The berry season is over. The entire crop is safely hidden in jars. For gardeners, the period of caring for currants does not end. Such a stage of work is coming, on which the future harvest depends. Processing currants in the fall involves the following types of gardening activities: pruning a currant bush, treating it from insect pests and diseases, applying fertilizers to increase the plant's immunity.

Currants have a number of specific diseases; they can be attacked by pests. During flowering and ripening of berries, it is impossible to process currants with special preparations. The most convenient time for processing is after harvest. In order for the currant bushes to remain healthy throughout the growing season, a number of actions should be taken in advance in the fall:
- The shrub is sprayed with special chemicals aimed at protecting plants;
- Loosening and cultivation of the soil under the bushes of black currant are carried out;
- Make top dressing;
- The bushes are rejuvenated by pruning currants in the fall.
The activities will be of a preventive nature.
Rules and secrets of processing currants in the fall


Sooner or later, many gardeners face the question of treating bush plants with special compositions. Processing currants in the fall, if it is done according to all standards, helps to reduce the risk of damage to the plant by pests wintering on the bushes. For comparison, the level of infestation of currants that have not undergone autumn prophylaxis doubles, and the treated bushes give 25% more yield in the next season.
Why is the autumn processing of currants necessary?


If you take appropriate measures in a timely manner, this will help protect the plant from such troubles as:
- powdery mildew,
- anthracnose,
- septoria,
- rust,
- striped mosaic,
- gray rot,
- kidney and spider mites,
- fire butterfly,
- sawfly,
- leaflet,
- aphid.
Temporary restrictions


Processing should be carried out in a certain time period: the ideal is the moment when the last crop is harvested and the bush is cut for the winter, this allows you to cover the main area of the root zone and branches. The first months are best suited for this framework: the end of September and the beginning of October. The autumn processing of currants should be carried out in dry and cool weather, in order to prevent the rain from washing off the product. It is also important to take into account the peculiarities of the climate in the regions and the type of plant (for example, many varieties of red currants should not be exposed from the foliage before processing, you should wait until the leaves themselves fall off).
Both black and red currants are susceptible to various diseases and pests, so prevention approaches will differ. First of all, it is necessary to divide funds into chemical and folk remedies.
Measures to prepare currants for winter
Briefly, you can highlight the main steps to prepare currants for winter:
- shrub pruning;
- soil preparation;
- bending branches to protect them from freezing and damage in case of very strong winds.
Now more about each.
THE BEST VARIETIES OF CHERRY!
Cherry varieties for the Moscow region
Bending currant branches before winter
Currant is a very frost-resistant crop.However, upon reaching - 25 degrees below zero, the shoots freeze, which leads to further freezing. Accordingly, the amount of the harvest also decreases. The shrub may die.
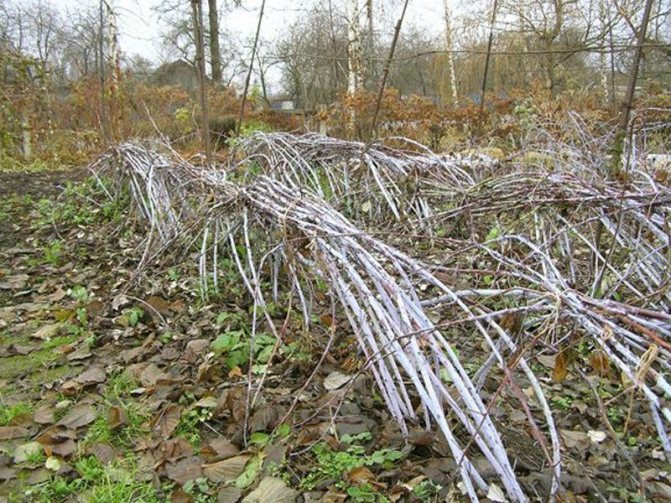


To prevent such an outcome, you need to bend down the branches. There are several ways to do this.
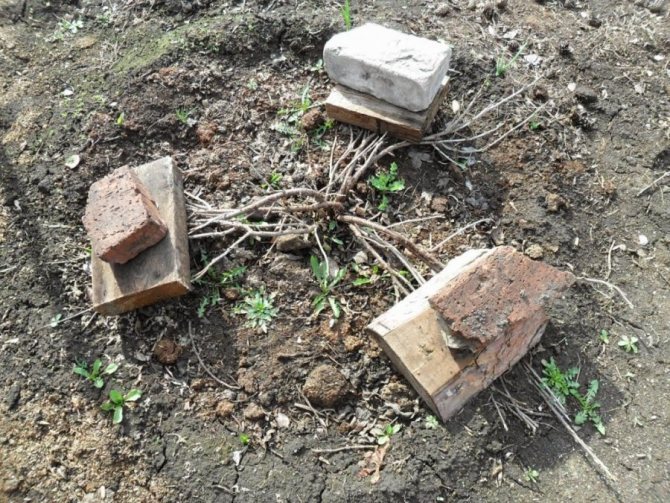
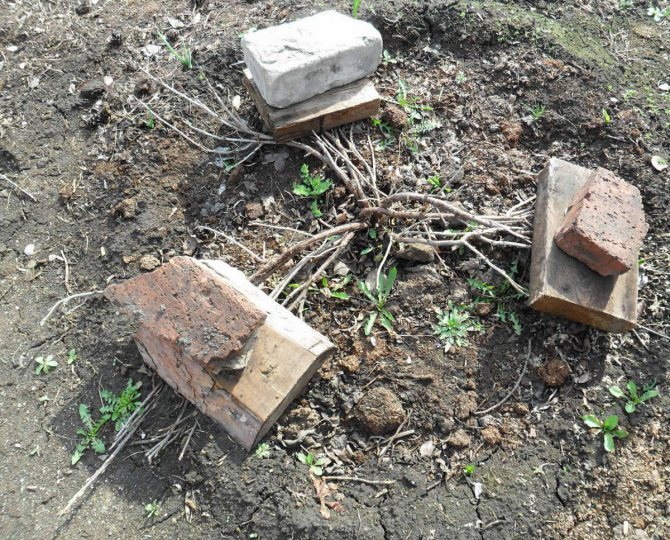
With bricks
The branches are divided into groups, each of which has from 3 to 5 branches. Carefully, in turn, they are bent to the ground, a board is placed on top, pressing it down with a brick. Instead of brick, non-metal tiles are quite suitable.
Photo of bending currant branches with bricks
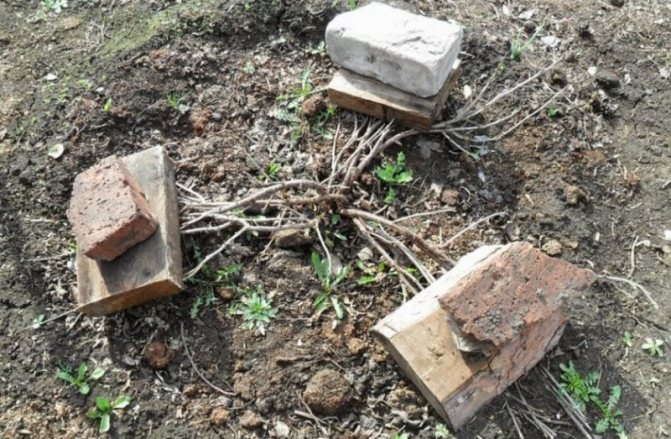


When using shingles, it is recommended to make grooves in the ground where branches should be placed. Bend down, strictly observing the direction of growth of currant branches. No more than 3 shoots under load. A larger quantity may lead to breakage.
Attention!
Metal should not be used for these purposes, as it will transfer cold to the plant due to its inherent thermal conductivity.
Burying
This method is used at a very low temperature of -35 degrees below zero, provided there is no snow cover. The currants are simply covered with a layer of soil at least 10 cm thick. It is important to watch that this shelter does not freeze so that the plant can breathe freely.
Chemical processing methods


The most effective remedies include insecticides, most of which can affect the nervous system of parasites by blocking enzymes. Suitable for autumn spraying of currants:
- "Tanrek" - for the fight against aphids.
- "Spark double effect" - from aphids, moths, sawfly.
- "Karate Zeon" - against aphids and ticks.
- "Confidor" - from aphids.
It is important to remember that you cannot mix or use several insecticides during one treatment. If it is necessary to protect the currants from fungal diseases, then fungicides should be used. They also come in several varieties.
Burgundy liquid solution
It deals with rust, powdery mildew and anthracnose. When mixing, it is imperative to observe the proportions indicated on the package, since if not observed, there is a risk of burning the foliage.
Bordeaux liquid
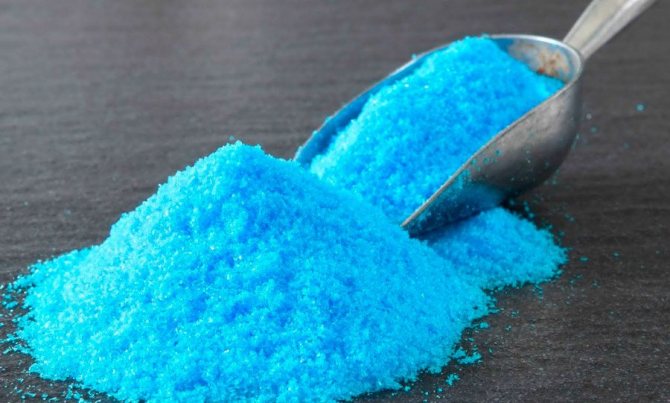
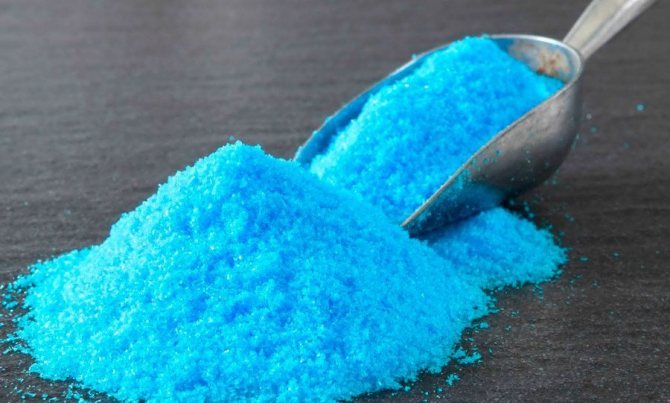
It is an emergency remedy that has similar application limits to a burgundy liquid solution, and it also fights rust and powdery mildew. To prepare it, you need to mix 450 g of quicklime, 100 g of copper sulfate and 5.5 liters of water.
Copper sulfate
It fights septoria and anthracnose. The solution has the property of drying and light burning, therefore it is advisable to use it for preventive purposes after leaf fall, when the ambient temperature is not higher than +5 5С. The ratio of copper sulfate is 50–100 g per 10 liters of water.
Urea or urea
This tool is considered the most important mineral fertilizer, since it allows you to saturate the soil with nitrogen, which has a beneficial effect on the overall health of the plant and an increase in yield in the next season. It also protects currants from fungi and parasites. 10 g of carbamide must first be dissolved in 1-2 liters of warm water, then bring the concentrate to 10 liters. The resulting liquid is used to water one bush.
Folk ways


You can also use a variety of decoctions and tinctures.
- tinctures tobacco, garlic, onion - due to their specific smell, they scare away pests. 10 g of chopped plant (tobacco, garlic or onion) should be poured with 10 liters of hot water and insisted for 4 days, then strain the infusion and spray the currants. It fights well against ticks and aphids;
- a decoction of wood ash - copes well with powdery mildew. Boil 400 g of ash in 10 liters of water and let it brew for 24 hours.
- infusion of celandine is an excellent remedy for combating aphids and a fire butterfly.There are two ways to prepare it: 3 kg of plants are infused in 10 liters of water or 1 kg of dry grass per 10 liters, for both compositions the infusion time is 48 hours.
Regardless of the method, the treatment of currants in the fall from diseases and pests is a necessary procedure that prevents problems during cultivation, increases the percentage of obtaining a better harvest and strengthens the health of the bushes.
Fertilization and soil care as a stage in preparing currants for winter
Care and feeding of currants in the fall is an important stage in preparing the currant culture for wintering.
The soil cleared of foliage, used mulch is treated with the following preparations:
- copper sulfate; potassium permanganate;
- Bordeaux liquid 1%;
- copper oxychloride solution 0.3%.
On a note!
Before leaf fall, if desired and with the time and effort, you can additionally spray the currant bush with a carbamide solution. This will eliminate all kinds of bacteria and fungi. To prepare a solution, it is enough to take 100 g of the substance per 10 liters of water.
Before digging, top dressing is applied under the currants in the fall, so that in its process they are evenly distributed along the entire perimeter of the treated area. Phosphorus and potassium are added. Phosphate feeding involves the introduction of superphosphate in the amount of 50 to 80 grams. Potassium sulfate is introduced in the amount of 20 to 40 grams.
In the complex, potassium and phosphorus are contained in wood ash. In addition, it contains other trace elements. Under one currant bush, up to 100 grams of solution is applied, simply by watering in the usual way.
After the soil was loosened, fertilizers were applied, the next stage was to cover the currants with mulch. Sawdust, onion husks are perfect as mulch. They must mulch until the soil freezes.
Processing currants from pests and diseases - how to spray the bushes in the fall?
Currant is one of the most common perennial shrubs in home gardens. The shrub belongs to the Gooseberry family and includes more than 150 different varieties. In order for the currants to give a rich harvest, the bushes must be periodically inspected for the presence of diseases.
Like many other fruit and berry crops, currants are very often exposed to the appearance of various insects and diseases. This significantly reduces the amount of harvest, and the bushes themselves begin to wither and dry out. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to prevent these problems in advance. It is important to inspect the bushes and, if traces of diseases or insects are found on them, immediately begin to fight them.
Processing currants in the fall is a very important event. Timely holding it will help prepare the shrub for the coming winter and the onset of spring.
In order to prevent the appearance of diseases and insects on currant bushes, preventive procedures can be carried out. Healthy bushes should also be processed in autumn. This will reduce the risk of damage to the plant in spring and summer.
It is better to spray it with a 2% solution of karbofos, this is the most effective remedy. But a 1% colloidal sulfur solution can also be used.
As a rule, the plant is subject to diseases such as:
- Rust;
- Powdery mildew;
- Anthracnose;
- Veined mosaic;
- 5. White spot (septoria).
It is worth talking in more detail about each of them.
The plant can be affected by two types of this disease - goblet and columnar rust. The goblet appearance is the appearance of convex orange warts on the leaves. Columnar is characterized by the appearance of small orange dots. The first species can be transferred with the help of the wind if there are bodies of water nearby with sedge growing nearby. The second species enters the shrub from coniferous trees. If these diseases are detected, the leaves should be treated with phytosporin. If this does not bring any results, then you can spray the bushes with fungicides.Four such procedures may be required. The break between each should be ten days.
- 2. Powdery mildew.
The first sign of the development of this disease is white bloom on the leaves, which can then spread to the berries.
Powdery mildew or spheroteca develops most often in the middle of summer. As a rule, spheroteka appears only on very weak bushes, therefore, with good care of them, this disease usually does not appear. But, if this nevertheless happened, the affected specimens must be sprayed with phytosporin or a solution of five percent iodine (one bottle must be taken for ten liters of water). If the disease has disappeared after the first procedure, it can be repeated after three days. In the event that the iodine solution did not help, you can treat the plant with Bordeaux liquid, copper oxychloride (1 tsp for five to seven liters of water) or a 1% solution of copper sulfate.


- 3. Anthracnose.
Autumn processing of currants from pests and diseases also provides for the fight against anthracnose. This is a common fungal disease. Most often, around the middle of summer, brown-red spots may appear on the leaves. They are no more than one centimeter in diameter. The spots that appear gradually cover the entire leaf. Then the leaflet petioles are also damaged, after which they fall off. Anthracnose development peaks during the rainy season. Most often, the fungus infects red currants. Fungal spores can hibernate in fallen leaves, so they must be removed to prevent the spread of anthracnose. To combat it, you need to spray the bush with Brodos liquid (100 grams per 10 liters of water). The procedure can be repeated after harvesting the entire crop in the fall.
- 4. Vein mosaic.
The first sign of vein mosaic appearance is yellowing of leaves along the main veins. Vein mosaic refers to viral diseases, which means that it cannot be cured. Affected bushes must be dug up and destroyed. The soil where they grew must be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate.
- 5. White spot (septoria).
With septoria, brown spots appear on the leaves. Over time, they begin to turn white until only the border remains brown. They can even appear on berries. Another disease is brown spot. In this case, the process of the appearance of spots is the opposite - brown spots with a white border around the edges. In order to get rid of septoria and cercospora, two procedures of spraying with Bordeaux liquid are required. The second procedure is performed ten days after the first.


Processing currants in the fall also comes down to fighting insects. Most often, such insects can be found on currant bushes:
It is worth talking in more detail about each of these insects.
Most often, it is the aphid that affects the bushes. There are two types of aphids - leaf gall and gooseberry shoot. A characteristic sign of the appearance of a gall aphid is the formation of dark red or yellow swellings on the leaves. As the insects spread, the leaves begin to dry out and then fall off. Gooseberry shoot aphids most often affect young branches. After this insect was found on the stems, the bushes need to be treated with a solution of actellik or karbofos. These are the most effective aphid remedies. If after the first procedure the parasites have not disappeared, it can be repeated after about a week or ten days.


If aphids were found on the bushes, then with a high degree of probability there will be ants on them. Ants play the role of a "shepherd". It is these insects that transfer aphids to new areas of the stems. In the fall, the ants transfer the aphids to their nest, and in the spring they again carry them out to the bushes. This behavior is due to the fact that ants feed on aphid juices. Therefore, the fight against aphids is carried out in conjunction with the fight against ants.The danger of the appearance of these parasites lies in the fact that they spread very quickly over the site and begin to parasitize on other crops. Therefore, you need to deal with them immediately after they appear. To do this, you can use folk methods, but not all of them give one hundred percent guarantee. The most effective method would be the use of chemicals. An anthill can be treated with Feverfew or Cuts, Globol or Raptor gels.
- 3. Fireball.
Moth butterflies, which emerge from the ground at the beginning of the flowering period, lay their eggs on currant inflorescences. After the caterpillars emerge from the eggs, they feed on the juices of the berries, while leaving behind a cobweb. One caterpillar can eat up to 15 currant fruits. In the event that the moth has already laid its eggs in the inflorescences, then it is impossible to fight this, so this problem must be warned in advance. To do this, in the fall or early spring, the soil around the bushes must be overlaid with linoleum or roofing material. The edges must be sprinkled with earth so that the moths cannot appear from under the soil, where they hibernate in the form of pupae. Linoleum can be removed after the flowering period is over.
Most often, two types of mites appear on the bush - spider mites and kidney mites.
A characteristic sign of the appearance of a spider mite is the formation of white dots on leaves, which then become transparent.
The kidney mite eats up the kidneys, which leads to a decrease in yield. In addition, ticks also carry a variety of diseases. When ticks appear on the bush, currants can be treated with sulfur-containing preparations, for example, colloidal sulfur or phosphimide.
Why process currant bushes
Systematic feeding and regular processing of currants will save the bushes from pathogenic insects that cause irreparable harm.
Powdery mildew
It appears as white spots or bloom on leaves and berries. Powdery mildew usually likes to appear in July or early August. During this period, you should be especially careful to prevent damage to the planted currants.
Anthracnose
It manifests itself throughout the summer. It is characterized by the formation of reddish spots on the leaves. Over time, the affected branches dry out, the leaves crumble. Such parts of the plant must be burned so that the disease does not spread throughout the entire area.
Moth butterfly
The moth lays its larvae in flowers, which causes their death. The parasite can hibernate in the soil, even tolerates severe frosts. Therefore, in order to avoid problems with currants, the soil should be loosened regularly.
Aphid-infested currants look unhealthy - they have red leaves that dry out and fall off over time.
Rust
The drug "Fitosporin" or Bordeaux liquid helps well against rust. Rusty currants have bulging reddish outgrowths.
Processing currants in the fall from pests and diseases
The berry season is over. The entire crop is safely hidden in jars. For gardeners, the period of caring for currants does not end. Such a stage of work is coming, on which the future harvest depends. Processing currants in the fall involves the following types of gardening activities: pruning a currant bush, treating it from insect pests and diseases, applying fertilizers to increase the plant's immunity.
Currants have a number of specific diseases; they can be attacked by pests. During flowering and ripening of berries, it is impossible to process currants with special preparations. The most convenient time for processing is after harvest. In order for the currant bushes to remain healthy throughout the growing season, a number of actions should be taken in advance in the fall:
- The shrub is sprayed with special chemicals aimed at protecting plants;
- Loosening and cultivation of the soil under the bushes of black currant are carried out;
- Make top dressing;
- The bushes are rejuvenated by pruning currants in the fall.
The activities will be of a preventive nature.
How to fertilize the soil


In autumn, it is categorically impossible to use nitrogen-containing mineral mixtures - the growth of new shoots will seriously reduce the frost resistance of the bushes. If the plants are severely depleted, then mineral supplements are indispensable.
In the fall, any varieties of currants need phosphorus and potassium dressings. You can apply a solution of superphosphate with potassium sulfate (a tablespoon per bucket of water).
On the advice of seasoned gardeners, it is recommended to use organic fertilizers (manure) as soon as cold weather sets in and the growth of shoots stops. The autumn use of organic matter is good because during the winter manure will acquire an easily digestible form and currants in the spring will better absorb useful elements and develop faster.
Do not neglect the autumn fertilization of the soil. Indeed, after the end of fruiting, the buds of the future harvest are laid on the bushes. And also nutritious dressings increase the immunity of currants.
Fertilization is combined with soil filling. For this, sawdust, peat are used. A great option is a mixture of sawdust (one bucket) and sifted wood ash (one glass). By the amount of bedding, they are guided by the thickness of the layer. It must be at least 10 cm.
Top dressing and fertilization
If the plant is strong and healthy, then it is not afraid of diseases and attacks of insect pests. The introduction of mineral fertilizers and timely dressings increase the immunity of black currant.
After harvest, the plant needs phosphorus and potassium. A sufficient amount of absorbed microelements makes black currants resistant to the upcoming frost, promotes the growth of root mass.
Potassium sulfate or potassium sulfate and double superphosphate is required to add 1 tbsp. l., scattering currants around the bush in diameter, and then spill well with water, taking at least 10 liters. Or dissolve fertilizers in a bucket of water and pour over the finished solution.
No less useful will be the introduction of wood ash, which is rich in various microelements. For feeding currants, take 1 tbsp. and scattered around the bush. It is better to combine the application of ash with digging up the soil under the bush. An ash solution can be prepared if the weather is too dry.
Gardeners who are fundamentally against the introduction of mineral fertilizers can overlay the currant bushes with compost or dig up the soil with it. During the winter, organic compounds will transform into a form that is convenient for absorption by currant roots. The organic fertilizing produced by the plant will be in full demand by the plant in the spring to build up the green mass.
If the planting of the currant bush was done correctly with the laying of all the necessary fertilizers in the planting hole, then within 2 years additional dressings will not be required. They begin to make them only from the 3rd year of the life of the bush.
Watch a video about feeding in the fall:
Useful Tips
Below are some useful tips for beginner gardeners that will help you to carry out all the autumn activities for caring for currants and, if necessary, cover them.
- Only a well-sharpened, sharp tool should be used for trimming. When cutting out thick shoots, the places of the cuts are covered with garden pitch.
- Top dressing of currants is carried out only with fertilizers, which contain large proportions of potassium and phosphorus. The introduction of nitrogen in the autumn will provoke an active growth of the shoots. As a result, the plant will not have time to prepare for winter, as it will spend energy on building up green mass, and will lose its frost resistance. Nitrogen-containing fertilizing ceases to be applied by the beginning of September.
- Feeding with fresh manure and chicken droppings is carried out after the onset of frost.During the winter, all excess nitrogen will evaporate, and in the spring the fertilizer will become easily digestible for the currants. The effectiveness of such feeding is observed in areas where melt water does not stagnate in spring.
- Bend currant shoots to the ground with extreme caution. You can do this only before the onset of frost, when the branches still have flexibility. You can fix them with bricks or tiles. In no case should a metal load be used - it has good thermal conductivity, therefore, it will transfer cold to the branches, and they will freeze.
- Another way to prepare for wintering is to throw the shoots with earth. Despite the fact that this method is rarely used, it is considered very effective at temperatures down to -350 C.
- If there is a need for additional protection of currants from frost, you need to use a dense material that allows air to pass through. Therefore, film will not work here. Insulation (for example, mineral wool) is laid in the voids between the material and the branches. In such a "fur coat" the shoots can withstand temperatures up to -500 C.
- If it is possible to get to the summer cottage in the winter, then you need to monitor the level of snow above the bush: rake from the site and scatter with a small amount of it. Too thick layer of snow can break currant branches.
- The layer of infusion, which forms during alternating thaws with frosts, is a particular danger for currants. In order to always have air access to the bush, you can stick crossed stakes in the fall. You can sprinkle the snow crust with any substrate of dark shades (for example, ash), which will attract the sun's rays. Under their influence, the crust melts.
- In the spring, as soon as the snow melts, the bush is first freed from shelter and old mulch. After a few days, the branches are unbent. If you open it too early, the March sun will burn the wood, and if it is too late, the roots and shoots will support it.
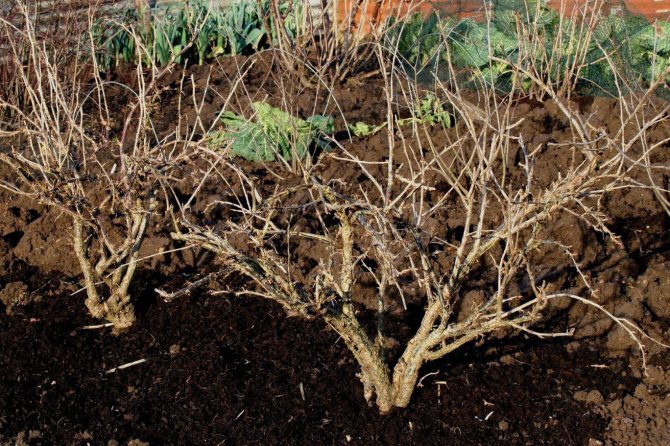
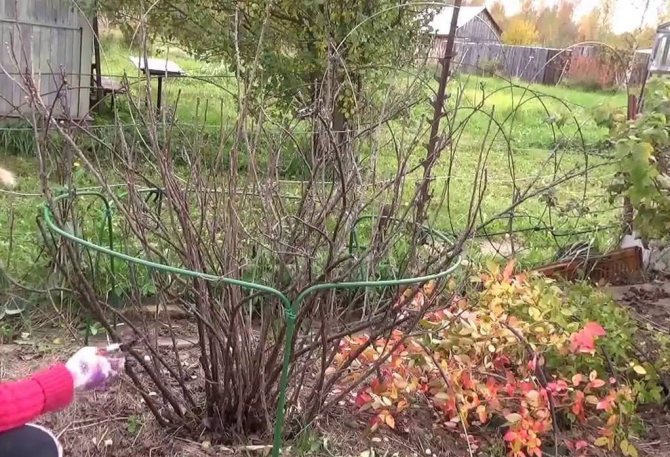
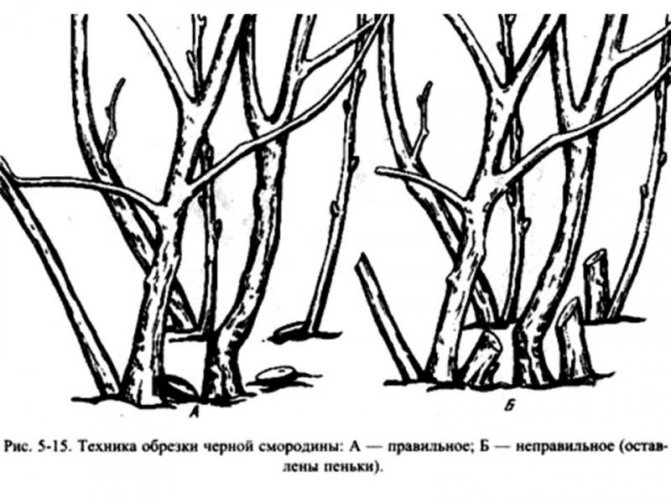
Currant pruning
Another important agrotechnical activity after the harvest is the autumn pruning of currants. This will require tools such as a pruner, a garden saw, and a garden shears. Regular saws and scissors will not work. All tools must be well sharpened and treated with disinfectants (kerosene, alcohol, potassium permanganate).
Pruning is started immediately after the foliage has fallen off. The first step is to cut off dried, broken branches, weakened and affected by diseases or pests. Contenders for removal are also currant branches that are too thin and lying on the ground.
The next stage is pruning and shaping the crown of the bush. Shoots 3-4 years old should be cut down. They carry an unnecessary load on the root system, which supplies the entire bush with nutrients. The berries on such old branches are small and there are too few of them.
Branches that grow inward or intertwine with others should be removed. In order to avoid infection, all sections are treated with either Bordeaux liquid or garden pitch.
Choose about 6 young shoots of the current year, they should be the strongest, healthiest and well-placed. They are left behind. The rest of the growth is cut out. If you follow this pruning plan annually, then there will be a currant bush of 15 shoots, of different ages (1, 2, 3 years), but which are the most productive.
Next, you should shorten the length of the branches. In the old, the tops are cut off, which usually dry up; in the young, no more than 6 buds are left. All trimmed material is best burned to prevent the spread of potential infection and pests. After pruning, protective measures are taken to process currants.
Which tool to choose for processing
Conventionally, all funds can be divided into 3 groups: ready-made preparations, solutions (potassium permanganate, Bordeaux liquid, etc.) and folk remedies - decoctions and herbal infusions, often with the addition of laundry soap.
The choice of option depends on many factors:
- Region of residence.
- The state of the bush.
- The prevalence of the disease or pest.
In the South of Russia and Crimea, winters are usually short, frosts below -30 0C are rare, and there is also little snow. Almost all pathogens and pests tolerate such conditions well and manifest themselves with renewed vigor in the spring. Therefore, in these regions, it is better to use strong insecticides, fungicides, antivirals, etc. for treatments in the fall.
On the contrary, in the northern latitudes, winters are harsh and folk remedies can work well here, then why poison yourself with chemistry in vain? However, if the plant is severely affected by the same anthracnose, then it is better to try Bordeaux liquid or a strong chemical.


Protection from pests and diseases
How to process currants in the fall to prevent the development of diseases and pests? After harvesting, it is recommended as a preventive measure to spray the Bordeaux liquid and the currant bush itself, and the soil around it, and the aisle.
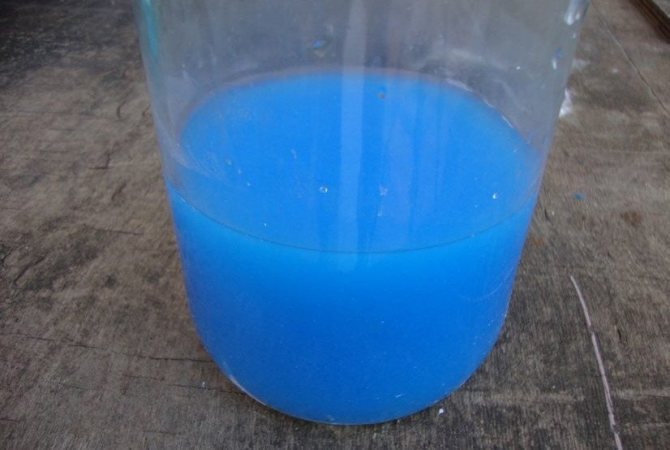
For beginner gardeners, we recall that Bordeaux liquid is prepared from 100 g of copper sulfate and 100 g of lime, which dissolve in a bucket of water, resulting in a rich turquoise liquid. Bordeaux liquid fights well against fungal infections; it can be used to process cuts and cuts on a bush. The tool has long been known to gardeners, is widely used, as it is quite effective. Process the black currants at least 2 times weekly.
Another substance that acts against fungi and their spores, insects and larvae is a concentrated solution of carbamide (urea). For spraying black currants, take at least 300 g of urea dissolved in a bucket of water (10 l). The whole bush is abundantly sprayed with the prepared solution.
Some gardeners recommend not to wait for the autumn leaves of the currant. And remove the leaves yourself at the first sign of wilting and yellowing. So the plant will focus on preparing for winter, all nutrients will be directed to the branches and buds of the currant bush.
Collecting fallen leaves, cleaning litter and dry branches from the soil is a must. Usually, pests and spores of bacteria and fungi hibernate in rotting plant debris. The collected waste is best incinerated.
And the soil under the currant bushes is loosened and treated with a light pink solution of potassium permanganate, Bordeaux liquid (100g / 10 l of water) or a solution of copper sulfate (50 g / 10 l of water).
Loosening around the base of the bush is carried out to a shallow depth of about 5 cm under the crown, going deeper by 15 cm, and in the row spacing they dig up to a depth of 20-30 cm. After loosening, the soil and the bush are treated with Karbofos according to the instructions or with boric acid.
Several rules, the observance of which will lead to success in the fight against insects and diseases:
- Choose disease-resistant currant varieties for future planting;
- If the first signs of the disease appear, do not be afraid to use insecticidal and fungicidal preparations, i.e. those aimed at protecting plants from insects and diseases;
- For spraying to be effective, apply it only in dry weather when no rain is expected. Do not process currant bushes immediately after rain or after dew has fallen.
Preventive measures will help protect currant bushes from such serious diseases and pests as:
- Anthracnose - initially looks like reddish specks on the leaves that appear in summer. Then they become larger and affect the entire leaf, it dries and falls off. In winter, spores persist in plant debris under the bush. In the fall, it is necessary to collect and burn the fallen leaves;
- Powdery mildew - its appearance is indicated by a white coating on the leaves and berries of currants in the middle of summer. The disease primarily affects weakened bushes. It is important not to allow the plants to weaken by feeding them regularly;
- Rust - manifests itself in the appearance of convex growths of orange color or as orange dots. Bordeaux liquid or Fitosporin will help;
- Damage with currant glass - a butterfly that lays eggs in the bark of a currant. Caterpillars appear from the eggs, which make moves in the middle of the shoots, which makes them dry out. Means of struggle - "Karbofos".
- Aphids - the leaves turn red, then darken and fall off. Karbaphos fights well with aphids. Autumn treatment with the drug will not allow the appearance of aphids in the summer;
- Moth is a butterfly whose pupae hibernate in the soil under a bush. It is necessary to loosen the soil around the bush. Moths lay eggs in currant flowers, causing their death.
It is much easier to take simple preventive measures than, without doing this, to treat diseases that can end very sadly: the complete removal of the diseased bush.
Mulching and shelter for the winter
After completing the basic measures to prepare for wintering, you should mulch the cultivated soil (up to 10 cm layer), if you have not done this earlier. As mulch, you can use all the same compost (fertilizer at the same time), leaves of ornamental shrubs or trees (only not fruit trees), rotten sawdust or hay, grass cut from the lawn (for example, left over after its autumn preparation for winter).
Important! You need to lay mulch only on still warm soil. If you do this already on frozen ground, then the effect of such mulching will be negative, as a result, the bush in the spring will only slow down in development.
Mulching on dry sunny days will prevent the rapid loss of nutrient moisture, and at low temperatures, such a shelter for the winter will save the roots of the plant from freezing, which are located close enough to the ground.
In general, currants are considered to be very frost-resistant cultural, they can withstand a drop in temperature to -25 ..- 30 degrees, so for the winter they are somehow not specially covered. But with a greater decrease in degrees, it is still recommended to cover for the winter, more precisely, it is to mulch, or use snow.
If you live in a private house (you can hardly get to the dacha if it already snows), then you can cover the currants for the winter with the snow itself. First, throwing it under the bush, and then filling it completely.