Category: Plant pests
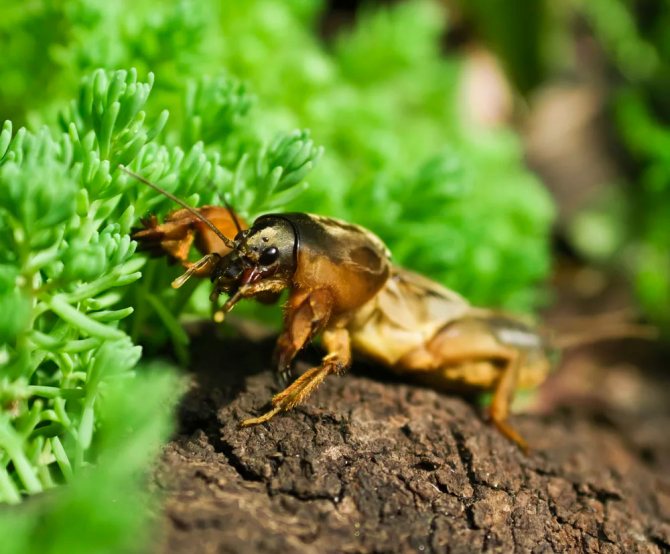
bug bear (lat.Gryllotalpidae) belongs to the family of large burrowing insects of the Orthoptera order, in which there are more than 110 species. The most common pest in our gardens and orchards common bear (lat.Gryllotalpidae gryllotalpa), or cabbage, which in Europe is not found only in Finland and Norway, but also lives in Asia, North Africa, Transcaucasia and Kazakhstan, preferring sandy, sun-warmed soils. The bear insect lives mainly underground, getting to the surface only at night, and hibernates at a depth of two or more meters or in warm compost heaps. The pest feeds not only on roots and earthworms - its danger is that it is omnivorous.
The victims of the bear, in addition to beets, carrots and potatoes, can be cucumbers, onions, lettuce, cabbage, garden strawberries, corn, barley, oats, rye, legumes, melons and flowers.
Bear insect - description
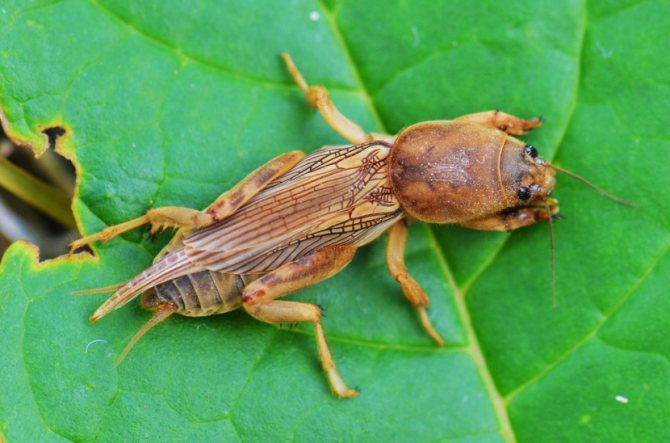
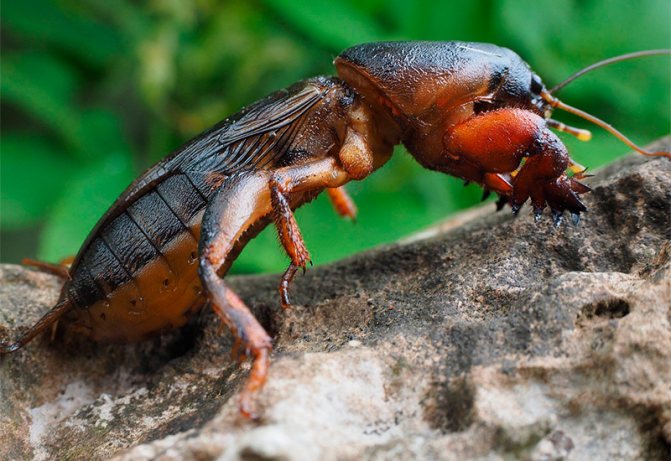
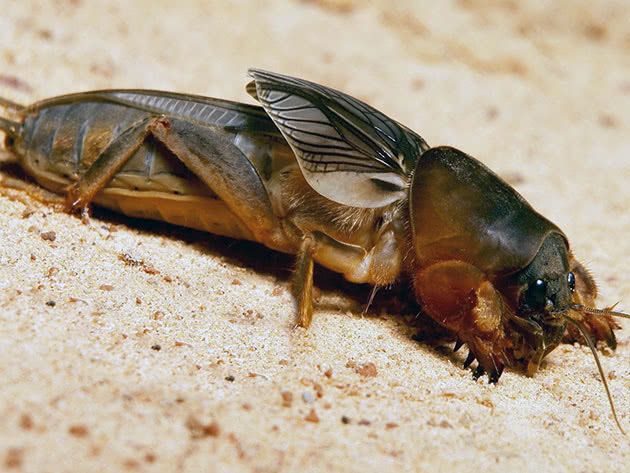
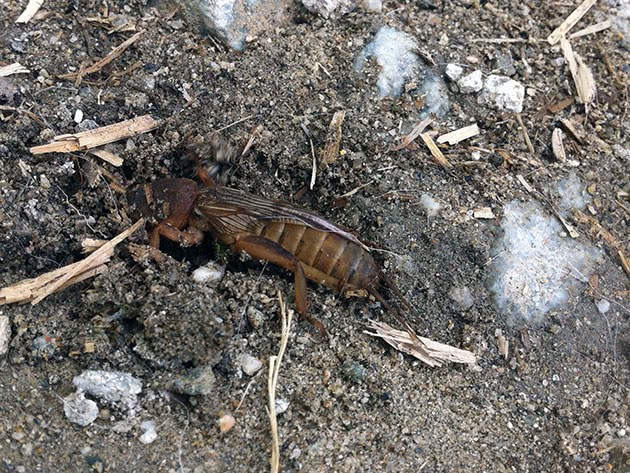
The garden bear is a large insect, reaching a length of 5 cm, although some gardeners claim that they have met individuals up to 15 cm long. What does a bear look like? Its soft abdomen is fusiform and about a centimeter in diameter is three times longer than the cephalothorax. At the end of the dark brown abdomen there are cerci - paired filamentous appendages up to 1 cm long. The chest is protected by a hard shell, under which the bear can partially hide its head. The eyes of the insect are large, complex; there are also a pair of tentacles on the head, long antennae-whiskers and very strong jaws. The front pair of the bear's limbs with pincers is arranged so that it is convenient for her to dig the ground.
The bear has wings, but in order for their muscles to work, warm air is needed, so the bears fly infrequently, but they swim quite quickly. At night, especially during the mating season, the bears sing - they emit powerful trills, chirp and chirp, using the friction of their wings for this.
- Cruciferous flea: how to fight, remedies and drugs
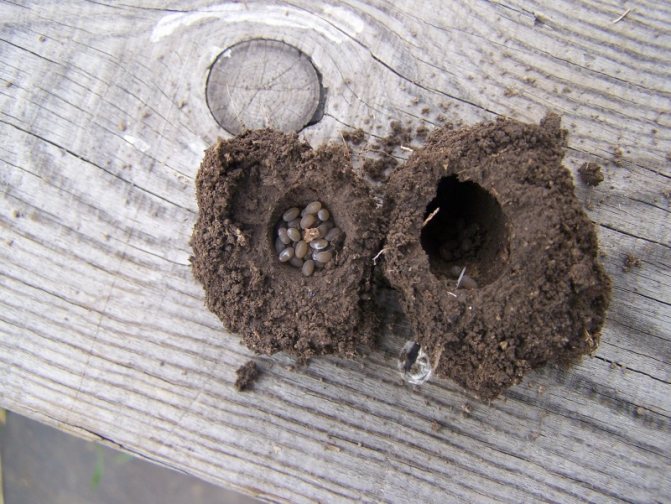
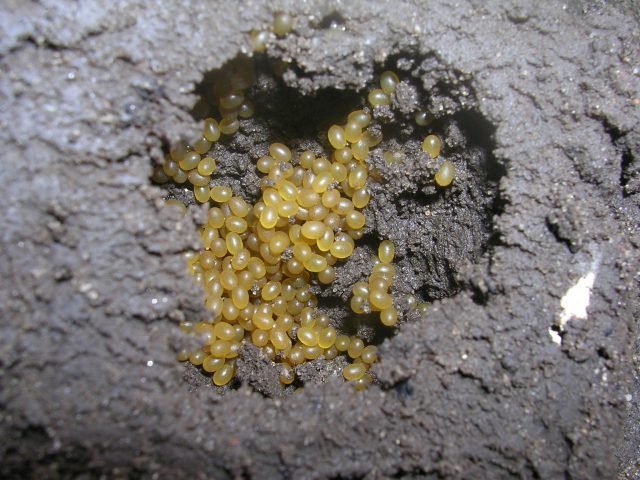
Bears at a shallow depth make a nest about 6x6 cm in size, lay in it up to five hundred dark yellow eggs with a diameter of 4-5 mm, of which larvae appear in two weeks. The bear beetle larva resembles an adult insect in body shape, but it is not dark brown, but gray. The larva of the bear has been growing for several years.
We will tell you what methods of dealing with a bear exist, how to deal with a bear in the garden with folk remedies and whether it is possible to get rid of a bear forever.
Medvedka does not like pungent odors
Knowing that the insect does not tolerate extraneous odors, we get rid of the bear in the following ways:
- you can pour gasoline / kerosene into the hole (if there are no crops nearby so as not to spoil them);
- soapy water is a strong irritant for the insect, therefore, when it is poured into the hole, the cabbage will immediately crawl out into the air (you can use liquid soap, solid, washing powder or dishwashing detergent);
- garlic solution (for 1 liter of water you need to squeeze out 2 cloves of garlic, mix and pour into the hole) will also quickly remove insects and will not harm crops.
You can purchase special poisons, but in order not to harm the plants, it is better to use proven methods.
How to deal with a bear in the garden
Fighting the bear
You can understand that bears live on the site by small mounds of peculiarly rolled lumps of soil on its surface, which are especially noticeable after rain. The greatest activity of these insects can be observed in May, when the bears crawl out of the already heated ground. It was at this time that shallow holes should be dug on the site and filled with chopped straw or fresh manure. Bears will crawl into egg-laying pits so that the hatched larvae can feed on manure or straw. After 3-4 weeks, the contents of the traps, together with the larvae, are removed and burned.

In order to destroy this dangerous insect, you need to find all the nests of the bear. Since they are not located very deep, they can be found when digging. The nests are carefully dug up, placed in a bucket and then destroyed. Try to do this so that the female does not crawl to the surface. Take a pesticide and spread its granules in all the passages leading from the nest - this way you will destroy the female too.
There is another way to get rid of the bear. As soon as you find the nest, fill it with soapy water so that it fills all the passages dug by the insect. Both the larvae and the female will die from the soap solution if she is in one of the passages. If she is not there, be prepared for the fact that after a while in the same place the female will again make a nest and lay eggs in it.
The soap solution is prepared as follows: 10 g of grated laundry soap and 50 g of washing powder are dissolved in a bucket of water. Instead of a soap solution for filling the passages, you can use water with vegetable oil - a tablespoon of oil is stirred in 4 liters of water - or water with kerosene - 100 g of kerosene per bucket of water at the rate of 30 g of solution for each hole.
- Cruciferous flea: how to fight, remedies and drugs
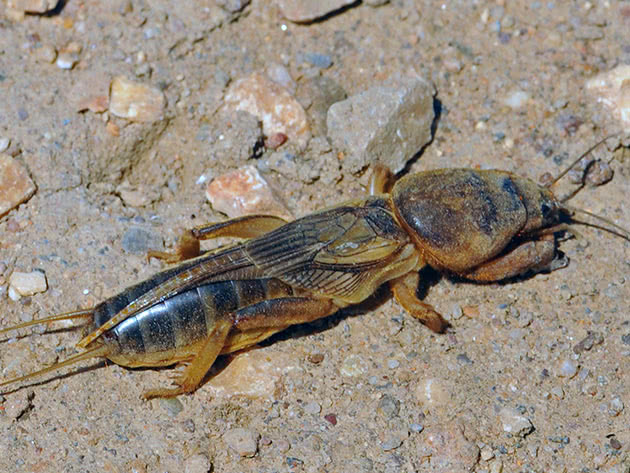


If the bears were found by you towards the end of the growing season, wait until autumn and at a soil temperature of at least 8 ºC, dig trapping pits 50-60 cm deep, line the bottom and walls of the pits with plastic wrap, fill them with manure that has begun to sweep and cover with an impromptu lid. As soon as persistent frosts set in, remove the manure from the pits along with the bears that crawled into a warm shelter for the winter, and scatter it over the site. The bears will die from frost, because already at a temperature of +5 ºC they become inactive.
Remedies for Medvedka (preparations)
The fight against bears in the garden is also carried out with pesticides, however, chemical preparations for bears are used only as a last resort, when other methods of struggle have turned out to be ineffective. Several effective remedies for bear are known:
- Medvetox - a unique granular preparation with an attractive taste for insects and a killer effect. To die, it is enough for a bear to eat just one pellet;
- Bugbear - one of the most effective remedies for the bear, which does not have a harmful effect on the environment, which is used in the form of a solution;
- Chops - an effective and relatively safe remedy for a bear in the form of brightly colored granules, which are laid out in the passages dug by the pest;
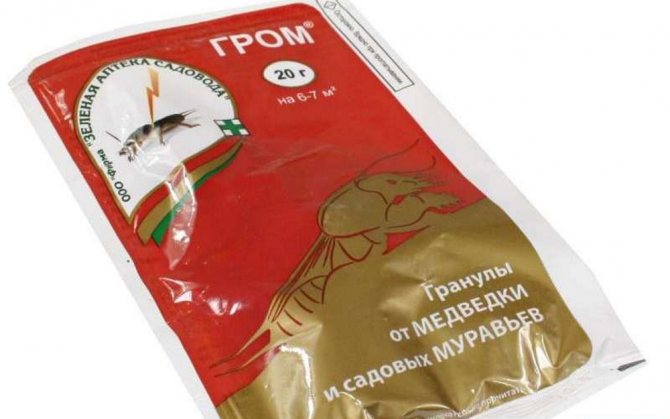
- Thunder - this drug is effective, but it includes carcinogens, therefore, it must be used with caution, laying out 3-4 granules in the moves of the bear;
- Grizzly - granules of the color of bread on the basis of Diazinon, which are used with great care, laid out in the passages dug by the bear;
- Bankcol - insecticide of contact-intestinal action, low toxic to humans, immobilizing the insect, which deprives it of the opportunity to receive food and leads to death in 2-3 days;
- Phenoxine plus - granules with an attractive aroma and taste for the pest, which should be used pointwise, laying out several pieces in aisles dug by bears;
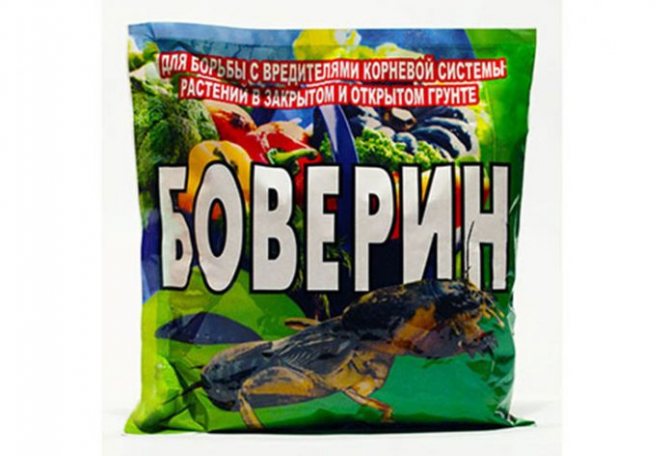
- Boverin - a biological preparation that causes a fatal illness in a bear. Boverin's advantage is that it is harmless to warm-blooded animals and beneficial insects.
Harm from the bear
The main food base of the pest is cultivated plants with juicy and tender stems, underground tubers and root crops. Bears almost do not gnaw on weeds, but they damage almost any garden, flower and vegetable garden crops.
At the beginning of the season, few overwintered individuals harm. They can enter the area with imported manure or fly from neighboring areas. The damage caused by several individuals is small. After 1 month after the beginning of the summer cottage, offspring appear: the female is able to make a clutch of 2-3 hundred eggs. Coming out of them, the larvae begin to actively grow and feed intensively, damaging the roots of plants, first near the clutch, and as they grow, throughout the site.
A strong and mobile insect for a short summer night is able to gnaw the roots of 10-15 medium-sized bushes (young tomatoes, peppers, potatoes, etc.). Small sprouts such as flower seedlings, cabbage seedlings suffer even more. As the seedlings grow, it becomes more difficult to destroy the root system, but the plants remain depressed, and the number of fruits drops sharply.
Fighting bear with folk remedies
We told you how to destroy a bear with chemical and mechanical means, but there are many effective folk methods and ways to combat this pest, which destroy or scare away the bear without harming beneficial insects, animals and people. For example, if you water the area several times at weekly intervals with infusion of onion peels, the garden bear will leave you forever.
How to get rid of a bear with onion infusion? In order to prepare this miracle cure, one kilogram of husk and onion waste is poured into 10 liters of water and infused for 4-6 days, after which the infusion is filtered and diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 5. Watering the site with onion infusion is carried out after the rain.


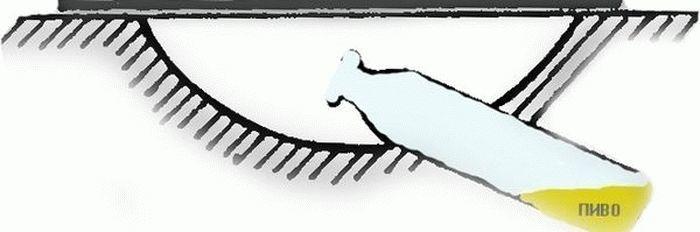
The folk methods of fighting the bear also include the device of traps, for example, with beer or honey. How to get the bear out using such traps? Dig a plastic container or glass jar into the soil, treating it from the inside a quarter of the height with honey for bait, cover the jar on top with a sheet of iron and sprinkle it with straw. Or dig a half-liter can with half a glass of fresh beer at an angle into the ground, cover it with thick cardboard or iron, and after a week and a half, dig traps with pests that have fallen into them.
We have already told you how to make traps for bears from manure.
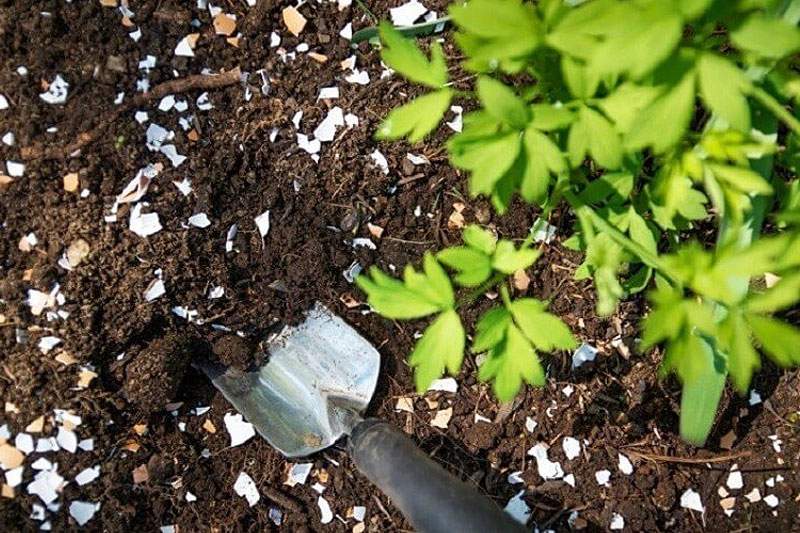
And there is also a way to get rid of underground pests with the help of eggshells, which are dried, crushed, mixed with fried sunflower oil and put in a spoonful of this mixture in all holes or furrows when planting seedlings or sowing seeds. Medvedka will definitely appear to enjoy this fragrant "dessert", which will lead to its death, and eggshells will become a good feeding for young plants.
- Cruciferous flea: how to fight, remedies and drugs
Pest prevention
The main preventive measure is the harvesting of dead leaves and other plant debris in the fall, under which the pest can overwinter. In the greenhouse and in the open field, autumn digging of the soil will be equally effective.
You should not use fresh manure to fertilize the site in the autumn - pests will be attracted by a convenient wintering place. To prevent them from settling in the compost, fresh chicken droppings are added to the heaps.
The natural enemy of the cricket is domestic chickens. If the farm has a bird, it is advisable to release it to the garden after harvesting.This is useful for laying hens and for future plantings: chickens will collect a bear, their eggs, and other pests not only on the surface, but also in the ground, digging it up in search of food.
Bears do not tolerate the smell of chrysanthemums, calendula, marigolds. Fragrant flowers can be planted around the perimeter of the ridges to drive crickets off them.
How to get rid of a pest with chemicals
Work on the destruction of the gluttonous insect should begin in early spring, since overwintered individuals, after warming up the soil and melting snow, begin to activate and reproduce. Various agrochemicals are used to destroy adult animals and their larvae.
These funds are poisons, and therefore unsafe for humans and plants.
When choosing a poison from a bear, you should be guided by the following recommendations:
- It is necessary to carefully study the composition of the drug and how it is used Some substances are designed to treat seed, others are aimed at destroying existing insects or to scare them away.
- Treatment alone is not enough. After 10-14 days, the concentration of the active substance in the tissues of the plant is significantly reduced, which makes it available for the pest to eat. Therefore, it is advisable to use traps and scarers along the way.
- Spraying tubers or soaking the roots of seedlings in special solutions will help protect crops.
Chemical agents for fighting the bear are presented in an extensive range. The most effective are chemicals such as Imidahloprid, Grizzly, Medvegon, Talstar, Antimedvedka, Acefat PRO, Regent, Rembek, Medvetsid, Bazamid, Thunder, Bison, Thunderbolt, Diazinon, Bankol and others.


However, gardeners prefer more effective drugs:
| Name | Operating principle | What crops are used to protect | How to apply |
| MEDVETOX | The substance attracts with a pleasant smell, and when consumed one granule causes a quick death | Potatoes, all types of cabbage, tomatoes | The drug is laid in shallow furrows or aisles and sprinkled with earth. Next, they begin to plant. The activation of the active substance occurs after watering. Consumption - 300 g per hundred square meters. |
| AKTARA | Broad spectrum insecticide, sold as a suspension. Used for pre-sowing treatment of tubers and roots of seedlings | Cabbage, bell pepper, eggplant, tomatoes | The working solution is prepared from 1 g of the substance and 2 liters of water. The planting material is soaked for 90 minutes, then it is planted in the usual way in the ground, without washing |
| TRAP | The poison is used as bait in traps, toxic to animals | Everything | The drug is placed in manure traps or scattered along grooves 5 cm deep, after which it is lightly covered with soil. After 10-14 days, the event is repeated |
| PRESTIGE | The suspension is used to prepare a solution in which the seedling roots are soaked | Any | 100 g of the drug is diluted in a bucket of water; the seedlings are kept in solution for 6 hours, after which they are planted as usual |
| CALCIUM CARBIDE | Crystal drug used to kill adults | Ubiquitous | 5 g of the substance is poured into each hole and watered. A reaction begins, as a result of which acetylene is produced, which kills the parasite |
| CARBOPHOS | Insecticide against many insects, used for bait and further poisoning | Everywhere | 50 g of the preparation and 30 ml of vegetable oil are mixed and treated with this composition 1 kg of grain. Such baits are buried in the ground, as they are poisonous and destructive to any animals. |
A little about the life of a bear
The concentration of bears in a certain geographic area directly depends on the average annual temperature - the warmer the climate, the more bears can be found in a certain area.
As already noted, the main harm of insects is from their love of digging. By the way, in the gardens, which are always found in a well-groomed condition, the bear is less common. But the lawns of these insects are attracted much more often, especially those that have an abundance of old dried grass that has begun to rot. Improper mowing, over-watering, or fertilizing can lead to this condition. Bears find such a neglected lawn a suitable habitat and end up hibernating here in deep burrows that are created by their active digging process. Once the soil warms up in the spring, insects will dig their way to the soil surface to feast on fresh grass, usually at night.
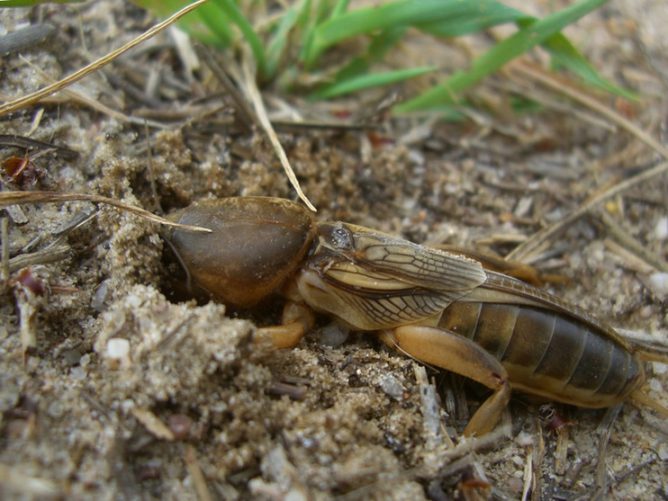


Females will start laying eggs just below the soil surface in spring and early summer. Nymphs will develop during the summer and will have gone through all the stages of molting into an adult by mid-August.
Causes and signs of appearance
The active life of a bear in the garden is fraught with loss of harvest.
The greatest activity of the pest occurs in the spring, when the air temperature is 10-15 C.
Gardeners have identified the main signs of the presence of an insect:
- the rapid disappearance of cultures;
- depressions in the soil 1-1.5 cm wide;
- slow and weak germination of plants;
- winding underground passages that are clearly visible after rain;
- vegetable crops are easily removed from the soil;
- plants get sick for no apparent reason.
Medvedka enters the site along with fresh manure. This is where the larvae live. Sometimes pests move from one neighbor to another in search of more moist and nutritious soil.


In the spring, the bear becomes more active