Garlic is exposed to various diseases and pests as often as other cultivated plants. To know how to prevent their appearance or development, it is necessary to be able to recognize the symptoms of garlic diseases, and to fight them regularly. Garlic dies from a narrow list of pests and diseases, and other pathogenic factors are simply not able to cope with this insecticide. Most often, garlic is exposed to fungal diseases, molds in the ground, in order to prevent this, you need to know what to do when the primary symptoms of such diseases appear.
How to determine what has affected the plant?
It is very simple to determine what affected the garlic - a disease or a pest.... It is enough to look at its appearance and determine whether the disease is fungal or bacterial in nature, or whether the plant was struck by small insects called pests.
And in either case, untimely protection can lead to the death of the crop.
Diseases

All garden crops of the onion family are attacked by various harmful insects and the spread of fungal and viral diseases by them.
The main damage to garlic is caused by diseases caused by mushrooms.... Often the causes of their occurrence lie in the violation of the systems of garlic cultivation techniques.
- With a very dense planting of garlic, air does not flow well to the leaves and root crops.
- Excessive soil moisture.
- Violation of the rules of crop rotation.
- The presence of a large number of weeds and remnants of last year's vegetation in the garden.
- Inappropriate storage conditions for garlic.
The main diseases of garlic and how to treat them
There are two main groups of diseases affecting garlic crops:
- fungal - provoked by spores of fungi that overwinter in last year's foliage, harvested crops and topsoil;
- viral - are provoked by viruses that settle in the soil and persist in plant cells.
Fungal diseases are mostly subject to successful treatment, and in the initial stages, their spread can be avoided by improving growing conditions and fertilizing in accordance with the growing season. Viral diseases are difficult to treat, so the main fight against them is aimed at increasing plant immunity and prevention. Even if the virus is successfully treated, there is no guarantee that its cells are not preserved in the soil and plants. When a provoking factor appears, such diseases begin to progress with renewed vigor.
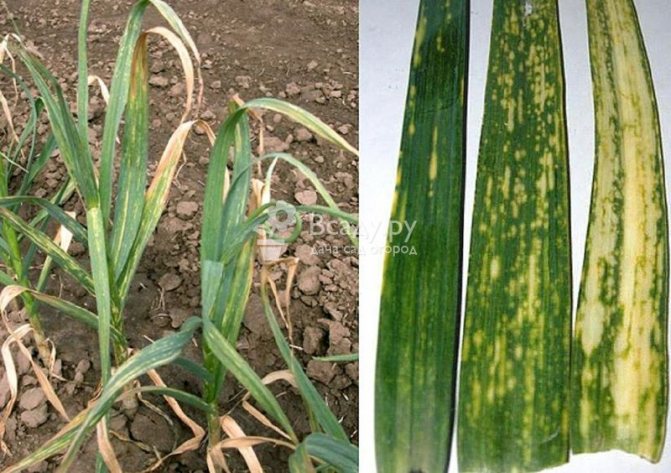
Why do the leaves turn yellow?
Garlic leaves turn yellow most often in spring... What to do with this?
- Many gardeners notice that mainly winter crops turn yellow. This occurs during a period of low temperatures in early spring, when the plant is most vulnerable. The root system weakens and garlic draws energy from the leaves.
- Leaves may turn yellow when planted deeply. Garlic should be planted to a depth of 5-7 cm. To prevent the leaves from turning yellow, young shoots are covered with transparent polyethylene foam.
- At the first spring frosts, the plant must be treated with stimulating drugs such as "Epin", "Zircon".
- There is another reason for the yellowing of the leaves - acidic soil.The acidity of the soil is reduced with lime.
- Leaves may turn yellow in early spring. This is due to the insufficient amount of nitrogen in the soil. What if the garlic turns yellow because of this? To fill this gap, you need to apply mineral or organic fertilizers to the soil.
- With insufficient moisture.
We recommend watching a video about the causes of yellowing of garlic leaves:
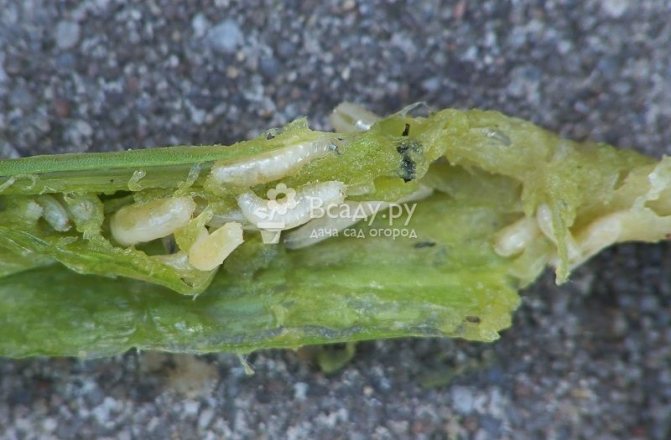
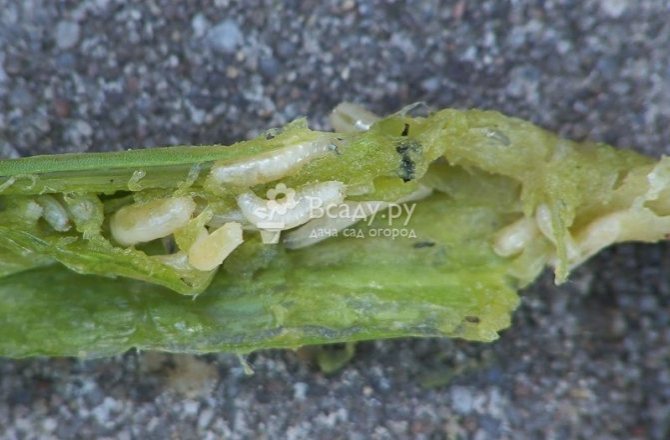
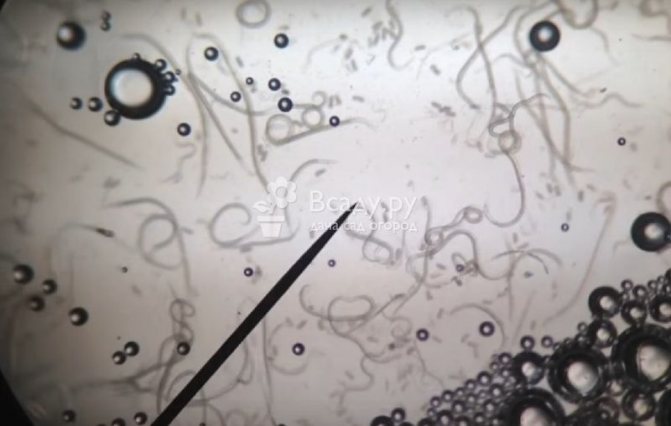
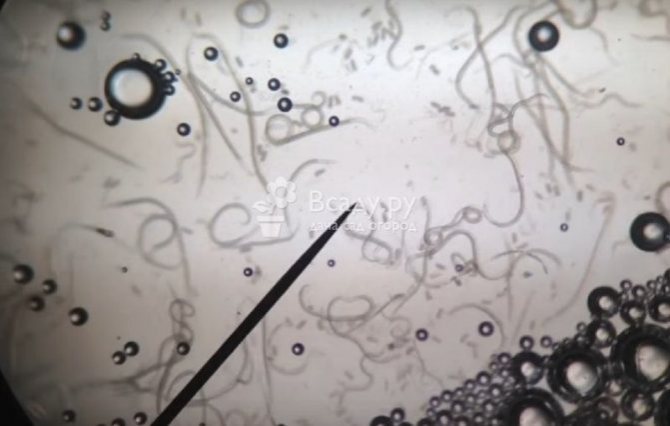
Onion (root) tick
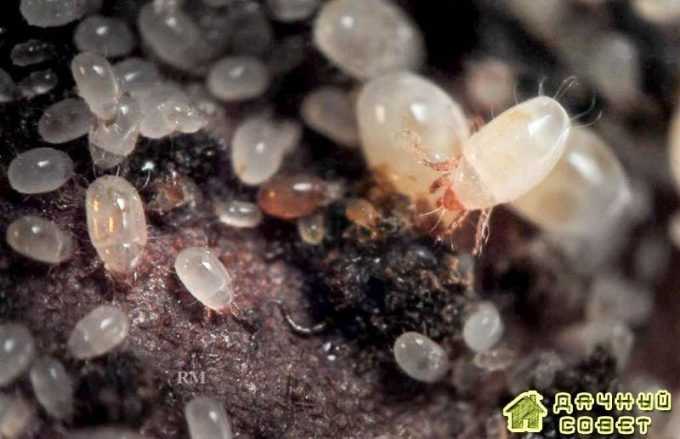


Onion (root) tick Tick 0.7-1 mm long, oval, whitish-transparent. Eight legs, their color is brown.
Mites persist in the soil of vegetable gardens, in plant debris, on infected bulbs. With soil and planting material, it is brought into areas free from it, into greenhouses. The mite is polyphagous. It damages the bulbs of garlic, onions, tulips, daffodils, snowdrops, hyacinths, irises, dahlias. Harmful to potatoes. Plant residues can serve as food for it. The tick causes damage to the onion during the growing season and during storage of the onion. The tick enters the bulb through the bottom, through the wounds. The damaged bottom of the bulb becomes flabby, crumbles, sometimes falls off. A diseased plant lags behind in growth, turns yellow. Settling between the fleshy scales of the bulb, the mites feed on them. Damaged scales become rotten, the bulb rots. Bulbs severely damaged by the mite dry out during storage.
The mite is hygrophilous. It is noted that at humidity below 60%, the development of the tick stops, but it does not die, but only goes into a stage that is resistant to dryness and starvation. As the humidity rises, the mites return to an active lifestyle.
Female eggs are laid in bulbs, preferring those damaged by other organisms. Each female lays up to 800 white oval eggs. The developmental cycle of a tick under normal conditions of temperature and humidity is completed in 20-25 days.
Onion mite control measures
- Compliance with crop rotation. Good predecessors of onions are tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage.
- Removing rotten bulbs and post-harvest residues from the garden.
- Fight against other onion pests that cause wounds to plants through which the mite enters the bulb.
- Harvesting onions in dry weather with drying them in the sun until the leaves dry out.
- Culling and destruction of diseased bulbs when laying onions for storage and during storage.
- Selection for planting healthy bulbs that are not infected with ticks and other pests and diseases.
- Disinfection of onions before planting by heating at a temperature of + 35 ... + 37 ° C for 5-7 days. This operation can be performed by placing a baking sheet (box) with the seed material on the radiator.
Folk remedies
Advice: Experienced gardeners are advised to use safer means in the fight against diseases, namely, herbal infusions and other gentle mixtures.
- Shag infusion... You need to take 250 g of tobacco and a spoonful of hot pepper. Pour the mixture with two liters of hot water and leave in a warm place for 3 days. Then filter and bring the volume to 10 liters. Some add an additional 30 g of liquid soap to the finished mixture. Plants and soil are sprayed once every 6-7 days in May, and then in July.
- Wood ash... You need to take 10 g of ash, a teaspoon of hot pepper and a tablespoon of crushed tobacco. This mixture is suitable for pollination plantings 2-3 times per season. This remedy is also effective as a prophylaxis.
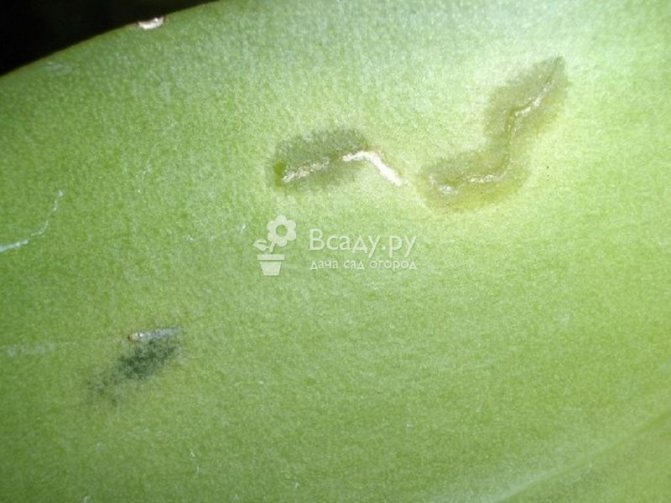
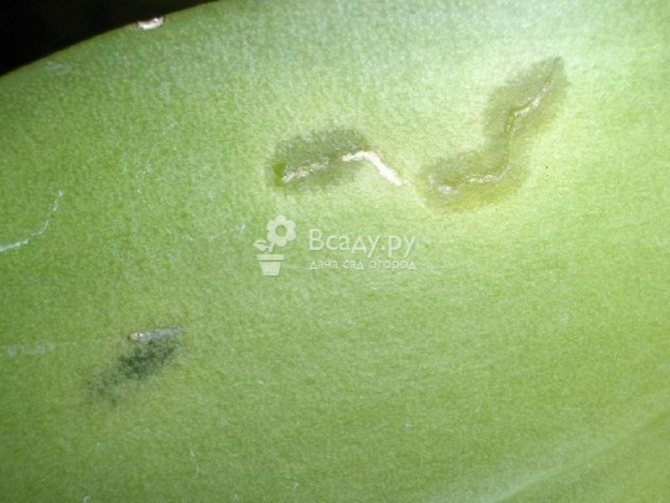
Onion miner fly
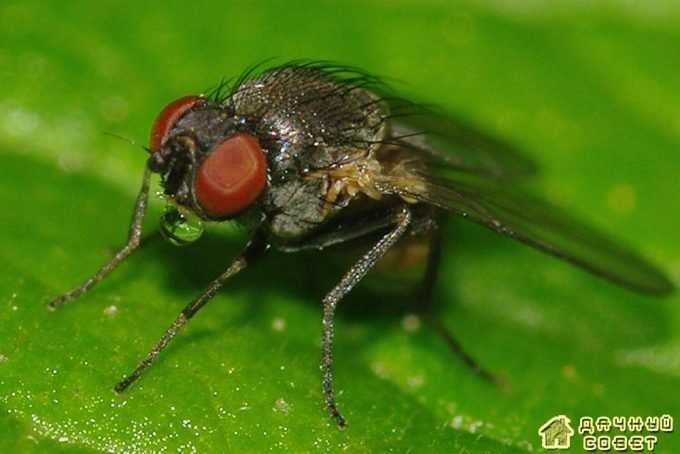


Onion miner fly
The fly is black in color with a yellow head and antennae. Its body length is 2-2.5 mm. The larva is whitish, up to 6 mm long.
The fly damages the onion, which is more often grown from the set for the turnip, and the testes of the onion. Onions of the first year of life, sown with seeds, are slightly damaged. Fly pupae overwinter in the soil in areas that emerged from the onion. Flies fly out in May. The fly lays eggs one by one or several on the inner wall of the leaf, pre-piercing it with the ovipositor.The larvae eat the flesh of the leaves from the inside in the form of small irregular areas. The integrity of the outer skin of the leaf is not disturbed. Outside, the mines appear as whitish spots. Eating several larvae in a leaf causes it to dry out.
The development of the fly is rapid: the egg stage lasts 4-5 days, the larva - up to 15 days. The larva, having finished feeding, leaves the leaf and goes into the soil to pupate. Adult flies feed on onion leaf juice. To do this, they prick a leaf with the ovipositor and lick the juice protruding from the wound. At the injection site, a small, like a dot, spot is formed, clearly visible on the green background of the leaf.
Onion fly control measures
- Observe crop rotation, avoid replanting onions in one place.
- Avoid, if possible, the neighborhood between the old and new sections of the onion.
- Deep digging of soil after harvesting onions.
Prevention rules


One of the main rules is observance of crop rotation.- In the fall, you need to carefully remove the beds from last year's plant debris.
- The planting material must be of good quality.
- Before planting, the cloves must be etched in a solution of potassium permanganate or in a saline solution.
- Since rot tends to accumulate in the ground, garlic can be planted on the same bed in 3-4 years.
- Planting needs to be thinned regularly and weeds removed.
For the successful cultivation of garlic varieties, it is also important to know about feeding, processing, seed propagation and the peculiarities of growing garlic as a business.
Onion fly
Onion miner fly
Damages onions, sometimes garlic. Onion seedlings, onion sets and onions intended for seeds are affected by the fly. Deals more significant damage with permanent onion cultivation.
The fly is ash-gray with black legs, its body length is 6-7 mm. The larva is up to 10 mm long, whitish, its body is narrow at the anterior end. There are 16 tubercles at the posterior end of the larva.
The fly develops in two generations a year. Pupae overwinter in soil at a depth of 15–20 cm. In spring, flies fly out in early May. The years of the flies coincide with the cherry blossoms. The flies first feed on the nectar of the flowers, then start laying eggs. The female lays several white oblong eggs on the neck of the onion, between the leaves, under lumps of soil near the plants. Egg development lasts 3-8 days. The larvae enter the bulb through the bottom or through the base of the leaves. Feeding inside the bulb, they make numerous moves.
Damaged bulbs rot, leaves turn yellow, the whole plant is easily pulled out. The development of the larva lasts 20-25 days. Having finished feeding, the larva goes into the soil, where it pupates, and after 15–20 days, flies of the second generation hatch from the pupae.
Measures to combat onion fly
- Sowing and planting onions as early as possible.
- Plants that have matured by the time of hatching of fly larvae are less damaged. Late crops are more damaged by the fly.
- Placing onions next to carrot beds. Substances (phytoncides) secreted by carrots scare off onion flies, and onion phytoncides scare off carrot pests. In order to scare off flies at the beginning of laying eggs, the soil along the rows is sprinkled twice (with an interval of 7 days) with tobacco dust or a mixture of tobacco dust with lime (in a ratio of 1: 1).
- Repeated inspection of onion plantings in order to remove and then destroy plants damaged by fly larvae.
- Collection and disposal of post-harvest residues.
- Deep digging of soil after harvesting onions and garlic.
Gluttonous weevils


A beetle with a proboscis, which begins its activity as soon as the snow melts. The female lays clutches on the leaves, as soon as the larvae appear, they begin to devour the plant. You can understand that plants have been attacked by a weevil by whitish stripes and yellow leaves.There is no prophylaxis against the weevil; agricultural techniques must be carefully observed. Do not thicken the bed, carry out frequent weeding. A powder of black ground pepper and ash can scare off the weevil.
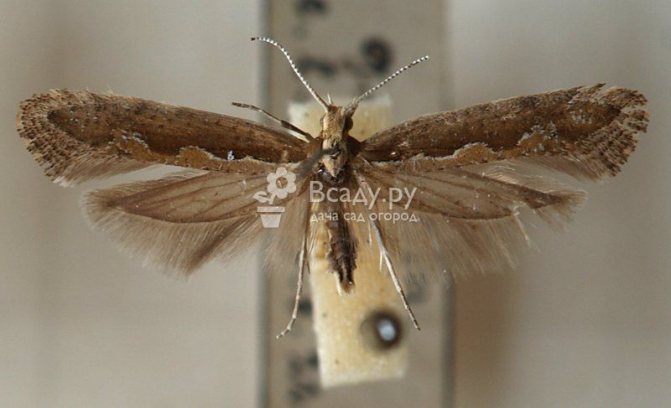
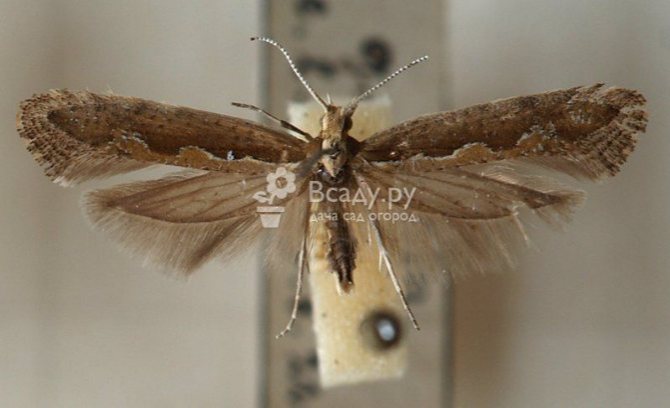
Onion moth


Onion moth


Onion moth
The moth is a butterfly of dark brown color, with a wingspan of 8-10 mm. On the front wings of the butterfly there are white transverse stripes, the hind wings are narrow, with a long fringe. Caterpillars are yellowish green, 10 mm long.
Moles damage onions and garlic. It develops in two generations. Pupae overwinter in plant debris, and butterflies - in crevices of buildings and other shelters. In spring in May, butterflies emerge from overwintered pupae. They are nocturnal, during the day they quietly sit on plants. Females lay eggs one at a time on the leaves, on the neck of the bulb, on the flower arrows. Caterpillars first mine leaves. Later, they penetrate into the tubular leaves and eat away the pulp in their wall in the form of winding stripes, while not touching the outer skin. Damaged leaves turn yellow and die off. The onion yield is decreasing. On the testes of the onion, the caterpillars eat away the rudiments of flowers that have not yet blossomed inflorescences.
The caterpillar stage lasts 15-16 days. After completing their feeding, the caterpillars leave the leaves and arrows of the onion. On onion plants, on weeds, on the soil, they weave cocoons and turn into pupae in them. The second generation butterflies fly out in July.
Onion moth control measures
- Compliance with the order of crop rotation on the site.
- Creation of favorable conditions for the growth and development of onions (loosening the soil, watering, weed control, etc.).
- Developed plants suffer less from moths.
- Deep digging of soil in areas that came out from under the onion.
- Thorough incorporation of plant residues with soil.
Onion Lurker
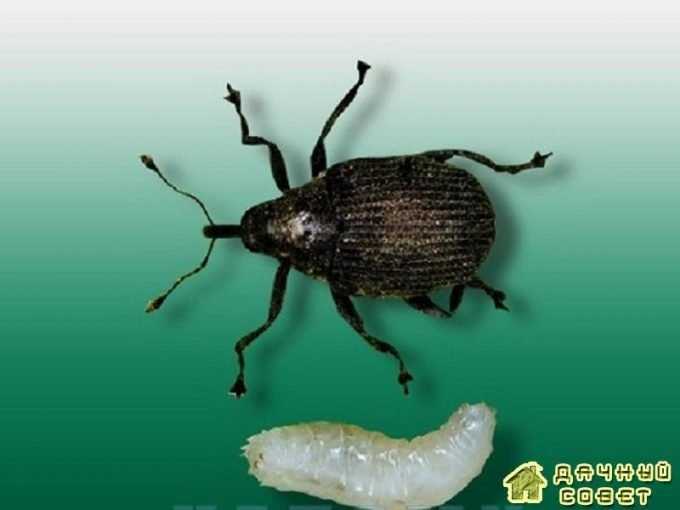


Onion Lurker
A beetle from the family of weevils. Its body is oval-convex, black, covered with gray scales, its head is extended into a tube bent downward. The beetle reaches 2-2.7 mm in length. The larvae are legless, yellowish, up to 6.5 mm long.
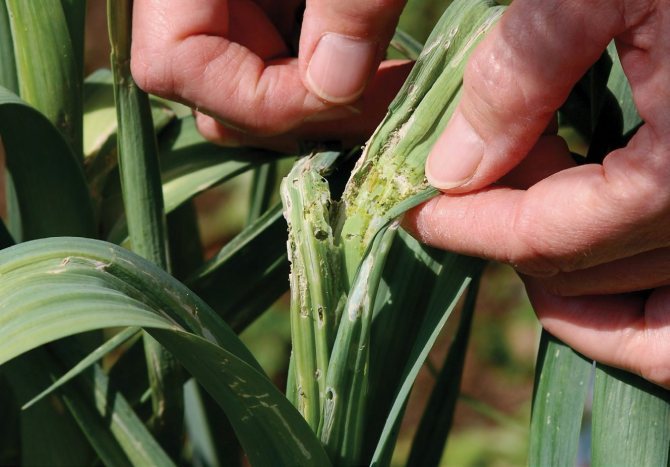
Damages the bow. Beetles overwinter under plant debris along roadsides, ravine slopes, on uncultivated turf lands adjacent to vegetable gardens, under lumps of soil. Beetles leave their wintering grounds in mid-April. At first, the beetles feed on the leaves of the sprouted bulbs left in the ground after harvesting, on the early growing perennial onions of the batun. With the emergence of seedlings and regrowth of the planted bulbs, beetles begin to damage the cultivated onion. They gnaw small holes in the leaves, eat out cavities in the pulp of the leaf from the inside. Damaged leaves bend and dry out. The beetle inflicts the greatest damage on onion seedlings from seeds, causing the death of damaged plants.
Onion hoverfly


Onion hoverfly
The fly is metallic-green in color; on the sides of its abdomen there are three pairs of narrow light spots. The body length of the fly is 7-9 mm. The larvae are grayish-yellow, wrinkled, with a process in the form of a short tube at the posterior end. The length of the larva is up to 11 mm.
The fly damages, in addition to onions and garlic, tulips, daffodils, irises, gladioli, and sometimes underground parts of carrots, beets, and potatoes.
The fly develops in two generations a year. Larvae overwinter in bulbs in the field, rarely in storage. Pupae can hibernate. Flies fly out in early June. Females lay eggs in groups of 5-9 on the soil near plants or on bulbs. The larvae take root in the bulb, live in it for 25-30 days, then go into the soil to pupate. Flies of the second generation fly out in July-August. Their larvae harm in August and September.
The larvae, feeding on the bulb, destroy it. The inside of the bulb completely turns into a rotting mass.
Measures to combat onion hoverfly
- The same as with the onion fly.In addition, the following actions are required: planting onions with bulbs that are not infected with hoverflies; careful control of wireworms, onion flies and other pests, since hoverfly larvae often colonize already damaged bulbs.
Preventive measures
Diseases and pests of garlic are not terrible if you adhere to the rules of growing a crop:
- Before planting, it is worth treating the bulbs with saline or potassium permanganate. In addition, the teeth are ground with chalk or lime at the rate of 20 g of powder per 1 kg of material.
- It is recommended to store seed in a room with a temperature not exceeding + 10 ° С. It is desirable that the humidity does not exceed 60–70%. The bulbs are thoroughly dried before storage.
- Before planting, it is recommended to warm up the cloves for 7–8 hours at a temperature of + 40 ° С.
- It is advisable to treat the soil of the beds with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. This will destroy the fungal spores in the soil.
- The affected parts of the culture, including diseased planting material, cannot be used for mulching the beds or preparing compost. Such plants should be burned immediately.
It is recommended to observe the crop rotation. Do not grow garlic after or near potatoes, carrots, cabbage, onions. The best neighbors for culture will be calendula, thyme, or mint. In addition, garlic should be grown in the same area after 3-4 years.
It is necessary to regularly weed the bed, remove weeds. Such plants are often inhabited by pests and pathogenic fungi. It is also important to observe the correct watering regime.
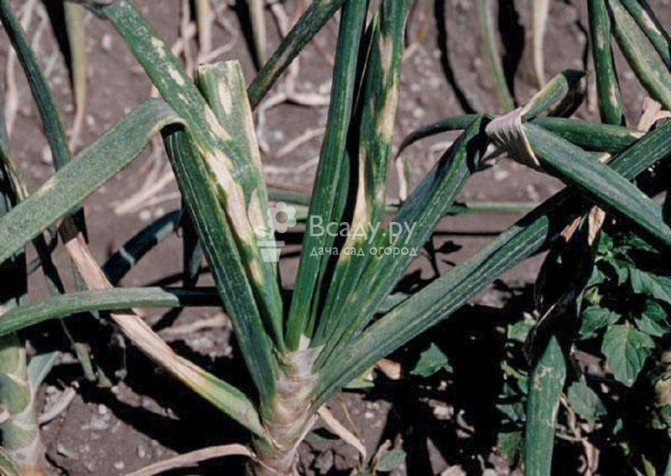
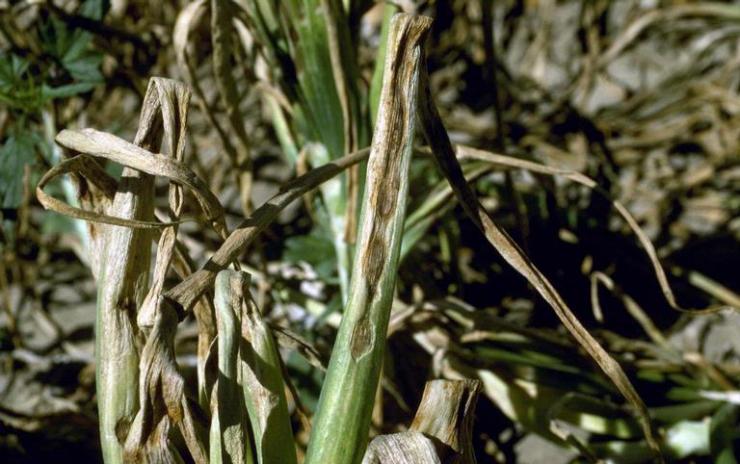
Downy mildew (downy mildew)
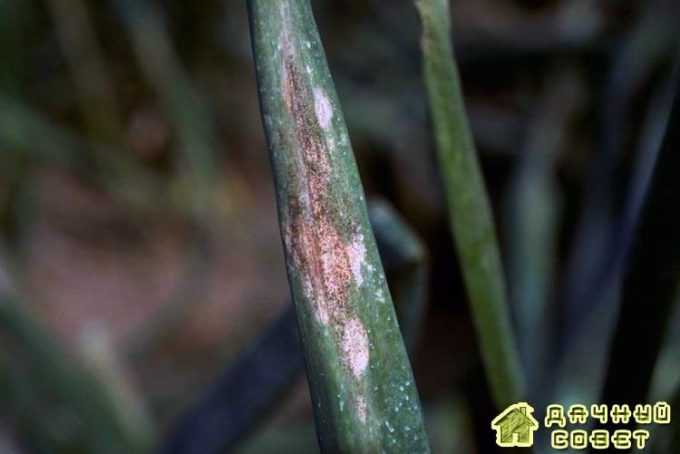


Downy mildew (downy mildew)
The causative agent of the disease - the mushroom Peronospora - affects onions during the growing season. The disease is especially dangerous for the testes of onions in wet years.
The mushroom hibernates in the form of a mycelium in the bulbs, outwardly without manifesting itself. Can overwinter in plant debris. The mushroom enters the garden with infected bulbs planted in the ground. In the first 20-30 days, plants develop from the infected bulbs without any external manifestations of the disease. However, mycelium grows along with the onion. It penetrates the leaves through the intercellular spaces. The disease manifests itself on the leaves in the form of rounded blurry yellowish spots, on which a gray-purple bloom of summer spores of the fungus appears in wet weather. Diseased plants are stunted, become stuck, turn yellow, and may die. In dry weather, the development of the disease is suspended.
Wind and rain scatter the spores, infecting healthy plants. Once on a healthy plant, the spore grows into the mycelium, which penetrates through the stomata into the tissue of a healthy leaf. After 10-15 days, a yellow oval spot with a bloom of spores forms on the leaf at the site of the mycelium penetration. Sick leaves dry out. Later, the mycelium penetrates from the leaves into the bulb, where it will winter.
On the testes of onions, the fungus affects the arrows, which turn yellow and break. In this case, the seeds on the inflorescences are either not formed at all, or are formed feeble. Perennial onion species (batun, leek, chives) are a constant source of spore formation. The mycelium overwinters in their roots.
Measures to combat downy mildew (downy mildew) on onions and garlic
- Crop rotation: onions should return to their original place after 3-4 years. Planting onions in open areas with good wind.
- If possible, remove the crops of blackberry from other plantings of onions.
- To isolate crops of perennial types of onions as much as possible from other plantings of onions.
- Planting onions with bulbs that are not infected with downy spores.
- Removal of diseased plants or diseased leaves during the growing season.
- Spraying of testes and other plantings of onions, except plantings of onions on a feather, with 1% Bordeaux liquid, oxychom or copper oxychloride. Spraying period - at the first manifestation of the disease.
- Disinfection of planting material in one of the ways: but) heating onion sets, turnips, samples obtained from infected crops at a temperature of + 40 ... + 43 ° C for 16 hours or at a temperature of + 35 ... + 37 ° C for 7 days. It is better to warm the sevok in the spring 12-14 days before planting; b) heating the planting material at a temperature of + 40 ° C for 8 hours, and large bulbs for 16 hours. In this case, the mycelium in the bulbs dies.
- Drying the onion in the garden until the leaves are completely dry and dry covering scales form on the bulbs. Cleaning of crop residues.
Disease control measures
Viral and bacterial diseases are incurable. Control measures include prevention, destruction of affected plants and soil treatment with strong fungicides such as "Karbofos" and "Hom".
Only fungal diseases of garlic can be treated, and their treatment depends on the stage and type of disease. In any case, you should fight at the first sign. First of all, the damaged parts of the plant are removed. From powdery mildew, the bed is processed with copper sulfate. After harvesting the recovered crop, it is important to dry the bulbs well.
Bordeaux liquid is used to treat rust. The same remedy is effective against fusarium and black rot. In addition, fungicides cope with fungal infections, for garlic it is worth using "Fitosporin", "Champion", "Kupraksat".
Folk remedies for fungal diseases
Not only chemical preparations will help to cope with diseases, there are effective folk recipes that destroy fungi and mold. The infusion of calendula and yarrow helps well. To prepare 50 g of medicinal plants, 1 liter of hot water is poured. The mixture is infused for 7 days, then filtered and diluted with water at the rate of 1 liter of infusion per bucket.
It is recommended to treat the soil and seed with the tool before planting. Another spraying should be done during the growth of the garlic feathers. The infusion effectively prevents fungal diseases, but does not accumulate in the plant.
It is useful to spray garlic for prophylaxis with a solution of fermented milk whey. To prepare it, the product is mixed with water in a ratio of 1 to 10. In addition, it is recommended to treat the bed with a solution of soda ash, made at the rate of 50 g per 10 liters of water.


Folk remedies for viral diseases
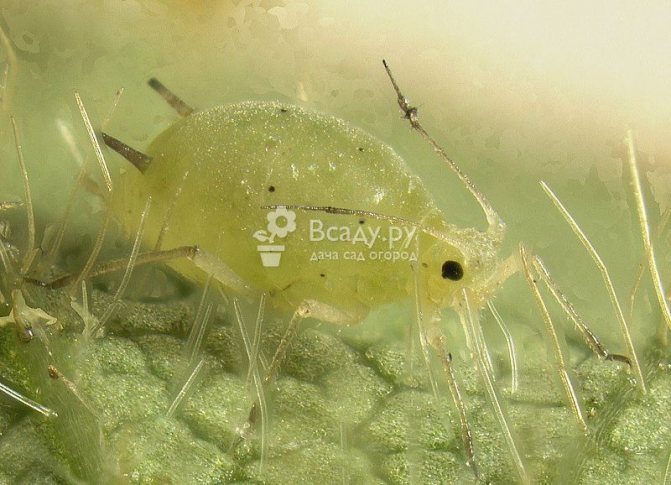
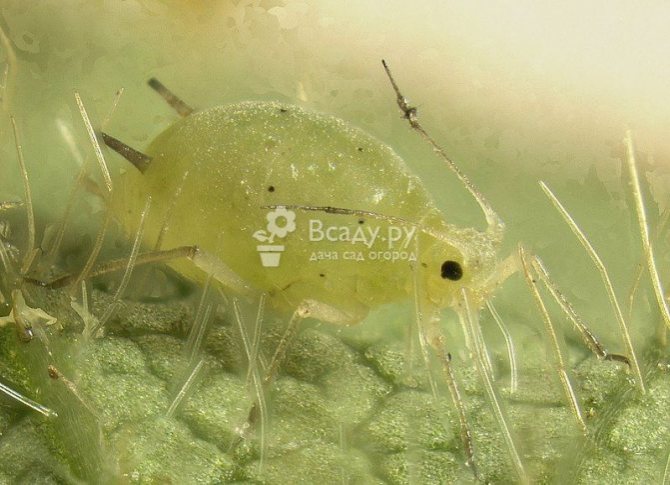
Infusions and decoctions will not be able to cure such diseases. But they will scare off aphids and garlic mites, which carry mosaic and yellow dwarf viruses. For these purposes, an infusion of tobacco is used. For preparation, dried and crushed leaves are poured with 10 liters of water. The mixture is infused for two days, after which it is filtered and used for spraying.
An infusion of wood ash helps to scare off the carriers of viruses. For cooking, a bucket of water is heated, a glass of ash is poured into it, after which the mixture is stirred and infused for a day. 40 g of liquid soap is added to the infusion, after which the soil and plants are sprayed with the agent.
Proper care is the head of everything!


Paradoxically, it turns out that garlic, which many gardeners use to protect plants from infections and some pests, often suffers from an invasion of insidious insects. And the reason for this is violations in the agricultural technology of culture, non-observance of elementary rules of care.


Have questions? Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. Ask a question >>
Among them:
- vegetable beds overgrown with weeds;
- uncut boundaries on the site;
- lack of crop rotation on the site;
- plant residues in the beds (garbage, leaves, weeded grass);
- mistakes in watering, feeding plants.
It is worth correcting the listed violations, and the result will be immediately visible. Of course, if pests have already appeared on garlic, you need to take prompt action and work with insecticides, broths, infusions.But it is much easier to keep insects out of the garden by following simple growing techniques.
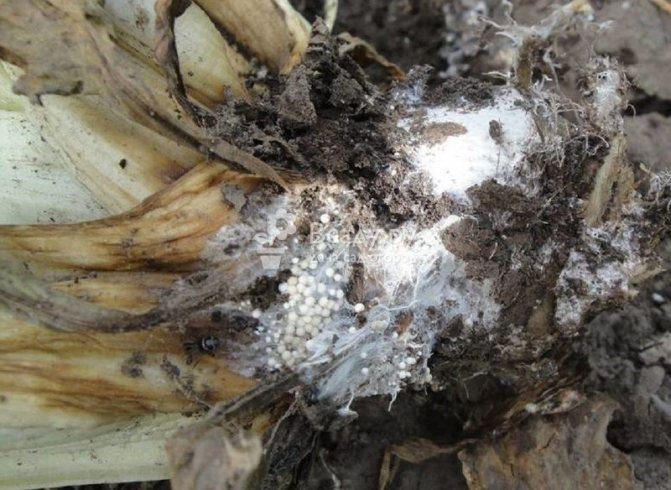
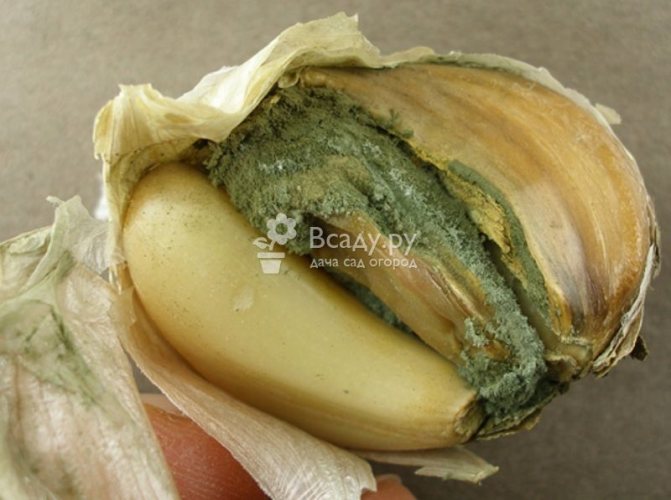
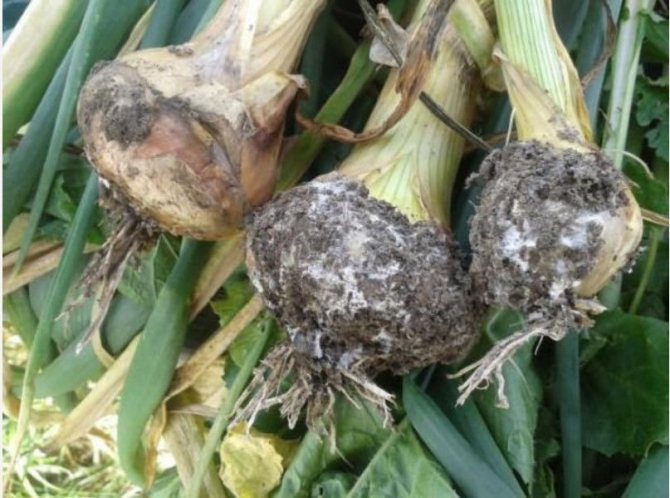
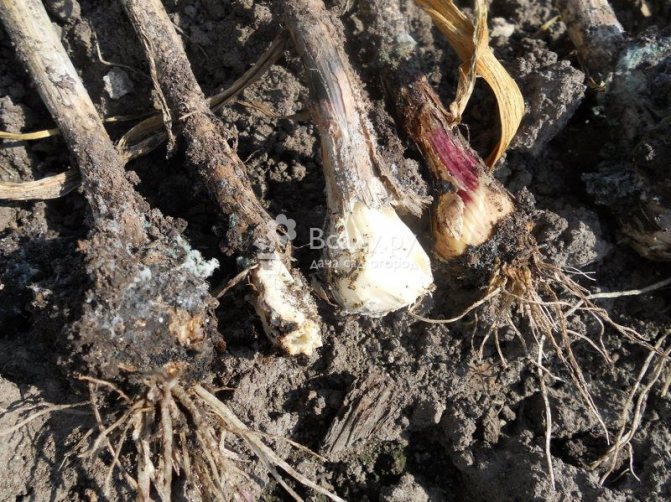
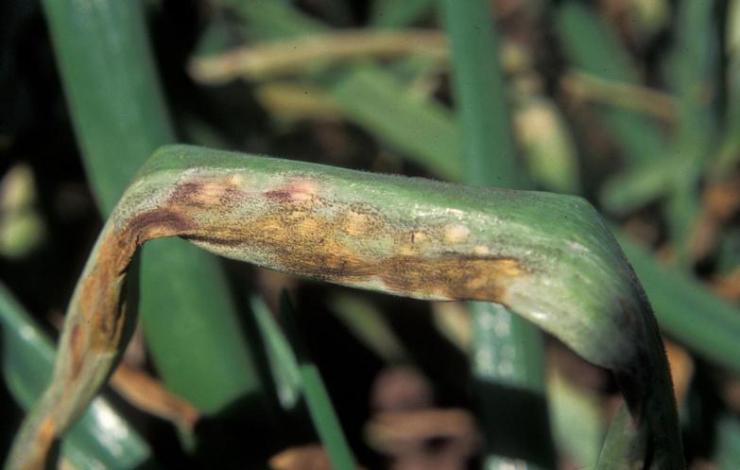
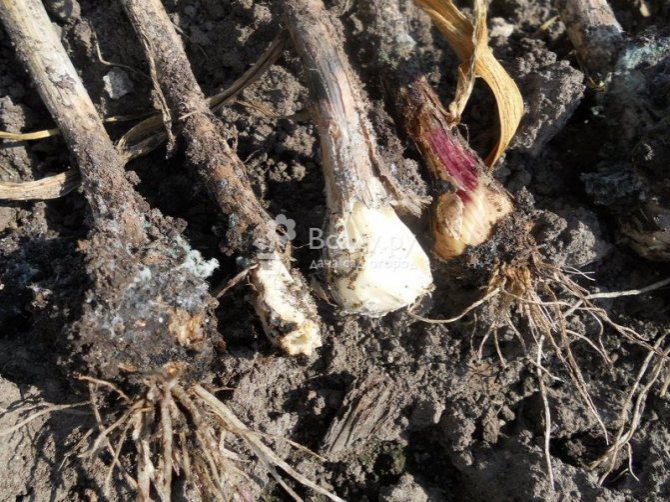
Cervical rot
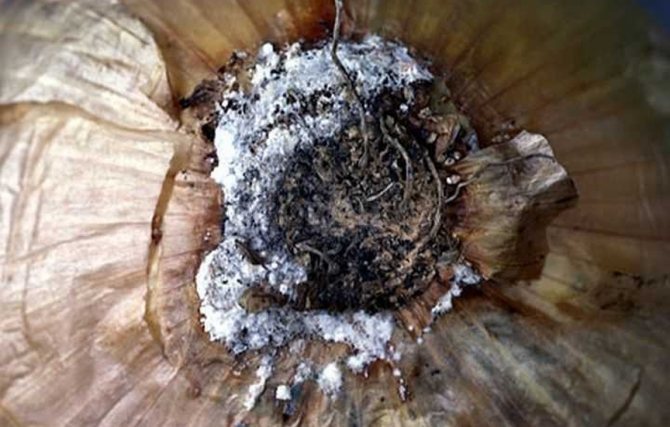


The fungus that causes this disease can infect garlic both during its cultivation in the garden and during storage of the crop. During the growing season, yellowing of the leaves begins. A white bloom appears on the root crop and roots. This is the white rot mycelium. The teeth become watery and quickly rot.
The activation of the fungus is facilitated by a decrease in temperature, up to 10˚С. The pathogen overwinters either in the soil or on roots.
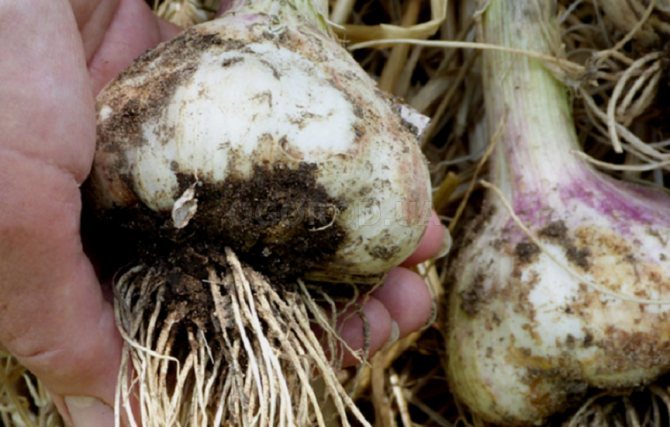


The fungus that attacks the root system of garlic is called Fisarium. Plant infection occurs both through the soil and through the seed. The first sign of the disease is yellowed leaves, followed by decay of the roots. A yellow-pink bloom appears on the roots, and mold can be found between the layers of husks. If you do not start treating the disease, the plant may die. A high air temperature contributes to the active development of the disease.
Treatment of the soil with the drug "Hom" (according to the instructions) will destroy the harmful fungus and protect the crop.
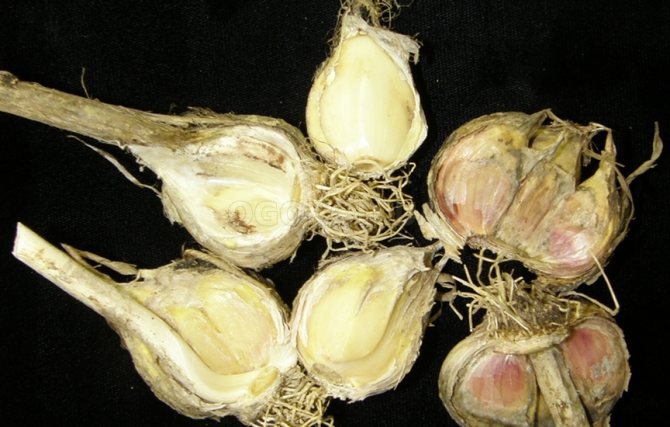


Garlic infestation occurs before harvest, most often during leaf lodging. Excessive soil moisture, a sharp cold snap, an excess of nitrogen fertilizers are the main causes of cervical rot.
Garlic begins to soften at the base of leaf growth, and during storage this process continues, infecting neighboring roots.
To avoid this problem, you must:
- Harvest garlic in dry warm weather.
- Dry the harvested crop thoroughly.
- Apply nitrogen fertilizers only at the beginning of the growing season.