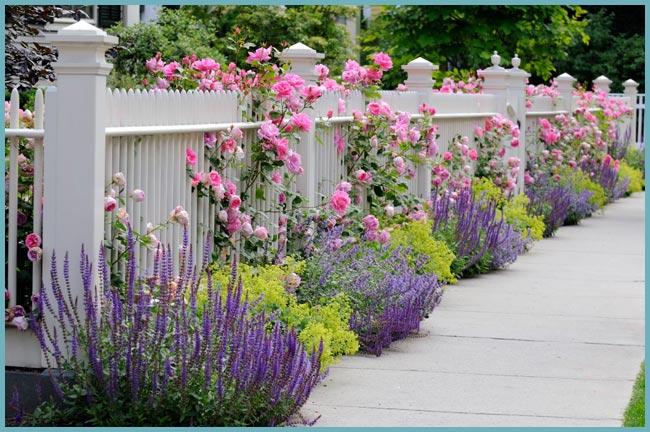


Lavender is often planted along paths and fences.
Of course, lavender in landscape design is not as common as planting roses or all kinds of loaches, but this is what will emphasize the uniqueness and originality of the decorative design of your garden.
Growing lavender is the perfect way to highlight your garden or flower garden with color, shape, and an elegant scent that will impress everyone who walks by.
Views
Today, many varieties of lavender are known, each of which has certain characteristics.


English
This plant is native to the south of Europe.It is a perennial shrub characterized by small lilac blossoms and silvery foliage. The culture blooms in July-August. It is very resistant to frost. The most common type of such lavender is the dolphin plant. It does not exceed 30 centimeters in height and has attractive silvery foliage. The Headcoat variety is very popular. It is used to decorate small hedges.
Common varieties of English lavender include:
- Headcoat Giant - has a compact size and reaches 60 centimeters;
- Alba - the plant grows 50 centimeters and has white inflorescences;
- Manstad - the bush grows up to 40 centimeters and is distinguished by rich blue flowers;
- Rosea - the culture reaches 40 centimeters and has a purple hue;
- Headcoat Blue - grows up to 40 centimeters and has purple flowers.
French
This lavender is also called broadleaf. It has an intense aroma and attractive flowers. They are pink, white, lilac. There are purple and burgundy tones. The culture begins flowering in April-May and ends in July. In August, the plant can bloom again.
The French culture can hardly be called frost-resistant. Therefore, it is recommended to grow it in warm regions. The most popular plant species is Lavandula stoechas pedunculata. The culture is characterized by original inflorescences.
From this category, the following varieties are most popular:
- Rocky Road - is a new variety, which is characterized by purple inflorescences;
- Yellow Vale - it is characterized by rich purple inflorescences and yellowish foliage;
- Tiara - has large blue flowers and cream bracts;
- Regal Splendur - has deep purple flowers;
- Helmsdale - differs in lilac color with a burgundy tint.
Hybrid
This lavender is also called Dutch lavender. This category includes highly decorative hybrids. They are massive bushes. They are characterized by large flowers. The plant has narrow leaves. They have a beautiful silvery color. Lavender blooms in July.


Famous varieties in this category include the following:
- Arabian Knight - has bright purple flowers;
- Alba - has a white color;
- Richard Gray is a small bush with purple flowers;
- Grosso - purple flowers are characteristic of lavender;
- Sawyers - has a pale lilac color.
See also
What hanging ampelous flowers are best for pots, how to plant and care
Toothed
It is a special type of plant that has silvery foliage. It is characterized by large flowers of various shades of purple. This crop is more suitable for indoor cultivation. It is not recommended to plant it in open soil.
Narrow-leaved
This is an unpretentious plant that tolerates low temperatures well. The shrub begins to bloom in the middle of summer. Narrow leaves are considered a characteristic feature of the culture. They are grayish in color. The bush is compact.