The Russian name for the mushroom champignon comes from the French word champignon, which simply means "mushroom". All of us have long been accustomed to the fact that edible champignons are grown in special greenhouses, and therefore we consider this mushroom almost artificial. However, there are many types of champignons that grow naturally: in forests, and in meadows and pastures. They are no less tasty than those grown in artificial myceliums and certainly do not contain any additives.
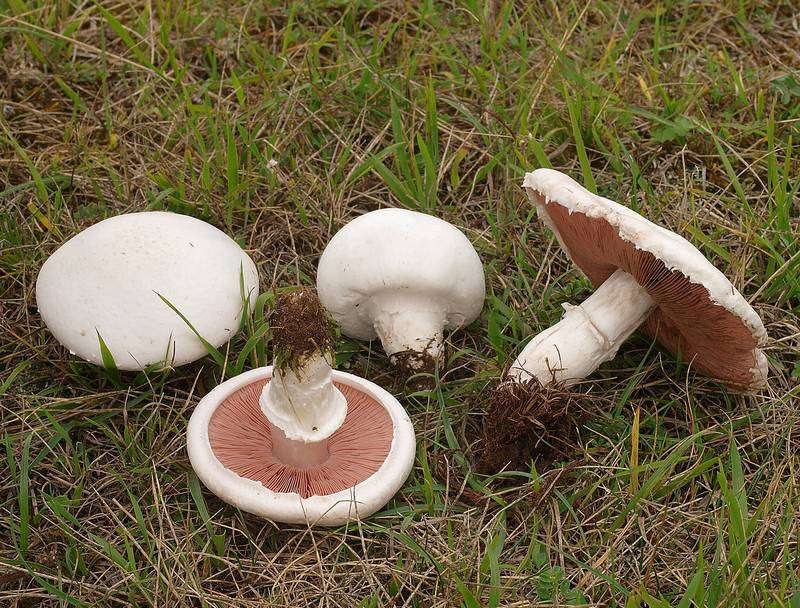
On this page you can see a photo and description of the types of champignons growing in natural conditions: field, common, two-ring and Bernard.
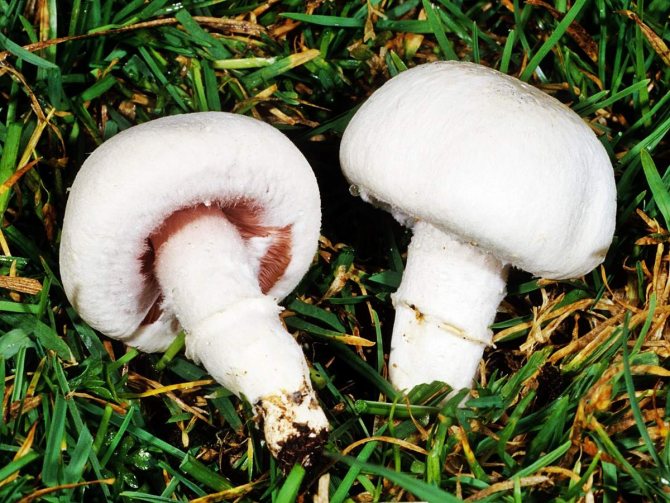
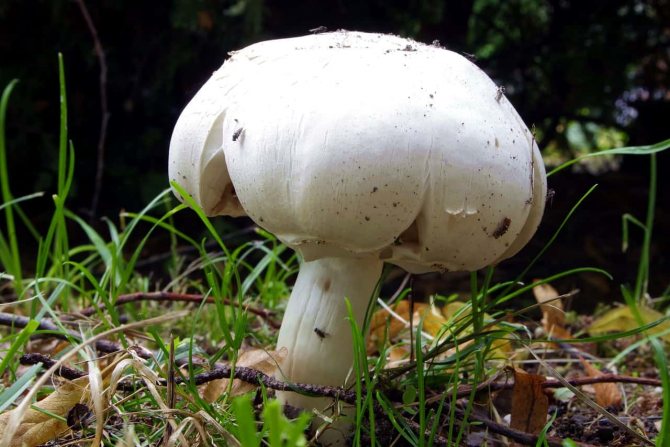
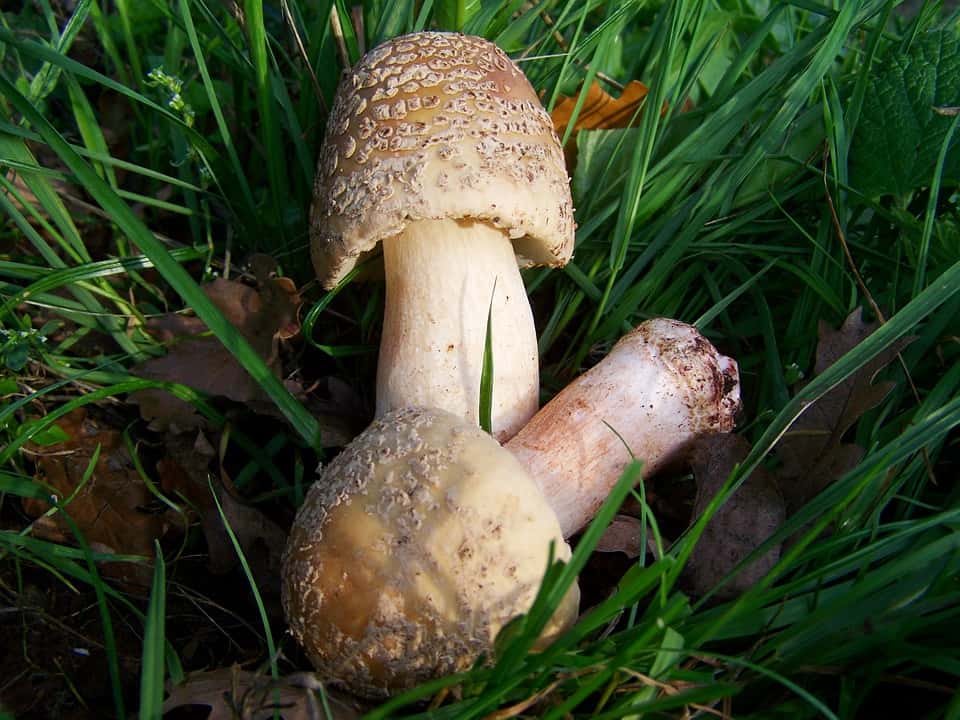
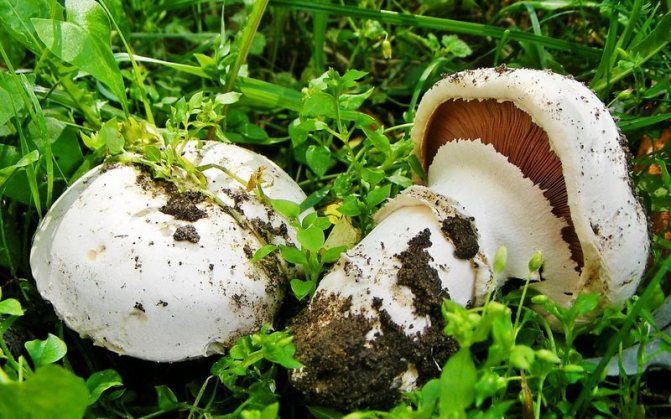
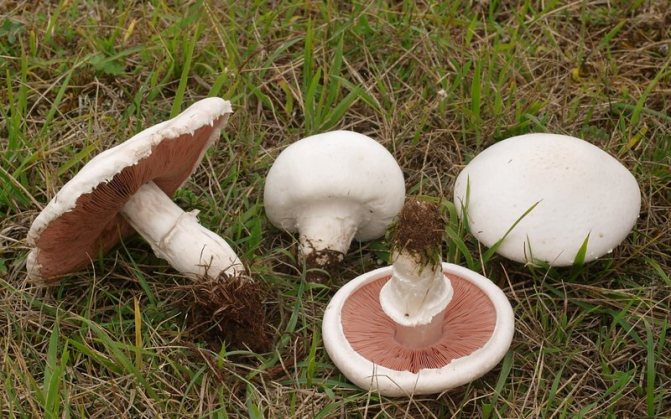
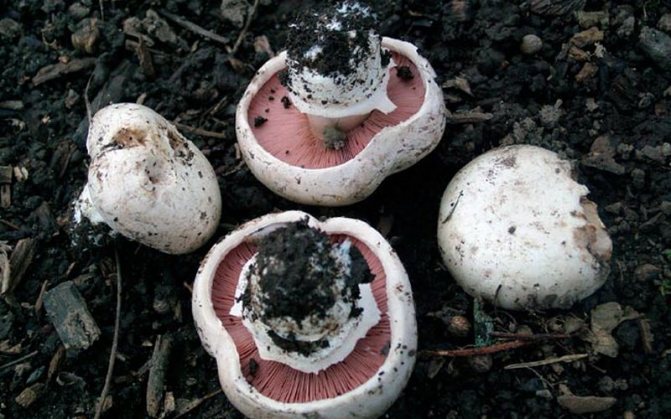
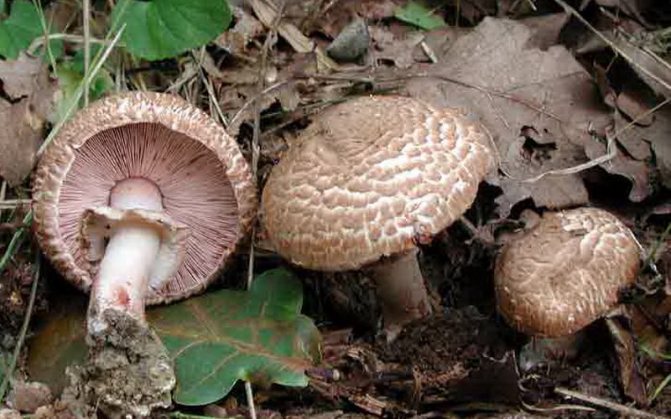
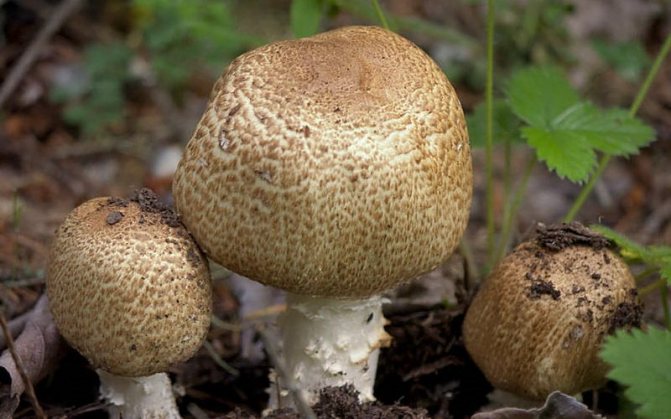
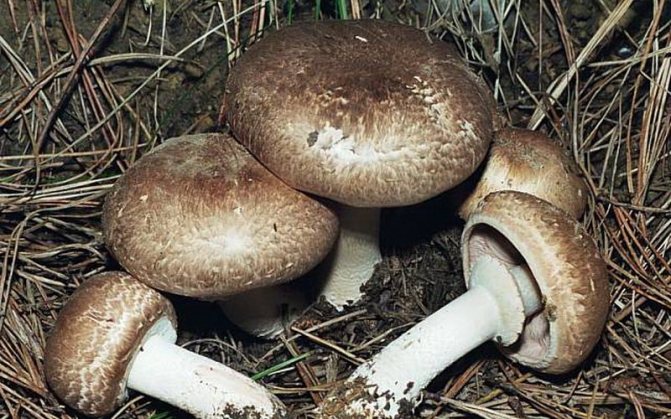
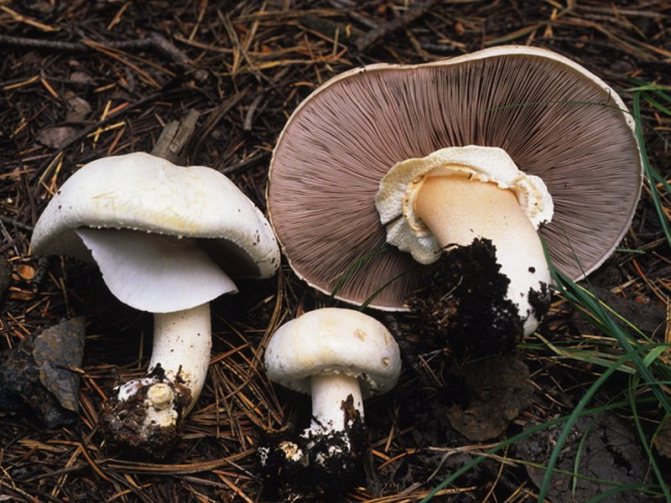
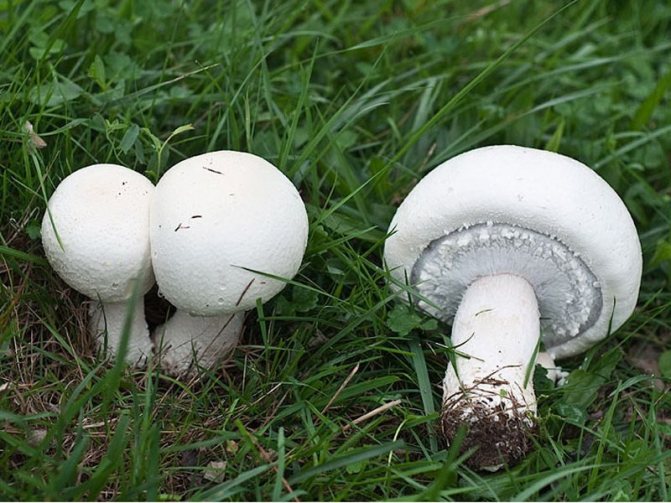
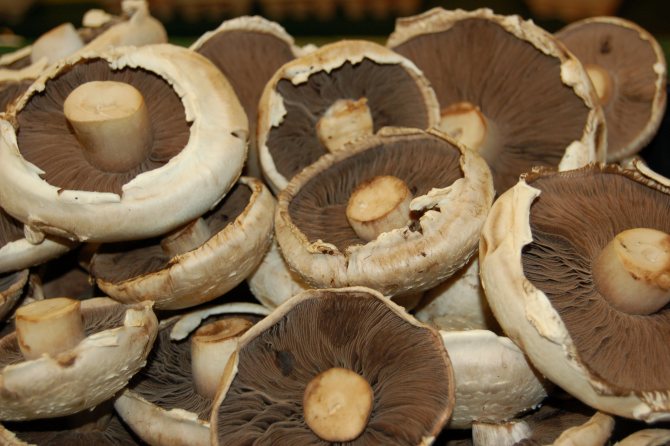
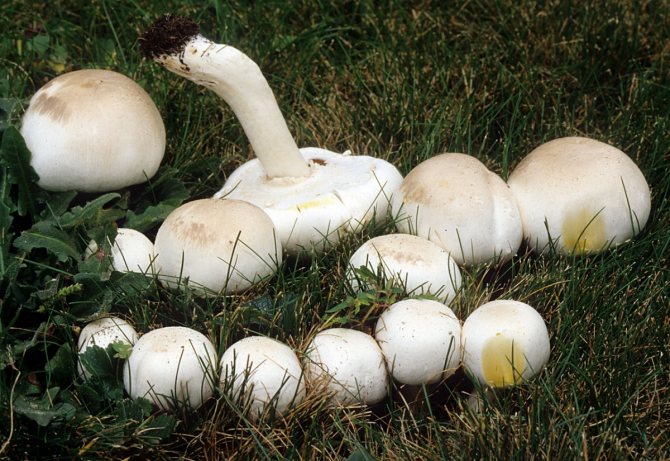
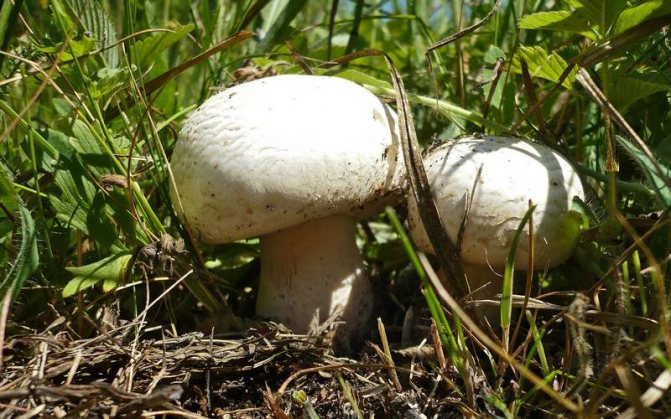
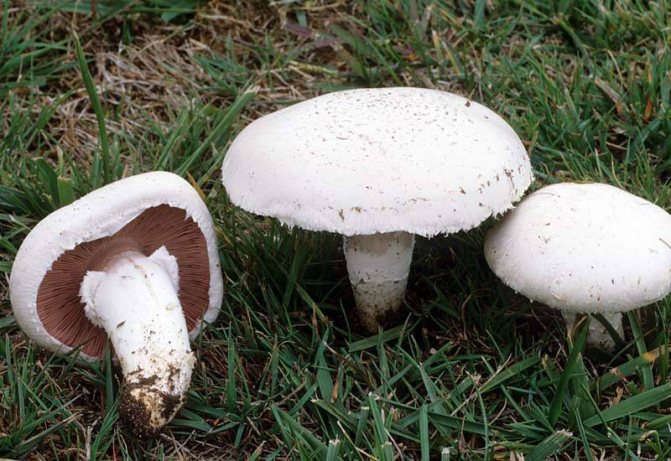
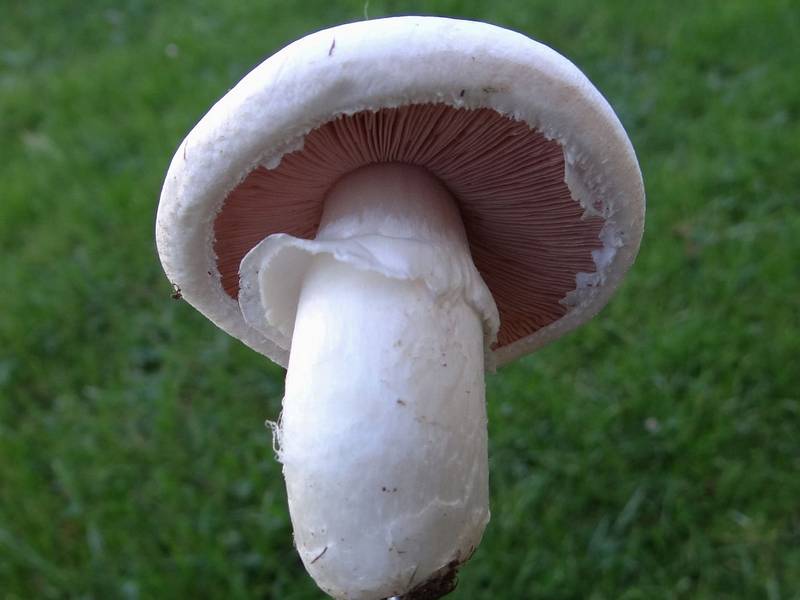
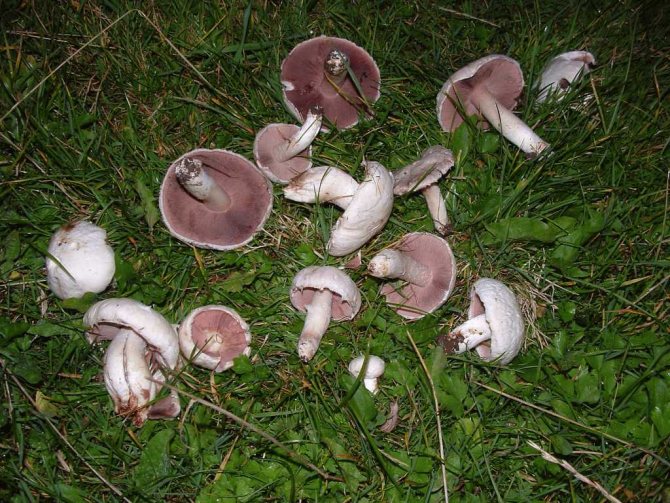
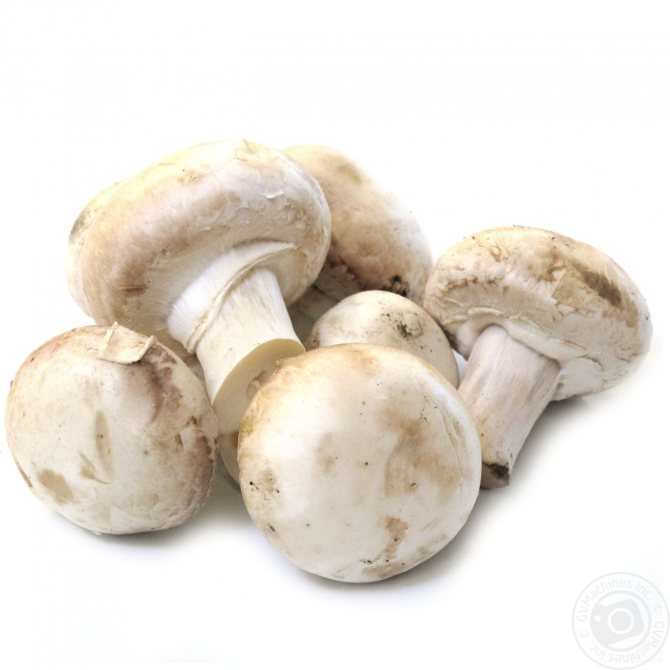
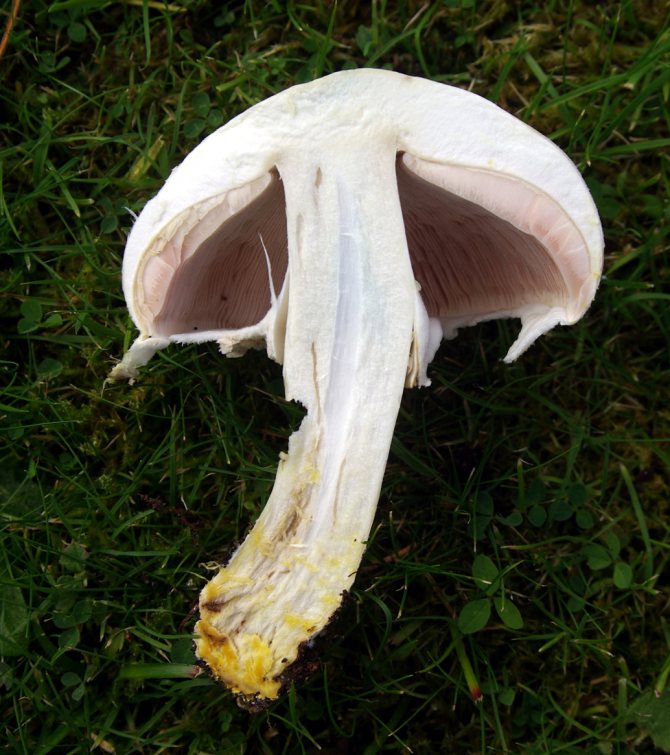
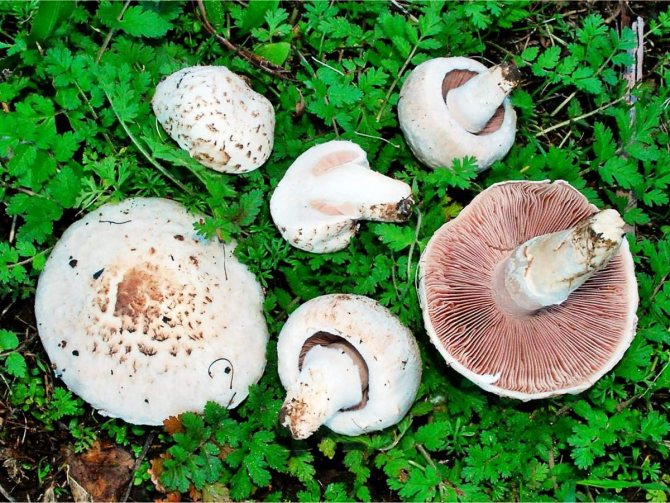
What champignons mushrooms look like
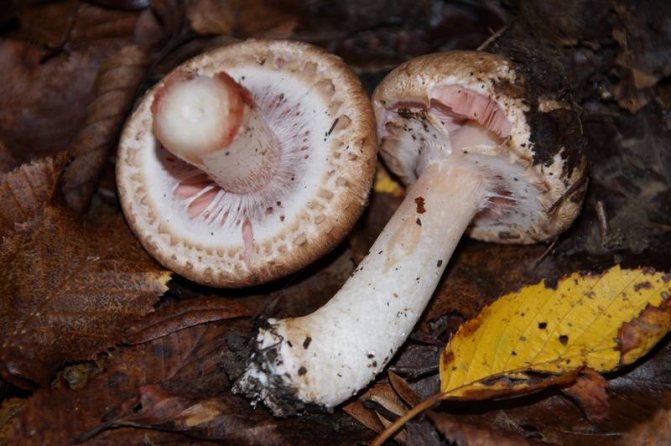
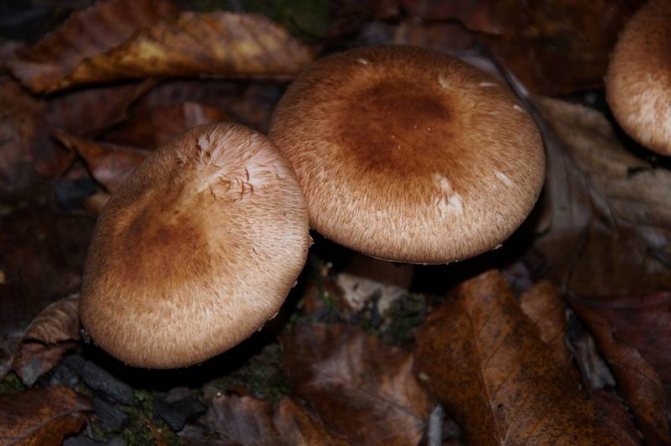
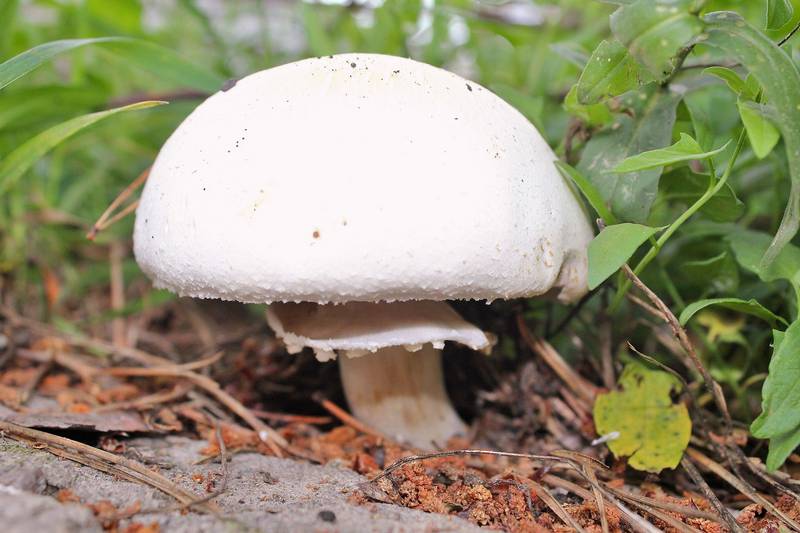
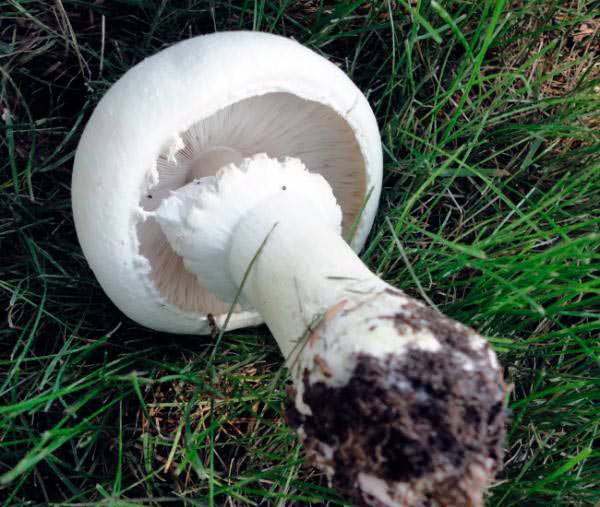
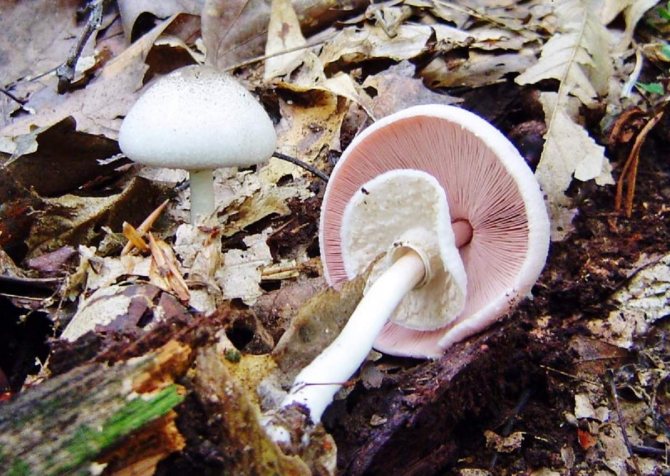
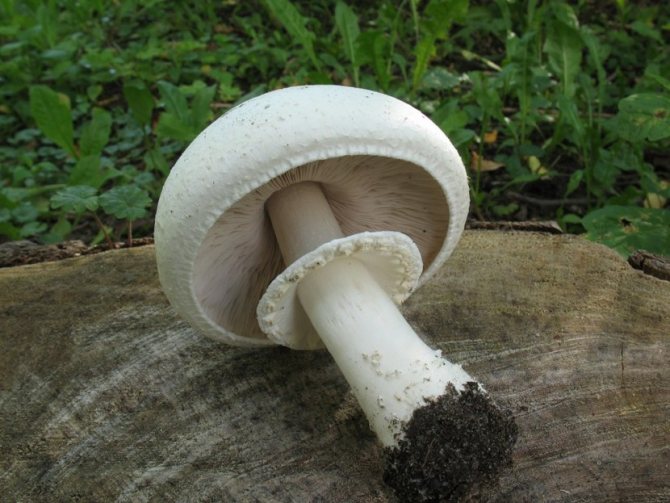
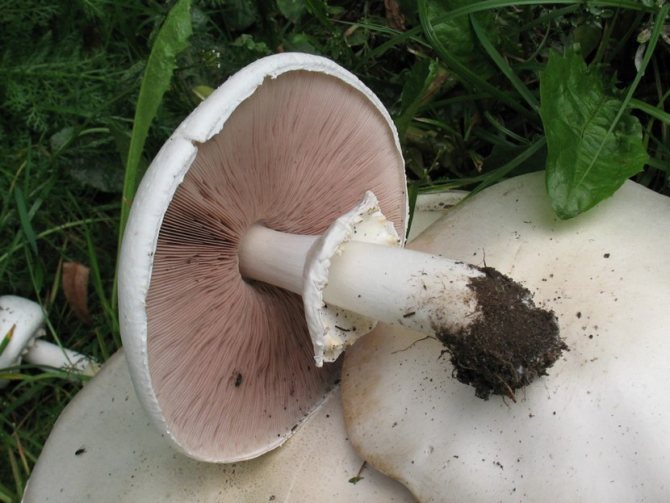
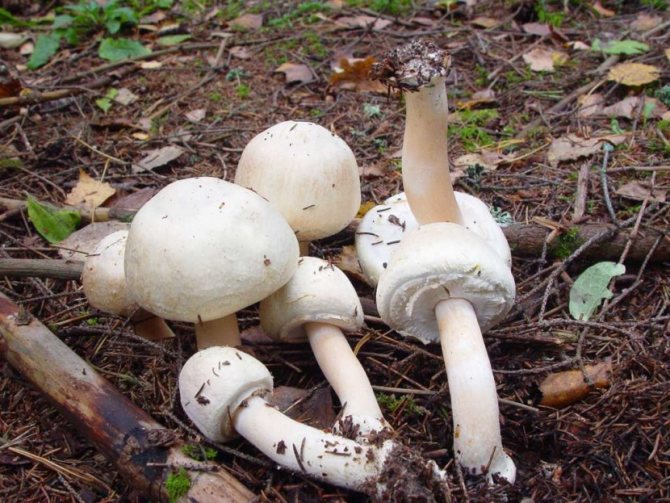
Adults, fully ripe and ready for harvest, are represented by a massive, rather dense, rounded or flatter cap with a white or brownish surface, smooth or covered with dark scales. The plates are loose, white, but darken with age. The leg is centrally located, flat and most often dense. May be hollow inside. There is a partial cover, represented by a well-visible one- or two-layer ring. The pulp can have various shades of whitish color.


Other names
Sometimes this mushroom is called common or sidewalk, because in cities and small villages it grows next to the roadway, often next to the curbs of sidewalks. If we recall the ability of mushrooms to accumulate toxic substances from the environment, then it is better not to eat such specimens.
Did you know? The field variety of champignons in English sounds like "horse mushroom", and it received such an unusual name due to its close growth to stables, on soils rich in manure.
Photo gallery
Season and collection rules
In the conditions of a temperate climatic zone, the collection of the considered mushrooms can be started already from the end of May, continuing to search for them until October or even November. It is possible to determine the mushroom ripeness optimal for harvesting by the film connecting its stem and cap: it is better to harvest when it is already well stretched, but has not yet had time to break (the diameter of the dome is 4–10 cm). Such specimens will be as fleshy and tasty as possible, which is what a mushroom picker needs.
Of course, it is better not to take damaged and unpleasant-smelling mushrooms, but healthy and evenly colored mushrooms can be carefully twisted out of the ground. Unlike most other forest mushrooms, you do not need to cut field mushrooms, which is due to the structural features of the plant mycelium. The holes remaining after them should be covered with a substrate, first removing all remnants of the previous harvest or remaining unusable specimens.
Did you know? Home cultivation of champignons in Europe began to be practiced back in the 17th century. Then it was considered a delicacy and was grown in underground premises that belonged mainly to monarchs. In Russia, this practice became relevant only in the 18th century.
Composition and useful properties of champignons
Mushrooms are classified as dietary and low-fat foods. 100 g of mushroom pulp contains about 26-27 kcal. Fresh mushrooms are less nutritious. The composition is represented by 4.3 g of protein, 1.0 g of fat, 0.1 g of carbohydrates, 1.0 g of ash and 91 g of water.The benefits of such a product for the human body are also undeniable that due to the presence of a significant amount of phosphorus in the composition, which allows:
- normalize metabolic processes;
- tone the body;
- relieve the feeling of fatigue;
- relieve irritability;
- calm the nervous system;
- reduce the risk of developing a heart attack or stroke;
- restore the function of the stomach and intestines;
- suppress appetite.
The product improves memory and concentration, has a positive effect on the state of the organs of vision, helps to strengthen the connective tissues of the body, including bones, teeth, skin, hair and nails. Mushroom juice is capable of bactericidal action. Dry mushroom powder is useful in treating hepatitis and stomach ulcers.
Where do mushrooms grow?
In addition to the question of what the champignon looks like, its habitat is also an interesting topic for discussion. These mushrooms can be found in almost all corners of the globe, except for the Far North and desert areas. Champignons belong to those species of living creatures that live on dead tissues of organisms and on animal secretions. Therefore, one should look for such mushrooms on abundantly manured or humus-rich soil.
Most often, they do not grow singly, but in families, the number of which can be quite significant. In the case of growing in colonies, they form oval rows, which are popularly called the circles of witches.
On a territorial basis, champignons are usually subdivided into those living in the forest zone, growing in the steppe area, and also growing in forest glades. There are also those that grow in places where vegetation is completely absent.
Next, we will consider the types of champignons (what the photos look like), which can most often be found on the territory of our country.
Harm and contraindications of mushrooms
Despite the significant number of beneficial properties that mushroom pulp stores, the presence of some contraindications should also be taken into account:
- preschool age;
- disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the stomach and intestines;
- liver dysfunction;
- individual intolerance.
Care should be taken when eating mushroom dishes if you have a history of unexplained allergies. It is also important to remember that strong heat treatment of fruit bodies makes them less nutritious and healthy.


Application
Forest mushrooms are used in various fields: in medicine, pharmaceuticals, cosmetology, dietetics and cooking.
Cooking applications
Wild specimens are classified in category 1, i.e. they are certainly edible. These mushrooms are fragrant and nutritious. They are superior to fish in phosphorus content. Suitable for food in all types: raw, fried, boiled, etc.
Culinary experts make a variety of side dishes from them. They are especially tasty when fried, with onions, in olive or sunflower oil.
Application in medicine and pharmacy
Champignons are widely used to create preparations with bactericidal properties, ointments or tinctures. They are used to treat typhoid fever.
Folic acid increases the production of red blood cells in the red bone marrow and promotes metabolism. It has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. In pregnant women, eating small amounts of champignons promotes fetal development and helps to form the placenta.
Amino acids, minerals and vitamins help to restore energy balance, stimulate the human immune system.
A large amount of protein and antioxidants helps to lower blood sugar, so mushrooms are indicated for patients with diabetes mellitus.
In older people, they improve memory, stimulate the brain and increase concentration.
Application in dietetics
Champignons successfully combine high energy value and low calorie content. They contain more B vitamins than vegetables. Plant fiber and fiber give a quick feeling of fullness, so nutritionists prescribe this product as a dietary food for those who want to lose weight.
For those who play sports or go to the gym, the use of champignons helps to build muscle mass.
Edible types and varieties of champignons
Some species grow exclusively in forests (A.silvaticus and A.silvisola), and soil saprotrophs (A.bisrorus, A.bitorquis and A.subreronatus) grow in open spaces, among grass stands of different heights. Among other things, there are desert species, which include A. bernardii and A. thabularis.
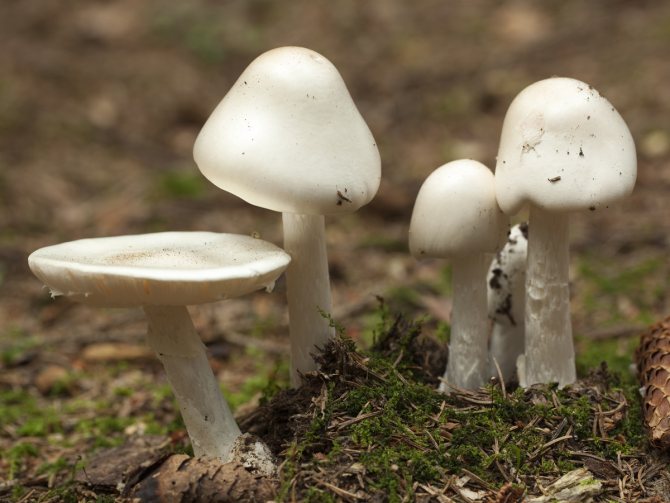
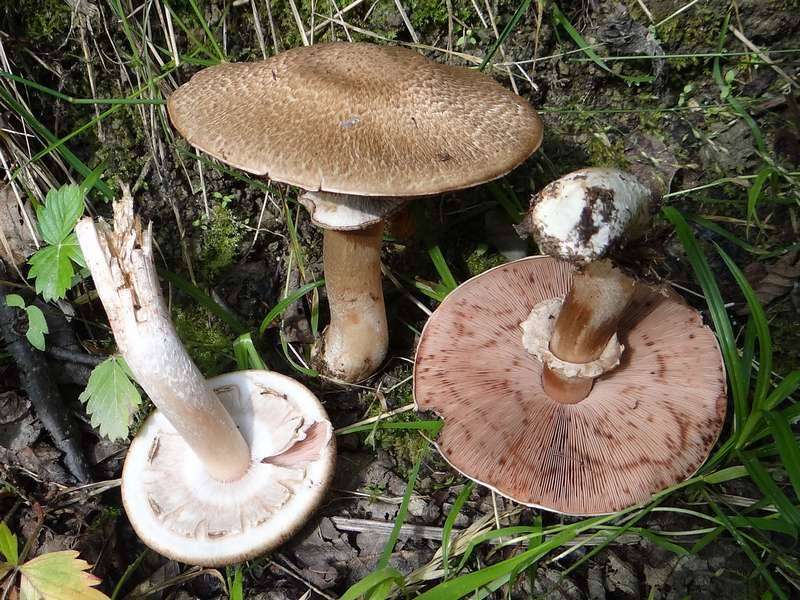
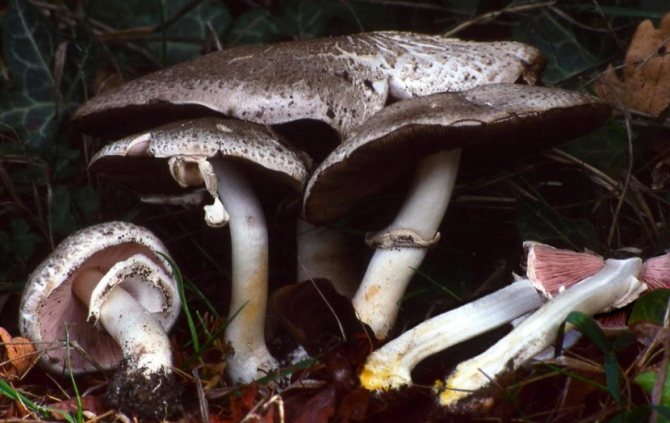
Field champignon
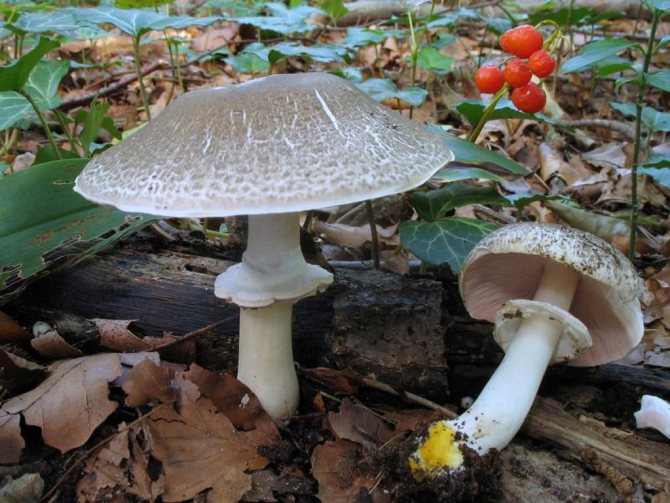
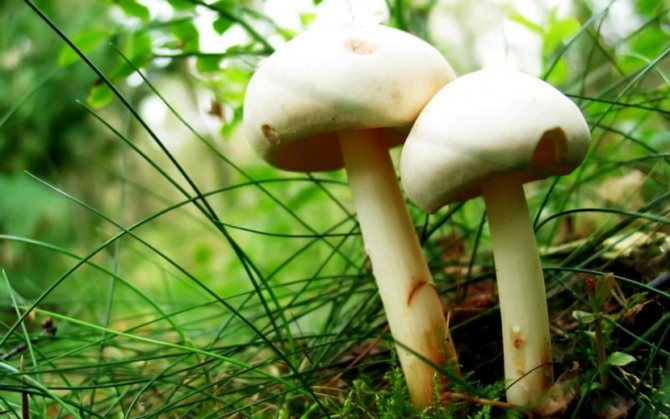
A. arvensis has a rather large fruiting body, with a thick-fleshed, rounded-bell-shaped or convex-outstretched cap, in the center of which there is a small tubercle or slight flattening. The pulp is white or creamy, with almond or anise aroma. An ocher tint and slow yellowing may be present. The surface is silky or smooth, covered with yellowish or brownish scales. The plates are often spaced and characteristically swollen. The area of the pedicle is cylindrical, smooth, with expansion or thickening at the base. Spores are black-brown in color.


Forest mushroom
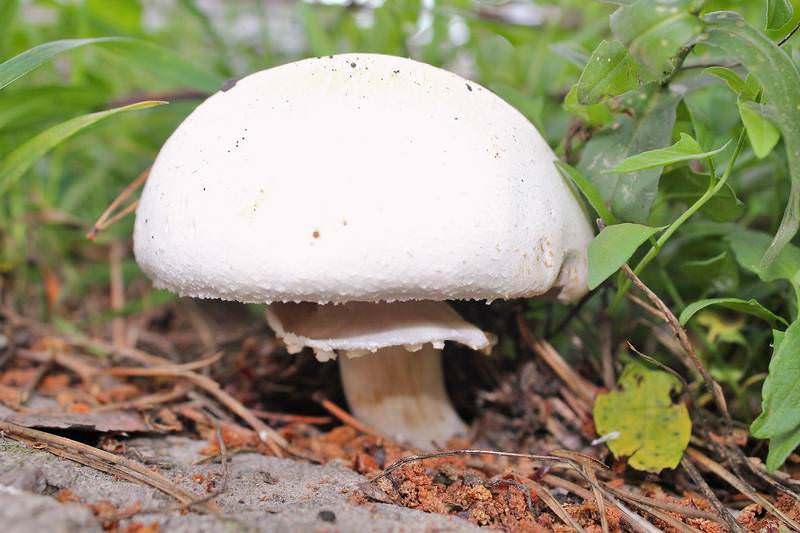
The fruiting body of A. silvaticus has an ovate-bell-shaped or flat-spread cap, often with a protruding tubercle, rusty-brownish brown coloration, with a large number of dark scales. The pulp is white in color, reddening at the cut. The plates are white, reddish or dark brown in color, narrowed at the end. The area of the leg is cylindrical, slightly swollen at the base, with a whitish filmy ring.
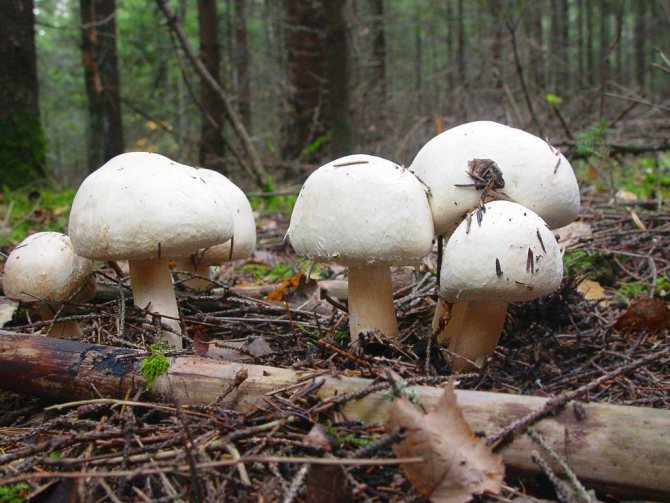
Common champignon
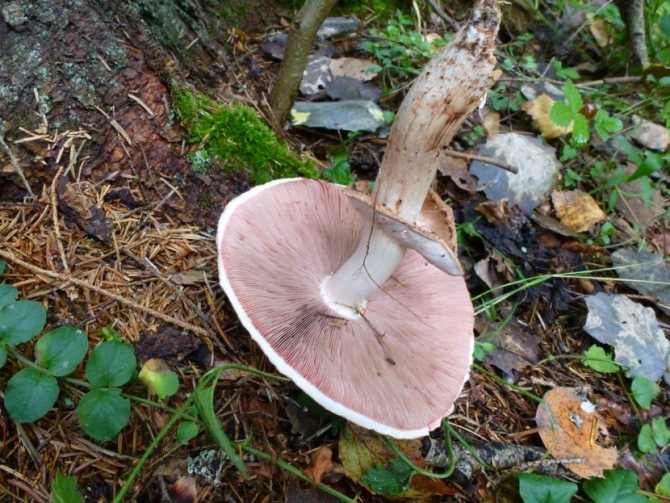
A.samrestris has a hemispherical cap with curved inward edges, flat-rounded or outstretched in shape. The central part is convex. The surface is white or brownish, can be dry, silky or finely scaly. The pulp is white in color, reddening at the cut. The plates are white, pinkish or dark brown in color, with a purple tint. The region of the peduncle is straight and even, with expansion or bulging at the base, with a wide whitish ring.


Small scale mushroom
A. squamuliferus is distinguished by a thick-fleshed, at first semicircular, later convex-outstretched cap, with a wide and obtuse tubercle. The surface part is of fine-scaled type, silky. The area of the leg is cylindrical, sometimes with a slight tuberous base, white, silky-fibrous type. The pulp is white in color, turning pink or reddening at the break. Dark brown spore powder. Plates are free type, often located, brownish in color. The spores are ellipsoidal, with a smooth surface, light brownish in color.
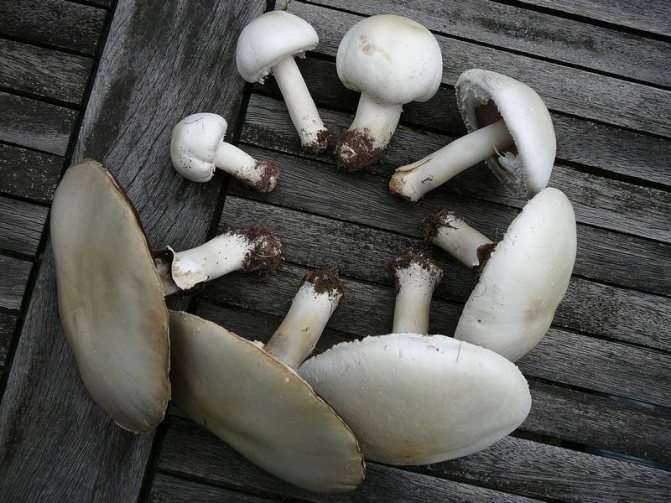
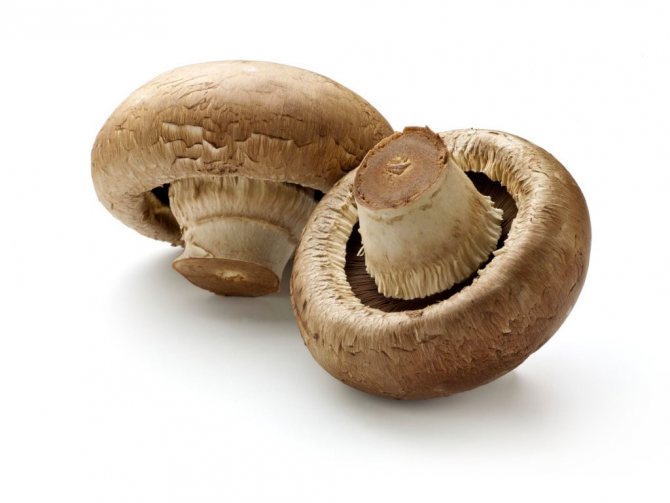
Garden champignon
A.bisrorus has a rounded cap, with curved edges and a residual private veil, represented by thin flakes, pure white or with a brownish tinge. The surface of the cap is smooth, with a gloss in the central part or of the radial-fibrous type, sometimes with scales. The pulp is dense and juicy, acquiring a pinkish or red tint at the cut. Plates of young specimens of pink coloration. With age, the plates turn dark brown with a characteristic purple tint. The leg is cylindrical, pinkish, with a well-defined ring.
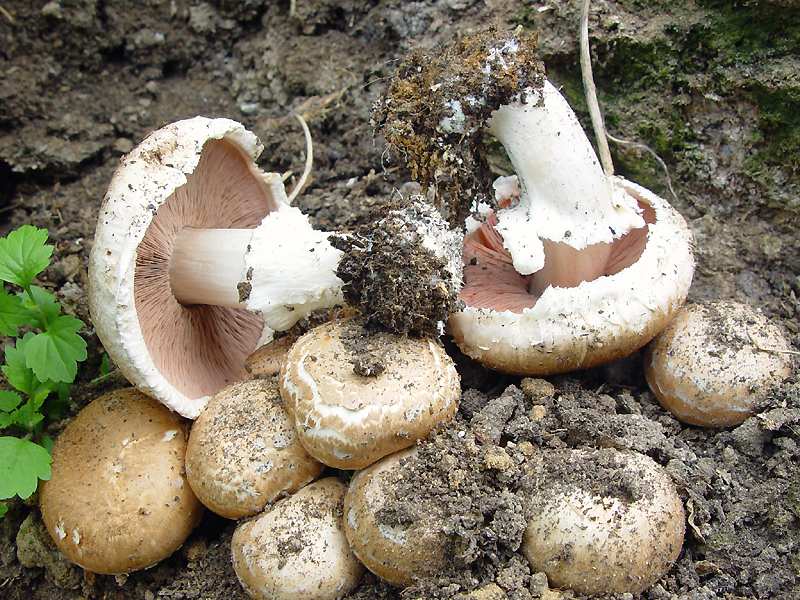


Champignon dark red
A. haemorrhoidarius is characterized by a convex or conical cap with a blunt apical part. At the ripening stage, the cap opens almost to a fully flat shape... The skin on the surface is brownish-brown, cracking into individual fibrous-type scales.
The pulp is white, with a thick red color on the cut. It has a not very pronounced mushroom or sour aroma, and also has a mild and pleasant taste. The stem is off-white in color, with a hollow interior and a scaly surface below the ring. At the base of the stem, there is a noticeable thickening immersed in the ground. A well-pronounced membranous ring. Free-type plates, often located, light pink in color.
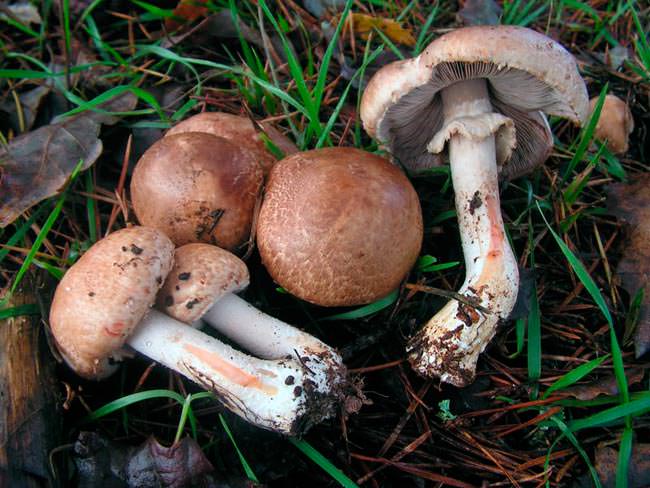


Mushroom chunky
A. spissicaulis is similar to the previous species and has a hemispherical, rapidly expanding to almost flat cap. The skin is whitish in color, with a smooth surface that is prone to cracking and the formation of brownish-yellow scales. The edges are folded down. The flesh is whitish in color, noticeably thick in the cap part. A grayish-red hue appears on the cut and there is a noticeable almond aroma... The leg is club-shaped. The plates are loose and relatively sparse, reddish or chocolate-blackish-brown in color.
Distribution and when to collect
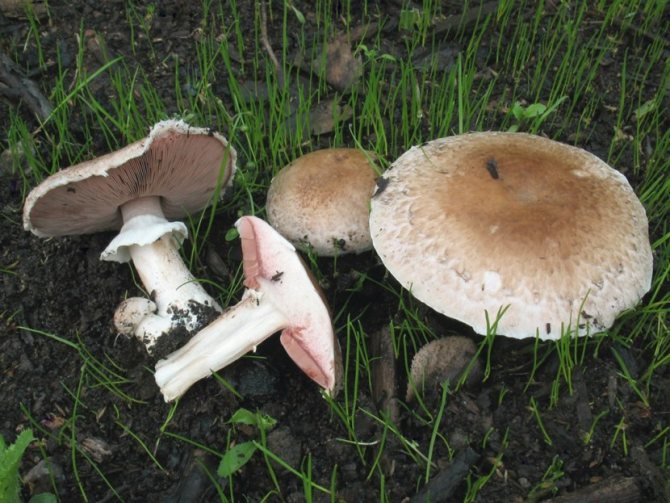
Field champignon is a saprotroph, and it grows on soils well fertilized with organic remains. He prefers to settle in areas free from trees, where there is a lot of grass - hence the name "field". Favorite growing places are forest clearings, roadsides along forest roads, parks, clearings, and sometimes pastures. Mushroom pickers find them both on the plains and in the mountains - most often where nettles grow. It is extremely rare to find it near trees - except perhaps under a spruce.


These mushrooms feel great both in the company of comrades and alone. Sometimes they grow in arcs or circles.
Common champignon is widespread throughout Russia, and also found in Europe, in the Caucasus. Often comes across mushroom pickers living in the northern temperate climatic zone. Mushrooms are harvested in May and continue until November, depending on the region.
Poisonous and dangerous champignon counterparts
There are several toxic species, as well as deadly and poisonous counterparts, which in their appearance resemble edible species.
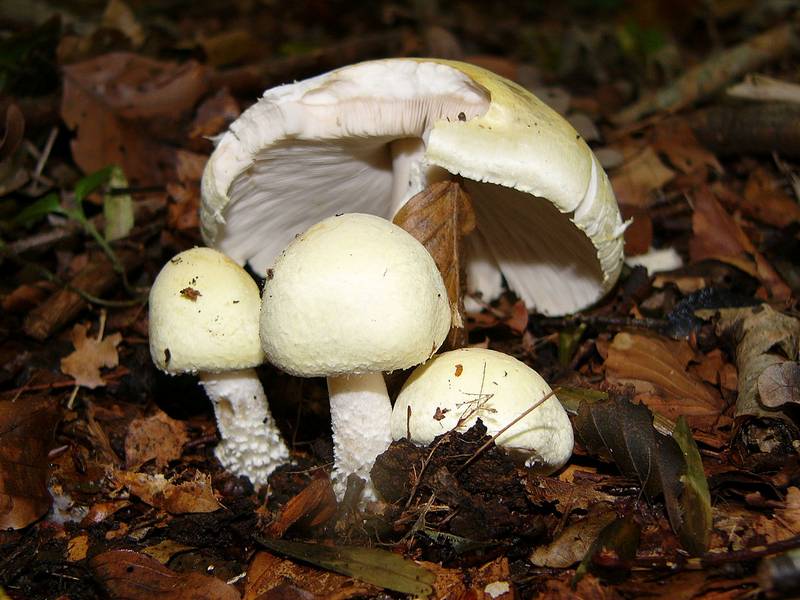
Yellow-skinned champignon
A. hanthodermus is a poisonous variety, widespread in nature. The external description is similar to the edible A. arvensis. It is characterized by bell-shaped, with edges slightly curved inward, fleshy, white or whitish-brown coloring in the upper part. The pulp becomes yellow in the process of pressing. The surface is smooth and dry, prone to cracking. A significant difference is the presence of an unpleasant phenolic or ink odor. The peduncle is hollow, distinctly white, with a noticeable swelling at the base.
Mushroom flat-lipped
A. Placomyce is one of the most poisonous species. The hat is conical, then convex and wide-convex in shape with a fairly flat central part and turned up edges.


The surface is white, covered with scales of gray or grayish-brown color. The central part has a very characteristic gray-brown coloration. The plates of the cap are loosely arranged, white, pink and chocolate brown. The pulp is white, with intense yellowing at the cut and the presence of a sharp ink or phenolic odor. The stem is cylindrical in shape, with a clavate thickening at the base.
California champignon
A. californicus is a poisonous variety characterized by a dry, whitish or brownish cap with a darker central part and a noticeable metallic sheen. The surface can be bare or covered with numerous scales.Hat margins on young specimens are turned inward. The flesh does not change color or is slightly darker at the cutas well as an unpleasant phenolic odor. The area of the leg is most often curved and has a characteristic membranous ring.


Interesting Facts
Champignons never release moisture when pressed. This type of mushroom is one of the most resilient. Such stalwarts are able to break through even a thick layer of asphalt pavement and concrete. The leg of the mushroom, or rather its pulp, is capable of changing color from simple contact with air.


When buying artificially grown mushrooms of this type, we should also pay attention to how the champignon looks like. The cap of the purchased mushroom should not be opened, and the plates should only have a light shade, otherwise, the mushrooms that you purchase are old. Overripe mushrooms lose most of their taste, moreover, the benefits of such mushrooms are practically nullified. It is best if the overlap between the cap and the leg remains intact. Shop mushrooms should have an even shade, without spots and blotches. Their skin should not have cracks or pits.
How to tell a false champignon
Pale toadstool, stinky fly agaric, as well as spring or white fly agaric in their appearance strongly resemble young edible champignons. Most often, inexperienced mushroom pickers confuse edible varieties with poisonous pale toadstool, therefore it is very important to know the main differences:
- has a fibrous surface and smooth edges;
- surface coloration ranges from whitish to pale, greenish-olive or grayish;
- young specimens have a hemispherical cap, and older ones have a spread or flat;
- the plates are always white and soft enough;
- at the base of the leg, there is always a pronounced bulbous thickening or the so-called clenched swelling;
- cut flesh does not change coloration;
- mushroom aroma is completely absent.
It is important to remember that false champignon or pale toadstool belongs to the category of deadly, poisonous species, and the mortality rate when eating such fruit bodies is 70% or more.


Description
The name of these mushrooms has French roots. In translation it sounds like this - "mushroom". What does champignon look like? It is impossible to give a more or less unambiguous answer to this question, since this species of representatives of the mushroom kingdom has a huge variety of varieties. Nevertheless, there are some distinctive features, in one way or another, characteristic of all owners of this French name.
If you ask the question seriously and study a large number of existing photos on the topic "What does champignons look like", then you will notice that the leg of these mushrooms is usually white, 3-10 centimeters long, although there are also higher specimens. Usually the leg is cylindrical in shape, in some cases expanding towards the bottom. This part of the mushroom is either whole or hollow inside. If the leg is broken, then white flesh will be visible at the fracture site, which sometimes, when pressed on it, acquires a different color, depending on the specific type of champignon (most often the color is yellow, reddish or brownish).
It must be remembered that all mushrooms of this species have a "skirt" on the stem, or a ring-shaped trace from it. Sometimes there are mushrooms with two rings. This identification mark can distinguish edible champignon from its inedible congeners, or from "doubles", which may be pale toadstools and some varieties of fly agaric.


Growing champignons in the garden
It is not too difficult to grow or breed edible mushrooms on your own in the garden, but before planting mushroom seeds or propagating fruit bodies with mycelium, you need to familiarize yourself with the technology of gardening mushroom growing. The main conditions for proper cultivation are presented:
- comfortable temperature range from 22 to 25 ° С;
- optimal humidity values within 85-95%;
- the presence of a gaseous environment and intensive ventilation with an influx of fresh air streams at different stages of growth and development;
- the correct chemical parameters of the substrate with a neutral or slightly alkaline medium at pH 7-7.5;
- almost complete absence of direct lighting and the presence of shading. If necessary, planting should be covered or shaded.
Planting mushrooms
The substrate was prepared and placed on shelves in the cellar. Now it's time to plant mushrooms - this is done with the help of mycelium, which is introduced into the substrate.


The mycelium itself is grown in laboratories under sterile conditions; it cannot be made at home, but you can buy it in a store or order it online.


For 1 m2 of substrate, 500 g of mycelium. It will be necessary to dig grooves 5 cm deep through every 20 cm, and fill the mycelium there.


Shiitake - appearance, composition, benefits and harms, mushroom cultivation + 72 photos- Talker - description of the species, distribution of the species, benefits and harms + 79 photos
- Gall mushroom - description of appearance, seasonality, taste + 69 photos


During the growth of the mycelium, before the mushrooms have appeared, a high humidity of 70-90% and a high temperature of +20 - +26 ° C must be maintained in the cellar. After twelve days, the substrate will need to be covered with a layer of peat and wait another 4-5 days.


After the end of the incubation period, the growth of the mushrooms themselves will begin, at this time it will be necessary to lower the temperature to +13 - +18 ° С. The growth of mushrooms occurs in waves, in turn.


The first wave will begin in 3-4 months, at which time the mushrooms will begin to grow very quickly, literally by the clock. The main thing is to keep track of them so that they do not overripe.


When harvesting from the first wave and subsequent ones, in order not to damage the mycelium, the mushrooms should not be cut off, but twisted.


How to distinguish champignon from pale toadstool (video)
With the formation of primary mass primordia of fruiting bodies, it is very important to gradually reduce the air temperature, within five days, to indicators of 14-16 ºС. The growing area must be regularly ventilated and sufficiently well ventilated. When the very first mushrooms appear, irrigation activities are carried out daily, but in a moderate mode. The average water consumption for each square meter of plantings should not exceed one and a half liters of water. Subject to the cultivation technology, the harvest of fruit bodies is formed in a wave-like mode for three or four months, with an interval of a week.
The collection is carried out at the stage of the maximum size of the aboveground part, at which the characteristic membrane under the cap should be fully preserved. In winter, it is necessary to pour snow on the roof, which will create a favorable temperature for growing inside the greenhouse space.
Evaluation of the taste of field champignon
it is an edible mushroom with excellent taste. Many connoisseurs of mushrooms prefer meadow champignon to all other types of champignons.
Dangerous resemblance
A large number of poisoning occurs due to the fact that people confuse field mushrooms with poisonous mushrooms. Most of all, the common champignon is similar to the crooked champignon, but the latter grows in spruce forests, and not in bright open areas, like its brother.


• White fly agaric looks like a young mushroom, especially for young specimens, whose plates have not yet had time to turn brown;
• Ginger champignon is a poisonous member of the family, and it resembles the real champignon, in addition, they grow in the same places. The nature of the toxic substances that make up the red champignon has not been established, but these mushrooms, 1.5 hours after consumption, cause severe diarrhea, vomiting, dizziness and headache. Such poisoning does not end in death, but they can seriously harm health;
• Yellow-skinned champignon is also a poisonous mushroom. This is a smaller species, these mushrooms are often found in the plantings of white acacia. They bear fruit from July to October. You can recognize a poisonous mushroom by the unpleasant "pharmacy" smell of carbolic acid. If the pulp is cracked, then it will quickly turn yellow.