Many people mistakenly believe that thorny and inaccessible plants called cacti came to us from arid and hot Africa. In fact, everything is completely different, but the cactus, nevertheless, is not at all in vain associated with the desert, stony and lifeless soil and the scorching sun. It is these parallels, drawn by the consciousness of those who are just undertaking to breed these Martian, alien plants, that prevent them from correctly reasoning and drawing correct conclusions, which gives rise to a huge number of errors and delusions. So which continent can be called the homeland of cacti and why are they so interesting that they attracted the attention of many people? This is what we will talk about today in our article.
Classification of cacti
These plants are divided into four subfamilies: Pereskievye, Opuntia, Mauhyeny and Cactus. They differ not only in external data, but also in a number of other features.


The Pereskievs are an evolutionary link connecting cacti and deciduous plants. This is a genus of shrubs with non-succulent stems and full leaves. Opuntia have reduced leaves, succulent stems and special thorns - glochidia. These are small and very fragile spines, hard and sharp with serrated notches. They grow in bunches, getting into the stomach of animals, causing irritation. The whole subfamily has a similar seed structure and flower shape.
The habitat of the cactus subfamily Mauhyeny is mainly Patagonia. Plants look like Opuntia in appearance, but without glochidia. They have conical leaves and pronounced succulence. Cactaceae unite the remaining genus of this plant. They have no leaves at all, except for small shoots on the trunk. There are no glochidia either. This subspecies includes epiphytic plants and numerous xerophytes.
How different are they?
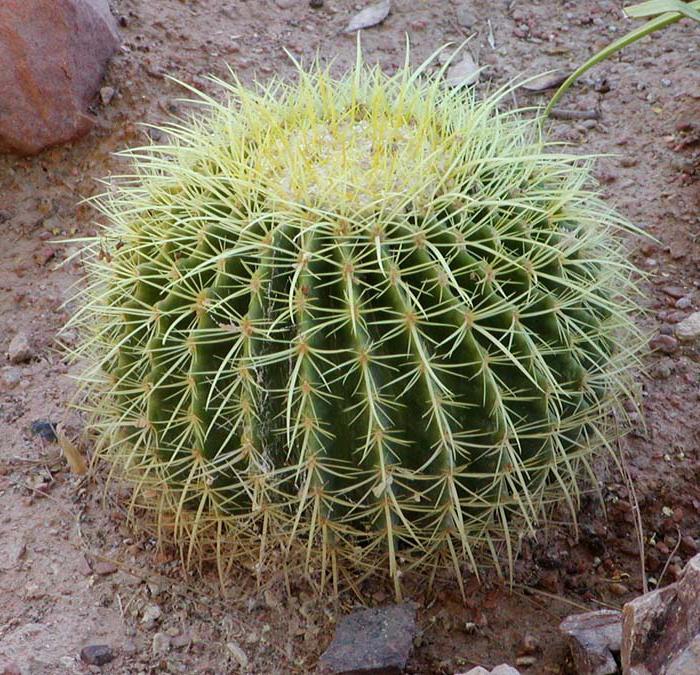
First of all, it is worthwhile to understand that all cacti, without exception, belong to succulent plants (plants in which, as a result of growing in arid regions, the mechanism of water accumulation in special tissues has evolved).
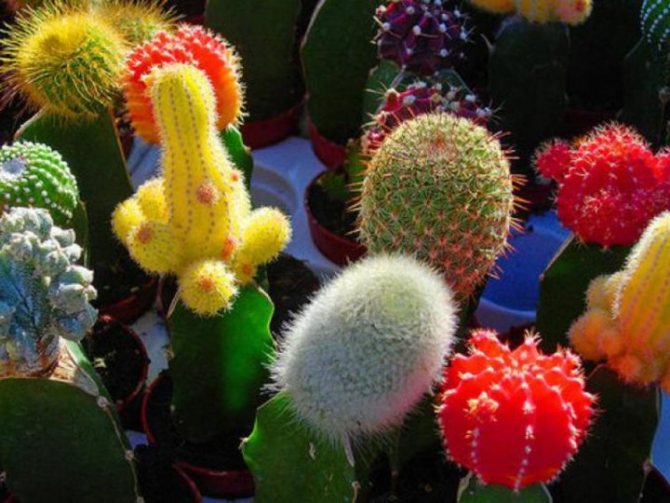


Cactus
A plant so inconspicuous in the eyes of some people, as we have already found out, has many types - most of us are unaware of all the diversity. Simply put, cacti can be roughly divided into 4 groups:
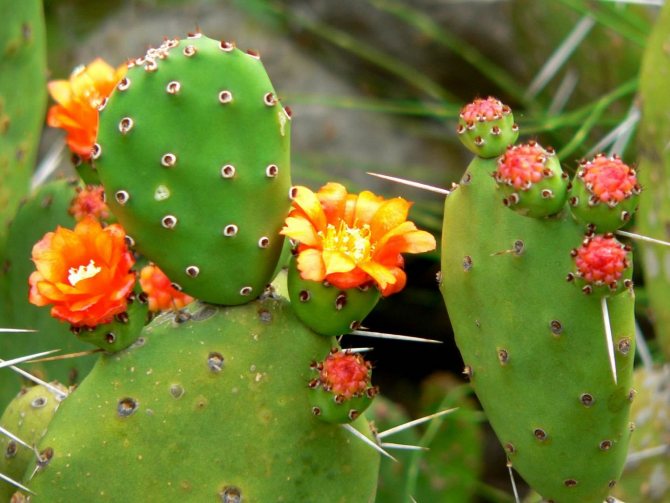
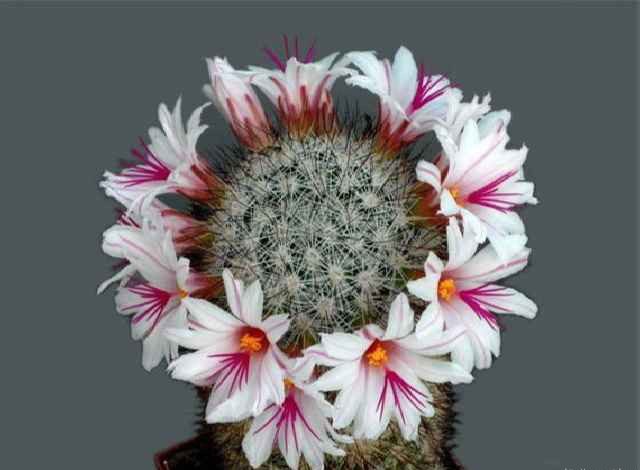
- Cactus... Directly that group that people have in mind when they pronounce the name of the species. It includes almost all types of true cacti, the appearance of which is stereotypically assigned to the plant - a round or cylindrical shape, large bright flowers on a kind of "tube". This subfamily has no leaves at all. There is a common misconception that the thorns, of which a cactus often has a huge variety, and there are only modified leaves of it (as with needles in conifers). But with cactus, everything is different - there the thorns are modified kidney scales. It is this subfamily that is famous for its excellent flowering, but cacti rarely bloom - once a year, perhaps 2. It all depends on the species, of course, but any cactus plant can usually be made to bloom by stress or an impromptu "drought" - the cactus is in a hurry to multiply in response to unfavorable conditions and eventually blooms. This subfamily also includes the genus of cacti, which is hard to imagine - Rhipsalis comes straight from Brazil, a thornless cactus.The genus belongs to forest cacti, has more than 60 species and is very popular due to its excellent flowering and "creeping" form.
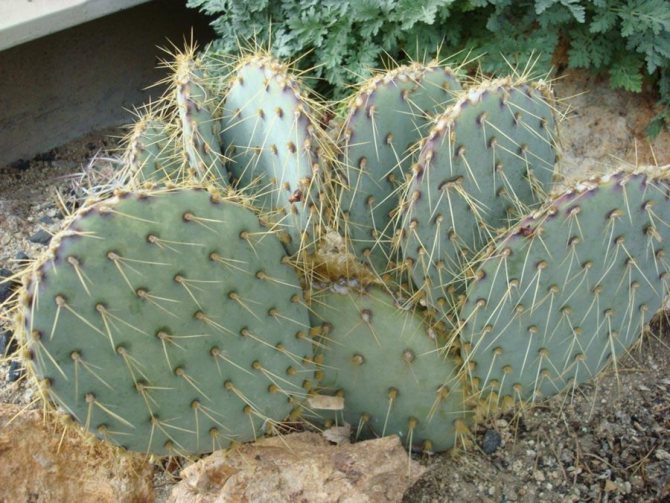
- Opuntia... It is also a very common type - it is used for food and as a decoration. It was brought by man to all continents and is densely settled in human life. It has reduced leaves and special thorns with tiny jagged hooks that easily dig into human fingers or animal fur (this is how the cactus reproduces - the animal transfers its parts to itself). The thorns can be easily broken off from the rest of the cactus to make the task easier.
Cacti "on the border"
- Pereskievye... Amazing cacti with leaves, a kind of transitional link between cactus and other plants. Despite the green and sometimes purple leaves they have, they also have thorns - in the axils. Usually in bunches, sometimes one by one, they are needed by pereskivs to cling to trees - their natural habitat.
- Mauhyeny... These adorable little cacti are considered very rare and form shoots with small leaves. It is not easy to grow such in captivity, but they are frost-resistant and grow quietly in the fresh air for several years.


Pereskia prickly
It is not difficult to understand why people are so interested in these perennial plants: they are surprisingly diverse and suitable for growing in almost any conditions, greenhouse or home.
Distribution area
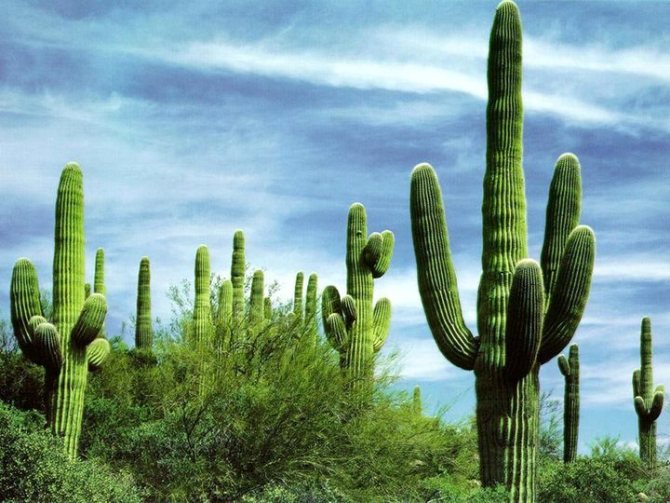
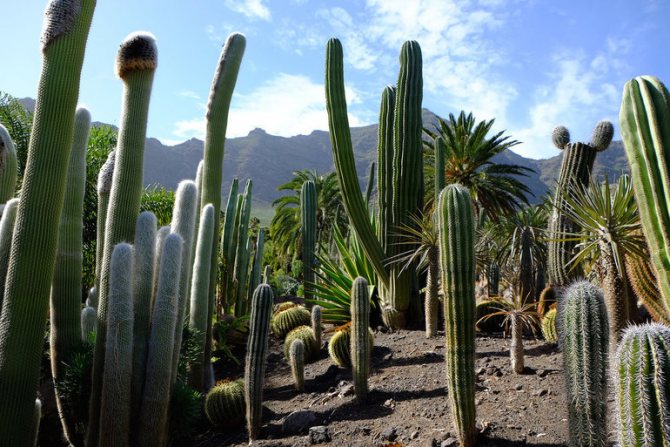
Where do cacti grow? Their main habitat is the deserts of North and South America. The most exuberant variety is found in Mexico, Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina. You can also find them in Africa and Asia. Many species have been brought to Spain, Italy, France, Australia, India and Russia. Although the homeland of the indoor cactus is South America, it can take root on almost any continent, if the necessary conditions are created for its life. For example, this plant does not like cold weather.
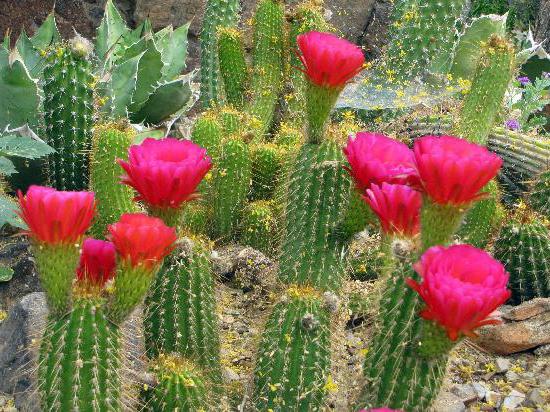


Cacti also live in high-mountainous deserts, adapting to the harsh climate. For example, mammillaria, neobessiya, escobaria, telocactus and other species. There are whole thickets in the savannas. There you can find cereus and prickly pears. But not always the habitat of a cactus is a desert. It is often found in evergreen rainforests. A distinctive feature of such plants is the complete absence of thorns.
I love you for your beauty
When choosing nicknames for pets, they are often associated with external signs, for example, a gray cat can be called a Smoke, and a red dog Fox, a chubby hamster a Keg or a Cistern. This approach works great with cacti too. What is the name for a green, prickly cucumber-like plant? The options are obvious: Thorn, Tadpole, Greenfinch, Cucumber, Fuzzy (a bit sarcastic for a thorny plant, but also reflects the essence), Thorn. Or maybe just a Cactus, because he is such.


Here, your imagination and the appearance of the plant play an important role. After all, cacti are visually diverse in shape, type of thorns. Sometimes they even look like an object. So connect all your resources, unlimited imagination and humor.
The adaptability of the cactus to the habitat
Nature has endowed cacti with grooves. Through them, water rolls down to the roots, which are thickened in order to store as much moisture as possible. They can occupy up to 5 square meters around the plant. At the same time, superficially lying roots absorb dew and moisture from the soil.
The adaptability of a cactus to its habitat depends on the growing area. For example, due to the spherical shape, low evaporation of moisture is achieved. And the ribs on the stem prevent cracking. A thick skin saves the cactus from the hot sun. Some species are covered with many thorns and villi that create a protective shade.For plants "living" in deserts, nature has provided for the absence of leaves in order to save precious moisture.


And why does he need a proper name?
Without breaking their brains and wasting time, some in communication with thorny friends call them simply affectionate words: cute, dear, fluffy, beloved. On the one hand, the conversation seems to be with a living person, on the other hand, the cactus becomes an unnamed interlocutor, an abstract living being.


That is, he is not endowed with any qualities from the nickname, the cactus remains a neutral listener, not personified.
This option is suitable for those who do not want to get too attached and close to the plant, but at the same time show care and attention.
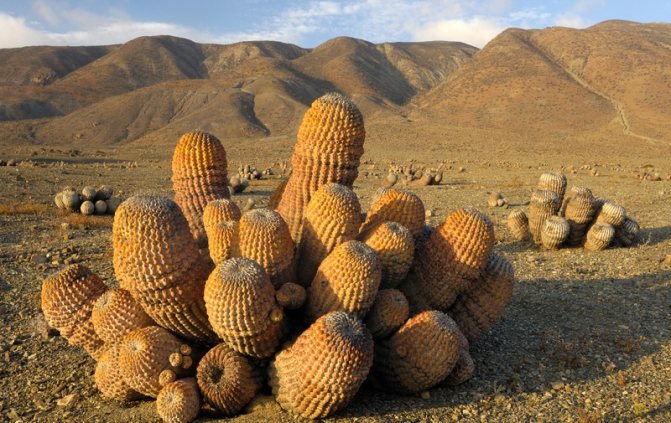
Desert cacti
They are the most persistent and unpretentious to the environment among all cacti. There are three main genera of these plants:
- Echinopsis. These are cacti with hard spines that run in even rows and round stems.
- Prickly pear. Plants have leafy, flattened stems, similar to green pancakes.
- Astrophytum. Its representatives are characterized by powerful ribbed stems and developed spines.
Desert cacti tend to have strong stems and many intermediate ribs. Moreover, they have strong long spines.


Dear and kind
Why doesn't a cactus become your former colleague or beloved relative? At the same time, the respectful address by name and patronymic adds a touch of humor and sarcasm. Then a clone of your dear uncle or aunt will live in your house, with whom you can at any time start a conversation over a cup of tea (it is better to clarify whether cacti like tea, maybe they prefer cocoa or coffee, or what is stronger).


If you do not contact your friends, you can choose your favorite combinations of name and patronymic. Make a list of what you prefer to call the cactus and solemnly announce it to the plant. On which combination cactus will smile, then choose (who knows, suddenly it will be a breakthrough in science).
For example, Sergey Stepanovich, Anatoly Bergamotovich, Ivan Kaktusovich or Valery Valerievich.
Indoor species names
The names of cacti are quite interesting, and few people hear them. These houseplants include Echinopsis crested, Peruvian, Echinocereus Knippel, Aporocactus whip-like, Echinocactus Gruzon, Woolly espola, Astrophytum ibex, Chamecereus Sylvester, parody of gold-leaved and blood-flowered notuccinate leaves, prickly pear others.


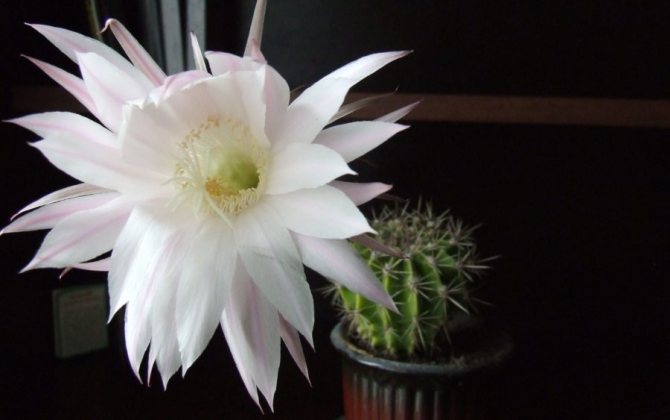
Phyllocactus with fleshy leaves are very good for indoor breeding. Their flowers are large and of different colors - from white to purple. They propagate by cuttings and seeds. They love light, in the summer they need good watering and spraying. Epiphyllum is considered the best indoor cactus. It is very hardy, the color of its flowers is different: from white to purple-red. In summer, these cacti should be kept in bright places, but not exposed to direct sunlight. They propagate by cuttings.
Houseplant as a small child
Many houseplant breeders are beginning to perceive them as their child. They can tell their joys, sorrows, discuss news. At the psychological level, an ordinary flowerpot with a plant turns into a ward, a child. Such relationships lead to the fact that the cactus gets its own name.
Common names of people are often chosen. When a plant becomes your child, you begin to treat it affectionately and caringly.
If you perceive a cactus as a boy, you can name it: Arkasha, Boriska, Mishulya, Kostenka. That is, the diminutive form of the name begins to be used.
In the case when your decorative flowerpot becomes a place for a girl's life, the names may be as follows: Anyuta, Glasha, Sofochka, Yanochka, and so on.


Such options are familiar to our own children. Alternative names can be foreign, not so typical for your area: Jack, Sam, Alfred, Russell.
Already in a sufficient assortment, dictionaries of names for various variants have been created. You can select based on religious, ethnic or other grounds.
The largest cacti
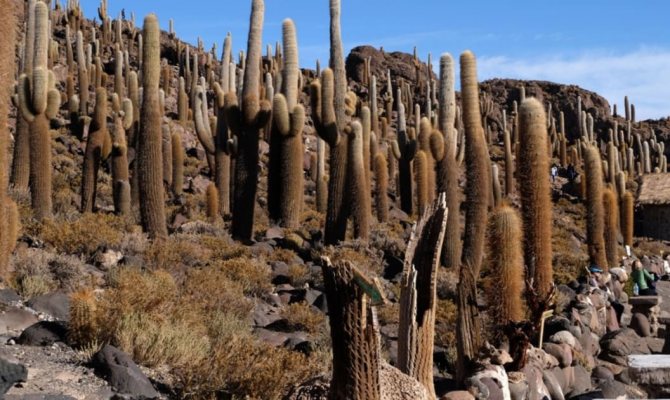
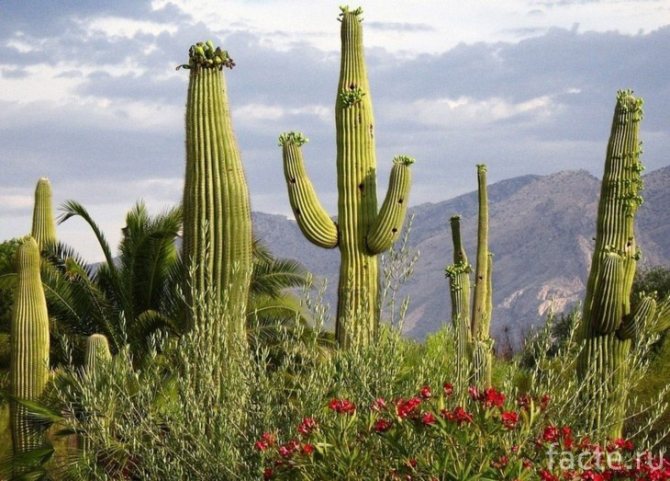
These plants can often reach enormous sizes. Where do cacti grow best? In America, they can be found in large numbers not only in the desert, but also on the streets of cities. Very often they grow much taller than human height, and people standing next to such a giant seem to be just "insects". Huge cacti in the desert are rare, mostly on the outskirts, but not in the center. They can grow so that they resemble trees. These cacti store a huge amount of water in their fleshy stems. They often grow in whole colonies.
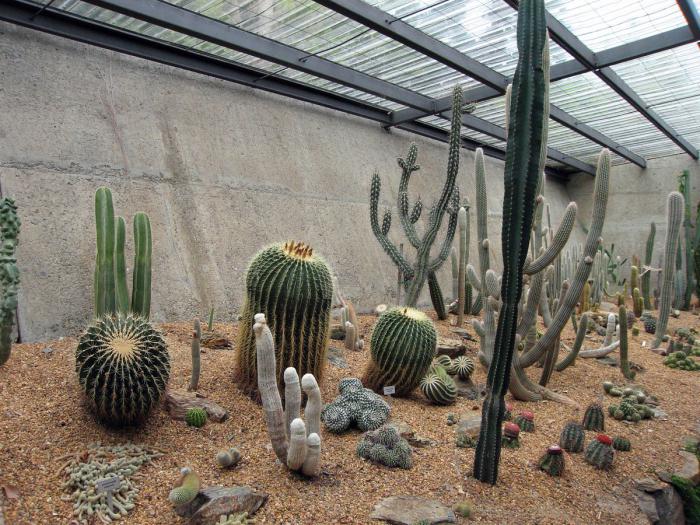
Photo
We bring to your attention a photo of desert cacti:
How cacti breed
They can be bred at home both with the help of seeds and by cuttings. In the first case, seedlings appear within a week, in some species - even after a month. Sowing is best done in the spring, mid or late season. A bowl with seeds is placed on heating, and the temperature is maintained at 25-30 degrees. Many people use indoor greenhouses or hotbeds, since the natural habitat of a cactus is mainly warm countries.
Sowing soil is poured onto the drainage layer. Seeds are sprinkled with it and pressed on top with a small plate. The dish is placed in warm water so that the liquid enters the drainage holes and moistens well. The emerging seedlings must be protected from direct sunlight. As soon as the first shoots appear, watering is reduced. A pick is made after the thorns have appeared.


Cuttings are also carried out in the spring by taking the upper or lateral shoots. A drainage layer is poured into the pot, and earth is on top. Cuttings should be cut with a sharp knife and dried well within a week. After that, plant in the sand to a depth of 1 cm. For greater stability, the cuttings can be tied to pegs. Then cover with a jar on top. Watering begins only after the cactus has begun, and until that time the ground is only slightly moistened. Cuttings can be prepared in advance in the fall and stored in dry sand until spring.
Indoor cacti
In indoor conditions, dwarf cacti are grown, which take up very little space. They can be grown on the same windowsill for several decades.
Cacti, like many other indoor plants, need a dormant period, which occurs in winter. Therefore, the main task when caring for cacti is to prevent growth in winter, because during the winter they stretch out and lose their usual appearance. In winter, cacti can be grown on windowsills. To prevent the roots from cooling, the pots must be placed on a stand.
Leaf-like cacti need the lightest places, but other cacti also like bright light. In winter, it is best to keep the temperature around 15-18 degrees. Desert cactus can withstand temperatures down to 5 degrees. and it can be kept in unheated rooms in winter.
During the rest period, in winter, watering is done once every 7-10 days. It is better to take warm water, several degrees higher than the air temperature. When watering a cactus, you need to ensure that water does not fall on the cactus stem, especially in winter. Water penetrating into inconspicuous cracks on the stem leads to decay of the plant.


With the onset of spring, cacti should be watered more often, and sprayed several times a month. In summer, cacti must be protected from direct sunburn. To prevent overheating of the pots, it is better to put them in boxes filled with earth or peat. You can take boxes with cacti to the balcony. It will be more useful to plant large specimens in the ground in the garden.In mid-August, they need to be transplanted into pots again so that they can take root before winter.
Watering a cactus depends on the size of the pot, the season, the age of the plants, and the temperature of the room. During the growth of cacti, in spring and summer, they need to be watered daily.
Old cacti need to be watered less often because they have a large supply of water. Especially in summer, abundant watering is required. Watering is desirable in the evening. The lower the air temperature, the less you need to water, since cacti evaporate less water. Watering in the fall is gradually reduced, and in winter it is rarely watered at all. If cacti are often watered in winter, they do not master the dormant period, become depleted and do not bloom.
It is better to replant cacti in spring, when they begin to grow. A couple of days before transplanting, you need to stop watering them so that the earth lags behind the roots more easily. The cactus is wrapped in strips with a strap or thick paper, then knocked out of the pot. Rotten and dead roots are cut to living tissue. Sprinkle the sections with charcoal powder.
All blooming cacti in early spring require replanting immediately after flowering. After transplanting, they are not watered for several days.
Star-shaped astrophytum: a description of the cactus
It belongs to small and monotypic species. It is considered a real gem among cacti. Differs in beautiful and long flowering, which can last all summer. He is unpretentious, loves warmth and sun in summer, and in winter - cool and dry. This cactus grows very slowly. It is very difficult to find: astrophytum is perfectly camouflaged. It adapts well to the surrounding area and blends in with the landscape. May take the form of stones or other plants.


The homeland of a cactus is not always a desert, as is commonly thought. Most often they grow in wildlife in more suitable areas. Desert species of succulents are more like dried thorns, although in their depths life is still glimmering, which blooms with the penetration of life-giving moisture. In many cases, the homeland of the cactus plant is the territory of modern Mexico and Colombia. Here and now, a huge number of succulent species grow, adapted to the hot and arid climate, in which periods of dry winds are replaced by rainy seasons.
About where cacti and succulents are common in nature and where they grow can be found in this article. She will give reliable information about the distribution areas of these plants.
Gender: myth or reality
There is a long debate on the Internet over whether a cactus has a gender, whether it can be divided into a boy or a girl.
The opinions are contradictory and ambiguous on this issue.
In any case, for the most accurate understanding of the plant, it is first necessary to determine its exact appearance.
For deep knowledge, it is worth contacting professionals in their field - botanists. With their help, you will be able to fully understand all the intricacies and nuances of the science of cultivation and determine what you can call a cactus.
But to choose a name, the plant does not need to go into such a jungle. It is enough to read detailed information about the type of cactus and remember the course in biology on pistils and stamens.
But if you don't want to go deep even into reading, then just choose for yourself: a girl or a boy. Usually, psychologically they choose a partner of the opposite sex: women will prefer to communicate with a boy cactus, men - on the contrary.
The habitat of cacti and succulents in nature (with photo)
The natural habitat of cacti in nature is limited to the New World. Several species of Rhipsalis, native to tropical Africa, Madagascar and India, may have been brought there by sailing ships or carried by birds. However, in America, cacti are found mainly only in arid areas.At the same time, two regions are distinguished by the greatest richness of species: the Mexican Highlands up to Arizona in North America and the dry mountainous regions of the Andes from Peru to Argentina and Southern Brazil on the South American continent.
Let us briefly consider the most important natural landscapes, in the vegetation of which cacti play a significant role. Most of the deserts are not home to cacti, since in deserts proper plants do not grow at all; there are few plant species only in special places, in valleys or at the foot of the slopes. Although there are also cacti among them, however, the number of their species is very small, and they are difficult to cultivate, therefore they are not of particular interest to plant lovers.
A typical landscape with huge columnar cacti and prickly pears (Arizona, Mexican Highlands, Baja California or certain high Andes valleys in Peru), on the contrary, cannot be called a desert. The vegetation of these places is quite lush, if there can grow, for example, multi-meter columnar cacti with lignified stems, in which hundreds of liters of water accumulate.
What do they still need?
Cacti are not at all dependent on aridity, as one might think. If your cactus grows slowly, then everything is more than okay with it - the slow growth is explained simply by the fact that the plant is unable to absorb many nutrients from the environment at once, but takes a little, without wasting its energy. In addition, cacti grow periodically, as it should be for a particular species. It is unlikely that it will be possible to speed up or change this process.
Cacti have such a concept as hibernation - during this period they do not need light, unlike the rest of the time, when the plant, on the contrary, requires a lot of lighting. It is because of this complexity that plant owners find it difficult to grow cacti outdoors, where it is not easy to control the light factor and some other conditions. However, ordinary cacti rarely require such diligence, and the plant will not die from insufficient lighting, but only stop growing.
With the soil, everything is a little more complicated: the distribution area of cactus is large, and many species live on radically different soil. Of the common signs, one can single out a slight looseness of the earth (similar to sand), and also impermeability to water and air. Difficulties may arise with the slightly acidic reaction of the soil, which is sometimes required by cacti.


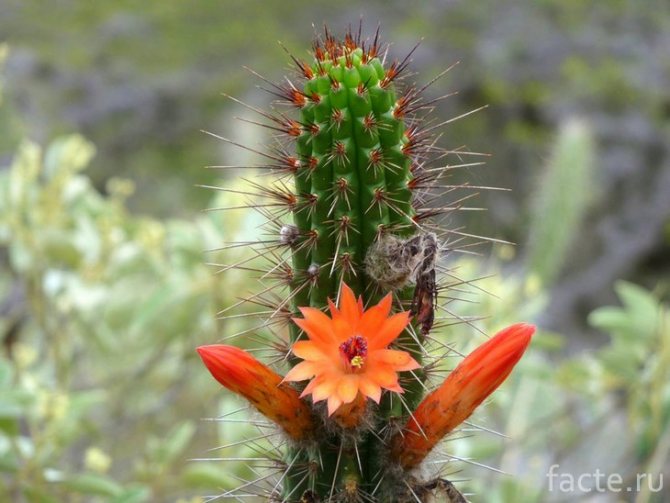
Cactus in bloom
Watering is where cacti show their legendary endurance. It is worth watering the plants during the period from spring to autumn, and for the winter to stop watering altogether. The plant will not only not fade from this, but will bloom much faster and more productively. The secret of this phenomenon is, again, in a kind of hibernation, during which the cactus needs practically nothing: no light, no water, no hot temperature. He draws everything he needs from the stocks accumulated over the favorable period.
At the same time, perhaps for an ordinary person, a cactus is unpretentious, but for some florist who wants to achieve a result, it suddenly turns into a rather capricious plant with its own very specific characteristics.
Where cacti and succulents grow
Smaller globular cacti are also found in these thorny shrubs, but in even greater numbers and varieties they grow in dry mountain areas: many mammillaria are native to the Mexican Highlands, and numerous species of Lobivia, Rebutia and Sulcorebutia ) come from the highlands of the Andes. There are several places where cacti grow in various types of development.
In drier steppes (campos) and savannas of southern Brazil. Uruguay and northeastern Argentina also host numerous small globular cactus species such as Notocactus, Gymnocalycium and Echinopsis.They grow most often among tall grains, therefore they do not tolerate direct sunlight very well.
We also offer you to find out about where succulents grow, and what conditions they need for successful development. In completely different conditions, namely in tropical humid forests, epiphytic cacti live in the forks of trees, such as various types of Ripsalis, "Christmas" (Schlumberger / Zygocactus) and "Easter" catuses (Ripsalidopsis), originating from coastal mountain forests in the vicinity of Rio- de Janeiro. They are used to fairly uniform temperature and humidity. However, it is not surprising that cacti grow in such areas, because, after all, and in very humid climates, epiphytes also have to absorb and, if possible, store rainwater quickly flowing down the branches of trees.
The next, however, again very dry habitat of cacti are rocks or a thin layer of sandy soil only a few centimeters thick. It is from such places that succulents growing in our country, such as sedum and rejuvenation, originate.
Plants do not have to always be tied to their original habitat: epiphytes do without plants as a support and grow just as well in soil.
Rocky plants are absent in natural conditions in the best places only because, with their slow growth, they cannot compete there with fast-growing, demanding species. In culture, we can grow them in suitable substrates.
Based on the conditions of natural habitats, the following conclusions, important for the cultivation of cacti, can be drawn: cacti are highly undemanding plants that drought is unlikely to kill, but which, on the contrary, easily rot with constant waterlogging. With a lack of light, cacti die very slowly, but they stretch ugly. Cacti react to low temperatures very differently depending on their origin. If you do not adhere to their usual pronounced seasonal rhythm with a dry and cool dormant period, then although cacti continue to grow further, they most often do not bloom.
Many cacti in their homeland are endangered. The rapid growth of the population led to the settling and introduction of more and more areas into agricultural circulation, as a result of which many large natural habitats of cacti were destroyed. In addition, collectors and traders deliberately exterminated some of the natural habitats of rare small cactus species. Meanwhile, recently we have begun to pay more attention to the issues of nature protection and conservation of rare species of animals and plants. As a result, national and international laws were adopted according to which the extraction of cacti in nature and the trade of such plants is either completely prohibited, or possible only in very limited quantities under the strict control of the relevant environmental authorities.
True lovers of cacti consider it their duty to preserve the natural habitats of these plants in their homeland. That is why we must learn how to properly cultivate and - whether it is an amateur or a specialized horticultural enterprise - to propagate cacti. If we manage to grow healthy, impeccable looking plants with beautiful thorns in our collections and horticultural farms, then at the same time it will also contribute to the protection of cacti in their natural places.


There is a widespread belief that the homeland of the cactus is the desert, in which for many kilometers there is nothing but sand and nomadic camels. Indeed, these inhospitable, thorny plants are primarily associated with desert landscapes. And they came to us from the hot African continent, and in addition, these succulents are able to exist in stony, lifeless soils, steadfastly enduring the scorching sun.However, they are not originally from the Sahara, Gobi or Kalahara. Their growing area is somewhat different, and today it has expanded so much that representatives of the family are found almost all over the world. What country can boast of being the real homeland of this unusual plant - the cactus?
Magnificent cactus: the birthplace of the plant, the necessary composition of the soil and other features of cultivation
In the modern world, scientists have already studied and classified more than two thousand species of a wide variety of cacti, which are very noticeably different in shape and size, color and those conditions that are required for their cultivation. Contrary to the prevailing stereotypes, cacti for the most part cannot stand direct sunlight, love moisture, and also some species do not bloom at all, while others are able to decorate our life with amazing, fantastic flowers. What can a cactus and its homeland tell us about itself, about the features and conditions of growing these strange, but such attractive plants.
The right pot is the key to success
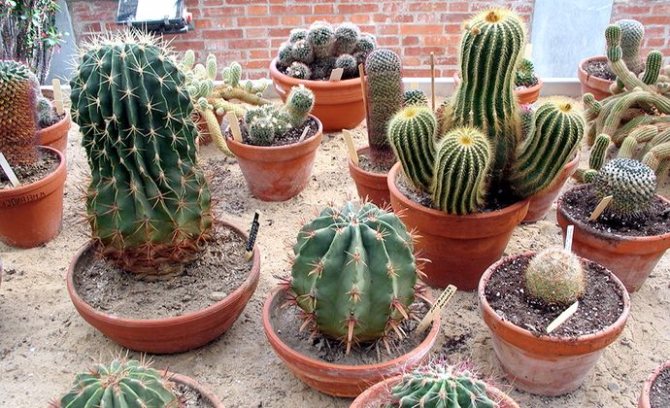


Before you get ready and finally decide that you will grow these particular plants, you need to understand that the homeland of the indoor cactus gave it a rather capricious nature. That is why it is extremely important to choose a capacity for neg, which will just correspond to its not very branched root system. In order to decide what kind of pot you need, you will have to remove the selected cactus from the temporary container and carefully examine the rhizome. Usually it is not very long, but rather branched; for such specimens it is advisable to take low but wide vessels.
However, some cacti have long enough roots, then you should think about deeper pots. It is optimal to use a variety of ceramic containers, as well as glass, and in extreme cases plastic, which practically do not interfere with cacti growing and developing. But metal pots for growing cacti are completely unsuitable, since corrosion products can destroy the root system, causing it to rot.
Suitable soil composition: making the life of a cactus as comfortable as possible
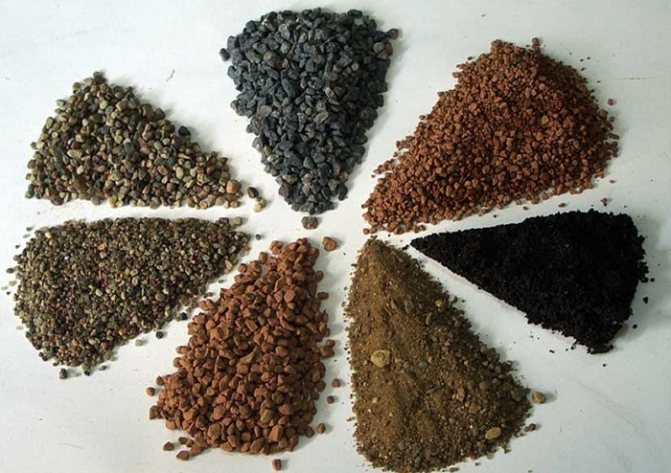


An extremely important and responsible process is the correct choice and preparation of the soil, which would be best suited for growing a wide variety of cacti. In our black earth, cacti will not feel in the best way, because it is fat and heavy, straining into a tight lump, which is not the norm in the homeland of a cactus flower. Moreover, the choice of soil qualities will directly depend on the type of cactus, as well as the conditions for its growth in the natural environment, but there are some general recommendations, which should be studied in more detail.
Main ingredients of "light" cactus soil
- Old land from greenhouses or greenhouses.
- Leafy soil.
- Clay-soddy soils.
- Washed coarse river sand.
- Brick chips as well as charcoal.
Among other things, it should be borne in mind that cacti love airy and light soil in which the roots of the plant will grow comfortably. But friability is not at all the main indicator, the main thing is that the acidity level fluctuates between five and six and a half, as in the homeland of the cactus plant.


It is also imperative to always remember about drainage, which should make up at least a third of all soil in a pot with a plant. Stagnation of water in pots is simply unacceptable, otherwise the roots will inevitably rot and the cactus will die. Anything will do for high-quality drainage, for example, crushed stone, crumbs of red brick, expanded clay and even ordinary foam, if nothing else is at hand at this time.
About the homeland of succulents and their distribution
Today, these cactus grow on any continent where climatic conditions are suitable for them.But even where the climate is not suitable, they are successfully grown in greenhouses and as indoor flowers.
It is interesting! As for the first historical mentions of the country of origin of cactus plants, in the second half of the 16th century, a German scientist, the "father of botany" Jacob Theodor Tabernemontanus, released his own herbalist, which gained immense popularity. In it, he described some of the varieties of these succulents, which were native to the shores of South America.
So it turns out that cacti became known outside the country of origin not earlier than the discovery of America by Christopher Columbus. And South America is recognized as the homeland of the indoor cactus. It was from here that these plants began to spread throughout the planet, taking root even where the climate was different from the usual. Some varieties were first discovered in North America, as well as in the West Indies.
Rhipsalis baccifera grows not only in America, but also in Africa, Madagascar and Sri Lanka. They got here without human help, because it is believed that the seeds of these plants were spread by migratory birds.
But the most beautiful prickly pear, consisting of flat palm leaves, can be found in India, the Mediterranean countries, Germany, Austria, Mozambique, on the islands of the Malay Archipelago and even in Australia, thanks to the intervention of human hands. Opuntia humifusa species grows far from its native shores, and not only in the Mediterranean, but also on the shores of the Crimea, in the southern regions of the Volga region, on the Russian Black Sea coast, in the regions of Gelendzhik and Novorossiysk.
And although their homeland is elsewhere, cacti almost everywhere feel at home, including on home windowsills. Especially if they receive proper care based on their needs.


What cacti go well with each other?
There is a popular trend to plant different types of cacti in the same pot. No wonder, because the variety of colors and shapes creates beautiful and attractive compositions.
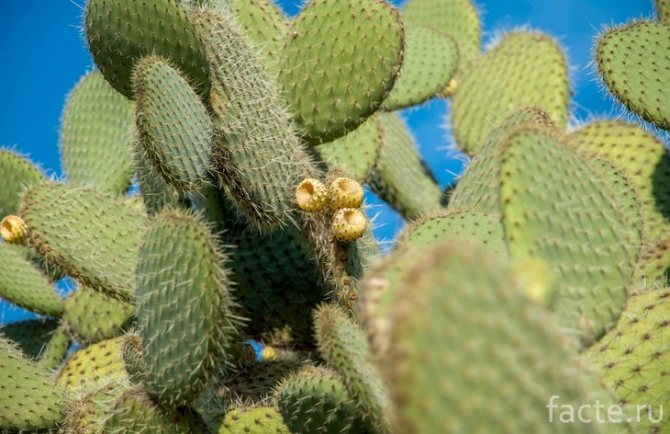
Opuntia cactus
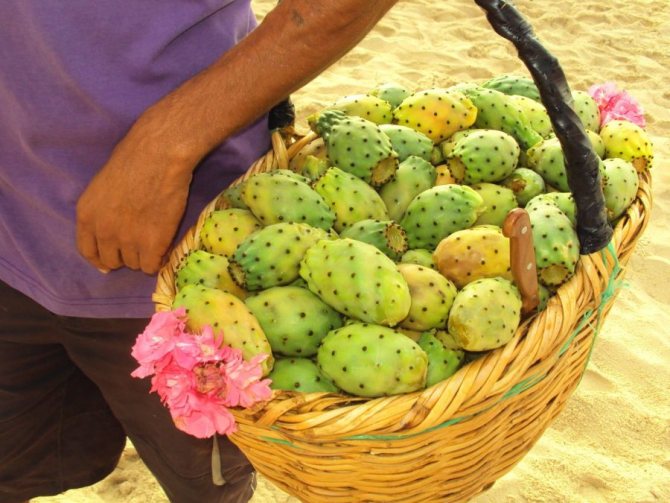
A popular species known for its beautiful flowers and edible fruits. The prickly pear species are low and covered with long and dense thorns, the prick of which provokes unpleasant painful sensations. Opuntia blooms with snow-white flowers, and after flowering, edible fruits of a flat elongated shape appear.
Store the cactus in a bright place, but during the summer heat, I recommend storing it in the shade to avoid burns. Otherwise, the requirements for care are the same as for other species.
Mammillaria
The next most popular is Mammillaria. Plants are spherical, pink small flowers located at the top. Mammillaria spines are thin and soft. There are many of them, which makes it look like hairs. The species does not need special care, and the flowering period begins at an early age, which makes it popular. There are several species that differ in shades of flowers and thorns.
Echinocactus
The owner of the largest flowers is Echinocactus. Flowers of different shades appear in young plants. The flowers are purple at the top. Plant height reaches 45 cm.
Gymnocalcium
Another popular species that blooms from an early age. The dimensions are small, thanks to which Gymnocalcium is easy to store and does not take up much space. The flowers are white, red, or pink.
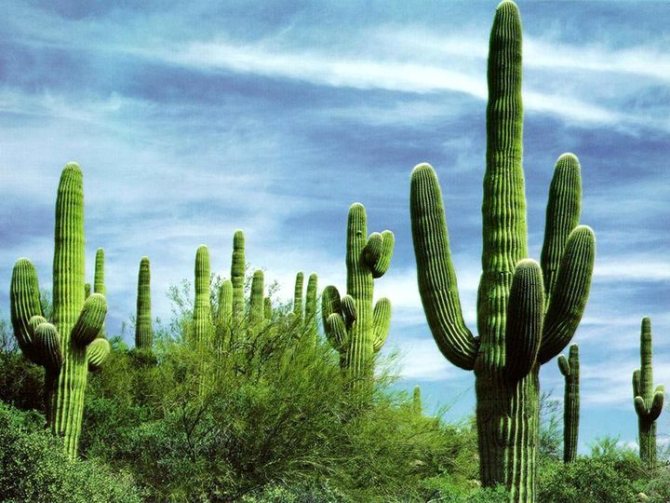
Saguaro
A species with a unique structure of branches, often becomes the object of attention of lovers of indoor exoticism. The largest species in size, and in natural conditions is protected by law. Saguaro supports the vital functions of living organisms, including birds, and therefore is considered an important plant.
Christmas
A vibrant species that is common in rainforests, with broad, thornless branches. Additionally, it needs moisture, which is typical for all tropical plants. It blooms with bright colors, therefore it is used to decorate the interior.
Mexico and cacti
There are not many places on Earth where the weather is as warm in winter as in summer, and Mexico is one of them. Maybe that's why a great variety of cacti grow here, about 1000 species - spherical, cushion-shaped, columnar, tree-like, compact and very large. It is not for nothing that Mexico was nicknamed "the country of cacti".
These plants are so deeply embedded in the lives of local people that it is almost impossible to separate concepts such as Mexico and cacti. The modern capital of the state - Mexico City, is located on the site of the ancient Aztec city of Tenochtitlan, whose name translates as "the place of the sacred prickly pear".
It is interesting! The largest number of these succulents grows on the territory of the Baja California Peninsula, it is not without reason that it was nicknamed the "planetary garden of the desert." Its shores are washed by the Pacific Ocean, and the Gulf of California separates from the mainland. Out of more than a hundred species of cacti growing here, 80 of them are endemic and cannot be found anywhere else on the planet.
In general, it is difficult to imagine the landscape of this country without these plants, because most often it, with some exceptions, consists of mountains, desert expanses and ... cacti. At the end of a 5-6 month drought, the desert will be transformed, it will turn green, and some of the cactus will bloom luxuriously. Some of them grab the attention more than others:
It is impossible not to notice the huge candelabra cacti, the height of which can exceed three meters. If you look closely, you can see small white flowers on them.


These tree-like cacti are successfully grown in pots, in such conditions it looks like a compact ball-shaped, sturdy succulent, decorated with bunches of colored needles. In their natural environment, ferocactuses are larger, their tops are dotted with dark reddish spines that secrete sweet nectar.
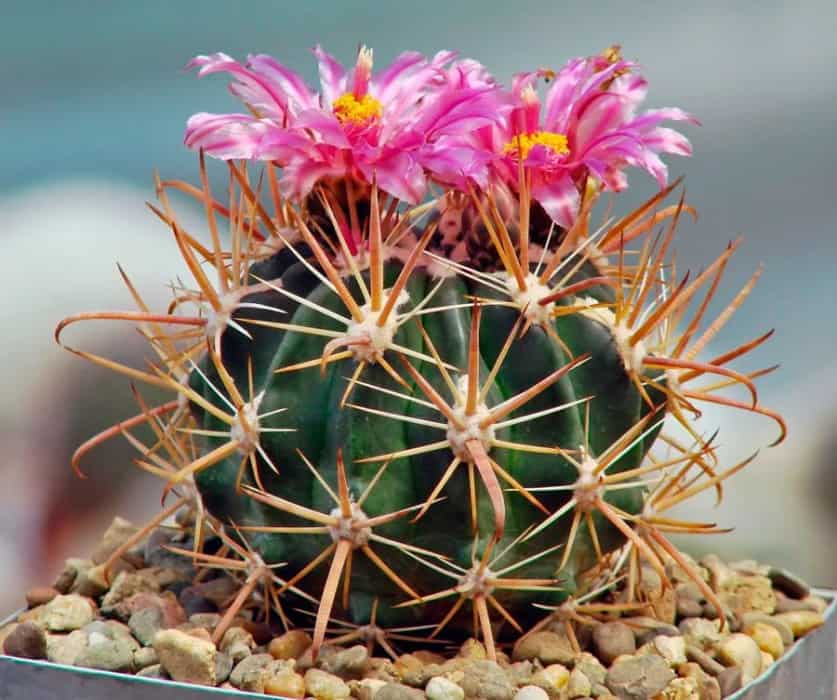


For us, it is nothing more than a pretty house and greenhouse plant, and for the Mexicans it is an important industrial crop. Here, whole plantations of prickly pears are grown, the fruits and shoots of which are eaten, fresh and canned food, drinks are prepared from them, used as hedges, feed for livestock.
And one of the varieties - polycantal prickly pear or multi-prickly, has become a symbol of the country and is depicted on the coat of arms. It is on this plant that an eagle sits, which eats a snake.
Opuntia are fast-growing cacti, therefore they often grow outside the plantations, reducing the area of pasture. Therefore, these landings need constant monitoring and restriction. Some succulent species brought to Australia have become veritable pest weeds. And to get them out, outside help was required - moths were imported into the country from Argentina.
As practice has shown, the most frost-resistant cactus also belongs to the genus of prickly pears. Dark-thorny prickly pear is successfully grown in the Astrakhan region, where it can withstand temperatures up to -20 degrees in the open field without additional protection.
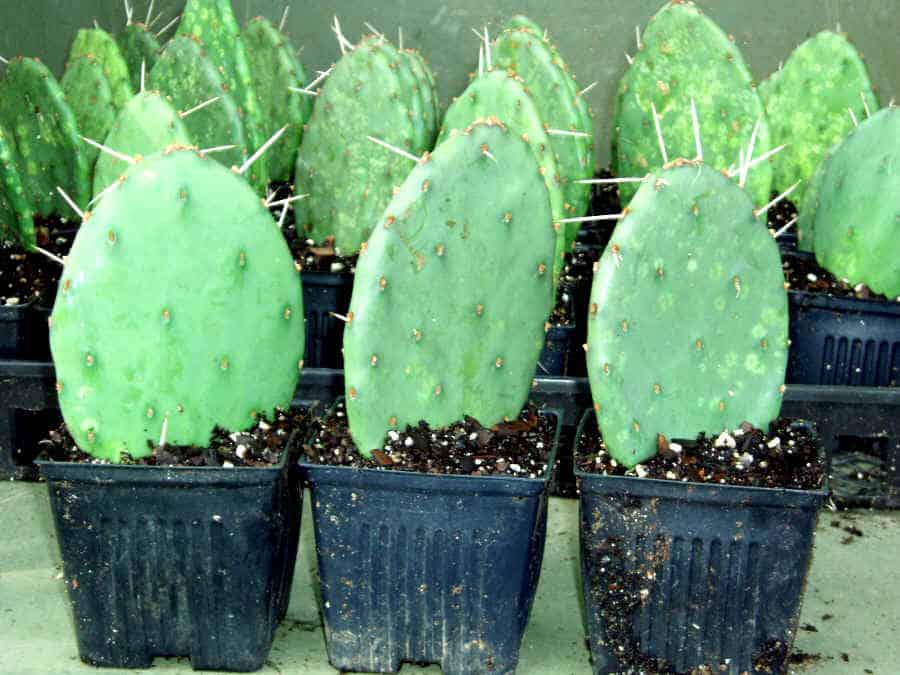


- Pachycereus Pringla (cardon cactus)
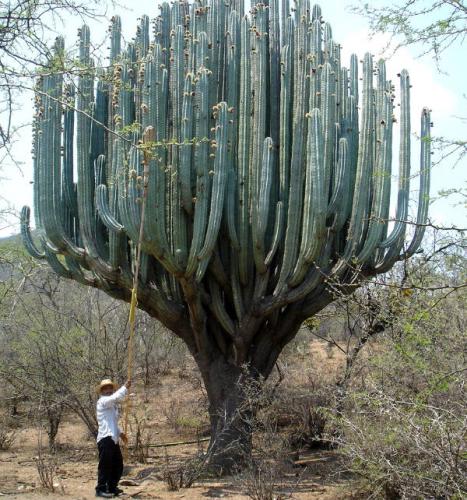
This giant, abundantly covered with thorns, grows up to 10 meters in height. Perhaps thanks to such natural protection, succulents live up to 350-400 years and gain weight up to 8000-10000 kg.
Pringle's pachycereuses branch at the base and the branches grow upward, rushing into the sky. The prickly fruits of the cactus are used to make brushes and combs.
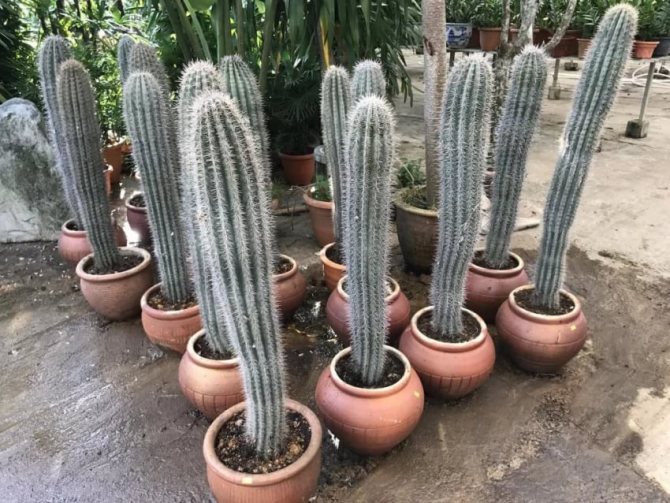


Diseases of cacti
Possible reasons
There can be a lot of reasons for the cactus to stop growing and fall off (decrease in size). Incorrectly compiled soil, sunburn, the cactus "shed" its roots, the period of summer dormancy in some species of cacti, diseases, damage to the root system of the cactus by pests, etc.
.
Ground problems
One of the most common reasons is problems with soil
... Souring of the earth or vice versa alkalization, as a result of frequent watering with tap water, not boiled or acidified water (hard with a high lime content). Incorrect composition of the soil mixture, which is not suitable for this particular type of cactus.Well, and the most banal reason is that the cactus is already quite cramped in the pot and lacks nutrients. So, in the absence of lesions of the root system, just transplant the cactus into a fresh
priming
, if possible, taking into account the taste preferences of your cactus. For example, Echinopsis prefer nutritious humus-rich lands and large pots, but astrophytum needs a poor organic, highly mineralized substrate with the addition of clay.
.
Cactus "shed" roots
It happens that from a sharp temperature drop, overheating of the pot, or vice versa, severe hypothermia, the roots of a cactus die off. Moreover, they die off, and do not rot away. At the same time, the cactus itself remains healthy and is often even able to take root without your help. But connivance in this case is very risky. If you do not know that a cactus is without roots and continue to water it vigorously and, God forbid, also feed it, then you can simply rot it this way.
Such cacti need to be reused root
... As a rule, small remnants of roots remain and there is no need to "sharpen" or cut the cactus. The cactus should be placed on light, nutritious, almost dry soil, overlaid with pebbles so that it does not fall. Three days later, you can spray for the first time. Caring for a cactus at the moment
rooting
gentle - warmth, no direct sunlight, periodically spray. Very often this is how the prickly pear sheds roots.
.
Cactus sunburn
Quite a frequent occurrence, especially in spring. In this case, the cactus is usually
the same "falls off" and the color of the epidermis (skin) changes, which acquires a reddish - bronze tint (color variations in a tanned cactus may be different, depending on the species). Photo 1 and 3. In mild cases, after a while the cactus received sunburn the healthy green color of the epidermis is restored. In severe, spots appear up to almost white, followed by drying out and necrosis of the epidermis, which remain for life and only become smaller over the years
noticeable due to the growth of the cactus. It is not necessary to apply any specific treatment measures to the burnt cactus. Move the affected person out of the sun, provide adequate watering and spray occasionally. To avoid sunburn, in spring, especially if you have southern windows at noon cacti
the first time is necessary
shade
To do this, just cover them with a napkin or just stick a sheet of white paper on the window.
Just do not be confused, the natural color changes of the cactus which


woke up and was about to grow up with burns. This is how some mammillaria behave, becoming crimson-pink in the lower part of the stem in early spring, thus informing the cactusist that it is time to water it.
Surprisingly, even a cactus accustomed to the sun can get a serious burn. Moreover, in the middle of the summer season. This phenomenon is relatively rare, and such burns are primarily susceptible to "naked" cacti, with a low perforation, and absent pubescence. Here is a young parody of the underground (Parodia subterranea). The cactus was burned at the end of July, after being turned 180 degrees for the first time in the entire season. It was hot and the sun was blazing mercilessly. The result is, so to speak, on the "face". Such burns on cacti do not disappear without a trace. The second photo was taken about a couple of months later. The color of the epidermis slightly recovered on the upper areoles, but a crust of dead tissue formed in the center.
The moral of this fable is as follows - a cactus accustomed to the sun, a relative concept. If you lay on the beach all day with your back to the sun, this does not mean that when you roll over, your chest and stomach will not burn :-).
In the culture of the windowsill, cacti often have to be turned so that they grow evenly, since, even on the sunniest windows, they lean towards the light source. Do not do this on especially hot sunny days, so that the cactus does not get burned.
In the photo on the left, another example, the problems of a cactus associated with
sun and heat. This is not a burn, it's just that Eriocactus is hot and lacks moisture (when this photo was taken it was hot and the temperature in the greenhouse reached 35 - 40 degrees). The epidermis became light, lost its luster, slightly wrinkled, and even small dents of a lighter color are visible. Such a cactus, you urgently need to water and temporarily remove from bright sun
, spraying the same will not hurt.
.
Physiological cactus growth arrest
Another reason for stopping the growth of a cactus can be purely physiological - a cactus falls into a state of stagnation under unfavorable conditions for it. Even if you have created ideal conditions for the cactus from your point of view, this does not mean that his
that's okay. July, sun, water, +27 degrees, what else does a cactus need for happiness and normal growth? And your rebutia is all shriveled, shriveled and does not want to grow into any ... It's very simple - the rebutia is asleep, because it is hot! In nature, it grows high in the mountains, where there is no such temperature, which means that it is unfavorable conditions for it. Attempts to make it grow by means of increased watering can end in disaster. On the contrary, it is necessary to reduce watering for the period of summer dormancy for those species of cacti that need it. These include rebuts, lobivia, ailosters, some parodies, and even certain types of hymncoliciums. For example, the Bruch's hymnocalycium (Gymnocalycium bruchii), both do not like heat, and in the middle of summer they fall into stagnation.
Interesting and peculiar representatives of the genus, can also demonstrate stagnation in the summer, but according to my observations, more often, this is due to insufficient watering. It is worth "missing" the fraile and she strives to fall asleep for the whole summer. Unlike the representatives of the mountain cacti described above, these cacti need to be woken up forcibly, with abundant watering, and, otherwise, they may die. I have listed far from all types of cacti that need summer rest .. Watching the cacti from your collection, you yourself can add to the list of "summer dormouse".
Growing places in the modern world
Today, succulents can be found in Patagonia. They also grow in the Galapagos Islands. Mexico is famous for its many types of cactus. In the Andes, there are incredibly bizarre forms of succulents. Cacti were also brought to the Mediterranean countries, and I must say that they took root there well. There are species of these light-loving plants that have spread throughout Europe. These plants are successfully grown in the south of Russia. Home cacti decorate apartments, greenhouses and gardens around the world. Colored succulents are very rare in nature.
Homeland of the thorn
Cacti grow in the tropics, savannah, deserts and mountains. The homeland of indoor cacti is North and South America. Various species grow in Europe, in the tropics of Africa and on the island of Madagascar, but the house cactus plant is native to the arid regions of the following states:
The most primitive species belong to the Pereskieae subfamily, more precisely, to the Pereskieae tribe. They grow in the tropics of America and southern Brazil. In Chile and Argentina, the Pereskiev tribes - Maihuenieae grow. The species of the South American genus Frailea and the Mexican genus Astrophytum have a similar structure of seeds; they are separated from each other by 2700 km.
For laughter's sake
If you are a person with a great sense of humor and a good dose of irony, then you can always approach the choice of how to name a cactus from this side characteristic of you. Maybe the cactus will respond in kind to you, gently firing needles.
Again, this can be a man's warped name, a sarcastic pet name, or even just any word.
Mr. Toos, Mr. Thorn, Sir Barrymore, Lady Gaga, Madame Sit, Pan Salo - that is, choose a respectful appeal to a person.
Hug, Fluffy, Hairy or Long-haired, Soft friend - a sarcastic nickname because of the thorns.After all, you are unlikely to want to squeeze a cactus in a strong friendly embrace.


Eggplant, Cucumber, Zucchini, Raspberry, Pumpkin - call the plant different. It goes well with the appeal: Mr. Fasolinka or Mrs. Pear.
Morphological signs and parts of a cactus plant: features of the stem
The stems of cacti, as already noted, have a different shape. They usually have ribs, most often divided into papillae, which are modified leaf bases. Most often, the ribs are straight, descending from the top of the stem to the base, but they can be spiral and wavy curved. Some cacti have flat ribs and barely rise above the stem. From above, the stems are covered with a skin (cuticle) made of a wax-like substance that protects them from external influences, including moisture evaporation. The cuticle is derived from a deeper layer - the epidermis. From the cells of the epidermis, bundles of elongated capillaries develop, ending on the surface with pubescence, which is able to capture moisture from the air and conduct it to the inner cells of the stem.
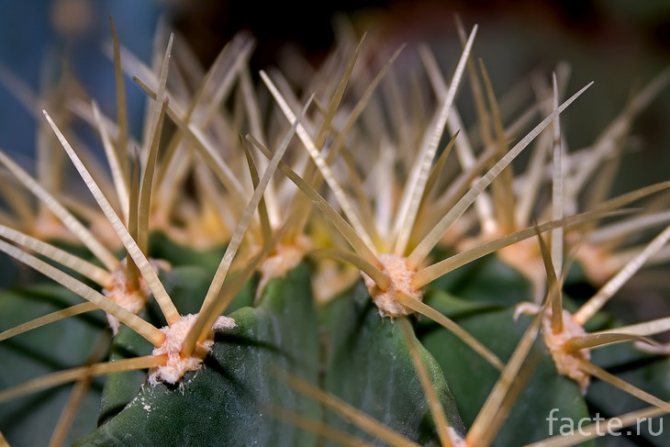
An important morphological feature of a cactus is the presence of thorns. These parts of the cactus plant can also capture moisture from the air and conduct it to the inner cells of the stem. This allows plants to efficiently use the moisture that condenses from the air during temperature changes.
The main difference between the structure of the cactus plant and other succulents is the presence of areoles, which are modified axillary buds. From the areoles located on the ribs of the stem, flowers and fruits develop, as from ordinary buds, and in some species, leaves. In the vast majority of cacti, areoles have spines and, in addition, may have pubescence of fine hairs. In mammillaria and some other cacti, the areola is divided into two parts. One part is in the sinus (axilla) and the other is at the end of the papilla. Flowers and processes in such cacti grow from the axilla, and spines develop at the end of the papilla. If necessary, the areola with a piece of tissue can be rooted and grafted to create a new plant.
One of the characteristics of the cactus stem is that it grows from the top, where the so-called growing point is located. Due to cell division at the point of growth, the cactus grows in diameter and height. Most cacti grow throughout their lives. Some of the cacti have a finite stem growth. In such cacti, division at the point of growth periodically stops, and new shoots appear from the areoles. That is, the cactus stem has a jointed structure. Violation of the growth point stops the growth of the stem and promotes the appearance of lateral shoots. This feature of the structure of a cactus is sometimes used for vegetative propagation of plants by cutting or drilling a growth point. The stem of cacti contains up to 96% water. A large amount of water, features of the structure of the stem (the presence of ribs, thorns, hairs) and features of the physiology of cacti help them survive in the harsh growing conditions.
In addition to the usual forms of stems, in nature and in collections there are two forms of cacti with an ugly growing stem: crested and monstrous. Normally, the growth point of a cactus is at the top of the stem. Annual growth of cells in this area increases the height and diameter of the stem. Substances secreted by cells inhibit the growth of the same cells scattered throughout the stem. If this mechanism is violated, cells begin to divide vigorously in different parts of the stem. At the same time, in crested forms, the apical point of growth stretches into a line, and the cactus takes on a comb-like shape, and in monstrous forms, cells begin to grow throughout the stem. As a result, the crested form takes on the appearance of ridges growing in different planes, and the monstrous form has a stem with separate randomly growing, asymmetric areas. These forms are very decorative and are often found in collections.The reason for such deviations is, most likely, a combination of several factors that has not been clarified so far. It is believed that deviations can occur in virtually any type of cacti. Similar phenomena are known among other plants. In addition to the named forms, the collections also contain chlorophyll-free plant forms (variegates) of red, yellow and other colors. Since the photosynthetic apparatus in such plants is absent, they cannot independently assimilate carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and are able to grow only in a grafted state. To maintain the shape of some species of cristates, they are also grafted.
The characterization of the cactus plant would be incomplete without a description of the thorns. Cactus spines are modified kidney scales. They are subdivided into central and radial spines. The central spine (s) is found in the center of the areola. It is usually larger, rounded or flattened, and quite often bears a hook at the end. More numerous and thinner radial spines are located along the periphery of the areola. The tissue of the thorns is saturated with calcium and some other substances that give it hardness. The number of radial spines in one areola can reach ten or more. Areoles of some species, in addition to spines, can bear hairs. The cacti of the Pereskiev and Opuntsev subfamilies bear small and easily breakable thorns on their stems - glochidia. There are types of cacti with flat and thin “papery” spines, for example, some types of tephrocactus. Of all the cacti, only peresky have well-developed leaves.
Homeland of cacti and the history of growing indoor flowers
The existence of cacti has been mentioned since Aztec times: scientists have found images of plants similar to cacti on the rocks. Such rock paintings, according to experts, appeared 50 million years ago.
Scientists found that the Aztecs used the plant for healing purposes, eaten it, and also used it in rituals to communicate with the other world. Experts say that this species has not undergone significant structural changes since ancient times. The ancient varieties are called melocactus, prickly pear and cereus.
In addition, in ancient Greece there were plants of small size with thorns, which were called "kaktos". The plants got their modern name thanks to Karl Linnaeus, who brought a new species from America to Europe in the 16th century. At the same time, the first collection of cacti was collected and exhibited in London by the pharmacist Morgan. And in 1958, Theodore Tabernemontanus published a book with a detailed description of the varieties of cacti.
The first mention of the place of origin of cacti dates back to the 16th century. It was at this time that information about unusual plants in South America appeared. It is the southern and northern parts of America that are considered the birthplace of this, now also indoor, plant.
Since the first mention, these plants have adapted to living conditions on different continents. The main feature of this species is considered to be its ability to live without water for several years due to its ability to store moisture. The water supply inside the body of the flower is created due to the synthesis of the juice of the mucous structure.
In addition, the plants have a special leathery shell that minimizes moisture evaporation in hot conditions. There are also subspecies - epiphytes that live in forests with constant rain. In the wild, cacti grow to large sizes and can form entire forests.
Popular types of cacti
Since their discovery, cacti have gained wide popularity and spread across all continents, in connection with which 4 large families have been formed:
- Opuntia cacti are considered one of the most numerous families with about 16 genera and 500 species. Their distinctive feature is the presence of a glochidia - a small thorn with a hook-shaped point at the end, which, when in contact with an object, easily clings to it.
This mechanism ensures the spread of the species and its reproduction. The succulent stems and reduced leaves at the top of the plant are also distinctive features of this family. Opuntia flowers have bright saturated various shades. Each species blooms individually; some representatives can flower all year round, and some only in summer, or do not bloom at all.
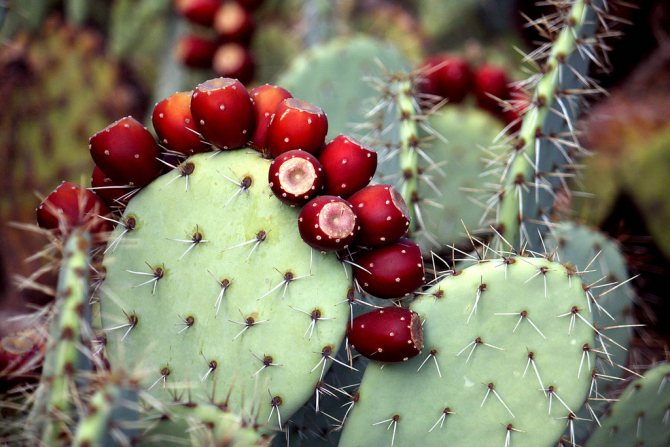


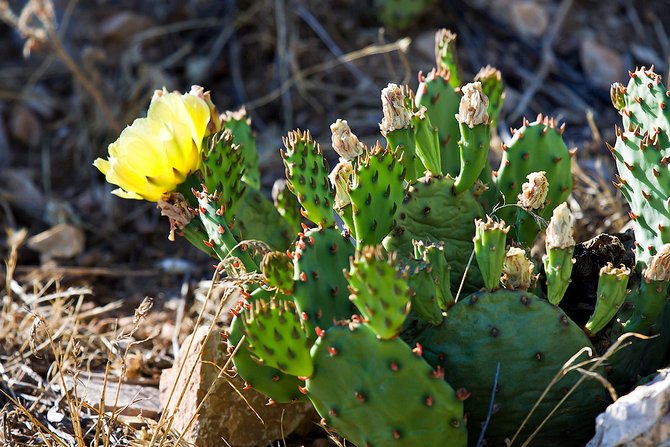
Prickly pear
In place of flowers, large round fruits are formed, completely covered with thorns. Inside, the fruits are soft and juicy, contain seeds. When properly collected, they can be eaten. Opuntia fruits are often called prickly pear. Opuntia are widespread in Canada, USA, Western India and Patagonia. Mauhyenia are a subfamily native to Pantagonia. Previously, this family belonged to the prickly pears, however, after lengthy research, it was decided to place them in a separate category due to significant differences. The Maukhinevs have only 2 species.
Cactus shoots have a cylindrical shape, on which small leaves are located. The bodies of cacti of this family grow rapidly, forming dense thickets. Mauchiens can easily tolerate low temperatures and can grow in a pot outdoors all year round. The lack of flowering is considered a deserving feature of the family. The Pereskiev family includes 8 species and 4 subspecies. The peculiarities of the family are that individuals grow from 1 to 8 m in height. Some species can grow up to 10 m. The stem of this cactus is woody at the bottom and densely covered with thorns. The leaves are round, elongated, fleshy, alternately arranged on the stem, attached with a small petiole. During periods of drought, the leaves fall off.


Pereskia
Peduncles are located on the top of each shoot. They can be spike-shaped, or represented by single flowers. The color is varied. In place of the flower, edible, berry-like fruits are formed. Representatives of the Pereskievs grow in South America, Western India and Mexico, where a tropical climate prevails. The Cactus family unites all the remaining species. A distinctive feature of this family is the complete absence of leaves or the presence of their rudiments. Unlike opuntia, there are no glochidia on cactus. The vegetative part has a spherical or cylindrical shape.
The family includes some types of epiphytes, which have a lash-shaped trunk, as well as xerophytes, the shape of which varies widely. They live in South America and Western India, and are widely distributed as decorative indoor plants.
Rare and exotic species
In addition to widespread representatives, there are also those that are rare and have an unusual appearance.
Navajoa is a flower native to the USA that is divided into 3 types. Its main features are considered to be a wide green stem with a blue tint, on which cylindrical papillae are located. The flowers are small, without a tube.


Navajoa
Encephalocarpus is a flower native to Mexico that resembles a conifer cone in appearance. The stem is rounded, about 10 cm high. At the apex there is a pubescence of white villi. On the stem, there are papillae arranged in a spiral. There are about 10 thorns, flowers are small, appear on the crown.
Using cactus
The use of cacti in the farm
Man is widely used for cacti. On the farm, people use the stems of cacti. So, for example, from the stalks of the cactus Helianthocereus pasacana they make light but rather durable furniture, as well as window frames, doors, and roofs. Many cereus (Pilosocereus lanuginosus, Ritterocereus griseus, Cereus repandus, Trichocereus cuzcoensis, etc.) are used as hedges that do not require any repair for many years.
Souvenir plant belts are made from the stems of the Ferocactus wislizenii cactus.To do this, the flesh of the stem is cut into long strips, and then they are treated with glycerin. The succulent stems of this cactus and the cactus Melocactus oaxacensis are used in the confectionery industry for the preparation of candied fruits, marmalades and sweets. And in Argentina, locals use the succulent stem and root of achacana for food, i.e. cactus Neowerdermannia vorwerkii, which tastes like potatoes.
The use of cacti in medicine
Since ancient times, cacti have also been used as medicinal plants, and the dried and pounded stems of a "soldering tree" of one of the types of prickly pears were applied by the Indians to wounds and sore spots as a plaster. The fruits of many prickly pears have a diuretic effect. In rheumatism, the juice of the Selenicereus stem was used externally as a rubbing, and the alcoholic or aqueous extract of the petals and stems of S. grandiflorus is still used in medicine as a remedy for cardiovascular diseases.
The Aztecs have long known the action of peyote, or peyote, Lophophora williamsii, in causing audible and visual color hallucinations. And the secret of this is that the bitter juice of the stem and root of peyote contains alkaloids mescaline, lophophorin, peyotine, etc. Therefore, in ancient Mexico, peyote was also raised to the rank of a sacred plant, and the Indians believed that the body of the god Yukili was enclosed in its stem. Religious holidays were dedicated to this deified plant, and the collection of peyote was accompanied by solemn ceremonies.


Use in cosmetology
Products obtained from the prickly pear cactus are actively used in cosmetology. The oil protects the skin from free radicals and prevents aging, perfectly nourishes and regenerates the skin, smoothes wrinkles. As part of hair care products, it has a beneficial effect on weak, brittle and problem hair, strengthening it, nourishing it along the entire length and preventing dandruff. Opuntia extract has almost all the beneficial properties of oil, it has a moisturizing effect on the skin, restores the natural water balance and serves as a source of beneficial substances that improve blood circulation and strengthen the capillary walls. Opuntia cactus oil and extract is used in cosmetic products for the care of mature and aging face skin, for the care of dry body skin and for the care of dry hair.


Cacti as ornamental plants
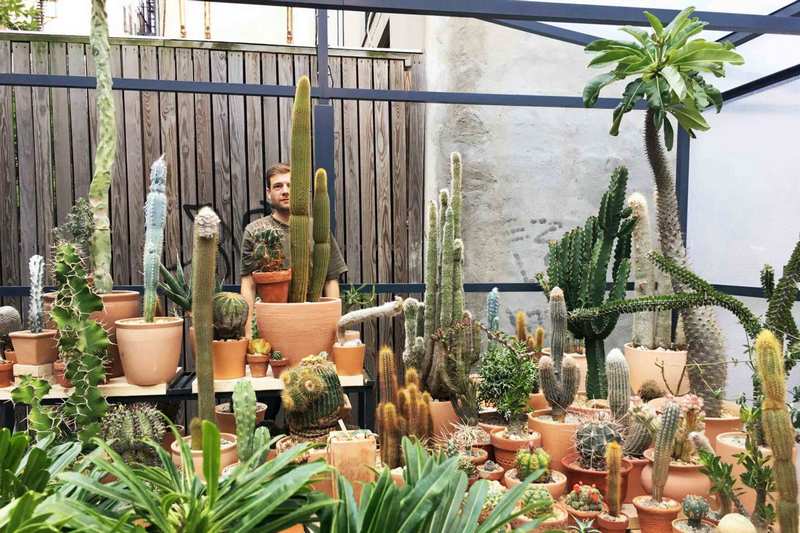
Cacti, due to their unusual appearance for Europeans, attracted the attention of the first colonizers of America and were introduced to Europe as ornamental plants already in the 16th century. The first known collection of cacti was collected in the second half of the 16th century. by the pharmacist Morgan in London. In the future, the popularity of these plants constantly grew, which was also facilitated by the biological characteristics of many cacti - unpretentiousness to watering and dry air (the latter is essential in room culture), easy vegetative reproduction. Also, indoor types of cacti, in particular Rebutia, can be added dropwise in the garden in their pots in the summer. In the botanical gardens of different countries, including Russia, as well as in the greenhouses of individuals, significant collections were collected.
Private collections in Russia were lost as a result of the October Revolution of 1917. However, large collections have survived in the botanical gardens of Petrograd and Moscow. Today they are the largest scientific collections of cacti in the Russian Federation. In the USSR, the mass distribution of cacti as popular indoor plants began in the late 1950s. Cactus lovers' clubs emerged, some of which still exist today. Nowadays, several dozen of the most unpretentious types of cacti are among the most common plants used in landscaping premises; on the other hand, enthusiasts collect collections of hundreds or even thousands of species. For lovers of cacti, the term "cactusist" is used.
What family are the thorny plants of the desert cacti: groups and subfamilies
From the point of view of taxonomy, cacti are dicotyledonous plants of the order of cloves, of the Cactaceae family. The order carnation combines plants that are very different in appearance and belong to different families.
The family, to which the cacti belong, is represented by perennial herbaceous, shrub-like and tree-like forms with a stem height of 2-5 cm (Blosfeldia tiny) up to 10-12 m (Carnegia gigantic). Until now, there is no established and generally accepted taxonomy of the Cactus family. Innovations in this area have not yet become generally accepted and are being disputed by specialists. According to the old and still widespread taxonomy of K. Bakeberg, the family consisted of up to 220 genera and about 3000 species. The presence of so many genera of cacti, these desert plants, has long been questioned. Recently, according to one of the new and most recognized taxonomy of E. Anderson, the number of genera has been reduced to 124. The Cactaceae family is divided into three subfamilies, a description of each of them is presented below.
Subfamily Peireskioideae (Pereskievye) is currently represented by one genus Peireskia, numbering 17 plant species, represented mainly by shrubs up to 8-11 m in height. The peculiarity of these cacti is the presence of a lignified stem, covered with long spines with well-developed or reduced leaves. The thorns help to cling to tree trunks. With age, the leaves lose their color, and during the dormant period in dry seasons they fall off. The flowers are large in the inflorescence, rarely solitary. The color of the flower is white, red, yellow, orange. Berry-like edible fruits. They grow in tropical regions of Mexico, West Indies and South America.
Subfamily Opuntioideae (Opuntia) is represented by cacti with spherical, disc-shaped, oval or cylindrical articulated stems and highly reduced and rapidly falling leaves, with glochidia (small spines) in the areoles. Represented by the genera Austrocylindropuntia, Cylindropuntia, Opuntia, Tephrocactus. The description of plants of cacti of this subfamily is as follows: these are erect or creeping shrubs, as well as shrubs, often forming cushion forms. The flowers are large, yellow, orange or white. The fruits are large, edible in many species. Another characteristic feature of the cacti of this subfamily is flat seeds, which, unlike other members of the family, have a hard shell. The subfamily has the largest distribution in the Americas. Opuntia grow from Canada to Patagonia.
Subfamily Cereoideae (Cereus) is the most numerous subfamily, represented by various life forms from epiphytes and dwarf globular plants to treelike giants. What are the features of the cacti of this subfamily? Representatives of Cereus do not have leaves and glochidia. The subfamily is divided into two groups (tribes). The group Tropical forest cacti (Hylocereeae) is represented by epiphytes, climbing and creeping cacti with aerial roots: the genera Rhipsalis, Hatiora, Epiphyllum, Selenicereus, Hylocereus, etc.
Group Cereus (Segeae) is represented by erect cylindrical or spherical cacti from small spherical and shrub plants to tree-like forms. The area of this group of plants, cacti, is close to the area of Opuntia. It is Cereus that are of greatest interest to collectors, both due to the abundance of genera and species, and due to the diversity of their life forms, as well as a wide variety of stems, thorns and flowers.
Next, you will learn about the morphological characteristics of cacti, how these plants bloom and what are their features.
Growing conditions for cacti under different climatic conditions
All recommendations regarding the composition of the soil for cacti grown indoors, watering are based on the natural conditions in which the cactus grows. Depending on the geographical location, the amount of precipitation in the territories where cacti grow varies from 14 to 300 mm per year.
It is also important that under such conditions there are very sharp fluctuations in day and night temperatures. As you know, in the daytime in the deserts, unbearable heat, and at night the temperature can drop to a fairly low level.Such races take place not only daily, but also depending on the season of the year.


In principle, it is difficult to talk about completely identical living conditions for all types of cacti, since climatic conditions in their habitats are too different.
For example, in coastal deserts, the frequency of precipitation is at an extremely low level - from 8 to 17 mm per year, but at the same time there is a very high air humidity - up to 98%. Therefore, in such areas, trichocereus chalsky cacti, several species of loxantocereus and cactus islaia, which are resistant to such habitat conditions, grow. In addition, you can observe dense thickets of hageocereus, and in rocky areas - neoromondia, corriocactus.
If cacti live in high-mountainous deserts, then they have to adapt even more to the harsh climate there. Basically, these are territories on the Mexican plateau with an altitude of 1000 to 2500 meters above sea level. Such natural zones are characterized by the fact that in winter the temperature can drop to zero degrees, precipitation often falls in the mountains in the form of snow, which the cactus plants growing there have to put up with. In such difficult conditions, the following types of cacti grow: Mammillaria, Echinocereus, Neobessia, Echinocactus, Escobaria, Coriphanta, Telocactus, Neoloidia and some other species.


You can also meet stormy thickets of cacti in savannas. This climatic zone is characterized by the fact that it is subject to long dry periods. Such habitats of cacti are found in the savannas of Venezuela, Uruguay, Brazil. There are very often such types of cacti as pereskii, prickly pears, cereus, as well as thorny plants from the bromeliad family.
In the subtropical savannas of North America, Mescal Neobuxbaum and Lindheimer's prickly pear are widespread, which often occupy very large areas.
We used to think that cacti live mostly in very arid areas, however, you can find plants from this family in tropical evergreen forests, where the average annual temperature is within +18 degrees, and there is a lot of precipitation - from 2000 to 3000 mm in year!
A distinctive feature of cacti that live in such conditions is the absence of thorns, their stems are not as fleshy and juicy as those of those plants that live in arid climates, they are often flattened in shape.


Most often, tropical cactus species live on trees (their branches and trunks), behave like typical epiphytes. Among them, the following species can be distinguished, which are well known to many lovers of cacti: hatiora, epiphyllum, amazon whitia, ripsalis and others.
As you can see from the examples described, cacti are very widespread throughout our planet, therefore, when deciding to have one or another species of them in your apartment, you should first familiarize yourself with the conditions in which this species lives in nature. Because success in growing cacti depends on how clearly the grower can bring home conditions closer to natural, natural ones.
«>
Homeland of the plant
So, where did the thorny cactus come from, we have already figured out. It turns out that it became known about succulents only when Christopher Columbus made his greatest discovery. And today the green "hedgehog", originally from South America, is already known to the whole world.
The Indians used it for various purposes: they treated it with a cactus, ate it, and used it for magical rituals. The origin of the prickly cactus remains a mystery today, and then even more so it was considered an alien creature. The succulent looks really unusual, so it was not for nothing that the Aztecs believed that it was a guide to other worlds. Modern man, even if he does not deify this plant, always admires the wonderful flower that suddenly appears on the thorny stalk of a cactus.
Morphology [edit | edit code]
In appearance, cacti are extremely diverse; all life forms can be found in the family.Trees include many cereus-like cacti, or non-branching (Cephalocereus columna-trajani
), or branching (
Carnegiea gigantea
,
Trichocereus pasacana
). Large trees up to 15 meters high form plants
Pereskia lychn> [14].
Root system
pivotal, in many cacti highly branched, with a near-surface arrangement of lateral roots, at a depth of 5-6 cm (
Ferocactus
,
Opuntia
). In large cereus, both the main root and the lateral ones are well developed. In a number of species, the main root tends to thicken (in the literature it is called turnip), turning into a storage organ, and sometimes the mass of the underground part of the plant is greater than the mass of its aboveground part (
Ariocarpus
,
Peniocereus
). Have
Peniocereus greggii
the root weight can reach 60 kg [15]. Creeping (lianas) and creeping cacti (
Stenocereus eruca
), as well as in epiphytes, adventitious roots develop [14].
Cactus stalks
differ in a variety of shapes and sizes. The leaf primordia that are laid in the apical meristem do not further develop into leaves in most species, but their bases grow, often in the form of tubercles (darios). In most cereus-shaped forms, darium, growing together, form vertical ribs. Distinct ribs are found in a number of spherical species. The number of ribs varies from two in phylloclades to more than 100 in species of the genus
Stenocactus
(formerly
Echinofossulocactus
) [fourteen] . Ribs function as stiffeners and impart strength to parenchymal stems; allow the stem to grow strongly in size without cracking the epidermis when moisture is stored during a wet period. In many spherical cacti, the ribs are not pronounced, and the gifts in the form of tubercles of rebuts or papillae of mammillaria are arranged in a spiral. Have
Leuchtenbergia principis
gifts are strongly elongated. The color of the stems is different shades of green, bluish, grayish, whitish, to brownish.
Leaves
... Normal, somewhat fleshy large leaves have
Pereskia
, at
Pereskia sacharosa
the length of the leaf blade can reach 25 cm, width - 6 cm; noticeably smaller leaves in
Pereskiopsis
; in drought, the leaves fall. Small short-lived leaves develop on young shoots of prickly pears. More durable than opuntia, but similar leaves in plants of the genus
Maihuenia
... Miniature leaves are found on ovaries and flower tubes (in descriptions they are called scales, the leafy nature is confirmed by the presence of areoles in their axils) [14].
The main types of cacti: the country of origin determined the development of varieties


Despite the fact that the cactus originates from the hot and arid regions of Central and South America, it has become a habitual inhabitant of many domestic apartments. And in nature, oddly enough, he quickly took root. In our area, cactus flowers, whose homeland is Argentina and Bolivia, can be found in Crimea, especially in the vicinity of Sudak, and some particularly tenacious representatives of the family have managed to take root even in the Astrakhan region, where the ambient temperature sometimes drops to minus twelve degrees, on the Celsius scale ... Experts classify all such plants into four large groups, which are worth a little understanding.
- Opuntia are distinguished by rather simplified, reduced leaves, as well as extremely thin and brittle spines, which are covered with tiny notches.
- Mauhyeny are distributed exclusively in their native Patagonia, they are very small, and their foxes grow in length by no more than ten millimeters.
- Pereskian species have quite full-fledged leaves. Scientists consider these species to be a kind of connecting link between cacti and common deciduous plants.
- The most widespread species in the world are considered, in fact, cactus, which reliably "nestled" on our windowsills. For the most part, these species are spherical, or cylindrical, covered with thorns of various sizes, and bloom with magnificent flowers, in the form of a raster.


It is remarkable that many indoor cacti, whose homeland has long become blurred and uncertain, can be used as a basis for shampoos, medicines, due to their beneficial qualities and properties, they are also used to make perfumes and hormones.Many tasty and nutritious dishes have already been invented from prickly pears, all parts of the plant are suitable for food, and candied fruits, extremely rich in vitamins, are even made from melocactus and echinocactus.
The real homeland of the cactus is America
At home, cacti grow to enormous sizes.
Among the great abundance of indoor plants, the thorn-cactus has found its place and its admirers.
In Hellas, the word "kaktos" was used to describe small plants with thorns. And it was precisely "cactus" that Carl Linnaeus called a group of plants previously unknown and introduced to Europe in the XVIII century.
The homeland of the cactus is the vastness of South America. But it is worth noting that cacti do not grow there everywhere, but only in arid regions, with poor soil and fairly pronounced fluctuations in daily temperature. And some of their species, such as epiphytic cacti, prefer rainforests with constant rain. Cacti grow in different ways: some form whole cactus forests, through which it is impossible to pass, others, on the contrary, grow one specimen per several square meters.
Dwarf cactus species are grown mainly by people who are accustomed to caring for indoor plants with a minimum of time. These plants are really unpretentious and only occasionally require watering or feeding. But if you want to see not only green thorns, but also beautiful original flowers, it will take some effort.
Since the homeland of the cactus is sunny and hot America, the plant should be placed on the windowsill of the lightest window and closer to the glass. There won't be enough light for him in the back of the room, and the air is dry there. Cacti do not tolerate drafts.
The next important rule - do not rearrange the plant from place to place, it does not like this. It is not necessary to turn a rather hardy indoor cactus in different directions so that it grows more evenly. This will prevent the plant from forming buds and blooming. Especially do not touch a cactus that has already released its buds. Water it with warm soft water (rain, snow or boiled). The watering period is from late spring to early autumn. In winter, with the exception of epiphytic species, cacti are not watered. The pot in which it grows must correspond to the size of the root system, be sure to put drainage for house plants on the bottom.
Although the real homeland of the cactus is America, and Mexico is considered the second, the cactus has taken root and adapted well in our conditions, an example of which is the numerous exhibitions of this plant and a large number of its admirers.
We also recommend reading:
- Homeland of houseplants Studying the features and rules of caring for a new flower, many housewives often do not even think about.
- Homeland of home violets Such a common flower as a violet for indoor plant lovers has a very modest history. This is a plant.
- Growing indoor cacti Cactus is one of the most exotic and fashionable indoor plants. The reason for its popularity is, v.
- Country of cacti Cacti are native to America. Their population numbers over 300 species and 220 genera. Habitat.
I love cacti! Indeed, there are no problems with cacti. We have about 20 varieties of cacti at home, which delight us not only with their cheerful appearance, but often with their flowering. It is a pity that many cacti, having thrown out a flower, bloom for only a couple of days.
Aporocactus has been standing at our house for almost 2 years now. An unusually beautiful plant. I have already seen it bloom twice. It blooms in early spring with huge flowers. Some are up to 8-10cm in diameter. And there are a lot of them. I would like to note that although cacti are resistant to dry air, I read somewhere that it would not hurt to spray them with warm water from a spray bottle. What I am doing.
I was once in Arizona, and there were so many cacti that I can't even describe. I didn't even know that they could be different. It turned out that it could be. The cactus grows in my house too, but it's not big.
We are all waiting for the cactus to bloom, this is probably the most pleasant moment. Cacti have the most delightful flowers in the world. When a cactus blooms, do not turn it, it will reflect badly on the flowers.
Well, something, but to visit the cactus forest is an incredibly "interesting" adventure, you don't really want to. There are also enough of those moments that arise when watering home cacti. I don't know about the others, but I will definitely catch 2-3 needles. One thing pleases - their delicate flowers.
Yes, the cactus is a very unusual plant, I even read stories that cacti in the deserts saved people's lives more than once, since this plant contains a lot of moisture, it is in American large cacti, people cut them and drank moisture, so that a very useful plant :))
When cacti bloom
These plants are beautiful in their own right. But it's still nice to see them bloom, which is very rare. There is an opinion that after this the plant dies, but it is erroneous. Healthy cacti produce flowers every year. Much depends on the conditions in which they are kept.


In order for them to bloom, they need a good root system. And the plant must be in a state of growth. Cacti that do not have living roots will not give flowers. They require top dressing - potassium phosphate. But it is often harmful to use it. Cacti should overwinter in a cool, dry place, and in summer - get enough fresh air. For an active and healthy existence of sunlight, they need three to six hours a day. It depends on the specific species. To the sun, the plant should always be turned on the same side.
Cacti of north america
Despite the harsh climatic conditions, some varieties of cactus grow here. More often than others, you can find unpretentious and persistent prickly pear, and this succulent from Canada differs in shape and size from species growing in other territories. Representatives of the species are more squat, stocky, for example, the common prickly pear of the compress practically hugs the ground with its fleshy leaves-palms.
It is interesting! Opuntia humifusa, which is native to Canada, has been chosen as the emblem of the British Cactus and Succulent Society.
Less often opuntia are spherical succulents from the genus Coriphanta, the diameter of which does not exceed 8 cm.
Opuntia and Coriphanta perfectly tolerate frosty, snowy Canadian winters.
History
Cacti occupy a special place among the whole variety of indoor plants and differ from them both in appearance and in keeping conditions. In Hellas, the ancient Greeks called cacti (kaktos) any thorny plant, like a thistle, which grow in abundance in nature. Much later, Columbus brought the first cacti to Europe, rare amazing plants were in the collections of the royal botanical gardens.
In 1571, the French botanist Mathias Lobel, in collaboration with Pierre Pena, in the illustrated book "Adversaria Stirpium Nova" described 1500 species of various plants, indicating the settlements where these species were collected, Melocarduus echinatus (the modern name of Melocactus caroli-linnaei) ... And in 1753, the famous Swedish botanist Karl Linnaeus used this word "cactus" in his two-volume work "Species Plantarum", while all the discovered and described plants belonged to a single genus - Cactus.
The cactus family came to Europe exclusively from the New World, i.e. North and South America. With the exception of the genus Rhipsalis, which was discovered in tropical regions of Africa, but, according to scientists, got there artificially, or rather with migratory birds. Now cacti are widespread, took root and became native to the Mediterranean, South Africa and Australia.
But the main distribution area of cacti is mainly South and North America, Mexico is especially rich in a variety of cacti.Most cacti grow in areas subject to prolonged periods of drought, some are found in extremely dry conditions, for example, the Atacama Desert (Chile is the driest desert, there are cacti of the Copiapoa Copiapoa genus).


Distribution and types
The Aztec rock carvings also depicted plants similar to cacti such as melocactus, prickly pear and cereus. Scientists say they have been around for over 50 million years. During this time, they have adapted to the climate. In the world, not a single plant has been found capable of vegetating due to its moisture for about 2 years. The most difficult adaptation for succulents is a desert with minimal humidity. To survive in these conditions, they become overgrown with a strong shell. During photosynthesis, cell sap is producedhaving a slimy structure. This juice helps to maintain water balance.
They appeared in European countries after the travels of Christopher Columbus. People used them as souvenirs. In Russia, they began to grow cacti in 1714 in the city of St. Petersburg. The first in Russia were prickly pears and cereus. What is the homeland of cacti is still not known, because not a single species has survived in fossil form.
The word "cactus" was used by the scientist Karl Linnaeus, which meant an abbreviation for melocactus. Melocactuses are all plants with thorns and sharp needles. There are many types and varieties.
The most common:
- Opuntia - has very sharp needles. Reaches 30 cm in height.
- Mammillaria is popular because of its easy care. It is covered with numerous "soft" thorns. Mammillaria has a large number of "papillae" from which flower buds bloom.
- Rebutia - refers to mountain cacti. The stem has a spherical shape, completely covered with thorns, blooms in spring. The flowers of this species are large. Unlike others, it does not tolerate dry soil well.
- Cereus - at home it can grow up to half a meter. This species does not tolerate direct sunlight, and it will not bloom without cold wintering.
- Echinopsis is a very popular indoor cactus. A hardy plant suitable for beginners.
- Echinocactus is a very large species, grows slowly at home and usually does not bloom.
- Echinocerius is very light-loving, flowers can grow to sizes exceeding the plant itself.
- Coriphanta - spherical or cylindrical shape, blooms in summer.
- Fraileys - have a small spherical stem, huge flowers in comparison with the stem. In winter, the optimum temperature is +12 degrees and a minimum of watering, but in summer, watering must be increased.
- Wilcoxia is an unremarkable plant before flowering. In early spring, it is covered with large flowers. Proper cultivation requires an abundance of light and fresh air.
- Rozhdestvennik - blooms in winter, because of this, abundant watering is required. Does not like direct sunlight, so diffused light is needed.
- Strauss's Cleistocactus - covered with abundant thorns and white hairs, the height can reach one meter. Quite a sun-loving plant, but at noon it is better to shade it a little.
- Lophophore cactus - the juice of this cactus has a healing effect when used in small quantities. In the central part there is an areola, from which many hairs come out, connecting in a dense bundle.
- Lubivia - was named after Bolivia, where the cactus was born. The young plant has a spherical stem, but stretches over time. The stem is weakly branching, many children are formed on it. Due to this, large cushion formations - colonies - grow on one stem.
These popular specimens grow both in the wild and on the windowsill of flower growers.
Why are succulents useful?


Cacti are used in many areas. Most of the species can be eaten, used as animal feed. There is also the famous blue agave, from which tequila is made.
Cereus is used as a building material, from which fences are made. Cacti are used in the manufacture of shampoos, vitamins, deodorants. Furniture, window frames, doors are made from the stalks of Pasakan heliantocereus.
Adaptation to arid habitats [edit | edit code]
Most cacti are succulents. Adaptation to arid habitats followed the path of leaf reduction, due to which the transpiration surface was reduced. The thorns slightly shade the plants, protecting them from overheating. The ribs and papillae also partially obscure the stem. An increase in the volume of water-storing parenchyma of the cortex, the development of a thick cuticle, a decrease in the number of submerged stomata, and the development of pubescence contributed to the accumulation and preservation of stored water. The intensity of cuticular transpiration in cactaceae is practically zero. The water-storing parenchyma is formed by cells with large vacuoles; there are few intercellular spaces in the water-storing parenchyma. According to the calculations of McDougal (1910), about 3000 liters of water accumulates in one cereus about 10 meters high [18]. Many cacti species are characterized by the presence of mucus cells in the bark (sometimes also in the core); crystalline cells with calcium oxalate crystals are common. Lysigenic lactates of some mammillaria contain milky juice. The near-surface root system maximizes the use of precipitation or condensed moisture.
Most cacti are characterized by CAM photosynthesis, a feature of which is the separation in time of gas exchange and photosynthesis. The stomata open at nightfall and close at dawn, thus gas exchange occurs during a period of minimal transpiration. Carbon dioxide is fixed at night, the resulting malic acid accumulates in the vacuoles (as a result, the cell sap is acidified). During the day, malic acid is decarboxylated with the formation of three-carbon acid and carbon dioxide, which enters into photosynthetic reactions (Calvin-Benson cycle), proceeding in cacti in the same way as in most green plants [19].
With the onset of a prolonged drought, after about 2 months, the stomata cease to open completely, the process resumes after precipitation falls, providing sufficient water potential of the soil for absorption by the roots. Cactuses that lack CAM photosynthesis: Pereskia
,
Maihuenia
.
Have Pereskiopsis
,
Quiabentia
and
Austrocylindropuntia subulata
the leaves absorb some carbon dioxide at night. In stems
Pereskiopsis
and
Quiabentia
gas exchange takes place during the day
Austrocylindropuntia subulata
- only at night [20].
There is a widespread belief that the homeland of the cactus is the desert, in which for many kilometers there is nothing but sand and nomadic camels. Indeed, these inhospitable, thorny plants are primarily associated with desert landscapes. And they came to us from the hot African continent, and in addition, these succulents are able to exist in stony, lifeless soils, steadfastly enduring the scorching sun. However, they are not originally from the Sahara, Gobi or Kalahara. Their growing area is somewhat different, and today it has expanded so much that representatives of the family are found almost all over the world. What country can boast of being the real homeland of this unusual plant - the cactus?
Interesting facts about cacti
- The fruits of some cacti are edible, they are very large, juicy and tasty. The yellow and red fruits look like a pear covered with small thorns. There are cacti that taste like strawberries, and they are used to make soft drinks. Various delicacies are made from cacti, their fruits are sold in the markets, Indian tribes use it as a medicine and as a drug to enter into an intoxicating state for ceremonies.Cactus fruits are eaten raw, jam and compotes, extraordinary-tasting creams and jams are made from them, they are put in wine for color and aroma, stewed with meat in the form of a stew.
- Growing and collecting cacti is a very exciting trend in modern floriculture. Collectors understand complex names and sophisticated agricultural techniques. It happens that completely different cacti are called by the same name. For cactus growers, there is still no reference book with a description of all species and varieties in Russian. Cactus lovers still use the old German guide by Kurt Beneberg and Walter Hage, or small guides with the main species.
- Contradictory opinions arise about the fact that the cactus protects PC users from the harmful radiation generated by the monitor from radiation. Many adherents of a healthy lifestyle arrange cacti around the apartment to protect them from radiation and even carry pocket cacti with them to protect them from mobile radiation. The opposite opinion suggests that its supposed usefulness of protection from radioactive radiation was imposed back in Soviet times. Cacti do grow better in conditions of increased electromagnetic radiation, but the opinion that the plant absorbs radiation is highly controversial. However, the thorns still serve as an air ionizer, this is a proven fact.
What are the natural features of cactus plants and what are they
Some features of biology and physiology. Cacti are succulent plants (Latin succulentus - juicy). Their stems contain a lot of water. One of the most important physiological features of these plants is a special type of photosynthesis, which is also characteristic of some other succulents. In the overwhelming majority of plants, photosynthesis, which takes place with the absorption of carbon dioxide and the simultaneous evaporation of water, occurs during the daytime. This process, which gives them the opportunity to live and increase their mass, depends on the intensity of solar radiation, temperature and water availability. The Cactus family was formed in the harsh conditions of a hot climate, where large losses of water during the daytime are unacceptable. Therefore, unlike most other plants, cacti have a fundamentally different type of photosynthesis. Its essence lies in the fact that the absorption and binding of carbon dioxide with the release of oxygen occurs not during the day, but at night, through the stomata that are open at this time. The acidity of plant sap becomes very high at night. During the day, when the stomata are closed and prevent the evaporation of water, carbon dioxide is released in the stem and used in the process of photosynthesis.
Thanks to these features of photosynthesis, cacti are able to grow in conditions of a severe temperature regime and a lack of moisture.
Another physiological feature of cacti is their slow growth. The root system and stem of plants are not able to quickly assimilate a large amount of nutrients and just as quickly transform them into an increase in the mass of roots and stems. This feature must be taken into account when cultivating cacti. The desire to quickly grow large specimens due to additional feeding can result in spoiled plant stems and even their death. At the very least, additional feeding should take into account all factors of the environment in which the collection is held. First of all, the illumination: the higher it is, the more nutritious the soil can be.
Economic and aesthetic value of cacti. At home, cacti have a certain economic value. Their stems are eaten raw and cooked. Fruits are also used for food, mainly prickly pears. Dry stems of large plants are used as fuel and light building material. Cacti are used as livestock feed. Due to the high content of alkaloids and other substances, cacti are used in medicine.A huge number of representatives of the Cactus family are decorative, greenhouse and indoor plants widely cultivated throughout the world.
How a cactus blooms: signs, a description of the structure of a flower and a fruit
Cactus flowers are solitary, in most cases located at the top of the stem, one at a time in the areola. They have a variety of colors, with the exception of blue. The structure of a cactus flower includes numerous stamens and a stigma of the pistil. In some species, they can differ in color, for example, yellow stamens and green stigma of the pistil in Echinocereus. Flowers appear on both old and young areoles.
There are types of cacti in which flowers develop on a special organ - cephalia (genus Melocactus, Discocactus), which forms at the top of the stem. The cephalic is an accumulation in the flowering zone of a large amount of fluff, hairs and bristles. It increases annually, reaching a height of 1 m in some species. Flowers can also develop on lateral pseudocephaly, for example, in cacti of the genus Cephalocereus, Pilosocereus, etc. The size of cactus flowers varies from small to huge, 25-30 cm long and in diameter (genus Selenicereus ). The flowers of some species have a scent (genus Echinopsis, some species of the genus Dolichothele, etc.). Flowering occurs during the day and night. Most cacti bloom during the daytime in the morning or afternoon. Most often, cactus flowers are bisexual and cross-pollinated. In the homeland of cacti, in addition to the wind, insects and birds, including hummingbirds, participate in pollination.
After flowering, berry-like juicy, less often dry fruits are tied. In many species, they are edible. Fruit sizes vary from 2-3 mm to 10 cm. The largest fruits are found in prickly pears. The fruits can ripen in the current season or next year (genus Mammillaria). A ripe berry can contain from several pieces to hundreds or more seeds. One of the smallest seeds in bloosfeldia, strombocactus and parodies. The large prickly pear seeds have a hard and durable shell. The rest of the cacti have a thin, fragile seed coat. Seed germination of most species lasts up to a year or more, in Cereus and Mammillaria up to 7-9 years. Roseocactus fissuratus has a known case of seed germination after 30 years.