How to understand that a root crop is sick?
Disease is the process of damaging a vegetable crop by infectious agents such as bacteria, fungus or a virus, which manifests itself in the form of spots, mold and rot, both on the foliage and on the root crop.
At first glance, it is difficult to understand why the culture is spoiling, be it a parasite or some kind of disease.
When the initial signs of damage appear, it is necessary to identify the cause of their occurrence.
If the crop is damaged by a pest, you need to examine the leaves and tops to find a dangerous insect that damages the vegetable. If a root crop is affected by a disease, you should determine its type and decide how to process the vegetable. What diseases and pests can infect a plant is described in detail in a separate article, and here you can read about the main pests of carrots.
Diseases of carrots: variegated dwarfism
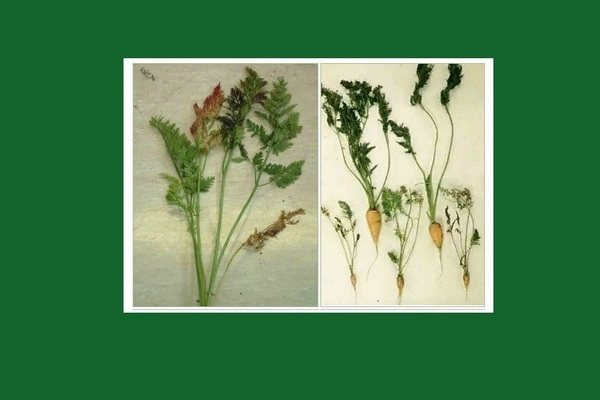

Diseases of carrots: variegated dwarfism
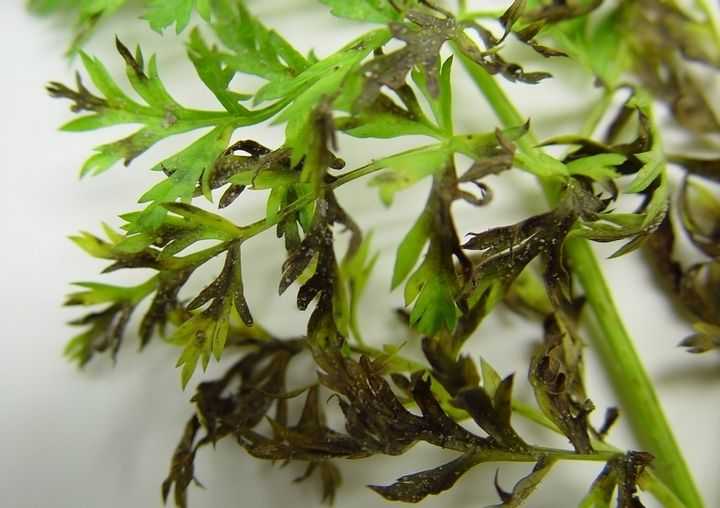
Description of the disease. Variegated dwarfism is a viral disease of carrots that causes, as you might guess, dwarfism of leaves and fruit. The virus infects the plant with the help of the willow-carrot aphid. Where wild or cultivated carrots are constantly growing, the aphid, together with the virus, hibernates right on it. As a result, at the very beginning of the growing season, the virus wakes up and infects crops of carrots and parsley. In colder places, the infected aphid hibernates on fireweed, and only after feeding on the infected host plant does it become a source of disease.
Diseased carrots begin to change from the leaves. Their length is significantly reduced, and the shape of the petiole begins to bend unnaturally. After that, the leaves begin to change their color. Fancy patterns of red, light green, dark green and even black colors begin to appear on them. If the carrots are too badly infected with the virus, the foliage will stop developing altogether, which will be the first herald of the loss of the entire crop.
Unpleasant changes also begin to occur at the root. Root hairs appear, stopping the formation and growth of root crops. After this, premature lignification begins.
Outwardly, motley dwarfism is similar to a lack of nitrogen and potassium: disorderly mottling and eerie redness appear along the edges.
Description of the causative agent of the disease. There are two main pathogens of variegated dwarfism: Carrot mottle virus and Carrot red leaf virus. They are transmitted, as already mentioned, through aphids and nothing else. In an infected organism, the virus can exist for an extremely long time, posing a danger even after the death of the carrier. Both viruses are small: the diameters of their virions are 52 nm. and 25 nm. respectively. After infecting the host, they attack the phloem cells and those that are next to them, causing disease.
Disease protection measures. The best way to protect your crops from this terrible scourge is to try to eradicate aphids in the early stages of carrot growth to prevent possible infestation.
Description, photo and treatment of all types of lesions
During storage
Failure to comply with storage conditions can lead to the following diseases.
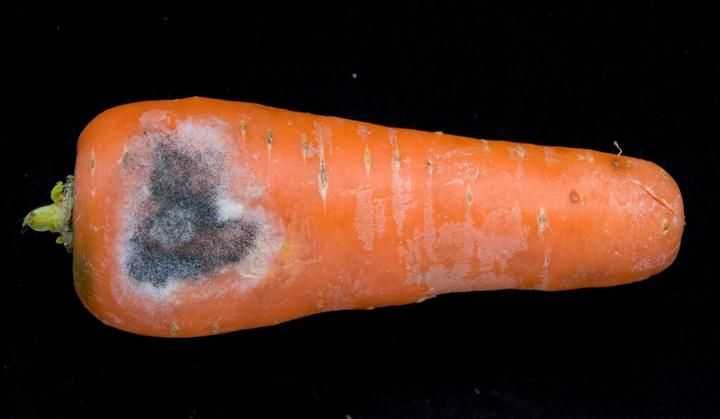
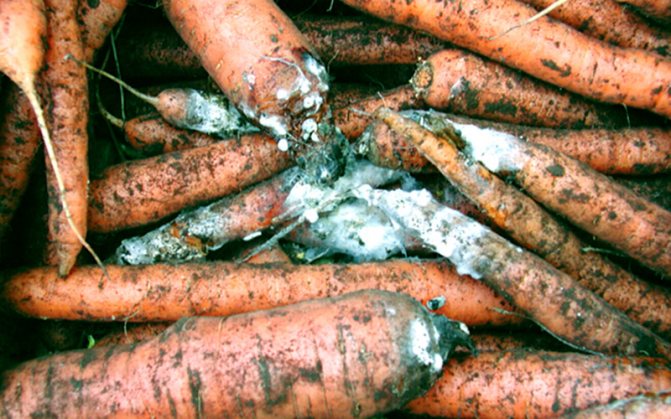
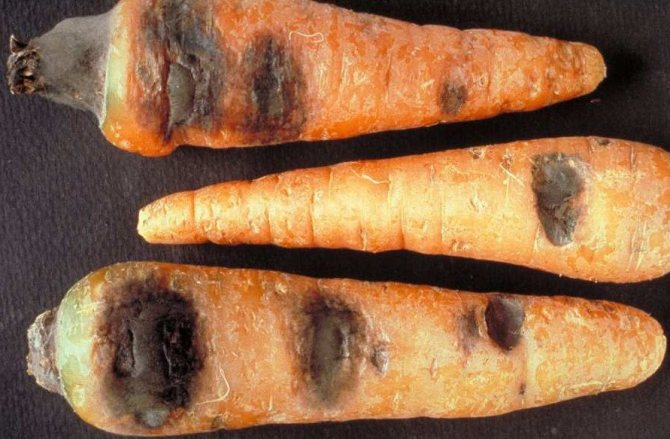
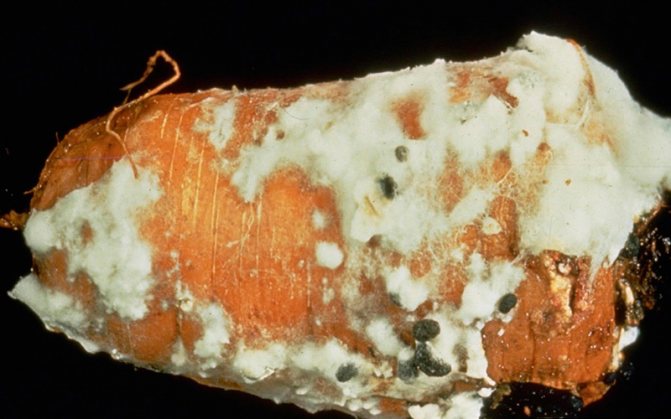
White rot or sclerotinosis
It is an infectious disease caused by a pathogenic fungus.The surface of the root vegetable becomes soft, after which a fluffy white bloom appears on the areas. At first, the color of the carrots does not change, but as the bloom covers the entire vegetable, it will turn black.
To combat white rot, you need to cut out the infected areas, and then treat with a composition prepared from ground chalk and a solution of potassium permanganate. But if most of the root vegetable is infected, it is best to simply get rid of the vegetable. To prevent infection of root crops, before storing them, they must be sprayed with the fungicide Thiram, for which 6-8 kg of the drug must be mixed in 10 liters of water (for 1 ton).
During the laying of a culture for storage, it can be difficult to notice the appearance of an infection, since at the initial stage there are no obvious signs.
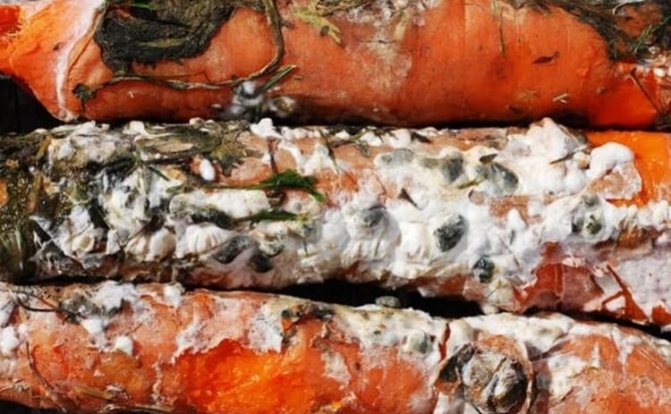


Wet bacterial rot
It is a disease caused by a fungus during storage. Dark brown dents appear on the top of the carrots, later they become covered with mucus, become soft and fall inward. As a result, a root vegetable with an unpleasant odor is completely decomposed.
To fight the infection, you need to start by processing the vegetable store, in which you need to spray the walls and floor with a special solution of 400 g of bleach diluted in 10 liters of water. For storage, you need to select only whole and healthy roots..
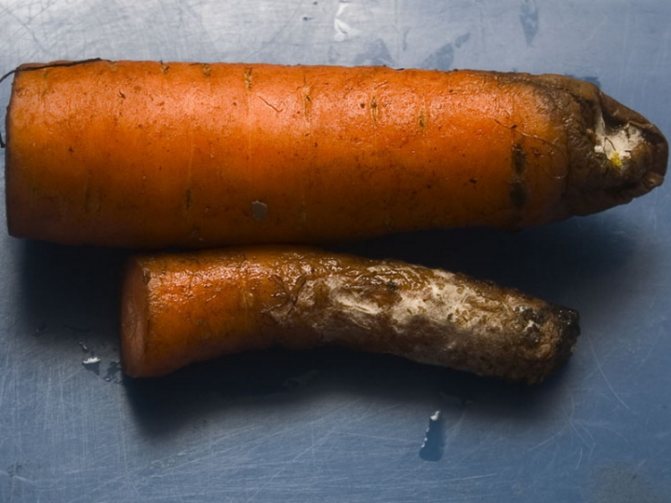


Alternaria
An infectious disease caused by the Alternaria fungus. Slightly depressed dry spots of a dark color appear on carrots, on which gray and then black bloom appears over time. The damaged area flows inward.
When the first signs of infection appear, the infected culture must be removed, and the rest must be sprayed with a fungicide such as Kuproksat, Thanos, Ordan and others. Spraying is carried out every two weeks until the signs of the disease are completely eliminated.
The infection can spread through soil or seeds.
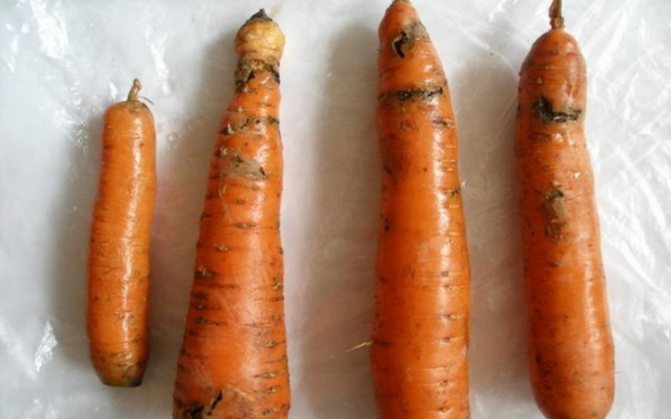


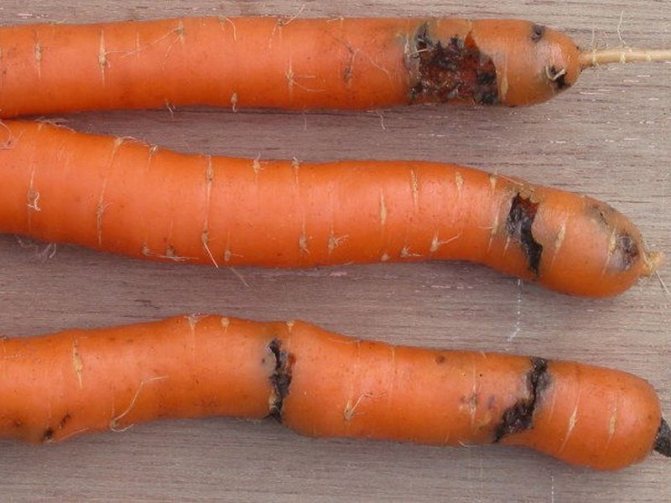
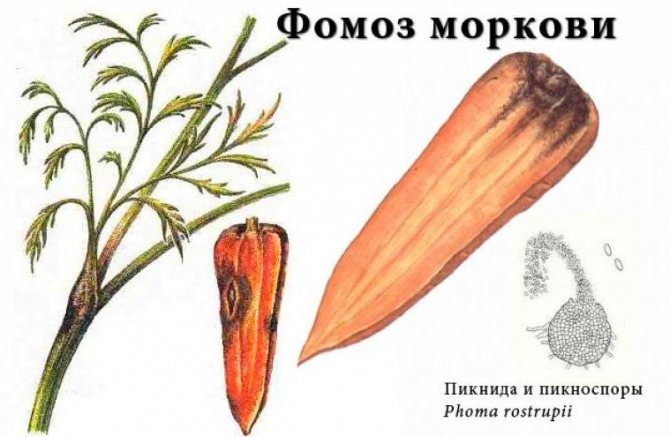
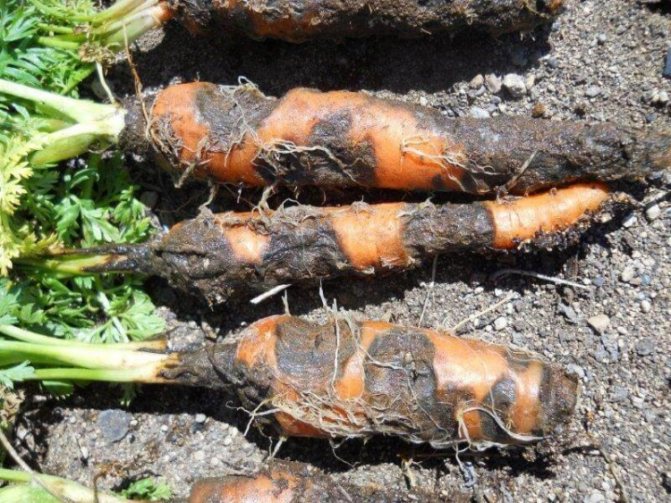
Fomoz
Also refers to an infectious fungal disease that can develop at any stage of growth or storage of a vegetable. Slightly depressed gray spots or stripes appear on the tip of the carrots, which eventually become soft and dark brown in color. Ultimately, the root crop becomes hollow.
It will not work to save a vegetable crop from a disease, but it is possible to use phosphorus-potassium fertilizers for prophylaxis during growth. Infected root vegetables must be burned.


You will learn more about what carrot phomosis is and how to deal with it from this useful video:
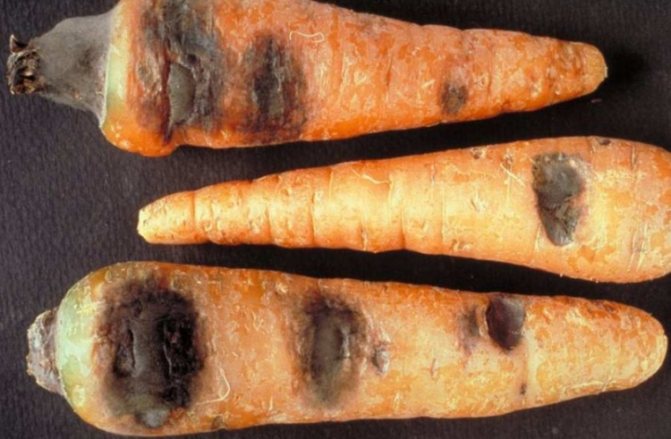
Botridiosis or gray rot
A disease caused by a parasitic fungus. Watery brown spots appear on the infected root vegetable, which later become wet, loose and soft. Over time, the entire surface of the vegetable is covered with gray spots.
To fight infection in the spring, you need to spray the culture with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate. The storage needs to be disinfected every year, whitewash the walls, before laying, the crop must be checked, the temperature in the room should be no more than 5 degrees.


In the garden
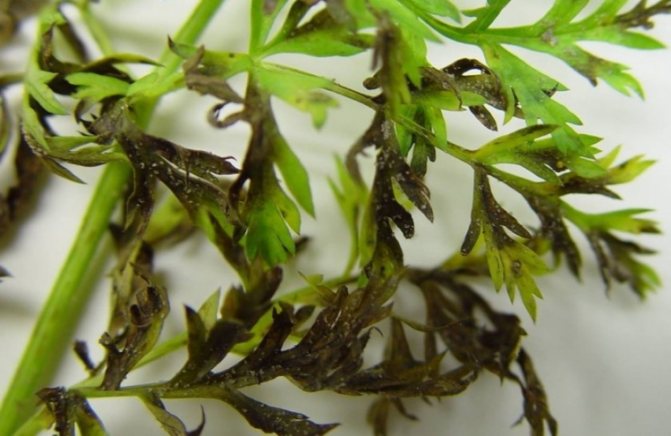
Brown spot
Fungal infection that occurs as a result of non-compliance with culture planting technologies. Initially, the disease affects the tops of the crop, the leaves turn brown and dry. After the infection passes to the root crop, it manifests itself in the form of dark brown spots, which lead to rotting of the culture.
After detecting the first signs of infection, the affected plants need to be burned, and the beds should be treated with a 3% solution of vitriol.


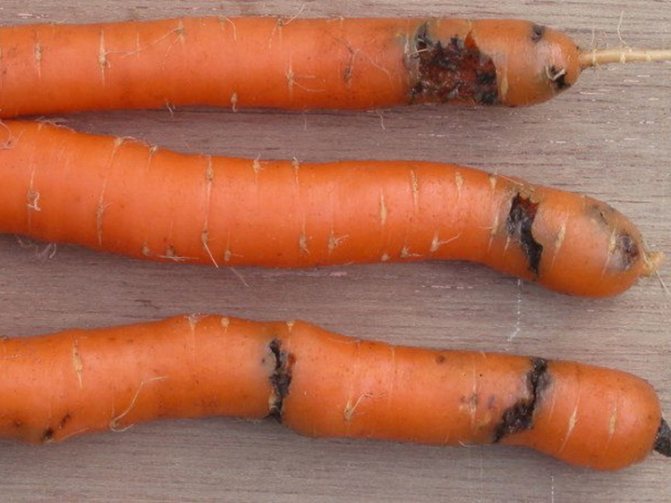
Bacteriosis
A bacterial disease caused by bacteria. The onset of the disease can be recognized by the appearance of yellow spots on the edges of the lower leaves of the culture. Over time, the spots or stripes turn brown, and sunken brown spots appear on the roots. An unpleasant, pungent odor emanates from an infected plant.
It is impossible to cure an infected vegetable, therefore, it is necessary to get rid of such a culture.


Rhizoctonia
An infectious fungal disease, which manifests itself in the form of gray spots with a reddish-purple tint. Leads to wilting, cracking and decay of the root crop.
To combat the disease, liming of the soil must be carried out., for this, before sowing, it is necessary to add about 400 g of limestone, calcium or dolomite.
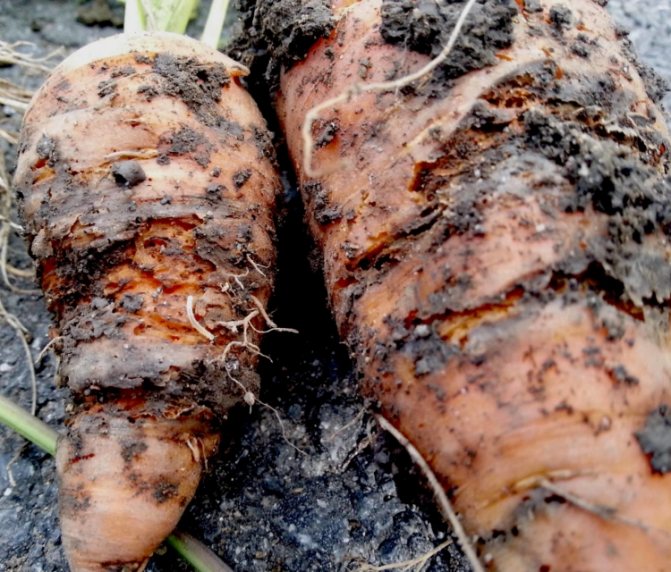


Powdery mildew
A disease caused by infection by two fungi at once. Yellow spots appear on the foliage, which spread throughout the tops and lead to their death. The root crop does not deteriorate from infection, but it grows in an ugly shape.
A crop that is infected with an infection must be pollinated with ash, and non-infected plants must be treated with a fungicide.


Red rot
Soil fungus infection... Depressed gray spots with reddish-purple dots appear on the root crop. Over time, the surface becomes covered with a red bloom, and the leaves become yellow and withered.
Damaged carrots are removed from the soil, they can be boiled and fed to animals, the leaves must be buried deep underground.
To avoid the appearance of the disease, it is necessary to alternate the sowing of crops, as well as liming acidic soils.
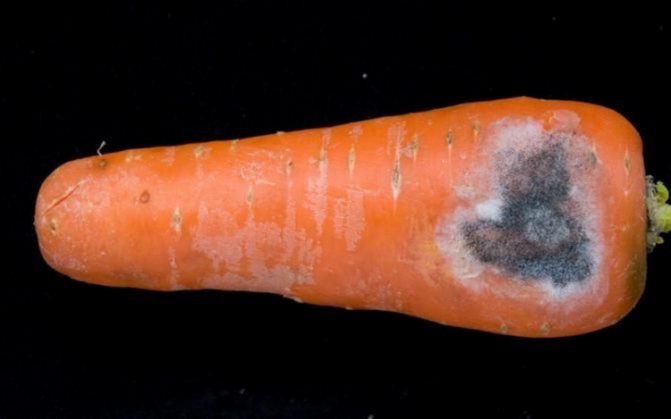


Root deformation
It occurs due to improper care during the growing season or when damaged by a pest such as a nematode (you can read about this and other major vegetable pests here). The root crop grows forked, crooked, gnarled and ugly.
Deformation can be prevented if rare but abundant watering, timely feeding and nematode control are carried out.
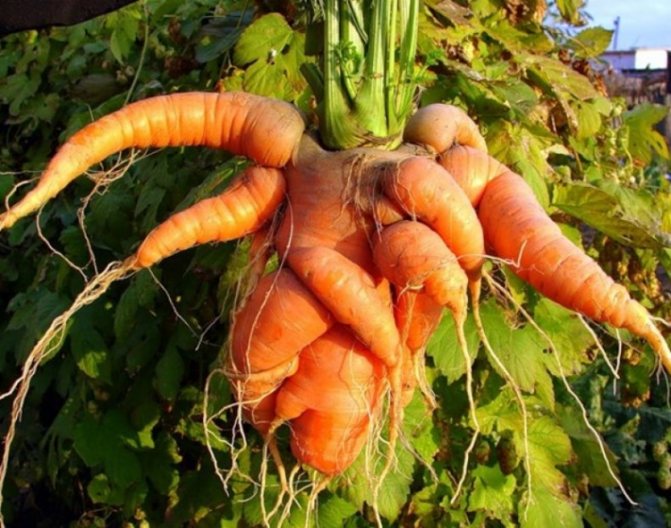


Soft bacterial rot or bacterial cancer
A bacterial disease that leads to decay of the root crop while still in the ground. Soft white growths appear on the carrots, which eventually darken and become hard. As a result, these areas are destroyed, while destroying the vegetable itself.
To prevent rot, it is necessary to cultivate the soil with bacteriophages., as well as timely destroy emerging pests.
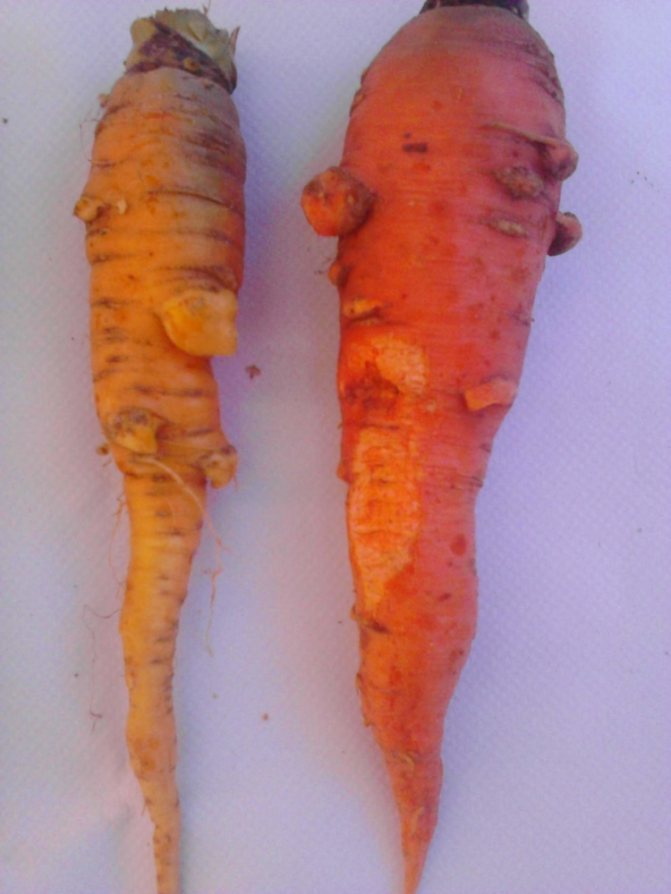


Cercosporosis
A disease that appears due to a pathogenic fungus. Brown spots with a light center appear on the foliage, over time, the leaves curl, and the vegetable itself stops developing.
For prophylaxis in the spring, you need to dig up the soil well, and during growth, water and irrigate the crop in time with drugs such as Quadris or Trichodermin.


Carrot pests and how to deal with them
Preventive measures, folk remedies and chemicals will help protect green mass and crops.
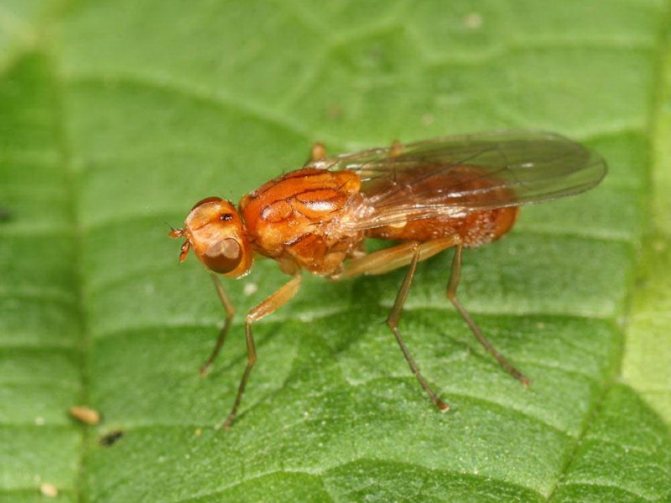
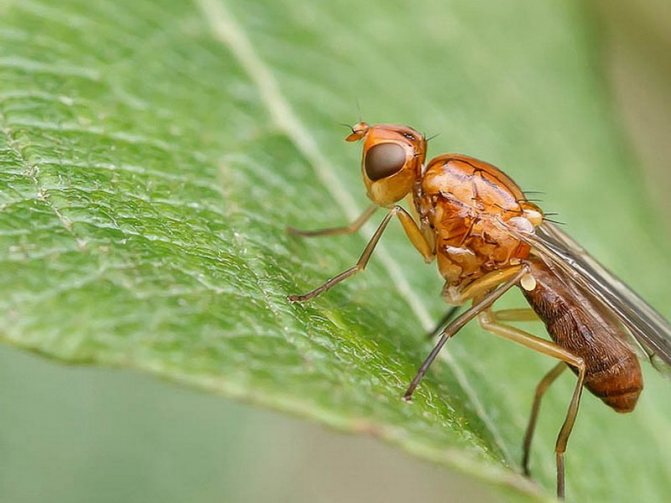
Carrot fly
The insect eats the tops and lays the larvae in the ground. The larvae penetrate the roots and eat them away, which leads to rotting of the fruit. Suitable breeding conditions for carrot flies are shaded areas, high humidity.
Preventive control measures: planting root crops in an open, well-ventilated and illuminated place, regularly thinning the planting, mixed crops of different crops. In the fall, be sure to dig deep into the beds so that the pupae cannot overwinter.
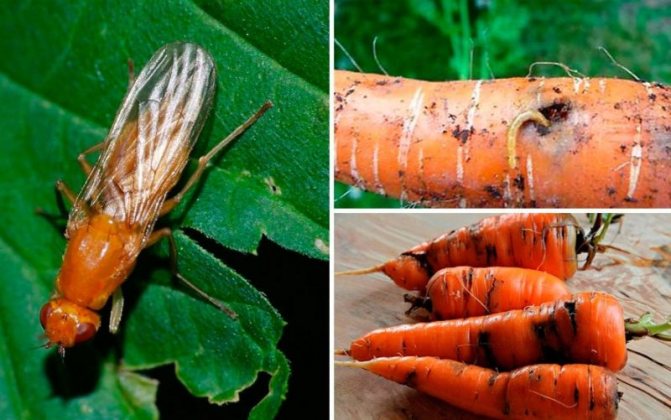


Carrot lily
The small insect lays eggs on the undersides of the leaves. Larvae and adult insects suck out plant sap. The affected foliage slows down growth, acquires a red-yellow tint. Root crops are formed small, with a bitter taste.
Spraying plantings with special preparations: "Actellik", "Inta-vir", "Tsitkor" helps to fight the pest. You can use a folk remedy: the tops are treated with a saline solution (a glass of salt is dissolved in 10 liters of water).
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Important! When spraying the plants, it is important that the brine falls on the underside of the leaves.
Carrot moth
The pest caterpillar damages the testes of the culture: it eats flowers, gnaws at the pedicels. During periods of weak flowering, the caterpillars eat the foliage. The carrot moth hibernates in the crevices of buildings, in cracks in the ground.
Preventive control measures: removal of wild umbrella plants (especially hogweed) around the carrot beds, feeding carrots with nitrogenous compounds. In case of massive damage to the beds by carrot moth, plantings are sprayed with insecticides "Entobacterin", "Lepidocide".
Naked slugs
The pest spoils adult plants and young seedlings. Slugs prefer moist soil, so they gather under stones, fallen leaves. Abundant rains provoke the reproduction of the pest. Slugs are especially active on cloudy and damp days.
The main preventive measures are drainage of ditches, weeding, cleaning of torn tops from the beds. The site needs to be treated with 30% lime mortar, to which wood ash is added. The carrot beds can be sprayed with 10% brine.
See also How to deal with aphids on carrots with folk remedies and chemicals
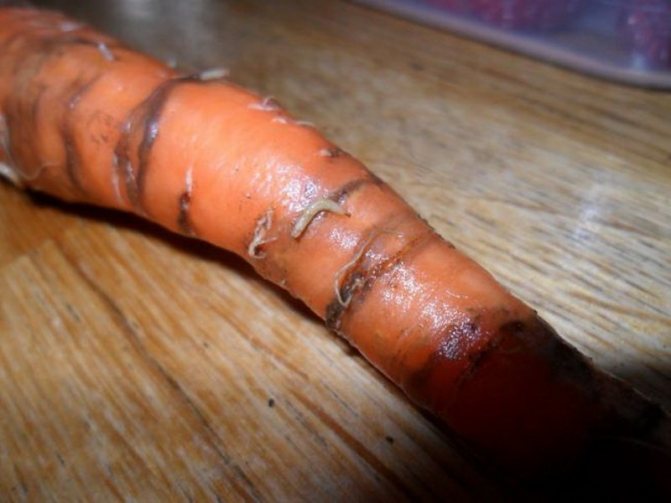
Wireworm
A hard, yellowish worm makes winding passages in root crops, which leads to rotting of carrots. The wireworm can easily move along the ground, in dry weather it can sink into the ground to a depth of 1 m.
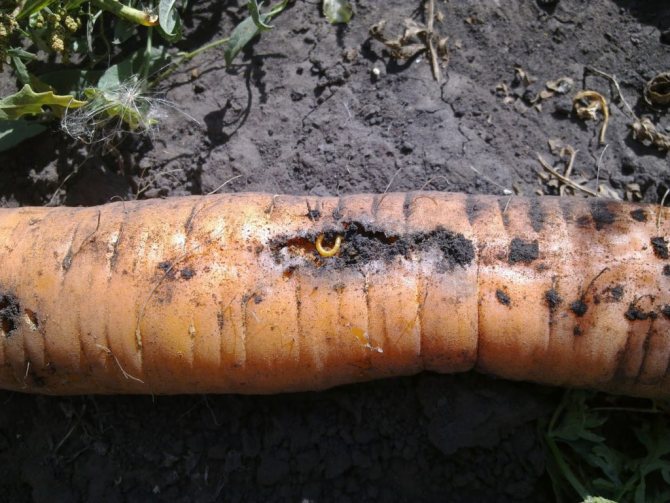


When growing carrots, regular loosening of the soil, weeding the beds (especially the removal of creeping wheatgrass), and attracting birds are of great importance. Chemical preparations "Bazudin", "Aktara" have proven themselves well.
Winter scoop
Caterpillars gnaw the petioles of the carrot tops, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of the fruit or to the death of the plant. One caterpillar can destroy 10-15 plants per night. Caterpillars overwinter in the soil at a depth of 20-25 cm. The butterfly is frightened off by the smell of yarrow, chamomile, and burdock. Therefore, the tops are periodically sprayed with plant solutions.
Advice! It is preferable to plant early varieties of carrots.
Agrotechnical measures: deep digging of the soil, destruction of weeds, if the beds are watered abundantly, then most of the caterpillars die. A good result is given by spraying the beds with chemicals (insecticides, organophosphates).
Gall nematode
Small transparent worms parasitize on the root system of plants, reproduce well in sandy soils. The pest easily tolerates cold, but low temperatures prevent reproduction. When plants are damaged, the tops have a sluggish, drooping appearance even after watering. The carrots stop growing and gradually dry out. It is difficult to protect plantings from pests.
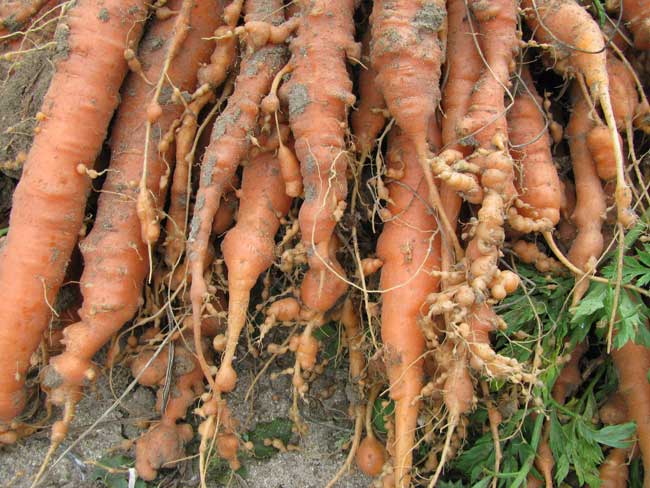


Several methods of struggle are used:
- an infected plant with a part of the land is removed from the site;
- from pesticides it is desirable to use nematicides ("Nematofagin", "Nematorin", "Bassamil"), which do not save the affected plants, but prevent the spread of nematodes.
Popular methods are popular: plots are watered with calendula infusion, marigolds and calendula are planted in the garden.
Medvedka
The gluttonous pest gnaws through the underground parts of the plant, eats the sown seeds, and gnaws at the roots. Favorable conditions for the breeding of the bear are sandy well-lit areas, soil rich in humus. Medvedka leads an underground lifestyle and gets to the surface mainly at night. Comprehensive pest control measures are considered effective:
- at the end of the summer season, special traps are set up: pits 40-50 cm deep are filled with rotted manure. Medvedki settle in manure for wintering and destroy pests in late autumn;
- insecticides are placed in the soil near the holes with seedlings;
- Thorough weed removal and deep digging of the soil are also useful.
The natural pests of the bear include birds (starlings, rooks), as well as rodents (moles, shrews), anathem larra - a wasp that penetrates underground passages.


Prophylaxis
When growing
Not every carrot infection can be cured, but it can be prevented with a number of preventive measures.
Pre-sowing treatment
- Seed - soak for 10 minutes in warm water (40-55 degrees), and then place in a container with cold water for 2-5 minutes. Also, the seeds can be soaked in a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, leaving them in it for 8-10 hours.
- The earth - before planting seeds, you need to pickle the soil with a solution of copper sulfate (30 grams), which dissolves in 10 liters of water. 1 liter of liquid is consumed per 10 meters of a square.
Competent choice of variety
Choosing the right variety that is resistant to many diseases can prevent the development of infection, which will save time and money, as well as get a good harvest.
For example, varieties such as:
- Artek or Callisto resistant to white rot.
- Rogneda has immunity to gray rot.
- Dolyanka - to fomoz, etc.
Watering with warm water
To prevent cracking of the root crop and to prevent infection, it is recommended to water carrots in the evening with water that has been heated in the sun during the day.
Other measures
To prevent the disease, crop rotation must be observed. It is forbidden to plant carrots in the same place for two years in a row. It is not recommended to sow a crop after beets, onions, mustard, potatoes and rye are ideal vegetable precursors.
During storage
- You need to store carrots in a cool place at a temperature of + 1- + 3 degrees and a humidity not higher than 85%.
- You need to place root vegetables in open boxes or plastic bags with holes made for ventilation.
- Only whole and healthy vegetables are selected.
- In order for the carrots to be well preserved, before storing them in storage, they need to be powdered with chalk dust, you can put them in sand mixed with chalk (1: 1) and leave them like this for the whole winter.
In the business of growing carrots, every stage is important: seed preparation, planting, care. If important nuances are not taken into account, then the appearance of diseases and pests is provided for the entire crop. Read about how to get rid of carrot flies and prevent the appearance of an insect on our website.
There are a lot of diseases in carrots, and most often it is impossible to save an infected crop. Therefore, to prevent their appearance, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures that will help to get a rich and healthy harvest.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
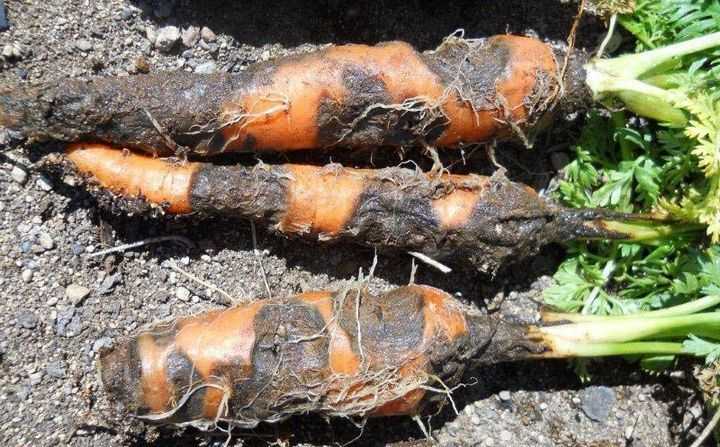
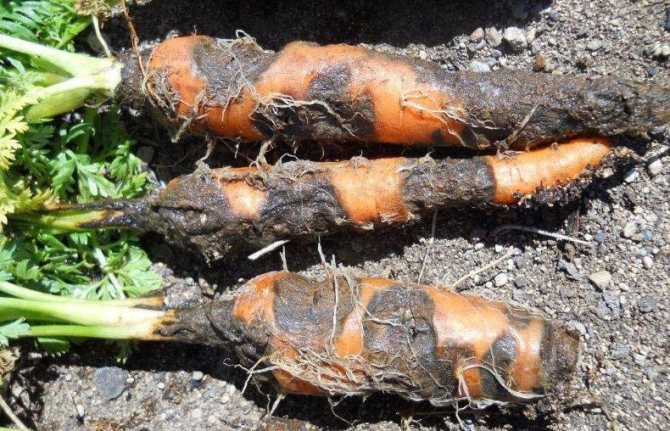
Phomoz (dry rot)
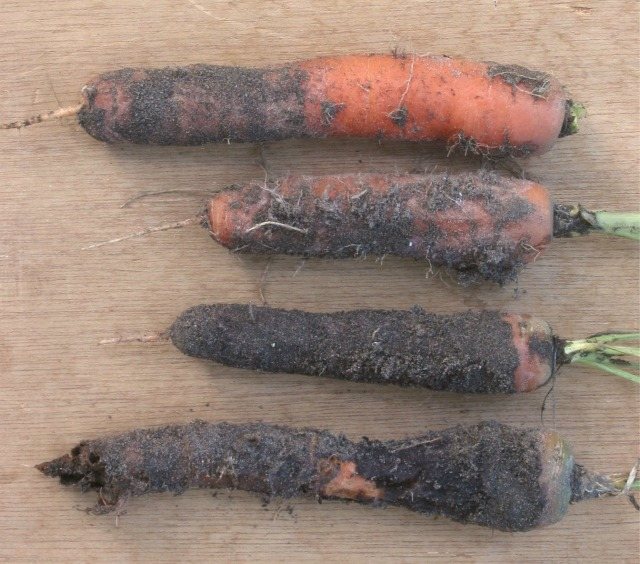


The next no less dangerous enemy that threatens carrots when stored in a cellar is phomosis (dry rot).
The infection appears already in the autumn period. Dry rot on carrot roots looks like bulging spots of a rich brown hue with numerous tiny black dots. In the affected areas, the carrot loses its hardness. Gradually, cavities form on the affected areas, which quickly become overgrown with white mycelium.
Seeds, roots and carrot greens left over after harvesting can carry the disease. On the beds, dry rot is spread by wind, rain or carrot fly larvae.
The development of phomosis is favored by excessive humidity and high temperature - + 21 ... 25 degrees.
What if the carrots began to rot in the ground?
So, white rot and bacteriosis affect not only carrots, but also cucumbers, lettuce, celery. Therefore, from the point of view of the effect on the soil, cucumbers are a good precursor for carrots, only if they did not show any signs of disease.
You can plant carrots after potatoes, legumes, tomatoes, cabbage, but after applying organic fertilizer to the soil.These crops have no common diseases apart from gray mold, which can damage any crop, although carrots rarely get sick.
Similar posts