The plant can get sick, so you should know all hydrangea diseases and their treatment. And in our article you will get acquainted with insects that can damage the plant. Hydrangea is a highly leafy shrub that literally blooms with flower caps of any color: snow-white, dawn-colored, scarlet, indigo, lilac.
Fungal diseases affecting hydrangea
Fungal diseases of hydrangea are rust, fusarium, phyllostictosis, septoria, peronosporosis and others.
White rot
First, the roots get sick, since the fungus that provokes the disease is in the ground. As a result, they will not be able to deliver the required useful macro- and microelements to the culture, the water and the plant become brown and die. Since the roots are located in the ground, the disease is recognized by darkened shoots, as well as a whitish bloom, reminiscent of cotton wool. Then blackish blotches form on the plaque - sclerotia.


Hydrangea disease white rot
To destroy the fungus, the culture should be sprayed with fungicides: Fitosporin, Fundazol, Hom. But do not forget that Fitosporin has a fourth hazard class (practically safe, it can cause slight inflammation of the mucous membrane on contact). Pour 20 g of Fitosporin powder into a bucket of water, inject hydrangea. And after 2 weeks, the spraying is repeated.
But Fundazol is classified as a highly toxic agent (second class of hazard). Pour 10 g of powder into a bucket of water. When spraying, 1.5 liters of composition are consumed per 10 m². To prepare a solution from the Hom fungicide, pour 30-40 g of powder into a bucket of water, and then spray the bushes.
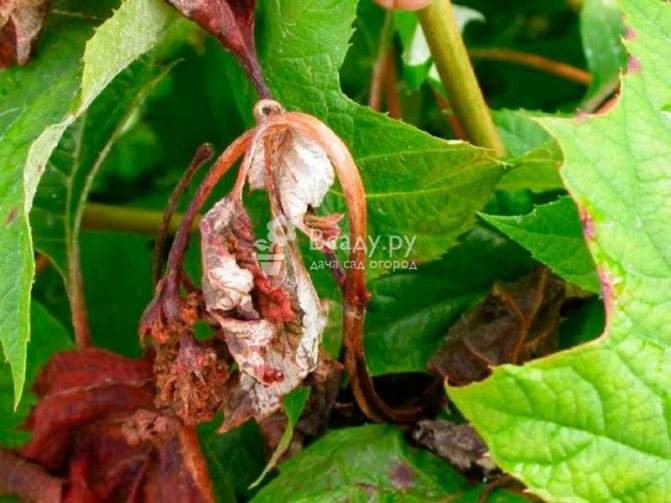
Gray rot
With her, the stems and foliage become soft, watery. If it rains constantly, then a grayish fluff is visible on the culture. If there is heat and drought, then the diseased parts dry out and fall out. As a result, holes are visible on the plant.


Gray rot hydrangea disease
Be sure to cut off any diseased parts. If your flower grows in a room, then spray it with Pure Blossom, Fast (both drugs have a third hazard class), Fitosporin.
Pour 8 ml of Pure Flowers into a bucket of water (10 l). When spraying, 0.5 liters are consumed per 10 m². And after 2 weeks they are sprayed again. If the plant is planted in the garden, then treat it with Rovral Flo 255 SC. And then after 21 days, spray again with the same solution. Then wait another 21 days and process the culture a third time.
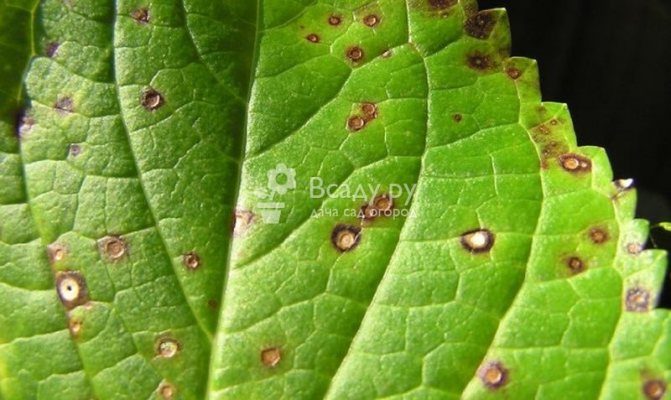
Septoriasis
The causative agent is the Septoria fungus. You can understand that the culture began to hurt if you found brownish specks (2-6 mm in diameter) on the foliage. They are beige in the center and dark brown at the edges. Then these spots spread, becoming more and more, and then the hydrangea begins to shed foliage. If the disease has spread strongly, then the spots are visible on the shoots.


Hydrangea septoria disease
To cure, tear off all diseased leaves. Spray the culture with compounds that contain copper, for example, Hom, copper sulfate, Ridomil Gold.
Pour 2.5 g of Ridomil Gold in 200 ml of water, mix, add another 800 ml of water, mix again and spray the plants.
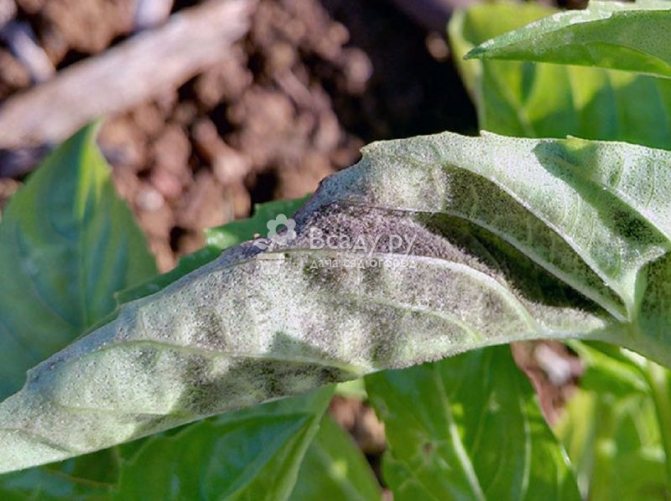
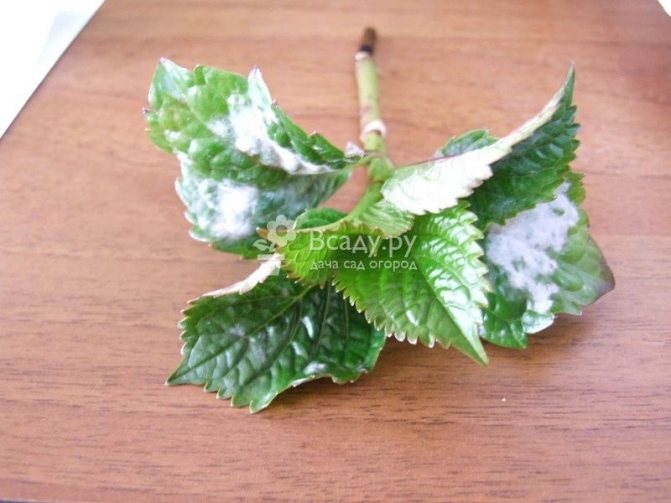
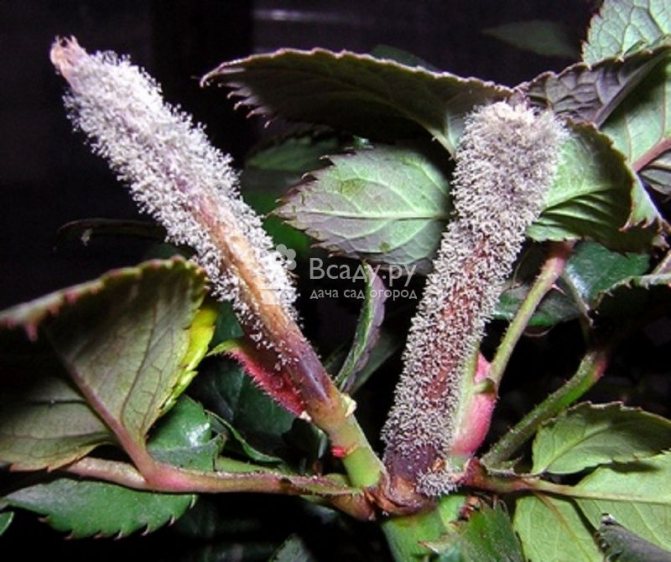
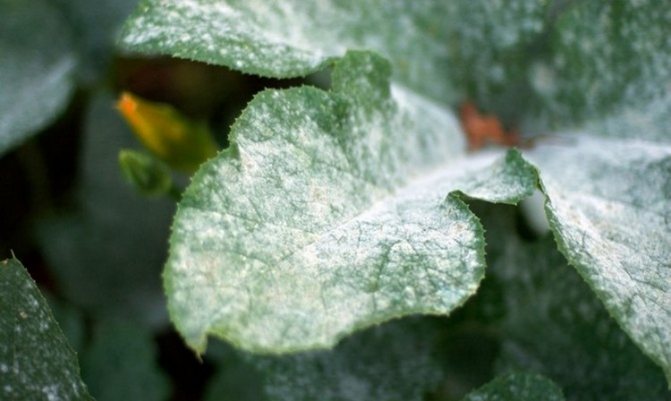
Powdery mildew
It is noticed by the appearance of blurry yellowish-green specks on the foliage. Subsequently, the spots become dark brown and more distinct. A grayish or purple bloom appears below the foliage.As a result, the crop sheds foliage.


Hydrangea powdery mildew disease
For the treatment of the plant, it is sprayed with Fitosporin, Alirin. If the disease has spread strongly, then it is treated with Skor, Topaz, Pure flowers. To get rid of powdery mildew, make a composition of 1 ampoule (2 ml) of Topaz and a bucket of water (10 l).
Peronosporosis
The disease appears during showers and warm weather. All foliage becomes covered with greasy spots, after which they become dark. For treatment, spray the plant with a solution: add 15 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of green soap to a bucket of clean water.
Rust
The disease is easily detected by its dark orange spots. The reasons are an overly dense planting of bushes, an excess of nitrogen in the soil.


Hydrangea disease rust
For treatment, it is better to spray the culture with a solution - place 40 g of copper oxychloride in a bucket of water (10 l). You can also treat the culture with Topaz, Ordan, Falcon preparations. To prepare Topaz solution, pour 2 ampoules (4 ml) into a bucket of water (10 l), and then process the bushes.
Ordan is used as follows: first, a sachet of 25 g of powder is poured into 1 liter of water, thoroughly mixed so that it completely dissolves, then the composition is poured into the sprayer tank and 9 liters of pure water are poured into it, tightly closed and begin to shake vigorously. After that, the mixture is ready.
For the treatment of rust, 10 ml of Falcon is poured into a bucket of water (10 l), and for the prevention of the disease, 5 ml of the composition is dissolved in 10 l of water. Bushes are being processed.
Fusarium (Tracheomycotic wilting)
The fungus enters plants through the contaminated soil, first it affects the roots, which soften, turn brown, and rot. As a result, nutrients cease to flow to the plant, the shoots wither, the foliage turns yellow, the buds fall off.
For treatment, 2-2.5 kg of nettle and celandine are collected, placed in 50 liters of water, and left for 24 hours. Then, 5 parts of water are poured into 1 part of the infusion and the plants are watered. You can spray the bushes with Fundazol solution.
Ascochitis spotting (ascochitis)
Irregular ocher or brown spots appear on the bushes. Before the foliage blooms, the plants are sprayed with a Bordeaux mixture. The diseased parts of the plants are cut off and burned. A solution is made in 1%, that is, 1 bag of Bordeaux mixture is poured into 10 liters of water.
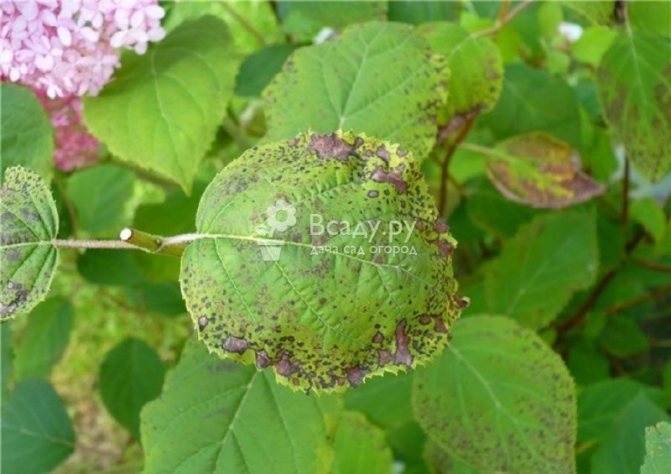
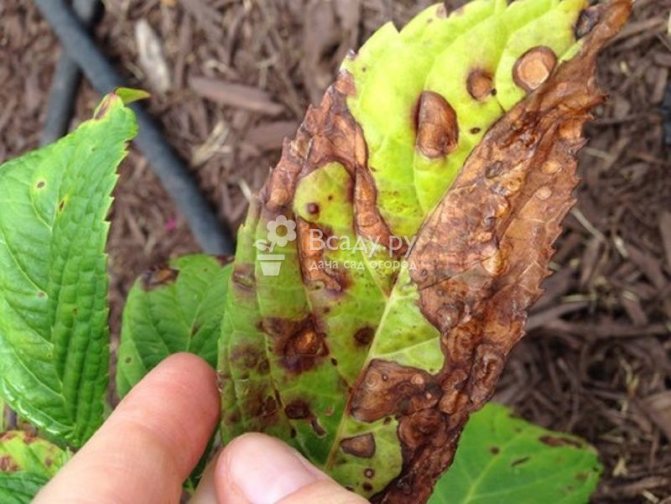
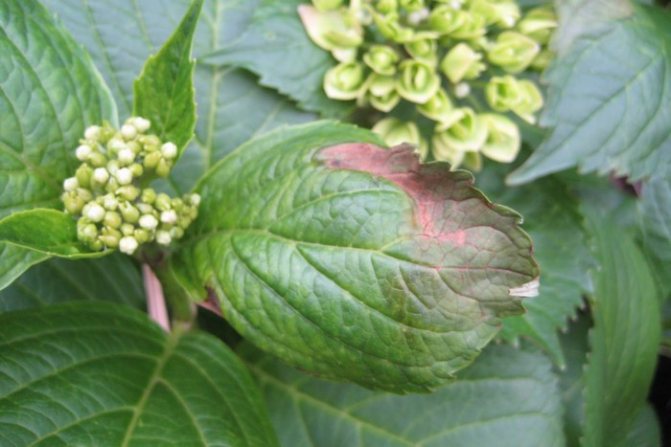
Phylostic spotting (phyllostictosis, brown spotting)
It is found when large brownish spots appear on the foliage with a wide crimson border. Then these places drop out. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Phyllosticta rosae.
For treatment, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of the Strobi drug, diluting 4 g in a bucket of water (10 l). You can also use Abiga-Peak, diluting 40-50 g in a bucket half filled with water (5 L).
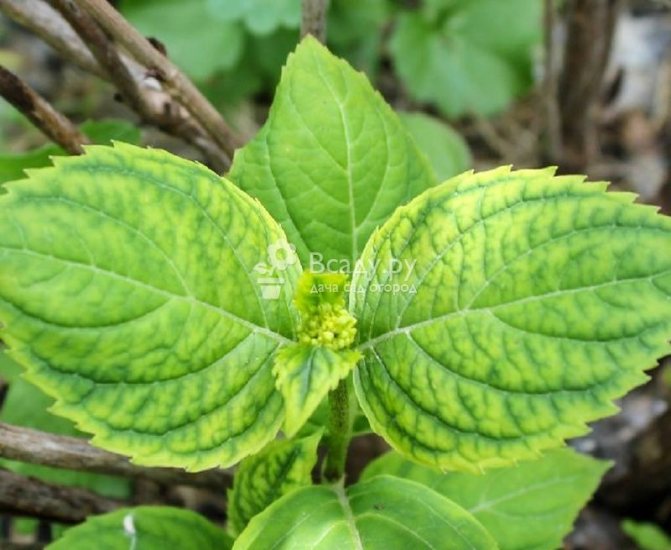
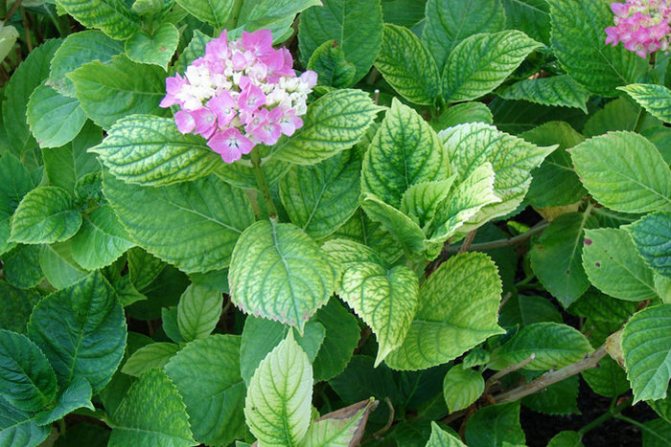
Chlorosis
It is determined by the fact that the foliage of the culture becomes lighter, it turns yellow, and the veins on the foliage do not change their shade. The disease appears due to a lack of iron in the soil. Chlorosis can also manifest itself by the way small leaves appear on the plant, the buds become deformed, the leaves curl, the stems dry.


Hydrangea chlorosis disease
For treatment, it is required to fertilize the culture with compounds that include readily available iron. For example, Antichlorosis. For treatment, you can make root dressing by dissolving 1 cap in 1 liter of pure water. An interval of 15 days is required between dressings. You can also fertilize foliage by dissolving 1 cap in 1 liter of water, but do not fertilize at the same time under the root and foliage. Ferovit can also be used instead.
You can also create top dressing by adding 2 g of ferrous sulfate and 4 g of citric acid in 1 liter of water. Then foliage is sprayed with this composition, and if the disease is in a serious stage, then it is poured under the root.You can also make a solution: pour 40 g of potassium nitrate into 10 liters of pure water. It is necessary to water the culture, and after 3 days make a similar composition and water again.
Chlorosis
The reason for the appearance is a lack of iron in the soil or a violation of the metabolism of the flower, which makes it impossible to assimilate this component. A sure sign of the disease - the leaves of the hydrangea turn white, after which they turn yellow. The veins themselves do not lose their dark green color. In addition, buds can be deformed, branches dry, the size of leaf plates can decrease, with their simultaneous twisting.
Among the ready-made mixtures, you can use Antichlorosis or Ferovit. Self-preparation requires mixing 2 g of ferrous sulfate and 4 g of citric acid with a liter of water. With a mild form, spraying is carried out, in more severe cases - watering at the root. An alternative option for your own treatment:
- Dilute 40 g of potassium nitrate in 10 liters of water.
- Perform 2-3 watering of plants.
- After 3 days, prepare a solution in similar proportions, only with iron sulfate.
- Repeat watering.
Viral disease
In addition to fungal diseases that can affect hydrangea, diseases of viral origin also require detailed study.
Ring spot


Hydrangea ring spot disease
First, fuzzy spots in the form of rings appear on the plant (their diameter is about 2 cm). Then the foliage becomes deformed, wrinkled, it falls off. Also, the plant may stop blooming or small and weak buds appear. Unfortunately, no drugs have yet been developed to treat ring spot. But you need to remember that the disease can be transmitted through seedlings. So get healthy, strong seedlings. And if you want to propagate the culture by cuttings, then cut off completely healthy cuttings.
Difficulties and problems when growing hydrangeas
Foliage can turn yellow for a variety of reasons:
- direct sunlight falls on the flower. Since he loves partial shade, you should not plant him in the bright sun;
- excess moisture in the ground. Although the flower loves watering, the foliage may turn yellow due to stagnant water;
- frequent drafts;
- if the plant blooms very profusely, and therefore uses a lot of nutrients and moisture, the foliage may also turn yellow;
- lack of macro- and micronutrients. The plant requires constant feeding for growth;
- alkaline or neutral soil acidity. The plant loves soil that has acidic properties (pH 3-6). The color of the buds depends on the acidic characteristics of the soil: indigo and dark purple flowers grow well in acidic soil, snow-white and pale pink in slightly acidic soil. To increase the amount of acid in the ground during irrigation, it is required to drop 2-4 drops of lemon juice in 1 liter of pure water.
Also, foliage can dry out and fall off for a number of reasons:
- lack of moisture in heat;
- too dry air. This happens if the hydrangea grows in a pot in an apartment or is planted in a greenhouse. Therefore, you should constantly ventilate the room, open the vents. Spray the plant;
- lack of elements necessary for the plant. Nutrient solutions can be added every 7-10 days. This is required during the formation of buds and blooming. It happens that the foliage of the plant turns black.
Dry blackening is the appearance of brownish specks on the edges of the foliage. Then, after a while, the foliage withers. This can happen due to:
- watering with too hard water. It is advised to water with water that has been standing for a day;
- burns on foliage from the bright sun. It is required to shade the culture.
Wet blackening occurs due to:
- sudden changes in air temperature;
- excess moisture in the soil;
- if the plant is planted in heavy clay soil, through which water and air pass poorly.
Preventive measures
Better than any treatment is timely and correct prevention.If the bush is healthy, it is unlikely to get sick, but if it does, the hydrangea will be resistant to illness. A weakened plant is very vulnerable to viruses, fungi or pests that can seriously harm it.
Disease prevention and protection from pests will be competent home care. For a healthy flower, it is necessary to correctly determine the place for planting it. Foliage and flowers wither quickly under the scorching sun. Therefore, hydrangea will grow optimally in partial shade conditions.
Adequate watering is also important for the plant. Hydrangeas prefer moisture, so it is important to keep the soil from drying out. In the heat, you need to water the bush every other day.
It is also important to choose the right soil for planting hydrangea bushes. It will be difficult for the plant to survive in heavy alkaline soil. It needs to grow in light, acidic soil. It is such a soil that "breathes" well and allows moisture to pass through.


Providing correct and timely feeding is also necessary for hydrangeas. For this, special ready-made nitrogenous fertilizers are useful. In the summer, phosphorus-potassium agents are used, and in the autumn season, phosphorus is mainly used.
Shrub wood also needs preventive treatment. In the spring, before the beginning of the growing season, it is recommended to irrigate the bushes with copper sulfate. As a replacement option - the use of "Topaz", "Iskra" and "Fitosporin" - the most modern effective drugs.
Proper grooming plus constant care equals a healthy hydrangea capable of delighting with lush flowers. It will become one of the brightest decorations of a indoor flower garden or garden plot.
For more information on diseases and pests of hydrangea, see the next video.
Insects attacking the plant
Diseases in hydrangeas often appear precisely because of pests that carry viruses from other plants or simply infect shrubs.
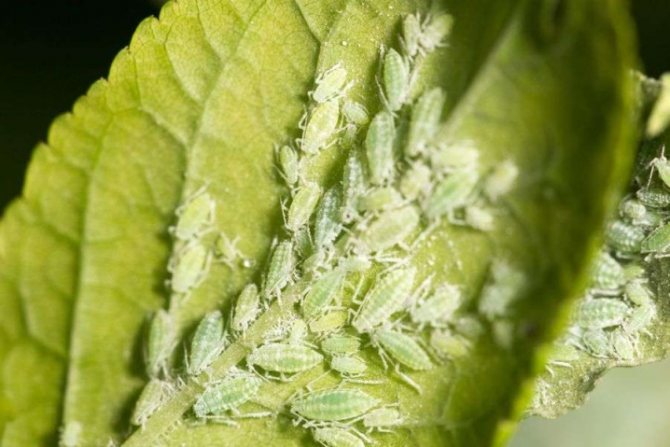
Leaf aphid
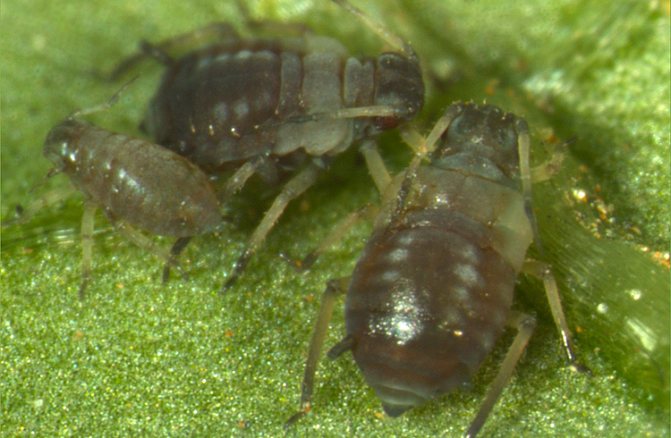


Leaf aphid
Aphids are a very tiny insect that moves with the help of 3 pairs of long legs. It is dangerous in that it sucks the juices from the culture, and also sugary discharge appears after it. A sooty fungus then develops on these secretions, and they also attract ants. As a result, the culture grows slowly. If there are a lot of aphids, then the foliage becomes yellow and deformed. If aphids are few, then you can wash them off the plant by watering them with a hose or rinse the culture with soap and water. Ladybugs also eat aphids. Therefore, if you plant marigolds near the hydrangea, it will attract ladybirds.
With a large number of aphids, only spraying with Fitoverm, Akarin will help.
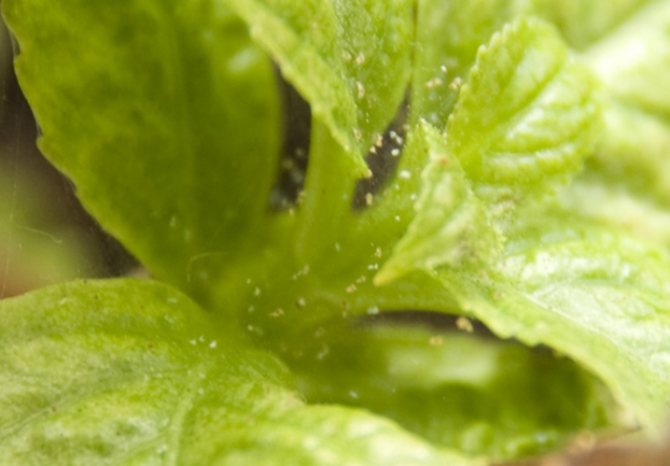
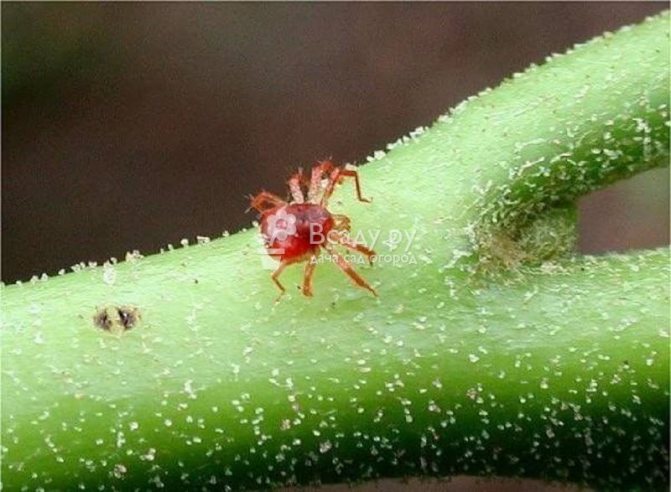
Spider mite
These are the smallest pests ranging in size from 0.2 mm to 1 mm. They can be found by small cobwebs and yellowish spots on the foliage that grow and merge. Ticks like heat and low air humidity, and they actively reproduce. As a result, the foliage dries up. And the plant begins to shed its foliage.


Spider mite
If there are not very many mites, then you can wash the plants with a solution of soap. If there are many parasites, then it is worth treating the plants with such means as: Fitoverm, Lightning, Akarin. When using the drug Lightning (the third class of danger for humans), 3-4 ml of the product should first be diluted in 2 liters of water. Then add another 8 liters of water.
Akarin is safe for humans and warm-blooded animals. To process hydrangeas, take a sprayer that has a fine spray. Since the product does not penetrate the foliage, it is recommended to add soap for better adhesion. To kill ticks, it is enough to pour 3 ml in 1 liter of water, and to eliminate aphids - 6 ml in 1 liter of pure water. Parasites begin to die 3 days after treatment, and the maximum number of pests dies after 6 days.
From spider mites and aphids, you can spray the bushes with the biological product Bicol, which is safe, that is, it can only harm parasites. To create a working solution, dissolve 60-160 g in a bucket of water (10 l).
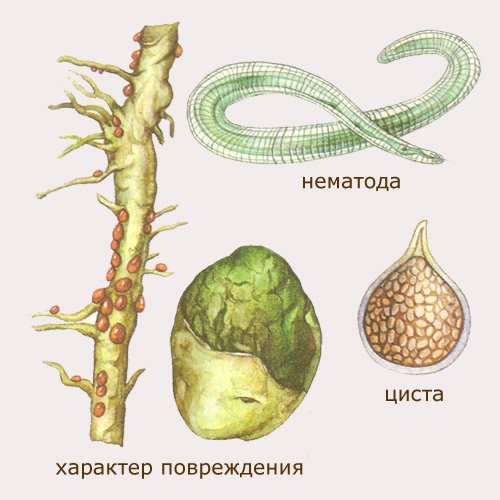
Gall nematode
These are tiny worms, they like high soil moisture. Their activity can be seen by the appearance of growths - galls on the stems, roots. These nematodes make their way through the roots to the stems and foliage, leaving a poisonous discharge. In this case, the plants stop growing, they may die.


Gall nematode
Professional gardeners advise to pluck and burn a plant that has been attacked by nematodes. True, you can still spray the bushes with Karbofos. But the remedy for direct sunlight quickly disintegrates and loses its effect. It is advised to spray with the agent in early spring, even before the flowering of the plants, as it destroys the bees. Make a working solution by adding 75 g to a bucket of water (10 L). Seedlings are sprayed on a warm sunny day, when there is no wind, and the air temperature has reached +15 degrees Celsius.
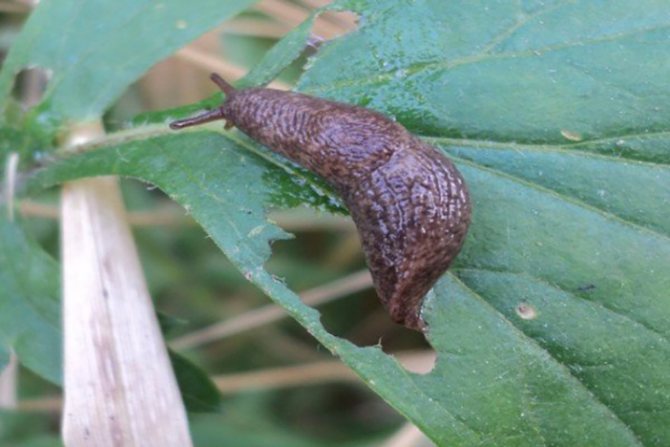
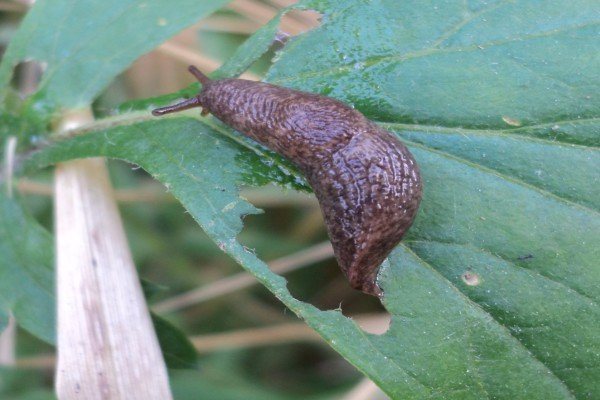
Slug


Slug
If the plantings are too thick, then slugs can multiply in them. They actively eat foliage. Slugs can be harvested by hand. You can also scatter the granules of the drug Molyuscid on the ground.
Damage to bushes by pests
| Leaf aphid Microscopic insect parasite 0.3 mm in size. The integument of the body is translucent, greenish tone. Harm:
Control measures:
| |
| Spider mite Microscopic arthropod (up to 0.15 mm in size). It sucks out hydrangea juices, spreads in dry, hot years. Sign of appearance - the thinnest cobweb on the leaf blades. When the colony grows, it is visible as tiny red dots on foliage and peduncles. Harm:
Pest control:
|
| Gall nematode It is a round small parasitic worm 1–2 mm long. His body is white or pearl. Symptom of infection - reddish galls (swellings) on the root system and at the bottom of the peduncles. These "blisters" rot and dry out. Harm:
There are no effective treatments for nematodes, so preventive measures are important.
|
| Garden slugs and snails These are small terrestrial gastropods. They make refuge in dense thickets, under stones, in the axils of foliage, in shaded and damp areas of the garden. Harm:
Pest control:
|