Deciduous and evergreen, hardy and thermophilic, undersized and tall rhododendrons require careful preparation for winter in the fall. For each species, and sometimes varieties, the requirements are different, because this plant is capricious. The risk of freezing and damage to rhododendrons will be minimal if you insulate the root system in the fall, prepare strong shelters for the aboveground part and do not wrap your bushes ahead of time.
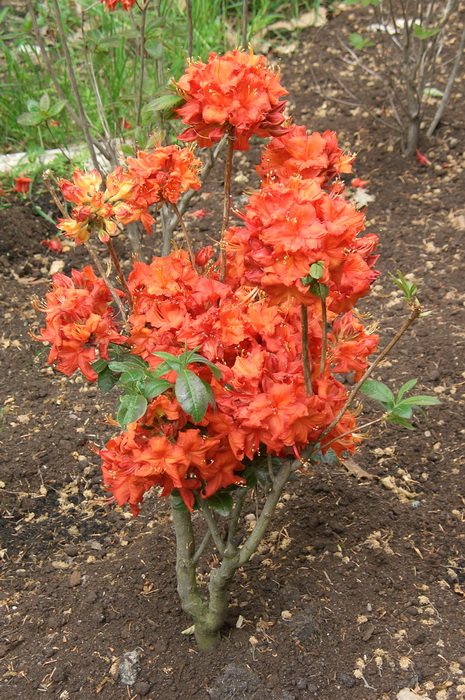

In the spring, it is necessary to remove the frozen tops of individual shoots
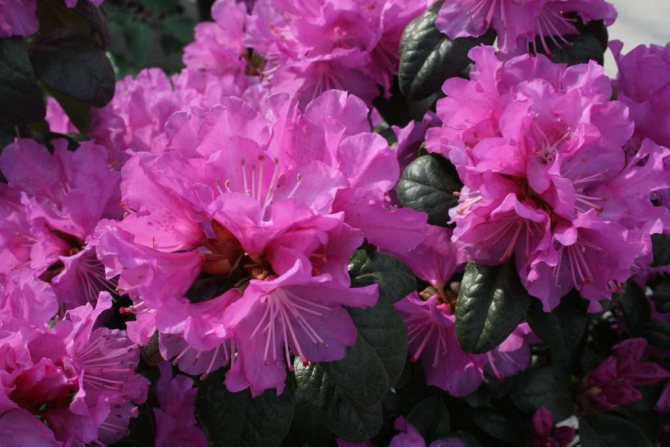
Types and varieties for cultivation: names, descriptions and photos
For the cultivation of rhododendrons in the conditions of central Russia, the following types are used:
| Name | A type | Height, m | Flower size, diameter, cm | Tolerable temperature, ° С | Features and Notes |
| Golden (kashkara) | Evergreen | 0,6 | 5 | -26 | |
| Katevbinsky | Evergreen | 4 | Inflorescences 12-15 | -32, roots up to -18 | Fast growing |
| Canadian | Deciduous | 1 | 2,5 | -32 | Spherical |
| Japanese | Deciduous | 2 | 6-8 | -26 | Fragrant |
| Daursky | Evergreen or deciduous | 2 | 2-4 | -45 | Often called wild rosemary |
| Rhododendron Schlippenbach | Deciduous | 2 | 5-8 | -26 | Fragrant, blooms at the end of April |
| Rhododendron Koster | Deciduous | 3 | 4-7 | Winter-hardy | Fragrant |
As for the varieties, the following can be recommended for growing in the Moscow region:
| Name | A type | Height, m | Color | Tolerable temperature, ° С | Features and Notes |
| Grandmother (Babuschka) | Deciduous | 0,5 | Hot pink terry | -30 | Spherical, growing slowly |
| Golden Lights. | Deciduous | 2 | Salmon orange | -42 | Spherical, fragrant |
| English Roseum. | Evergreen | 2,5 | Lilac-pink, with orange splashes | -30 | Not afraid of rain and direct sunlight |
| Karens | Evergreen | 1,5 | Reddish purple | Winter-hardy | Fragrant |
| Mount Saint Helens | Deciduous | 1,8 | Salmon pink with golden tangerine spots | -32 | |
| Nova Zembla | Evergreen | 2,5 | Hot pink with maroon spots | The most comfortable - from -15 ° to + 25 ° С, but withstands up to -32 ° С | Resistant to heat and direct sunlight, ball-shaped |
| PJM Elite (PJM Elite) | Evergreen | 2 | Raspberry pink | -32 | Loves partial shade |
| Rosy Lights | Deciduous | 1,8 | Hot pink | -42 | Fragrant |
| Roseum Elegans | Evergreen | 3 | Pinkish lavender | When protected from wind - up to -32 | Fast growing, heat resistant |
| White Lights | Deciduous | 1,5 | Pink pearl | -42 | Fragrant |
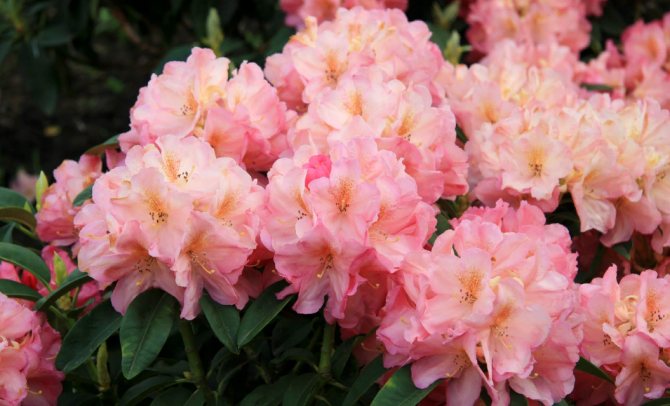
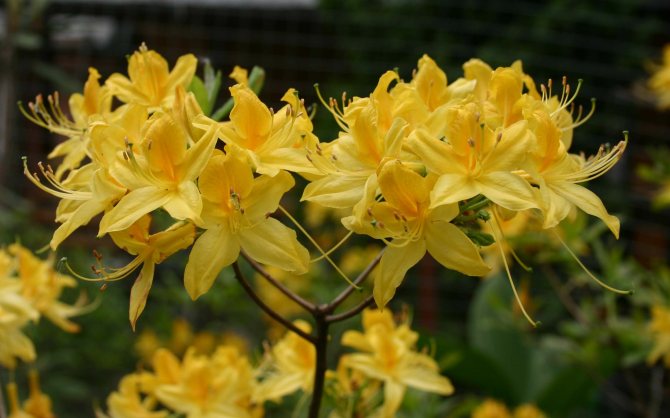
These are far from all varieties suitable for cultivation in central Russia. So the choice is very, very extensive. Below are photos of some of the varieties.
Regional features
When preparing rhododendrons for winter, it is necessary to take into account the regional characteristics listed in the following table.
Care depending on the region: table
| Regions | Fall | Spring | ||
| Partial cover | Hermetically sealed shelter | Airing | Full opening | |
| Southern | Not required | Not required | Not required | Not required |
| Northern | Mid October - November | After the onset of frost 8–10 ° C | After thawing the soil 20-30 cm deep | Second half of April |
| Middle zone of Russia | Mid November - December | After the onset of frost 8–10 ° C | After thawing the soil 20-30 cm deep | First half of April |
Taking care of rhododendron in the fall is not as difficult as some other ornamental plants. But this does not mean that leaving can be neglected. If you work a little in the fall and create favorable wintering conditions for the plant, in the summer the bush will delight you with exuberant flowering and good health.
How to plant?
Site and soil preparation
Rhododendrons do not like wind and direct sunlight. They can be planted on the northern or northeastern side of the site, while it is very good if the walls of the buildings cover the planting walls from the southern and western sides. At the same time, it is important to exclude falling snow from the roof on the plants.
Good neighbors for rhododendrons can be apple, pear, cherry, larch, pine trees, in the shade of which they will feel at home. In the place where rhododendrons grow, there should be no stagnant water and nearby groundwater.As for the soil, it has already been mentioned that these plants love acidic, nutrient-rich soil with good drainage.
Before planting, it is recommended to prepare a mixture of the following composition: red peat, loam and pine needles in a ratio of 2: 3: 1. Then determine its pH. A good indicator is considered to be from 4.5 to 5.5. If it is higher, then the mixture must be acidified. To do this, you can add an additional portion of high-moor peat, sulfuric acid fertilizers or superphosphates to it. There is also a special soil for rhododendrons on sale.
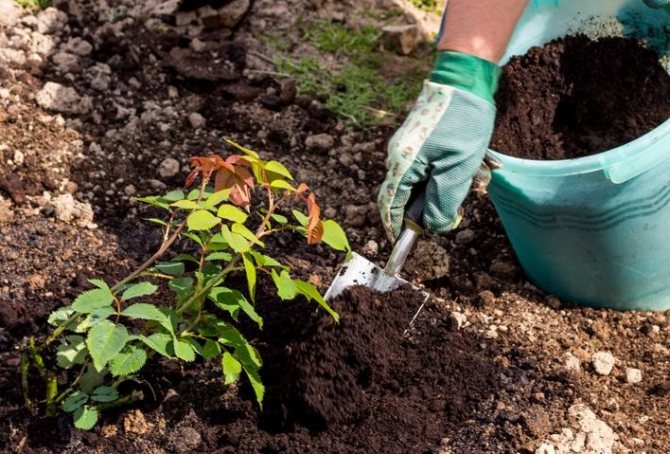
Planting rules and terms in the Moscow region
You can plant rhododendrons at any time, except for the period when the plant is blooming, but it is best to do this in the spring. This procedure is performed as follows:
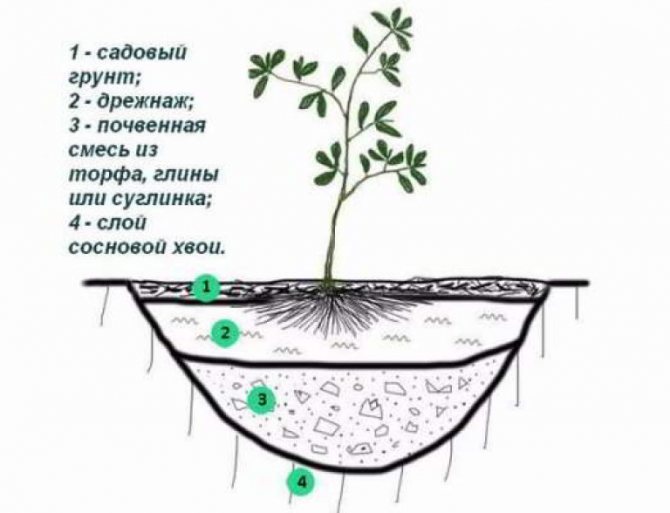
- A hole is dug 60x60 cm in size, 40 cm deep. For seedlings with an undeveloped root system, the size can be reduced to 40x40x30.
- A drainage layer is laid on its bottom, for example, sand.
- The bulk of the rest of the space is filled with earthen mixture.
- A hole is pulled out and a seedling is carefully placed in it. Its roots must first be soaked with water in order to exclude the possibility of damage with the obligatory spreading of the roots. You also need to check if a crust has formed from old dead roots. It needs to be removed.
- The mixture is poured and compacted. At the same time, the base of the root should not sink into the ground.
- Watering is carried out (it is desirable to slightly acidify the water with vinegar) and mulching of the trunk circle with needles, peat or oak leaves.
- If necessary, a temporary support is installed.
Video instruction on how to plant a rhododendron:
Helpful care tips
In the first year after planting the plant, it is very important to let it experience a lack of moisture. It is recommended to irrigate with rainwater. It is best not to loosen the soil near the shrubbery, as you can damage the root system. Weeds are pulled out by hand.
You also need to regularly feed. Experienced gardeners recommend using mineral fertilizers.
Favorable growth of shrubs occurs when using granular fertilizers, which can be applied even dry, scattering around the plant. Top dressing takes place in May and June.
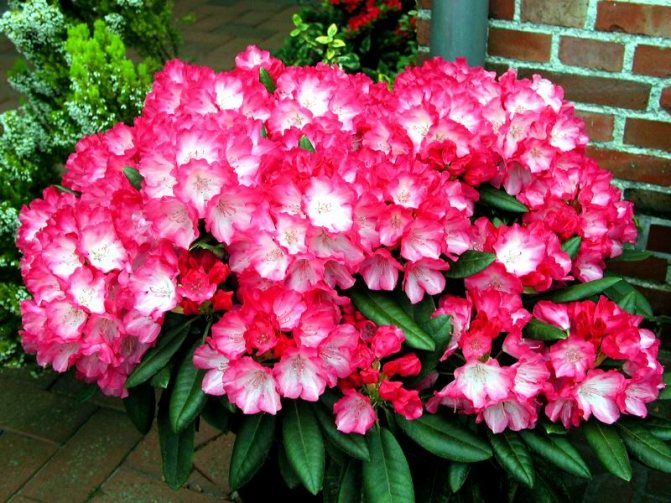


How to care for a plant?
Watering
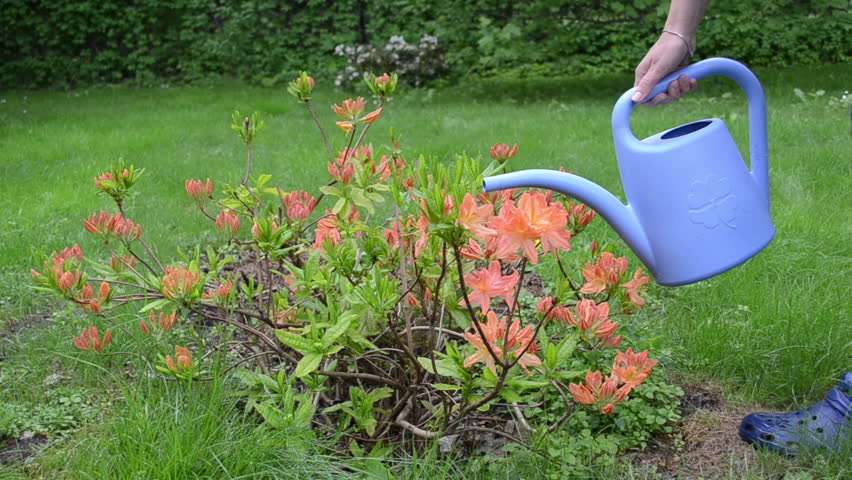
It has already been said that rhododendrons love moisture. They should be watered frequently, but it is important not to overdo it. The soil should be moist, but not wet. The norm is 1-1.5 buckets per bush 2-3 times a week. Plants need watering in summer as well as abundant watering before winter. It is best to use settled rainwater, acidified, for example, with vinegar.
During flowering and in the heat, foliage must be additionally sprayed. This is best done in the morning or evening so that the sun does not burn the leaves.
Attention! Reduce watering in August to help the plant prepare for winter.
Top dressing
In the spring in Pomoskovye, plants are fed with nitrogen mineral fertilizers, and in the middle of summer - with potassium and phosphorus.
It is strictly forbidden to feed rhododendrons with ash - it alkalizes the soil. Calcium must also be eliminated.
Organic fertilizers in the form of blood or horny meal, as well as semi-rotted manure, are applied in early spring, after moistening the soil well. For acidification, it will be useful to introduce into the soil special acidifiers containing sulfur (preferably in the form of soluble chelates). It is brought in at the rate of 40 gr. per 1 m2.
Transfer
The transplanting process is not much different from that when planting. Plants usually tolerate this procedure well. The best time for her is April-May or September - mid-October. Deciduous species are best planted in spring so they can take root well.
Attention! Plants can be transplanted only after they get stronger. This usually takes about two years.
Other operations
- Mulching. The operation is performed after rain. Mulch is poured on loose soil, the layer thickness is 4-9 cm. Most often, peat or coniferous litter is used for this purpose. The root system of the flower is located superficially, so the soil cannot be dug under it.
- Weed removal. Weeding is only allowed by hand! At the same time, it is advisable to leave the acidic acid, since it is an indicator of soil acidity and a natural neighbor of rhododendrons.
- Removal of faded inflorescences. This operation reduces seed formation, which allows the plant to form more buds the next year.
- Pruning. Allows you to adjust the shape of the bush. It is carried out immediately after flowering (no later than 20 days after its end).
Pests and diseases
Unfortunately, rhododendrons in the Moscow region are affected by a large number of pests and are susceptible to a large number of diseases. Among the pests, we single out such as:
- acacia false shield;
- rhododendral fly;
- sawfly;
- bug;
- whitefly;
- spider mite;
- tobacco thrips;
- garden beetle;
- furrow weevil;
- narrow-winged miner moth;
- mealybug;
- blue moth;
- field slug.
The main method of dealing with them is the treatment of plants with special preparations, but slugs will have to be collected by hand.
The number of diseases of various natures is also great.
- Fungal:
- late blight rot;
- tracheomycosis;
- septoria, pestalcium, anthracnose and phyllostictic spotting;
- rot of seedlings and young seedlings, buds, root and gray rot;
- dry white rot of the root collar;
- dying off of shoots;
- wax disease;
- cercosporosis;
- rust.
- Viral - leaf mosaic.
- Bacterial - root cancer.
- Associated with deficiencies in soil and care:
- chlorosis;
- soaking;
- sunburn;
- winter drying.
The methods of struggle, respectively, are also varied. A detailed overview is beyond the scope of this article, but the information is readily available on the Internet.
Video about diseases and pests of rhododendron:
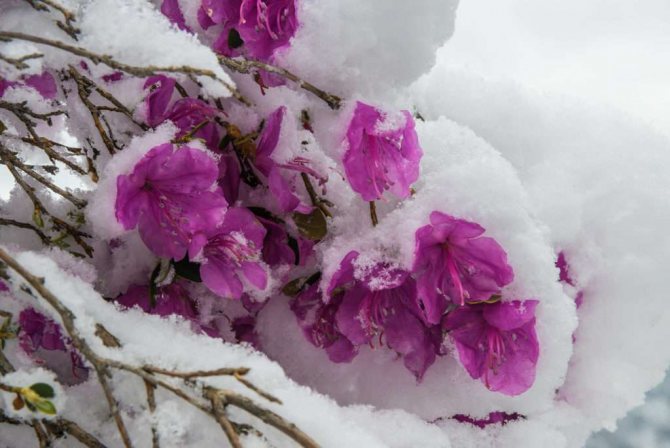
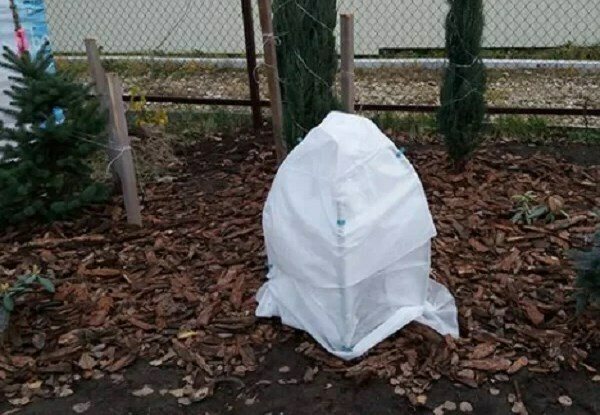
Preparing for winter
In addition to mulching, it is recommended to prepare a groove for the drainage of melt water., but at the same time remember about the superficial root system.
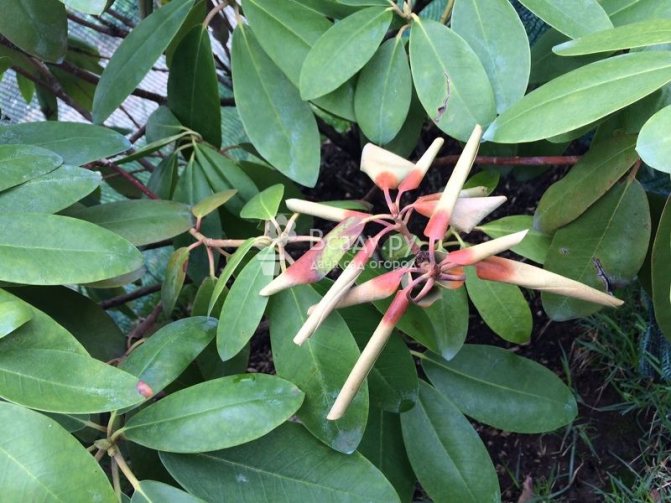
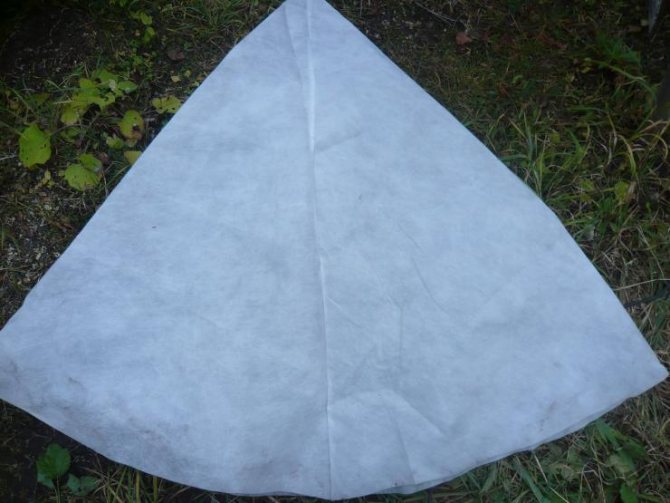
Deciduous varieties, as a rule, do not require additional shelter, while evergreen and semi-leafy varieties can be covered with spruce branches, peat, or a frame shelter can be built not only for the plant itself, but also for its root system. The shelter is removed gradually, ending at the end of April.
Effects of exposure to wind and sun
Caring for rhododendron in the Moscow region in the cold season involves the use of shelters for the winter. Of course, they can protect themselves from the cold themselves and do it in peculiar ways. During low temperatures, their leaves curl into a tube. This measure reduces the evaporation surface. This allows them to survive the winter unharmed. But, unfortunately, everything can be spoiled by the strong sun, which heats the leaves.


At night, frost affects overheated leaves, especially their central parts, because the edges are curled.And it is precisely because of this temperature difference in early spring that the leaves develop brown pigmentation right down to their very tip.


Reproduction methods
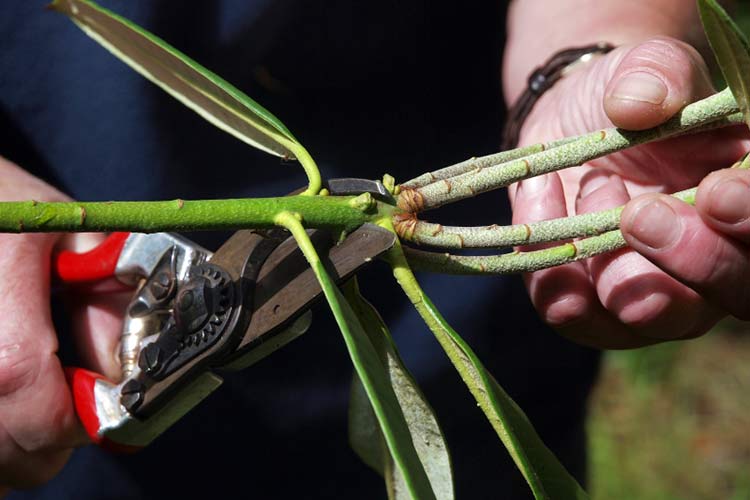
Cuttings
It is best to carry out this procedure in the summer. We need semi-lignified cuttings from the tops of the shoot about 10 cm in size, which must contain at least 5 sheets.
- The cuttings are soaked for 12 hours in a growth stimulator (for example, 0.02% solution of succinic acid).
- Then they are planted in pots with a sand-peat mixture and placed for rooting.
- By autumn, they are transferred to the basement or cellar.
It can be planted in open ground after 2 years.
Leafy cuttings
Cuttings are used containing at least two leaves and two developed buds. The rest of the process does not differ from the one already described.
Layers
This method works best for deciduous species.
Reference! Plants obtained in this way live less than those grown from seeds.
In the spring, several young shoots are tilted and buried to a depth of 15 cm. The upper part is fixed vertically. Further care is carried out in the same way as for the main plant. Layers are covered for the winter. After a year or two, they are separated and transplanted.
There is also a method of "air layering", but it is used mainly abroad
Seeds
- Seeds pre-stratified in the refrigerator are mixed with sand and placed strictly on the surface of a sand-peat mixture sterilized in a microwave oven.
- The boxes are covered with glass and placed in a warm, lighted place.
- Planting is watered and aired.
- By the fall, each seedling is transplanted into a separate pot. By this time they will consist of 5-10 sheets.
- In the summer, the pots are transferred to the garden, and in the winter they are returned to the warmth, continuing to water and ventilate.
Only in the 5th year are the plants ready for transplanting into open ground.
Dividing the bush
In the spring, a large healthy bush is cut into several parts with a shovel., small roots are removed, after which the planting material is planted in a new place.
Important! In the first year, wintering in a greenhouse is mandatory.
Graft
At the beginning of autumn, the stock is dug up (its age is 3-4 years), transplanted into pots and placed in a greenhouse at a temperature of 5-10 ° C. The inoculation is carried out in two weeks, and they try to do it as close as possible to the roots of the rootstock.
Two methods are used:
- budding (a bud of a grafting shoot is placed on a branch of the stock);
- copulation (the stem of the grafted plant is placed in a cut of the main one).
It becomes obvious that, subject to not very complicated rules for choosing varieties and locations, planting and care techniques, protecting plants and fighting diseases and pests, luxurious rhododendrons can be grown in the climatic conditions not only of the Moscow region, but also of Siberia. The main thing is not to be afraid.
Rhododendron care in the fall: preparing for winter
Like any ornamental plant, the rhododendron needs special care for abundant and lush flowering. It is important to take into account not only the place of planting of such a shrub and the proximity to other plants, but also other factors that can affect its growth and development. Also, autumn work plays a significant role in preparation for the winter period: pruning, feeding, watering and shelter.


In the natural environment, you can observe up to eighteen species of rhododendron
Top dressing of the bush in spring, summer and autumn
During the growing season, we carry out three dressings:
In the spring
- early May: 1 st. l. urea and potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water. This solution is enough for 3 roots.
In summer
- early June: 1 tbsp. l. "Agricola for flowering plants" and potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water, we spend for 2 - 3 plants.
In autumn
- after flowering: 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate and superphosphate per 10 liters of water.
Foliar dressing - after 1 - 2 years. We take a bucket of rotted manure and peat, add 1 tbsp. l. ammonium sulfate, superphosphate, potassium sulfate.We bring it into the trunk circle and close it up to a shallow depth.
The best varieties of rhododendron for the Moscow region
Unsurprisingly, this diversity has caught the attention of breeders. Having subjected one of the local species to selection, the British began to send botanical expeditions to Asia. Thanks to the botanist-researcher George Forest, more than 300 wild-growing varieties were discovered in Southeast Asia, which formed the basis of selection. Since the beginning of the 19th century, the development of scientists has made it possible to breed over 3 thousand garden cultivars.
Rhododendrons are most often used in ornamental gardening in regions with a temperate continental climate:
- Ledebour;
- ketevbinsky;
- Smirnova;
- golden;
- Schlippenbach;
- Japanese;
- short-term;
- daurian;
- Canadian.
Let's take a closer look at their main characteristics and popular varieties.
Ledebura, or maral, grows in the forests of Siberia, Altai and Mongolia. It is a semi-evergreen erect bush 50-200 cm high. Shiny small leaves are covered with small scales or edging. They hibernate, and are replaced after flowering, which occurs in March and repeats in September. Corollas are bell-shaped, painted in pink-violet shades. The flowers are asymmetrical with long pink stamens. Resistant to temperatures down to minus 32⁰C.
Daursky. Outwardly, it is difficult to distinguish it from the maral. The leaves do not hibernate, but fall off with the onset of autumn. Decorativeness begins in the period from late April to mid-June. Blooms for about 20 days. Corollas are light pink with a purple tint, funnel-bell-shaped, 2-4 cm. Grows in the territory located east of the Altai Range - Eastern Siberia, the Far East, Korea, Japan, Manchuria. The second name is wild rosemary. The seeds are highly germinating and hardy. Cultivars are more squat with purple flowers. Its frost resistance is much lower than that of the botanical wild rosemary.
Know! The Daurian wild rosemary, unlike its marsh relative, contains much less essential oils, therefore it does not cause headaches. It is used in medicine and perfumery.
Katevbinsky. It formed the basis of most frost-resistant evergreen hybrids. Grows in the forests of North America. The height of the spreading crown is 2-4 m. The leaves are large, elliptical, 10-15 cm long, 3-5 cm wide. The surface of the plate is dark green, glossy, with pronounced veins, the lower part is pale. Corollas are bell-shaped, painted in lilac tones or white, sometimes with yellow-green specks. Flower size 5-6 cm, no smell.
Decorative throughout the month in late spring or early summer. Several compact hybrids with white and lavender speckled petals have been bred - Catawbiense Album, Catawbiense Boursault, Catawbiense Grandiflorum, Nova Zembla, Alfred. Life expectancy is about 100 years.
Smirnov. Dense evergreen bush 1-1.5 m in height. Leaves are large, elongated-elliptical, glossy above and with dense white pubescence in the lower part of the blade. Length 10-15 cm, width 2.5-4 cm. Corollas purple-pink, funnel-shaped, up to 7 cm, dense inflorescence. Inside there are 10 pubescent stamens and a bare pistil. There are yellow specks on the petals. Grows in Turkey on the high mountain slopes. It is used for hybridization of cold-tolerant varieties. Varieties - Dorothy, Laika, Gabriel.


Kashkara, or golden rhododendron, lives in Siberia and the Far East, often forms impassable thickets. Yellow flowers 4-5 cm in size are collected in large umbrellas. It blooms in early summer. Leaves are dense, small, evergreen. Growth rate is very slow, winter hardiness up to minus 26⁰C.
Know! Despite its unpretentiousness, the low (up to 0.5 m) creeping bushes of Kashkara are very difficult to take root outside their natural habitat.
Schlippenbach. One of the most luxurious deciduous rosewood species. The spreading crown 1.5-1.8 m high is crowned with medium-sized leaves. Large fragrant flowers 7-8 cm appear in early May. The petals are pink or white, the inflorescence consists of 4-5 pieces.
Canadian. A low-growing compact shrub with a height of 0.7-0.9 m. It is found in the eastern part of North America. Small leaves are colored greenish-blue. Flowers are collected in small shields of 3-7 pieces. The main range of petals is pink-violet, odorless.
Japanese. It grows in Southeast Asia. It is widely used in Russia as one of the most decorative, unpretentious and frost-resistant. The average height of the highly branched crown is about 1.5 m. It blooms profusely in late May for 3-4 weeks. Corollas reach 6-8 cm, collected in lush inflorescences. Painted in salmon or red tones with a yellow spot. On its basis, a lot of hybrids were derived.
Short-fruited. Evergreen giant with a height of 4-6 m. Habitat - Asia, Kuril Islands. Leaves are leathery, dense, large. Flowers pink or white, collected in umbellate shields of 12-15 pieces. Blooms in the middle of summer. The first budding occurs in a tree at the age of 18–20 years.
Hybrid rhododendron is a collection of different cultivars grown in the garden.
On a note! Among the mass of hybrids, give preference to samples of the Finnish selection - Elvira, Mikeli, The Hague and the "Northern Lights" series.
Watering
Young seedlings need daily morning or evening abundant watering. Each plant requires at least 5 liters of liquid. As it grows, hydration can be carried out every two days, while increasing the volume of water to 10 liters. During the flowering period, half a teaspoon of citric acid is added to a bucket of water, the frequency of watering is increased and the foliage is additionally sprayed.
Rhododendron does not tolerate drought well, drying out the soil can lead to root damage and foliage. The plant should be moistened in the morning or evening hours, not during the day, to avoid burns.
The soil near the trunk must be loosened and cleaned of weeds. Lack of oxygen leads to the death of young shoots. Loosen the substrate carefully so as not to damage the root system, which is close to the surface.