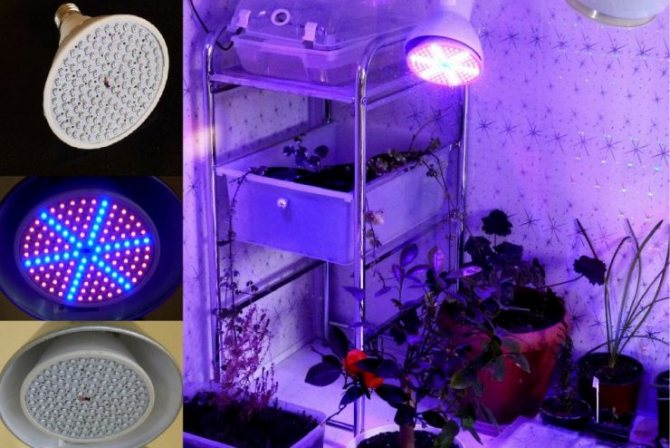
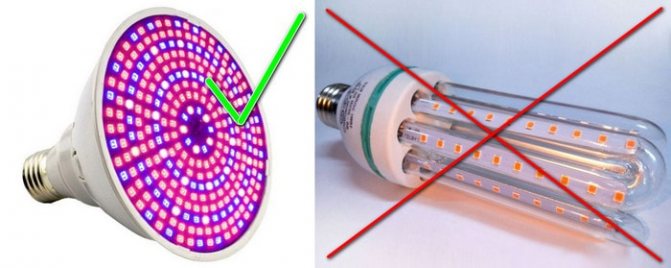
It is very important to choose the right bulbs for growing indoor, greenhouse and aquarium plants. If you make a mistake in the choice, further consequences can be disappointing: the seedlings (or algae) may simply not have enough light, which can halt their growth, or more serious problems - too bright lighting and the release of heat will burn the leaves, which will lead to the death of the plant world. In order not to have various kinds of trouble, you need to know which lamps for plants are better to choose, buy and use in the future. Below we will provide you with a comparison of all the most popular types of light sources: from incandescent bulbs to LEDs.
Lamps for lighting indoor flowers
Let's get acquainted with the main characteristics of lamps that are used for artificial lighting of indoor plants.
The most popular sources of additional lighting for indoor plants are
(picture 3):
- Incandescent lamps
they get very hot, but their light output is low, and the spectrum lacks blue waves, which are so necessary for the development of the body. Therefore, it is recommended to use such lamps in combination with fluorescent lamps or with sufficient natural light. - Fluorescent lamps
also called fluorescent lamps, although their spectrum is not absolutely ideal for plants. These lamps heat up slightly with high heat transfer and are in operation for a long time. - Phytolamps
are considered more effective. Their luminous flux carries waves of blue and red spectra, which, when mixed, give a pink tint. Such lighting activates the processes of photosynthesis and, accordingly, affects the growth rate of flowers. However, such light is often unpleasant for humans. - Discharge lamps
allow you to illuminate large areas, for example, greenhouses, winter gardens, greenhouses. They are not suitable for home use, as they have a very strong light output.
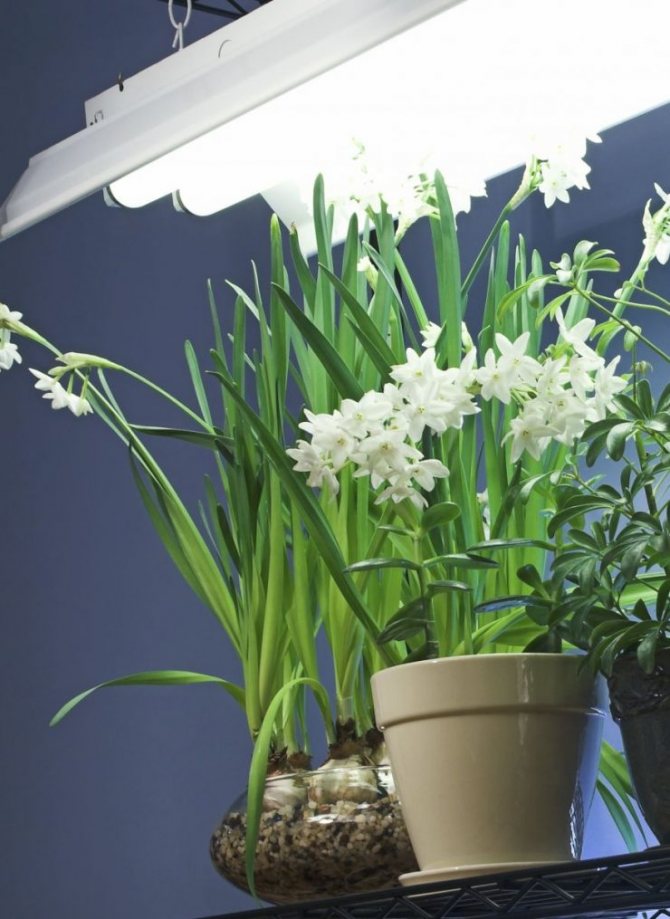
LED lamps have proven themselves quite well at home, in which you can combine the desired colors of the spectrum (for example, red and blue) to achieve the desired result. Such lamps do not heat up, they are economical and durable.
Features of using various lamps to illuminate plants are shown in the video.
How to choose a lamp
Having familiarized yourself with the technical characteristics of lighting devices, it is also necessary to know well what requirements for the intensity of illumination and its spectrum are imposed by the plant itself. Armed with the necessary baggage of knowledge, proceed to the selection of lamps.
Features of the
Immediately discard the idea of purchasing incandescent lamps, since they are absolutely not suitable for organizing artificial lighting of plants.
Stop your attention on more modern, and therefore more efficient and economical types. For example, fluorescent lamps are versatile
They can be used both at home and in a greenhouse, as well as in an aquarium. But special phytolamps are suitable only for seedlings and flowers.
Among the great variety of gas discharge lamps, the most advanced are metal halide lamps. They have high power, optimal radiation spectrum and long service life.The most effective, in terms of light output, are called high-pressure sodium lamps. A ceiling lamp made from such lamps can illuminate a large collection of indoor plants or a winter garden. However, they can only be used in non-residential premises. It is also recommended to combine the action of sodium lamps with the action of mercury or metal halide. An alternative can be modern LED lamps, the cost of which is quite high, however, it is justified by low consumption and a large resource.
Overview of existing bulbs
To make the information easier to perceive, we will simultaneously list all the existing types of lamps that are best suited for lighting and growing plants, and immediately talk about how rationally to use each option.

So, today, to illuminate the plant world in the house, you can choose and use such light sources as:
- Incandescent lamps. The cheapest and not recommended option for many reasons: they have a short service life, low light output (up to 17 lm / W) and significant heat generation. As a result, seedlings or indoor flowers in a pot will not receive the required amount of light, as a result of which this will negatively affect the growth rate and, accordingly, the correct cultivation. In addition, a light bulb that is too powerful can burn the leaves if it is placed next to the plant. Bottom line - this option in no case should be used at home, because it is best to choose more modern and efficient types of lamps, which we will talk about below.


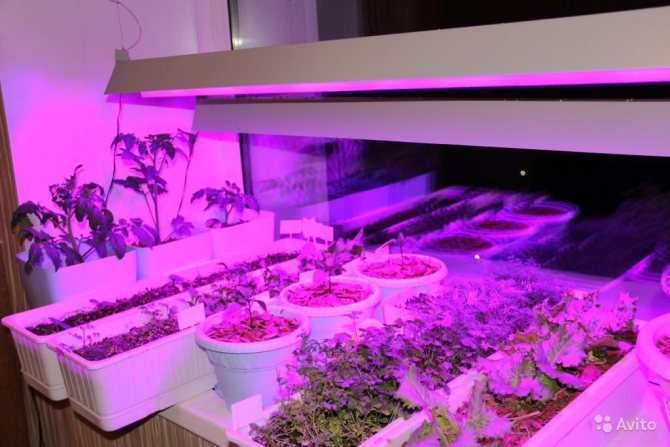
- Fluorescent (energy saving) lamps. It is much more advisable to choose this option and use it to illuminate vegetation in the house, greenhouse and directly in the aquarium. Energy efficient light sources have many advantages, such as high light output, low heat generation and economy, which makes them a good option for lighting indoor and aquarium plants. In addition, there are special fluorescent phytolamps that are intended only for growing seedlings and flowers.


- LED bulbs. LEDs are the youngest type of light bulbs, which in a short period of time managed to gain high interest in various fields of application. LED lamps are better for plants due to the fact that they consume a minimum amount of electricity, generate practically no heat, and besides, there can be different spectrum of light radiation, which allows you to choose suitable LED bulbs for your own type of plants in the house.


- Gas-charged (sodium, mercury, metal halide). It is necessary to dwell on this version of lighting products in more detail, because not all gas charging lamps are suitable for growing plants. Mercury lamps are among the worst options for plant growth in the home, greenhouse, and aquarium. This is due to the fact that DRL bulbs have a luminous flux almost 2 times less than sodium and metal halide light sources. In addition, the light spectrum of mercury products itself is not quite suitable for the development and further growth of seedlings, flowers, and algae. As for the sodium lamps - HPS, they glow brightly yellow-orange, which is very much in line with natural sunlight. Expert opinion - it is better to choose and use mercury bulbs for growing flower plants. Well, and the last option - metal halide lamps are the most expensive, but at the same time, the most suitable light sources for those representatives of the "green world" who prefer vegetative growth rather than flowering.


So we told you which lamps are suitable for lighting and growing indoor plants.We draw your attention to the fact that for the home, the most optimal options for price and efficiency will be CFL fluorescent lamps, which have a luminous efficiency of 80 to 100 Lm / W. If you can waste a little more, it is better to opt for LED plant bulbs, which still outperform the sodium bulbs previously used in greenhouses and greenhouses!
To learn more about which bulbs are best suited for growing seedlings (for example, tomatoes) or flowers, you can watch the video examples:
How to place indoor home flowers on a windowsill
How to place flowers on the windowsill in a way that doesn't resemble grandma's geranium design? The windowsill is a favorite place for houseplants. But don't place them in a line of scattered pots evenly spaced along their entire length. It is better to use one attractive specimen - low and curvy in the center, or tall and narrow if placed on one side.
The size should be appropriate for the environment - small and discreet plants on a large window will not add anything to improve the decor. Choose house flowers on the windowsill carefully - if the window faces east, south or west, you will need a variety that can withstand some direct sunlight. A window on the south side will need a screen to protect the house flowers on the windowsill from the hot summer sun.
What level of illumination do colors need?
The variety of forms and varieties of indoor plants involves the creation for each type of its own level of illumination, when organizing lighting with your own hands. Here you need to know the following points:
- for shade-tolerant indoor flowers, you should create an illumination level in the range from 1000 to 5000 lux. For some varieties, 700 - 1,000 lux will be enough;
- for light-loving people - from 10,000 lux.
You can measure the level of illumination in an apartment using a special device - a luxmeter. Moreover, if you want to achieve flowering in houseplants, then the illumination level should be as follows:
- for shade-loving plants - 1,000 - 2,000 lux. This group includes: Dieffenbachia, Anthurium, Dracaena, Monstera, Ficus, Spathiphyllum, Phalaenopsis, Fuchsia, etc.;
- for light-loving plants - 2,500 lux and above. For example, some exotic citrus fruits will bloom and form fruits at a light level of at least 8,000 - 9,000 lux.
After you figured out the level of illumination, you should decide on how you need a lamp. After all, the lamps that are used to illuminate indoor flowers can be very diverse. Moreover, you can not buy them, but do it yourself.
Benefits of LED plant lighting
There are a number of advantages to using LED lighting when growing plants at home:
- efficiency (such a lamp has a high efficiency - 96% and saves electricity in comparison with fluorescent lighting 3 times less, with incandescent lamps - 10 times);
- durability (the service life of such lamps reaches 100 thousand hours, which is equivalent to 10 years of continuous operation);
- safety (LED lamps do not contain mercury and other hazardous substances, there is no danger of fire or explosion if water gets in, they are almost impossible to break, since they do not contain glass and such lamps are resistant to voltage surges);
- does not require additional maintenance costs;
- heats up a little (the heating temperature fluctuates between 30-40 degrees, which means it does not have a negative effect on plants, excluding the risks of leaf burns);
- it is possible to install LEDs of different spectrum and power, which in turn ensures the full and rapid development of seedlings, regardless of the season;
- has a different variable spectrum (so to obtain blue, green, yellow or red colors, activating the growth and improving photosynthesis of plants, preventing the plants from getting sick, you should only replace it with a suitable diode in the device).
Types of phytolamps
We recommend reading our other articles
- Fertilizer for currants
- Biotlin insecticide
- Boreas insecticide
- Horse manure as fertilizer
There are several types of phytolamps. Each species has its own qualities, differences, nuances, which are important to know about even before purchasing and using.


Photo of a sodium gas discharge lamp (DNAT)
- Sodium Discharge Lamps (HPS)... These lamps are used for plants in greenhouses that specialize in growing seedlings and garden crops. They are basic (light spreads in all directions) and mirror-coated (directional light flow). Such phytolamps are economical, serve for a long time, work at temperatures of -60 ... + 40 degrees. At the same time, they have a yellow-green light, heat up quickly (in greenhouses this is unsafe), need special lamps, and do not reproduce colors well. The lamp warms up time up to 10 minutes. There are mercury vapors in the bulb, so disposal is difficult.
Important!
The phytolamp of the sodium gas-discharge type is not suitable for home use. It is only used in large, tall specialized greenhouses.
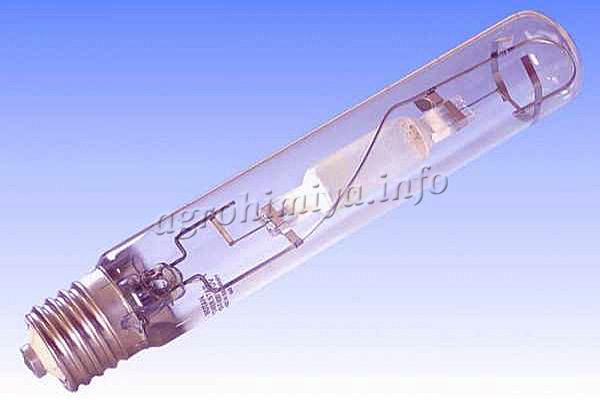


Photo of a metal halide lamp (MGL) for plants
- Metal halide (MGL) Is a kind of gas discharge lamp. The bulb of such a light bulb contains halogen vapors. They need a special luminaire with durable protective glass. Such lamps are among the most expensive, need a stable voltage, have a high pressure in the bulb (they can explode), and turn on at full power after 7 minutes. At the same time, metal halide lamps are distinguished by high luminous efficiency, give 2 years of luminescence (continuous). There are such lamps of different emission spectra, which makes it easier to use for plants.


Photo of a mercury gas-discharge phytolamp (DRLF)
- Mercury gas-discharge phytolamp (DRLF) can be used in any luminaire. It has a mirror coating, so the light is directed to a specific place. The light gives bright, consumes little energy, long service life. As for the main problems of this phytolamp, it is demanding on voltage, warming up for 3 minutes, color distortion.
Important!
If the mercury gas-discharge lamp goes out, it must be kept for 15-20 minutes before being switched on again.


Photo of a fluorescent phytolamp
- Fluorescent lamps Is also a kind of gas discharge lamps. They are used mainly in everyday life. Phytolamps of this type are chosen for plant illumination, those that have the desired spectrum of colors. The cost of these bulbs is low, they are economical, they come with a different spectrum of colors and do not particularly heat up during the glow (safe). As for the disadvantages, it must be borne in mind that such lamps have a low degree of luminescence, can tire the eyes (use in greenhouses is difficult), refuse to work at temperatures below +5 degrees.
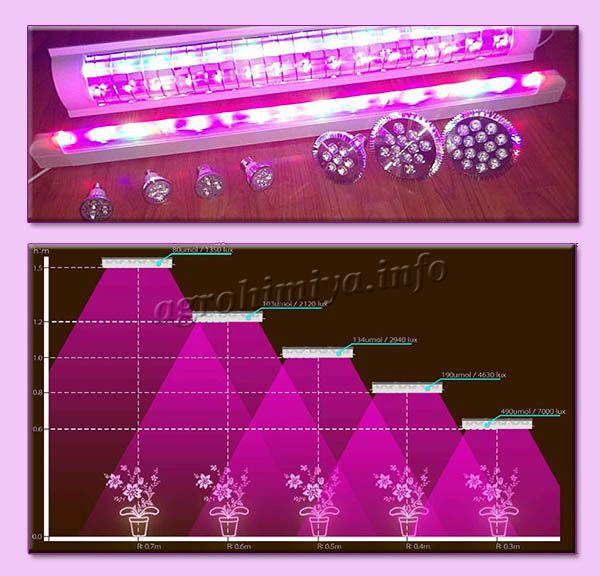

Photo of LED phytolamp for plants
- LED phytolamps have recently become available and are cheap. They come in different spectra of radiation, so when buying, you need to choose exactly those that are needed for plants (with the designation "phyto"). It is easy to work with such a lamp and to assemble the lamp; if you wish, you can arrange LEDs for any needs. Energy consumption is low, these lamps can work even at reduced voltage. The service life is long. Immediately after switching on, they can work at full power. The main disadvantage is that the duration of the LEDs depends on the quality of the crystals. In addition, it is impossible for them to heat up to more than +40 degrees.
As you can see, there are many types of phytolamps. They have significant differences, features of use, work. So when choosing it is worth weighing all the pros and cons.
Fluorescent tubes what to recommend to amateurs
Despite the wide variety of modern seedling lighting fixtures, fluorescent lamps and tubes are still popular. They have a fairly warm radiation, they do not overheat, which makes it possible to hang them at a short distance from the plant. Extruded tubes can be conveniently placed in the window opening on hooks and adjustable chains. The productivity of such lamps is high. They are capable of working up to 10,000 hours without reducing the luminous flux intensity.
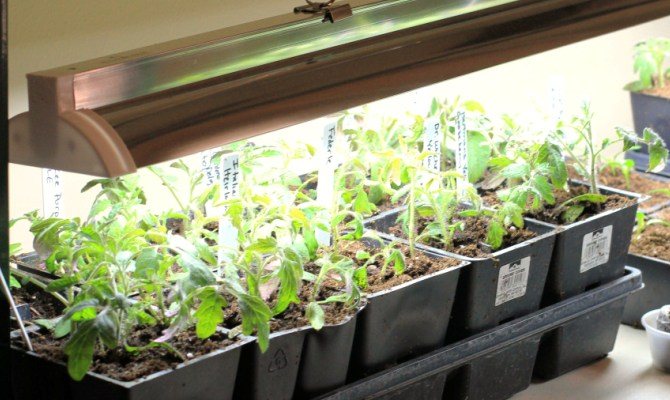


Seedling fluorescent lamps
The color temperature of fluorescent lamps may differ, and its indicator is always indicated on the packaging and indicated by the unit of measurement K (kelvin). The lower the value, the softer the light from the lamp. The yellow hue of the lamp is in the range from 2700 to 3000 K, cooler tons with a blue tint - 5000-6000 K. For seedlings, it is preferable to use fluorescent lamps, the color temperature of which is in the range of 4000-4500 K.
Among the ready-made options for illumination, we recommend a 3-harvest OZhZ lamp based on three fluorescent lamps. In addition to the luminaires, the kit includes stands and a panel where lamps are suspended and inserted. The lifting height is adjustable with built-in fasteners, which is very convenient. According to the manufacturers, such lamps provide illumination of 10,000-15,000 lux, thanks to which you can get strong and healthy seedlings even in the absence of the sun outside the window.
Requirements for phytolamps
The design of phyto-lamps and the distance from the phyto-lamp to the plants
Should allow them to adjust and correct the direction of illumination, as well as the distance to the plant. Ideally, the light should be directed from top to bottom, like the sun. The minimum distance to plants is 10 cm, the maximum is 25–45 cm.
If the distance from the plant to the lamp is doubled, then the light intensity will decrease by four times. Therefore, when installing, follow the manufacturer's recommendations.


phytolamps
How to organize lighting correctly
You are familiar with what kind of lamps for growing plants are, and you probably already know which version of light sources to choose for your own conditions. Now we will briefly tell you how best to organize the lighting so as not to harm the flora in the house.
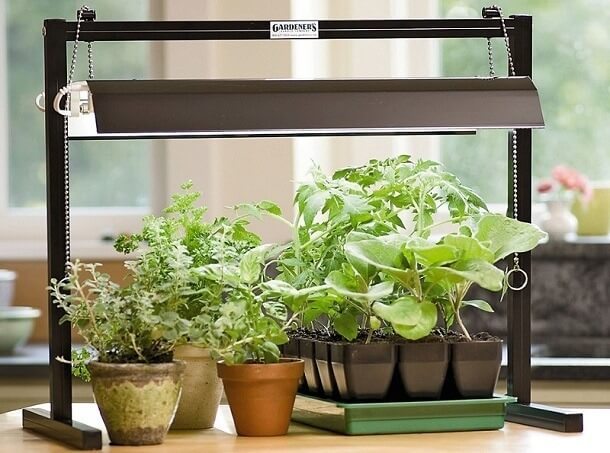


The first thing to consider is the height from the fixtures to the leaves. The minimum distance should be 15 cm if the plant is light-loving and 55 cm if shade-tolerant. In addition, the light should fall on flower pots or seedlings (or aquarium flora) strictly at right angles. Otherwise, the plants will reach for the light and take on an ugly shape.
Second, each specific species of flora requires its own specific light spectrum. Some flowers need a blue spectrum, some need a red one. First of all, you should ask florists or read on the Internet about the requirements for growing your favorite plant, and then choose the right lamps.
Third, if for some reason you did not find a light bulb with suitable light output and spectrum characteristics, you can organize combined lighting, for example, fluorescent lamps along with phytolamps, etc.
0 )
Lamps for plants are an opportunity to compensate for the lack of light, which is especially important in the autumn-winter period. After all, even if you put the plants on the south side of the house (which is far from always possible), the duration of natural daylight hours, especially in the northern regions, will be completely insufficient for the normal development of flowers or seedlings
For the full development of some plants, the duration of daylight hours must be at least 15 hours, otherwise the flowers begin to ache - flowering stops, growth slows down, leaves wither and turn yellow, which can lead to their complete death. Phytolamps, an artificial substitute for the sun, prolonging the daylight hours, create optimal conditions for growing pets.
In industrial conditions phytolamps often completely replace natural light - by adjusting the lighting mode (as well as adjusting climatic conditions), you can control the process of development and maturation of plants as accurately as possible.
How to choose a phytolamp for plants
The above describes what types of phytolamps exist. But how do you choose the most appropriate option? In the store and in the market, sellers can guide the buyer, tell about the characteristics of the product, its features of use. But, in order to choose a good phytolamp, you need to know what to look for when studying the characteristics of a future purchase.
The first step is to decide for what purposes the phytolamp is purchased and where it will be used. There are appliances that are recommended for the home, they are easy to install simply on the windowsill, and there are those that are installed exclusively in greenhouses with high ceilings! You also need to take into account how long the lamp is needed (continuous operation time), the period of operation (by days, months). After that, you can pay attention to the characteristics of the lamps:
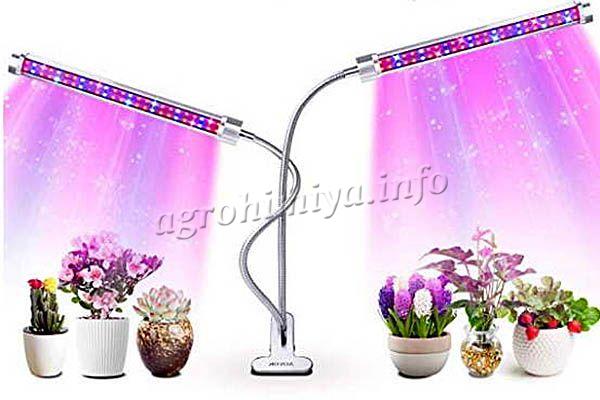


How to choose a phytolamp for plants
- profitability;
- demanding voltage (there are lamps for which power outages are unacceptable).
And finally, the spectrum required for plants is selected.
Important!
The quality of the material from which the phytolamp for plants is made is not the last criterion when choosing. If any parts of the lamp or phytolamp are made of cheap, low-quality material and this is noticeable even with the naked eye, then it will not work for a long time, especially in a greenhouse.
Air humidity, feeding and watering are important indicators for plants
The optimum moisture content for indoor plants is 45-60%. However, in winter, when batteries and air conditioners are constantly running, the air becomes drier, as a result of which the humidity drops to a maximum of 20%. If you do not want the flowers in your home to dry out during the winter, you can purchase a special humidifier.
You can also use the "old-fashioned" method, for example, you can spray pots with plants every day or use pallets with wet pebbles or expanded clay.
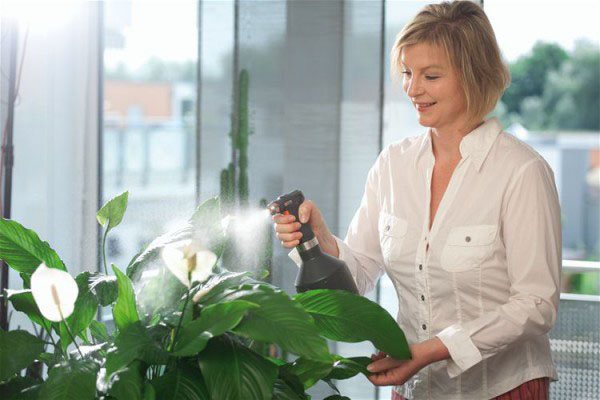


Remember to keep the flowers away from the batteries, otherwise you might just burn the petals. Despite regular spraying, you should remember that in the winter season the plants need to be watered less than in the summer - this is done only when necessary. Do not forget to loosen the ground at the same time as watering, giving the root system air. There are plants that do not need watering at all in the winter season - these include succulents and cacti.


It is also important to remember about feeding. Whatever fertilizer you use, in the period from December to March, their amount must be reduced to once a month.
If you strongly "feed" your "green pets" with fertilizers, it will have the opposite effect, because your flower can shed all the foliage, and eventually die.
General rules and important nuances when supplementing seedlings
Lighting for seedlings will give the desired effect only if everything is organized correctly. Otherwise, the lamps will be more harm than good:
- To see if the seedlings have enough light, watch the stems. If they become thinner and stretched, then there is not enough. Add more lamps.
- It's also easy to check if the seedlings are too hot. Place your palm directly over the leaves.If you feel warmth coming from the lamps, you need to raise them higher.
- The seedlings will signal that it is time to turn off the lamps themselves - by the evening their leaves rise and close a little. Only non-germinated seeds are illuminated around the clock during the first 3-4 days.
- If you are in doubt whether you need additional lighting during the day, turn on the lamps. When the light level changes noticeably, it is clearly needed. If there is no visible difference, turn them off.
- The most common mistake is to think that seedlings do not need additional lighting on the southern or eastern windowsill. It is necessary at least in the morning and evening hours, on cloudy days.
- Until the emergence of shoots, place the lamps 10–12 cm above the containers and strictly vertically. Then - raise it to a height of 40-60 cm and turn it at an angle of about 60 °. It is advisable to immediately make or purchase height-adjustable brackets and / or lamps on hooks in order to be able to change the height of their location without any problems.
- Once the seedlings have been cut open, reduce the light intensity by 2-3 days to allow the plants to recover.
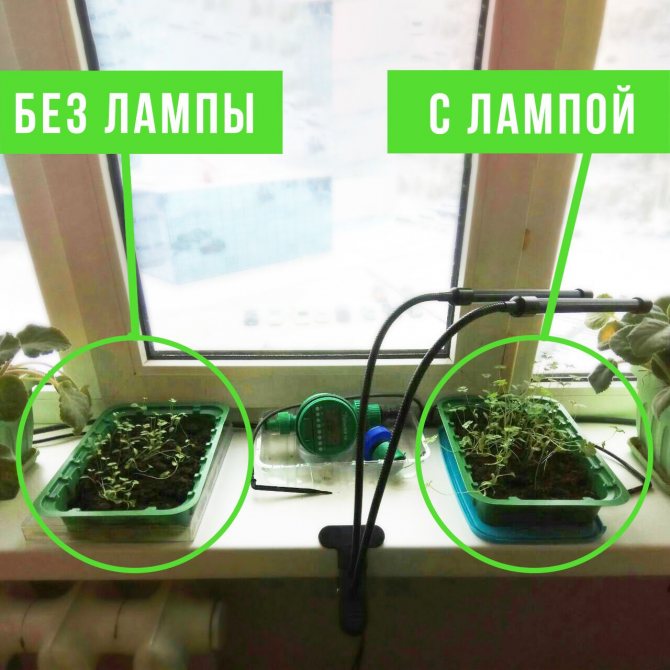


The photo clearly demonstrates how effective additional illumination is with the correct use of lamps.
Light is how important it is for plants
Light is an important component of plant life, because a plant (more precisely, its dry mass) consists of 45% carbon obtained from the air. At the same time, the process of assimilation of carbon - photosynthesis, occurs only with the participation of light, the intensity of photosynthesis is influenced by many external factors, but the main one is still the intensity of light.
First of all, young plants and shoots suffer from a lack of illumination - their leaf plates become pale, unsaturated, and their size becomes smaller. Their stem and internodes stretch out, and the plant itself bends / stretches towards the light source. In addition, there are other signs (Fig. 1):
- plant growth slows down
- the formation of new buds stops, old flowers gradually die off, with a large deficit of light, flowering can stop completely
- in variegated species, their decorative color is lost, they become monotonous green
- the lower leaves dry up and fall
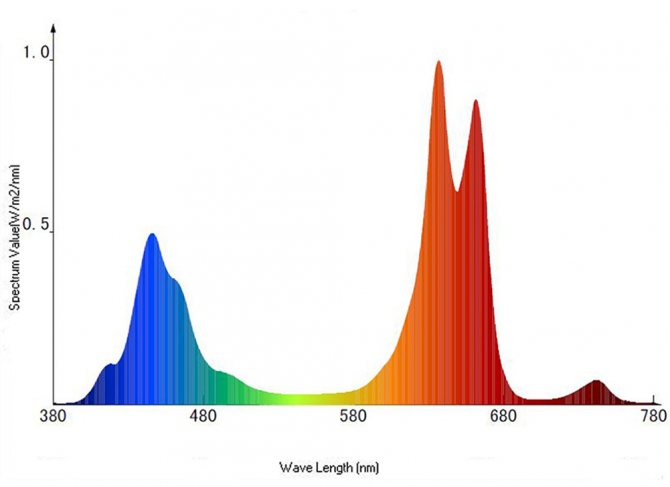
However, it is not entirely correct to say "light" - flora perceives spectral components differently:
red (wavelength from 600 to 720 nm) and orange (from 595 to 620 nm) are the most important and necessary radiation ranges for a plant, they supply the energy that is necessary for photosynthesis
In addition, they affect the speed of plant development, for example, an overabundance of orange and red rays allows you to delay the transition to flowering, which is important if, for example, forcing bulbs by a certain date purple and blue (range 380-490 nm) - also are directly involved in photosynthesis. They are needed, first of all, for the formation of protein, and also affect the growth of the plant.
Plants that naturally grow in a short day, when grown at home, bloom faster precisely under the influence of the violet-blue part of the spectrum, ultraviolet rays (spectrum 315-380 nm) do not allow plants to "stretch", and are necessary for the synthesis of some vitamins. Other rays of this range (wavelength 280-315 nm) help to increase the cold resistance of plants; waves of green (490-565 nm) and yellow (565-595 nm) are not equally important for plant development.
That is why, when organizing supplementary lighting or artificial lighting of plants, it is necessary to take into account their needs only in a certain part of the spectrum.
Signs of a lack of light and how to create backlighting
For indoor plants, with a lack of illumination, certain changes are characteristic, which appear in the following:
- for indoor flowers, the color of the leaf plate changes. It loses its brightness, acquires pallor;
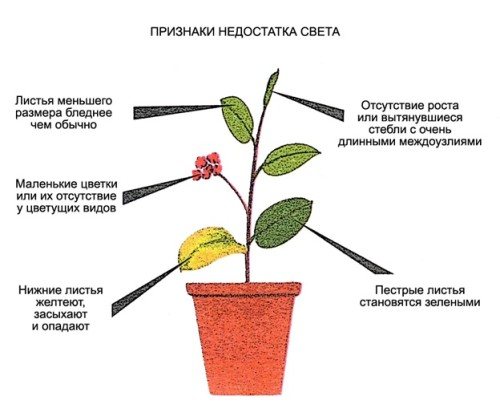

Signs of a lack of light in plants
- the leaves themselves become small and may even fall off;
- the lower leaves begin to turn yellow. If the situation does not change, the entire plant may lose its leaves and die;
- pulling out a shoot that seeks to find a more illuminated place in the house. Elongation of internodes can be up to 2-3 times;
- lack of flowering period. This parameter is typical only for flowering varieties.
Pay attention! The above signs of a lack of light are typical for all indoor flowers.
If you find the above parameters of ailment in home flowers, you need to organize additional artificial lighting for them with your own hands. And here you should be very careful, since many novice growers believe that the more light, the better. But this is a delusion, because of which more than one indoor flower has already died. To properly organize the lighting of indoor plants, the following parameters should be taken into account:
- flower variety (light-loving or shade-loving);
- what level of illumination is required for it, according to its biological characteristics;
Note! The peculiarities of growing a particular indoor flower can be found in an encyclopedia or the Internet.
- the duration of the light mode for each specific case. For many flowers, the light regime has a direct effect on the flowering period (for example, flowering Kalanchoe varieties). Therefore, if you want to get a bright and colorful window sill, this parameter must be observed without even the slightest deviation;
- season. Most often, additional lighting is needed in winter. This must be taken into account when choosing a luminaire for a permanent or periodic work pattern;
- what luminaires should be used (LED, fluorescent, etc.).


Luminaires for illuminating flowers
Note! It is important to create the correct artificial day and night for the plants.
Only by taking into account these selection parameters, you can choose an adequate lighting option for your indoor plants and organize everything with your own hands.
The simplest backlight
Today, gardeners prefer to make phyto-lamps on their own: firstly, this is a significant savings for the family budget, and secondly, having studied the characteristics of various artificial light sources, you can choose the most useful combination.
You can place seedlings of tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, potatoes, leeks, cabbage, zucchini, and strawberries on a self-made rack.
Sunlight, falling on the foil, is refracted and reflects on the seedlings. This method is economical and simple, but absolutely useless in cloudy weather. Foil by itself will not provide illumination for plants.
Types of indoor decorative lights
Decorative lighting for indoor plants can be different both in the nature of the impact on their perception, and in the effect on the surrounding space.
There are three types of lighting for indoor plants:
- directional illumination;
- simple, or bottom lighting;
- backlighting.
Directional illumination
This type of decorative lighting involves placing an additional light source above an indoor plant or a group of crops to emphasize the decorative qualities of the plants and create a special atmosphere.
It enhances the feeling of using carefully selected and thoughtful landscaping products. Directional light enhances the integrity of the collections, distinguishes them from the general background, unites them, and for individual plants it allows them to move from the rank of a background gardener to one of the main decorations of the room. In fact, overhead decorative lighting can equate a plant to a work of art.
Simple, or bottom lighting
Illuminated light frame opposite to directional illumination is a decorative technique that involves placing an additional light source below, under the plant, composition or in front of them. Such illumination does not so much unite the plants into one group or highlight them from the background, but highlight individual details and create a play of shadows on the walls and in niches, allowing you to perceive the space and secluded atmosphere in a different way.
Backlighting
This type of lighting involves placing a light source behind the plant, usually from below. The backlighting creates the impression of a clear, catchy, contrasting silhouette.
Manifesting lines and play of contours, backlighting neutralizes the influence of color and allows you to create a special atmosphere that is associated with modern minimalism, revealing the value and beauty of exotics or filling the interior with a special mysterious charm, drama or intimacy. Backlighting "works" only with large, salty plants with expressive lines.


Directional decorative lighting of plants
Installing the lighting fixture
Placement of the lamp above the pot
Another important consideration for illuminating indoor flora is the correct placement of the light source. One rule applies here: with an increase in the distance from the lamp to the pot by 2 times, the intensity of the luminous flux and its effect on the plant will decrease by 4 times.
The selection of the distance can be done experimentally:
- when burn marks appear on the sheet plate, the lamp is pushed back;
- when the shoots are lengthened, the lamp is brought closer.
These manipulations are done until the optimal effect is achieved. Having found the optimal distance, it is not recommended to move the pot and the lamp, so as not to knock down the "settings".
How to make artificial lighting for indoor plants
It is well known that the level of illumination plays perhaps the most important role in growing flowers. After all, the processes of photosynthesis, which provide them with energy, occur exclusively in the light. At the same time, some species need bright light, others feel good in partial shade, and some generally prefer to stay in the shade.


Here artificial lighting comes to the rescue of a lover of home flowers, which is the easiest and most affordable way to provide the required amount of light, if not enough comes from a natural source (Figure 1). Proper placement of artificial light sources allows you to grow fresh flowers in almost every corner of your home.
Why do you need to light plants
To understand the need for artificial lighting, you need to know that under the influence of sunlight in the green parts of crops (leaves, stems), photosynthesis processes take place, as a result of which the energy necessary for the growth and development of living organisms is released (Figure 2).
In addition, it would be nice to know in what conditions this species grows in nature. For example, representatives of the tropics and subtropics are accustomed to short daylight hours, while those from the temperate zone are accustomed to long ones. For this reason, the former must be shaded in the summer and highlighted in the winter.


The highlighting procedure can be carried out both in the morning and in the evening. At the same time, it is desirable that the dawn and dusk of home flowers are experienced in natural light. The total duration of artificial lighting should be within 12-14 hours a day, since green crops also need rest.
How much light do indoor plants need
Very often, when organizing artificial lighting, the question arises about the amount of additional light. A special device - a luxmeter, which measures the illumination level, will help to answer this question. So, for shade-loving varieties (poinsettia, begonias, ivy, calathea, arrowroot), illumination at a level of 700 - 1000 lux will be sufficient.At the same time, the lower limit of this indicator guarantees only the maintenance of the vital activity of the flower, therefore, to obtain flowering, the values must increase.
Shade-tolerant species, such as dieffenbachia, monstera, dracaena, ficus, fuchsia, prefer bright diffused light, but they can feel quite comfortable in the shade. Therefore, the additional illumination level for them is from 1000 to 2000 lux. But to ensure the normal functioning of light-loving varieties (pelargonium, roses, cacti, hibiscus), an illumination of 2.5 thousand lux will be needed, which must be increased to start budding and subsequent flowering up to 5000 lux. Indoor citrus fruits require a high level of illumination, which can form ovaries only at 8-9 thousand lux.
You can find more information about artificial lighting in the video.
Light source specifications
All light sources, both natural and artificial, emit energy, the magnitude of which is determined by wavelength. In this case, one source of energy can emit waves of different lengths. Their total number forms a spectrum, the indicators of which range from 300 to 2,500 nanometers.
Therefore, when choosing a source of artificial lighting, you should pay attention to its technical characteristics, since an incorrect choice can lead to a negative result.
You should be aware that deciduous and flowering varieties need different spectra of lighting, therefore, the lighting devices for them should be different. So, in order to stimulate the growth of green mass, blue-violet light is used, and for rapid germination of seeds and growth of shoots, red is needed. The spectrum of daylight is optimal for all, without exception, species. This spectrum is possessed by fluorescent lamps.
Reviews of gardeners and gardeners about phytolamps
Phyto lamps are used by gardeners and gardeners all over the world. Below are the reviews of people who use them to grow flowers or garden crops.
- Varya Plotnikova: “I have heard about phytolamps for several years, but I always thought that it was just an advertisement, no more so that people would buy more expensive lamps. But last year, a friend bought herself a new phytolamp for tropical flowers, and gave me the old one for testing. I grew simple garden seedlings under it. And to be honest, the result impressed me! Usually, I used growth stimulants and fertilizers to get persistent, strong stems. But this was not required with the phytolamp. The plants grew strong, did not fall, even though I overexposed them in the container and transplanted them to the garden too late! So now I will use it annually! "
https://youtu.be/fAsBZNFutK8 - Ekaterina Glezer: “I collected the phytolamp for my flowers myself. I bought everything I needed for an LED lamp and did it myself. It is not difficult, as it turned out, and the price is cheaper than buying a ready-made lamp. I turn it on for 2-3 hours after sunset so that the flowers have enough light in winter. Under such a lamp, they grow much better, the leaves do not fall off, as before, and the Decembrist released flower stalks for the first time in 3 years! "
- Alexander Kanev: “2 years ago I was choosing a phytolamp for one of my greenhouses. Opted for MGL. A phytolamp for plants of this type is certainly expensive, but it serves for a long time and does not spoil the eyes when working in a greenhouse. The installation did not take much time, the light is directional, the power is good. In comparison with conventional lighting, I noted a faster growth of greens (for lettuce, onions), besides, electricity consumption decreased, which is pleasantly pleasing. So I will change lamps in other greenhouses as well. ”
Useful Tips
Having taken care of creating additional lighting for plants, it is necessary to consider both their needs and the place where they are located. All factors related to lighting are difficult to take into account.Even dust on the window can reduce the amount of incoming light. Here are some more tips:
- Light-colored curtains and drapes behind the plants on the windowsill can act as reflectors, while the tulle curtains on the windows in front of the flowers reduce the intensity of the sun's rays.
- Phyto-luminaires with reflectors are very effective. LED shop lights are most often a combination of blue and red. This has a positive effect on the condition of flowers, but is unpleasant for the eyes, and UV lamps are harmful to vision.
- When creating artificial lighting, you must adhere to a certain regime. It is recommended to turn on the backlight at 7-8 am and off by 8 pm.
Led phytolamps for illumination
LED plant lamps can be used for greenhouse and indoor lighting. The light spectrum (red, orange, blue) is selected depending on the stage of seedling development. The most modern LED bulbs combine several colors of the spectrum, are economical in energy consumption, and emit little heat.


The main difference from other lighting devices is that the led light bulb is a semiconductor device without a filament and a bulb with gas. The electricity used is converted into a luminous flux without generating heat. Therefore, led phytolamps are considered the most progressive. Safety for flora and humans is ensured by the absence of the infrared and ultraviolet part of the spectrum.
Various LEDs can be placed in the led lamp, choosing them depending on the stage of development of the seedlings, which allows you to get both lamps for greenhouses and for lighting in rooms. Consumers believe that the only drawback of these devices is the relatively high cost.
Lighting for indoor plants in winter
In winter, almost all indoor plants lack natural lighting due to the short duration of daylight hours. Therefore, many species lose their decorative effect and stop growing.


To preserve the attractive appearance of plants in winter, it is imperative to organize additional lighting (Figure 5). In this case, it is necessary to increase not only the intensity of illumination, but also the duration of daylight hours. Here are some useful tips on how to do this correctly and effectively.
Features of the
Conventional mirrors can help slightly increase the intensity of artificial light. To do this, they are installed on the side slopes of the windows, thus contributing to additional reflection of sunlight. Also, to increase the efficiency of additional lighting, reflectors are installed (foil, white glossy fabric, reflectors for lamps). At the same time, they are positioned so that they reflect light in the direction of indoor flowers.
Do not forget to monitor the cleanliness of the window surface and reflective surfaces, regularly clean them from dust and dirt, because even the thinnest layer of dust significantly reduces the level of illumination. You should know that indoor plants, like all living organisms, have their own biorhythms, which are not recommended to be broken. Therefore, increasing the length of daylight hours, it is necessary to ensure that the additional illumination procedures are carried out regularly and at the same time.
Additional lighting of indoor plants is a guarantee of their full growth and development. Light is the energy that is vital to support the natural process of photosynthesis. Consider the rules for choosing a lamp for a flower.
In the summer, the green inhabitants of the apartments receive it unilaterally from the window through which the sun's rays break through. With the advent of cold weather, they are in constant semi-darkness, spend extra energy, do not bloom, grow poorly.
The situation can be remedied by creating artificial lighting.
To choose a full replacing the sun's rays
, you should know that light has two characteristics - spectrum and light power. It is necessary to correctly select these parameters, taking into account the stages of development of the indoor plant.
Seedlings are easier to grow with the right lighting
Young seedlings especially need additional light. It affects cell division, elongation and formation.
For germination of seeds, growth of seedlings, more blue spectrum is needed. Only he can provide active photosynthesis and, accordingly, active growth. The power of the device at this stage can be low - up to 200 watts.
With the red spectrum shoots are getting stronger
, flowering intensifies. But each spectrum cannot be considered separately. Chlorophyll, influenced by different parts of the spectrum, absorbs light, transforming energy.
Therefore, artificial lighting must match the spectrum of daylight.
Why seedlings need lighting
Most gardeners begin planting seeds for seedlings in February or March. Light days at this time of the year are short, and seedlings of different cultures need 10-16 hours of light per day for harmonious development. With its deficiency, the seedlings stretch out strongly, the leaves turn pale and wither, after planting in the ground, the plants either do not take root at all, or they adapt to the new habitat for a long time. And on the contrary, those specimens that had enough light turn out to be powerful, hardy to the vagaries of the weather, they are characterized by a more developed root system, better resistance to diseases and pest attacks and, as a consequence of all this, increased productivity.


It is impossible to grow high-quality seedlings without good lighting, there is not enough sunlight at the end of winter and at the beginning of spring
Decorative lighting in interior landscaping
Techniques and means in the organization of interior lighting have developed very successfully in recent years. Spot, strip and background, illuminating and classic, color and dramatic, playing with the perception of space, lamps and lamps allow you to control both the functional side and the decorative role of light in the furnishings of rooms.
The expansion of the range of modern methods and ways of using light could not but affect one of the most important elements of interior design - gardening. Indeed, in a favorable light, you can present not only furniture and decor, but also your favorite plants.
Decorative lighting for indoor plants is called all decorative techniques aimed at representing the special role of a plant in the interior with the help of an additional light source located nearby.
Decorative lighting has two main functions:
- creates an atmosphere, sets style and special mood in the room;
- reveals, emphasizes or enhances the beauty of the plant and its most decorative features - leaves, flowers, inflorescences, shoot lines.
What plants are decorative lighting used for
But decorative lighting is not appropriate for all plants. Most often it is used for plants placed one at a time, solo, but sometimes it is also used for groups, creating a special atmosphere of integrity of the created composition.
Decorative lighting is a technique for enhancing or revealing the beauty of the most valuable indoor crops, exotic plants, large-sized plants, shrubs and trees or rare blooming stars.
Usually, with the help of backlighting, they emphasize the beauty of modern plants, which can boast of original texture, lines, laconic expressiveness or their graphic details. Backlighting affects the perception of the lines of branches or large leaves and silhouette most of all, so it is more appropriate to use it for plants with really beautiful outlines.