How to process a greenhouse in the fall after harvest. After harvesting, vegetable growers begin their autumn worries. In greenhouses, urgent work is carried out to disinfect soil, structures, equipment, tools. Their purpose is to destroy the larvae and eggs of pests, pathogenic viruses, fungal spores, and bacterial organisms overwintering in greenhouse conditions. The yield of vegetable crops in the next year largely depends on the high-quality autumn processing of the greenhouse economy.

- 4.1 Similar entries
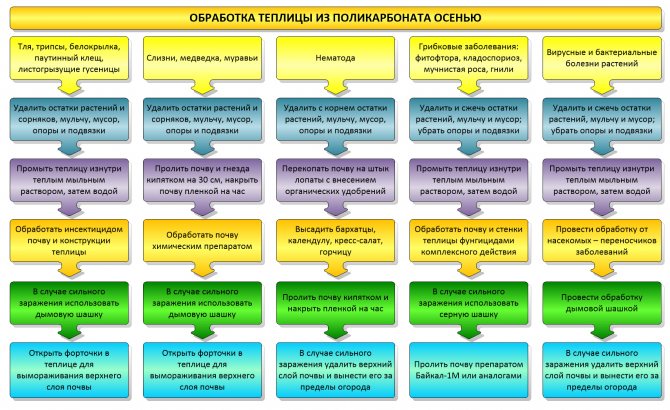
Cleaning and cleaning
There is no exact time for the start of autumn processing of a polycarbonate or film greenhouse. It all depends on the crops that were grown there and the general weather conditions. But if the harvest time is over, and there is only one tops left in the greenhouse, then the time has come.
For more information about processing a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall and preparing the soil for the new season, see the video:
Cleaning in autumn
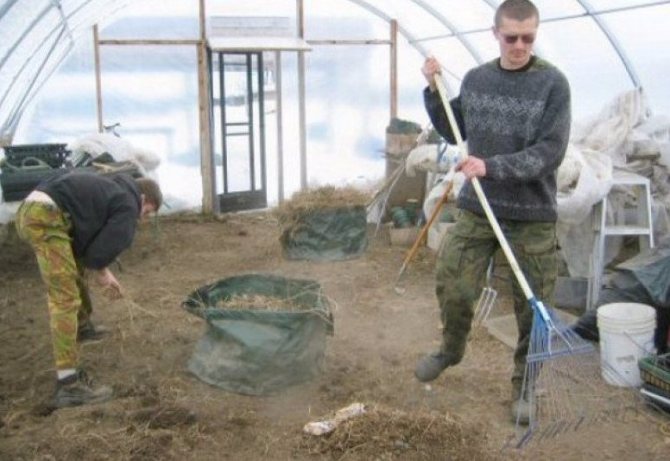
We completely clean the beds and paths from plant residues. Particular attention should be paid to the space between the sides of the beds and the material of the frames, as well as the wrong side of the paths if they consist of stones or other hard and flat materials. Usually under them you can find a whole zoo of pests: bear larvae, beetle or wireworm. They must be carefully collected in the fall, as they are not afraid of freezing of the soil and most pesticides.
Treatment of the greenhouse in the fall from pests and diseases, collection and destruction of the larvae of the bear (1), the May beetle (2) or the wireworm (3)
Cleaning the greenhouse material and preparing the frame for wintering
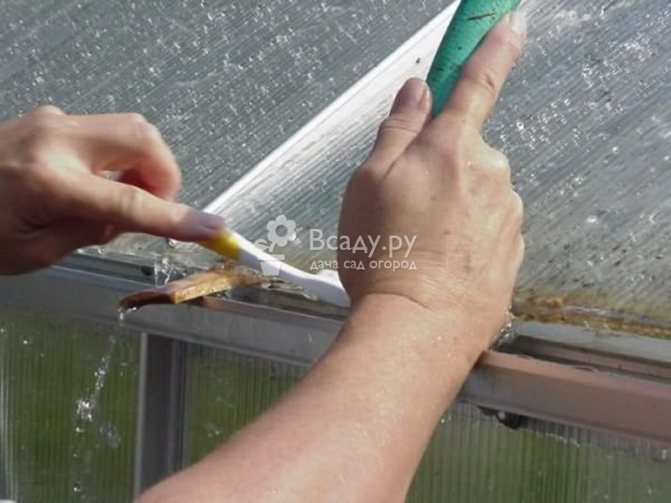
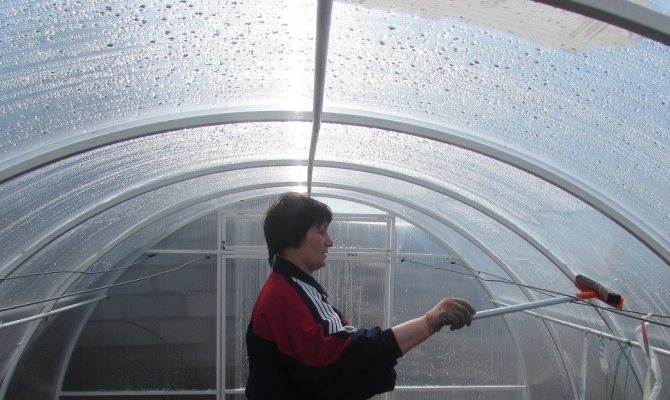
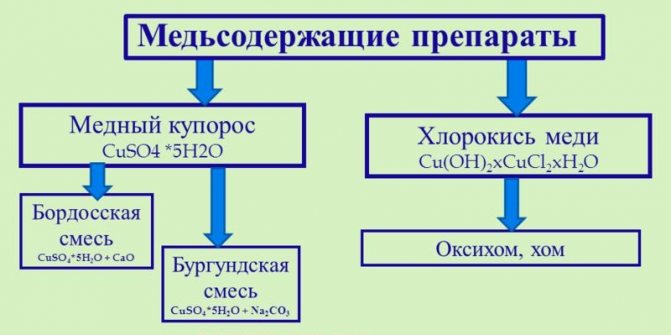
It is imperative to process the polycarbonate greenhouse in autumn with copper sulfate, 5% - 10% solution is applied to the wooden frame, disinfecting it. PVC structures can be simply washed using vinegar essence, soapy water or other non-aggressive household chemicals, the same applies to glass. How to wash a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall to obtain an additional disinfecting effect? It is advisable to treat glass surfaces and polycarbonate sheets with a mild solution of potassium permanganate. But the film coating is strongly recommended to be removed in the fall before wintering. It must also be cleaned, dried, folded neatly and stored until spring in a dry and frost-free place.
With a metal frame, if it is not made of aluminum or its alloys, it is somewhat more difficult. All supporting structures must be carefully inspected. If traces of corrosion are detected, the detected places should be cleaned with a metal brush. Treat with a special primer to prevent further spreading of corrosion and increase adhesion and cover with paints and varnishes.
The greenhouse frame is reinforced in the center with several additional posts in the area of the ridge, where the greatest snow load will be concentrated in winter. Such maintenance of a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall is not necessary, but it will help preserve the integrity of the greenhouse and significantly increase its service life.
In autumn, doors, vents and all ventilation vents are closed and secured with latches.All the threads for the suspensions are cut off (they will still rot during the winter and begin to break when used again); the supports for supporting the plants are removed from the ground and removed.
Cleaning the "edging" of the beds
Most greenhouse owners separate the beds from one another with various materials. If earlier these were bricks, asbestos sheets (slate) or wooden boards that rotted in 2 seasons, now these are special plastic boards of various designs resistant to mechanical stress, weather conditions and high humidity.
Their important advantage is quick and easy dismantling. In the fall, you need to pull them all out and rinse in a potassium permanganate or vinegar solution. Reinstallation takes place in the spring.
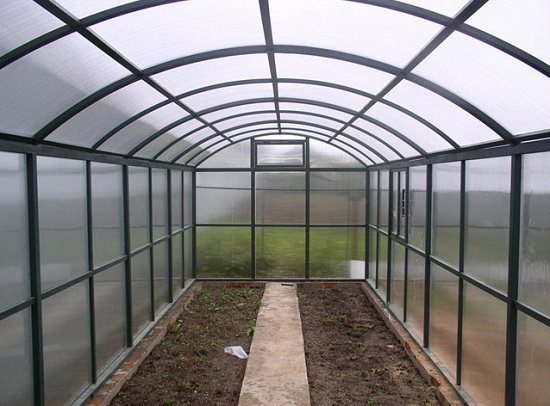


Preparing the greenhouse for winter in the fall - all unnecessary is dismantled and taken out
When to start greenhouse processing in autumn
All planned work on the processing of the greenhouse is carried out after the completion of the harvest and preparatory work. First you need:
- uproot all vegetable tops;
- remove residual mulch;
- get rid of all weeds;
- remove consumables from the structures - twine, fastening tapes, pegs.
Read our article about the benefits of mulching HERE


Plant residues are best disposed of, or treated with disinfectants (copper sulfate at the rate of 2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water or phytosporin according to the manufacturer's instructions) and sent for composting.
Then inspect the frame of the greenhouse. They are doing current repairs. If corrosion is found on metal parts, the damaged area is treated. Rust spots are cleaned with a metal brush, primed and painted.
Read about "Fitosporin: how to use and what for"
Soil preparation
The greenhouse creates ideal conditions not only for the growth of plants (including weeds), but also for various pests that can ruin the standing crop if not dealt with. The processing of the greenhouse in the fall from pests and diseases should be complex. The use of chemistry - various insecticides during the growing season is not a very good idea. The chemicals accumulated in plants end up in our bodies. Therefore, special attention should be paid to disinfection and other soil cultivation in the greenhouse in the fall.
Soil replacement
Quite a laborious and expensive process, but after it the number of pests decreases by several orders of magnitude. Such a procedure as preparing the soil in a greenhouse in the fall, with a complete replacement of the fertile layer, is recommended at least once every three years. The soil is removed to a depth of 7-10 cm.Then peat, humus (manure), sand and ash, proportions are very different depending on the presence of one or another ingredient, but rarely exceed 1 bucket per 1 m2 of soil. The cultivation of the land in the greenhouse in the fall may include fluffing, for heavy and oily soils, using sawdust. However, with this method, you must be careful and, if possible, do not use sawdust of coniferous wood (spruce, pine, larch) and wood species with a large amount of tannins (oak, walnut).
The resulting mixture is dug up. Distribute evenly over the planting sites and cover on top with a thick layer of straw or fallen leaves. After the snow falls in winter, it is necessary to independently throw some of it into the greenhouse with a shovel (a layer of 15-20 cm) in order to prevent deep freezing of the soil and provide the earth with the necessary moisture in the spring. Some gardeners additionally water the enriched earthen mixture with a weak solution of potassium permanganate before adding fertilizers.
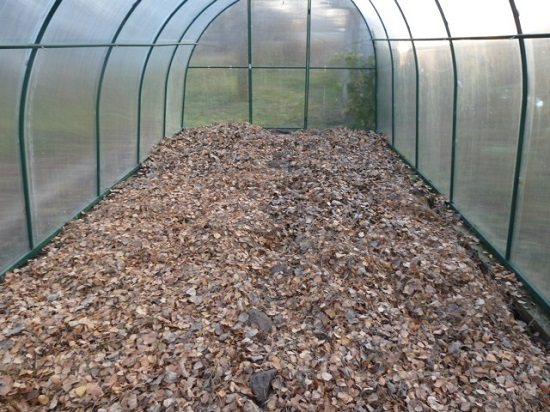


A thick layer of fallen leaves will help keep warm
Soil infected with pests and diseases can not be thrown away, but treated.How to treat the soil in a greenhouse in the fall in order to disinfect it qualitatively without resorting to strong chemicals. For this, a pile is formed with an area of 1-2 m2 and with a layer thickness of 20 cm.When it is arranged, each layer is generously sprinkled with lime at the rate of 250 g per 1 m2. It remains in this state the whole next year, having frozen out over the winter, the pile will need to be re-dug up next fall and used after the second winter.
Fertilizing the soil
How to fertilize the soil in the greenhouse in the fall depends not only on the type of soil, but also what crops are planned to be planted in the spring. To achieve the highest yield, not only special means are used, but also special methods of processing perennial plants:
- Strawberry. After the last harvest, at the end of August, all the greens are mowed so that the upper buds remain intact. The bed is watered abundantly and the soil is loosened. Potash and superphosphate fertilizers are introduced in the proportions recommended by the manufacturer. All this is sprinkled with a small layer of fertile soil so that new shoots do not dry out. Before the onset of cold weather, no later than October, the roots of strawberries are covered with peat. In winter, be sure to pretend to be a thick layer of snow to prevent freezing.
- Tomatoes. One of the most common greenhouse crops. They are very demanding on the quality of the soil and the composition of the dressings. For a tomato, soil preparation in a greenhouse in the fall consists in the introduction of organic, chemical or combined dressings, which must contain:
- Manganese - promotes faster ripening of fruits;
- Copper, boron - stimulate flowering and abundant fruiting;
- Potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, nitrogen - contribute to the rapid growth of the plant.
- Cucumbers. The most common "inhabitant" of greenhouses. There are many varieties available for greenhouse cultivation. However, the processing of a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall for planting cucumbers in it has its own specifics. First of all, you need to check the acidity of the soil. With an acidity of more than 6.5-7 pH in autumn, it is necessary to liming the soil. Also in the fall, the soil is fertilized with the following specialized mixture:
- Potassium salt - 10-25 gr.;
- Ammonium sulfate - 10-25gr.;
- Ammonium nitrate up to 25 gr.
Important! There is a very simple way to check the acidity of the soil at home. You need to pour a handful of dry earth with simple 9% table vinegar. If a reaction starts with the release of gas, then there is enough lime in the soil, and it is neutral.


Determination of soil acidity with 9% vinegar, reaction to neutral soil
What pests and diseases can I winter in a greenhouse
Not all greenhouse dwellers harm plants. Soil is a living organism, it contains billions of bacteria that work incessantly to process organic matter into chemical compounds that are consumed by plants for growth and development. In addition, worms and insects inhabit the soil, and only some of them are dangerous to plants. Do you need to kill everyone clean using potent chemicals?


Recommendations for disinfecting soil in a greenhouse
First you need to figure out which pests and pathogens can survive the winter in a greenhouse and what conditions contribute to this.
Aphid - a small insect that feeds on plant sap. Aphid colonies are able to grow rapidly in a greenhouse, which leads to damage to young shoots and a decrease in yield. In addition, aphids release a sweetish sticky liquid, creating conditions for the development of fungal diseases.


Aphid
Aphids overwinter in greenhouses and greenhouses in the egg stage, hiding in weeds and uncleared plant debris. In the spring, larvae emerge from the eggs, which soon turn into an adult insect that can harm young plants.In addition, ants hide aphids in their nests - they use this insect as a cash cow, feeding on sweet secretions, and even carry it around the garden in search of new "pastures".
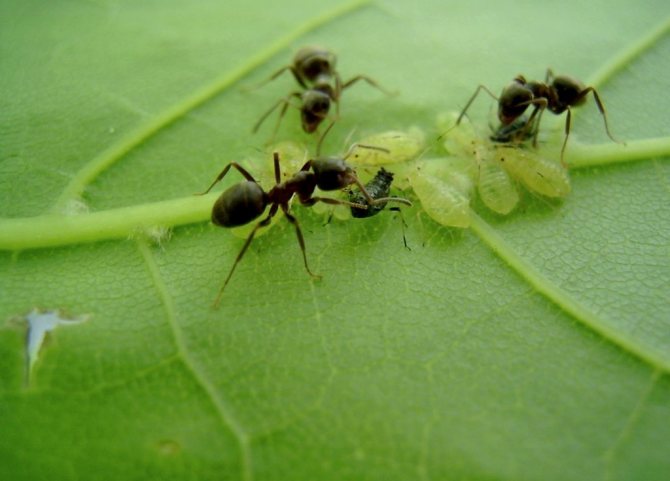


Ants carry aphids
To lime aphids in a greenhouse, it is necessary to carry out a thorough pre-winter cleaning of weeds, dead shoots and tops of plants. Experienced gardeners also recommend driving ants out of the greenhouse and destroying all anthills built in it.
Whitefly - a flying sucking insect, similar to a moth. Whitefly colonies settle on plants and suck sap out of them. The plant gradually withers and dies, the yield is significantly reduced. In the greenhouse, the whitefly is able to overwinter, provided that the temperature does not drop below -5 ° C, in severe frosts, the pests freeze out.
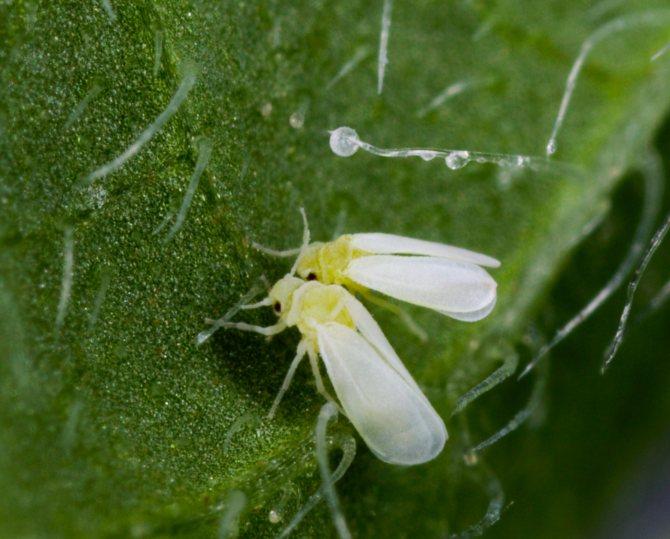


Whitefly
In the middle lane, to combat the whitefly, it is enough to open the windows in the greenhouse for the winter so that the temperature equals the outdoor temperature. In more southern regions with mild winters, the greenhouse and the topsoil should be treated with one of the systemic preparations, which will be discussed below.
Spider mite - a fairly serious pest that can destroy all vegetation in the greenhouse in a matter of days. It can be identified by small dots on the back of leaves and a fine, disordered cobweb on plants. The spider mite hibernates in the cracks of the frame and base of the greenhouse and in wood debris. Natural and chemical preparations help against spider mites, but they should be used only after thorough cleaning.
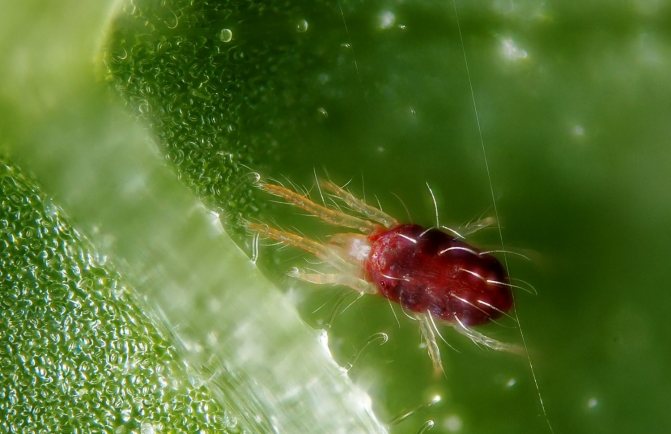


Spider mite
Slugs gardeners are also annoyed in the greenhouse. The fight against them is also complicated by the fact that they are active only in the dark, so it is sometimes difficult to understand who is eating shoots and fruits. The slug larvae hibernate in the ground, in the upper soil layer. You can kill them with boiling water or chemicals.
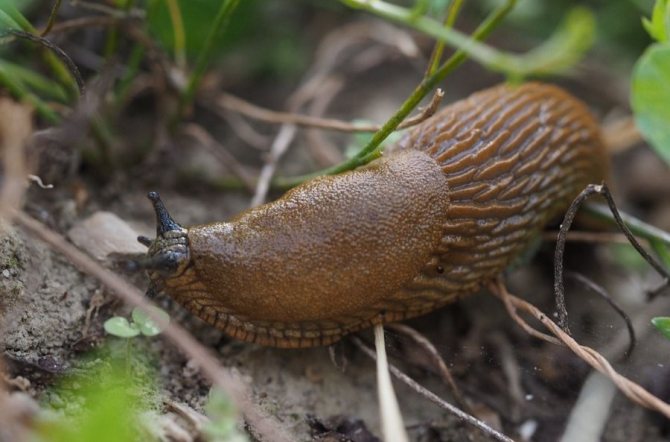


Slug
Nematode - small parasitic worms that live in the stems, roots or leaves of various vegetable crops. Nematoda is a real scourge of greenhouses, it is extremely difficult to remove it. Nematodes overwinter in the ground, at a depth of 20 cm, or in galls - thickenings on the roots of plants. Stem and leaf nematodes can also overwinter in plant debris.
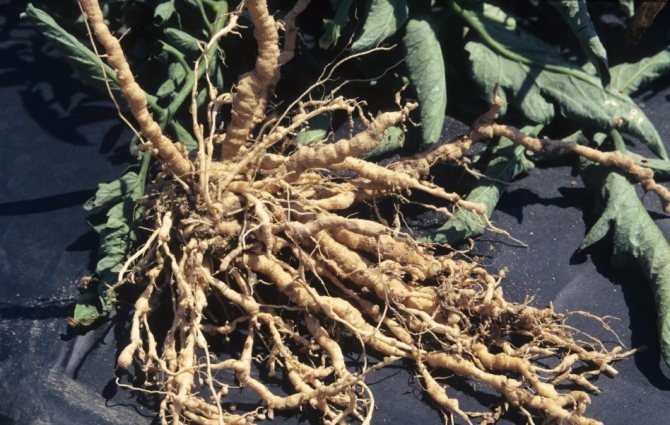


Nematoda - damaged roots
For the destruction of nematodes in the garden, crop rotation is most effective. In this case, plants of the same species are returned to their original place no earlier than after 3-4 years. However, in a capital greenhouse, this method is unacceptable. Replacing the soil is also of little help, since it is quite difficult to remove the soil to a depth of 20 cm.
To combat the nematode in industrial conditions, powerful chemical preparations are used - systemic nematicides. They are extremely toxic to humans and kill all useful microflora in the soil, so they are used with caution in a home greenhouse.
Warming up the soil up to 50-60 ° C using hot water, as well as the introduction of organic fertilizers and sugar can be beneficial. At the same time, saprophytes actively begin to multiply in the soil, attracting natural enemies of nematodes.
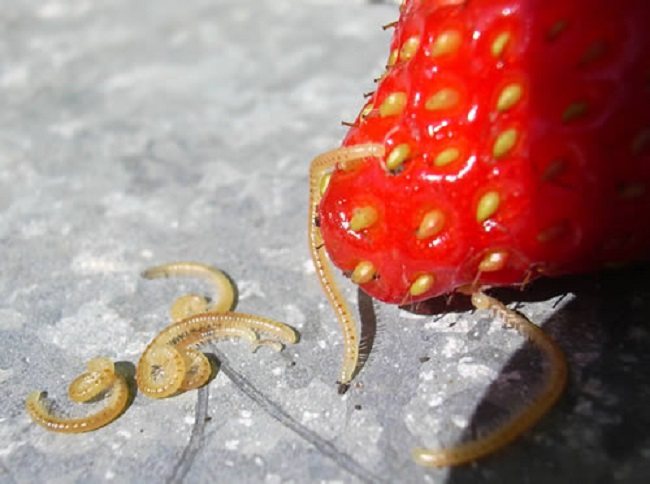


Strawberry nematode: pest photo
Another effective method is planting plants that oppress and scare away the nematode. These include marigolds and watercress. You can sow these cold-resistant plants immediately after harvesting vegetable crops, in two to three months they will have time to thoroughly clean the soil.
Fungal diseases - late blight, cladosporium, fusarium, powdery mildew and various rot - appear in the greenhouse in unfavorable conditions and quickly infect plants. It is difficult to cope with them, and sometimes it is completely impossible - most of the crop perishes.
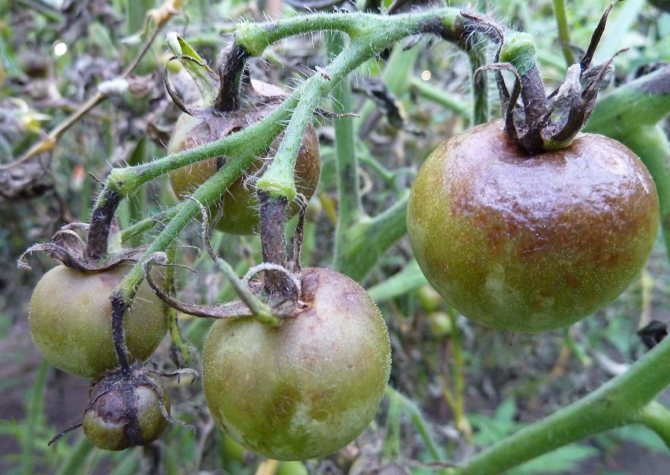


Phytophthora - a fungal disease of tomatoes
Fungi have great resistance to external conditions and winter well in closed ground, settling on the soil, the walls of the greenhouse and garden tools. To combat fungi, fungicides and copper-based preparations are used.
Viral and bacterial diseases can be introduced into the greenhouse with soil and planting material, they are also carried by sucking insects. Therefore, the prevention of viral and bacterial diseases in the greenhouse is reduced to cleaning, removal of harmful insects and preventive treatment of soil and structures with antibacterial drugs.
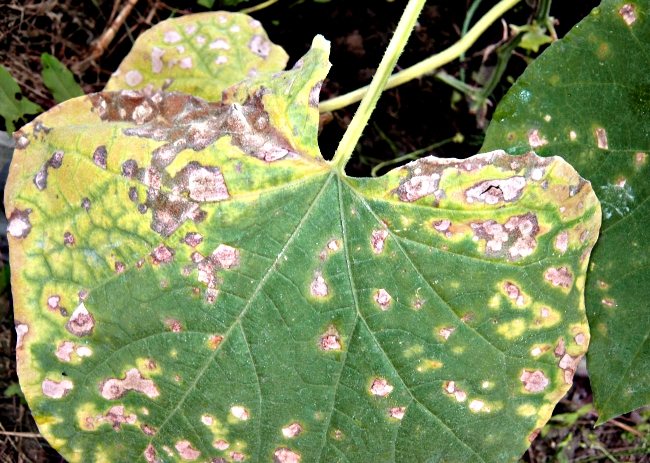


Bacteriosis - a disease of cucumber
Disinfection
There are several ways to disinfect a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall:
- Fumigation;
- Spraying with pesticides;
- Sprinkle with bleach.
Before proceeding with the disinfection of a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall, you need to take care of personal protective equipment. Without fail you need:
- sealed glasses;
- latex gloves;
- respirator;
- tight clothing (preferably working overalls).
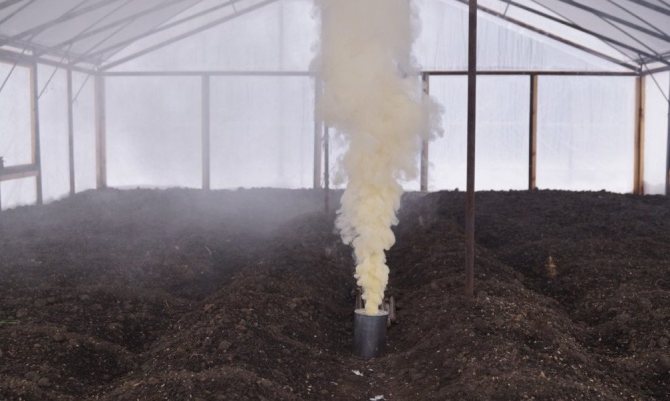
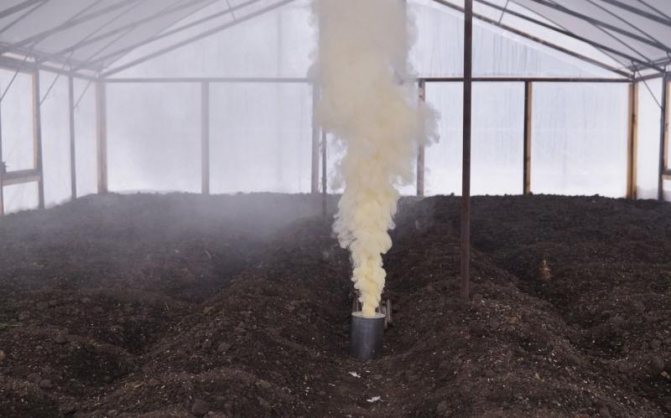
Fumigation
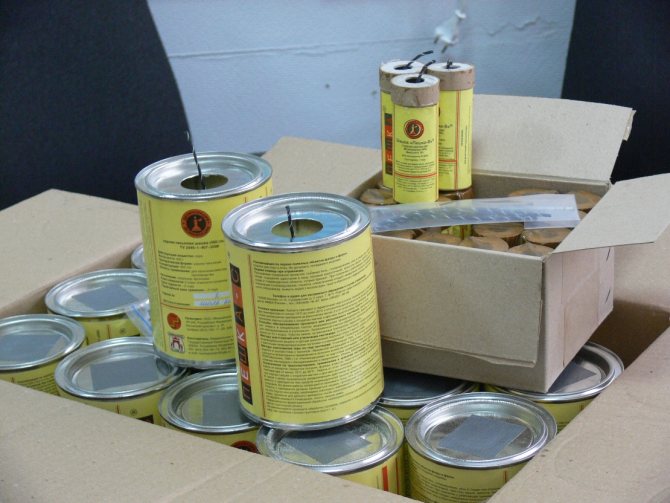
How to disinfect a polycarbonate greenhouse in autumn using sulfur fumigation? For this, special sulfur checkers can be used, or you can prepare the composition yourself. This requires fodder sulfur, mixed with kerosene to the consistency of thick sour cream. A dose of 50 g of the mixture per 1m3 of the greenhouse. The effectiveness and the required number of checkers are indicated directly on them.


Fumigation of the greenhouse with special checkers
Cigarette lighters are evenly spaced throughout the greenhouse. All surfaces are shelving, walls and ceilings are sprayed with water. After the mixture is set on fire and the smoke begins to actively emit, it is necessary to quickly seal the greenhouse, sealing all the cracks from where the smoke comes from with tape. Processing time 4-5 hours for checkers and 2-3 days for self-made mixture.
For your information! If the greenhouse is infected with a spider mite, then the dose is increased 3 times to 150 grams.
For the disinfection of the greenhouse in the fall, see the video:
Spraying
How to wash a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall, so that the structure is not only clean, but also disinfected? The easiest way is to use a 0.75% solution of copper sulfate 75 grams per 10 liters of water, the resulting composition is enough to process 10 m2 of land. Bleach is prepared at the rate of 400 gr. for 1 bucket of water (4% solution). The mixture should be allowed to brew for 4 hours. The solution is applied in the fall as follows. Slightly mixing the contents of the bucket, the upper third can be used to disinfect the soil, and the lower third, the most concentrated for processing greenhouse parts.
To effectively combat spider mites, the land is cultivated in a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall with a 10-15% solution of bleach.
To get rid of the keel of cabbage, use 40% carbation. 0.5 kg of this substance is diluted in 10 liters of water and simply watered the ground immediately after excavation.
How to treat a greenhouse in the fall from black leg and rootworm nematodes and aphids? Can be eliminated with karbofos. 90 g is diluted in 10 liters of water, the resulting composition is used to process 1m3 of soil. After watering, the surface is dug up so that the area treated with karbofos is at the bottom.
Processing of polycarbonate greenhouses in the fall from late blight and late blight is carried out with specialized biological preparations based on hay bacillus: phytophthora, phytosporion-M, alirin, gamair, baxis.
Dusting (dusting)
Sprinkling with chlorinated lime powder is the cheapest and simplest, but nevertheless, quite effective way to combat late blight, fusarium and other fungal diseases of plants. It is produced on not dug up soil, consumption is up to 50 grams per 1m2. After processing, the beds are dug up.
Important! All actions to disinfect a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall must be carried out at a temperature of at least 10-15 ° C. Otherwise, the efficiency drops sharply.
Traditional methods of pest control
There are many popular recommendations on how to process a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall - this is the use of various infusions and extracts.These mixtures include:
- Garlic, tobacco and mustard tinctures;
- Extracts from pine needles or pine cones;
- Ash solutions.
The effectiveness of such drugs is rather doubtful and is rather psychological in nature. Although their use can somewhat reduce the activity of pests, complete elimination is out of the question. The only advantage of these formulations is their environmental friendliness.
How to process?
- Without using chemicals, you can get by with laundry soap. It is shaved into a bucket of water until a not very saturated solution is obtained, with which the walls of the greenhouse are washed from the inside and outside with a soft cloth so as not to leave scratches. If there are pieces of dirt, they are soaked with soapy water and after a while they are wiped off with a rag.
- When using a sulfur checker in a greenhouse, all doors and crevices must be sealed.
The use of sulfuric acid is not advised by the manufacturer. This is especially true for structures with a poorly painted iron body. Inside, an iron stand is placed under the saber, which is set on fire with closed doors and windows.
- Disinfection with copper sulfate solution, diluted in an amount of 75 g per bucket of water. Working tools are wetted and the frame, wall and ceiling surfaces are wiped. In the presence of diseases and infections, dilute 200 g of copper sulfate in a 10 liter bucket. The surfaces are washed twice.
Winter crops in autumn
Despite the intensive preparation for winter, in the fall, you can take care of the future harvest. You can set aside a small corner in the greenhouse for planting sorrel or wild garlic. This place should be insulated with leaves or spruce branches more carefully, and after the first snow falls, throw a small snowdrift up to 1 m high on the garden bed.Already in early March, when the snow melts in the greenhouse, it will be possible to see the first shoots, and in April to harvest.


Planting winter crops in autumn
People's preventive measures
- Tinder fungus shredded and covered with boiling water insists... Plants are sprayed with its broth at least once every 2 weeks.
- Chalk and sieved ash solution used to combat late blight.
- Manganese potassium is dissolved in warm water and infused with garlic gruel for 3 days. The resulting solution is sprayed with seedlings 2 weeks after planting, and every 10 days.
- Removal of late blight is possible by increasing the greenhouse temperature... Why, in the heat, the doors and vents are closed, maintaining the temperature at 40 ° C for several hours. After that, intensive ventilation of the greenhouse is required. Pollen on tomatoes is sterile with a temperature rise of up to 30 ° C.
Greenhouse maintenance in winter
For the winter, only polycarbonate or glass frames remain non-removable. Particular attention must be paid to the latter, as glass is a more fragile material that may not withstand the pressure of snow. In case of heavy snowfall, the greenhouse roof must be cleaned. Polycarbonate structures, as a rule, have an arched - semicircular shape. so the snow just slides over it. The exception is temporary thaws in the middle of winter. In this case, it is necessary to clean off the formed ice. To strengthen the frame, internal supports are used, which are installed in the fall.


Strengthening the frame with struts
How to process a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall: ways
The strength of the polycarbonate allows you not to disassemble the greenhouse structure in the winter. To reduce the development of diseases, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures. Greenhouse processing takes place in October after harvest. It is necessary not only to carry out disinfection work, but also to clean the structural elements of the room.
Polycarbonate greenhouse, can be washed with soapy water or water with added manganese.
In order not to damage the surface, soft tissues are used, for example, rags, foam sponges.Do not use abrasive substances and hard brushes, which can scratch the coating. Particular attention should be paid to corner pieces that are rinsed with clean water. Metal frames are cleaned from corrosion and painted with paint. Wooden structures are disinfected with a 5% solution of copper sulfate.
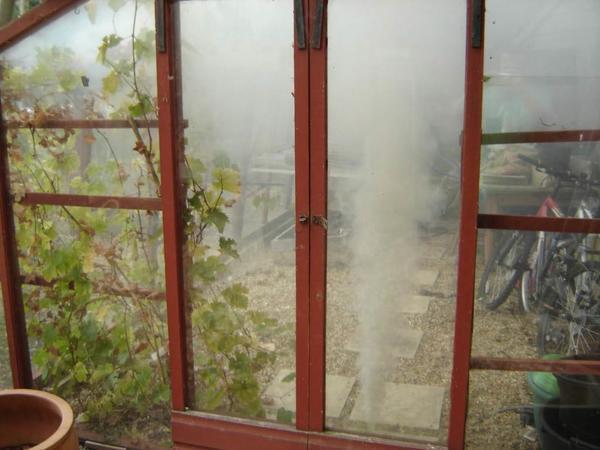


There are several types of greenhouse processing:
- Chemical exposure;
- Biologically;
- Heat treatment.
Each has advantages and disadvantages. Chemical agents act quickly, but remain in the ground, penetrating into the fruit. Biological ones require a laborious process, they fight pests less effectively, and act gently on the soil. Heat treatment kills not only pathogens, but also essential elements, worsening the condition of the soil.
Land cultivation
In case of severe soil contamination by pests, it is removed (layer from 7 to 10 centimeters). Further reuse of this soil for growing another crop is prohibited. The soil is taken out of the site and disinfected. In place of the unsuitable soil, a new one is poured. If the infection was moderate, then in this case it can be treated with chemical additives. Before disinfection from bacteria, the soil is not dug up. Pre-digging is necessary only when treating against harmful insects, since they can hide deep underground. During digging, it is best to treat the soil with copper sulfate to avoid the appearance of fungal diseases.
Rules of conduct and safety during disinfection
Most disinfectants are biologically active and aggressive substances that, in high concentrations or in direct contact, can harm human health. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly observe safety measures when processing greenhouses, hotbeds, vegetable gardens and garden plants. When using bulk preparations for disinfection, use anti-dust respirators, gas and smoke mixtures require the use of a gas mask, and liquid preparations require protective clothing, gloves and glasses.
During the processing of the greenhouse, you should not store garden tools in it, various containers (especially wooden ones), wire partitions and sticks for fastening.
Before entering, it is recommended to spread a rug moistened with bactericidal compounds, copper sulfate, ammonium nitrate, chlorinated lime.


Personal protective equipment for greenhouse disinfection with copper sulfate or other pesticides
Ready-made chemicals for the prevention of greenhouses
Fufanon used to combat spider mites, whitefly and aphids. A solution from this drug is sprayed on the cracks of the frame and other places where insects can spend the winter.
Storm gives a positive effect in the fight against snails and slugs. After collecting the plants, the preparation is scattered onto the soil surface.
Muracid - has proven itself in the fight against ants. Ampoules of 1 milliliter are watered ant nests and their paths.
«Marshal»Effective against aphids, nematodes, spider mites and thrips. One ampoule is diluted in 9 liters of water. The resulting liquid is processed 10 square meters of soil. For humans, this drug is toxic.
Fitosporin - a biological preparation that is used for fungal infections. 5 grams of powder is stirred into 10 liters of water. It is used for disinfection of walls and ceilings of greenhouses, and the top layer of soil. The drug is effective at temperatures of 10 degrees and above.